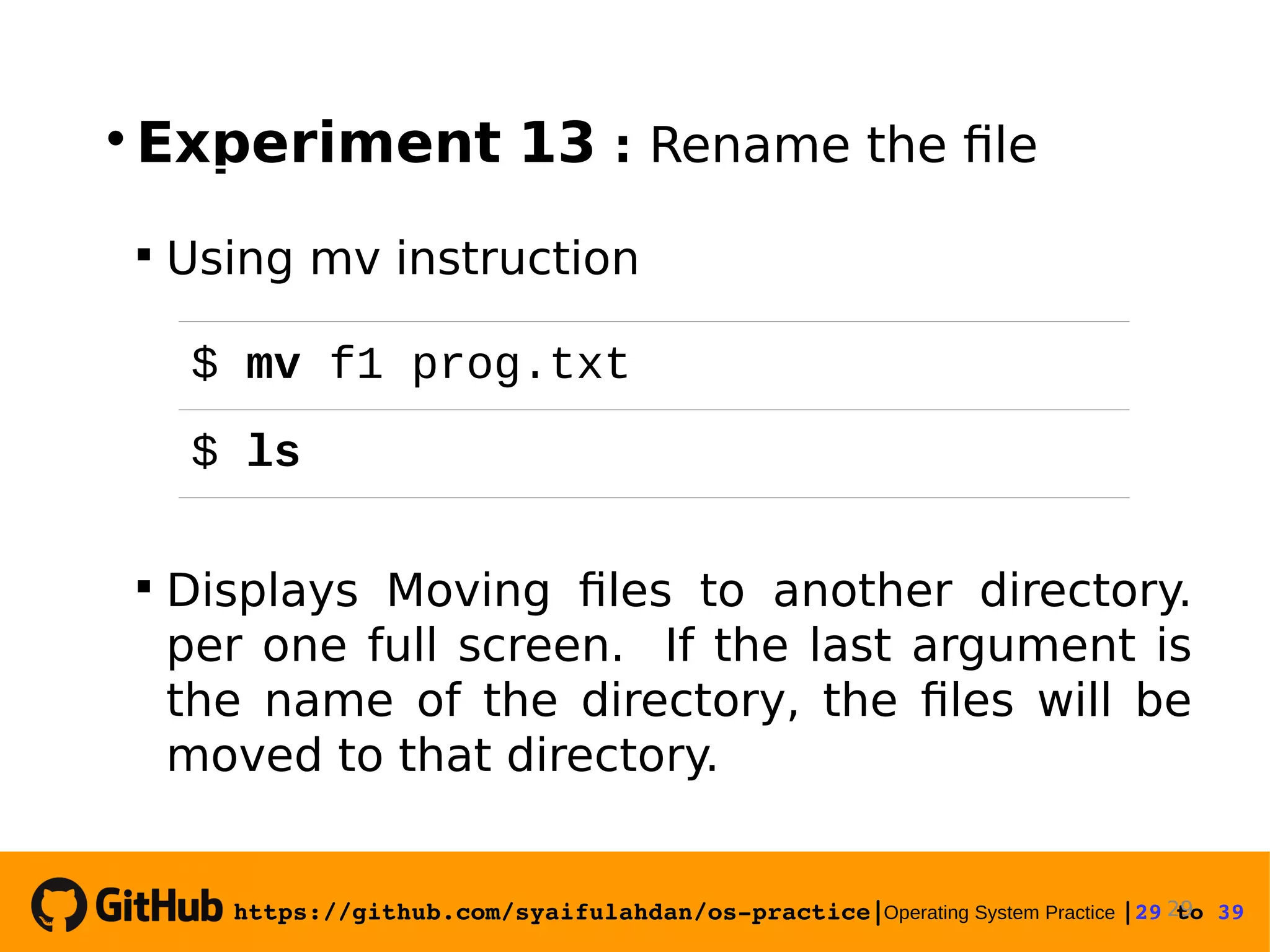
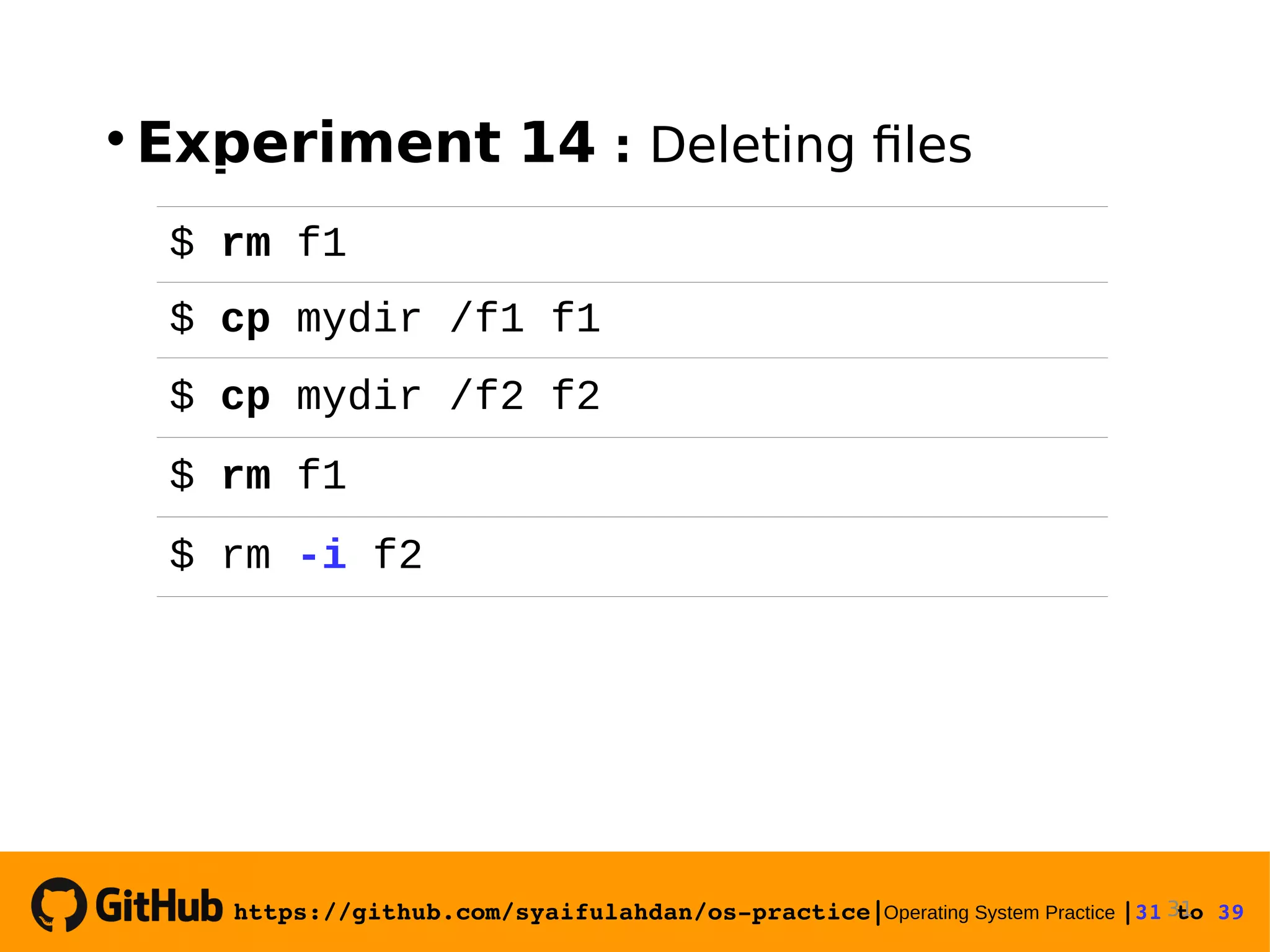
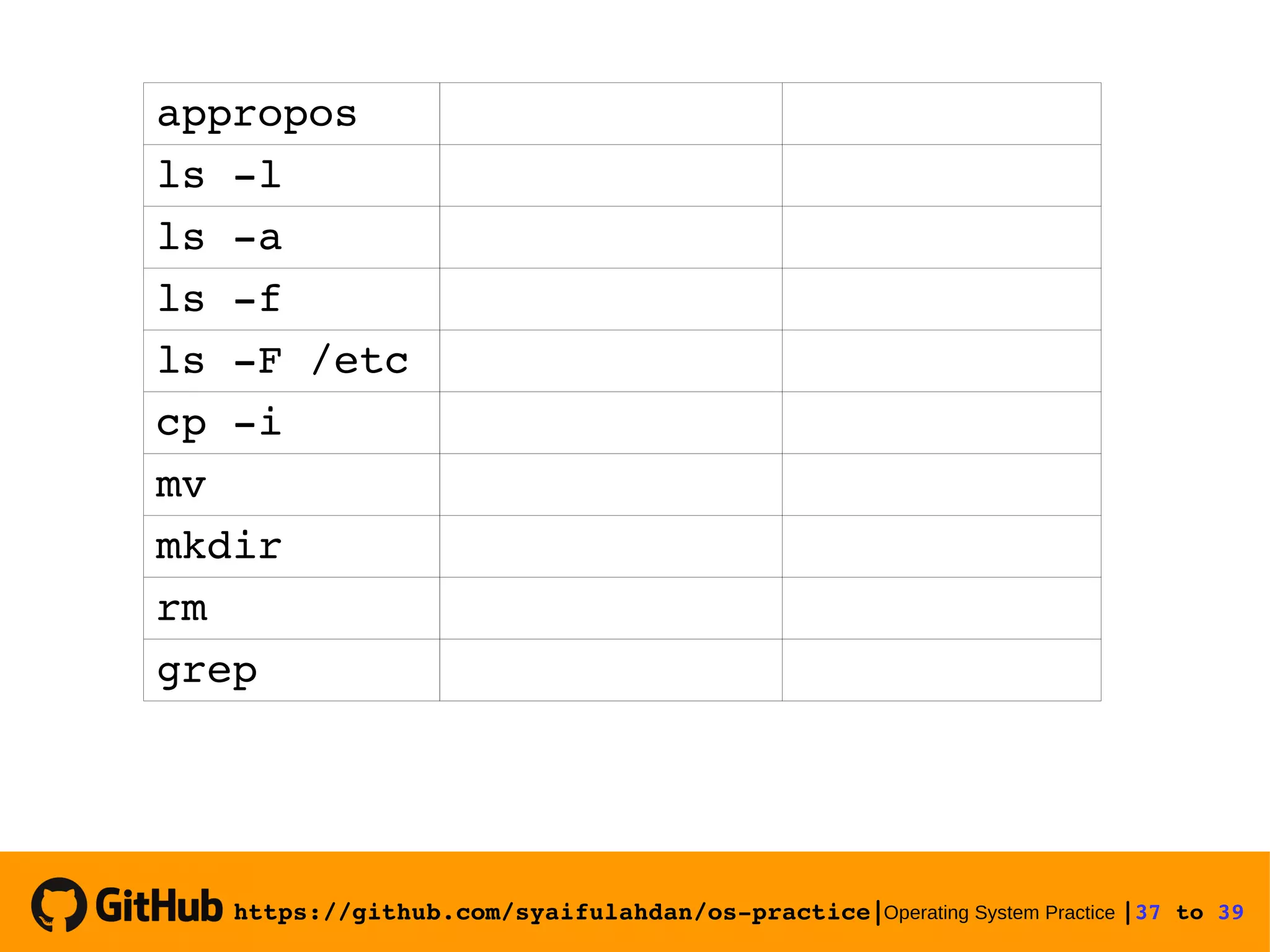
This document provides instructions on basic Linux commands. It begins with objectives of learning basic commands for user information, instruction formats, and basic utilities. It then covers Linux instruction formats, the manual system, basic theory of user accounts and shells. Experiments are presented to practice commands for user information, file manipulation, directory navigation, and searching files. Exercises are provided to reinforce skills like changing user information, viewing calendars, copying and moving files.




