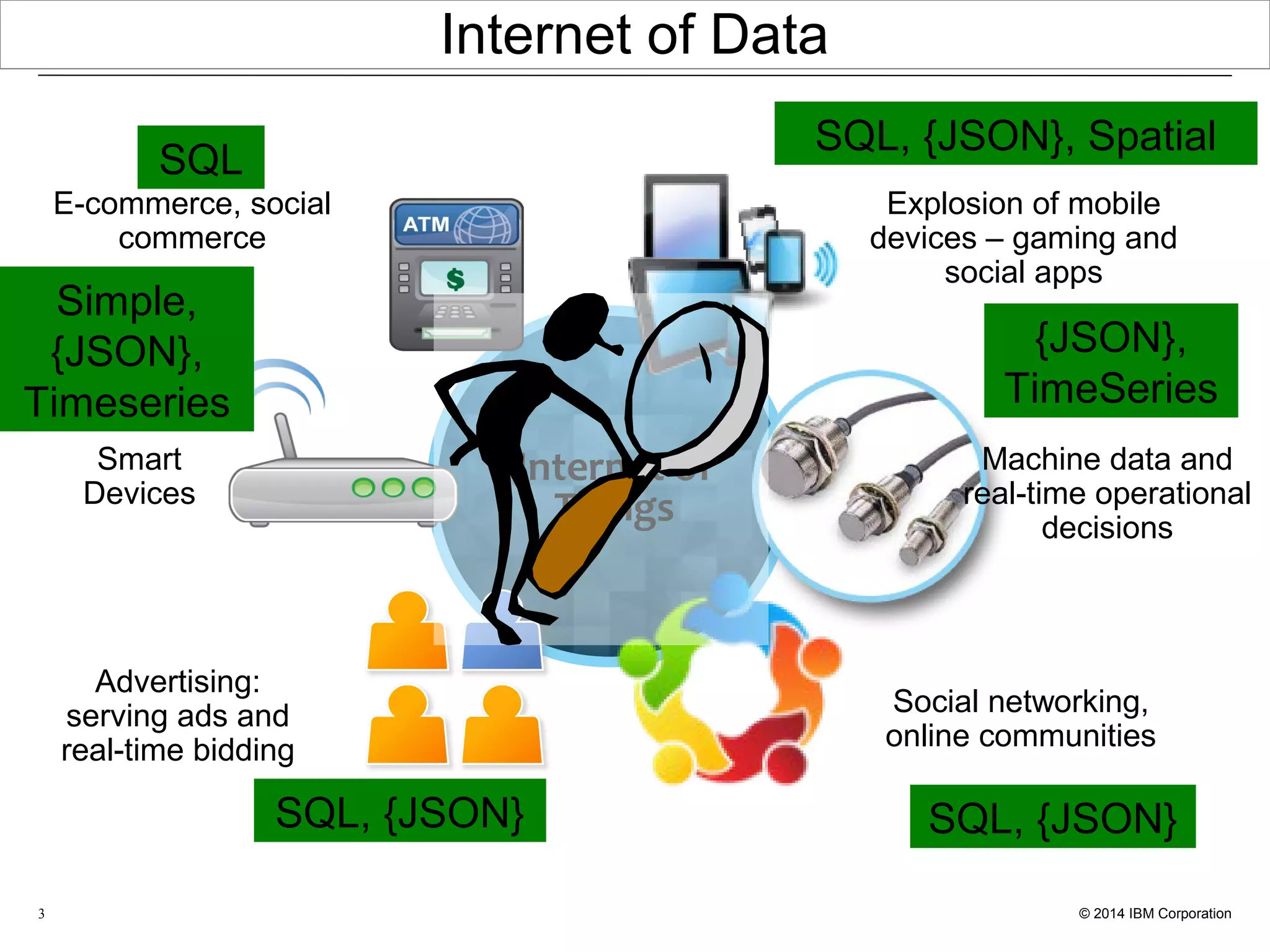
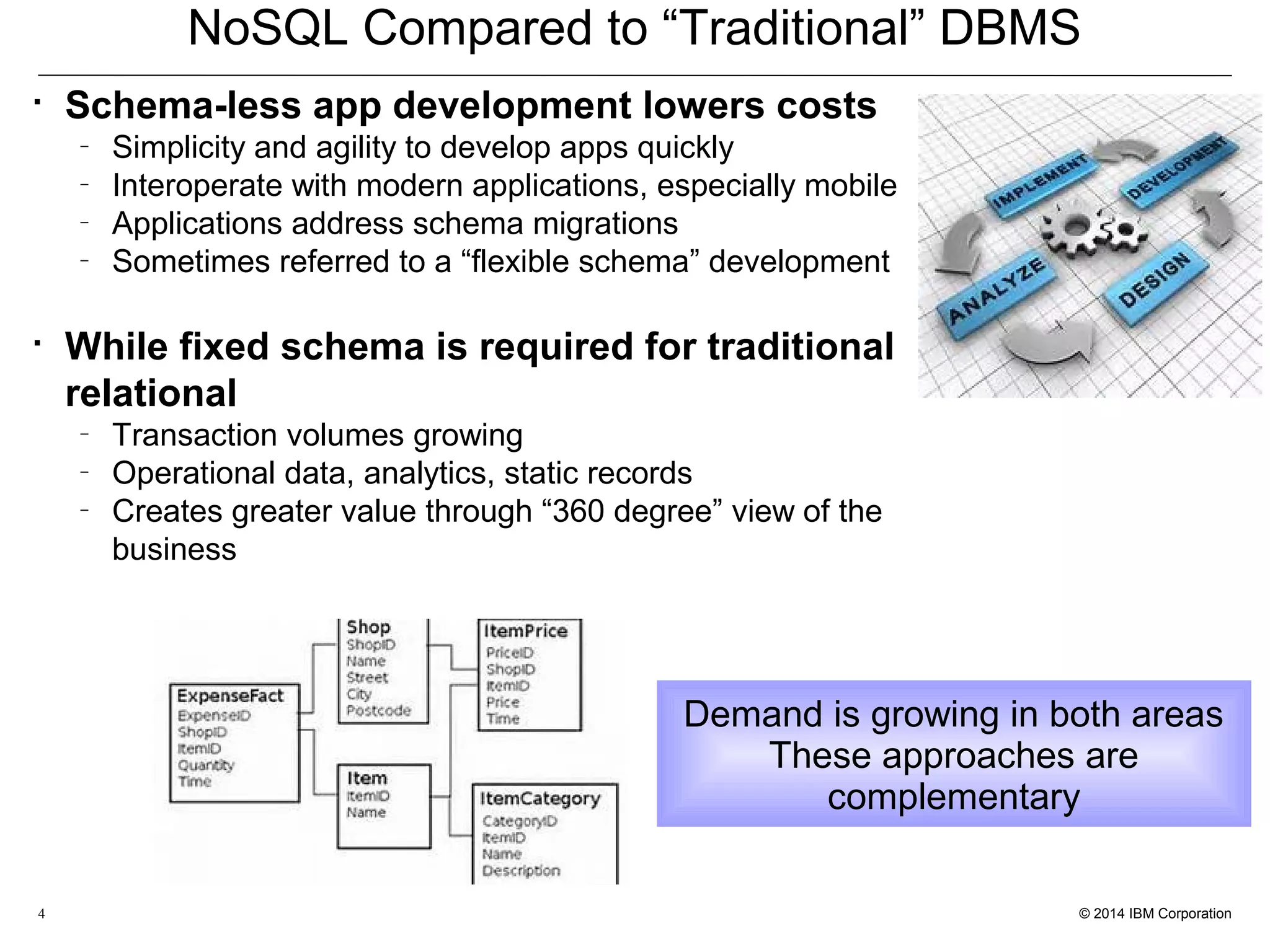
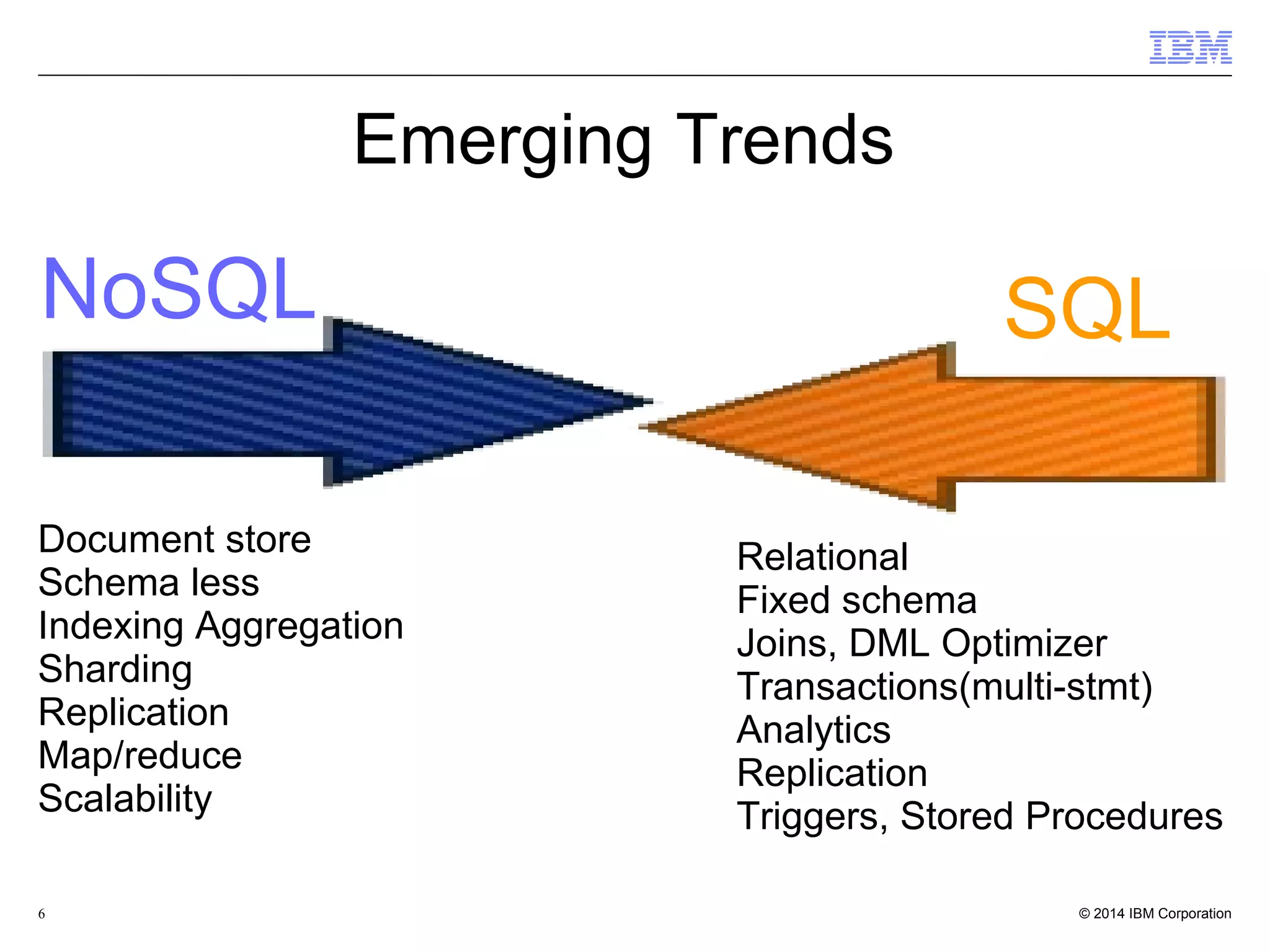
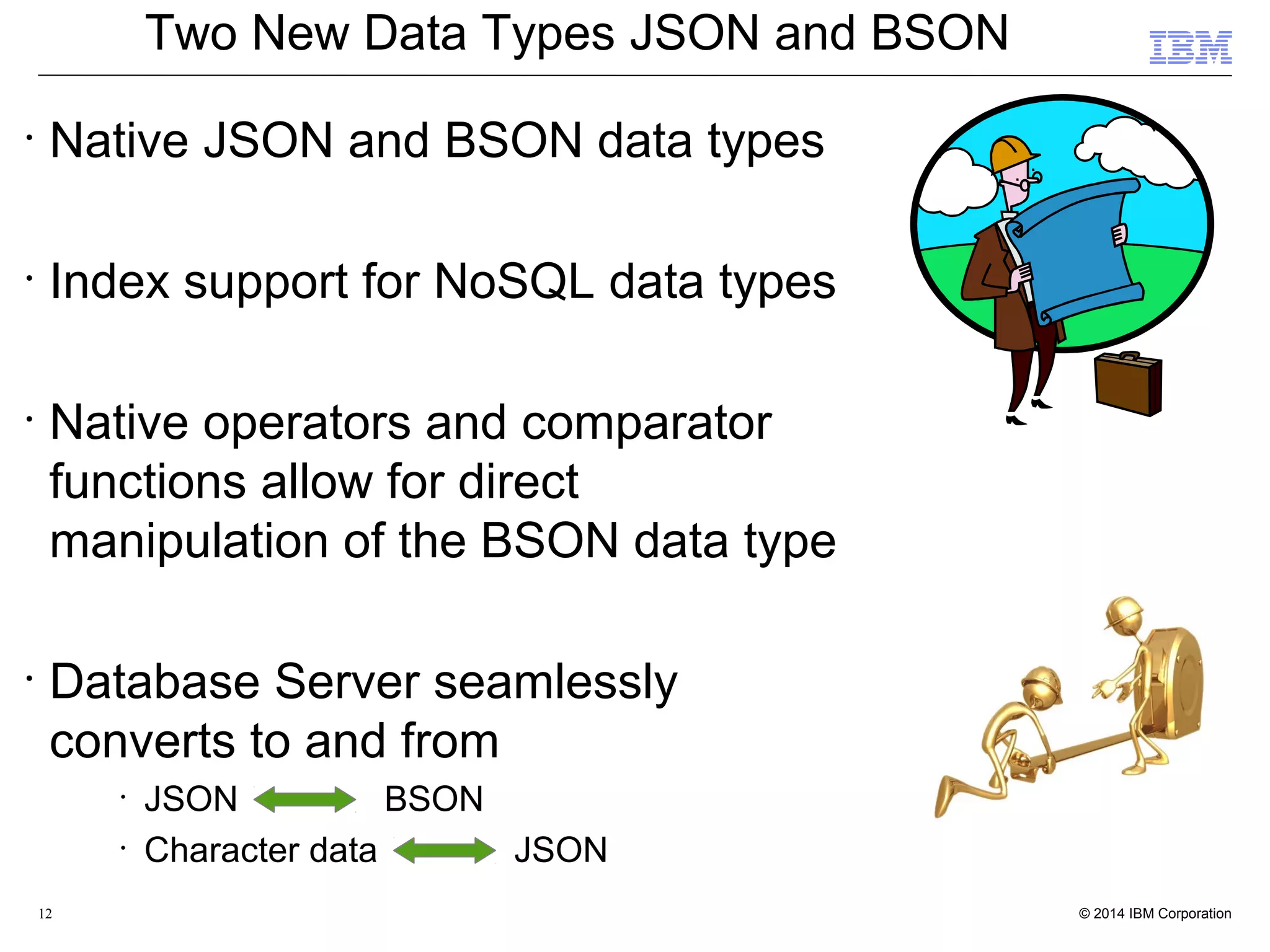
