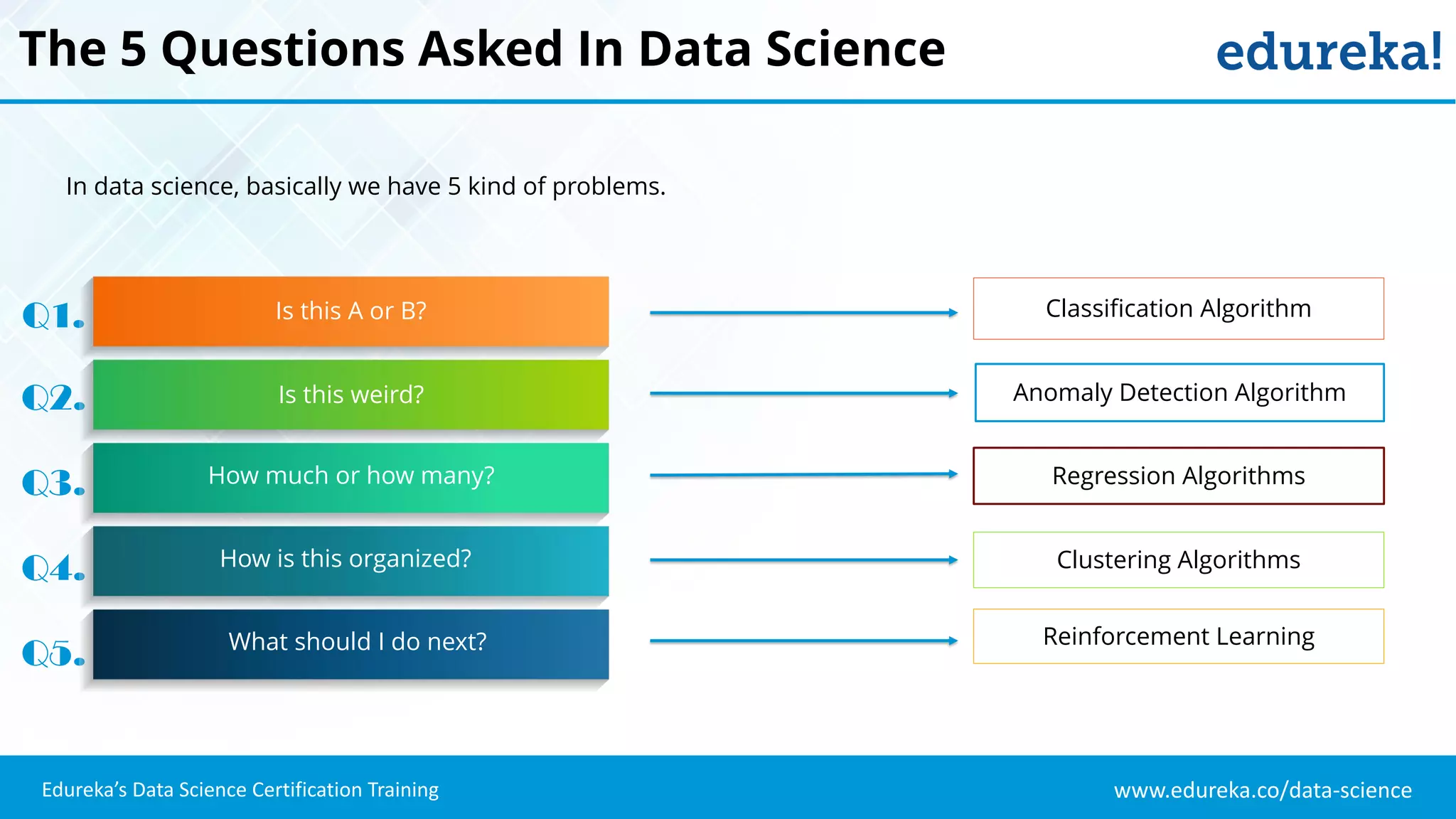
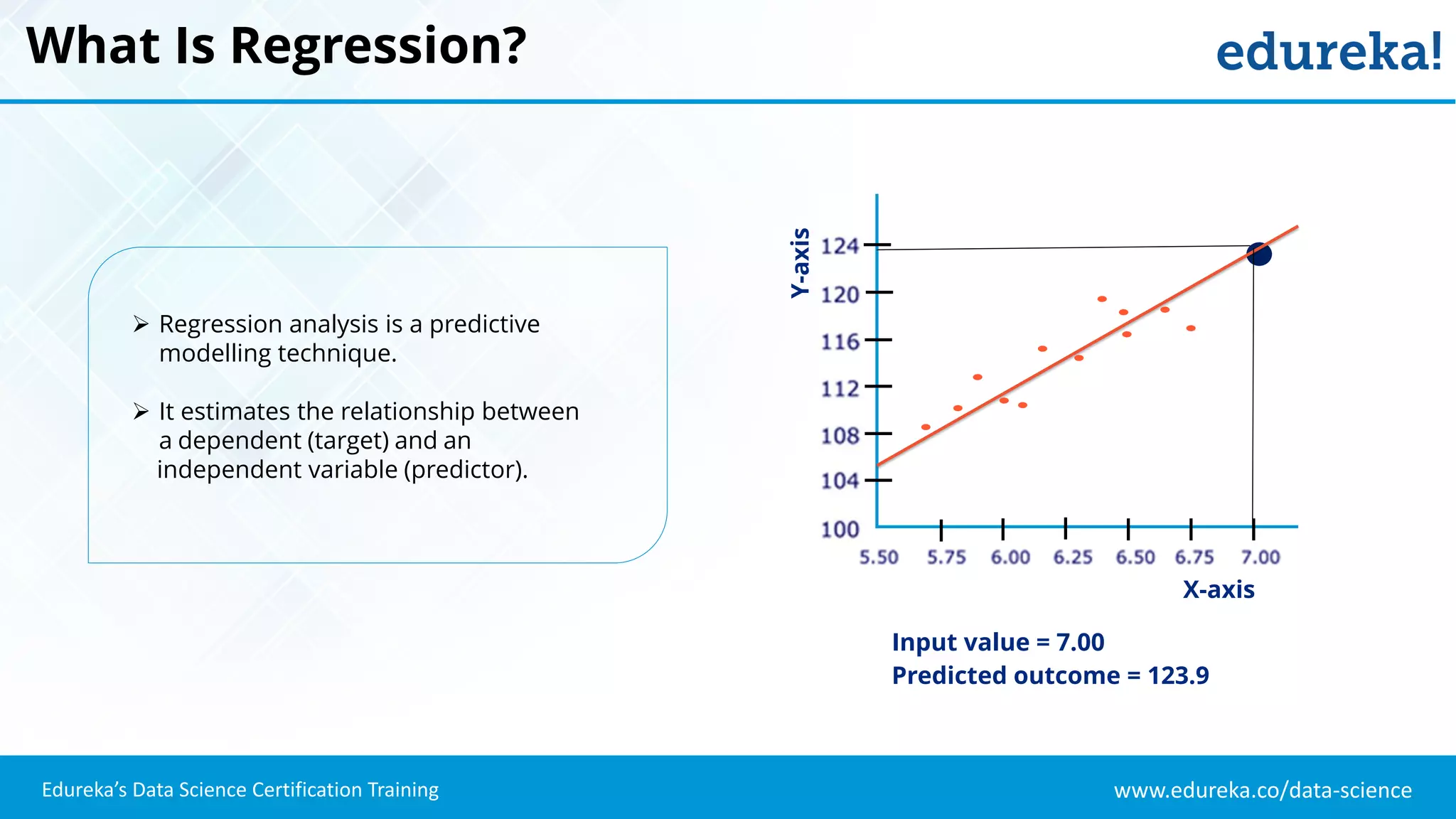
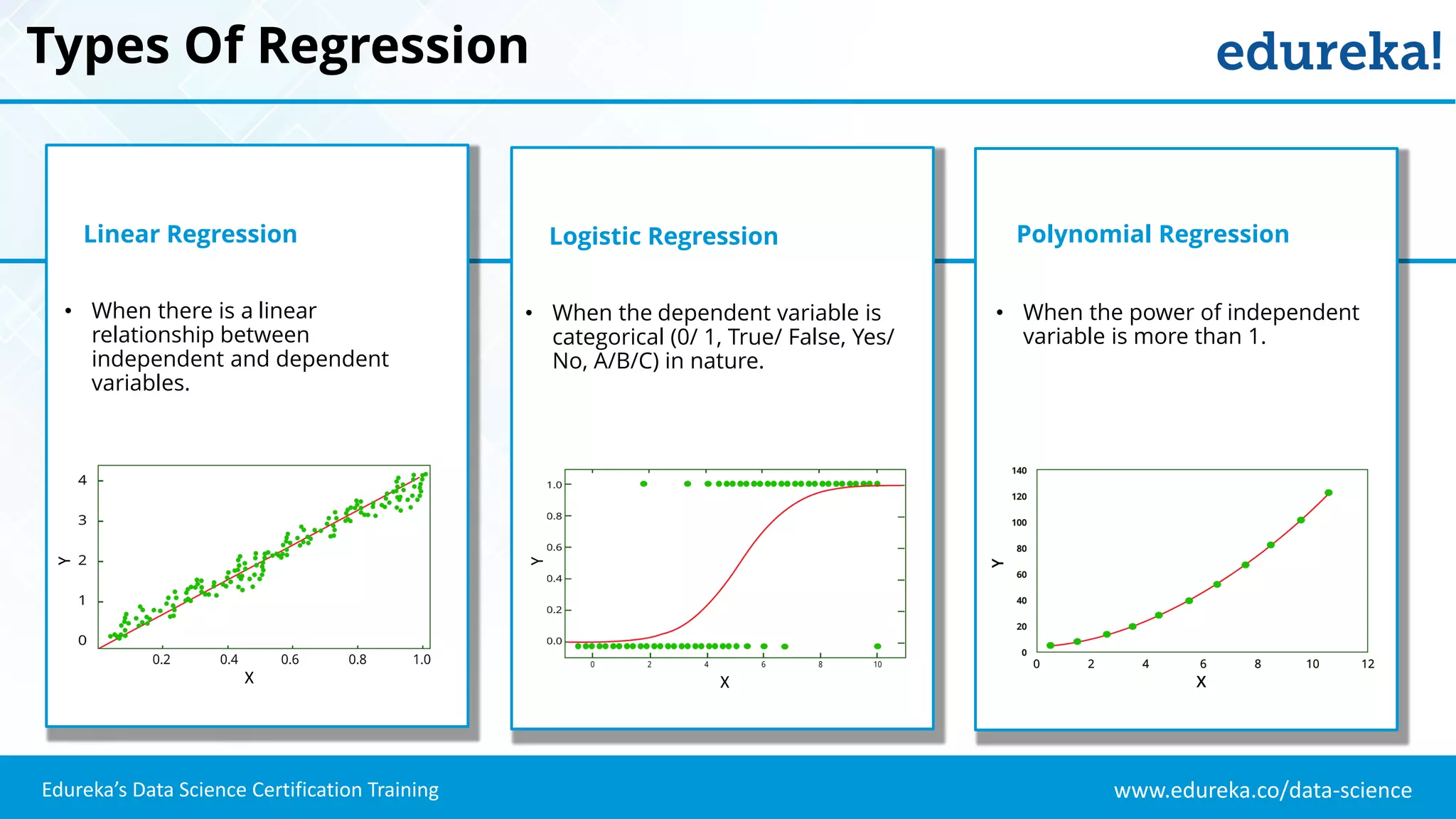
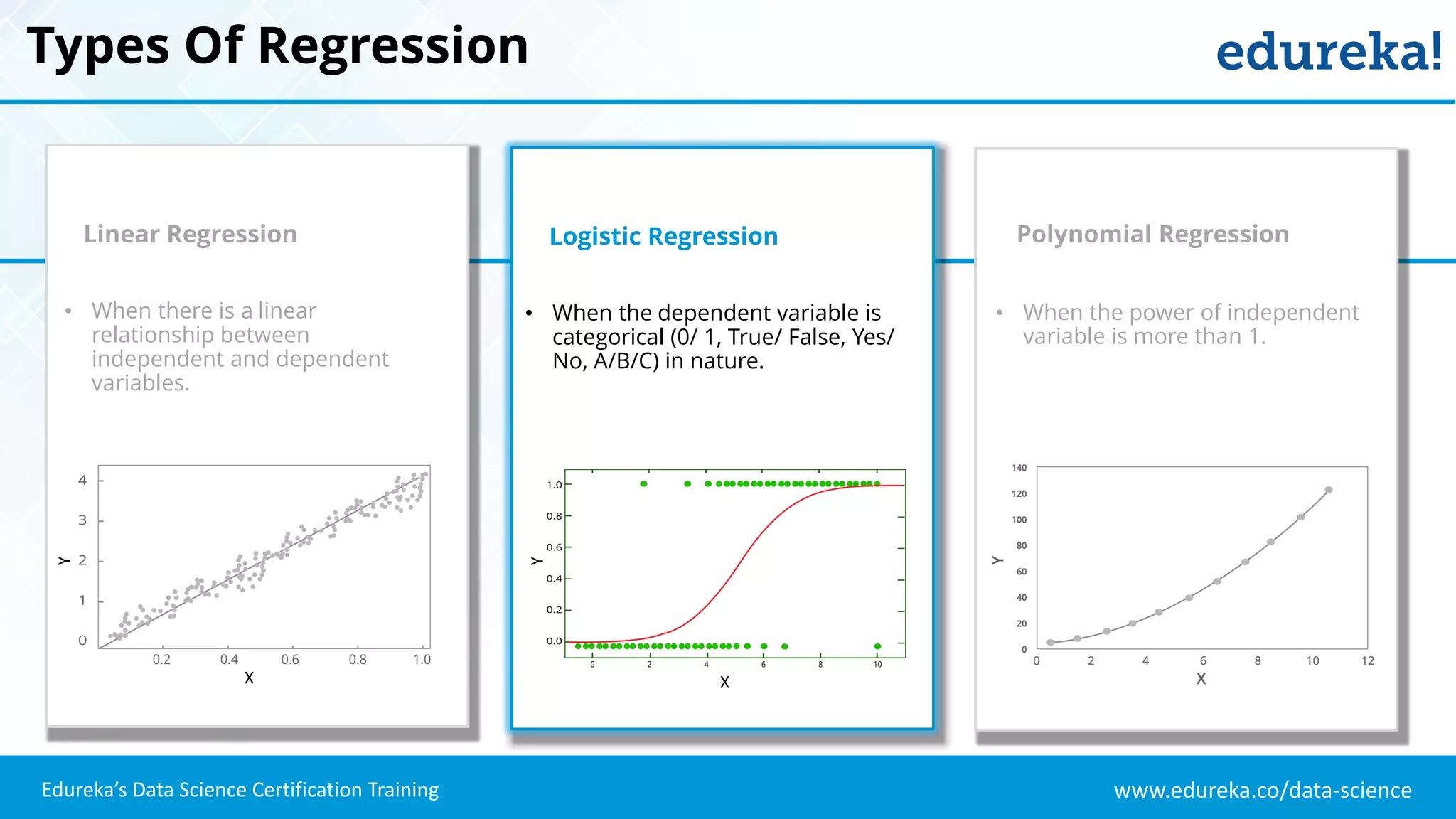
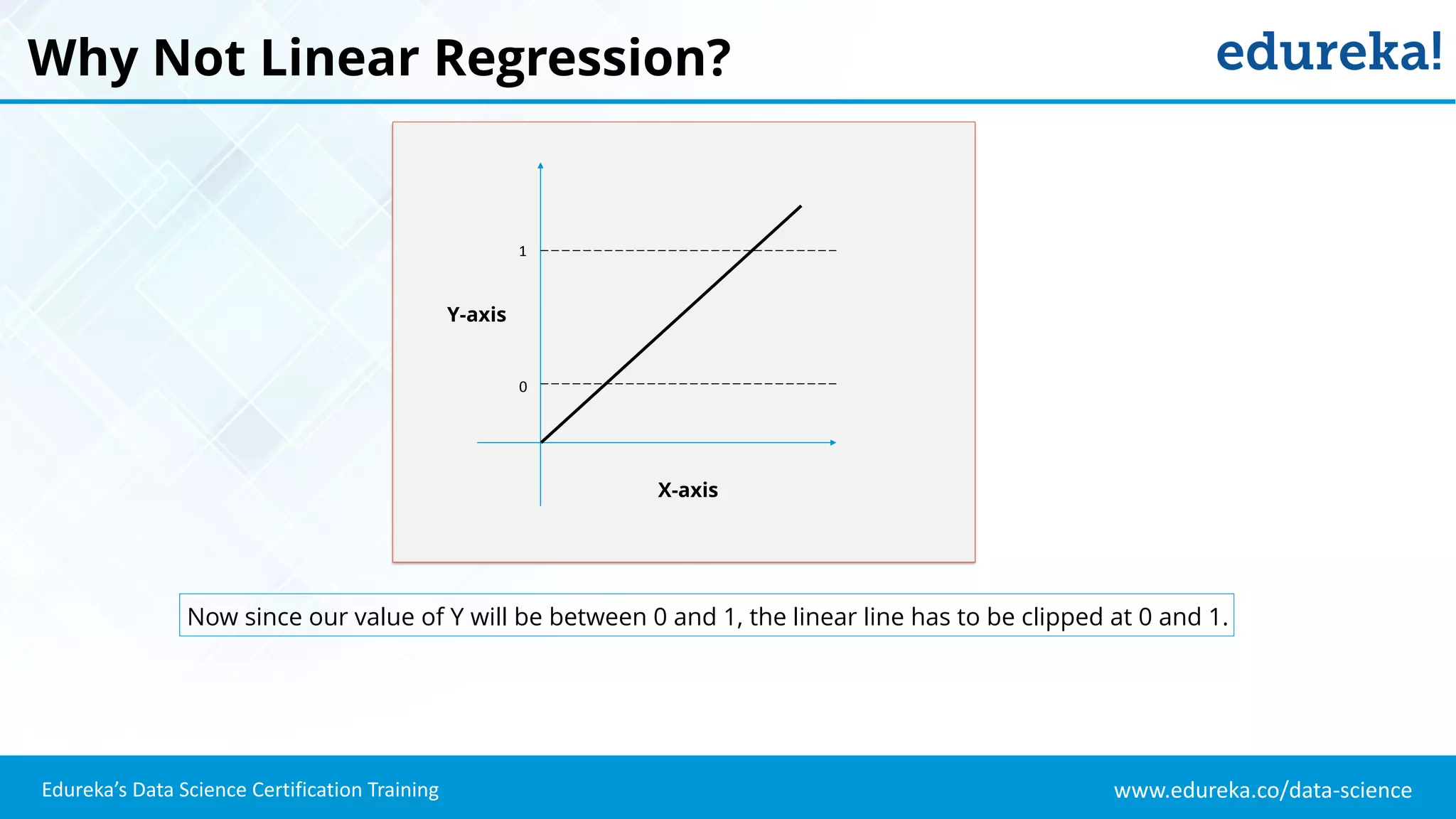
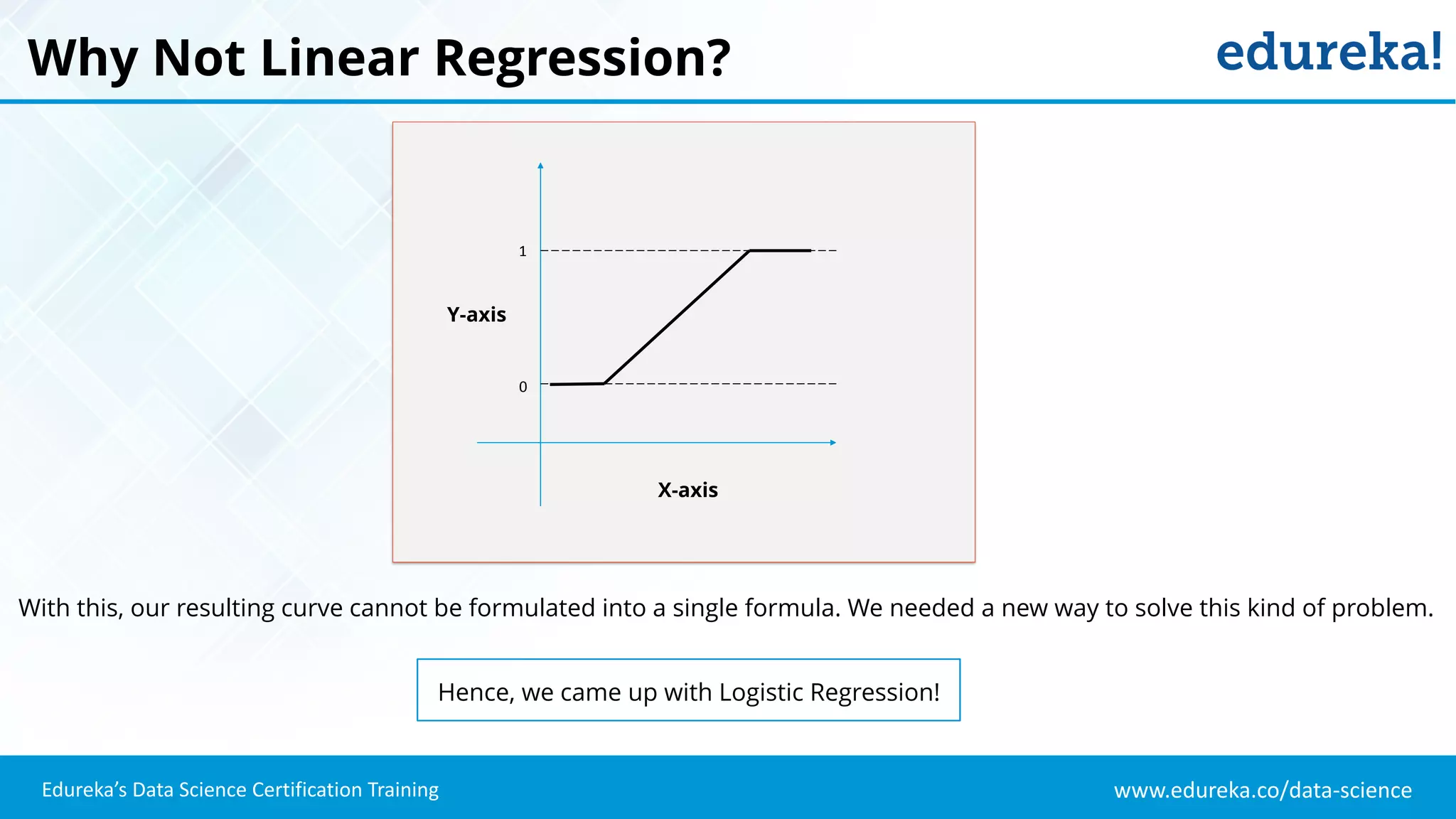
