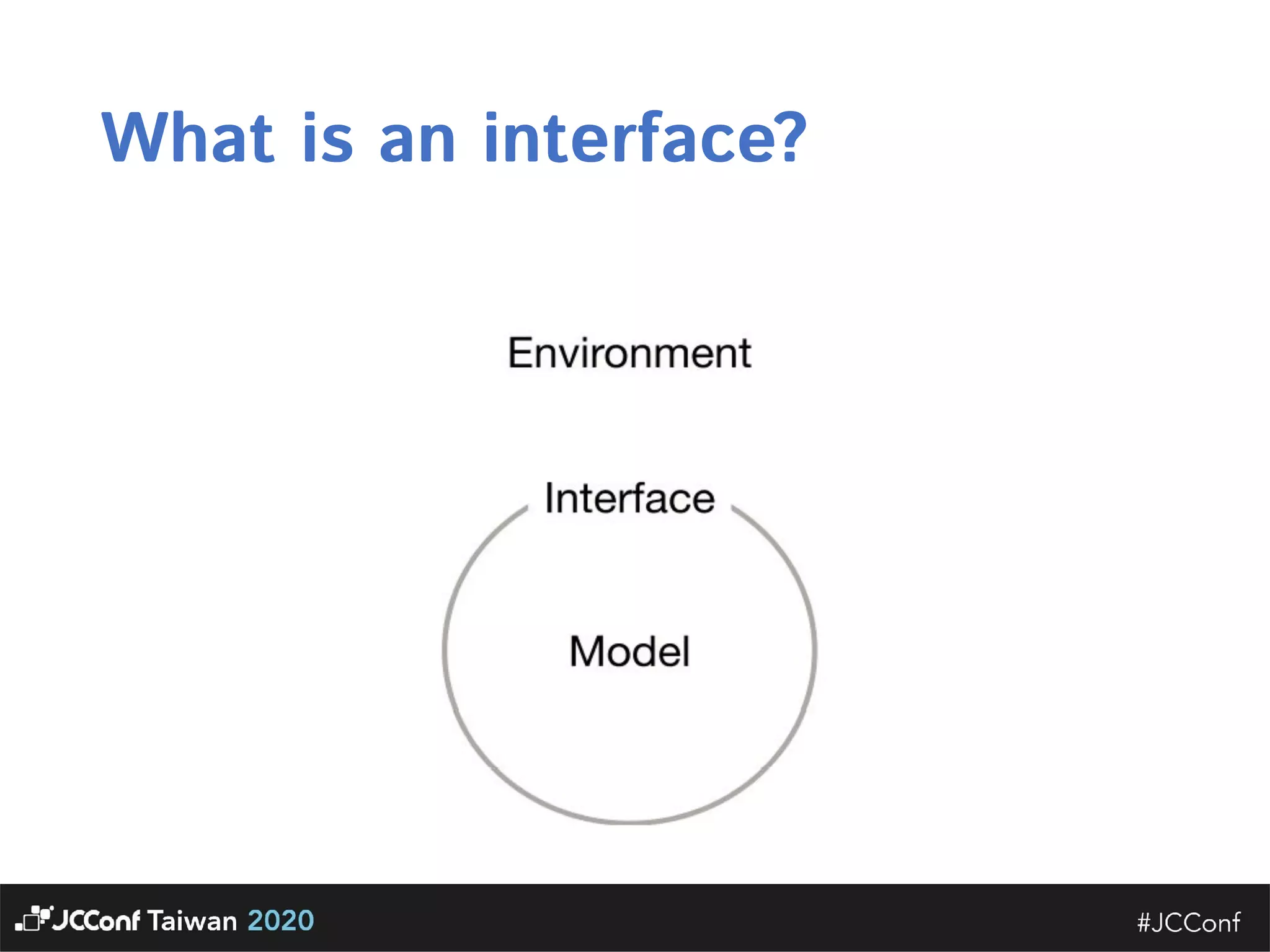
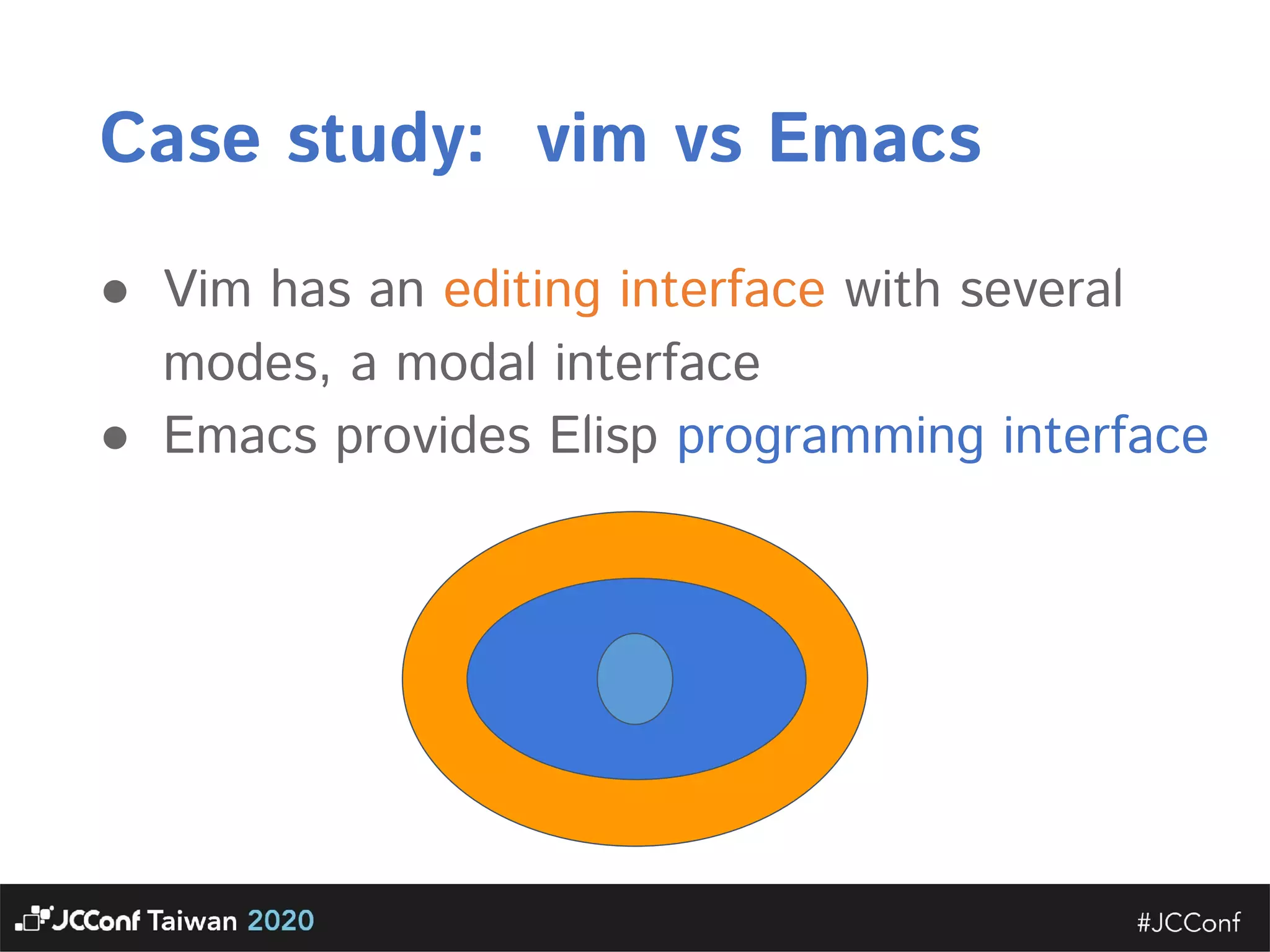
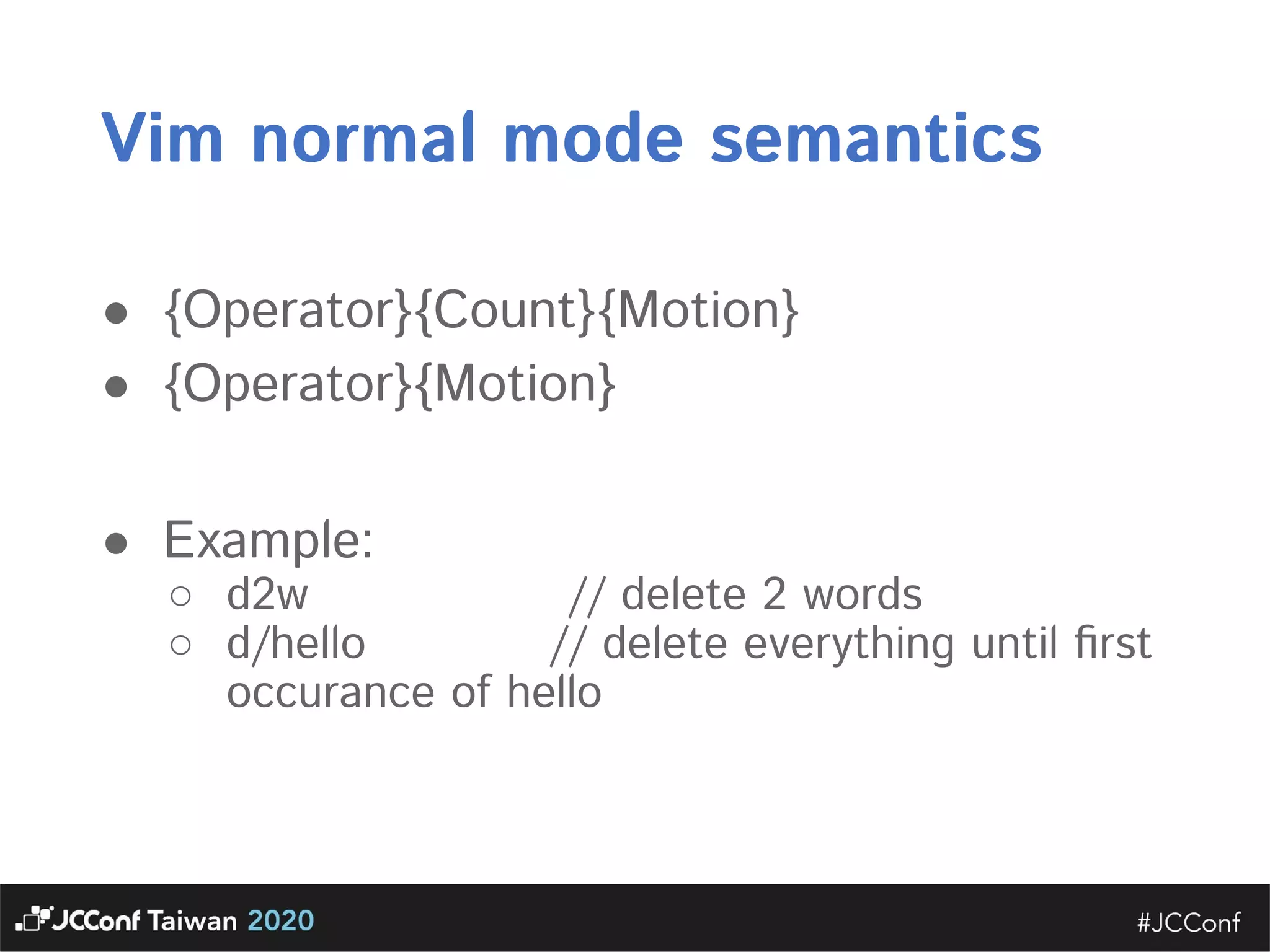