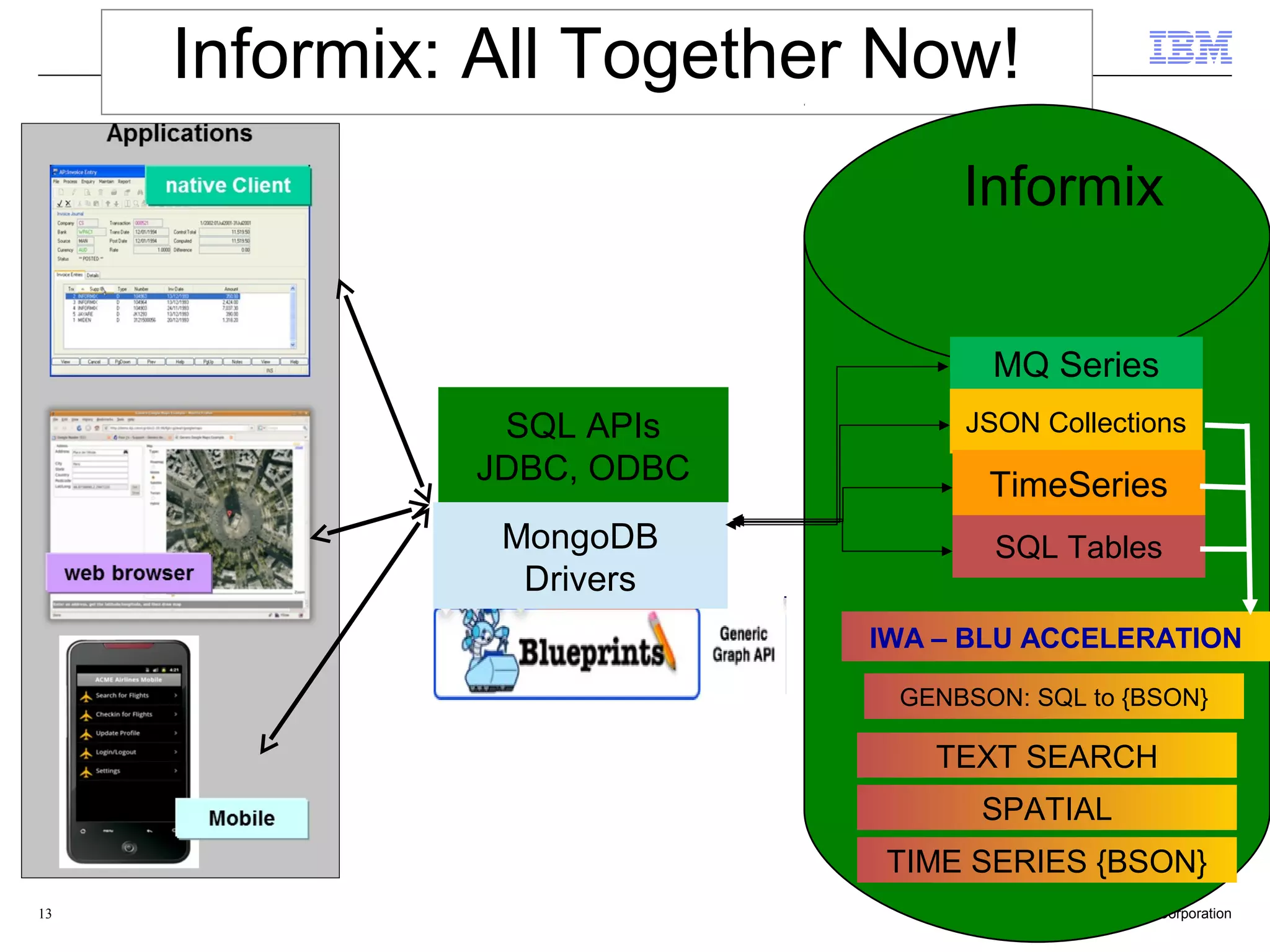
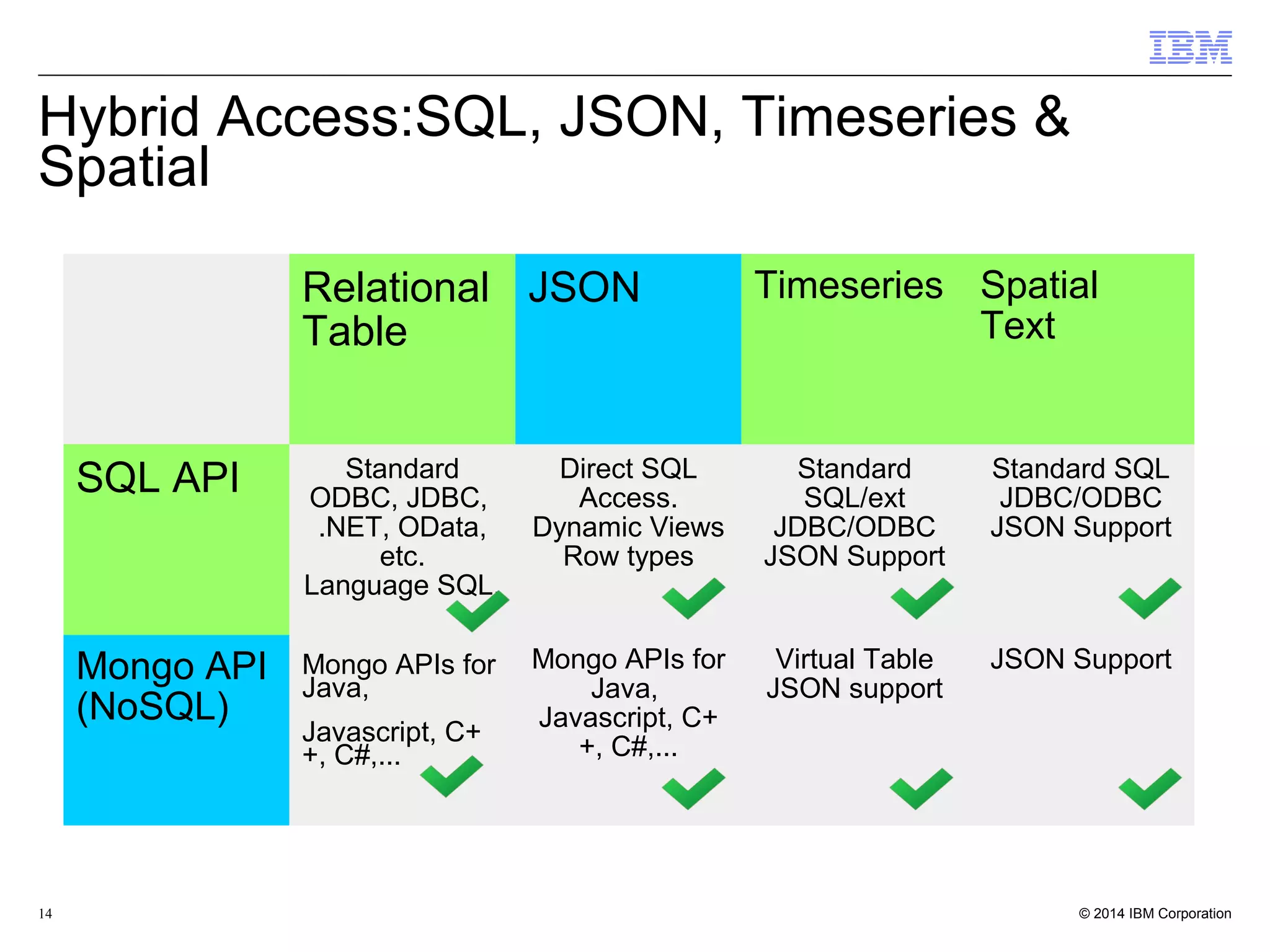
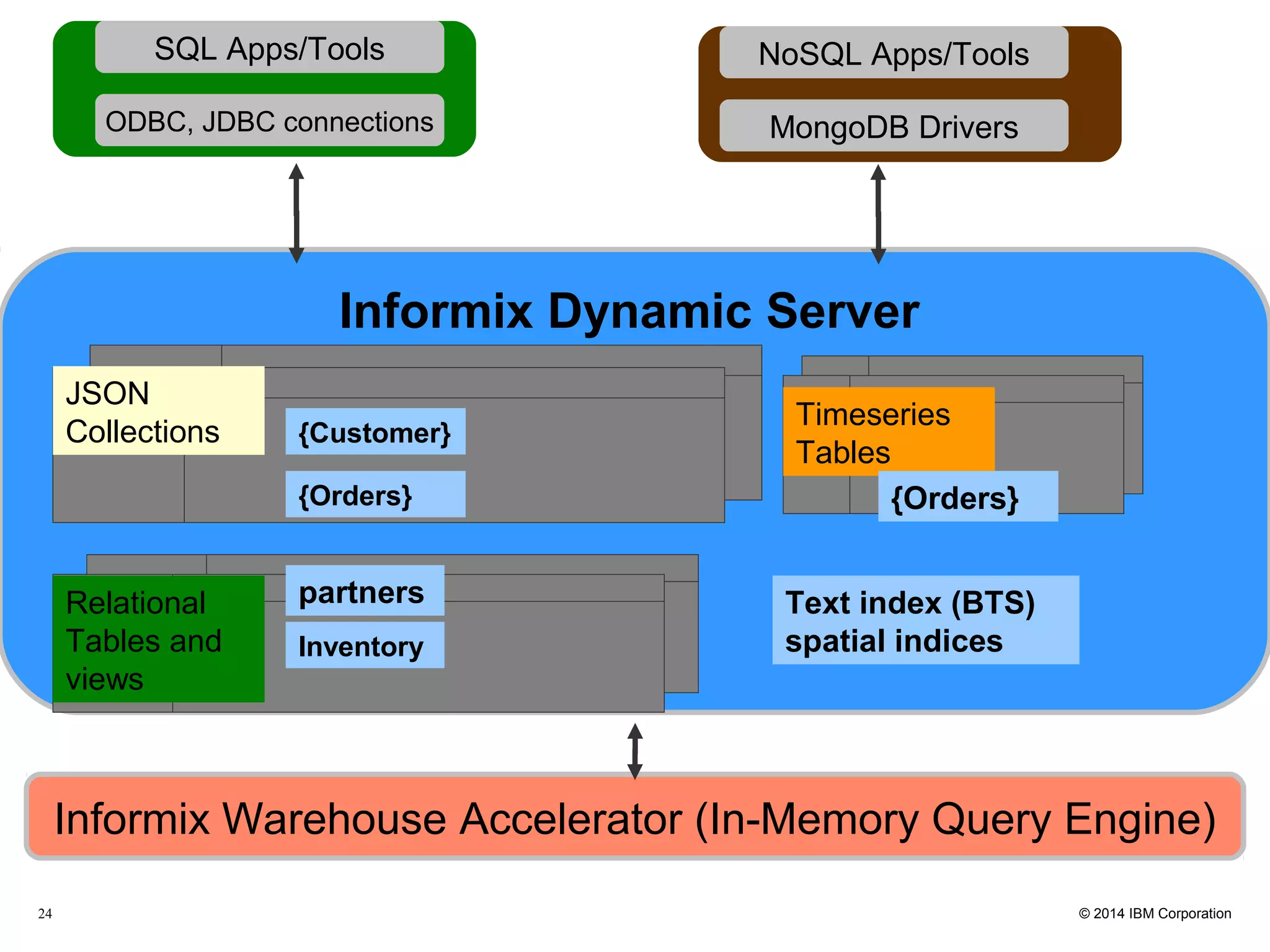