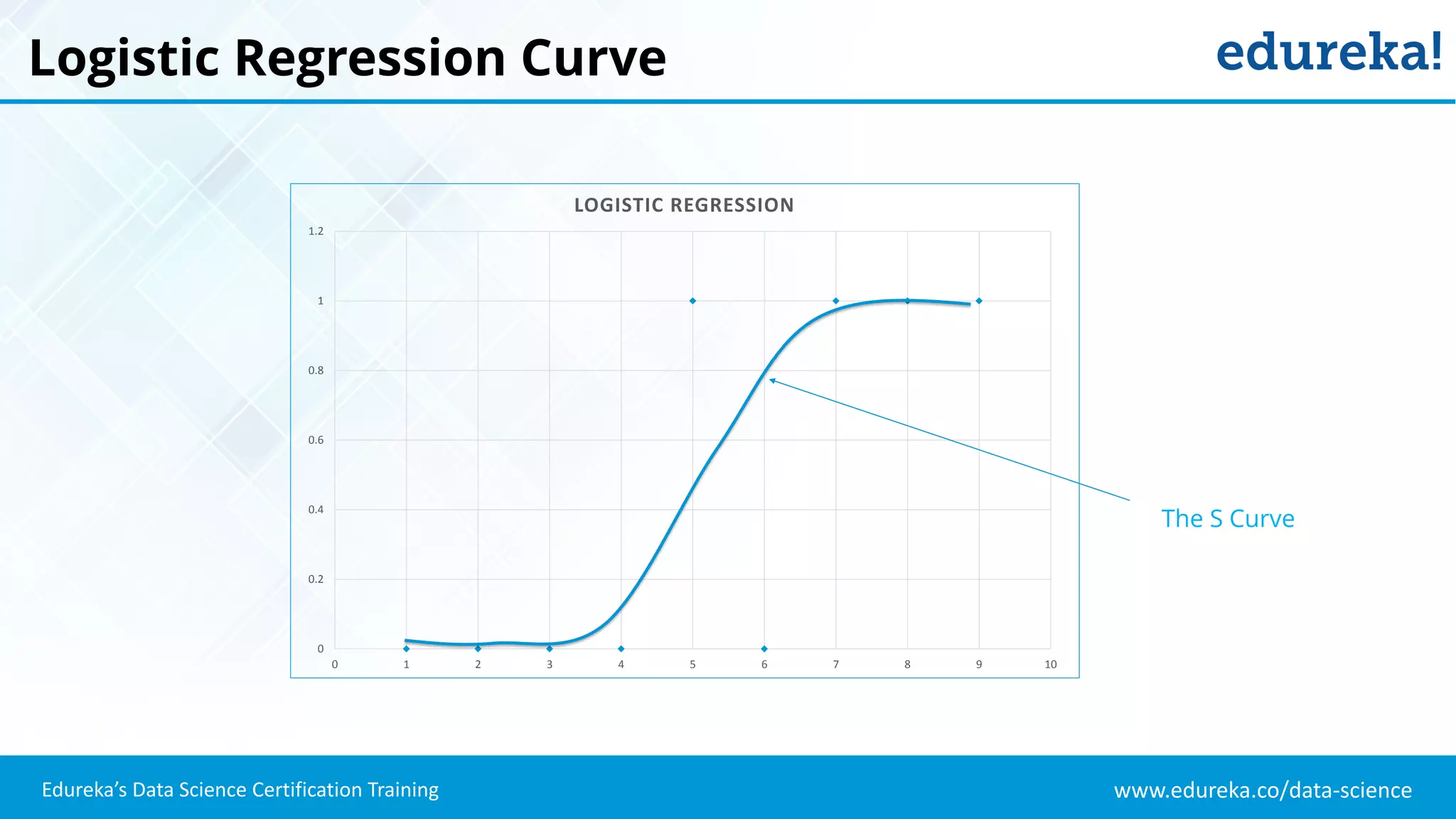
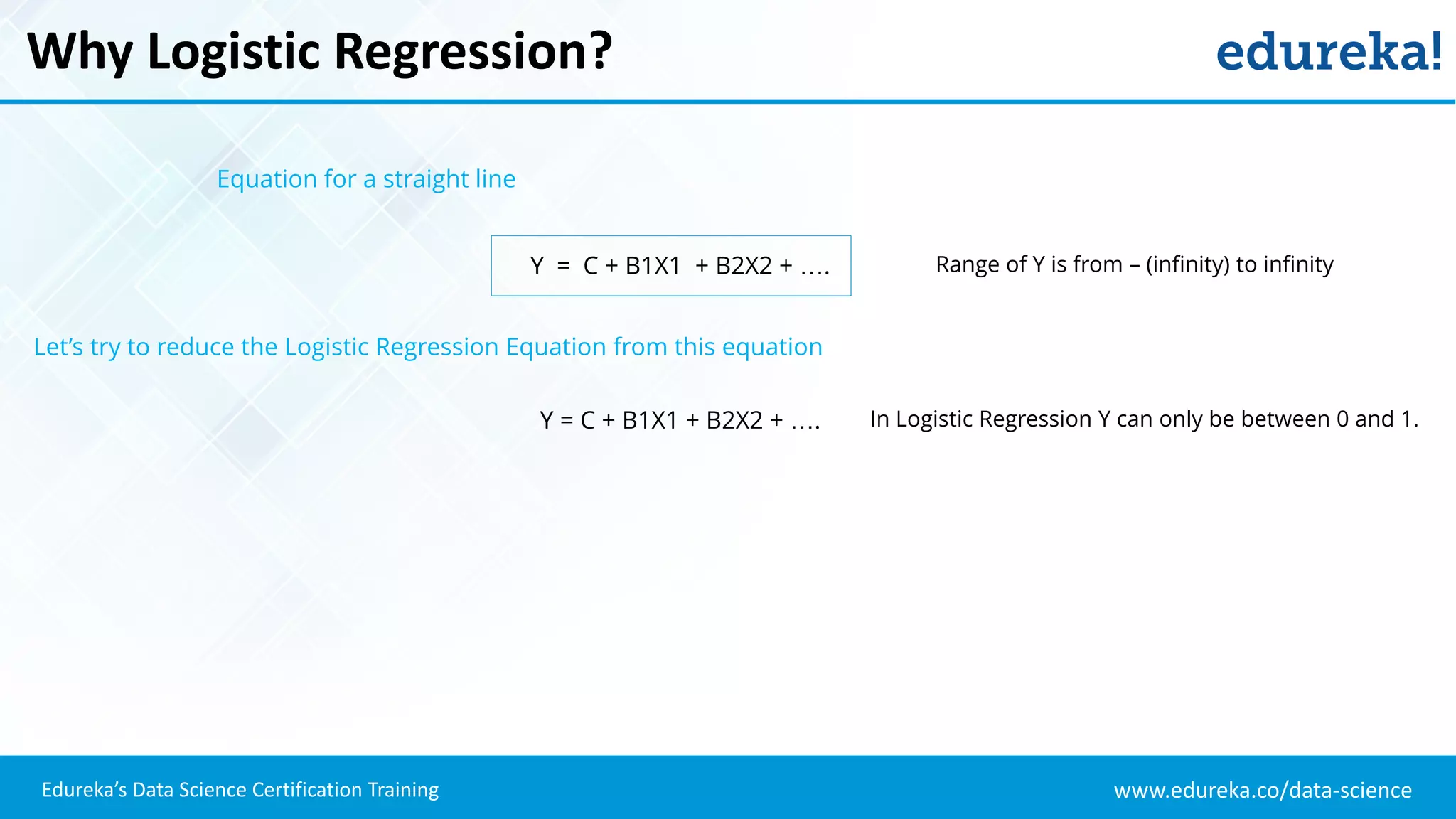
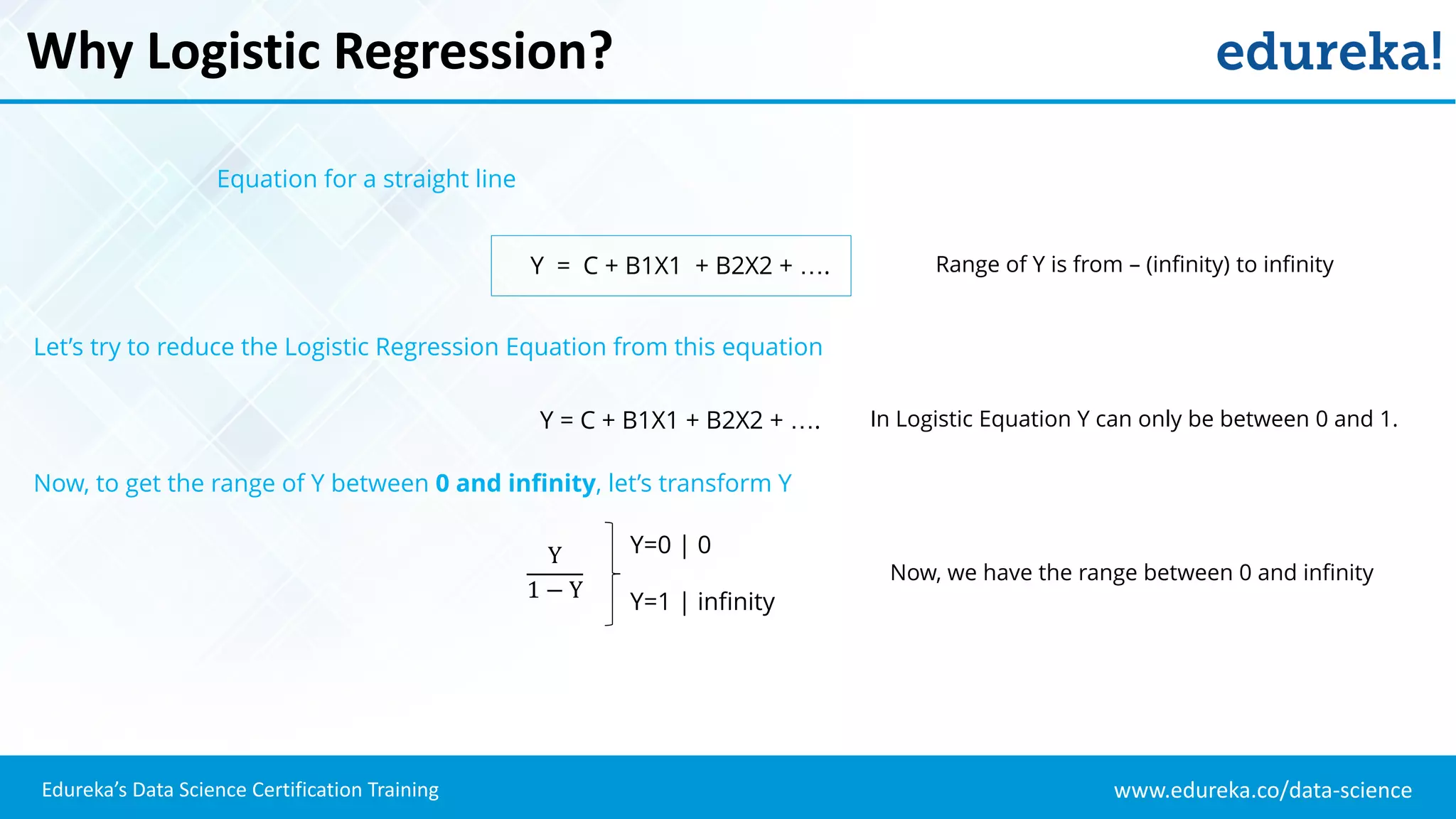
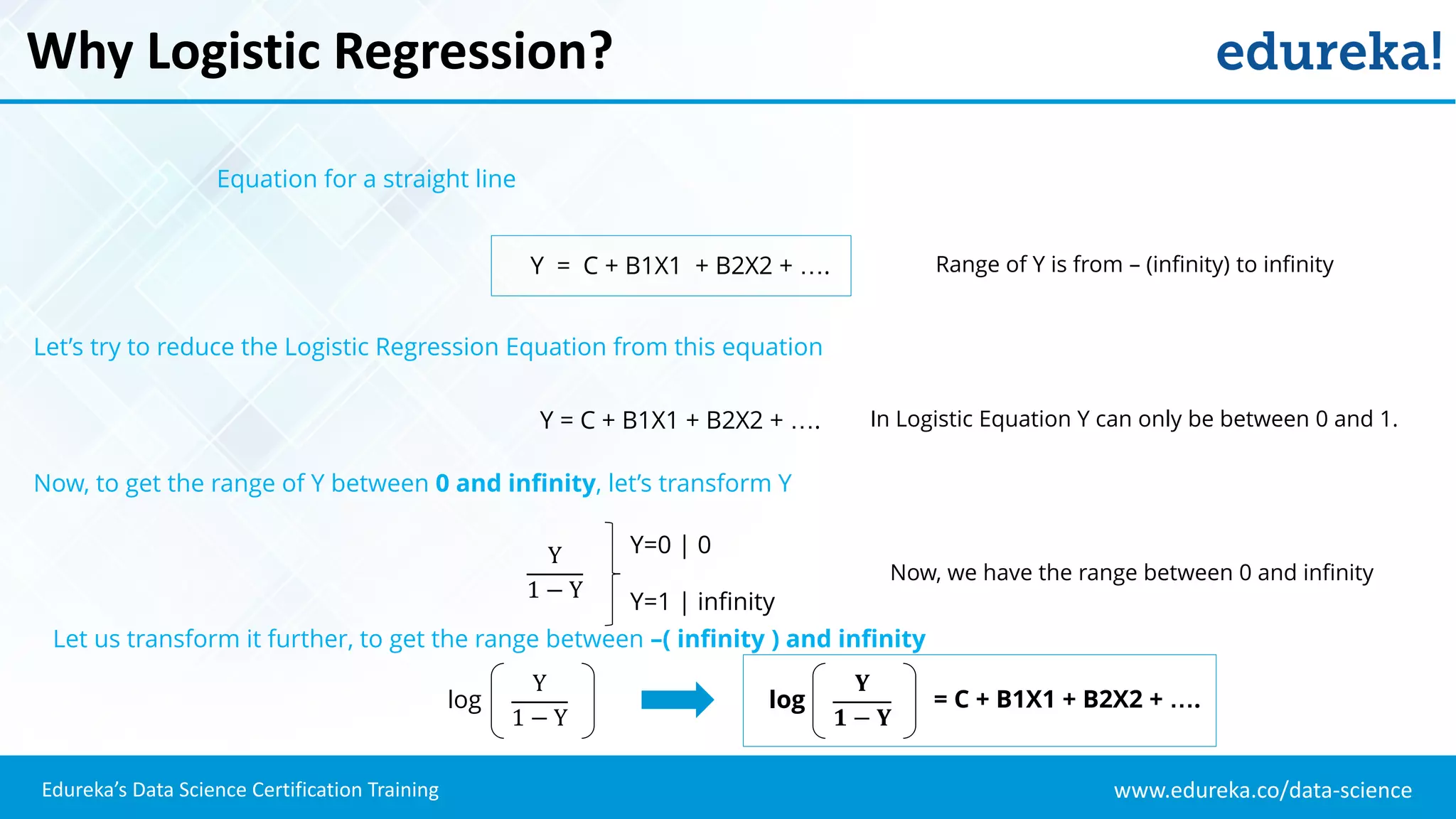
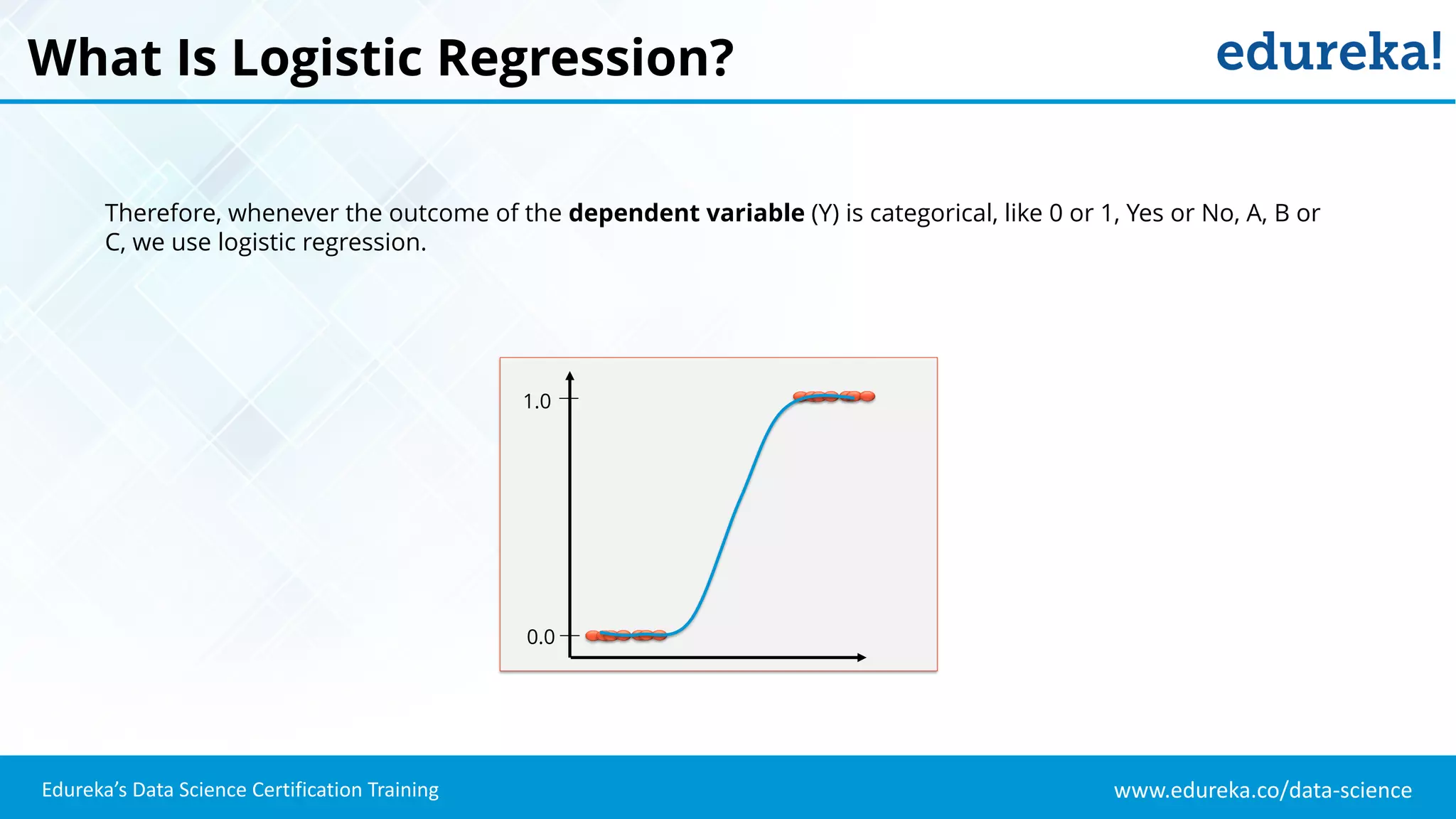
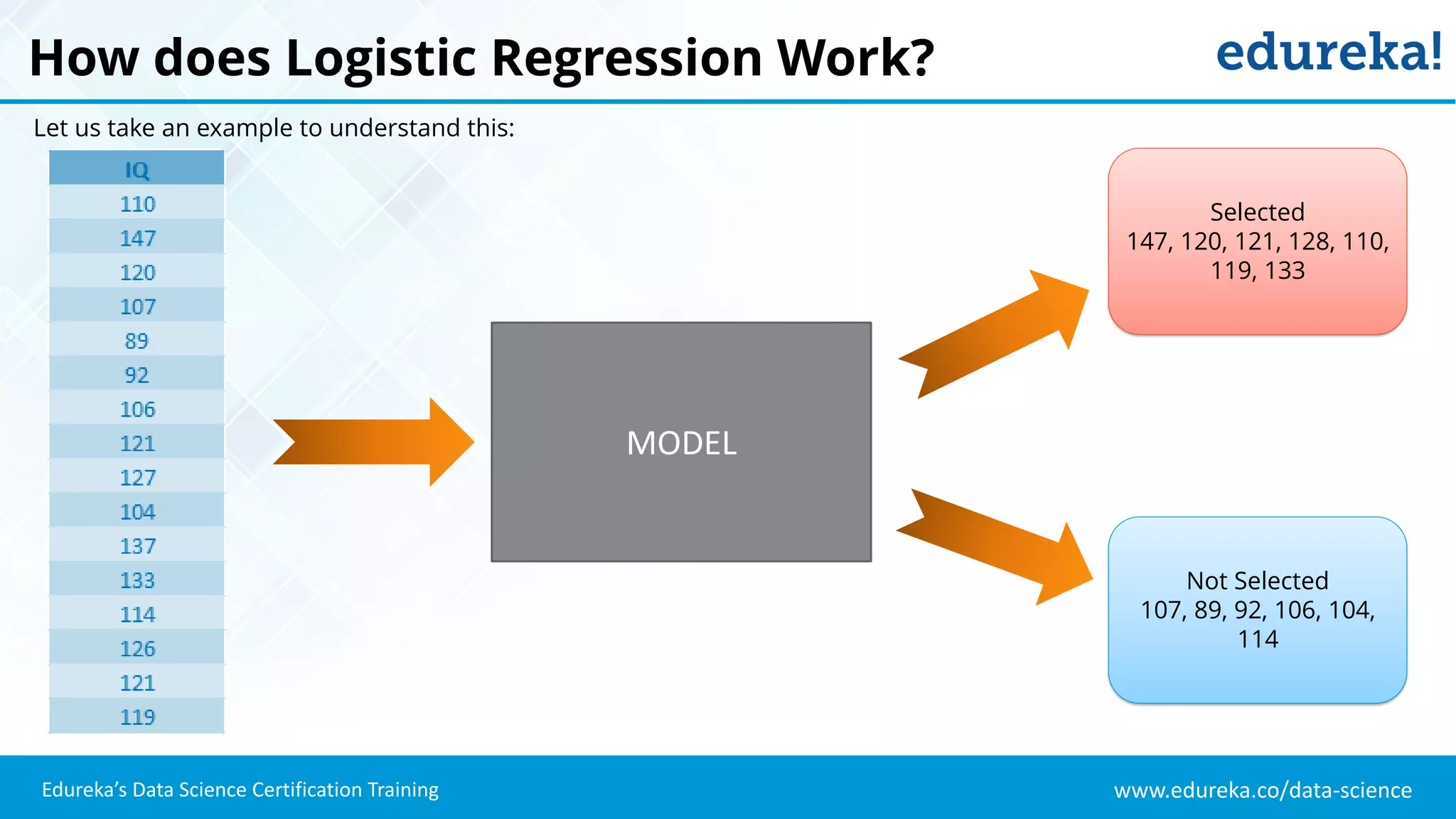