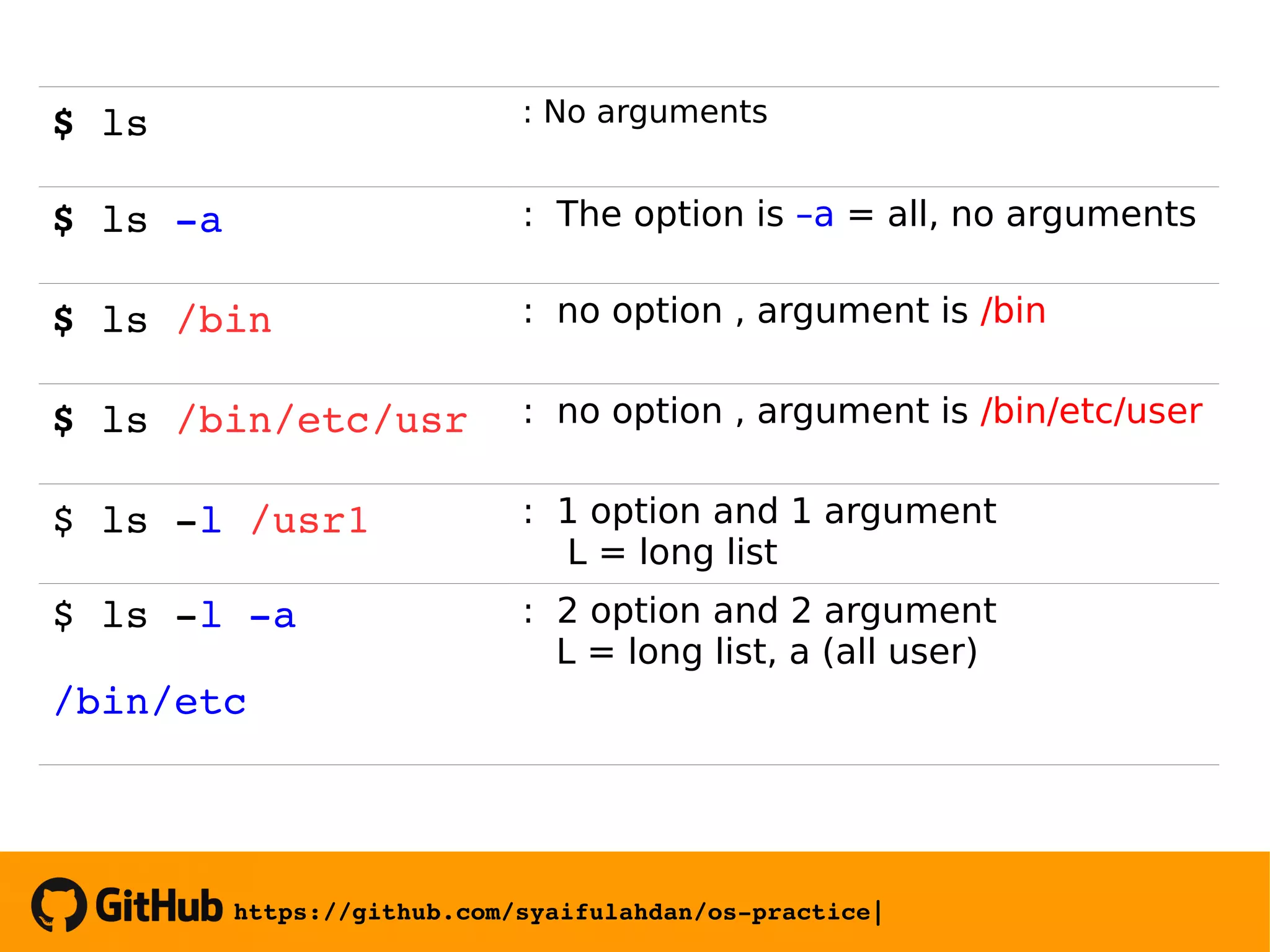
![https://github.com/syaifulahdan/ospractice|Operating System Practice |5 to 39 Linux Instruction Format • $ Instruction Name [option] [argument] • option begins with the sign – (minus). • Arguments can be empty, one or more arguments (parameters). • Example: $ ls : No