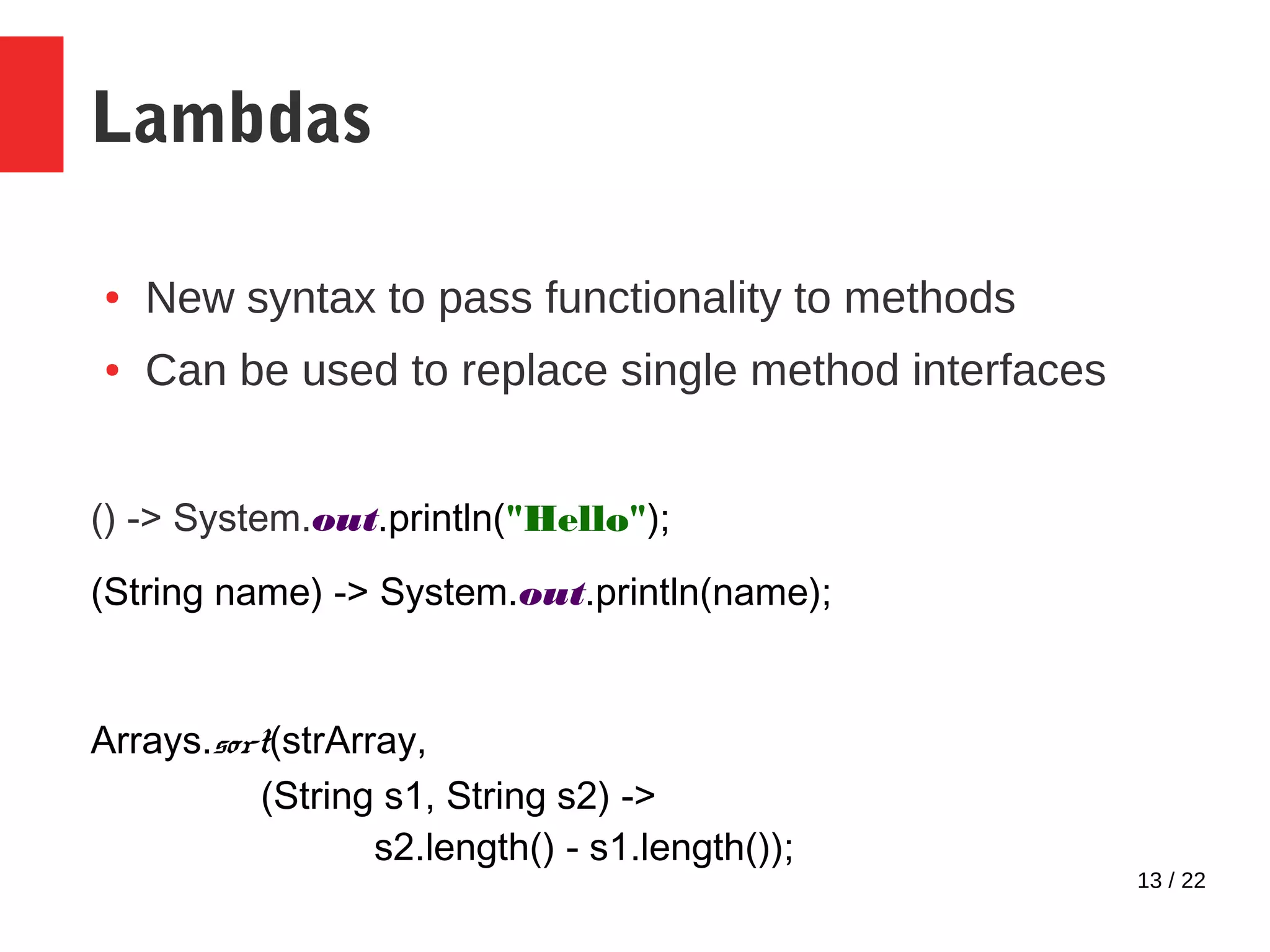
This document discusses several modern Java features including try-with-resources for automatic resource management, Optional for handling null values, lambda expressions, streams for functional operations on collections, and the new Date and Time API. It provides examples and explanations of how to use each feature to improve code quality by preventing exceptions, making code more concise and readable, and allowing functional-style processing of data.