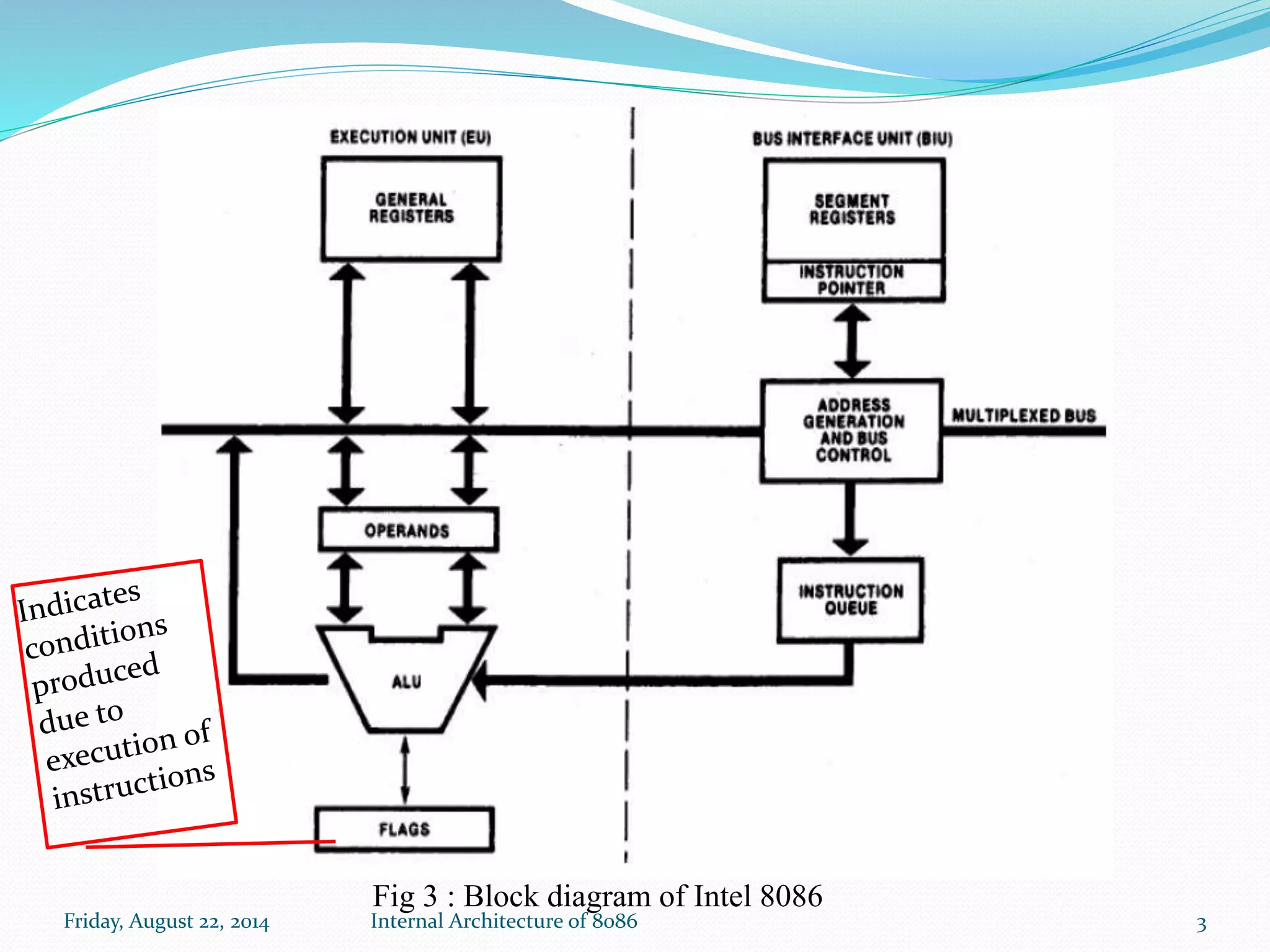
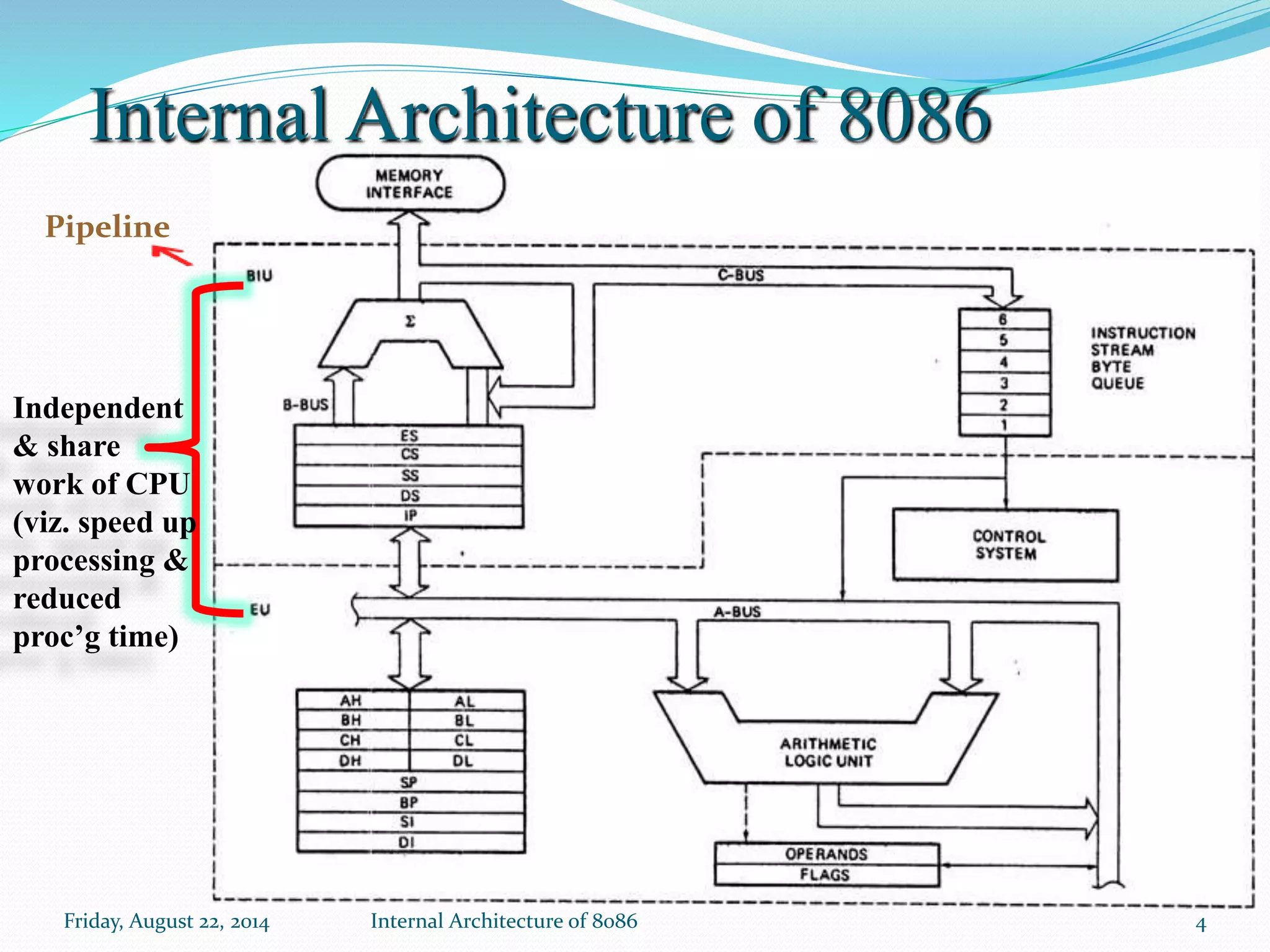
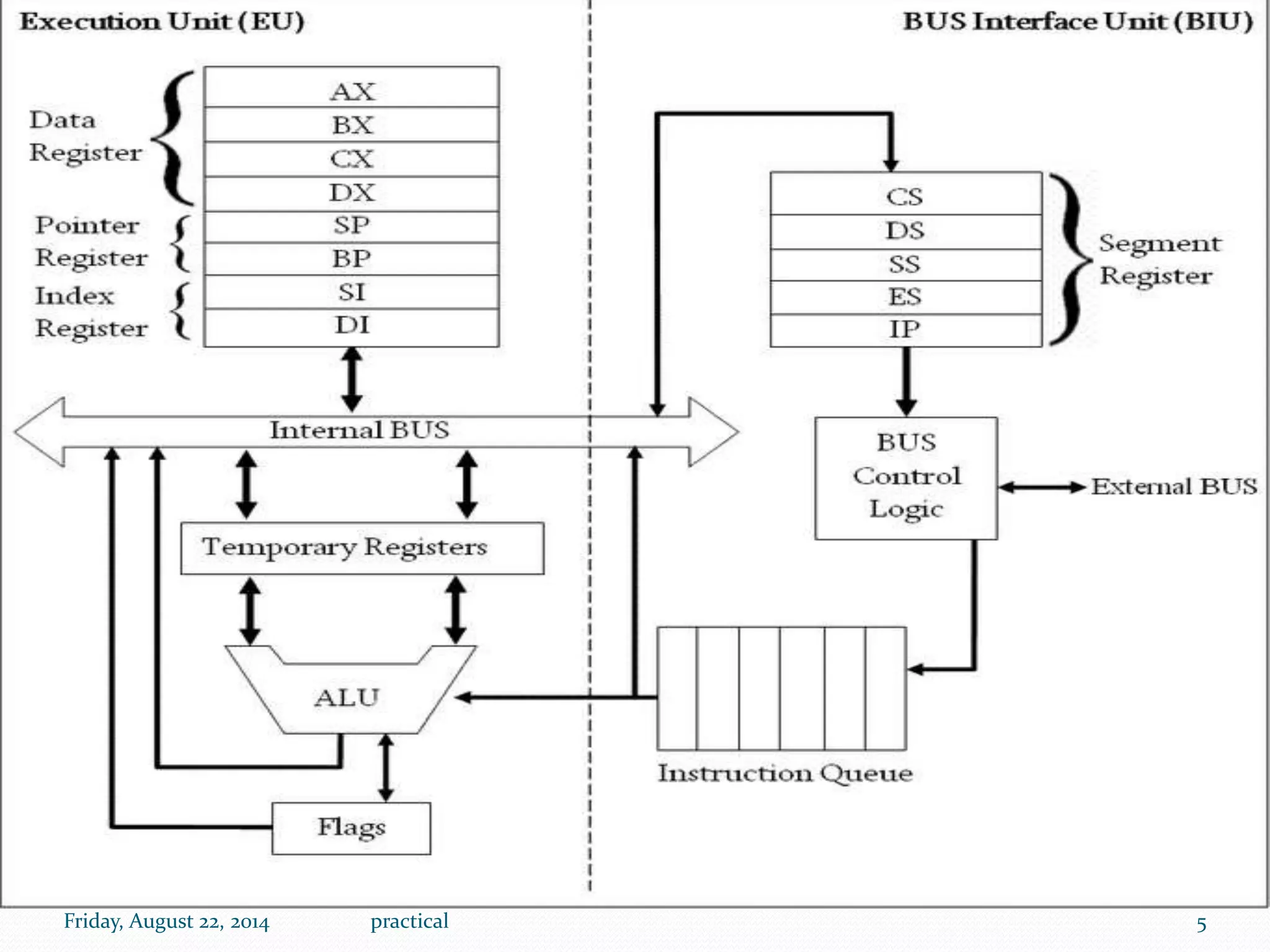