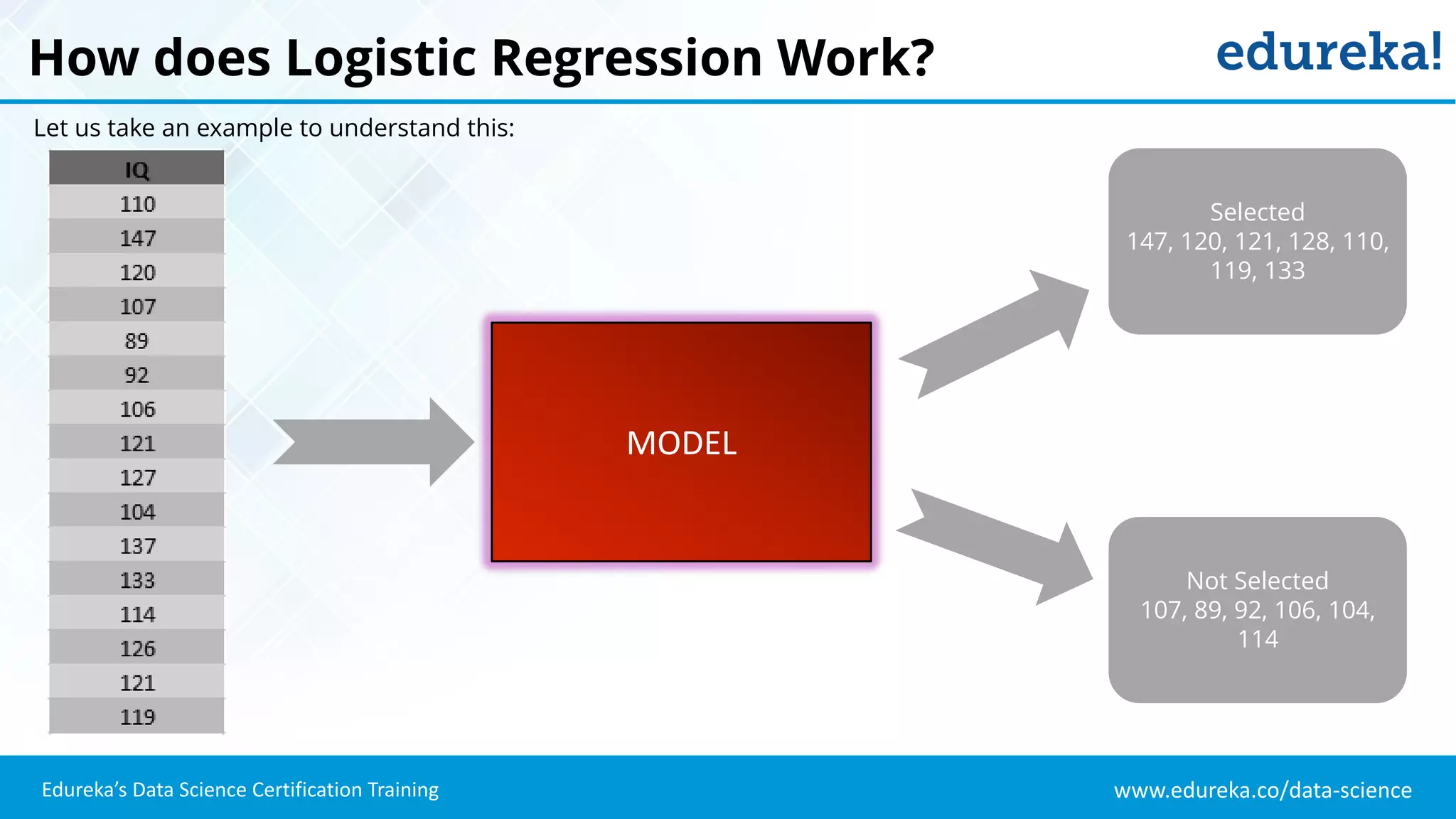
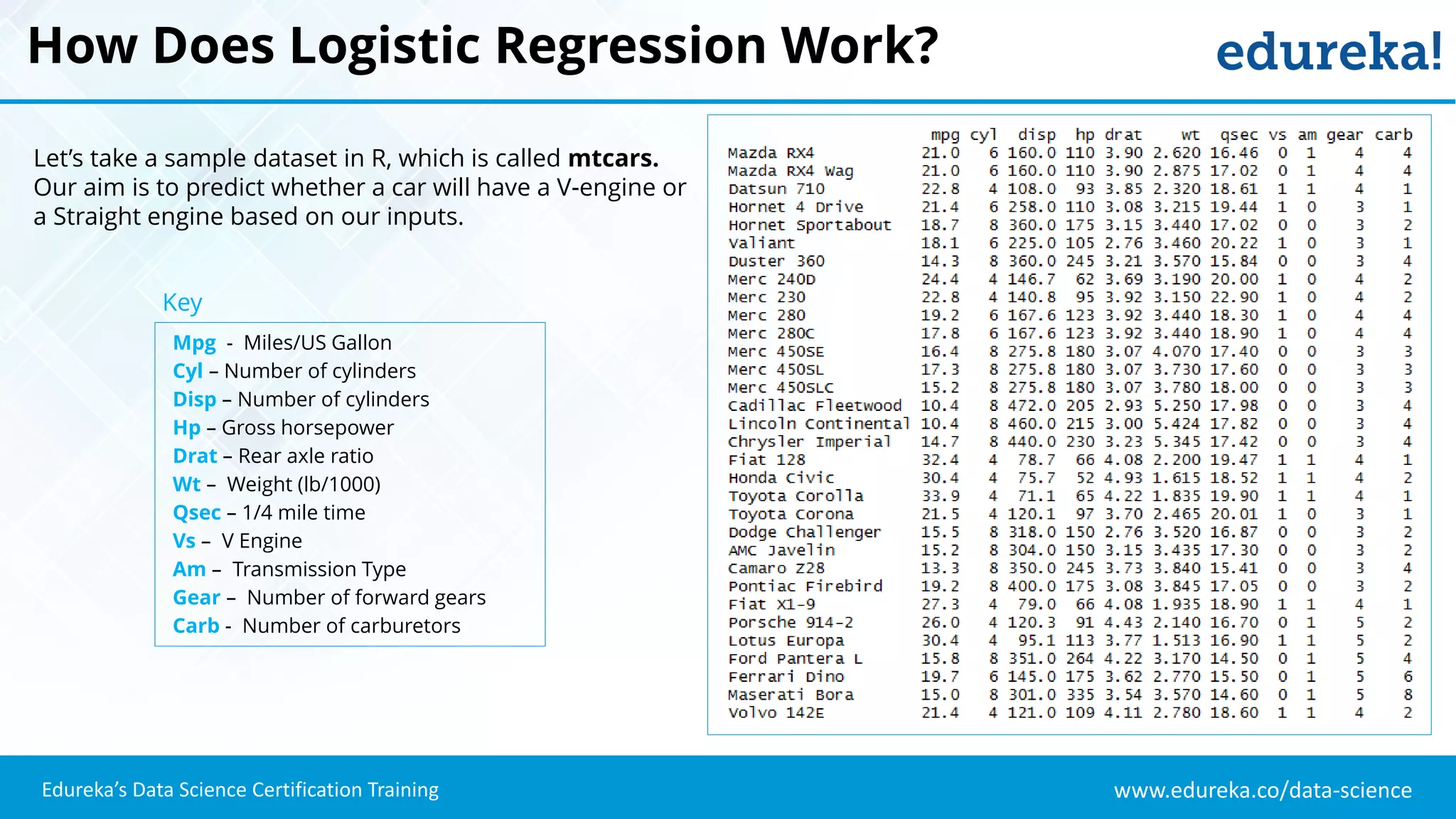
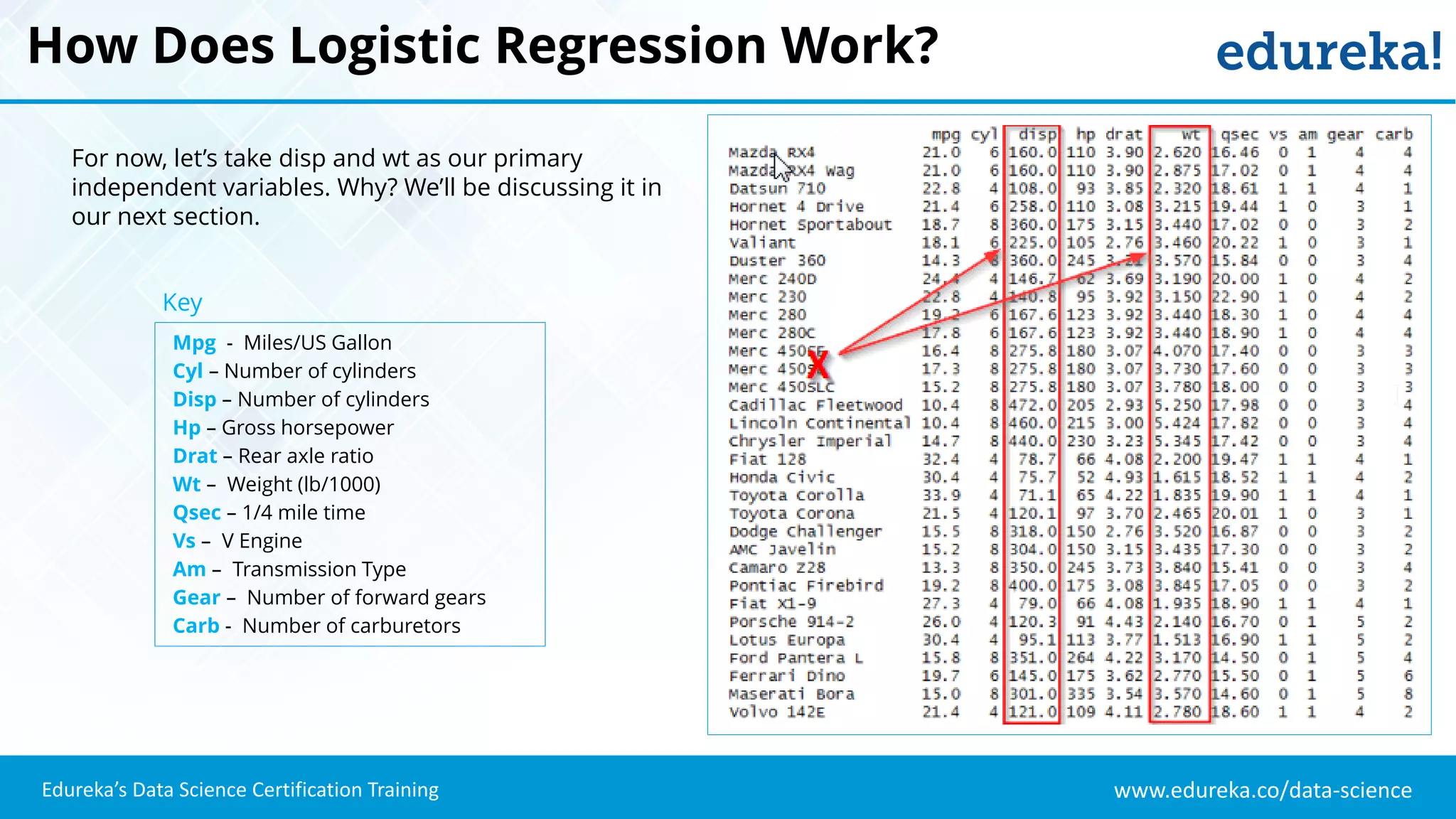
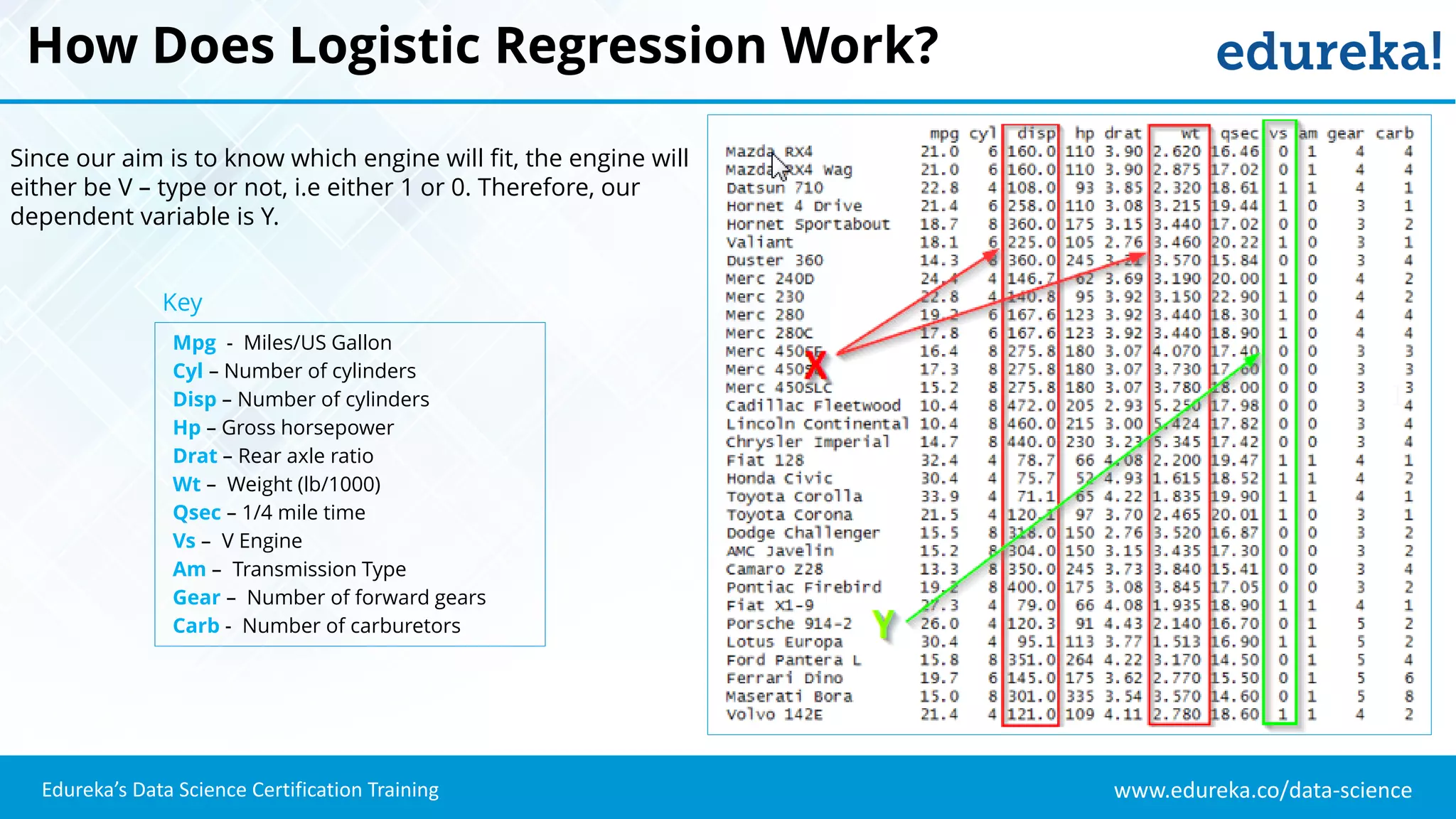
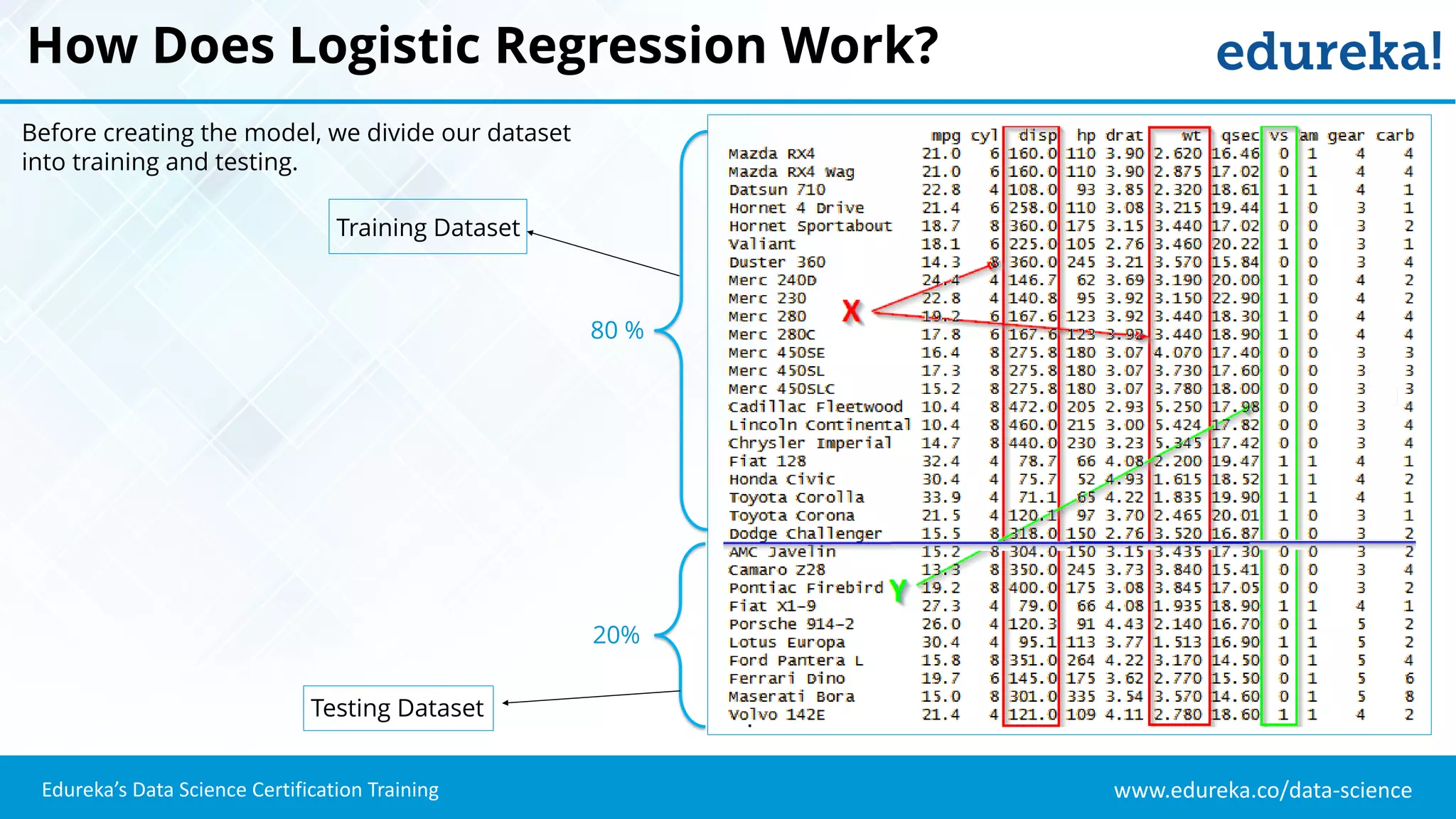
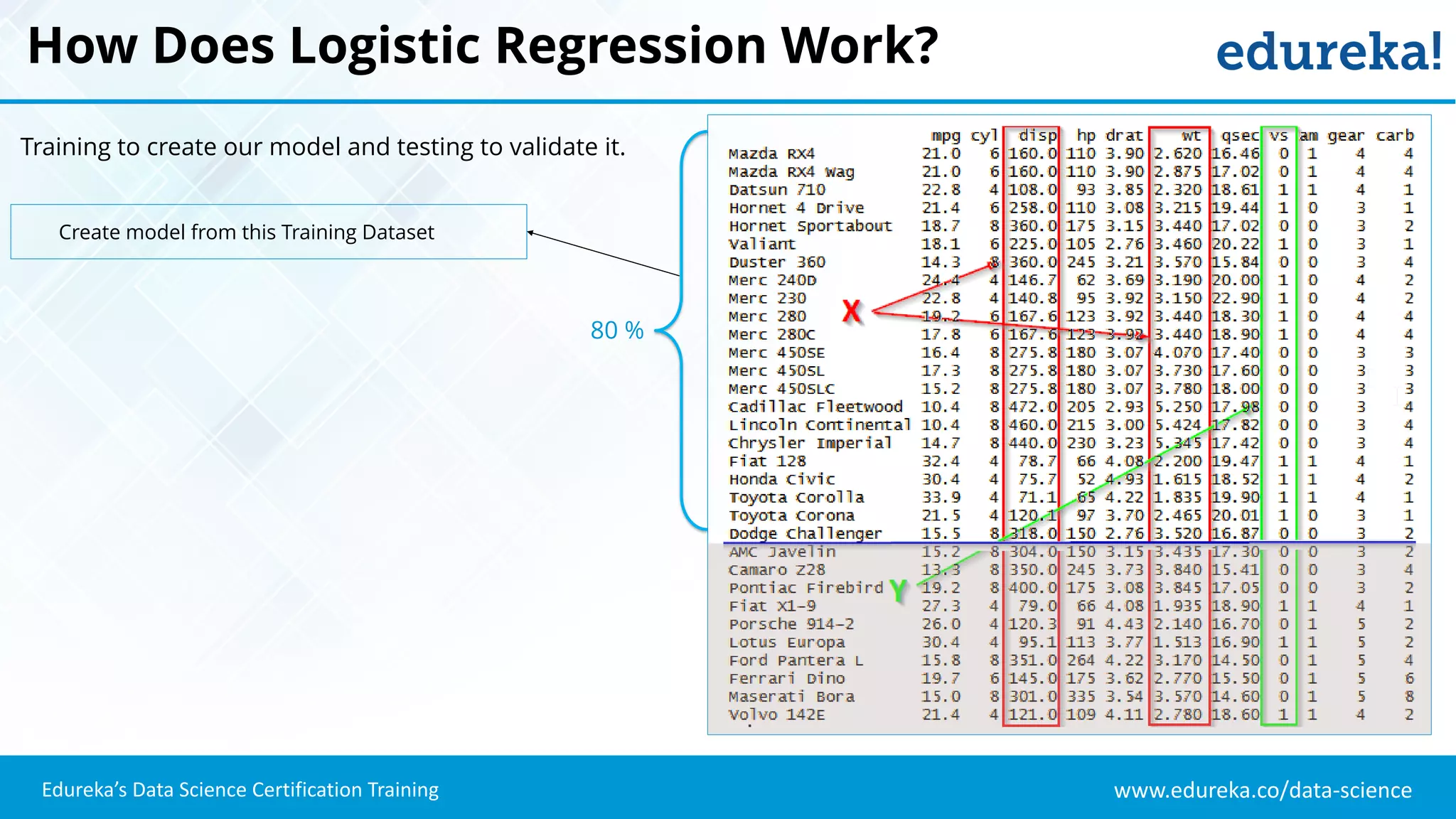
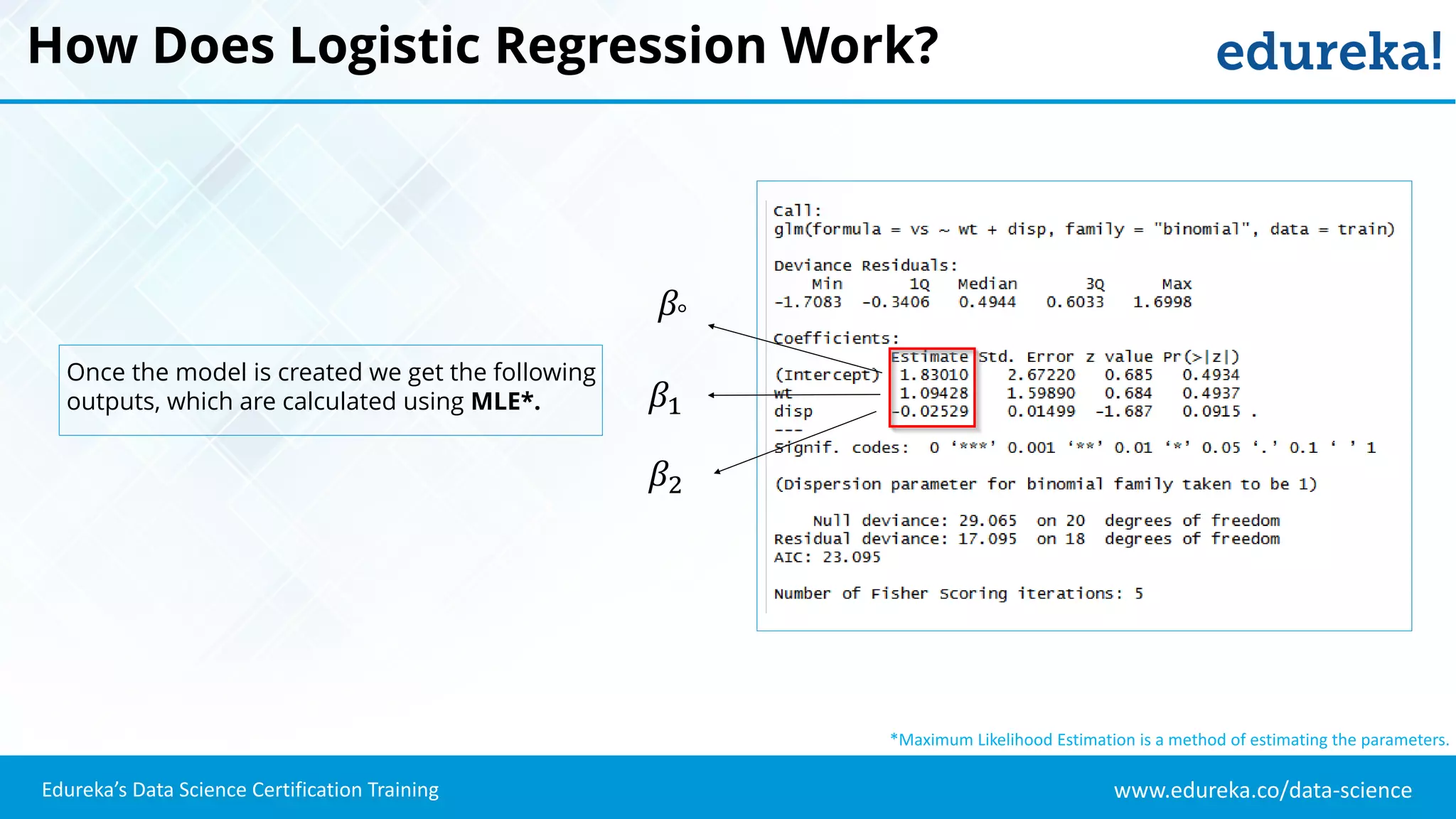