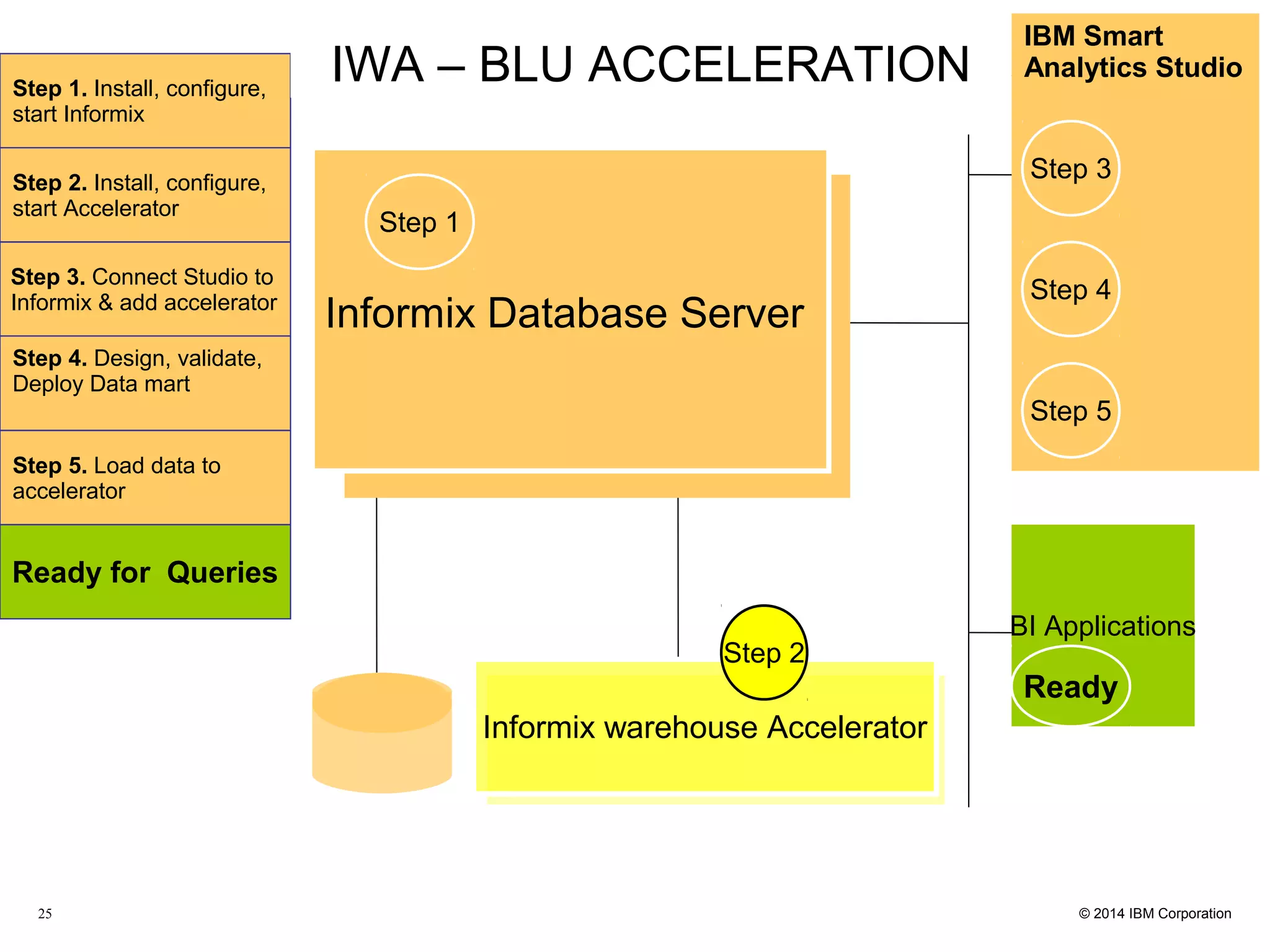
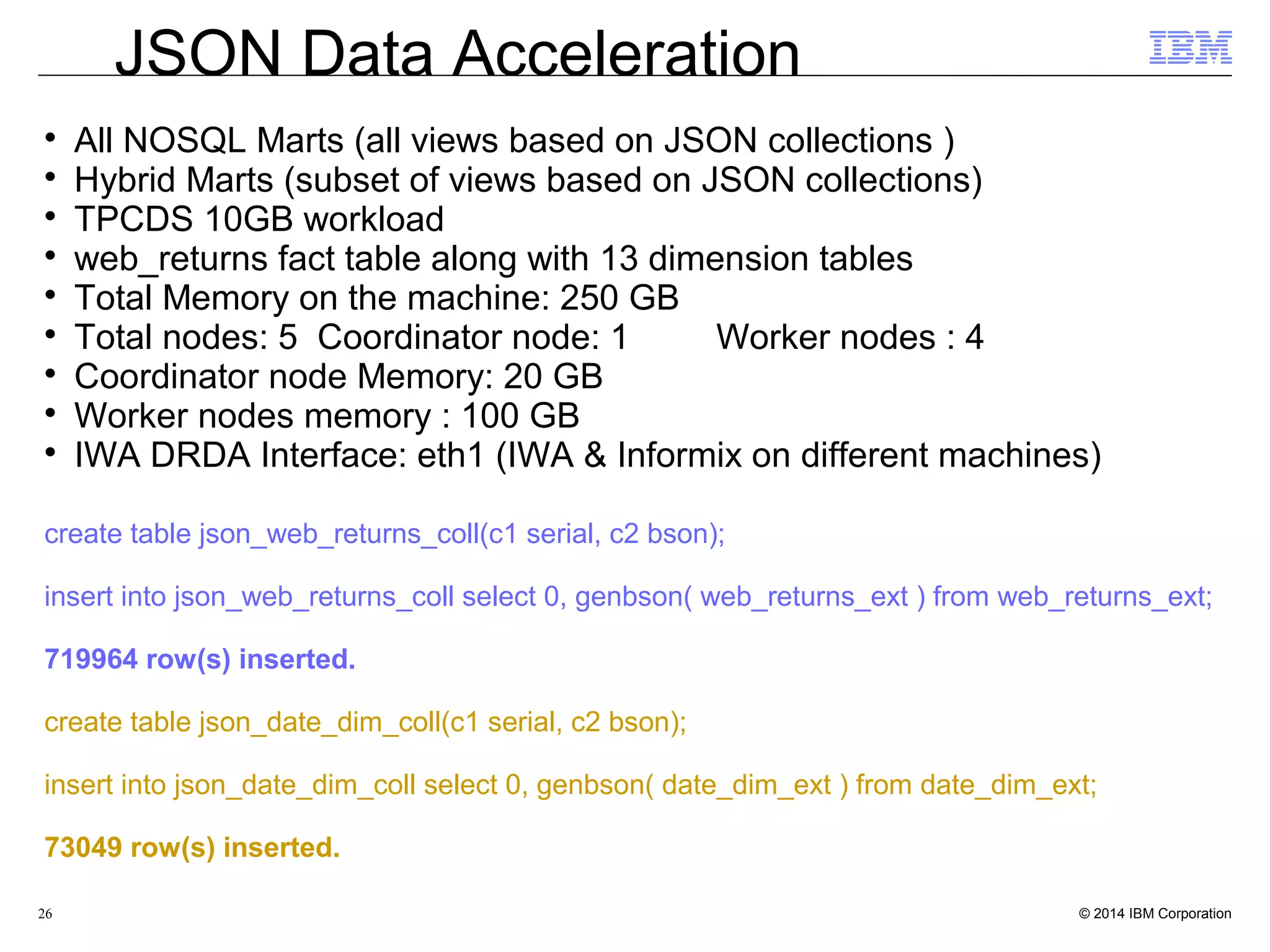
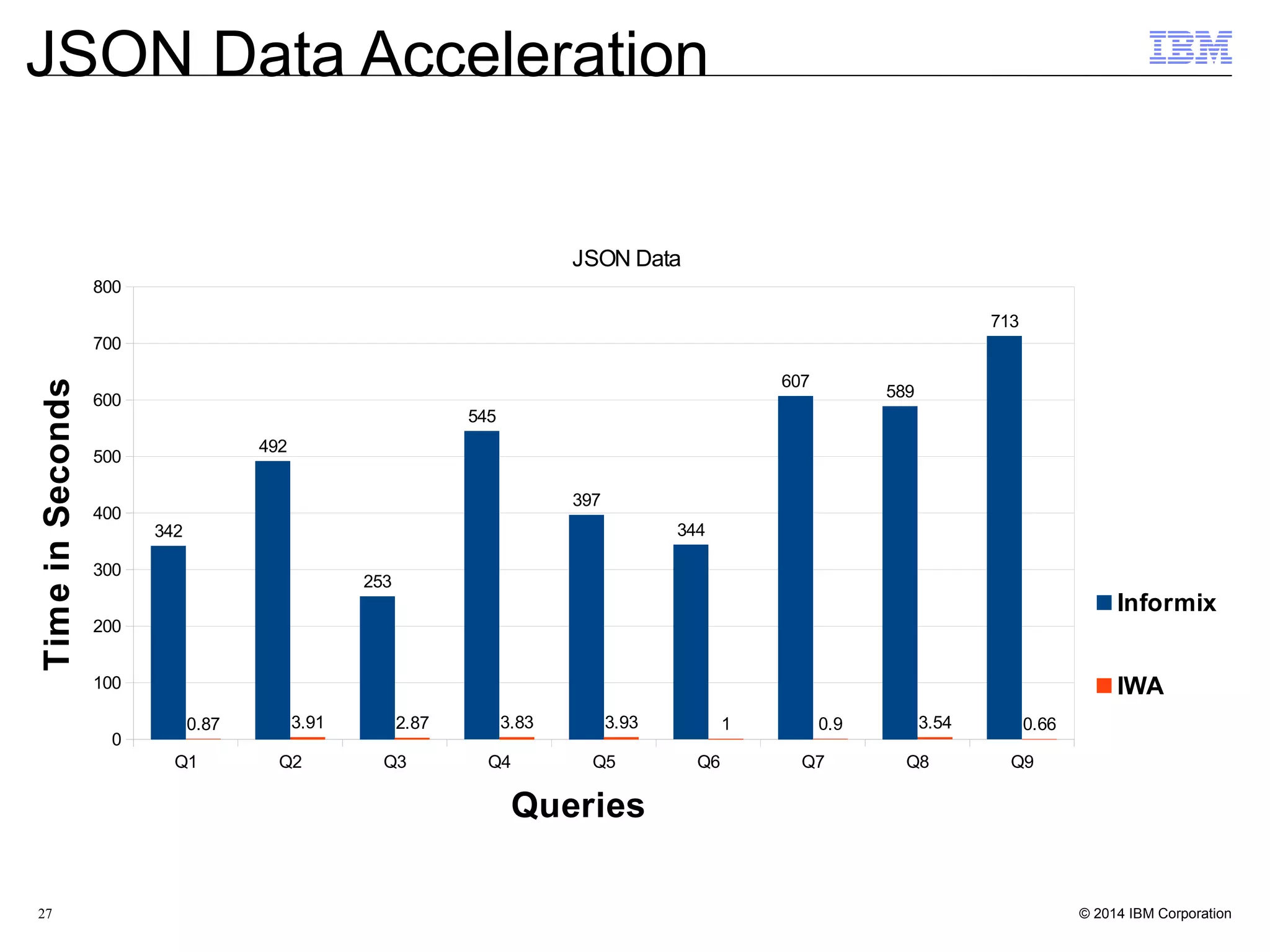
This document discusses the integration and performance of NoSQL analytics, specifically focusing on JSON data management and MongoDB within IBM's Informix environment. It highlights the advantages of hybrid databases that incorporate both relational and NoSQL capabilities, emphasizing real-time analytics, schema flexibility, and seamless transactions. Key features include support for JSON and BSON types, hybrid data marts, and the use of an in-memory accelerator to enhance query performance.