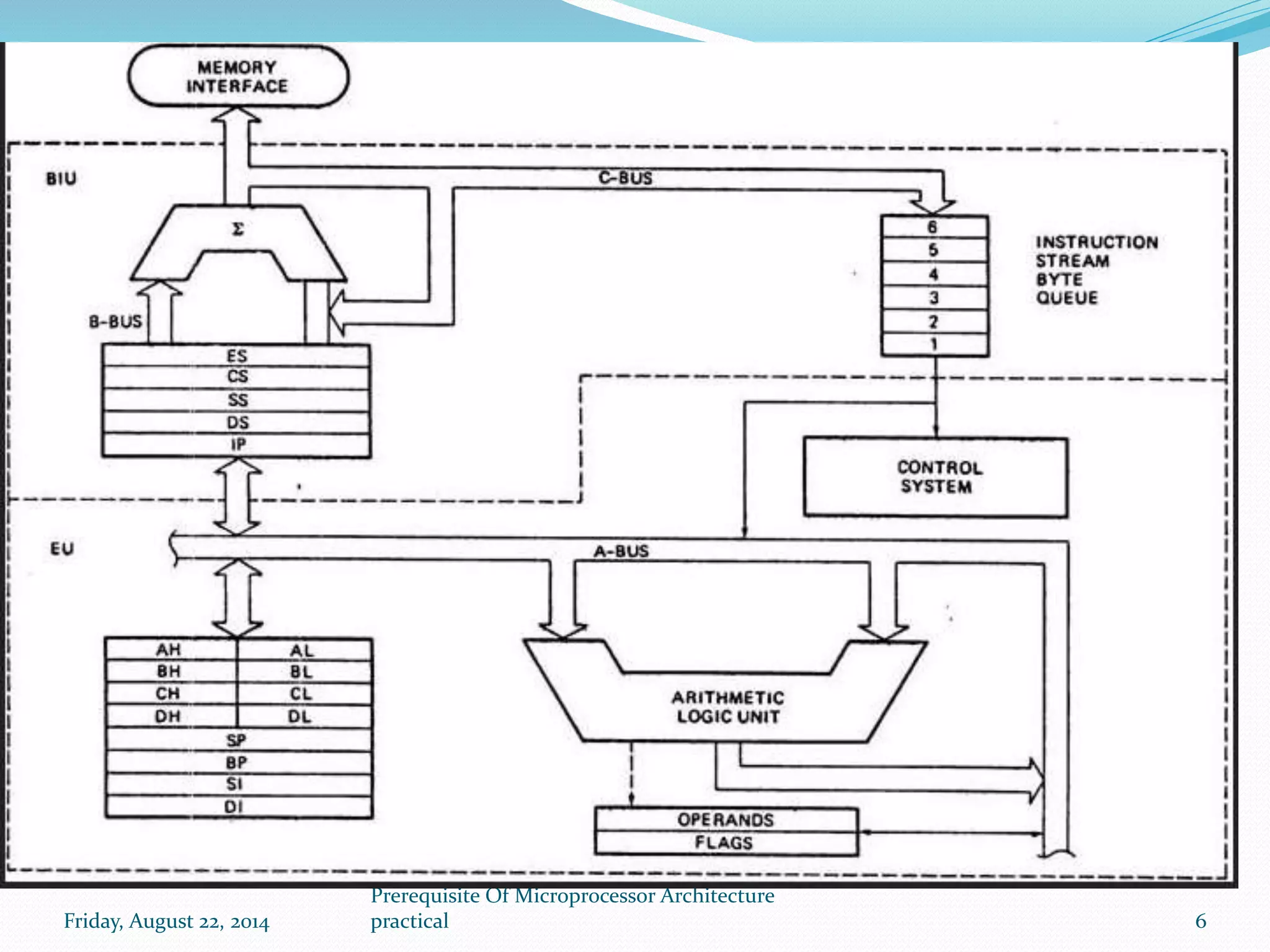
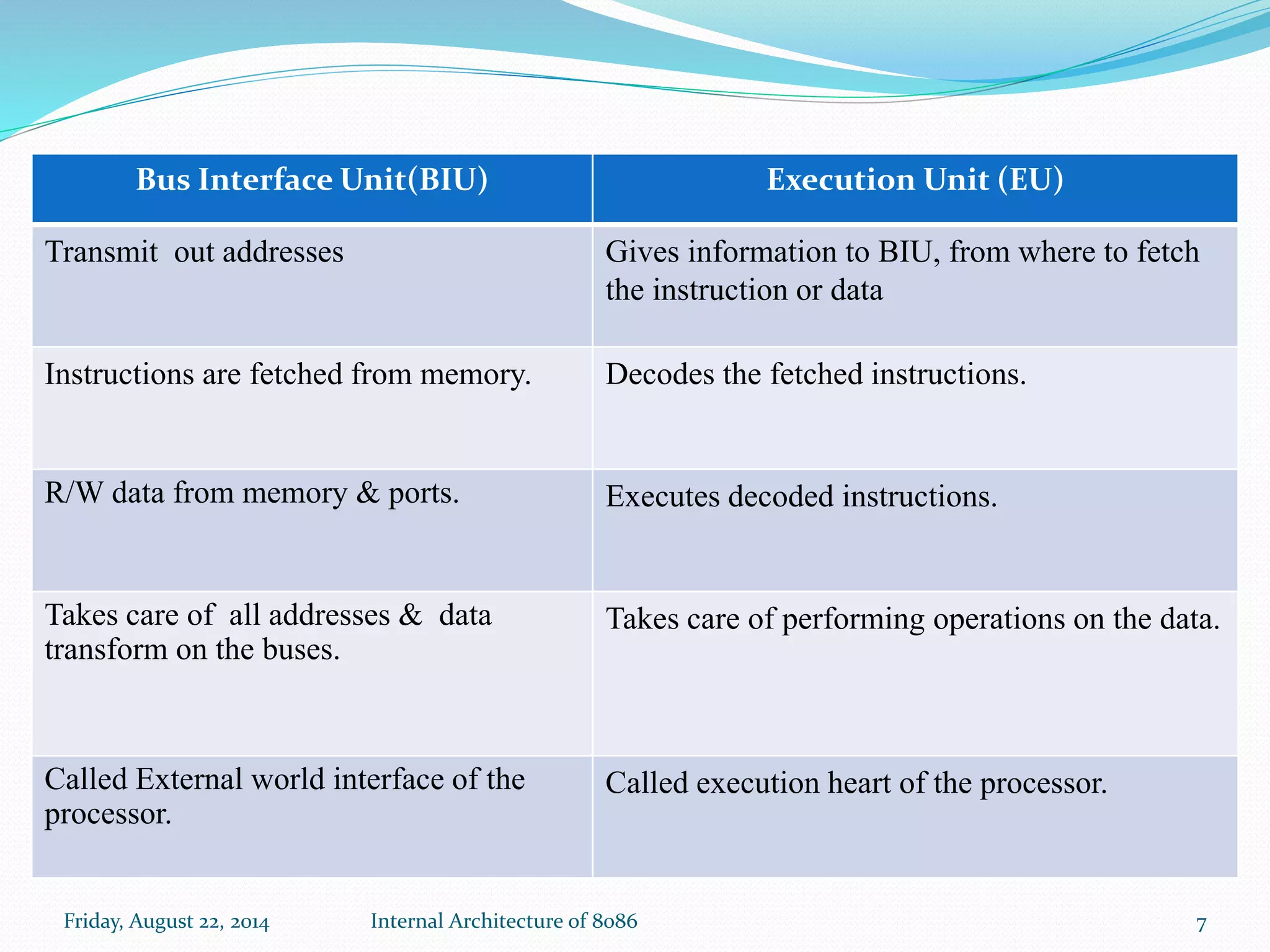