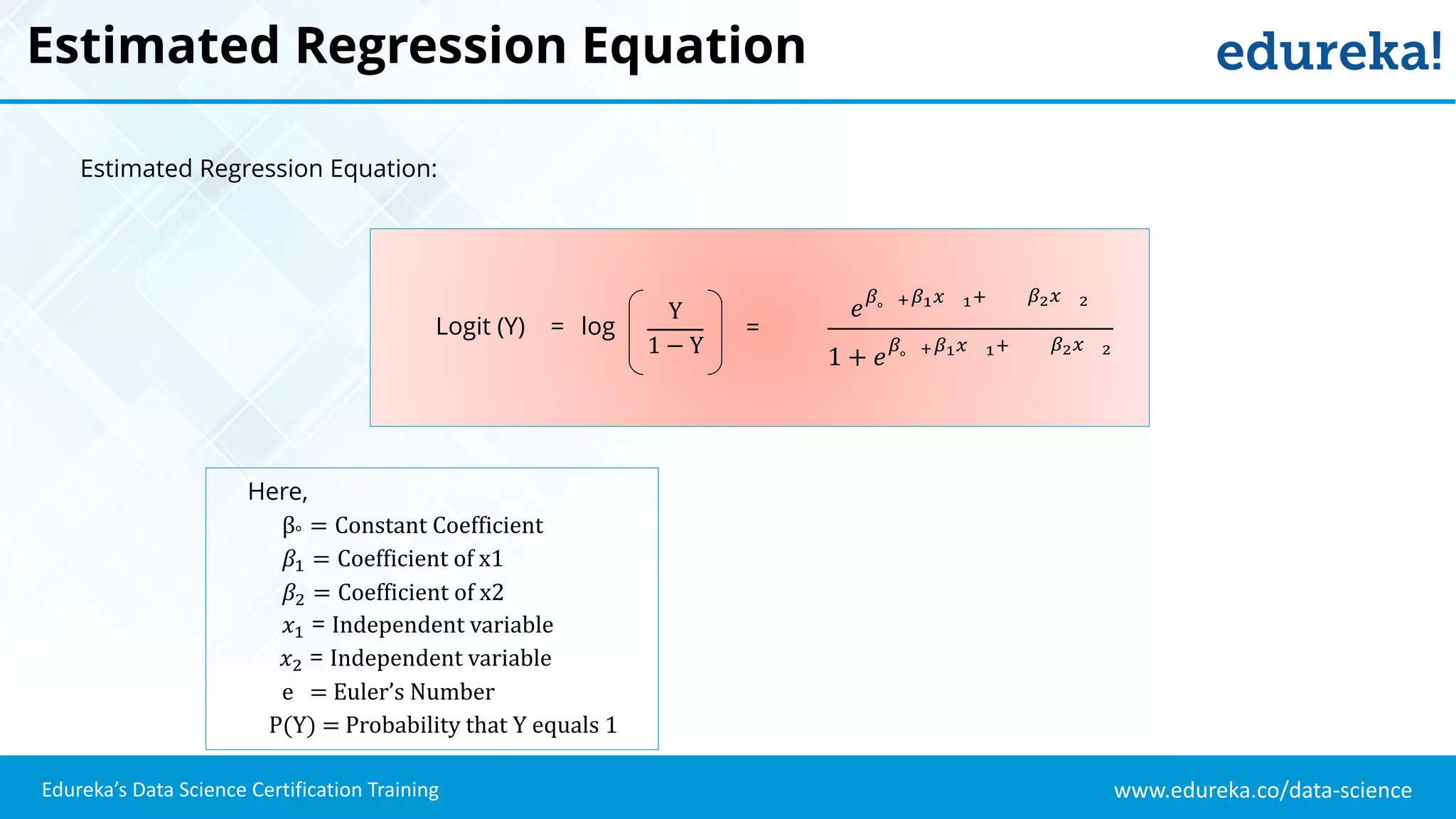
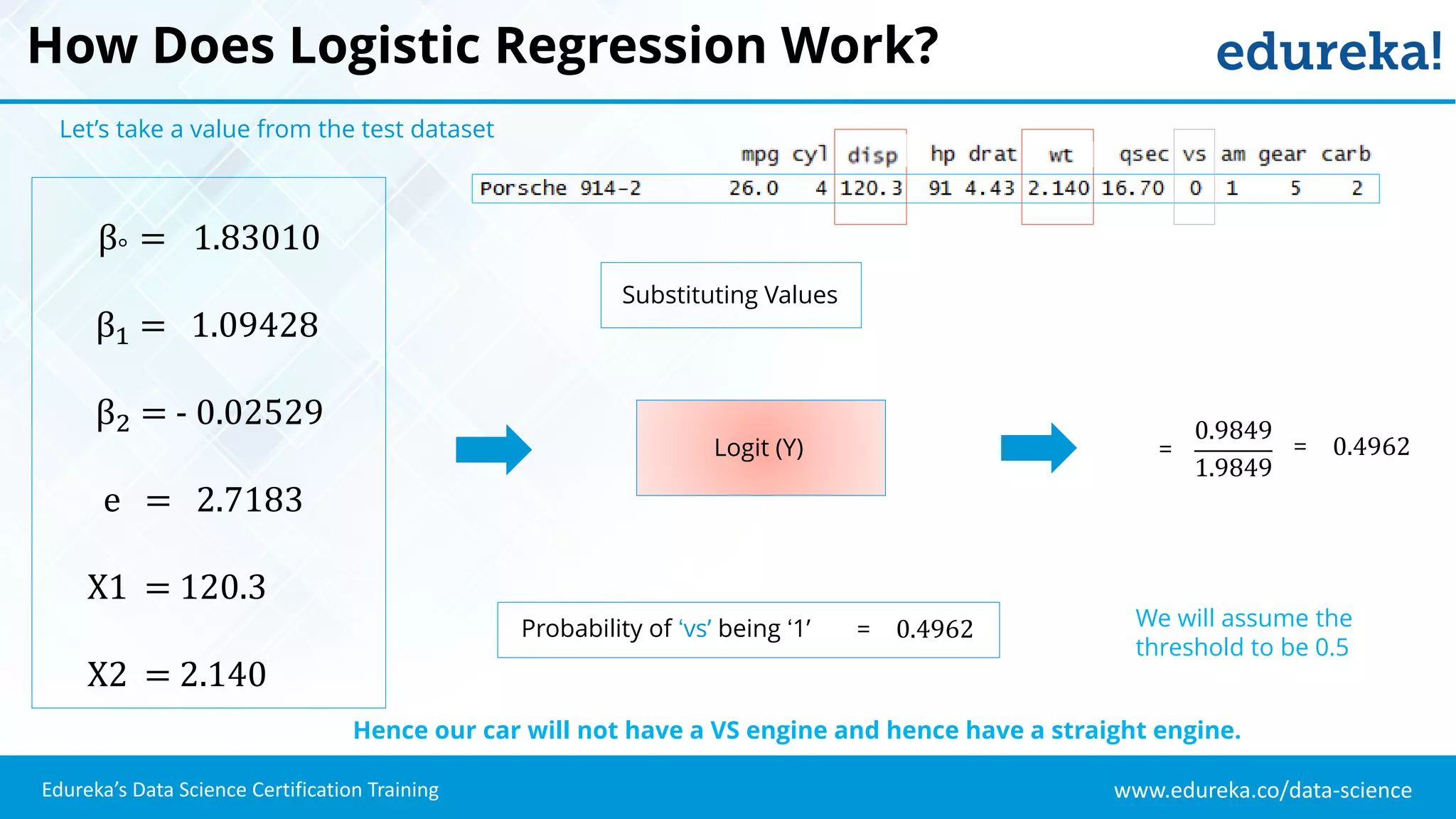
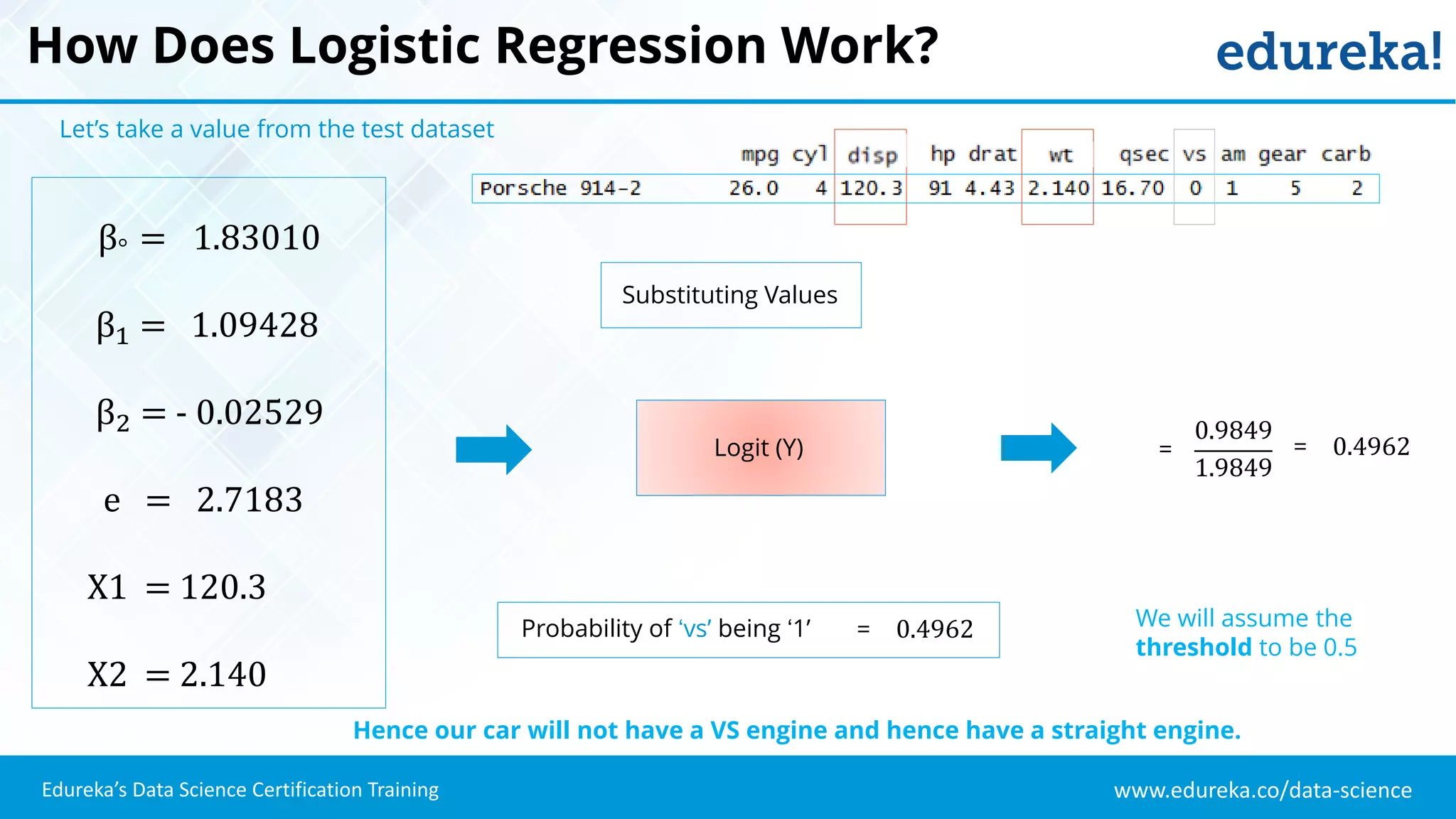
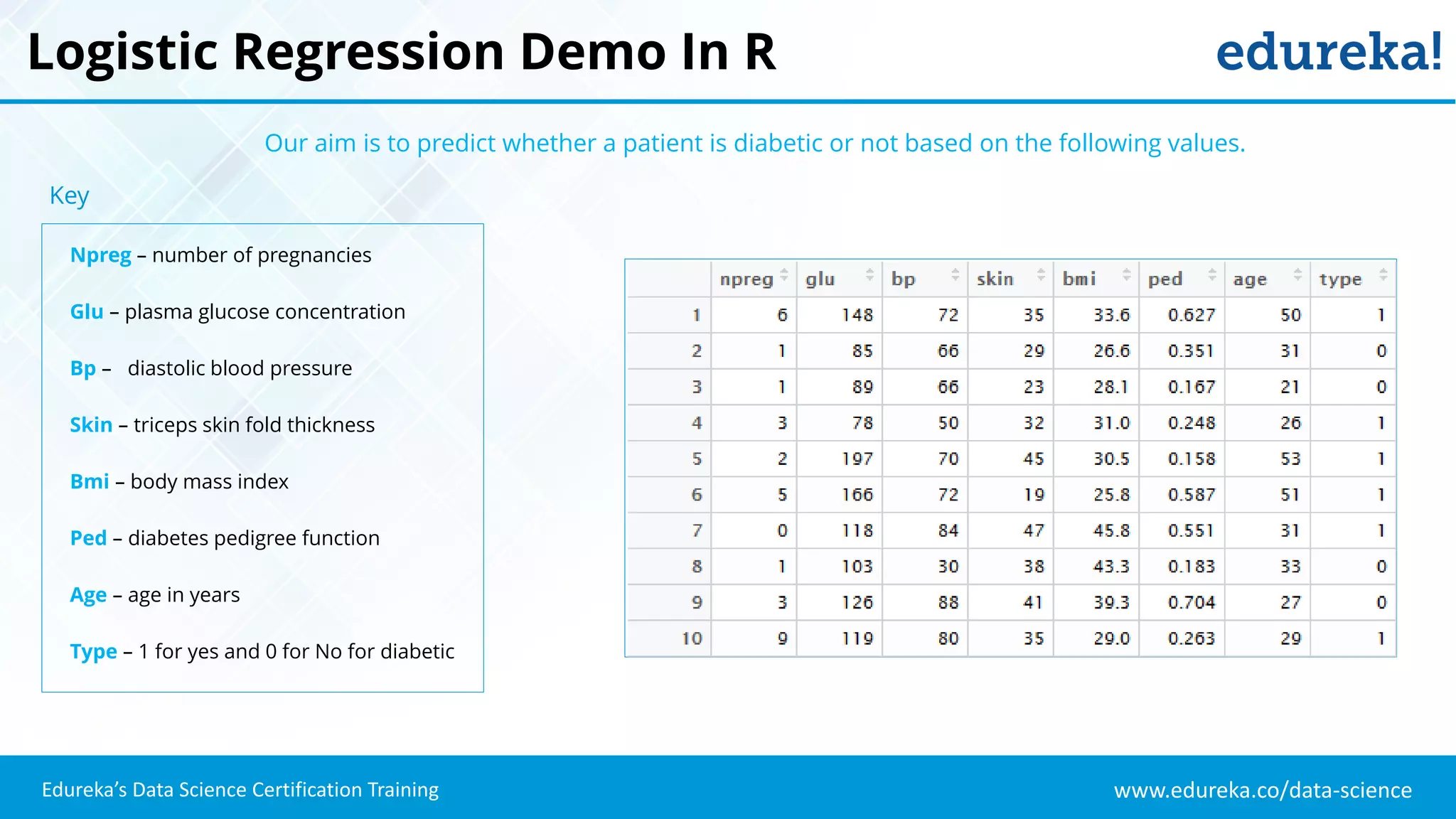
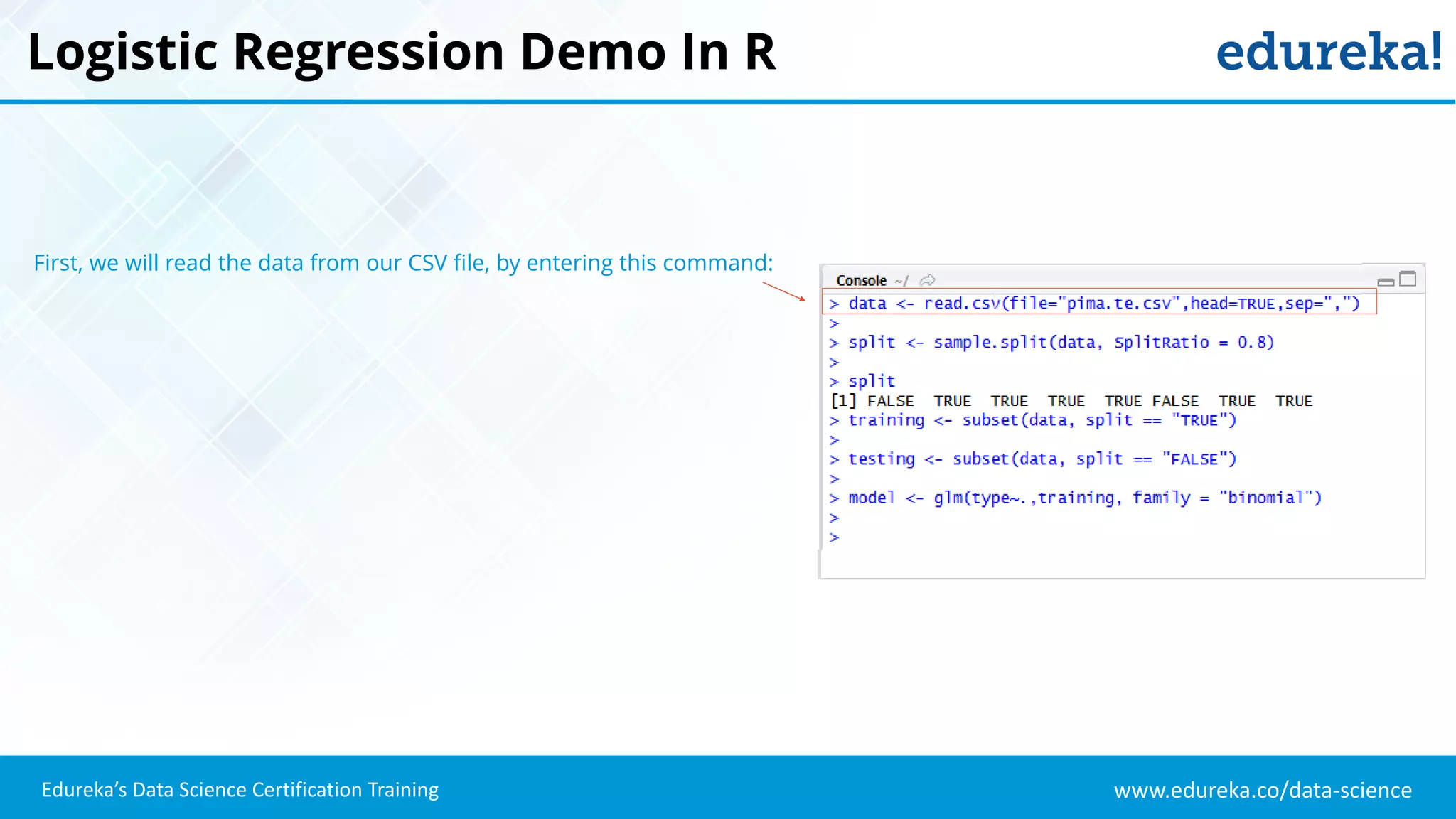
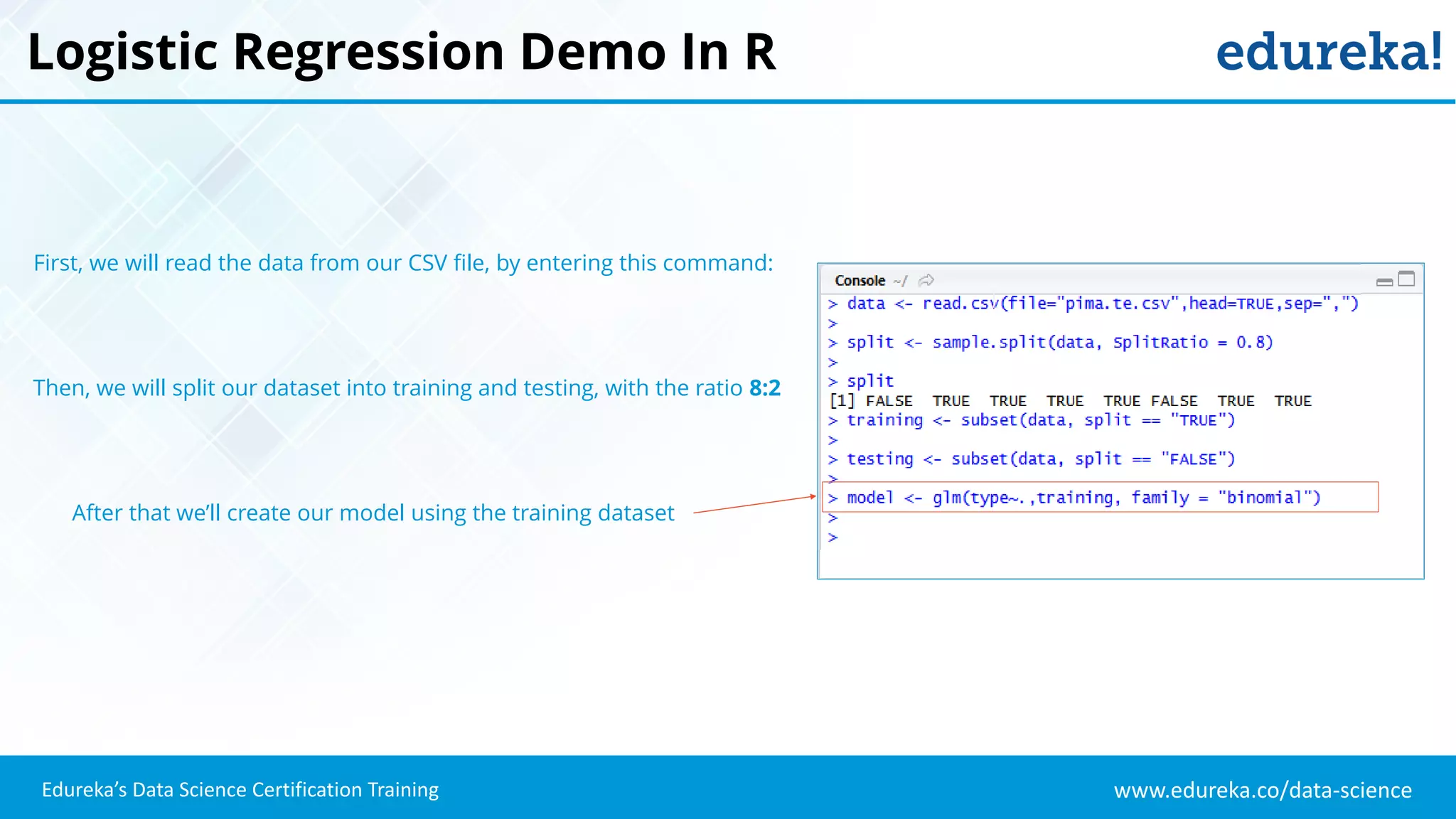
