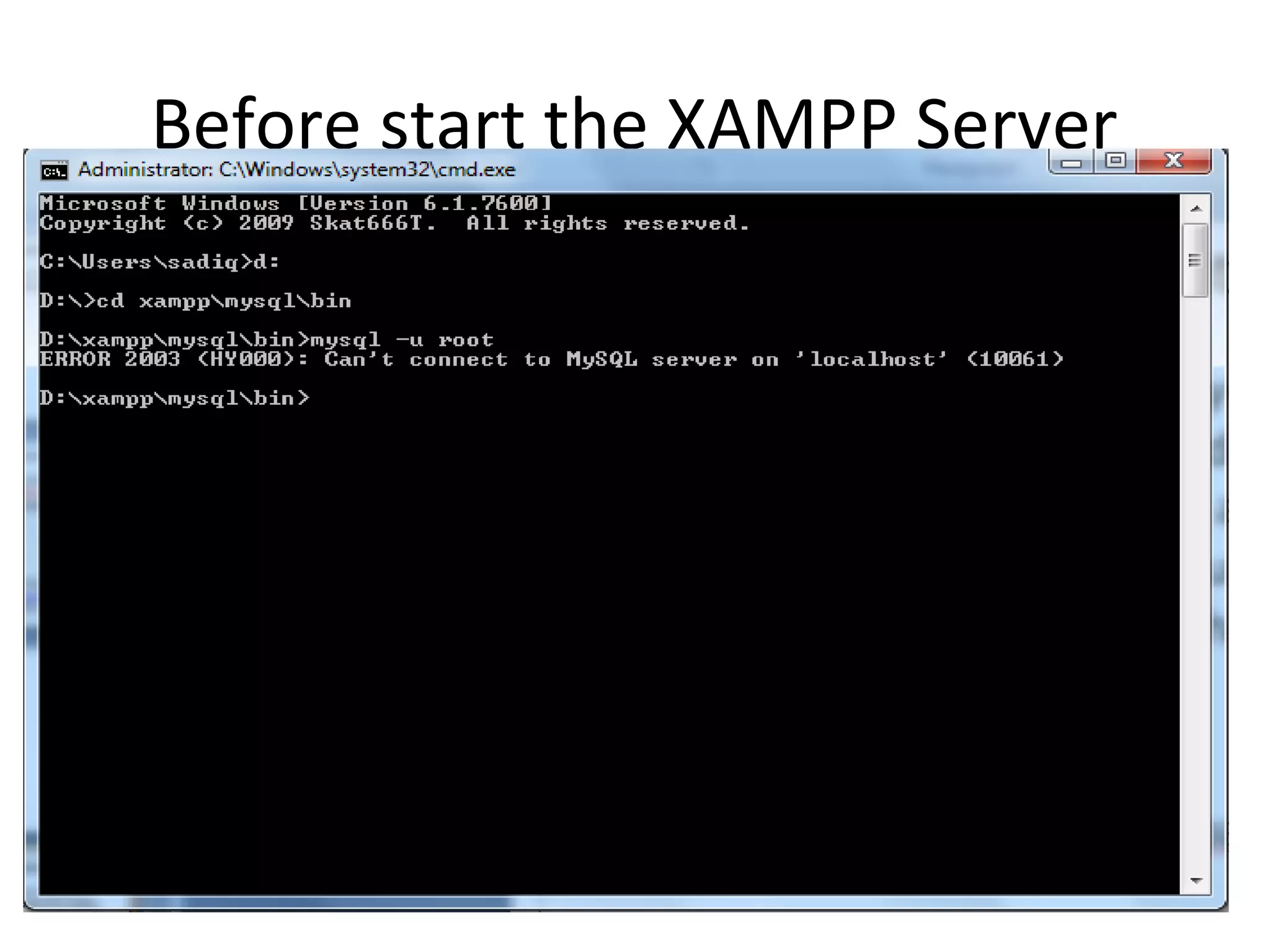
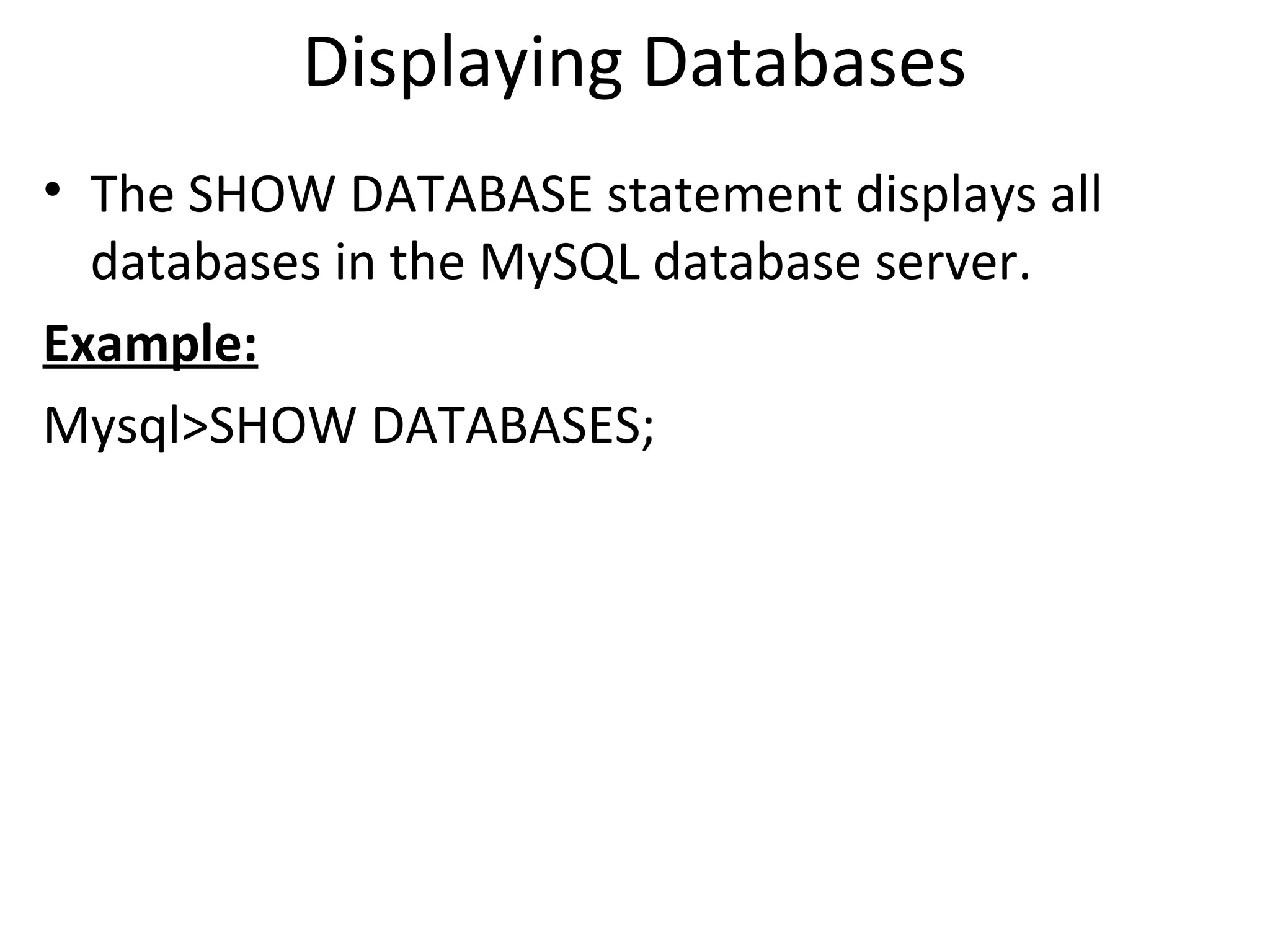
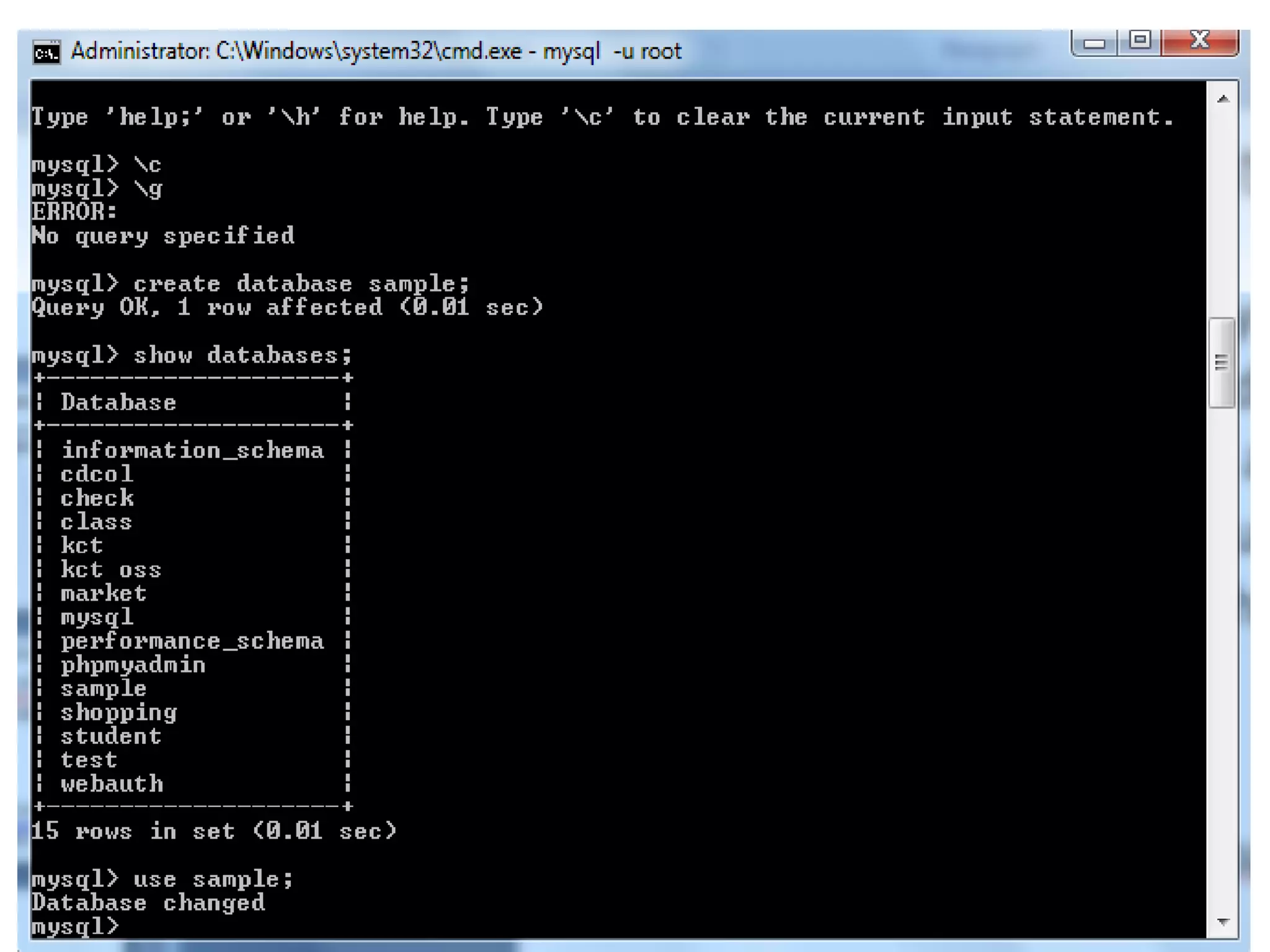
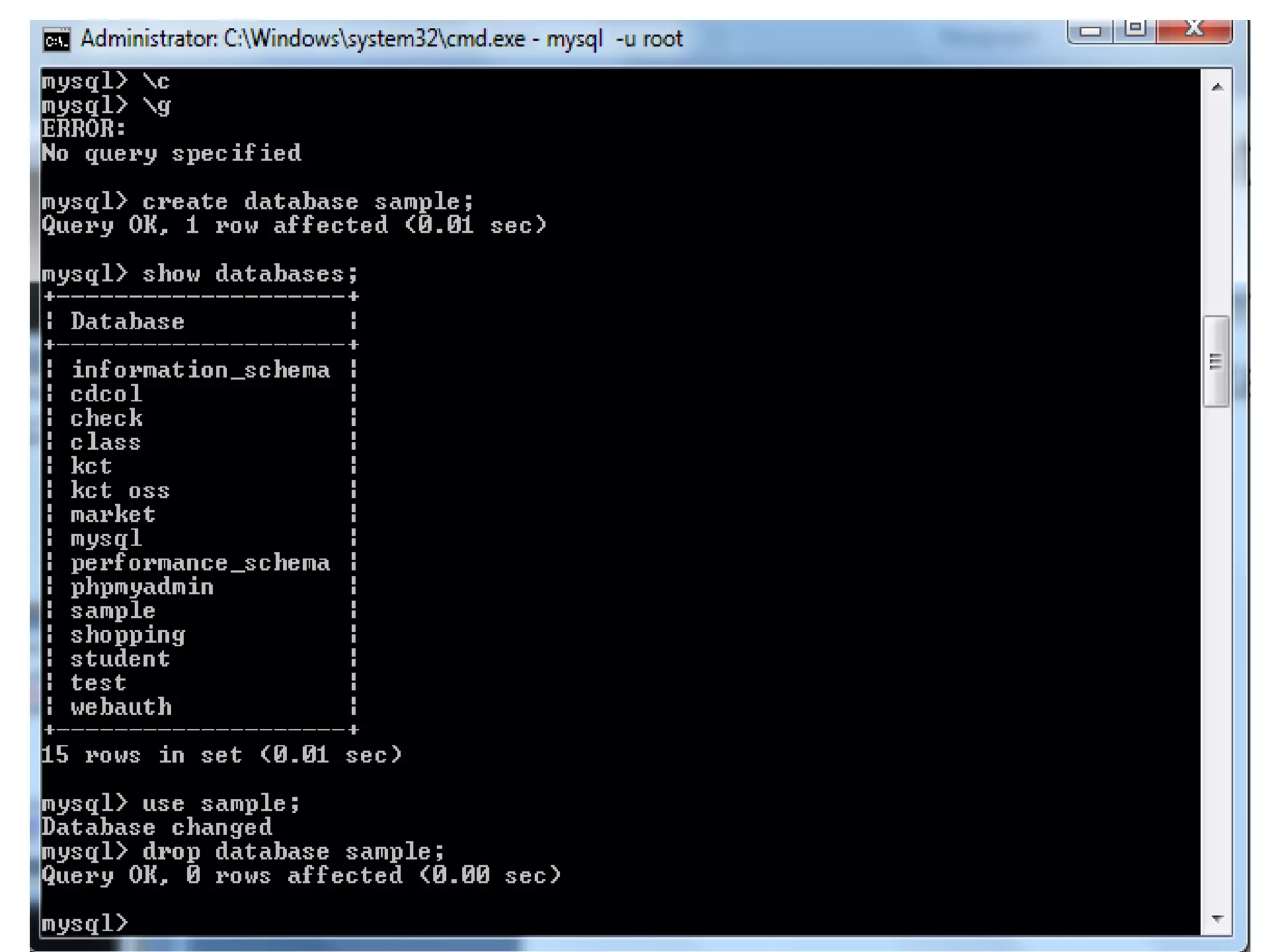
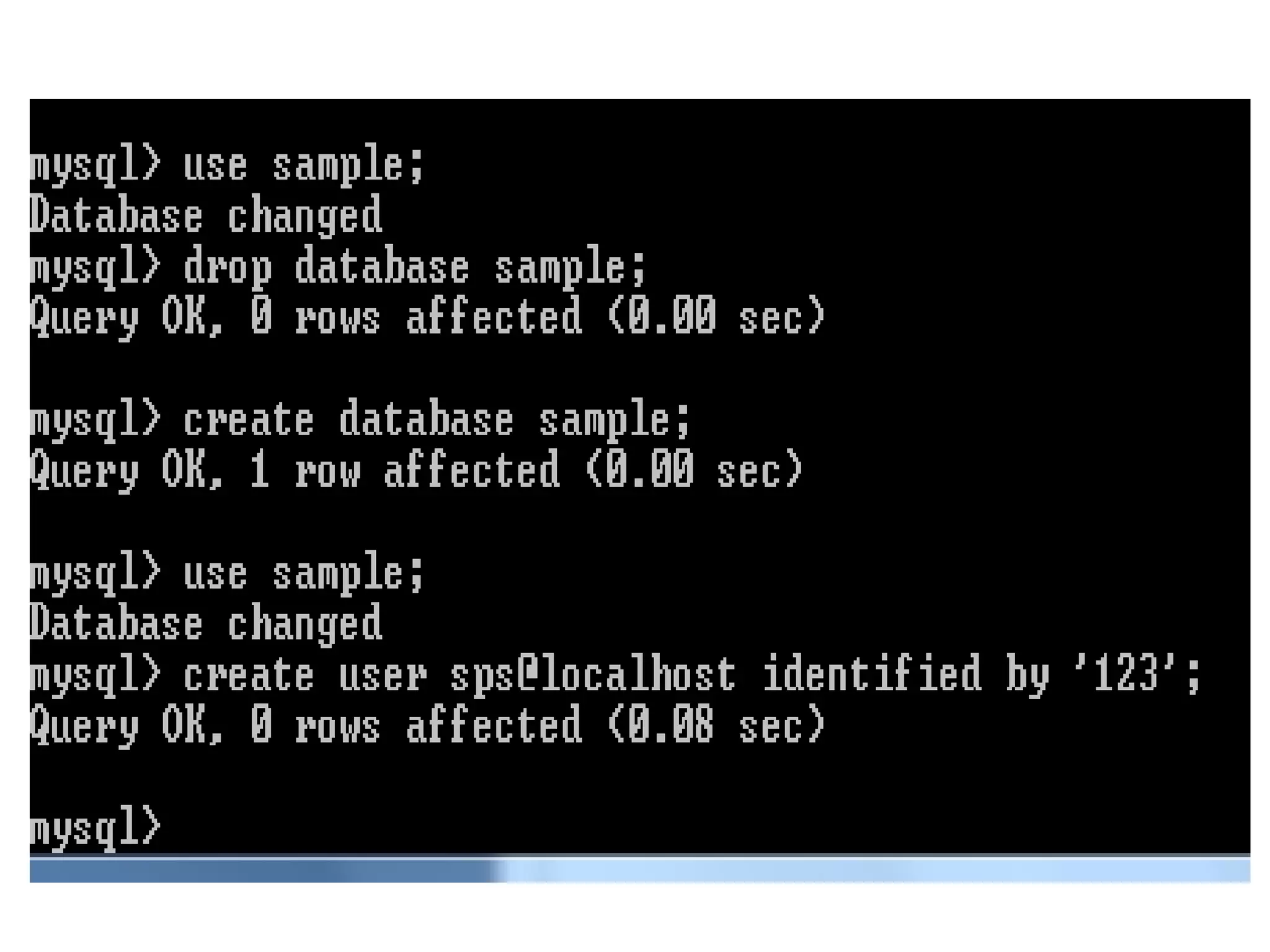
