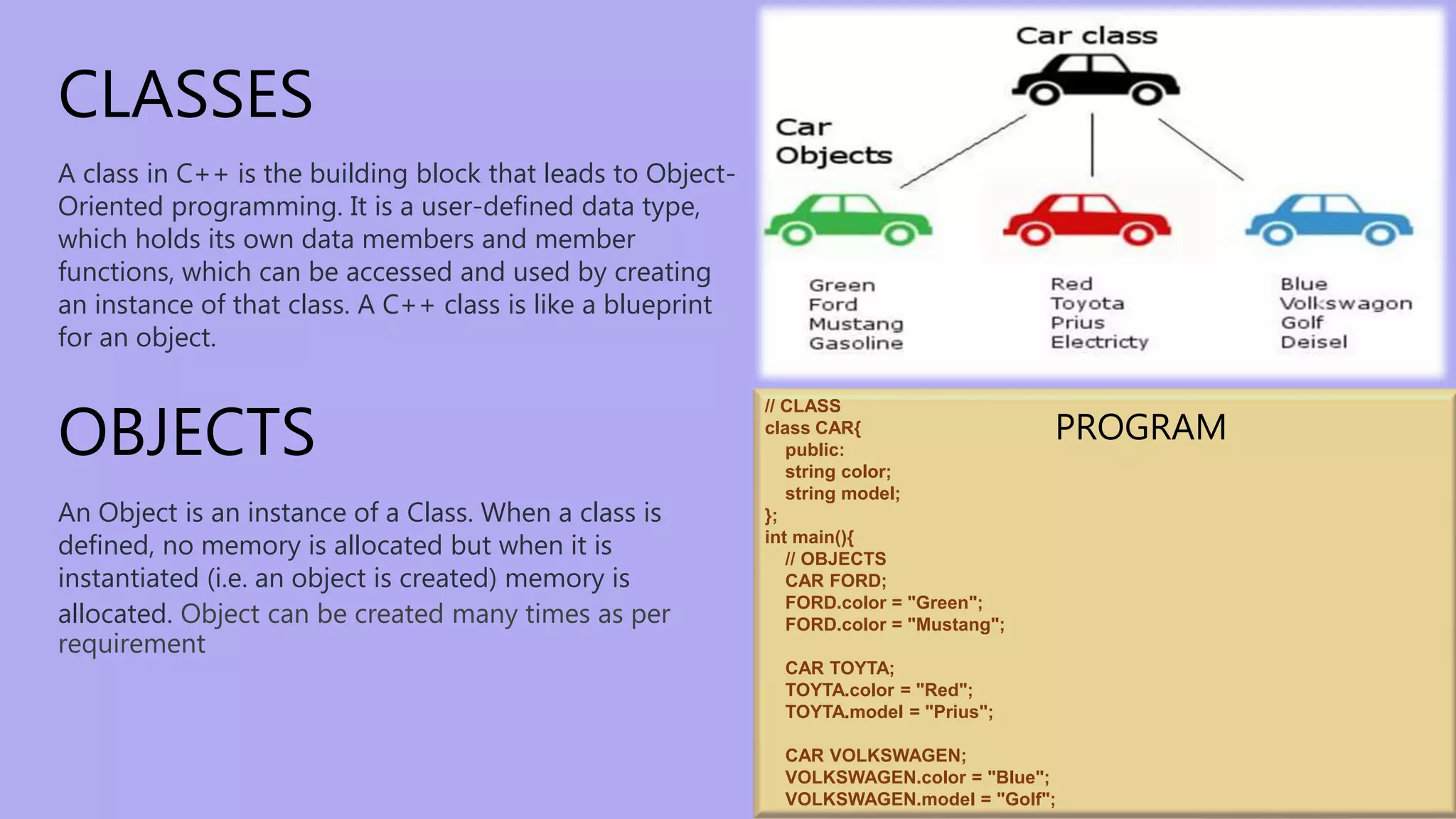
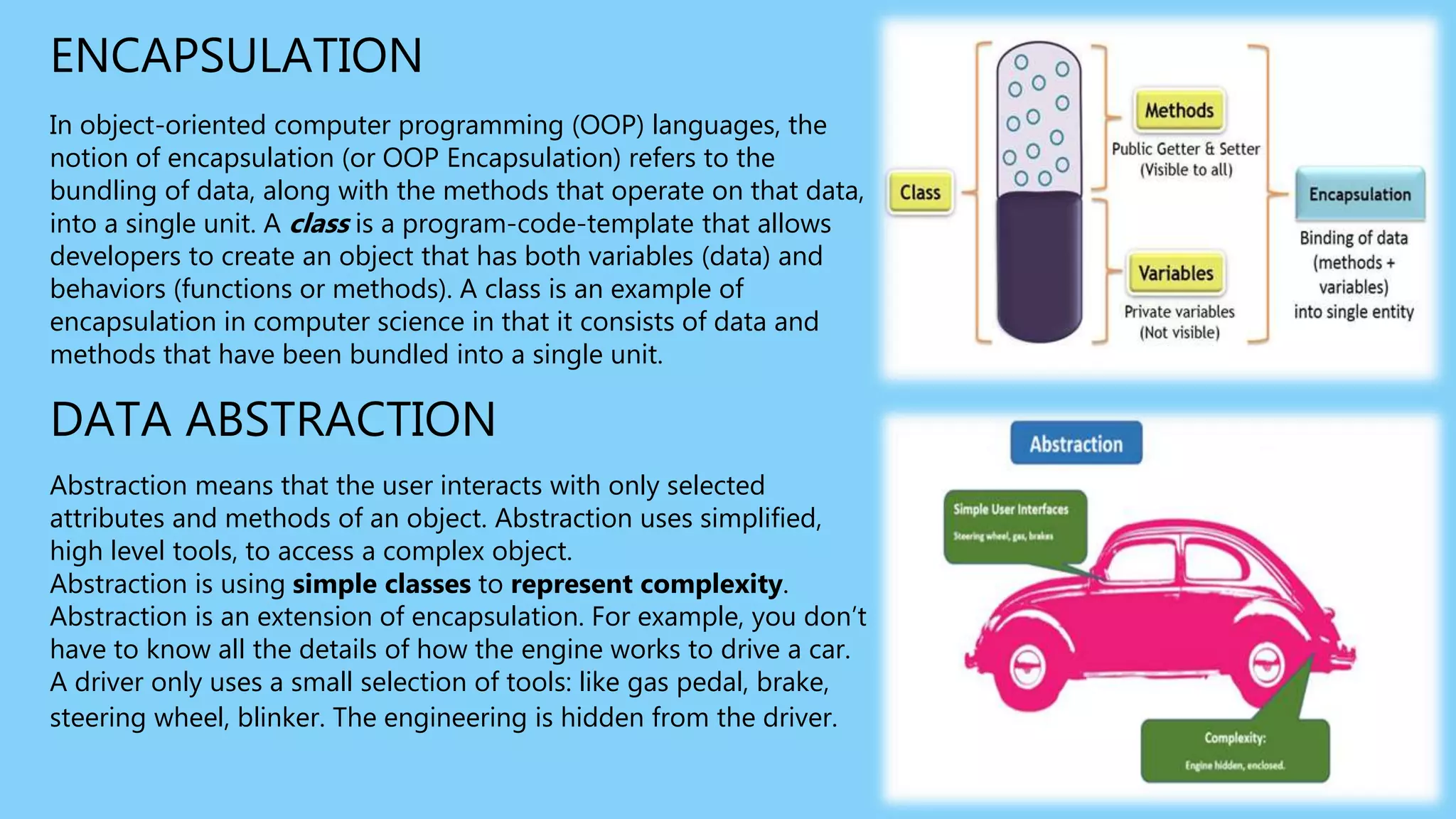
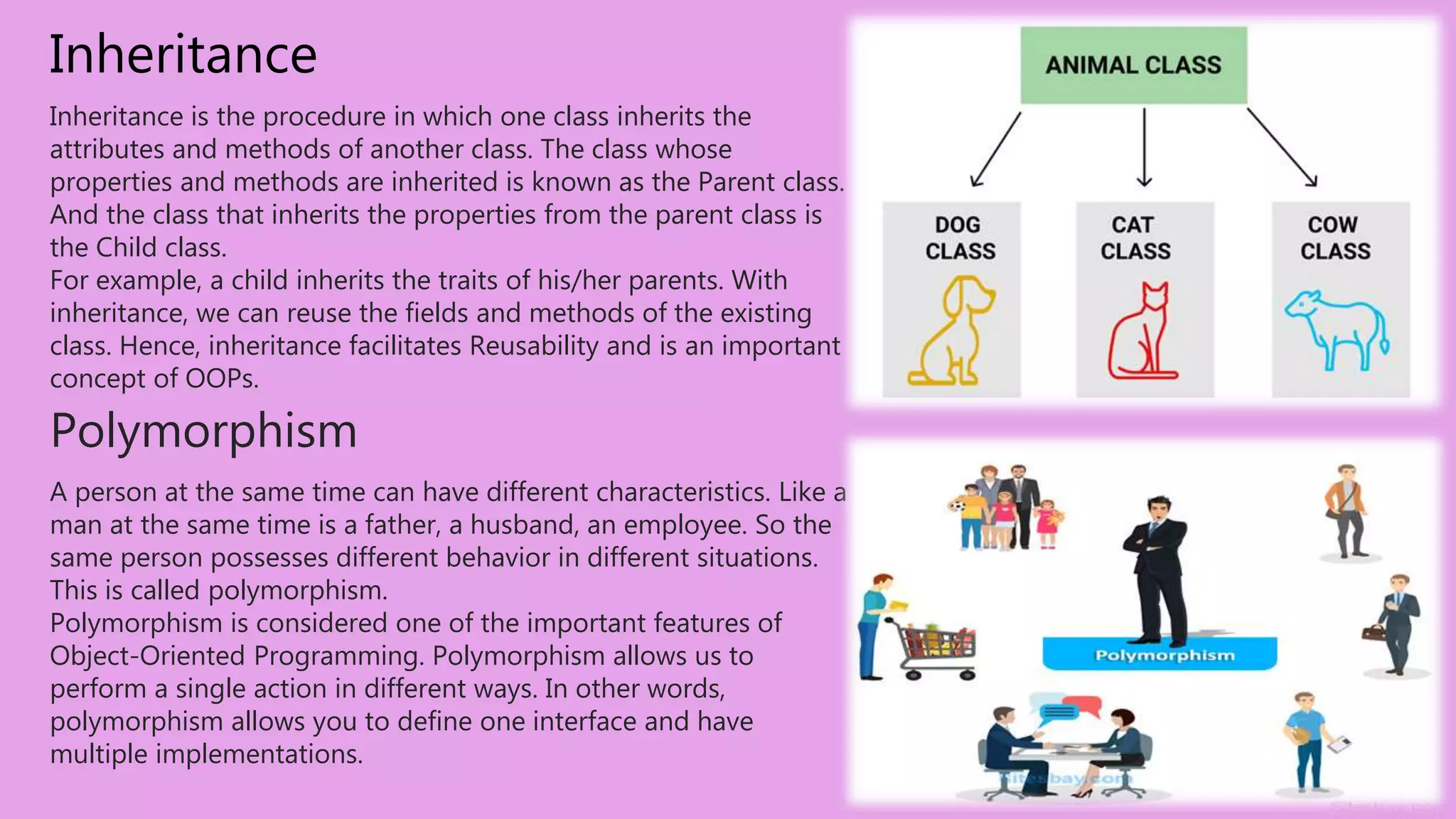
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that focuses on using classes and objects to structure software. It emphasizes encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, allowing for better data management and code reusability. While OOP has many advantages, such as facilitating program upgrades and secure coding, it also has drawbacks like longer program lengths and the requirement for a clear object-oriented mindset.