arguments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meeting-2-basiccommandslinuxoperatingsystem-slide-180413083841/75/Operating-System-Practice-Meeting-2-basic-commands-linux-operating-system-slide-5-2048.jpg)





![https://github.com/syaifulahdan/ospractice|Operating System Practice |14 to 39 Experiment 1 : See identification (id and group id number) Replace the prompt with "$" [syaiful@tekno]$ id [syaiful@tekno]$ PS1=”$”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meeting-2-basiccommandslinuxoperatingsystem-slide-180413083841/75/Operating-System-Practice-Meeting-2-basic-commands-linux-operating-system-slide-14-2048.jpg)


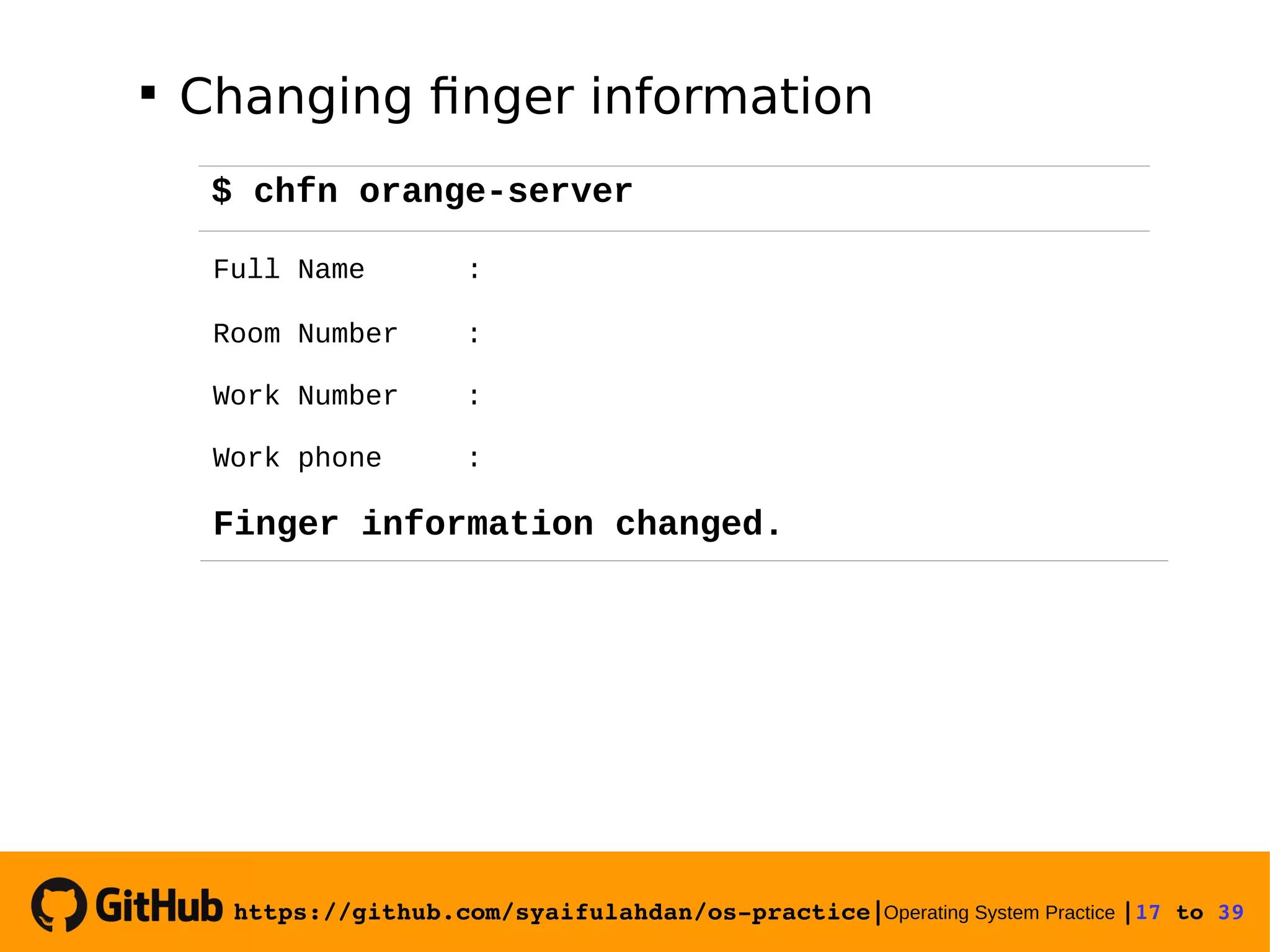
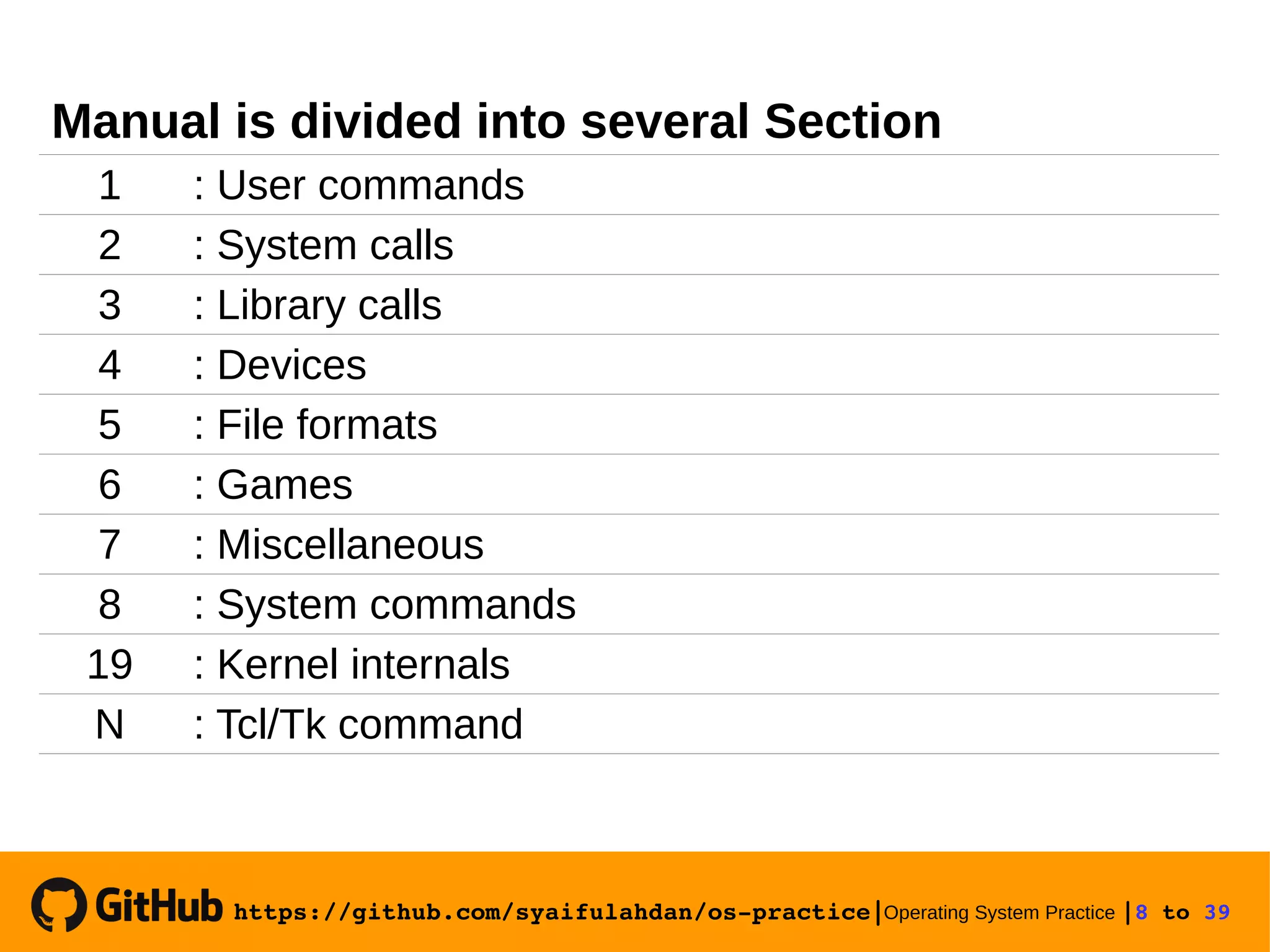
