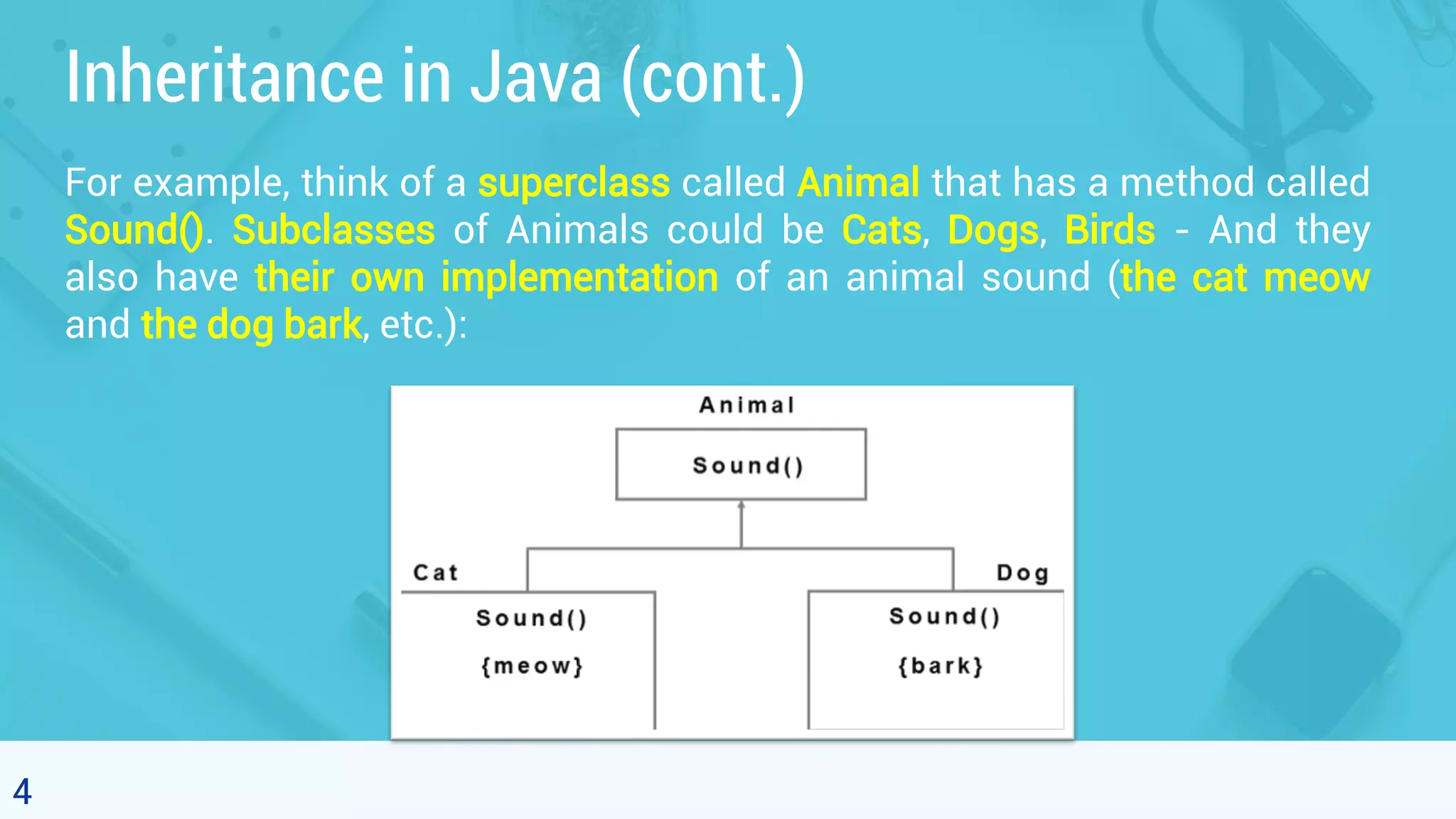
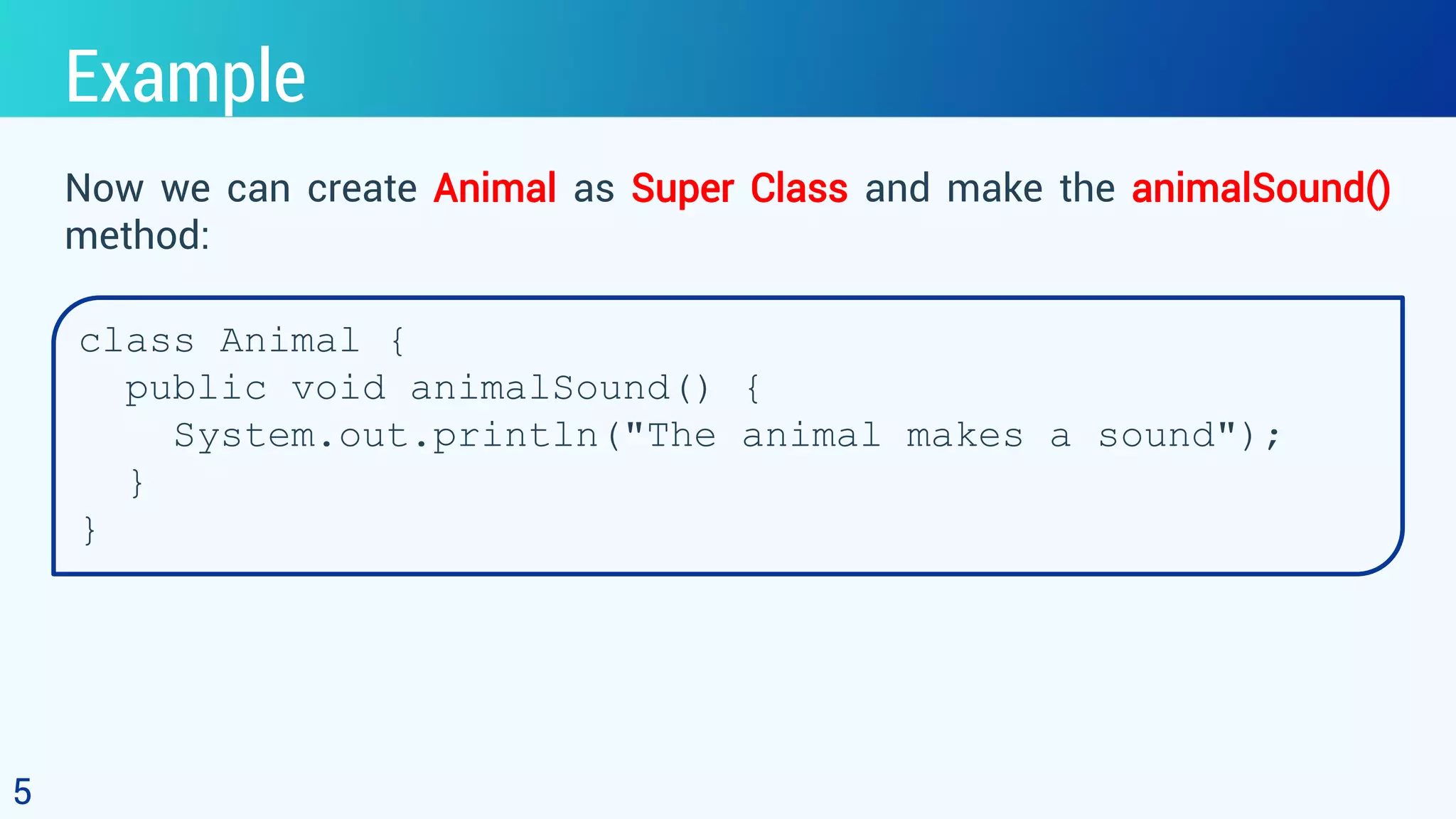
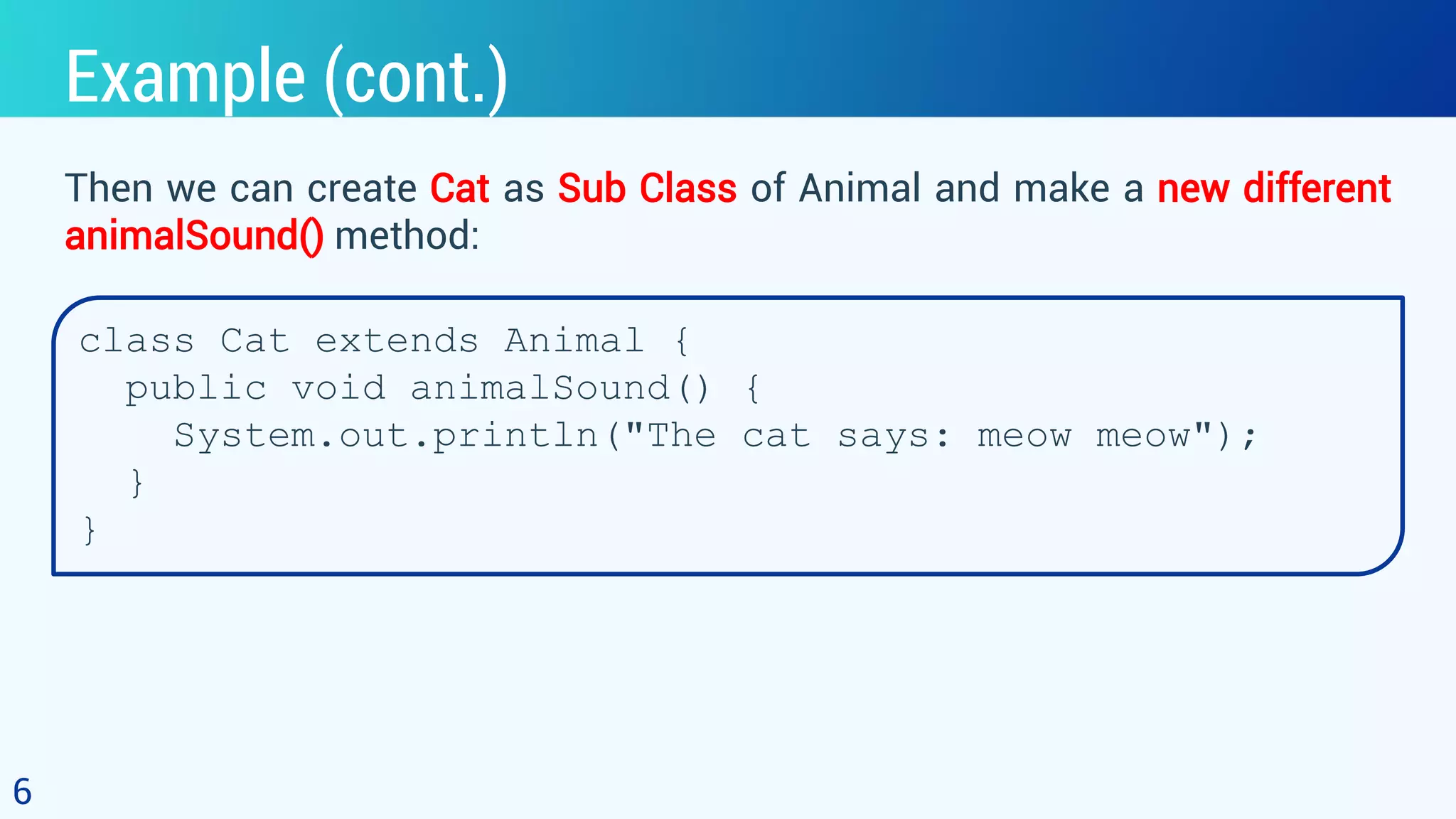
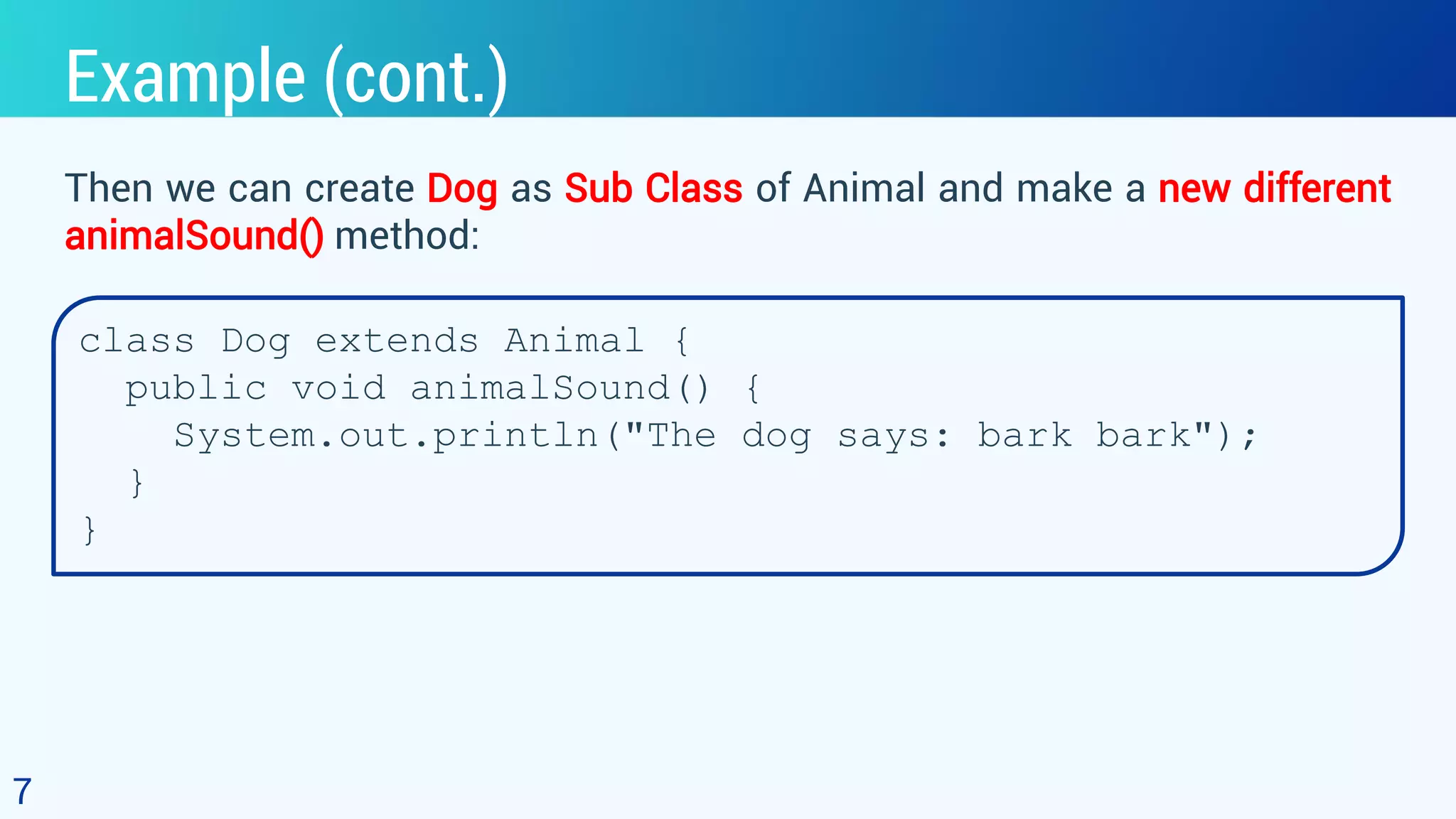