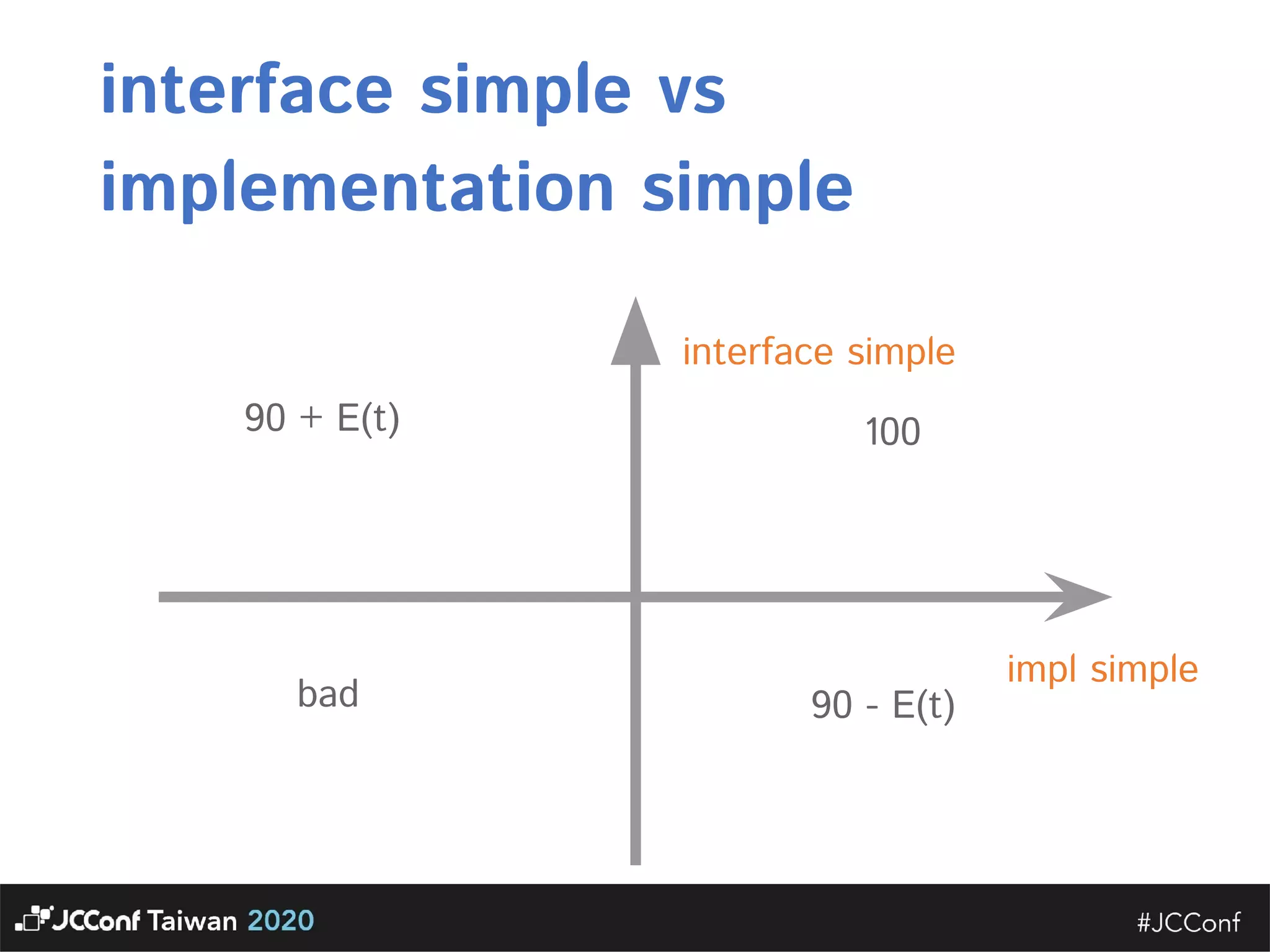
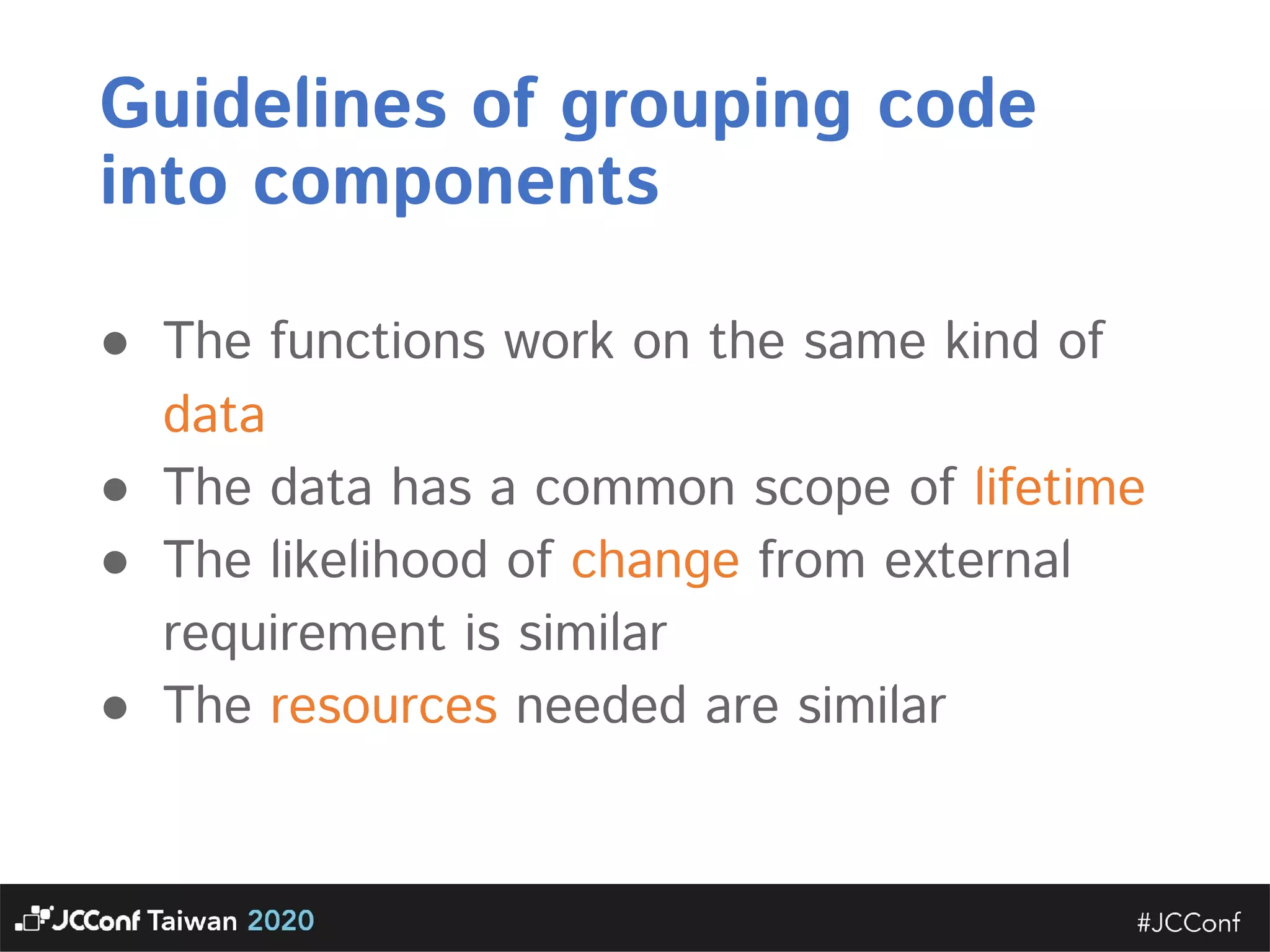
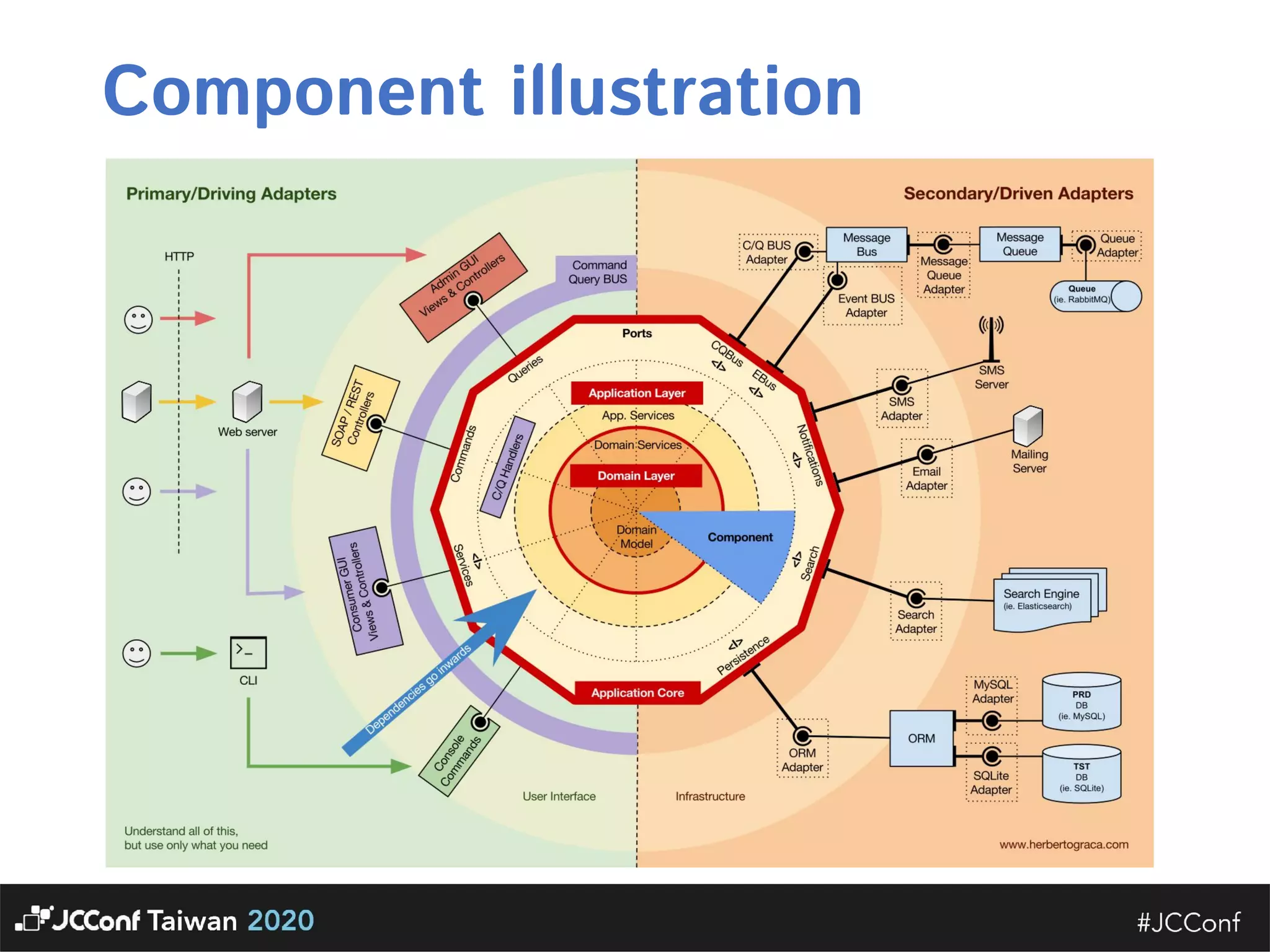
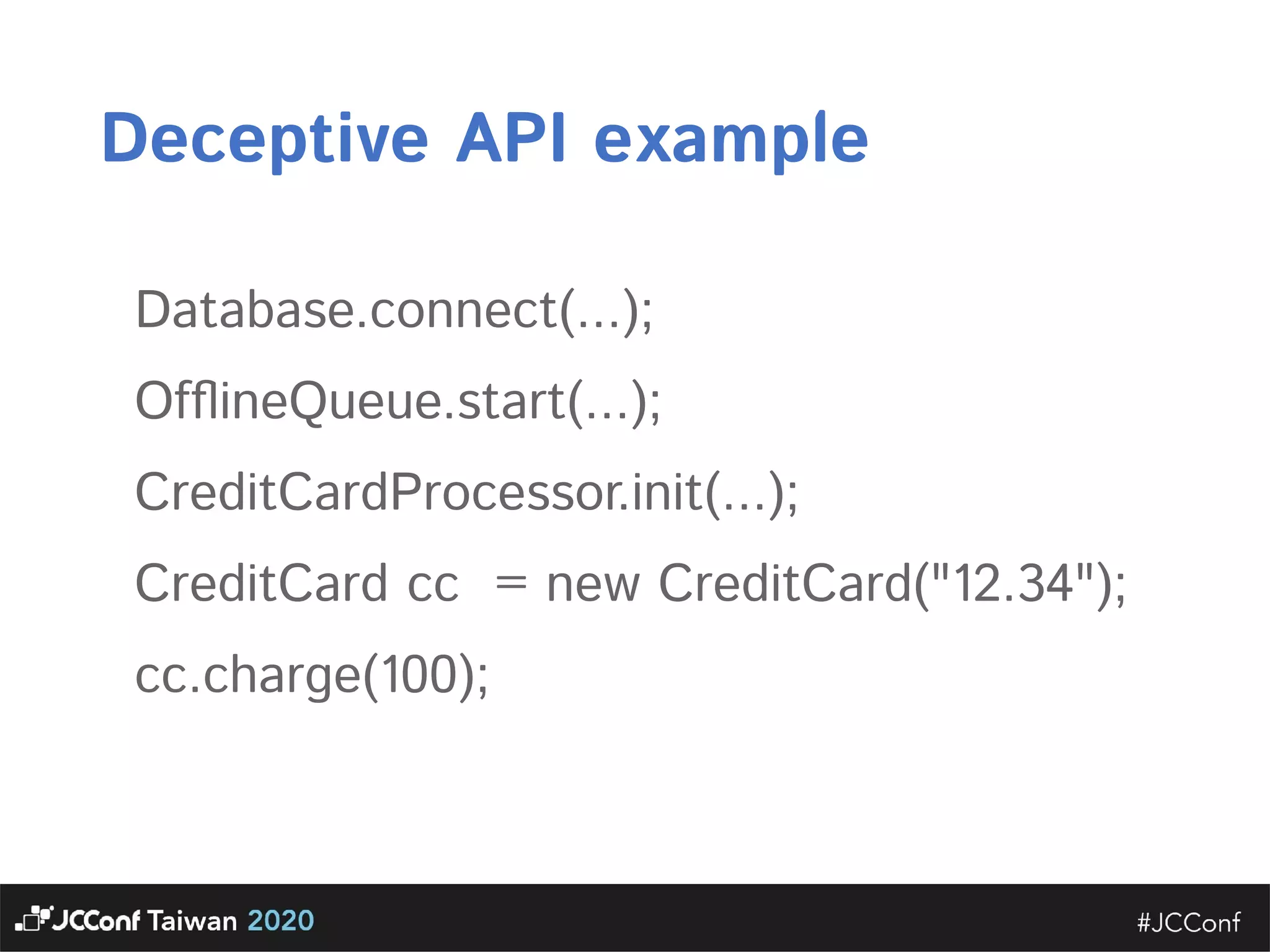