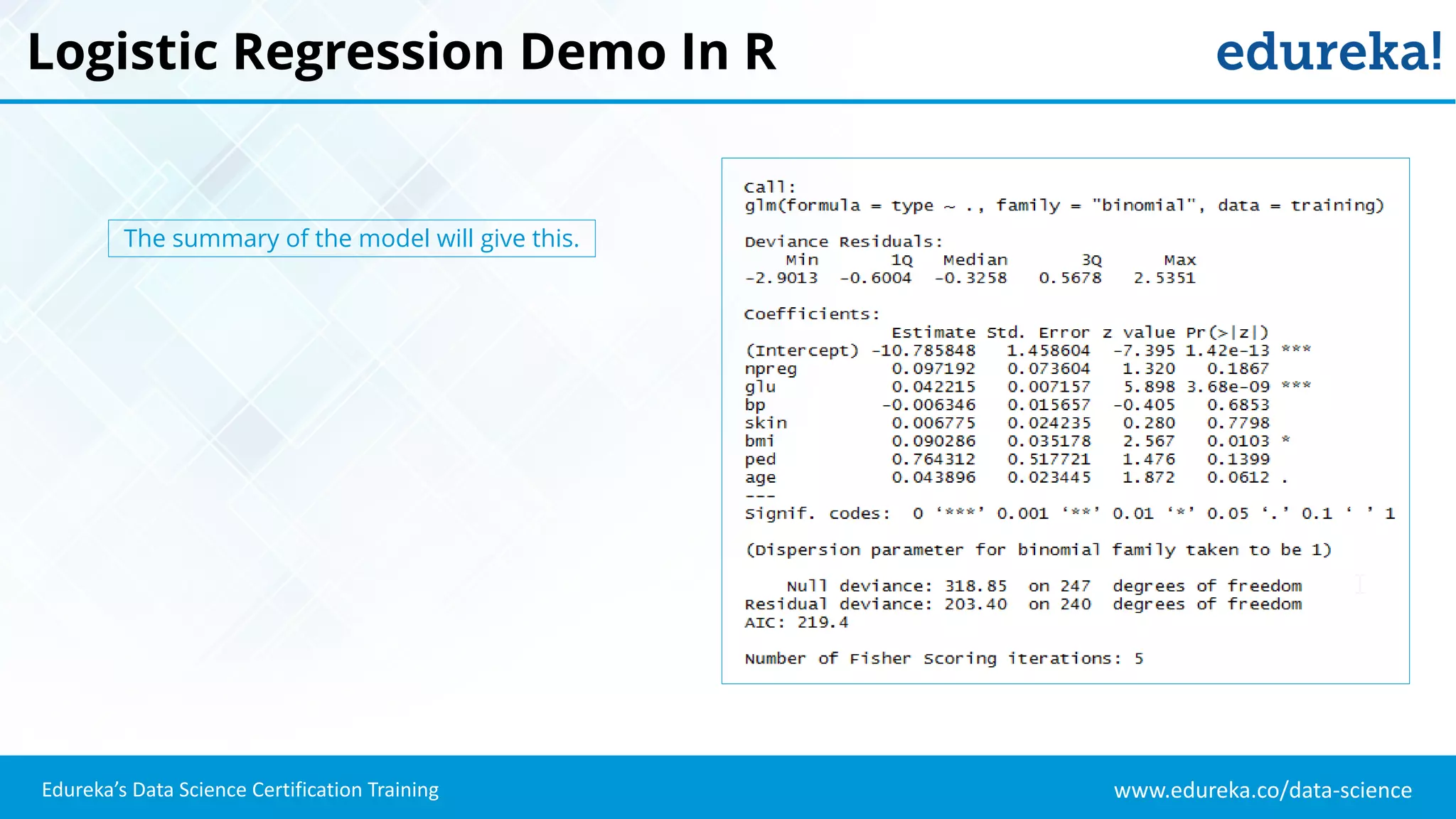
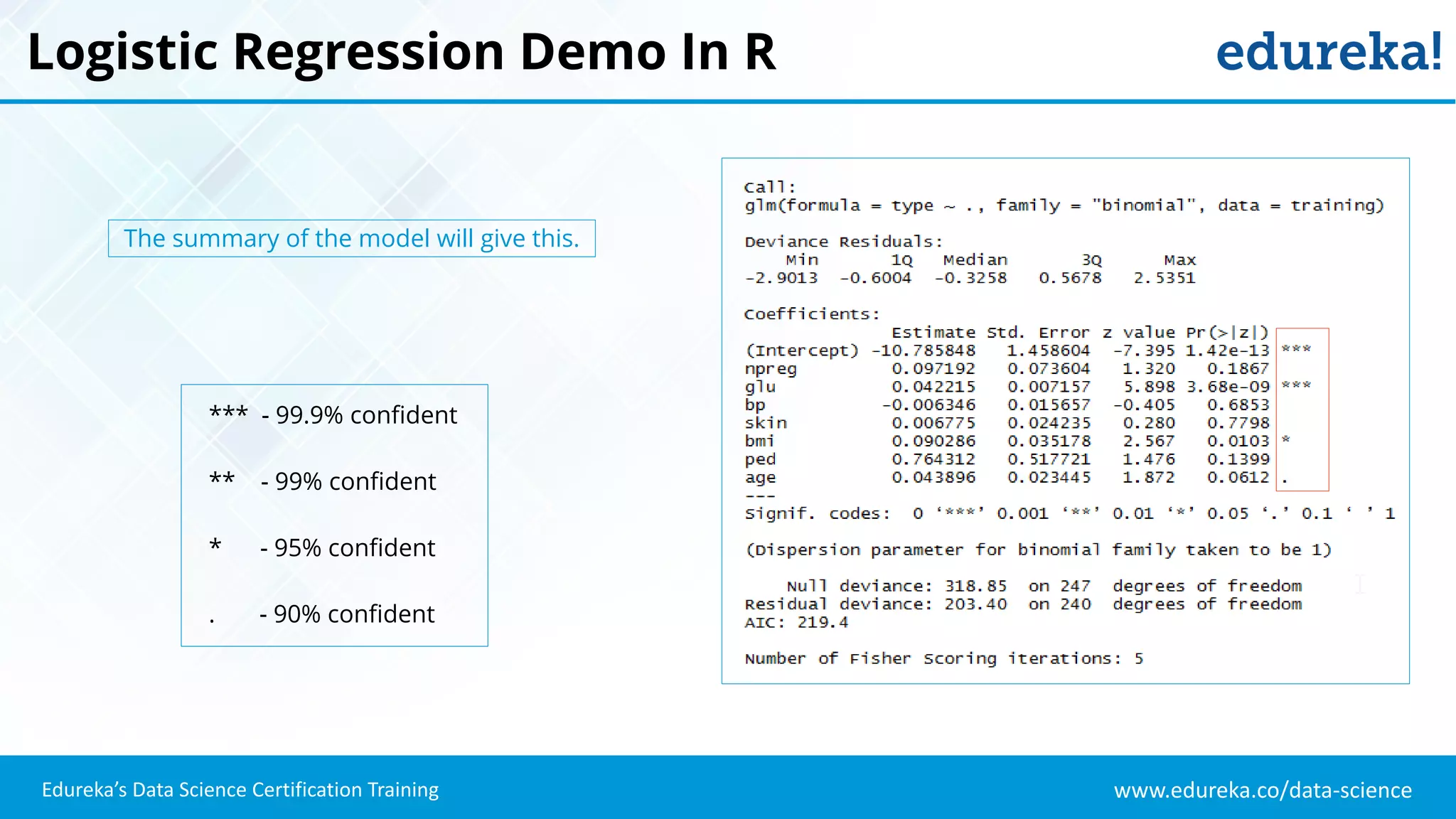
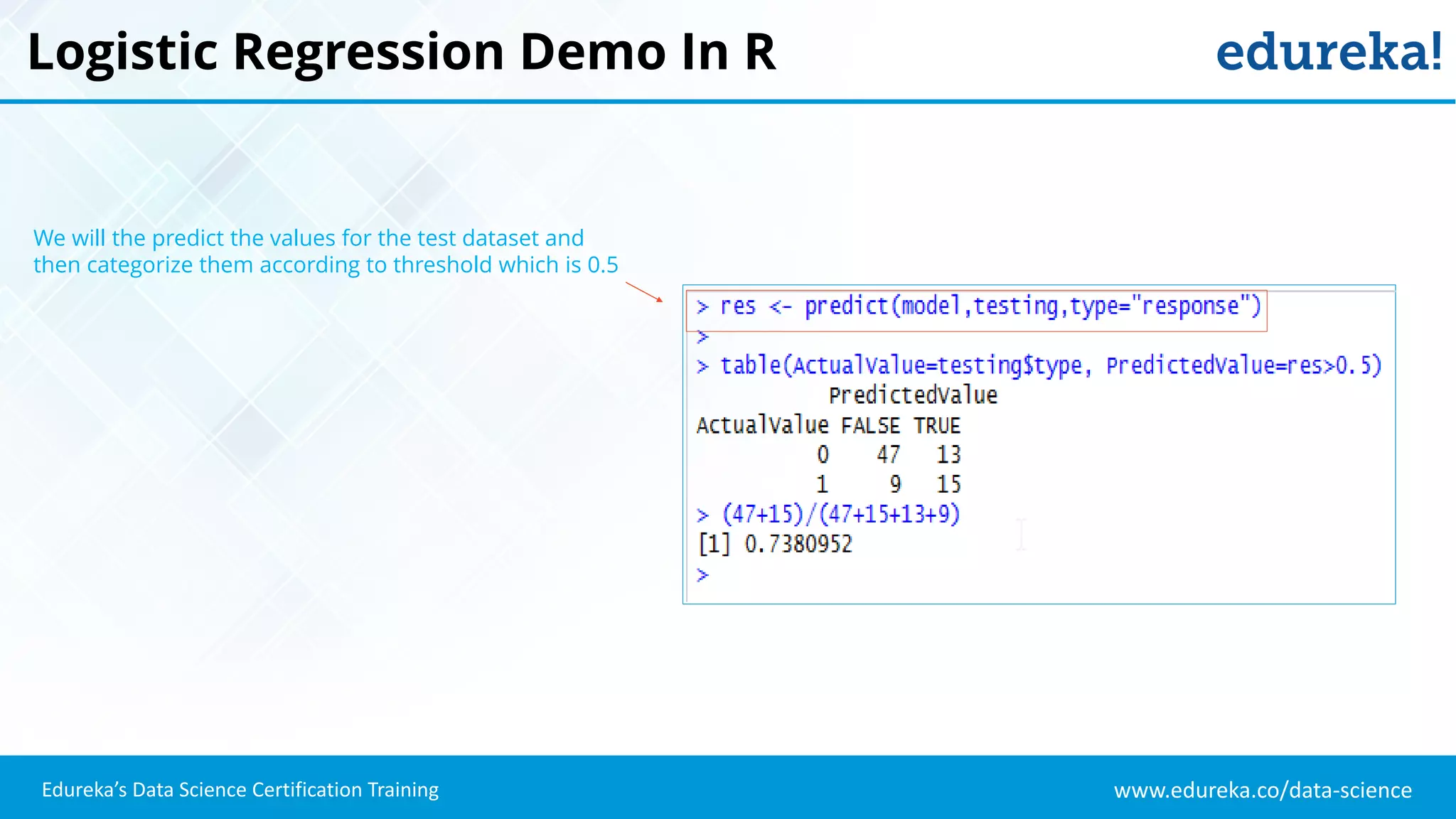
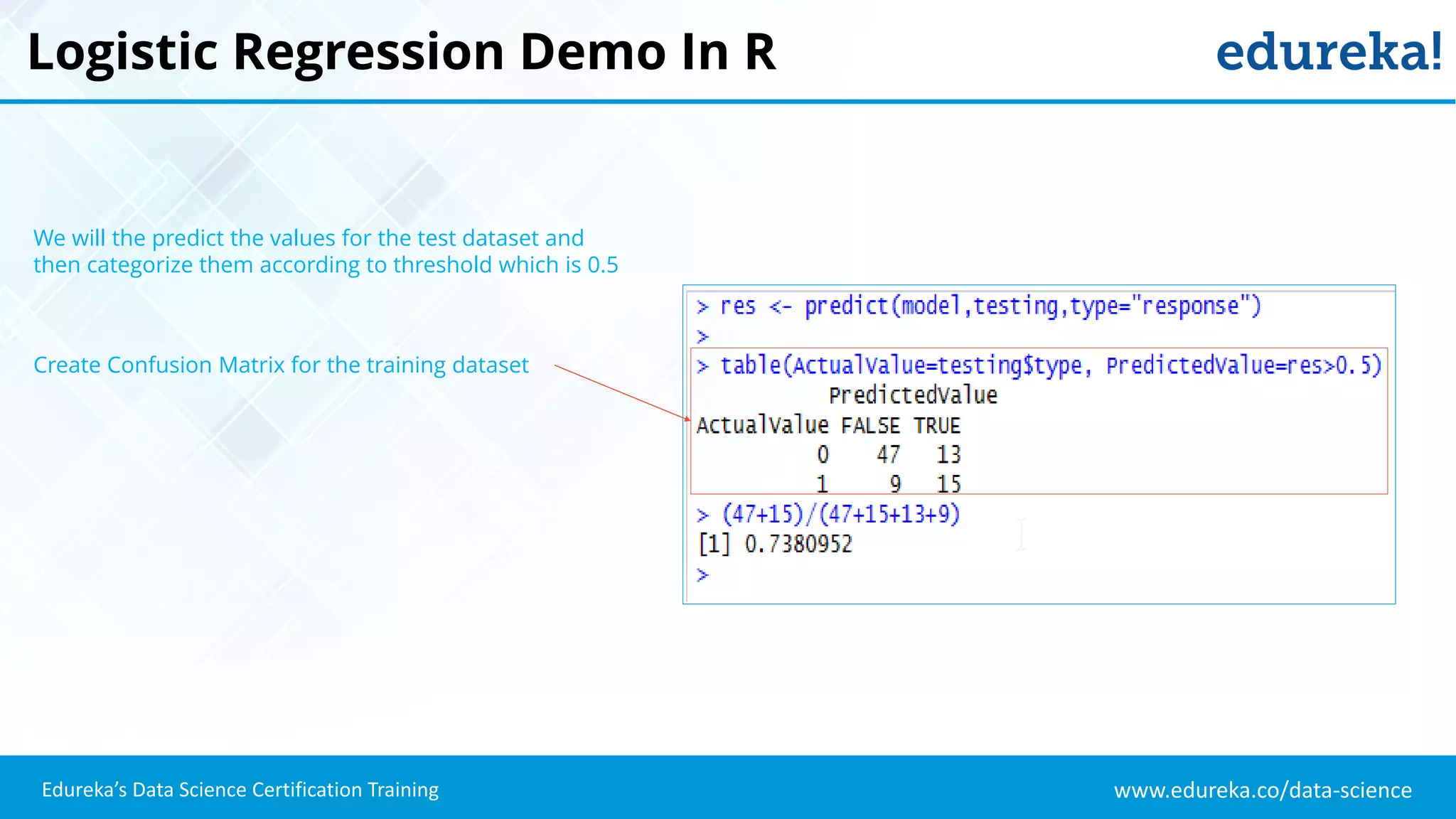
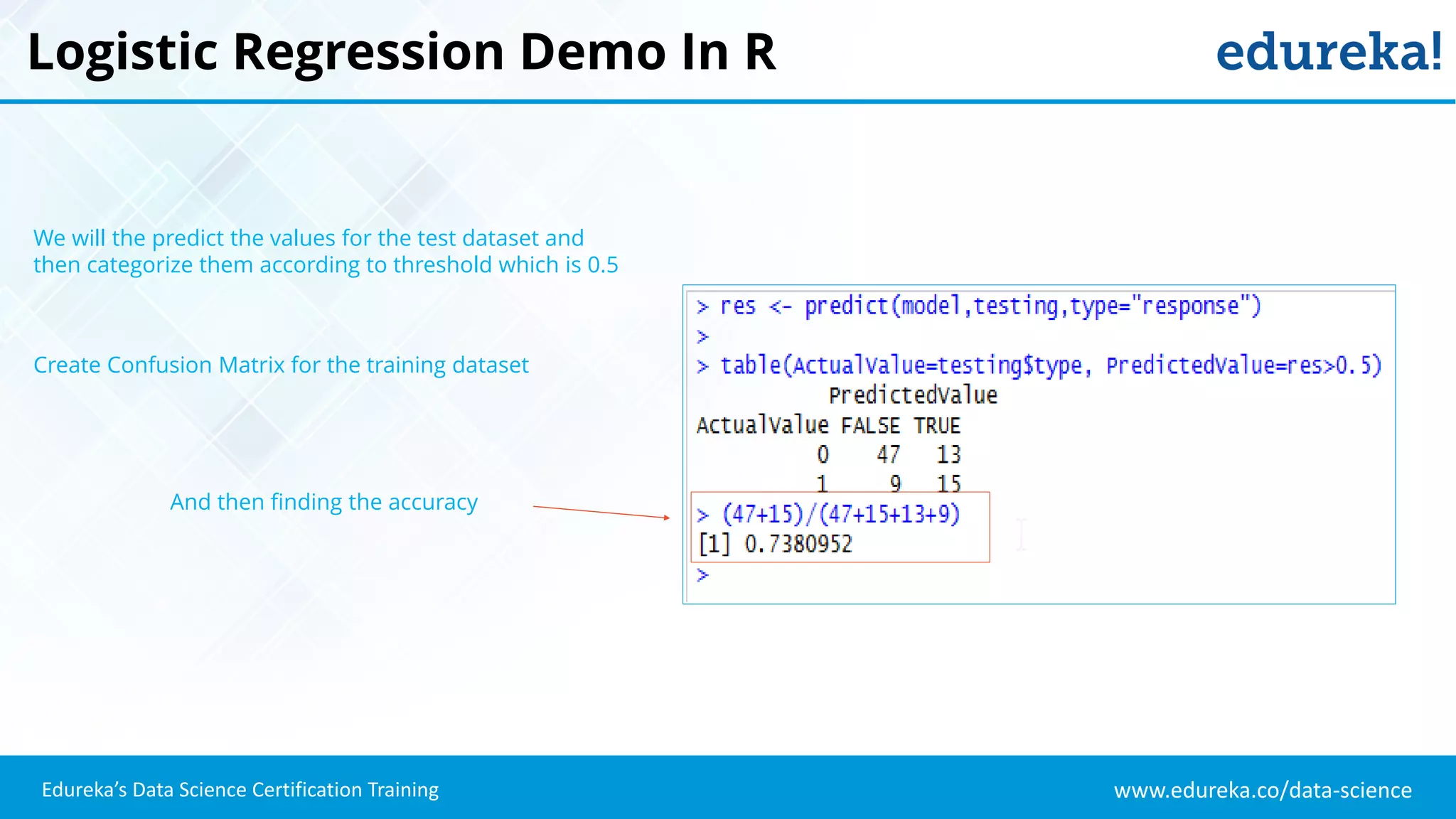
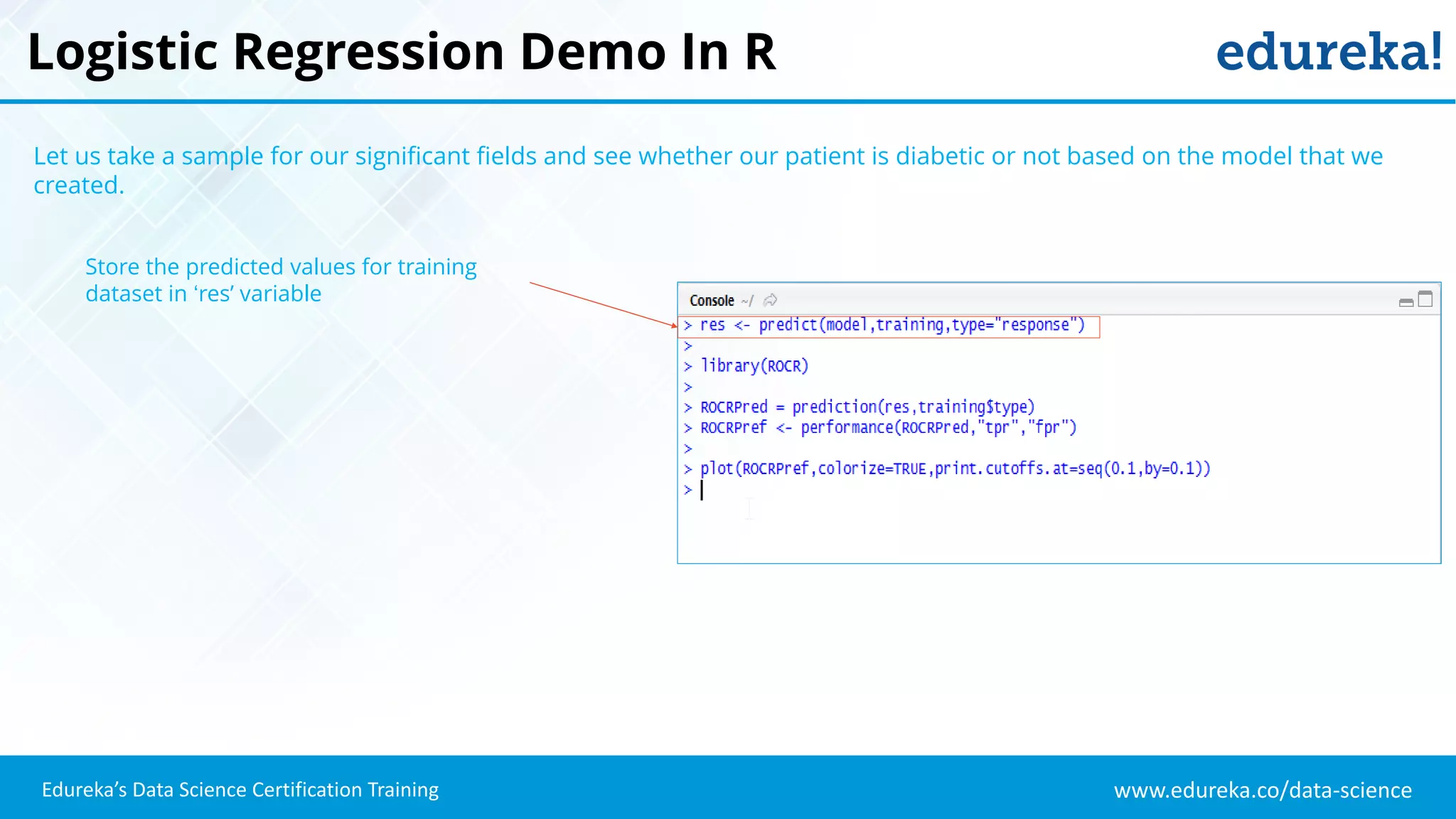