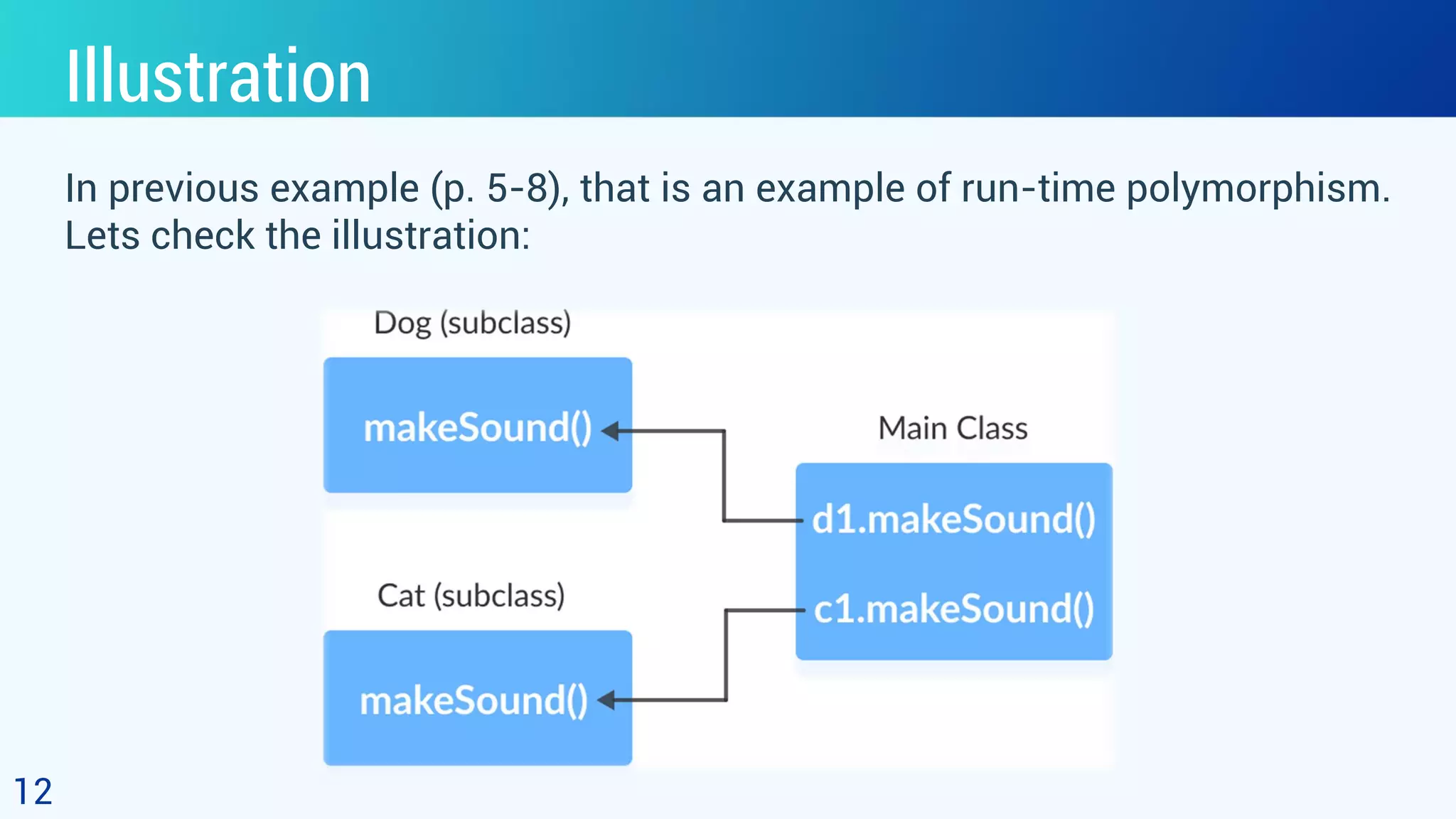
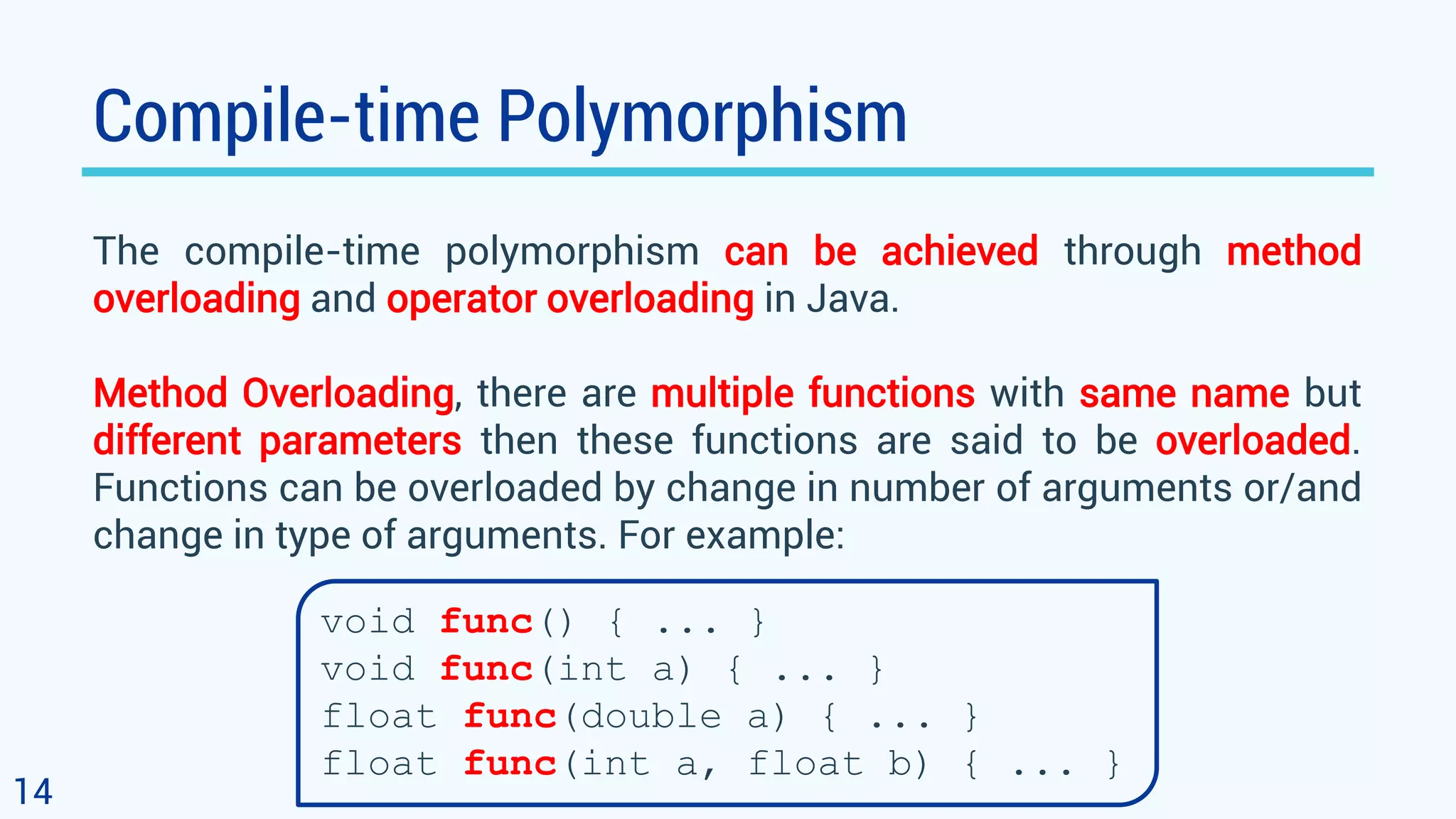
This document discusses polymorphism in object-oriented programming using Java. It defines polymorphism as having many forms, where classes related by inheritance can perform the same task in different ways. It provides an example of an Animal class with a sound method, where subclasses Cat and Dog override the method to output different sounds. This demonstrates runtime polymorphism, where the method called depends on the object. Compile-time polymorphism through method overloading is also discussed, where methods have the same name but different parameters. Polymorphism allows for consistent code by using the same method names for related tasks in different classes.