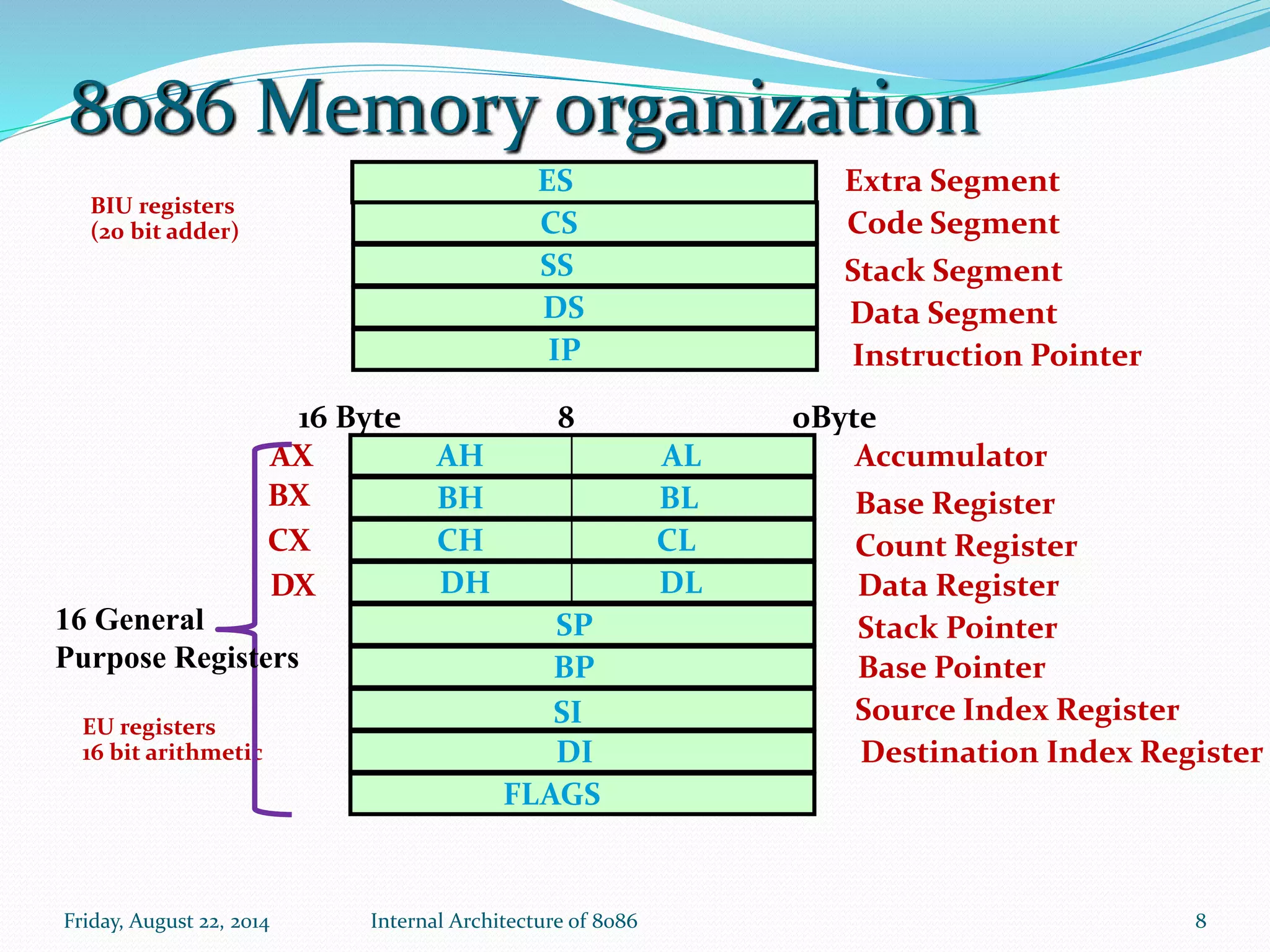
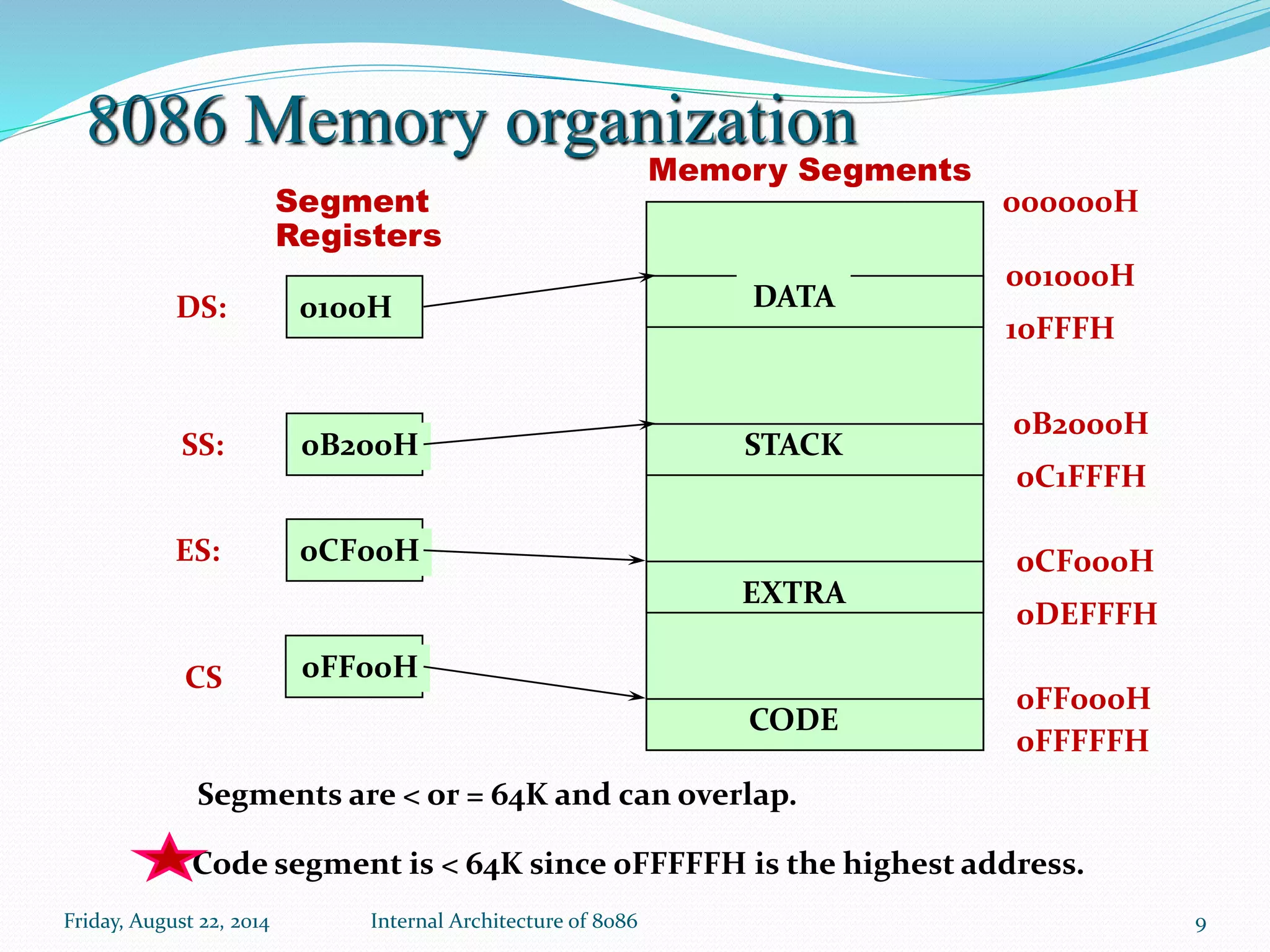
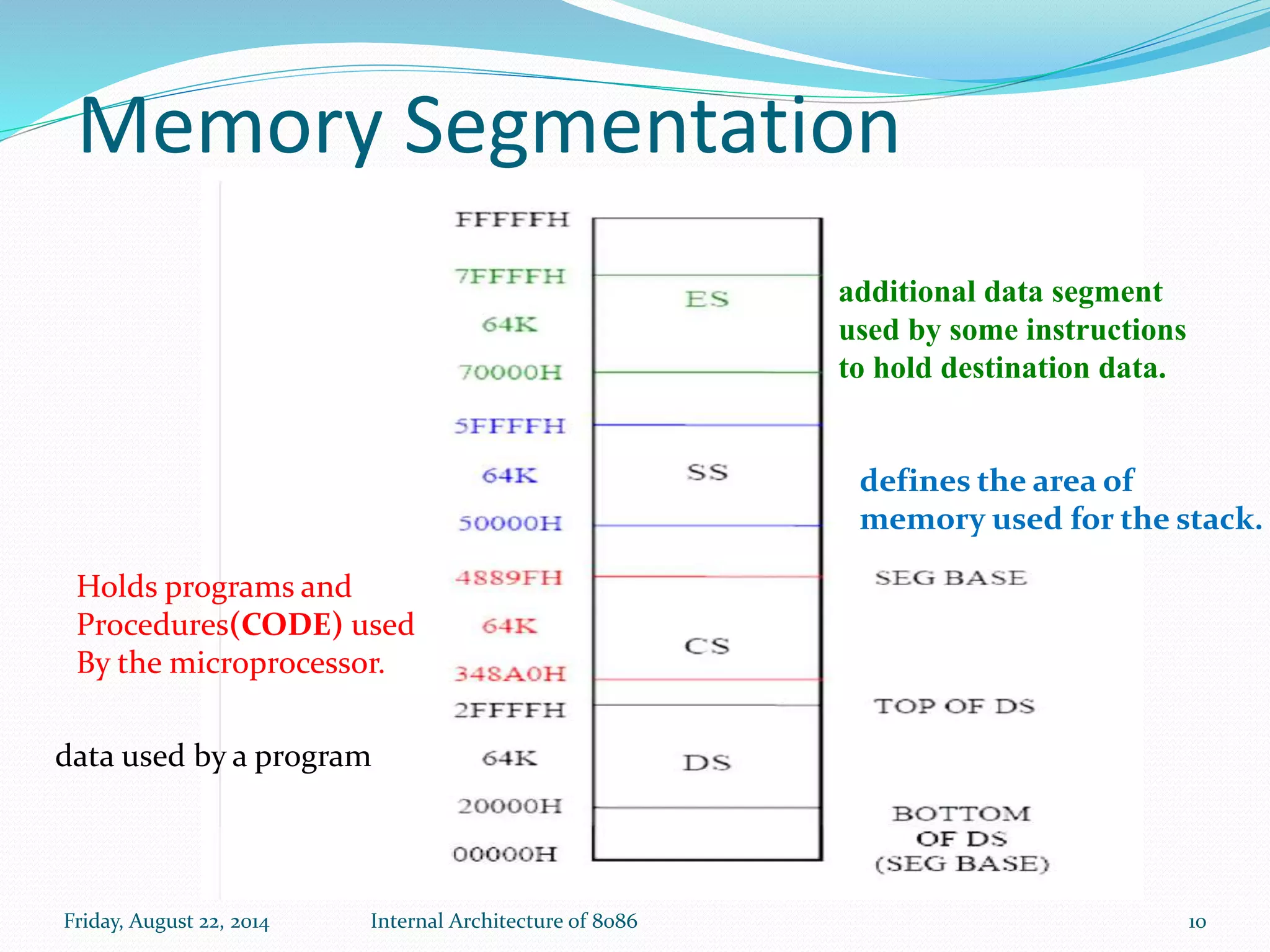
The document discusses the internal architecture of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. It describes the main components of the 8086 including the Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and Execution Unit (EU). It also covers the memory organization of the 8086, including the use of separate memory segments for code, data, stack, and extra segments. The Flag Register contained within the EU is also described, which stores condition and control bits used during instruction execution.