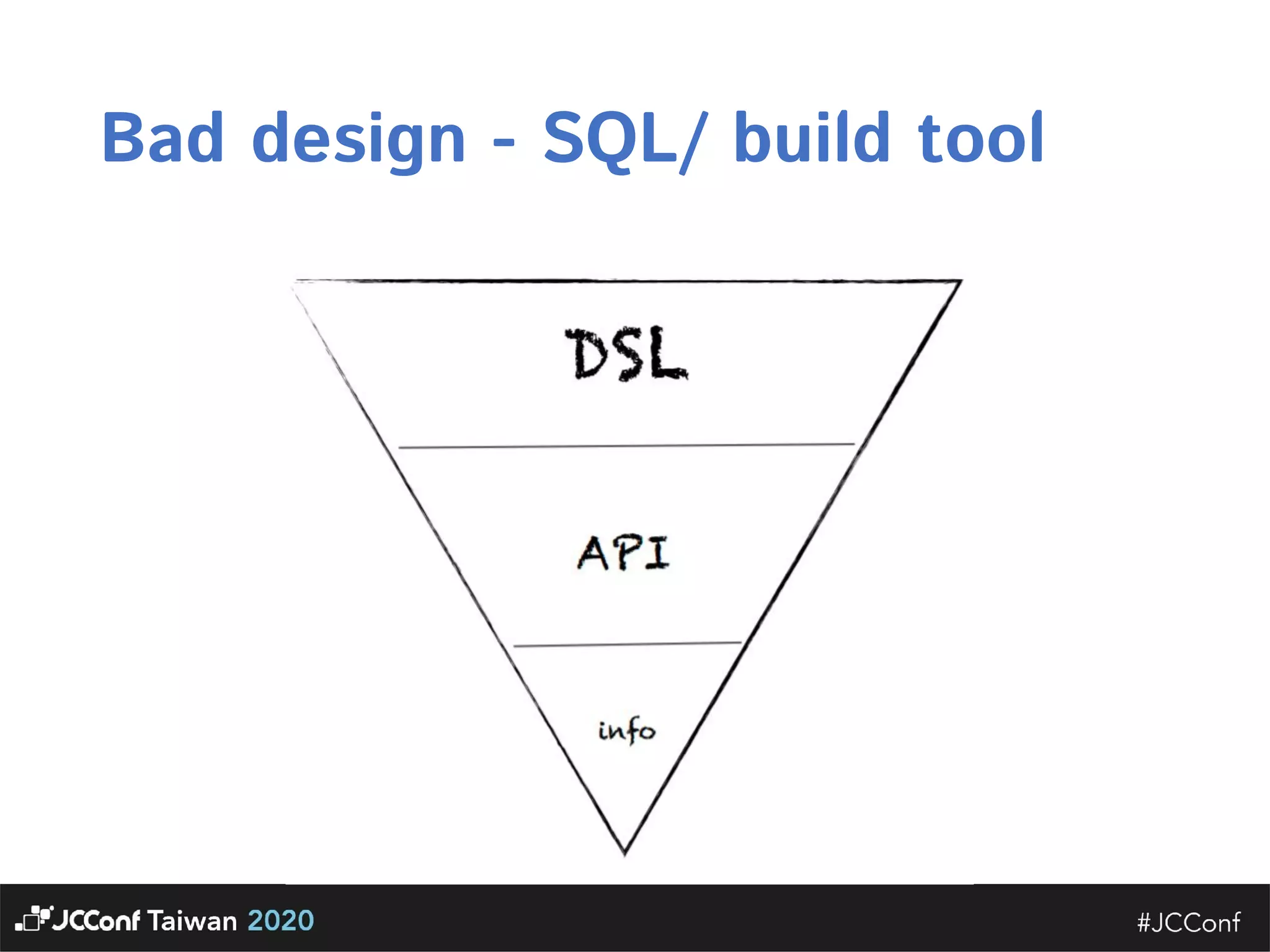
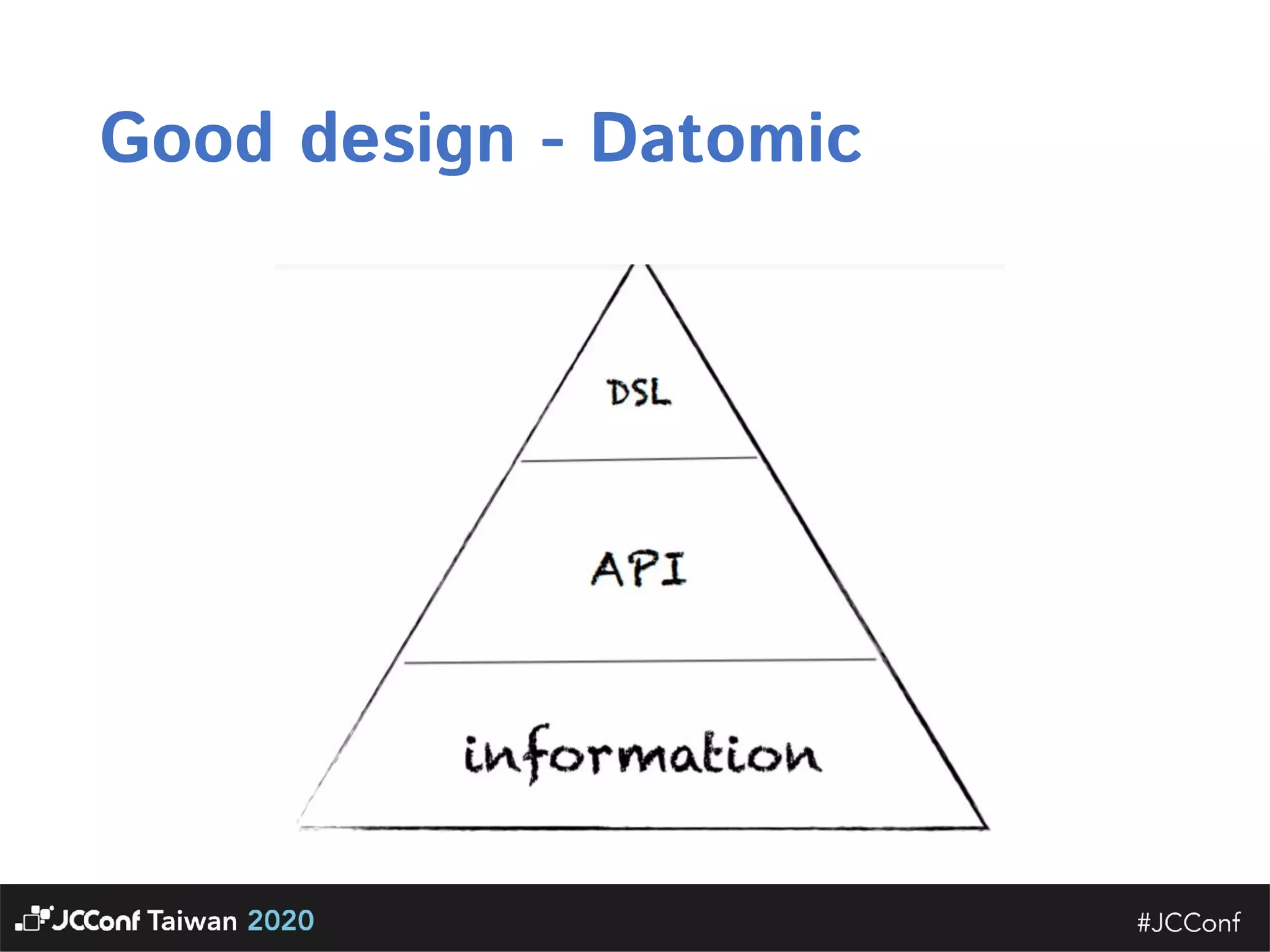
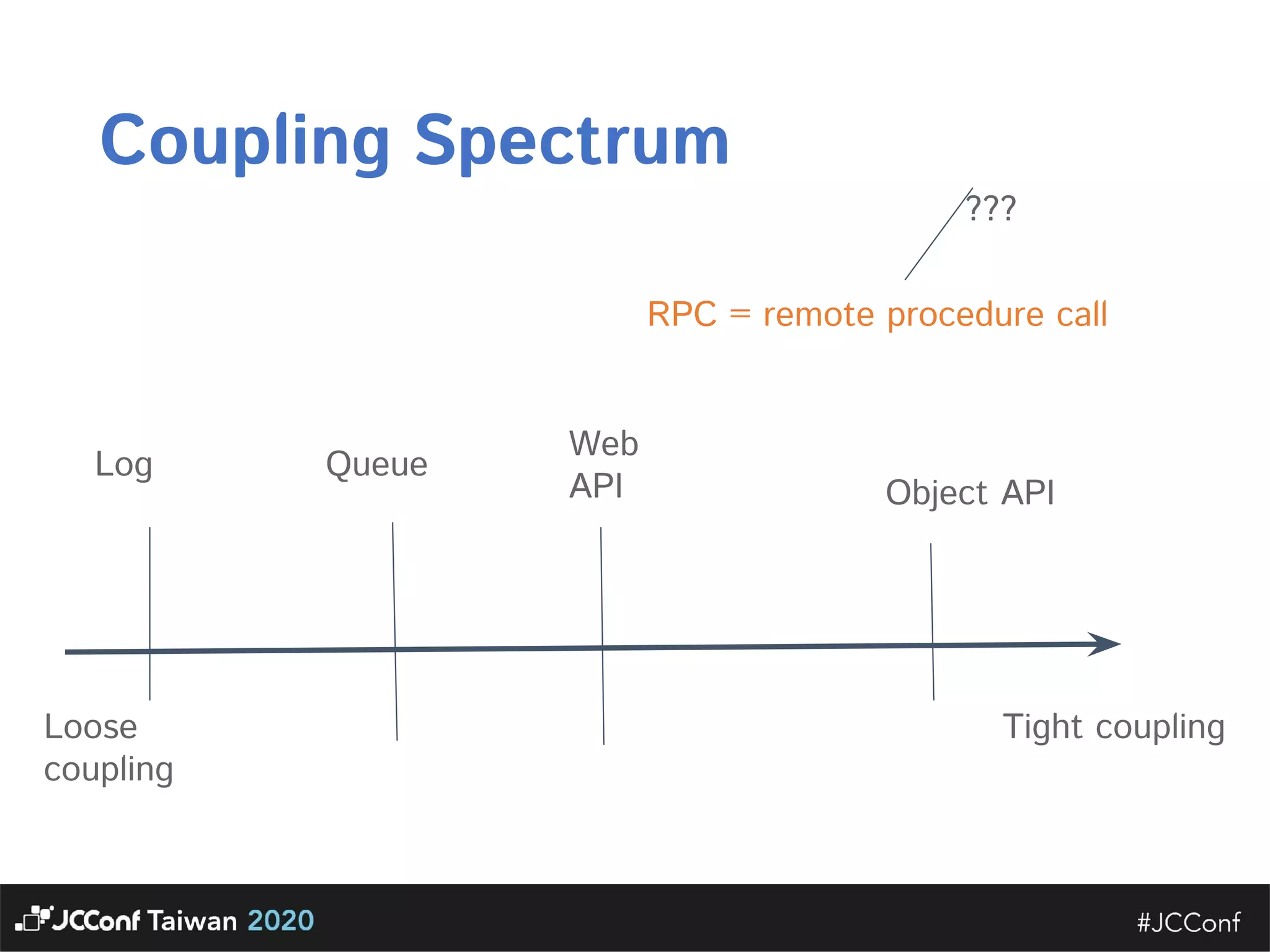
