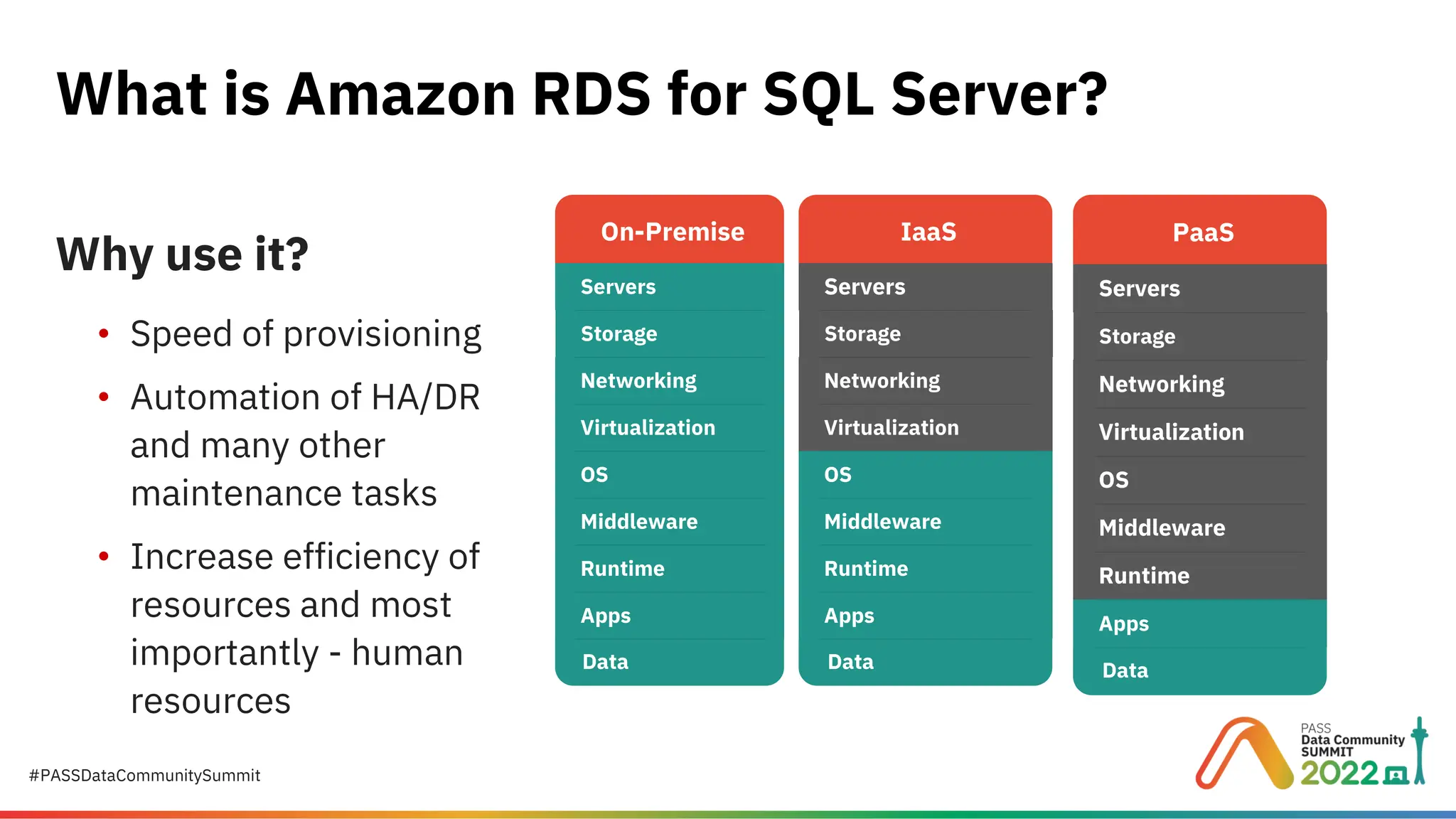
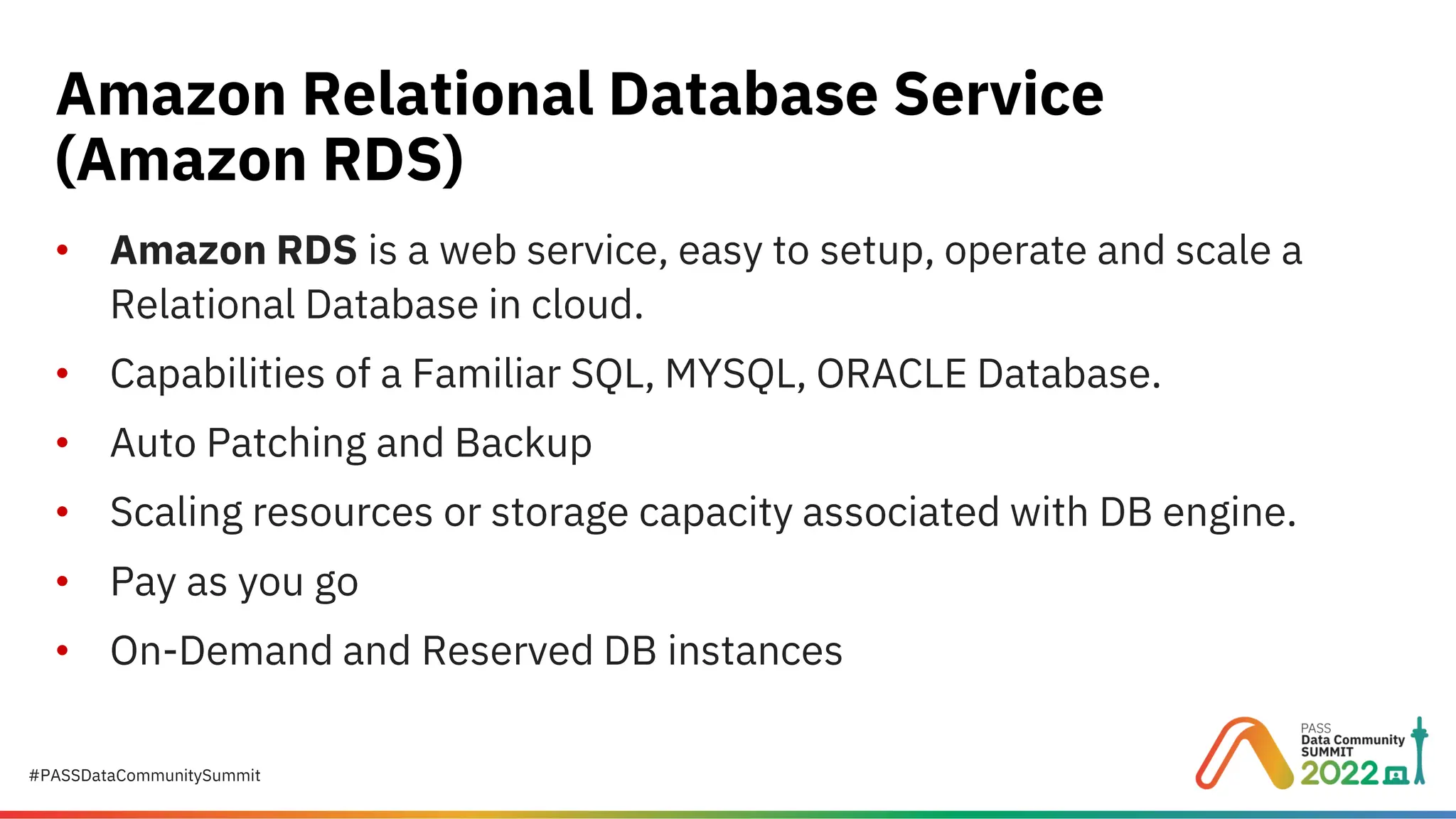
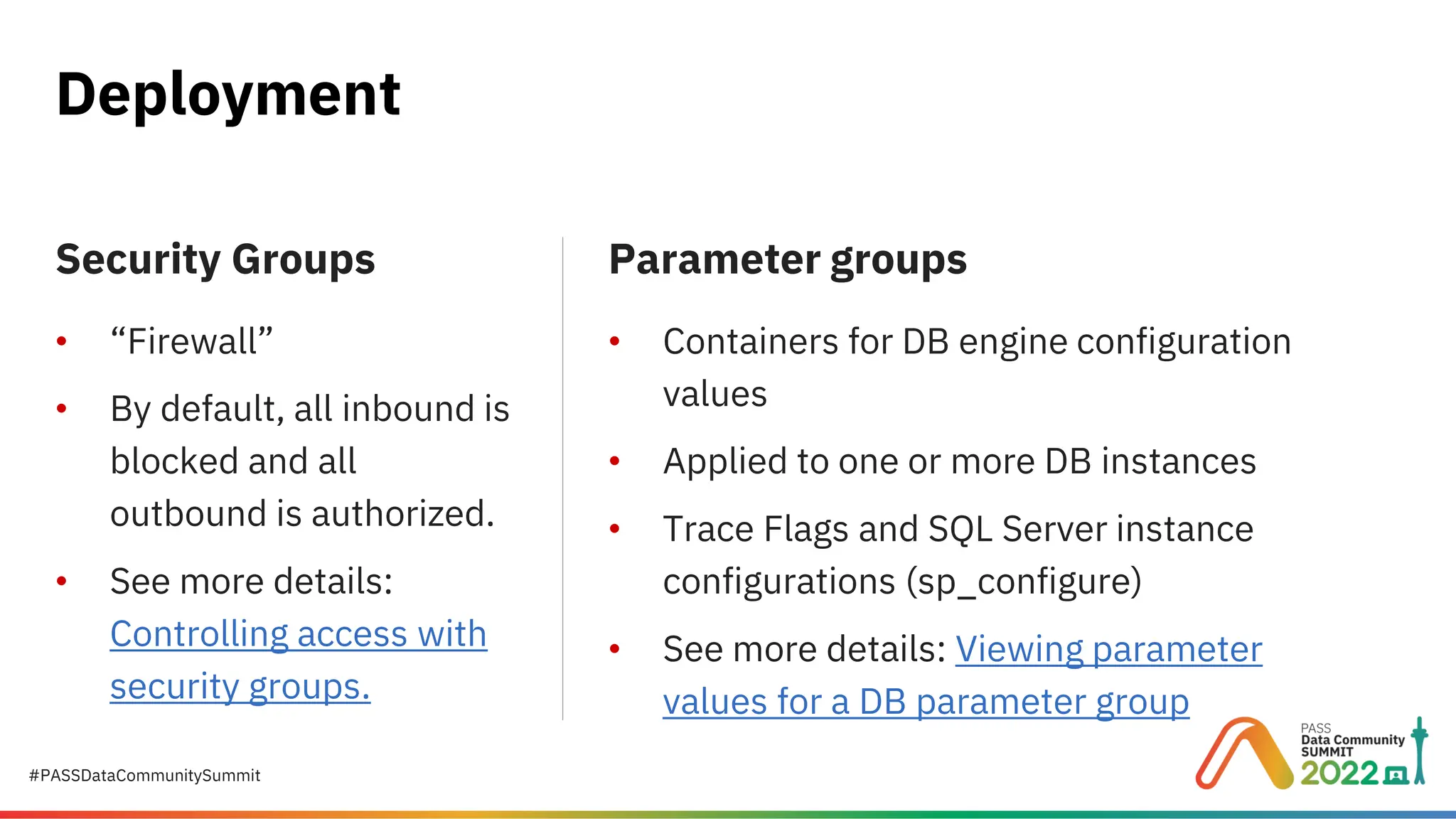
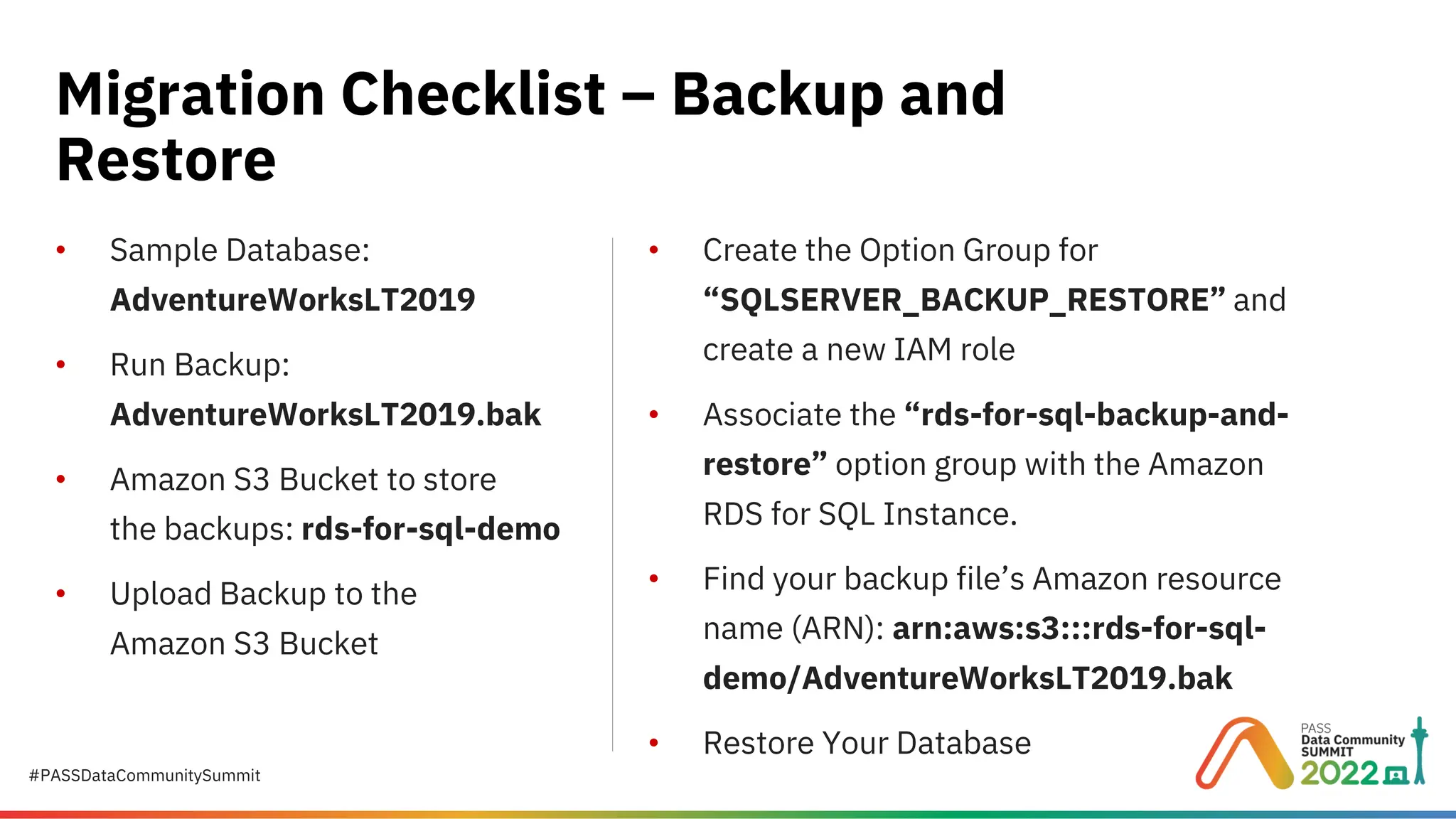
Migrating to Amazon RDS for SQL Server: A Practical Guide to Cloud Database Success Migrating your on-premises SQL Server to Amazon RDS for SQL Server is a strategic step toward scalability, cost efficiency, and operational simplicity. But how do you plan, provision, and execute this migration without disruption? This presentation provides a step-by-step roadmap for DBAs and IT leaders to successfully move SQL Server workloads to AWS. Presented by Suyog Pagare, Senior Technical Specialist at Datavail, this