![Example (cont.) 8 class MyMainClass { public static void main(String[] args) { Animal myAnimal = new Animal(); Animal d1 = new Cat(); Animal c1 = new Dog(); myAnimal.animalSound(); //same function name d1.animalSound(); //same function name c1.animalSound(); //same function name } } Now we can create Cat and Dog objects and call the animalSound() method on both of them:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-200420141041/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-7-2-Polymorphism-8-2048.jpg)




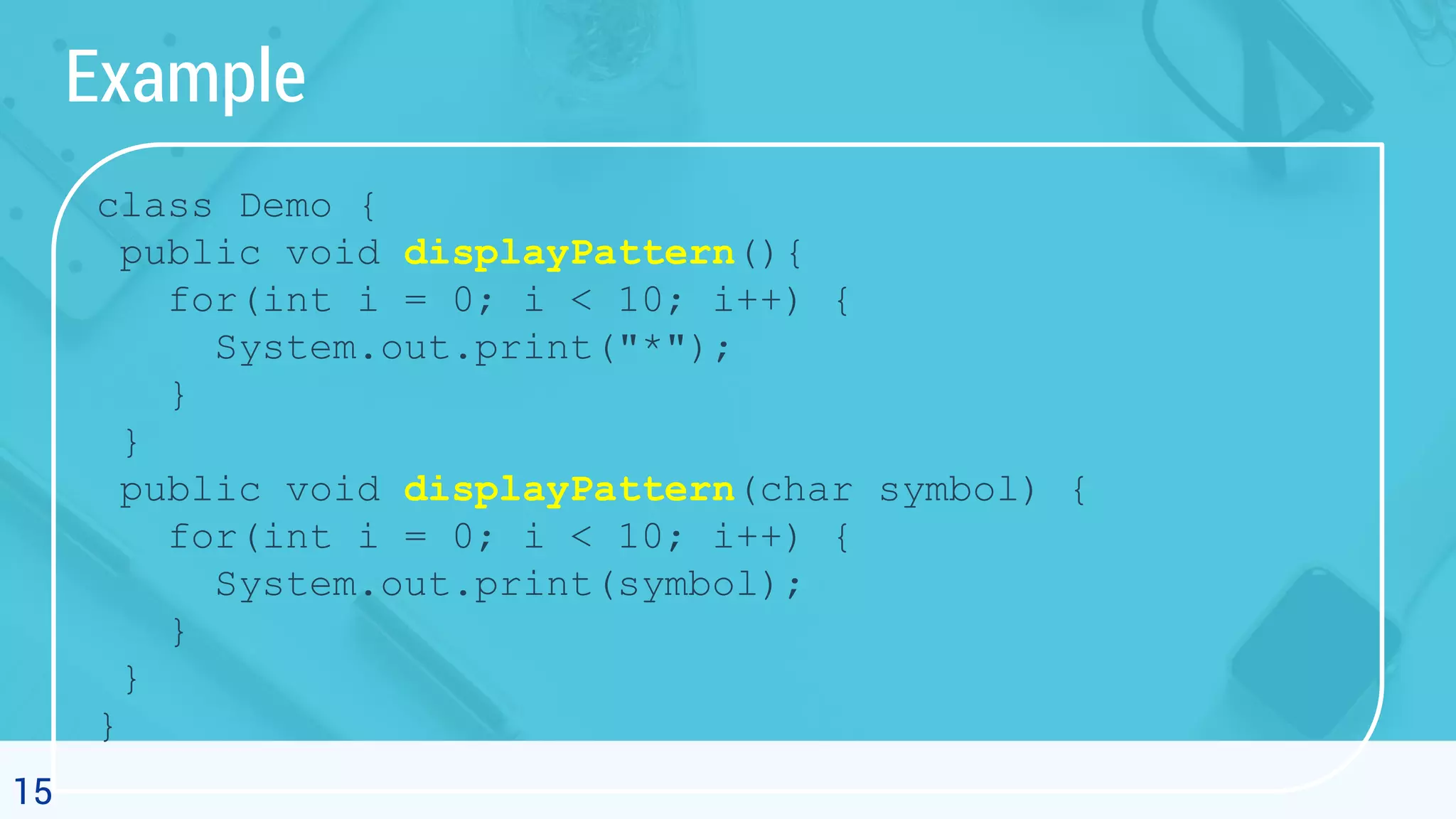
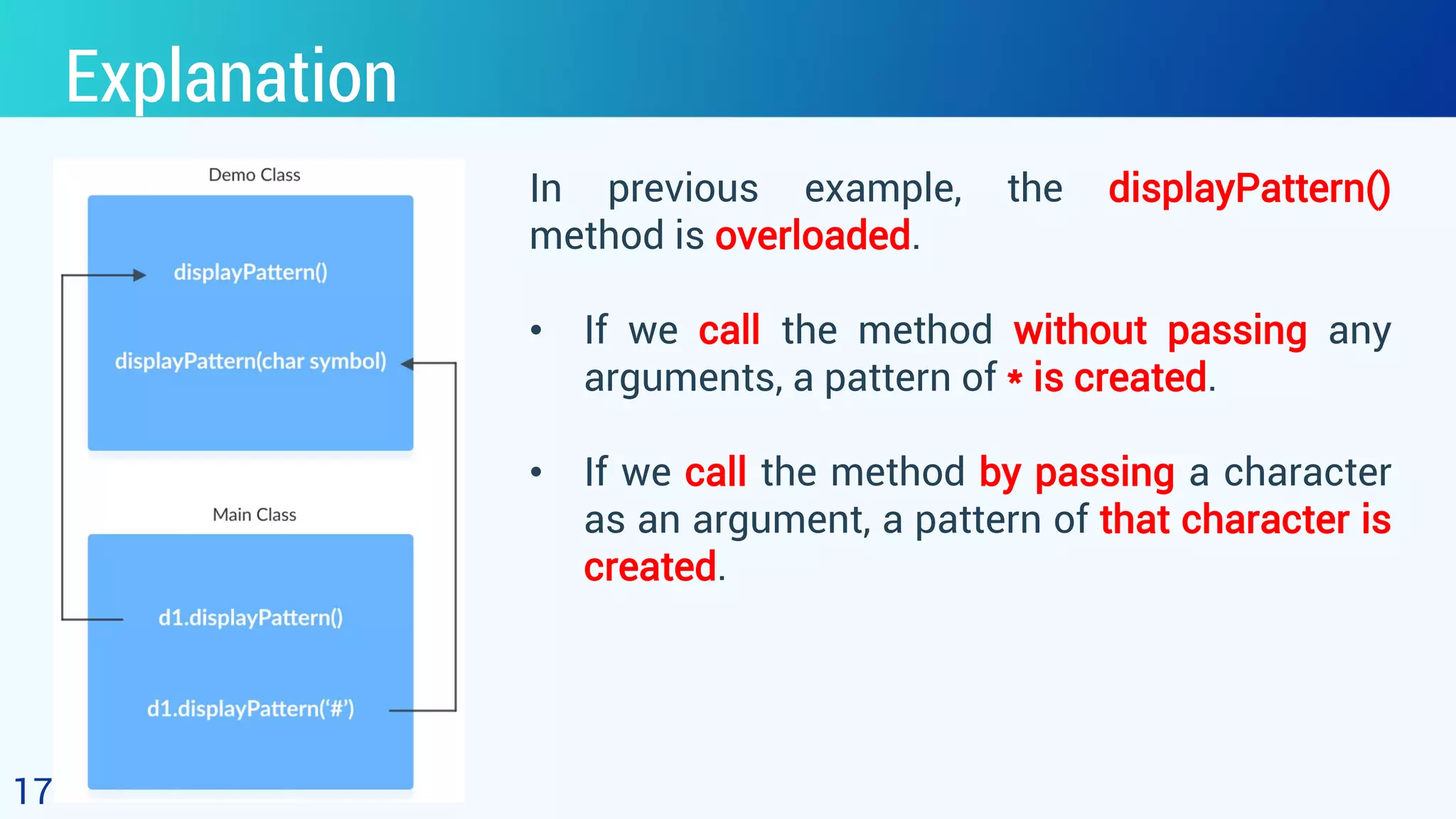
![16 Example (cont.) class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo d1 = new Demo(); d1.displayPattern(); System.out.println("n"); d1.displayPattern('#'); } } //output ********** ##########](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-200420141041/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-7-2-Polymorphism-16-2048.jpg)