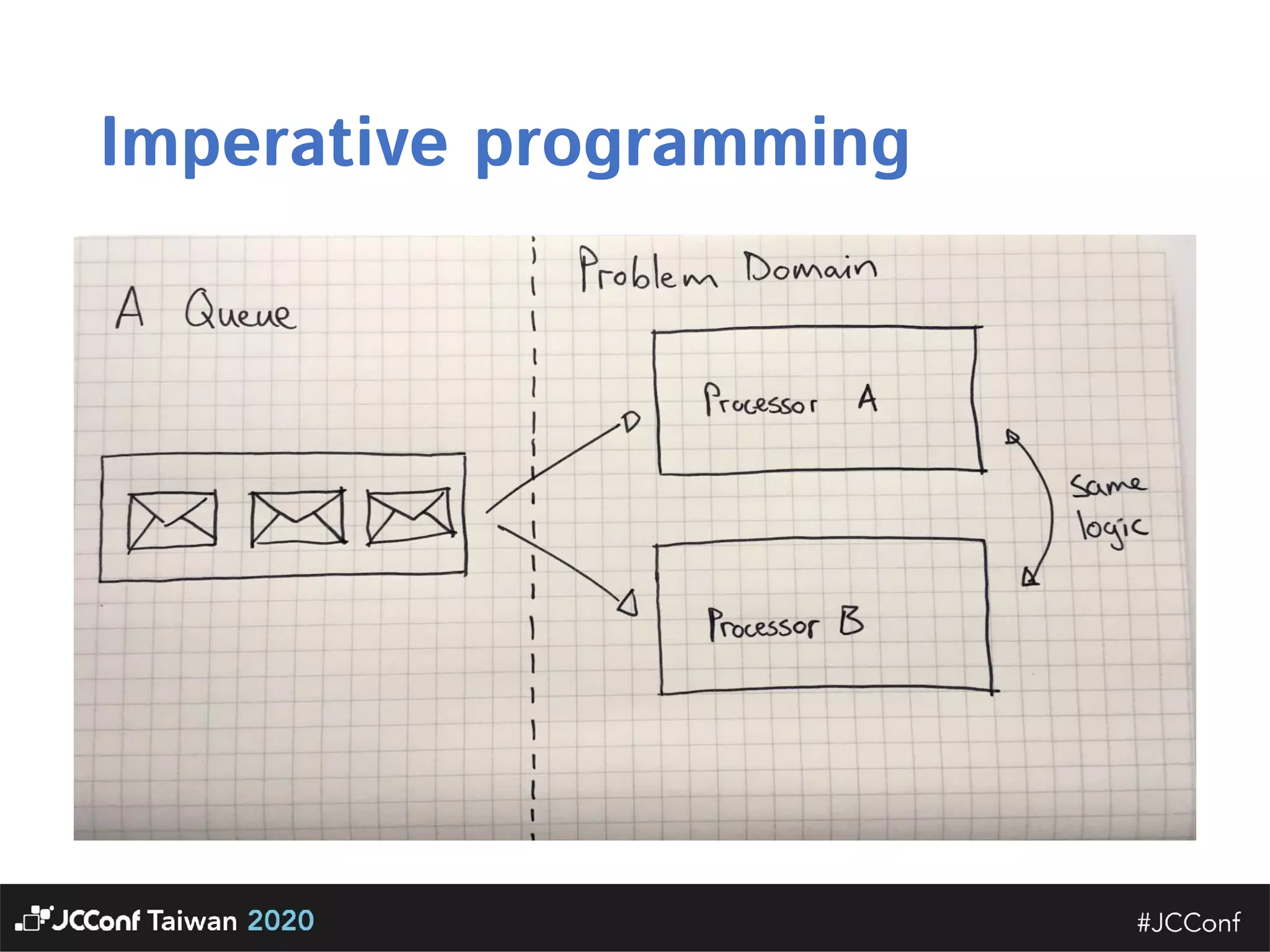
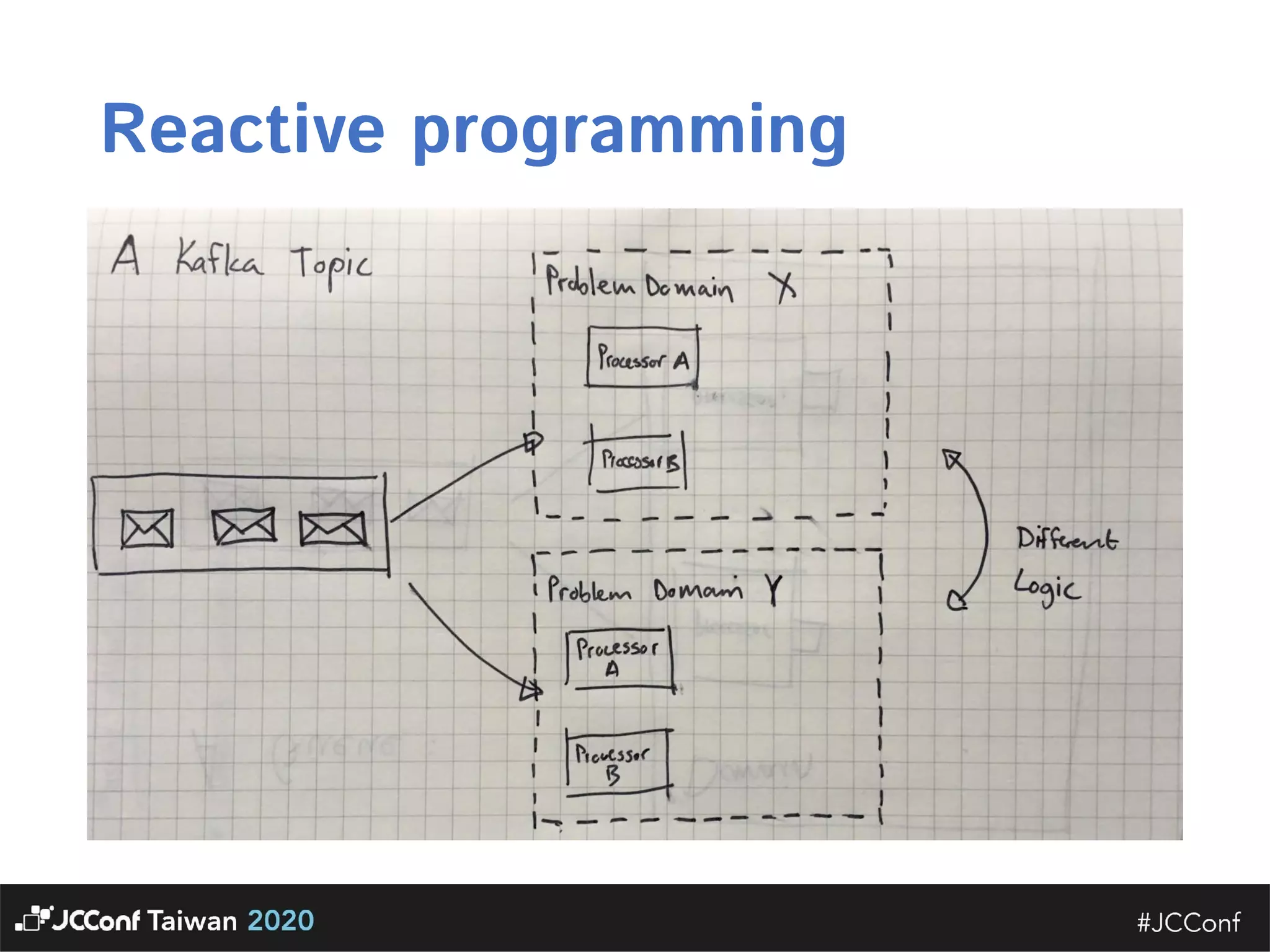
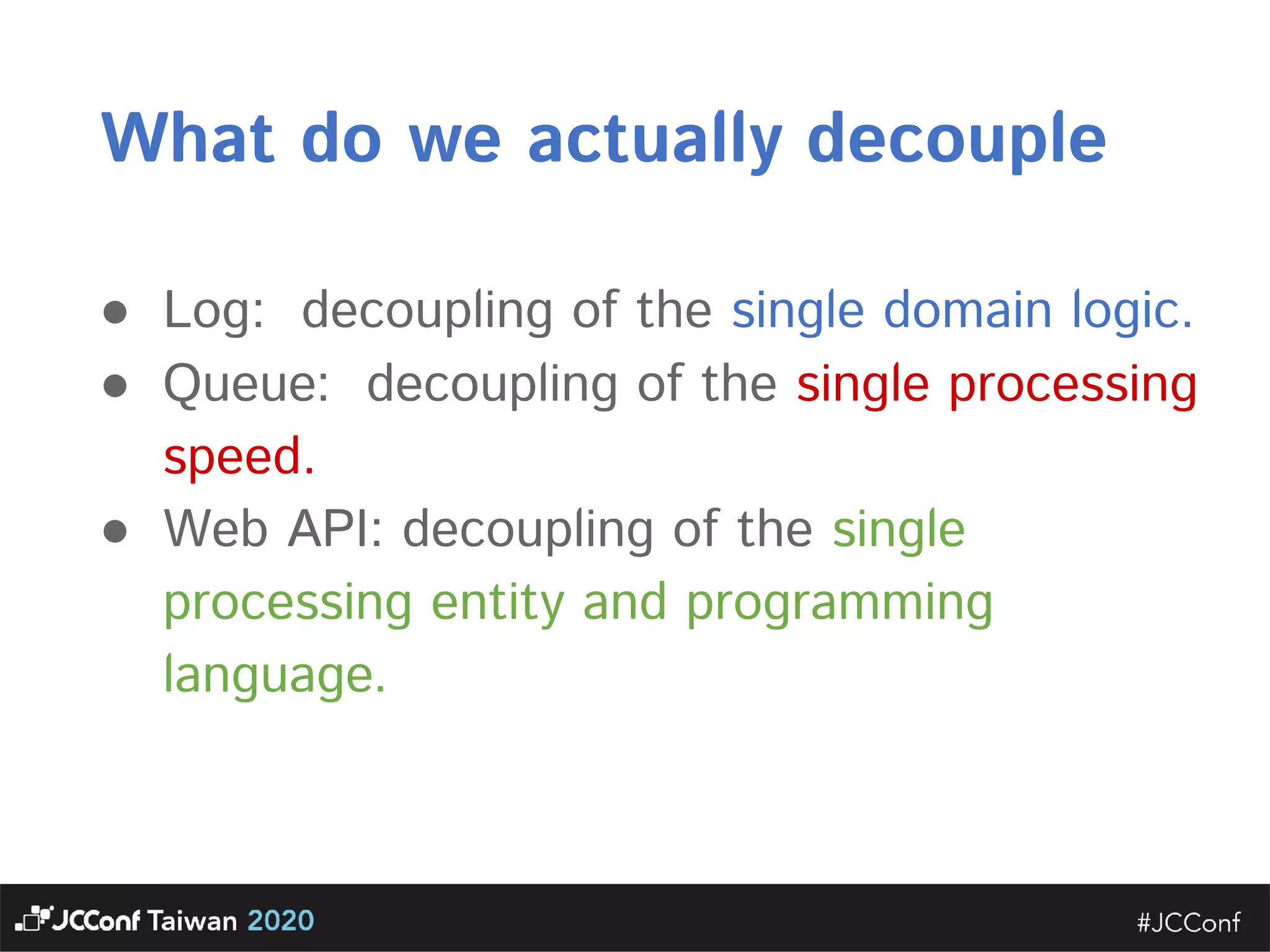