![https://github.com/syaifulahdan/ospractice|Operating System Practice |18 to 39 View finger information Experiment 5 : Using manual $ finger $ finger [username] $ man ls $ man man $ man -k file $ man 5 passwd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meeting-2-basiccommandslinuxoperatingsystem-slide-180413083841/75/Operating-System-Practice-Meeting-2-basic-commands-linux-operating-system-slide-18-2048.jpg)


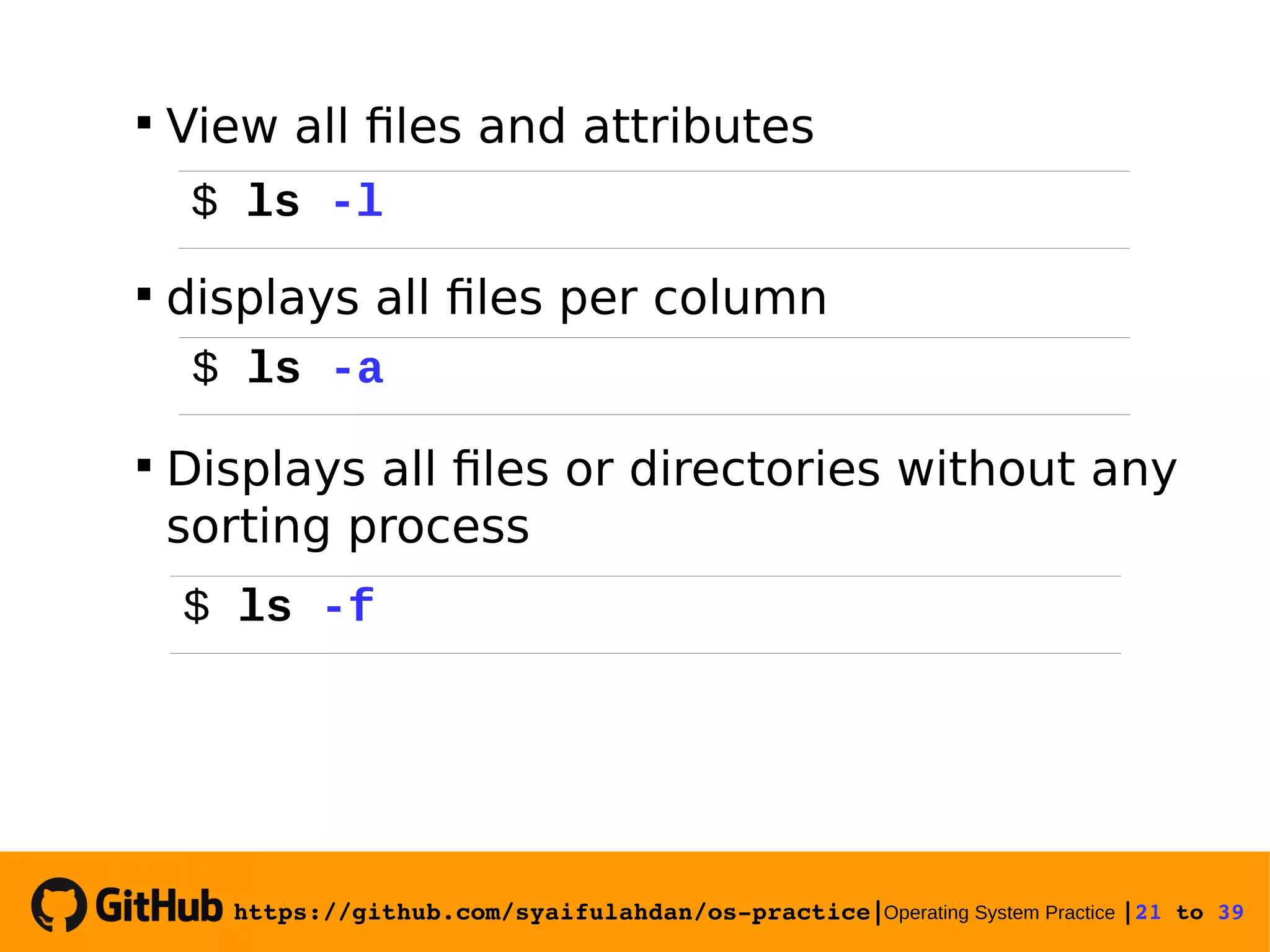
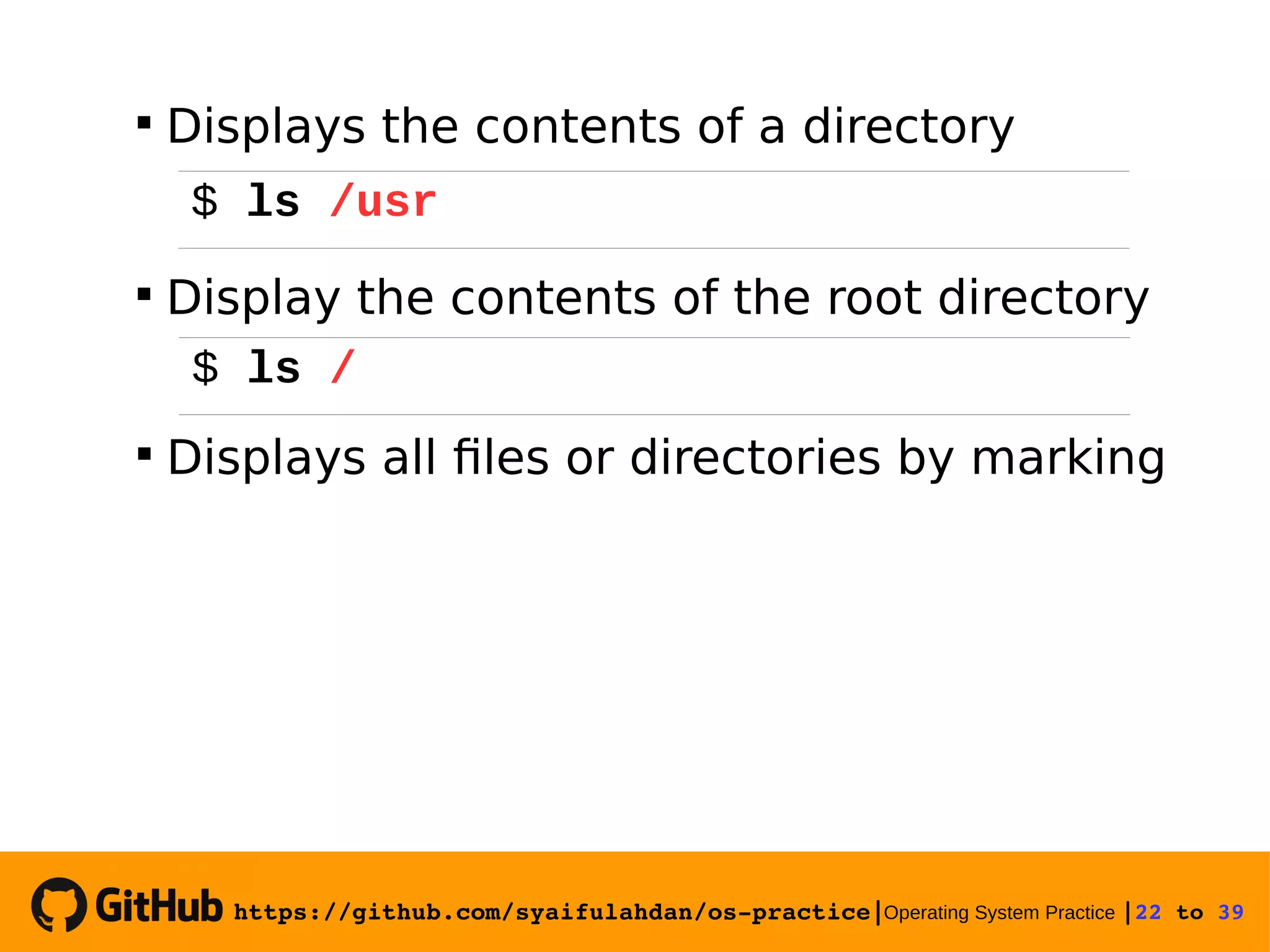
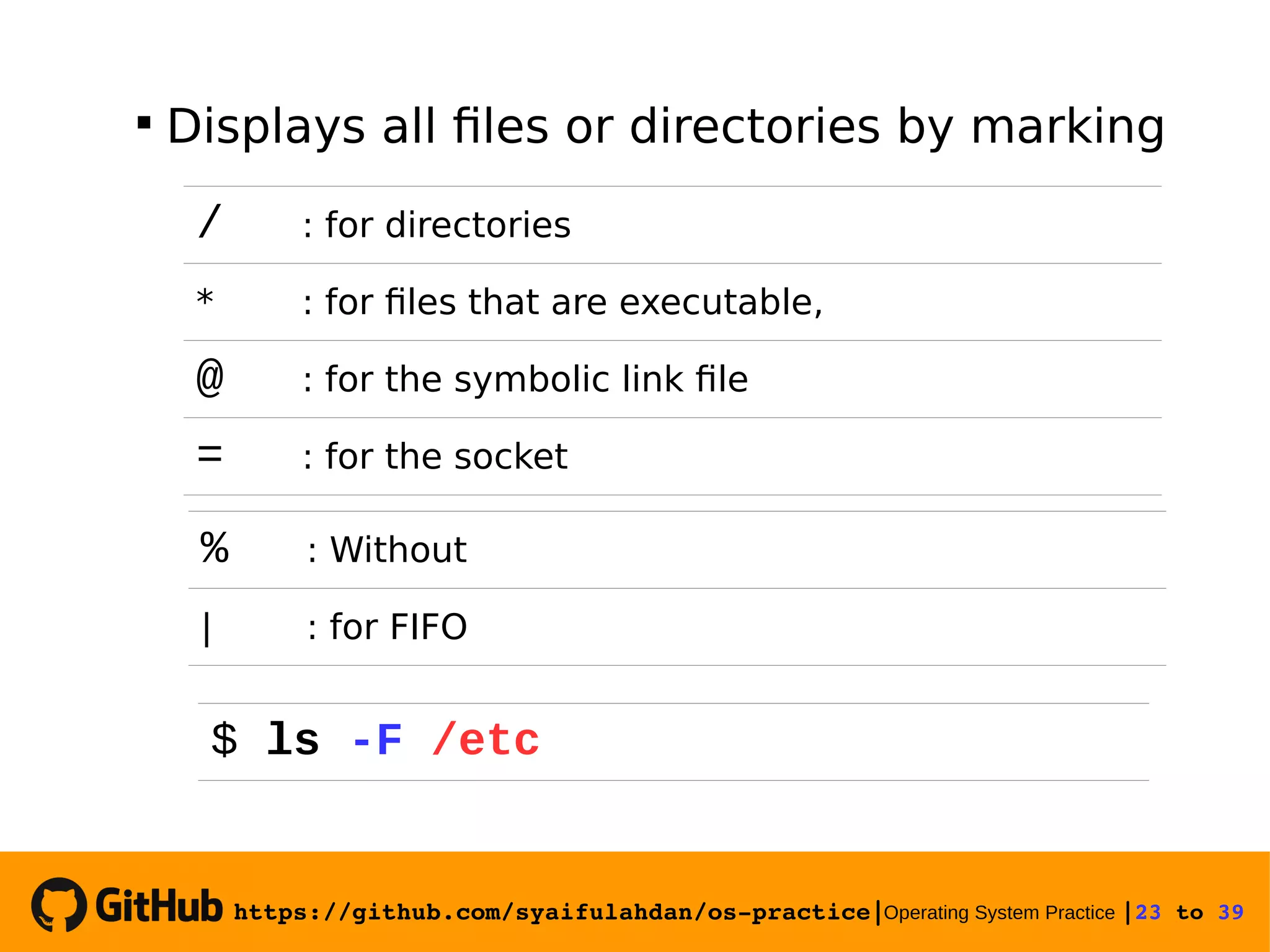
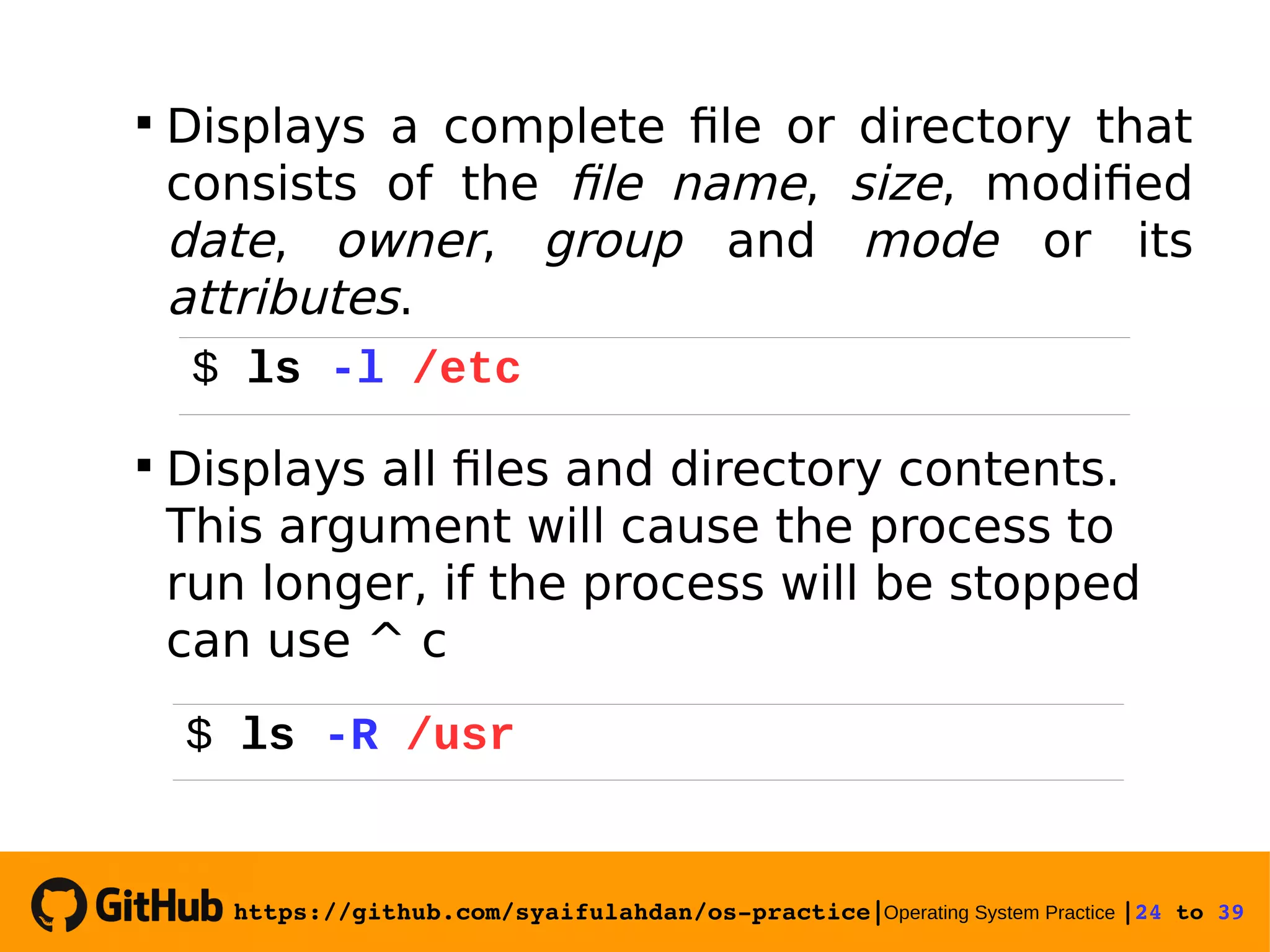
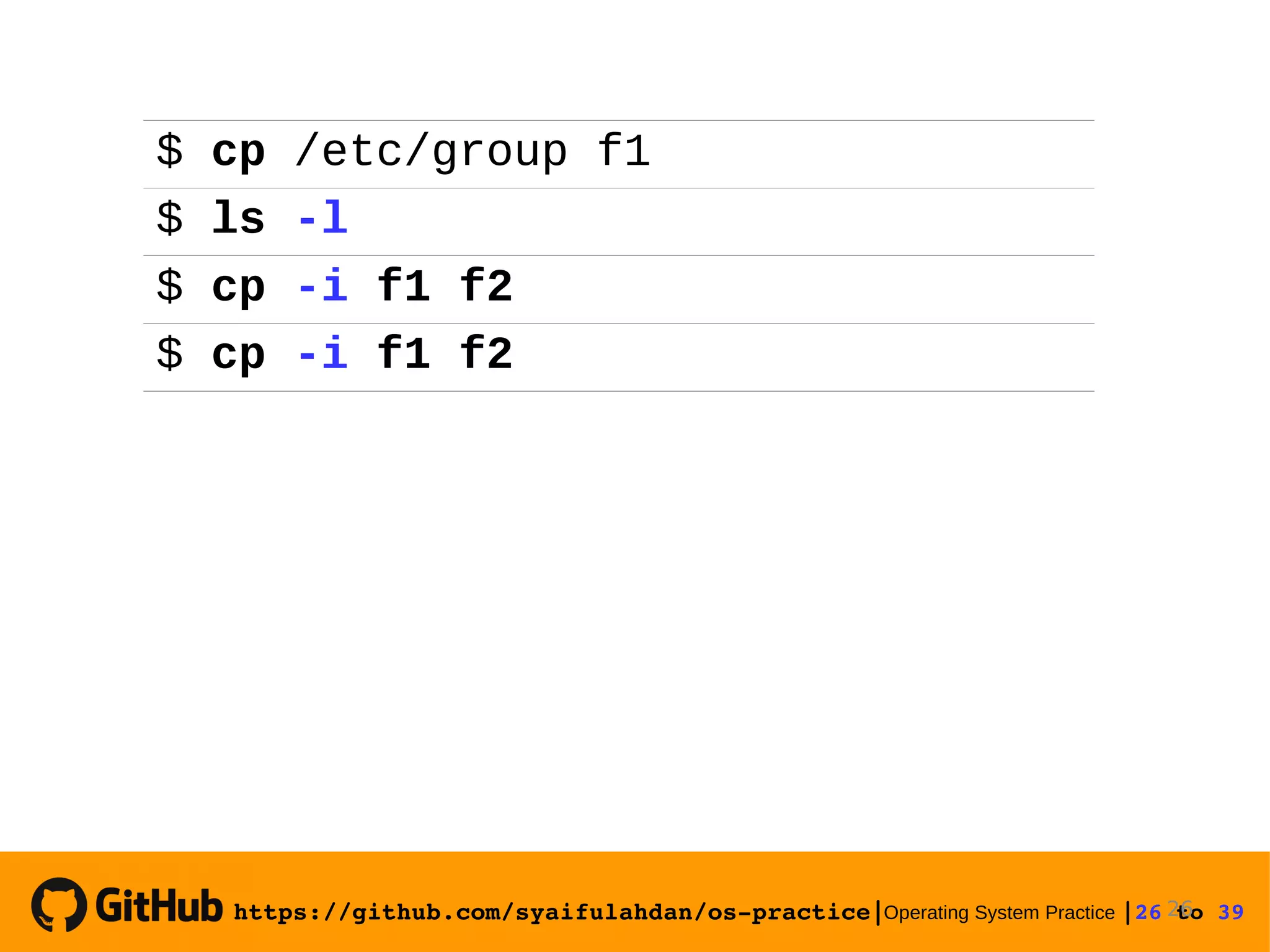
![https://github.com/syaifulahdan/ospractice|Operating System Practice |25 to 39 Experiment 10 : View the file type Experiment 11 : Copying files Copying a file. Give the -i option for interactive questions when the file already exists. 25 $ file $ file * $ file /bin/ls $ cp -i [sourcefile] [filecopy]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meeting-2-basiccommandslinuxoperatingsystem-slide-180413083841/75/Operating-System-Practice-Meeting-2-basic-commands-linux-operating-system-slide-25-2048.jpg)