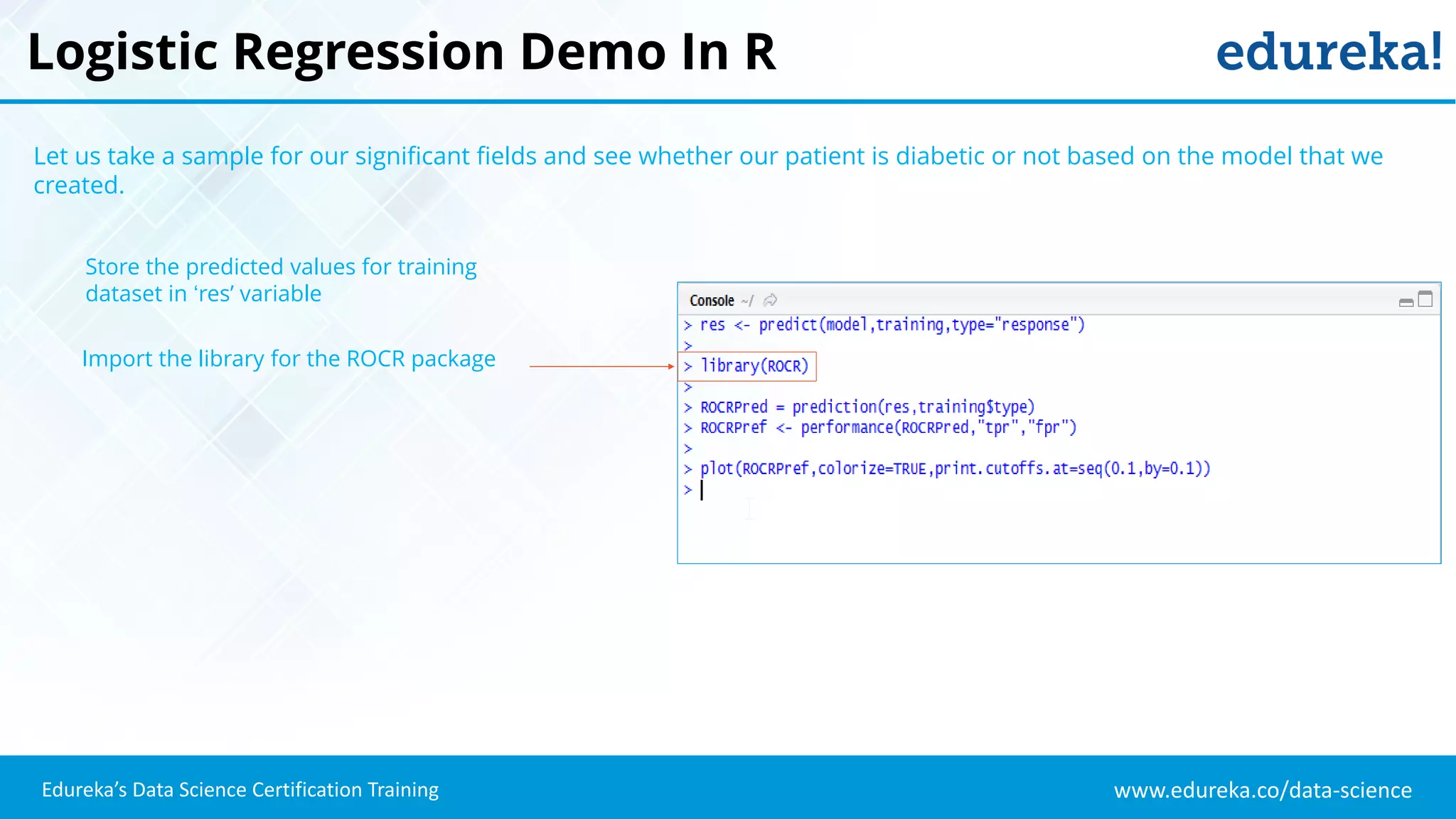
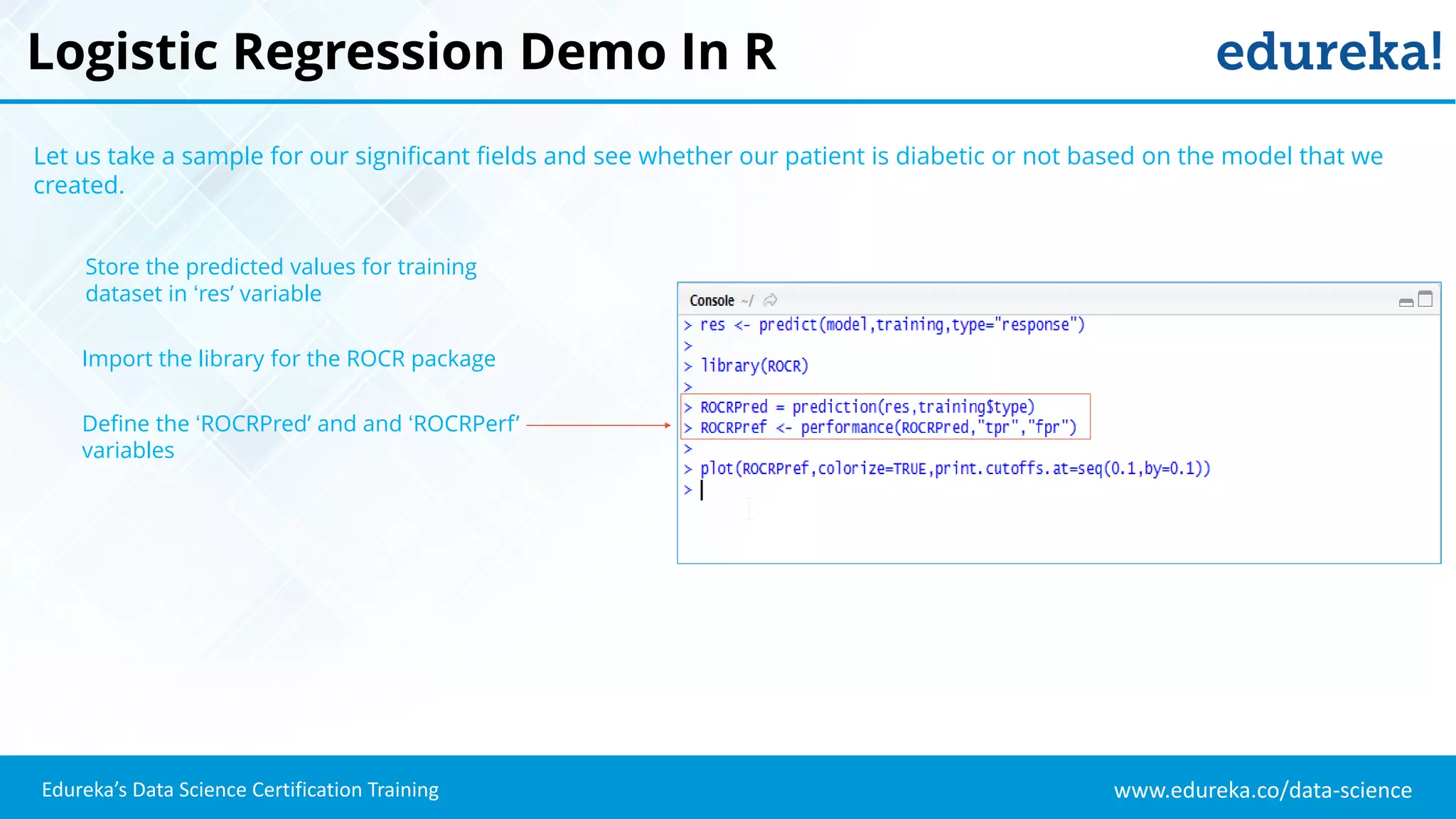
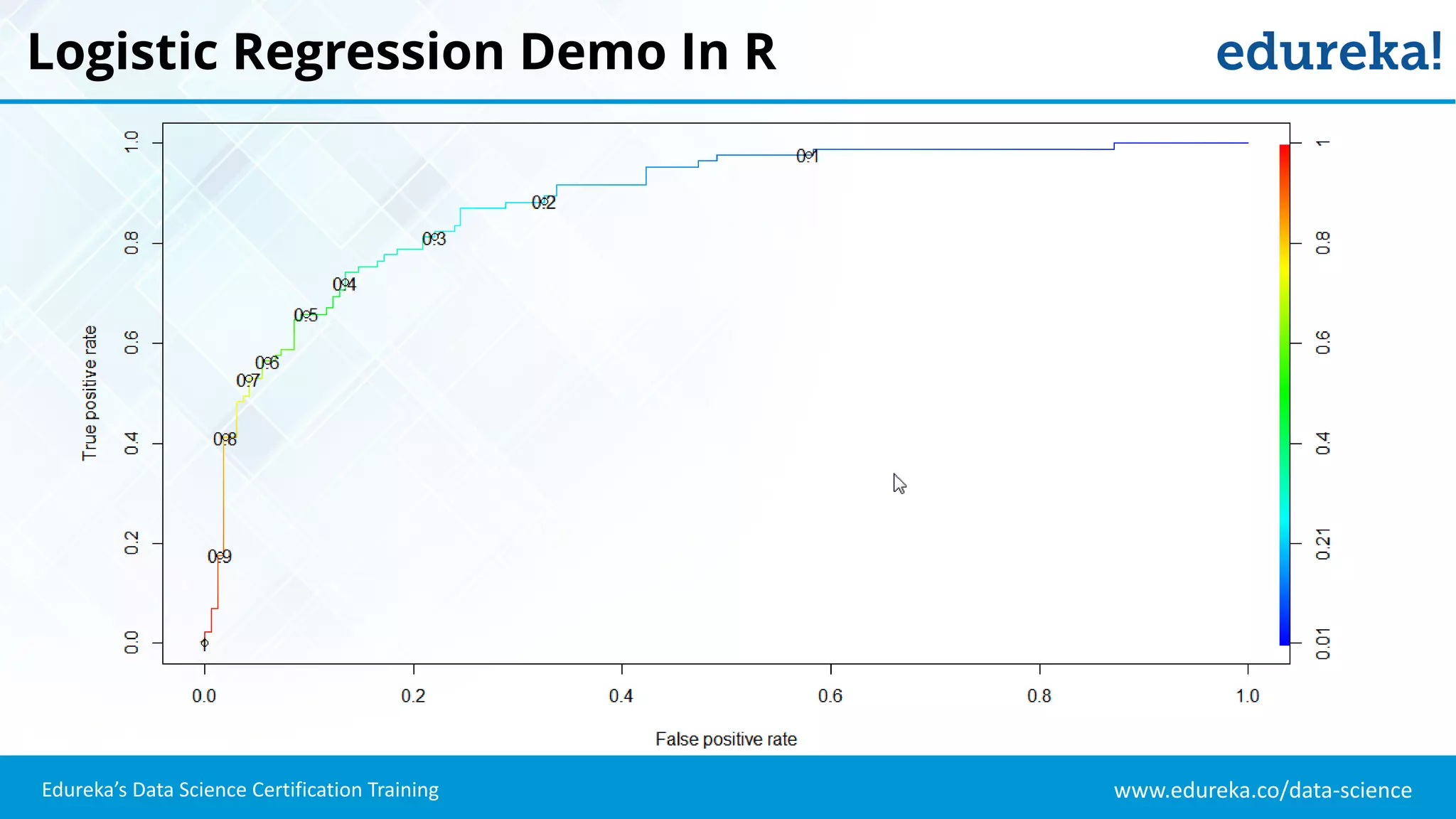
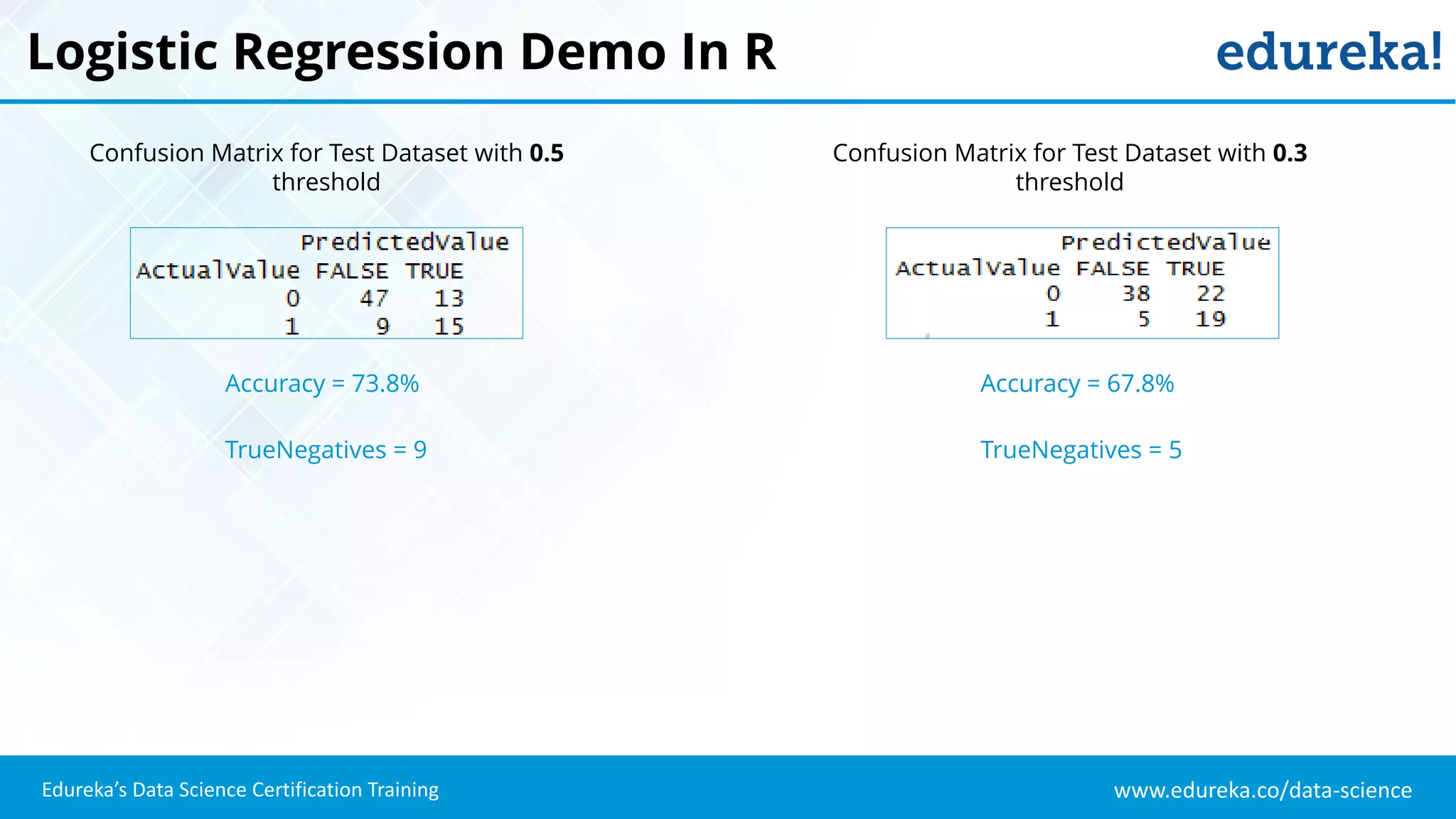
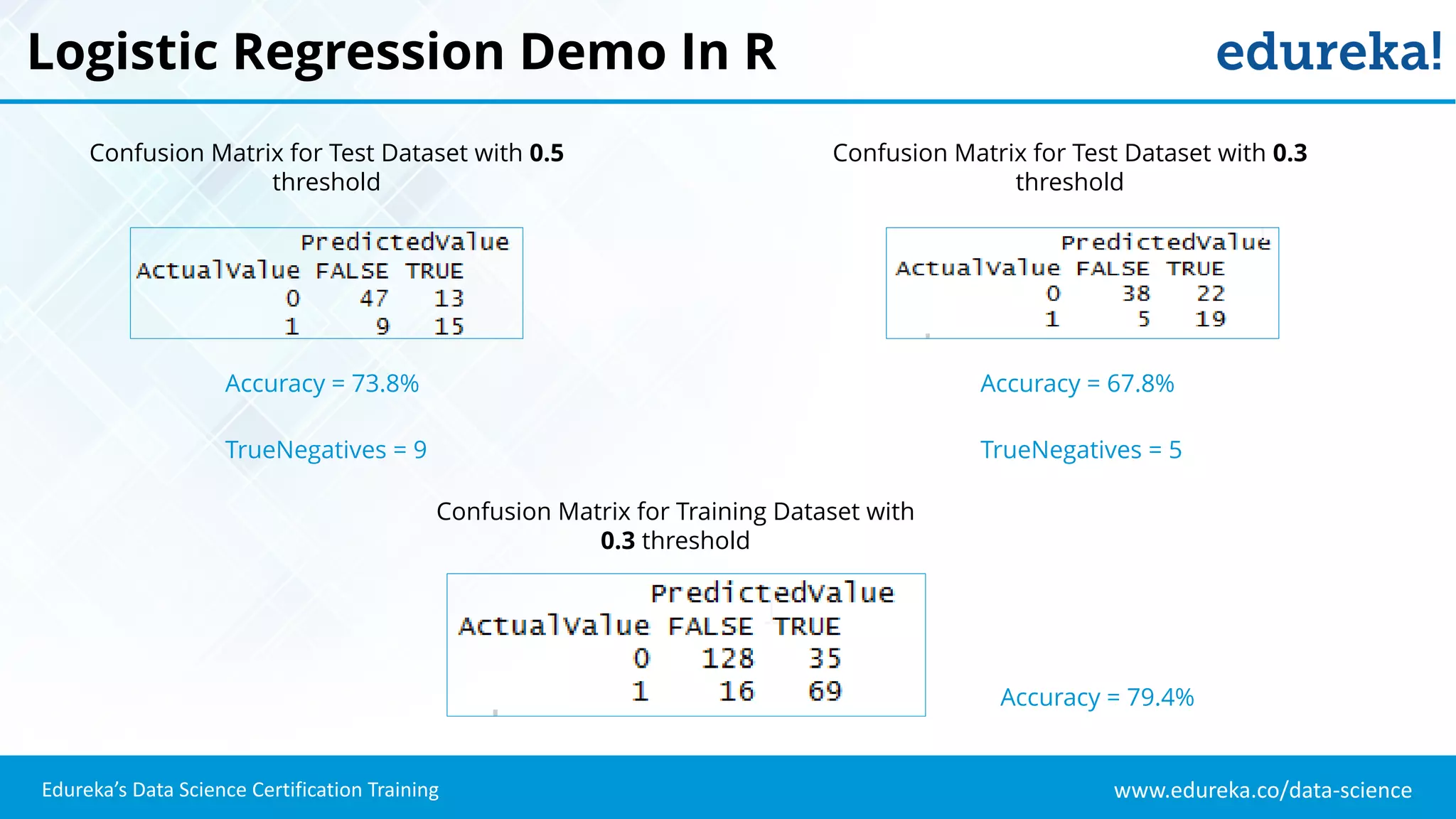
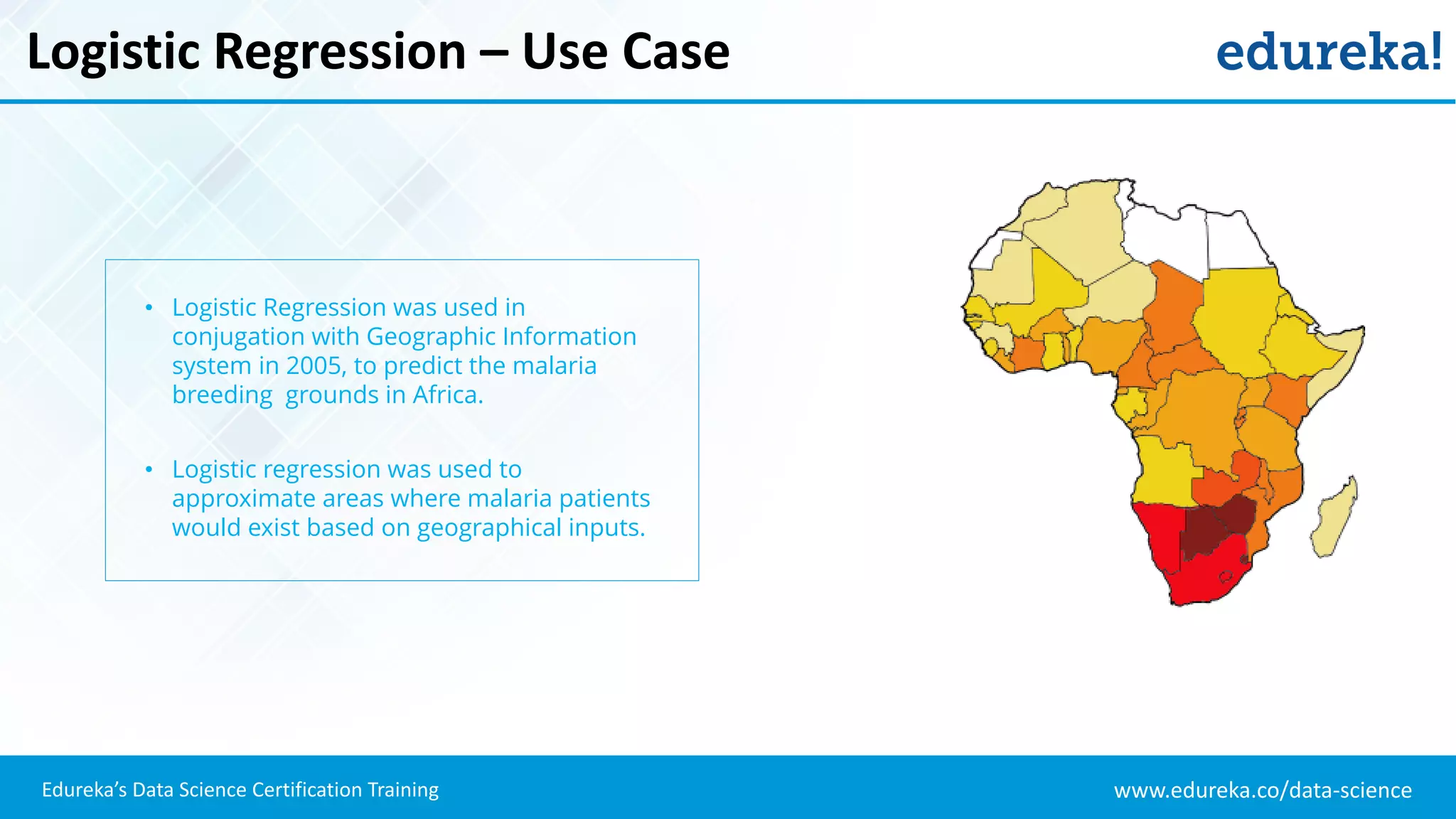
The document provides an overview of logistic regression, a statistical method used for predicting binary outcomes based on independent variables. It discusses key concepts such as the differences between logistic and linear regression, the use of a logistic function to constrain outcomes between 0 and 1, and the process of implementing logistic regression with practical examples, including data analysis in R. Additionally, it covers logistic regression applications in various fields such as healthcare and marketing.