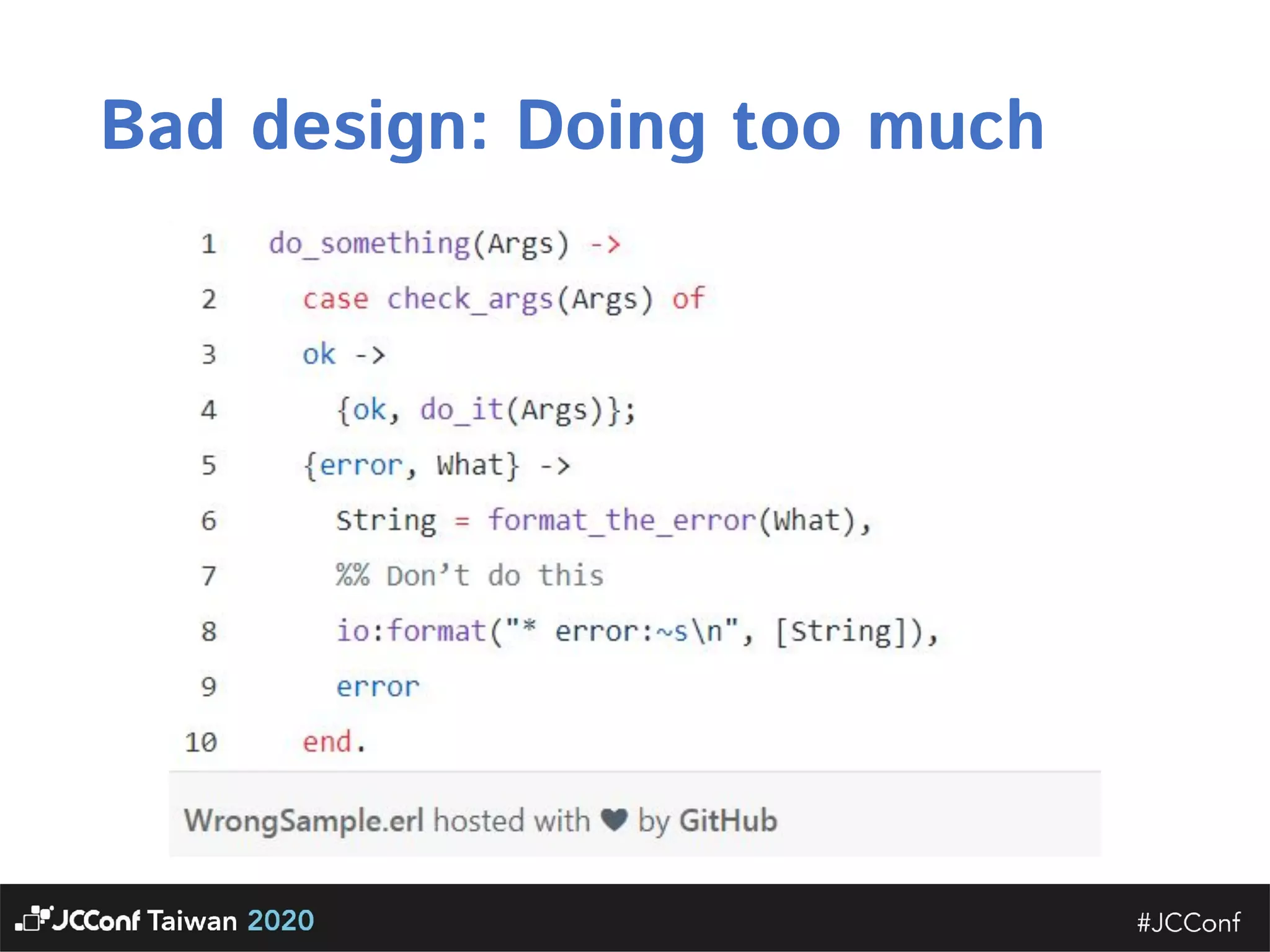
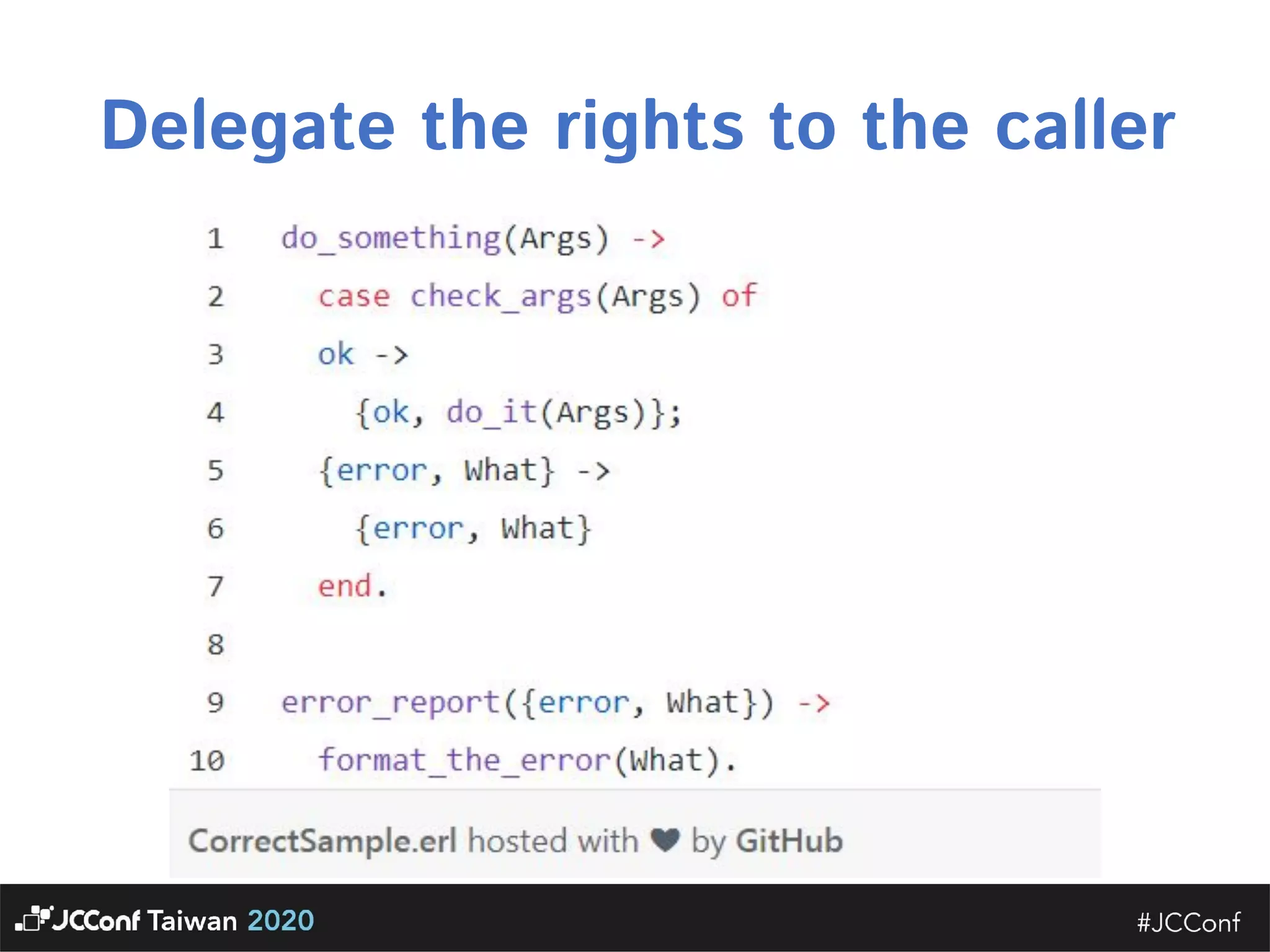
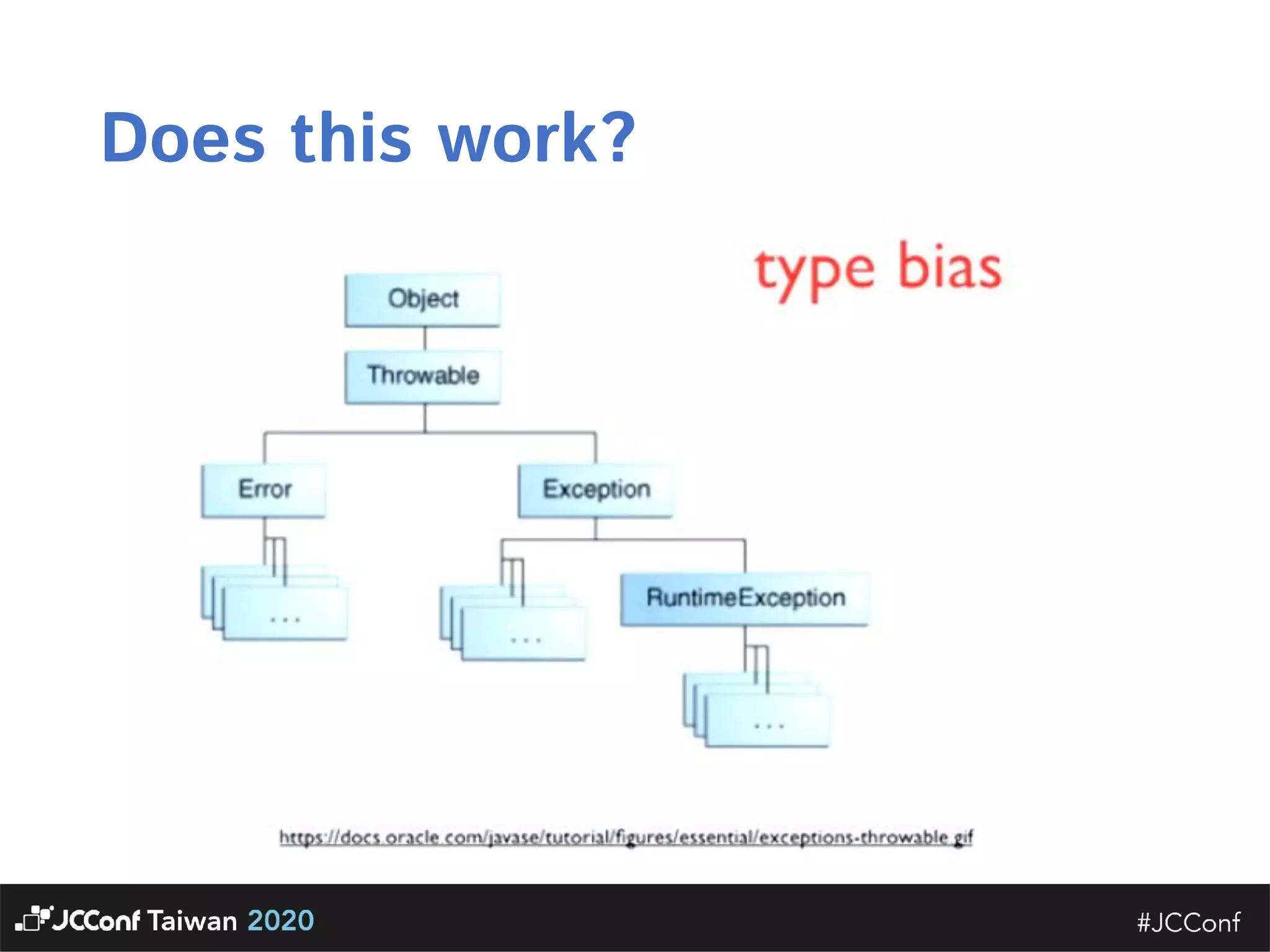
The document discusses component interface design. It defines an interface and contrasts an API approach with a protocol approach. It provides examples of common bad interface practices like deceptive APIs and DSLs as APIs. It also discusses issues with distributed systems like idempotency keys and the coupling spectrum. The document emphasizes designing error messages for the caller and distinguishing component purpose from implementation.