![22 IBM Informix Warehouse Accelerator (IWA) Results Analytic query Linux on Intel / AMD 64-bit TCP/IP Query Optimizer In-Memory Compressed Columnar Database Partition Bulk Loader Query Processor Yes Analytic query Results Accelerate Query? Most Unix/Linux 64-bit platforms In-Disk [Compressed] Relational / Row-based Database Informix database server Informix Warehouse Accelerator No POWERFUL HYBRID DATABASE PLATFORMPOWERFUL HYBRID DATABASE PLATFORM Extreme Performance Transactions Extreme Performance Analytics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-analytics-ibm-final-151222223623/75/NoSQL-Analytics-JSON-Data-Analysis-and-Acceleration-in-MongoDB-World-22-2048.jpg)
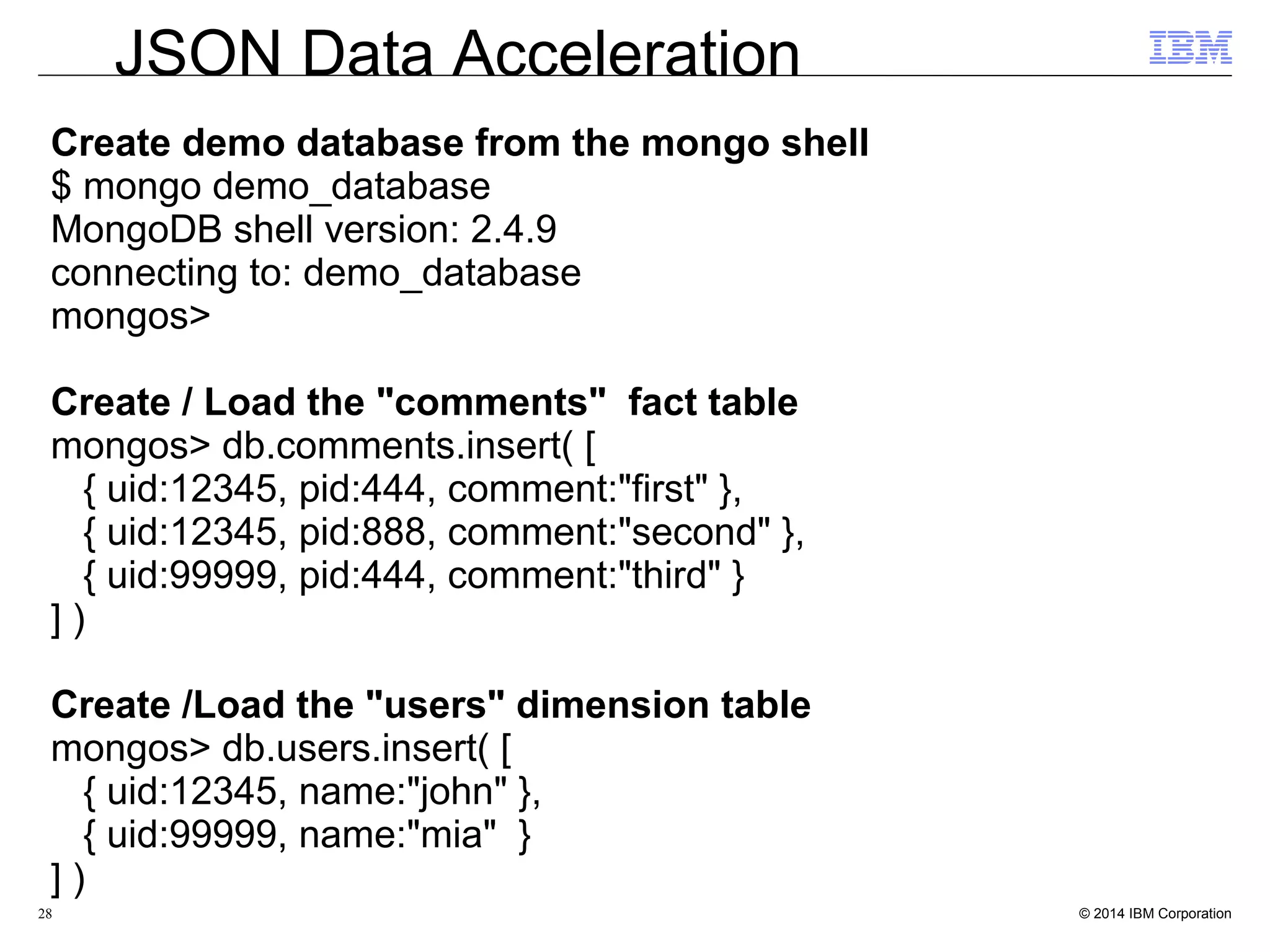