session covers everything from AWS fundamentals to advanced migration techniques, ensuring you have the knowledge to make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls. Key Highlights: What is Amazon RDS for SQL Server? Understand Amazon RDS as a managed Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering that automates patching, backups, and scaling—without OS-level access. AWS Fundamentals Learn the basics of AWS Regions, Availability Zones (AZs), Amazon S3, and IAM roles—critical components for secure and efficient deployments. Planning Your RDS Instance Explore considerations for instance class types (Standard, Memory-Optimized, Burst), storage options (General Purpose SSD, Provisioned IOPS), and Multi-AZ deployments for high availability. Creating and Configuring RDS Step through the checklist for provisioning your RDS instance, including security groups, parameter groups, and option groups for features like native backup/restore, TDE, and auditing. Connecting to Your RDS Instance Learn how to configure inbound rules, retrieve connection endpoints, and connect via SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). Migration Strategies Backup and Restore: Fastest method for off-hours migrations; supports native restores up to 16 TB. AWS Database Migration Service (DMS): Ideal for minimal downtime migrations. Real-World Demo See a live example using AdventureWorksLT2019, including S3 bucket setup, IAM role creation, and database restoration. Why This Matters Amazon RDS simplifies SQL Server management, but successful migration requires planning and understanding AWS services. This session equips you with practical insights to: Reduce migration risk. Optimize performance and cost. Maintain security and compliance. Whether you’re considering a lift-and-shift migration or planning for cloud-native modernization, this guide provides the foundation for success. 👉 Download the full presentation and learn more here: https://www.datavail.com/resources/migrating-amazon-rds-sql-server/