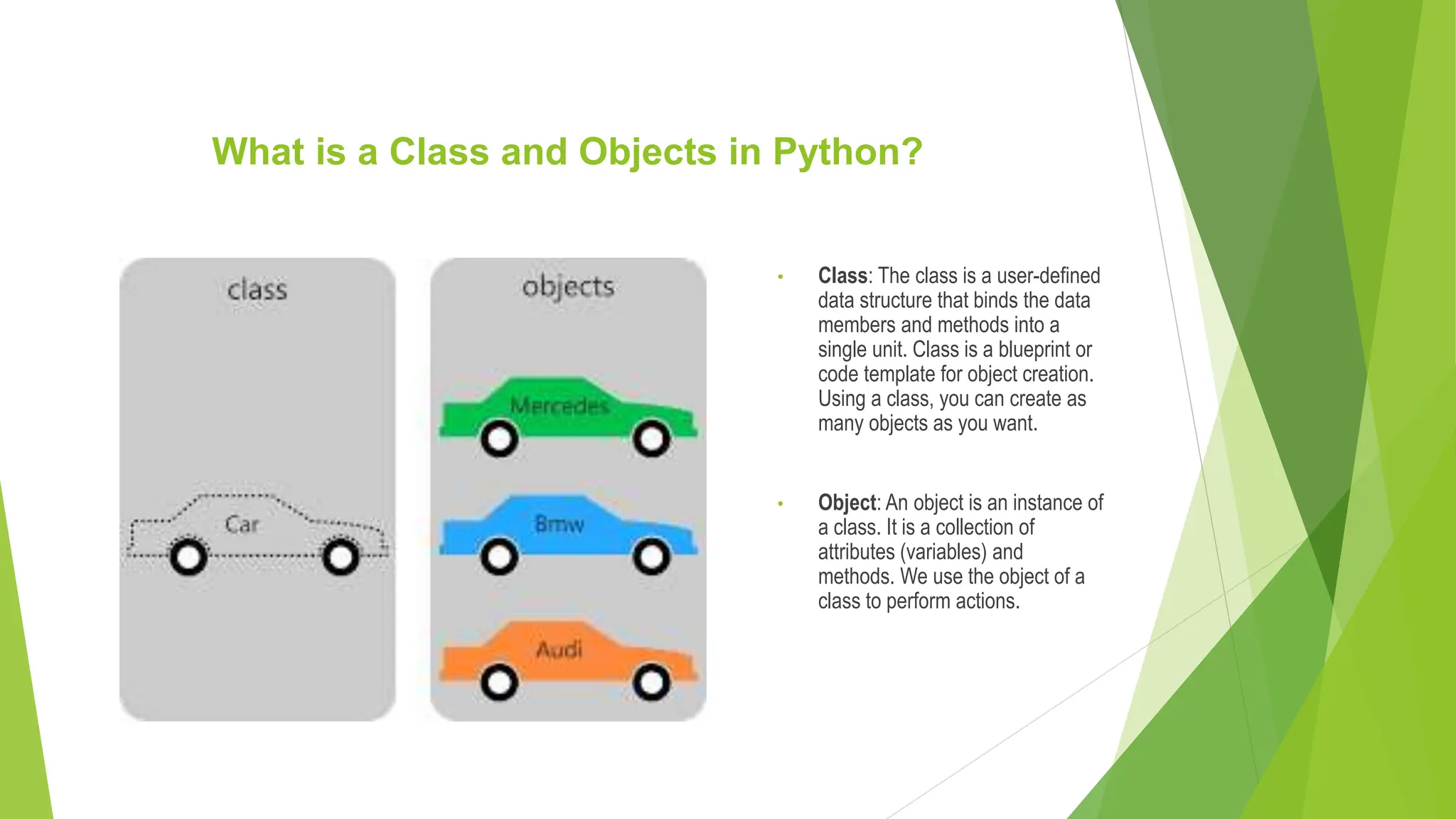
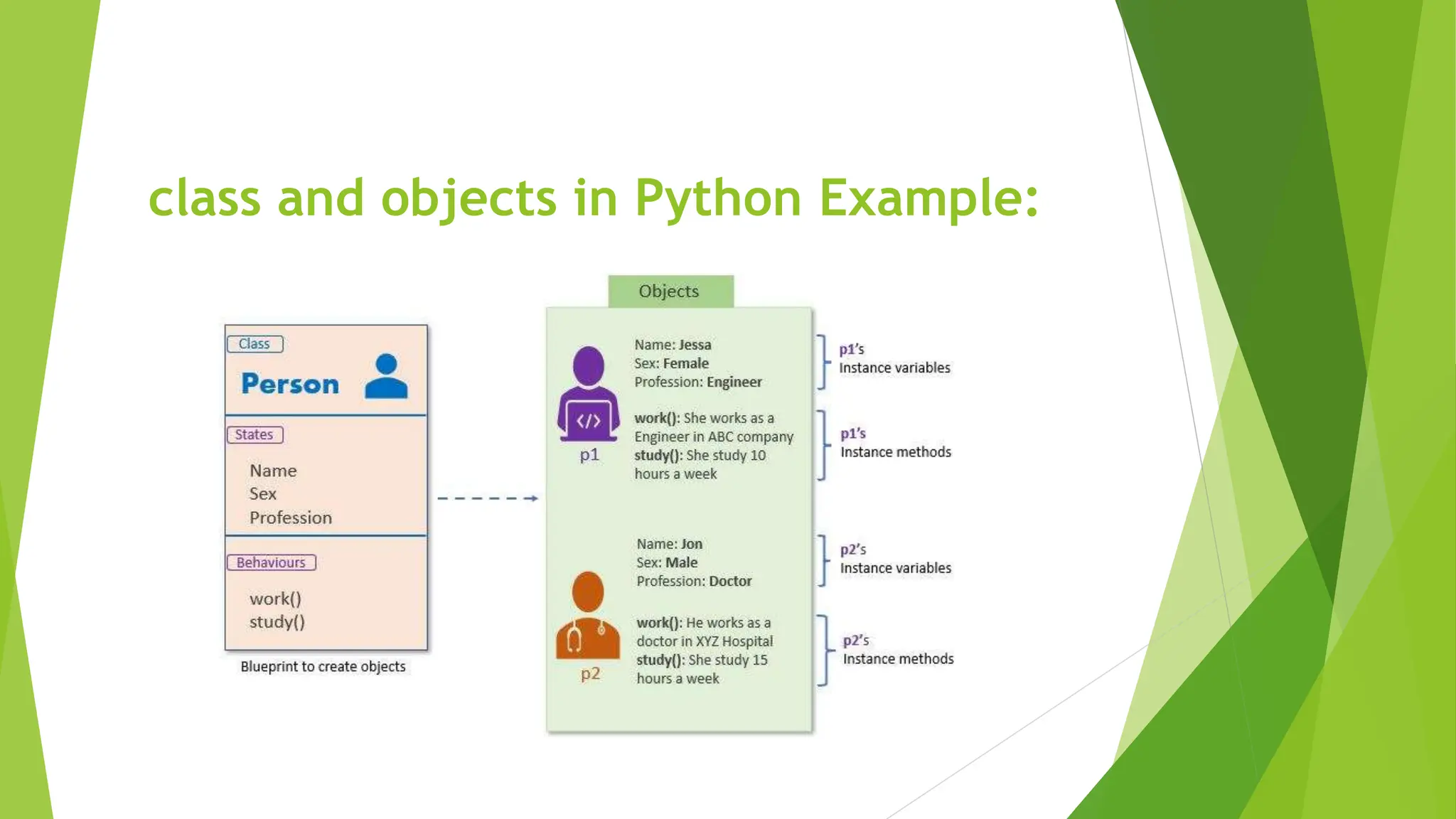
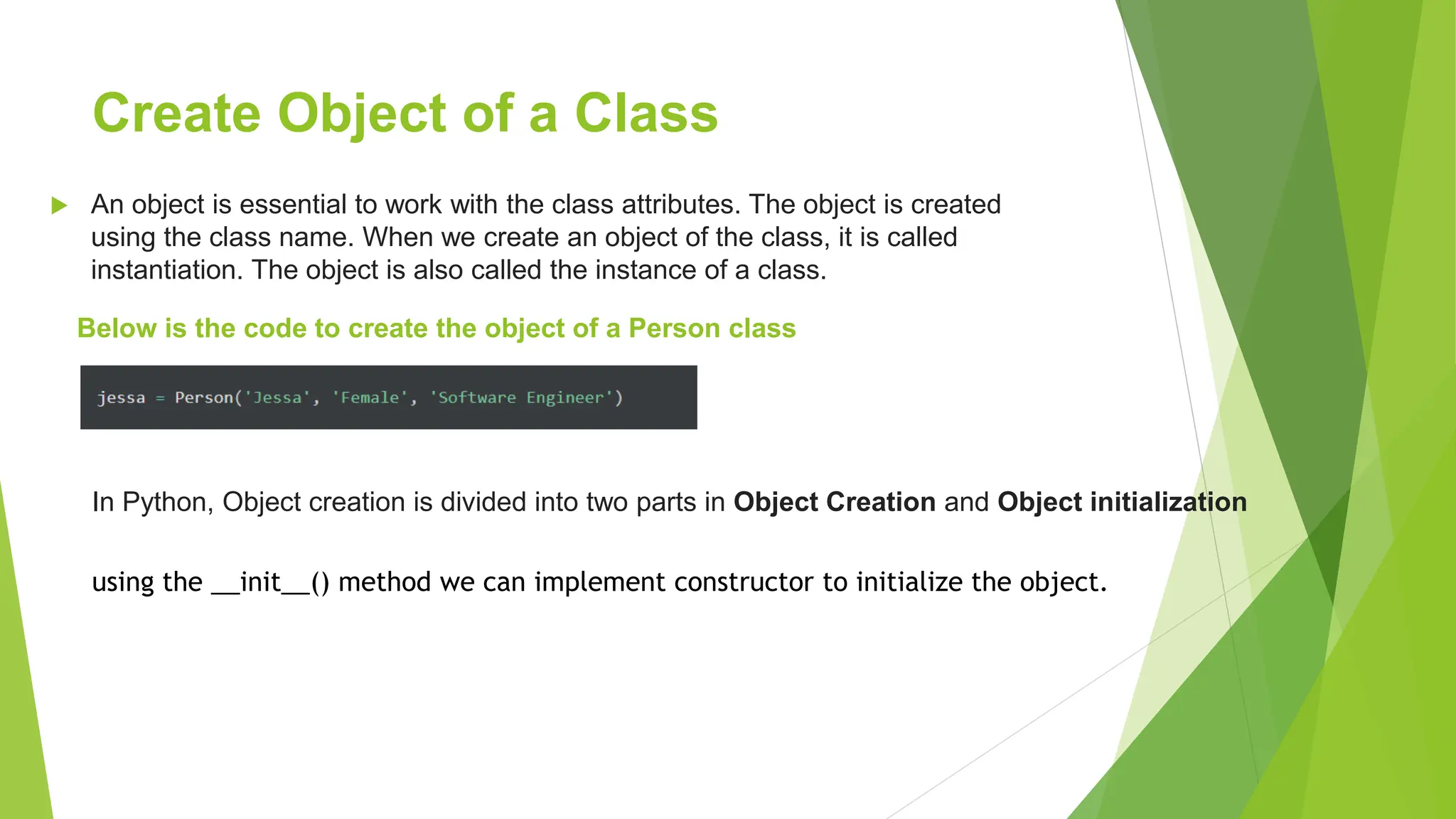
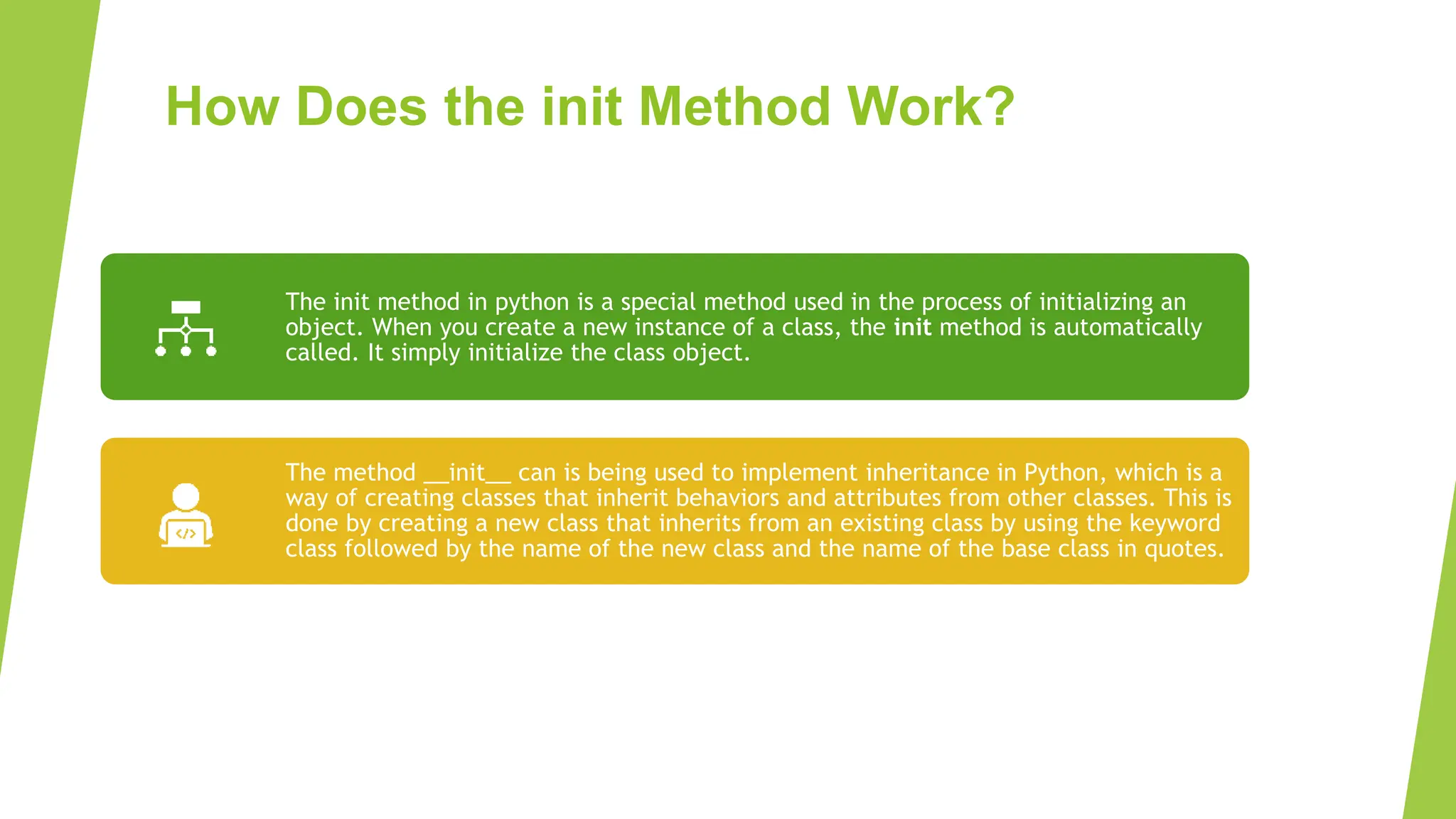
Object oriented programming (OOP) in Python uses classes and objects. A class defines attributes and behaviors that objects can have. An object is an instance of a class that represents a real-world entity with unique attribute values and behaviors. The __init__() method initializes new objects by assigning values to attributes. Classes allow for code reuse through inheritance, where child classes inherit attributes and behaviors from parent classes.