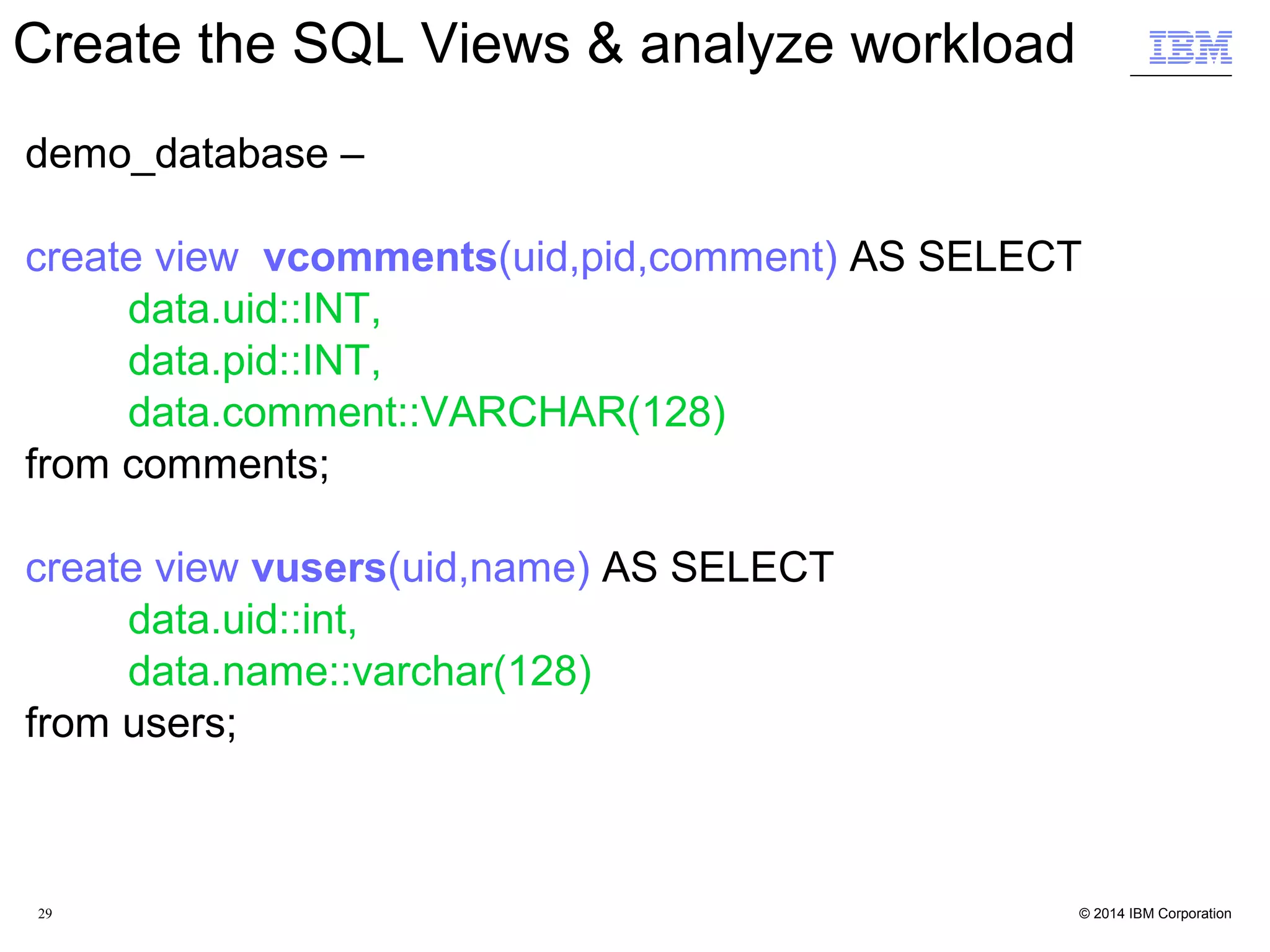
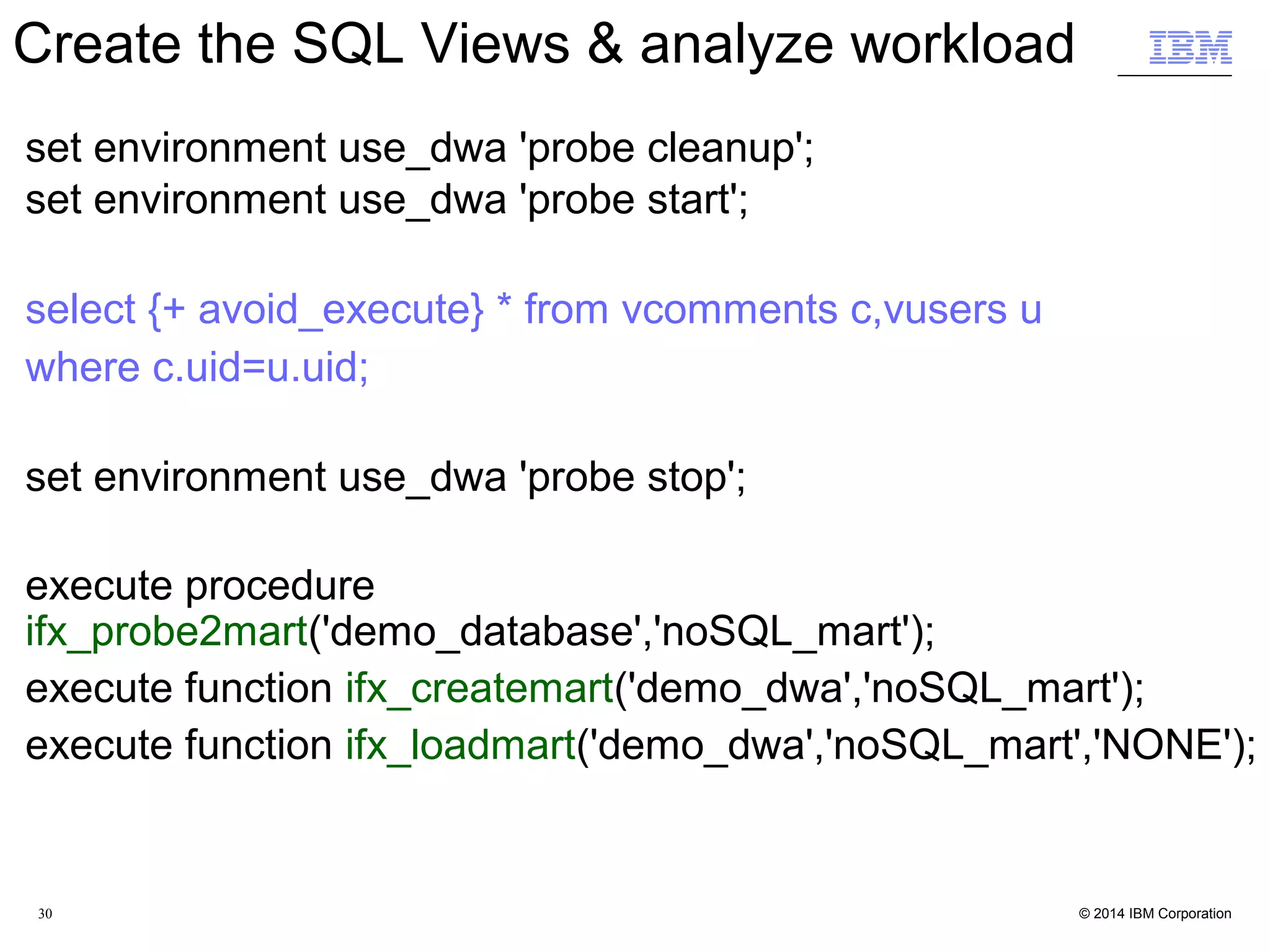

![32 Create demo database from the mongo shell $ mongo demo_database MongoDB shell version: 2.4.9 connecting to: demo_database mongos> Create / Load the "comments" fact table mongos> db.comments.insert( [ { uid:12345, pid:444, comment:"first" }, { uid:12345, pid:888, comment:"second" }, { uid:99999, pid:444, comment:"third" } ] ) Create /Load the "users" dimension table mongos> db.users.insert( [ { uid:12345, name:"john" }, { uid:99999, name:"mia" } ] ) JSON Data Acceleration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-analytics-ibm-final-151222223623/75/NoSQL-Analytics-JSON-Data-Analysis-and-Acceleration-in-MongoDB-World-32-2048.jpg)



