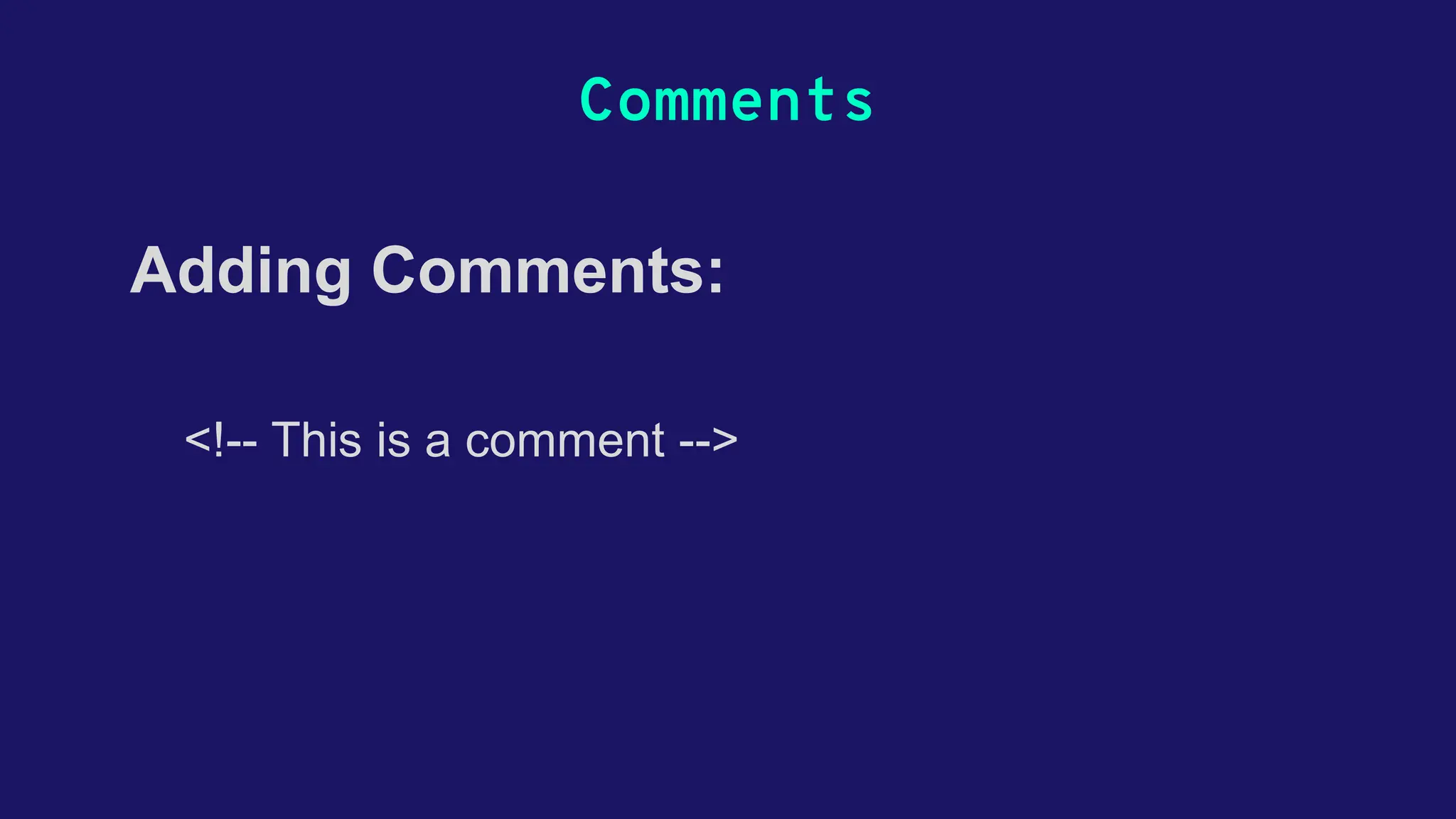
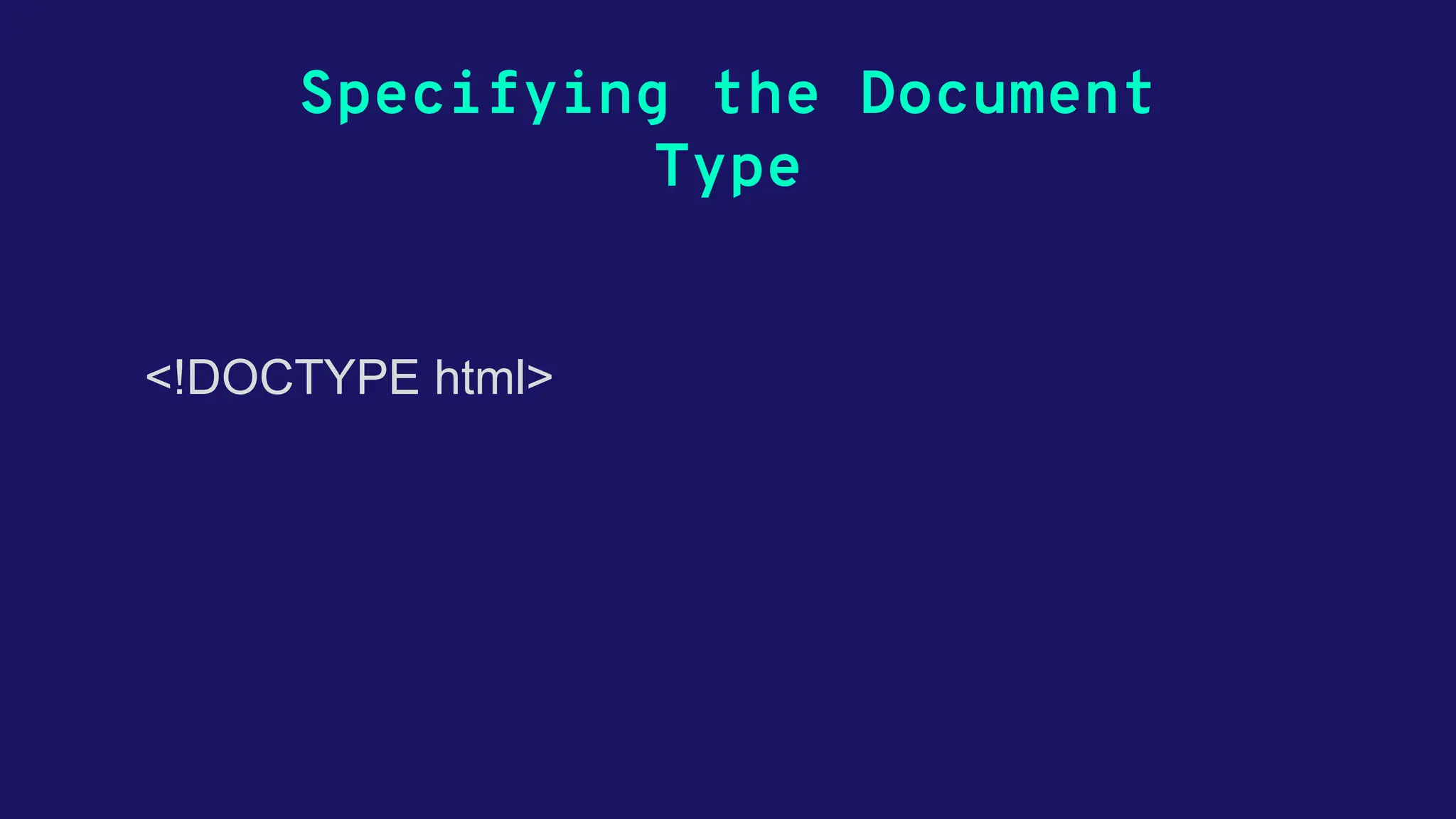
This document provides an overview of HTML, detailing its structure, basic tags, and essential elements needed for creating web pages. It covers topics like lists, links, images, tables, forms, and semantic HTML5 tags, while also discussing attributes, multimedia integration, and concepts of responsiveness and accessibility. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for beginners to understand and build HTML documents effectively.