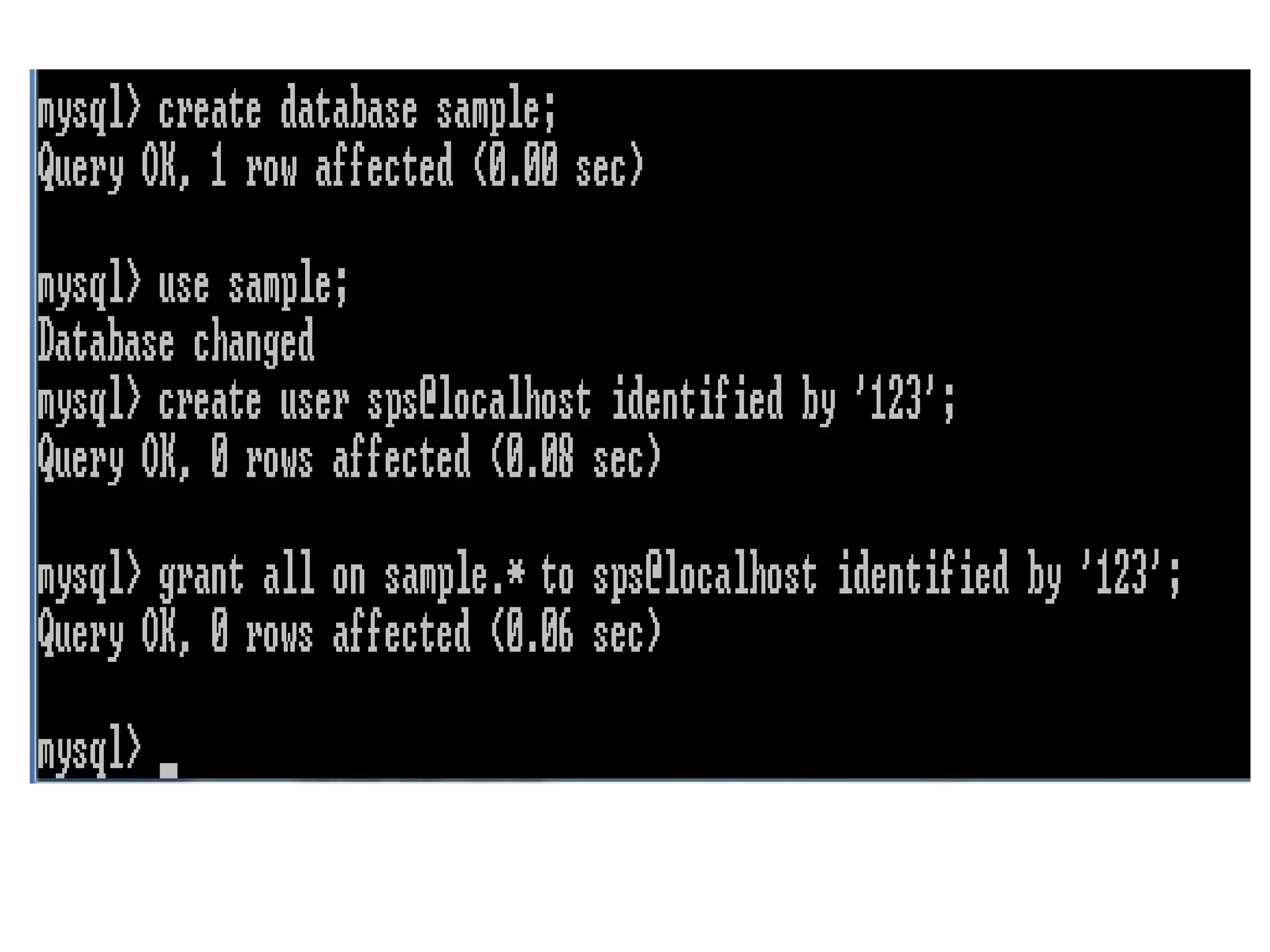
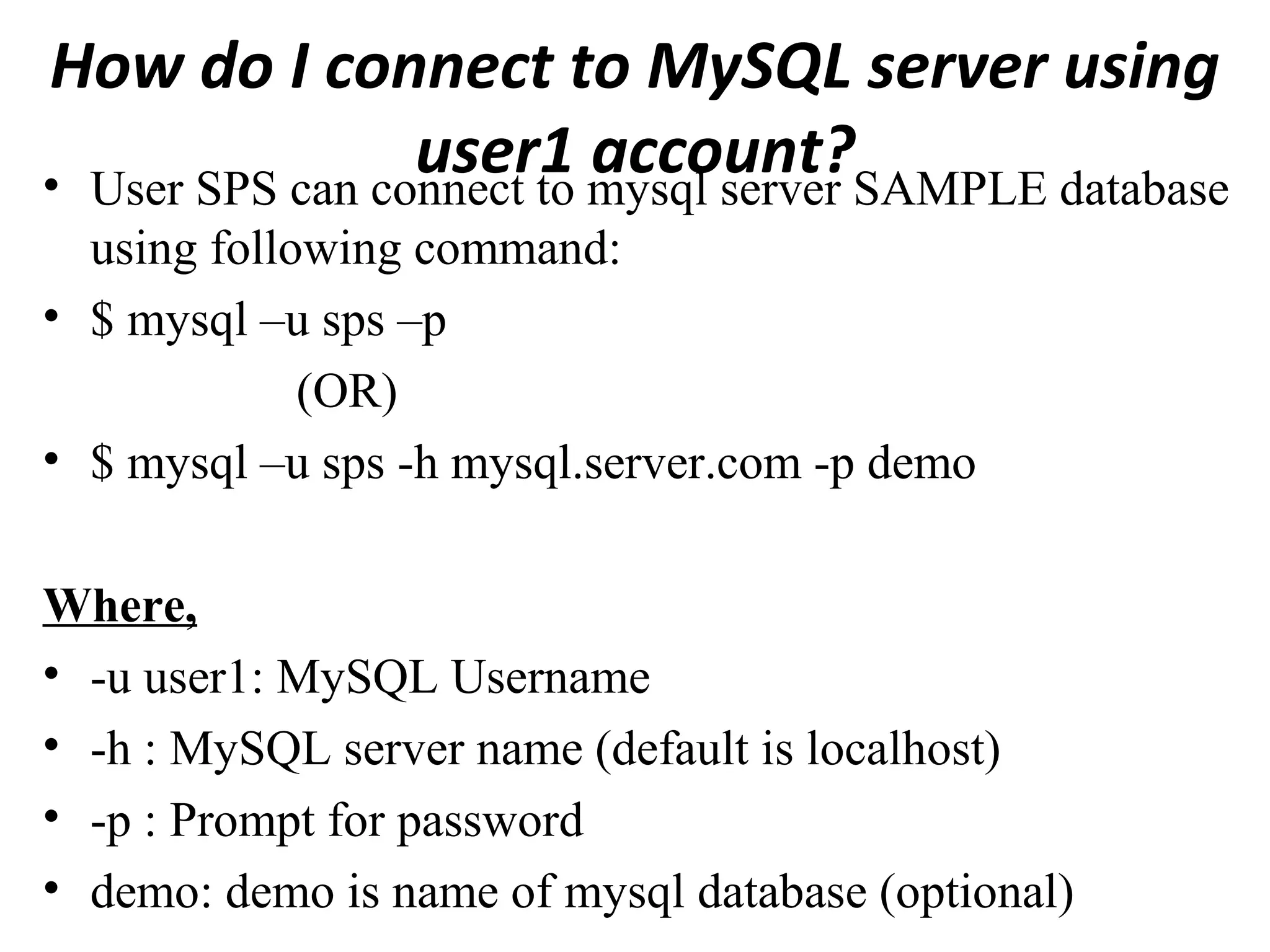
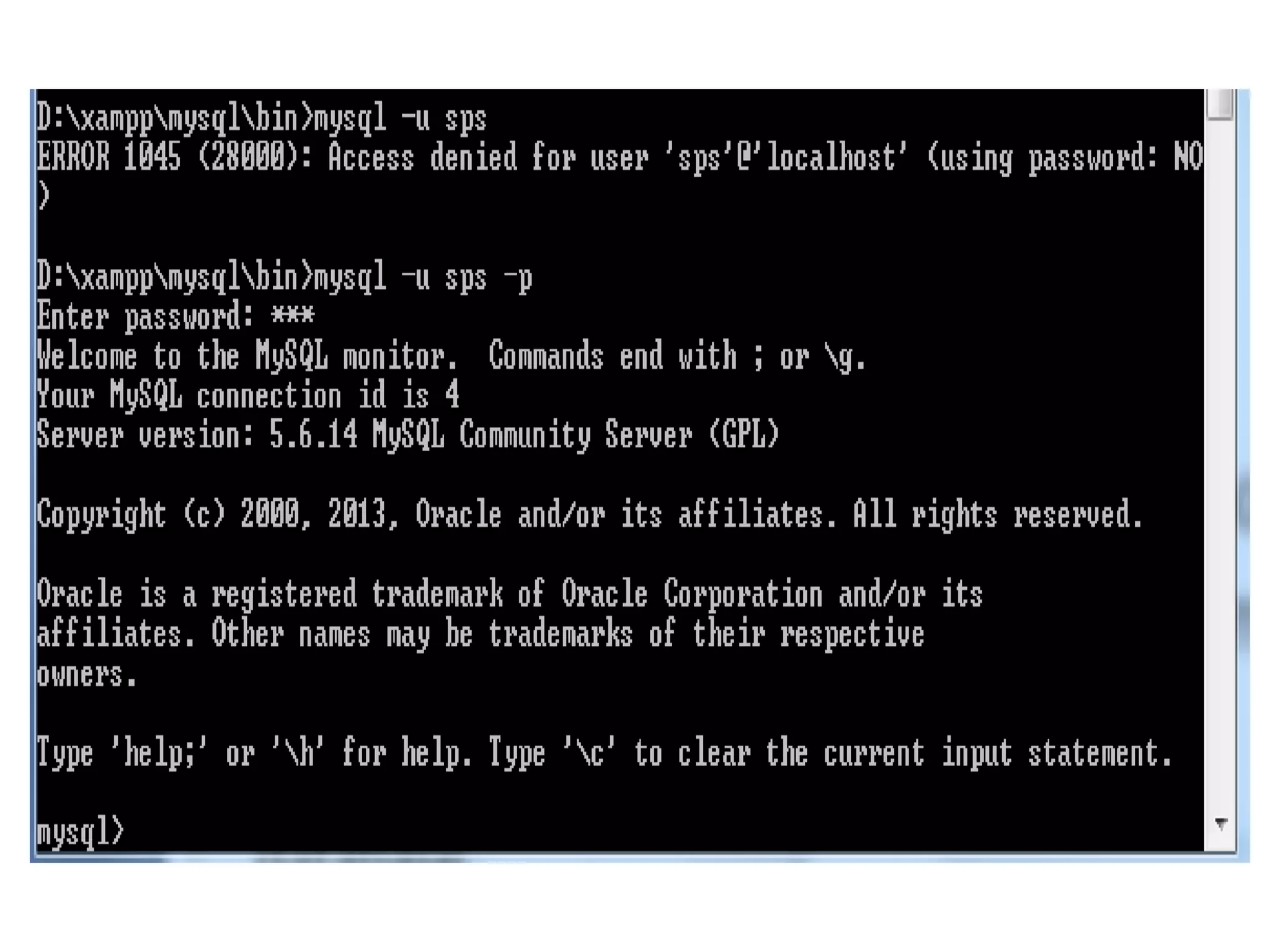
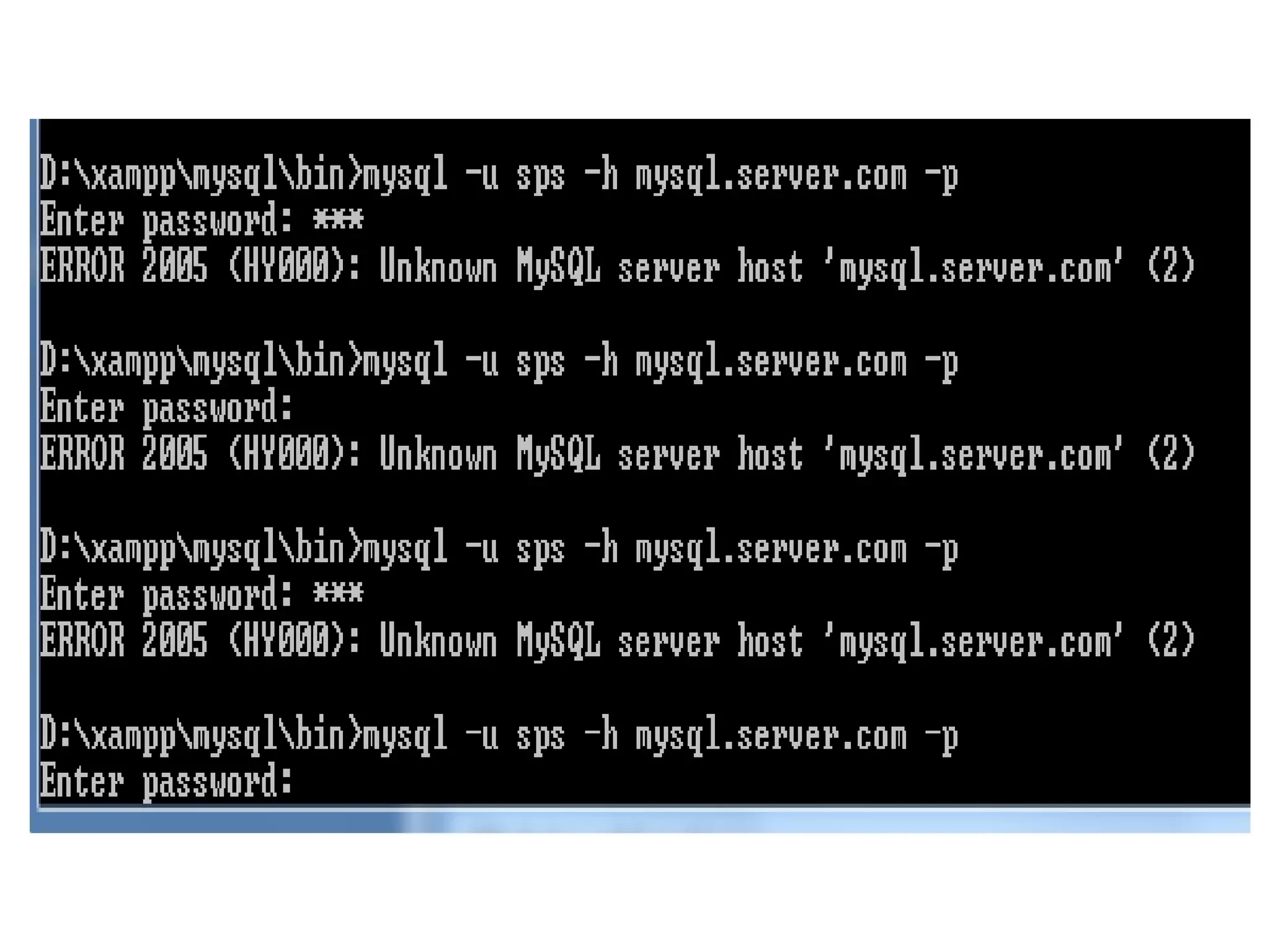
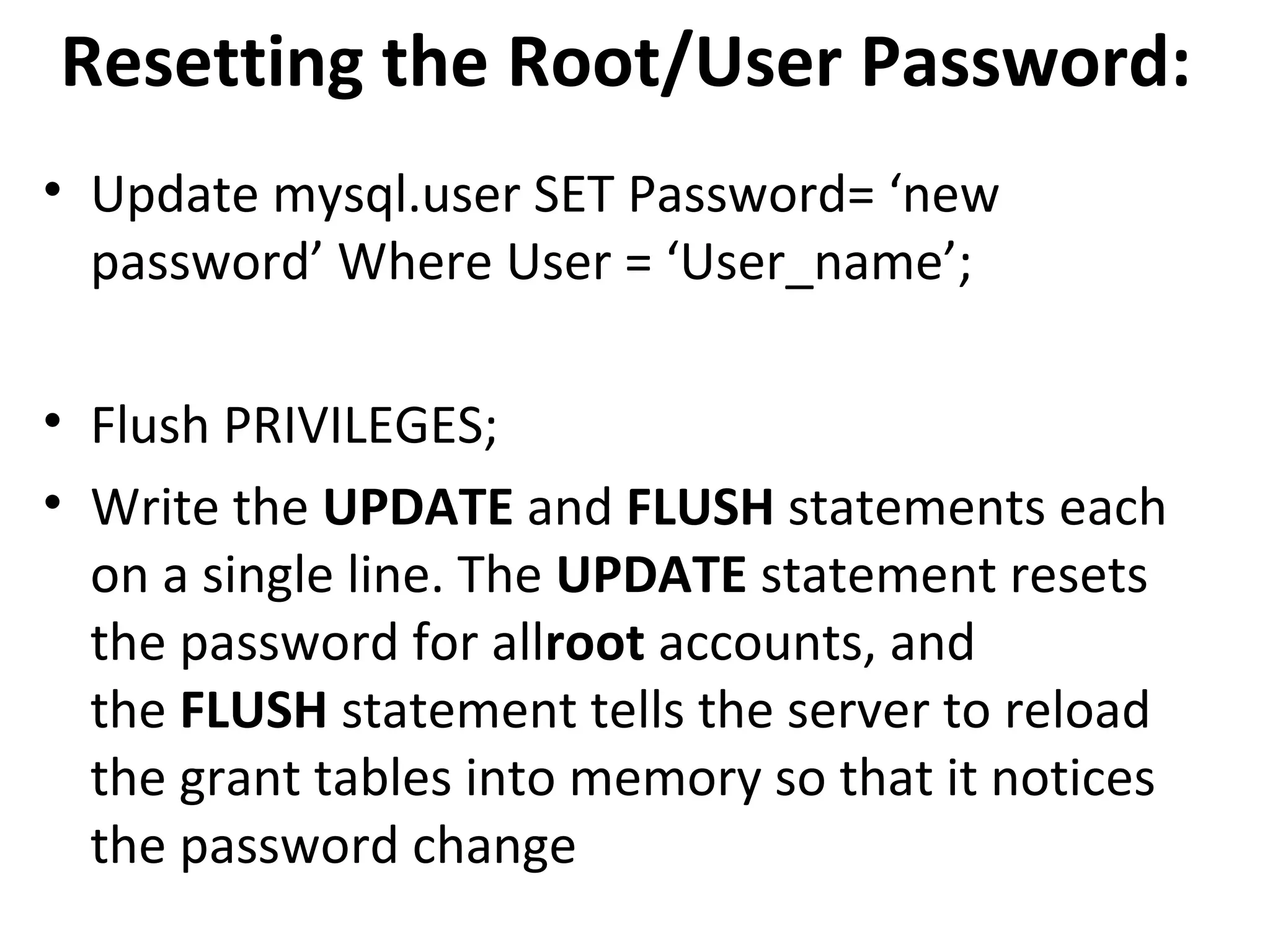
This document provides instructions for creating and managing MySQL databases. It describes how to create a database, display existing databases, select a database to work with, remove databases, create user accounts, grant privileges to users, connect to the MySQL server using a user account, reset passwords, and revoke privileges from users. Key steps include using SQL statements like CREATE DATABASE, SHOW DATABASES, USE, DROP DATABASE, CREATE USER, GRANT, and REVOKE.



![To create a database in MySQL • CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS]database_name; • Example: • CREATE DATABASE student;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/createdatabaseandgrant-150225225137-conversion-gate02/75/Mysql-grand-4-2048.jpg)




![Revoke • The REVOKE statement enables system administrators to revoke privileges from MySQL accounts. • REVOKE priv_type [(column_list)] [, priv_type [(column_list)]] ... ON priv_level FROM user [, user] ... • REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES, GRANT OPTION FROM user [, user] ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/createdatabaseandgrant-150225225137-conversion-gate02/75/Mysql-grand-19-2048.jpg)
