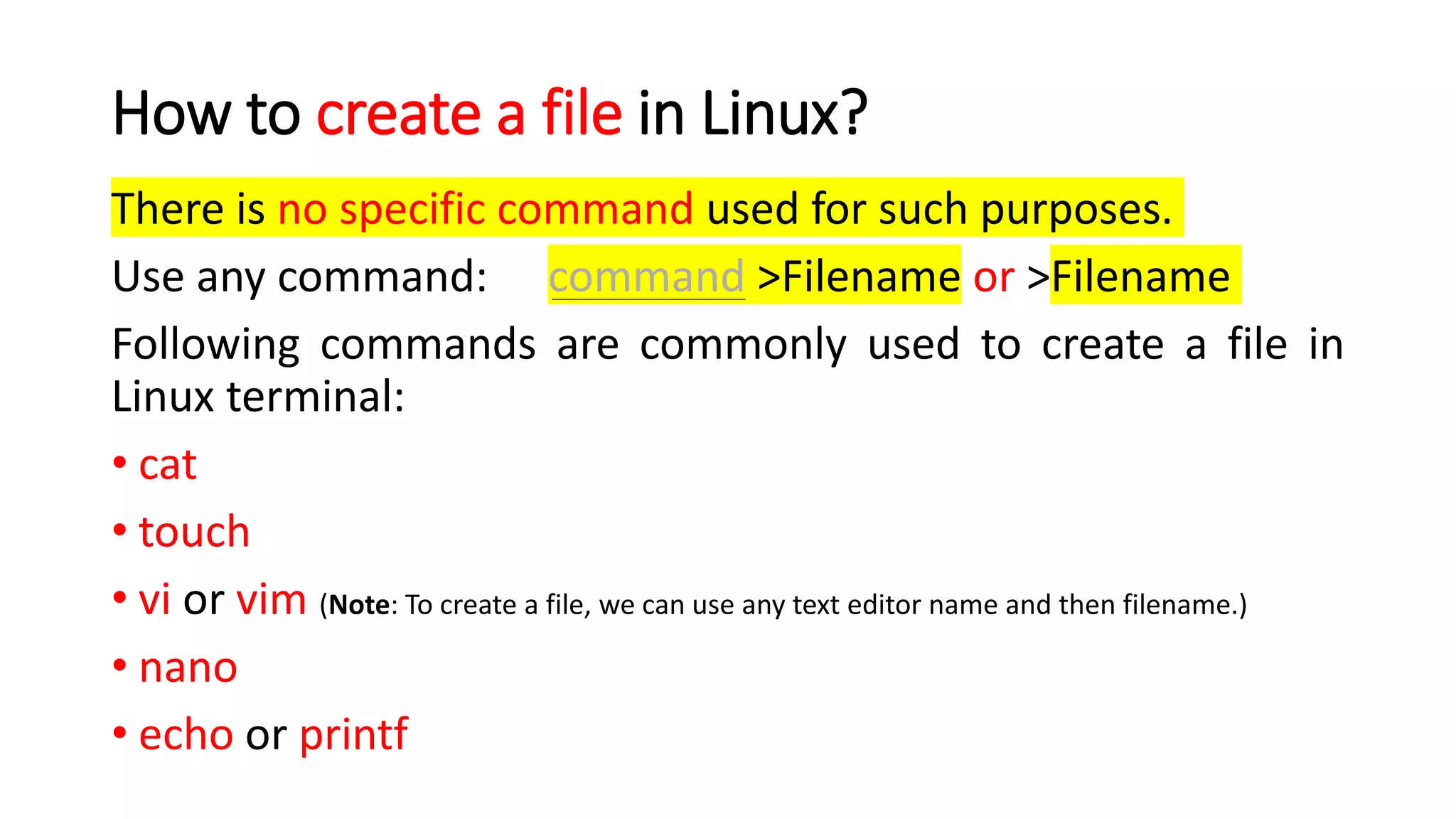
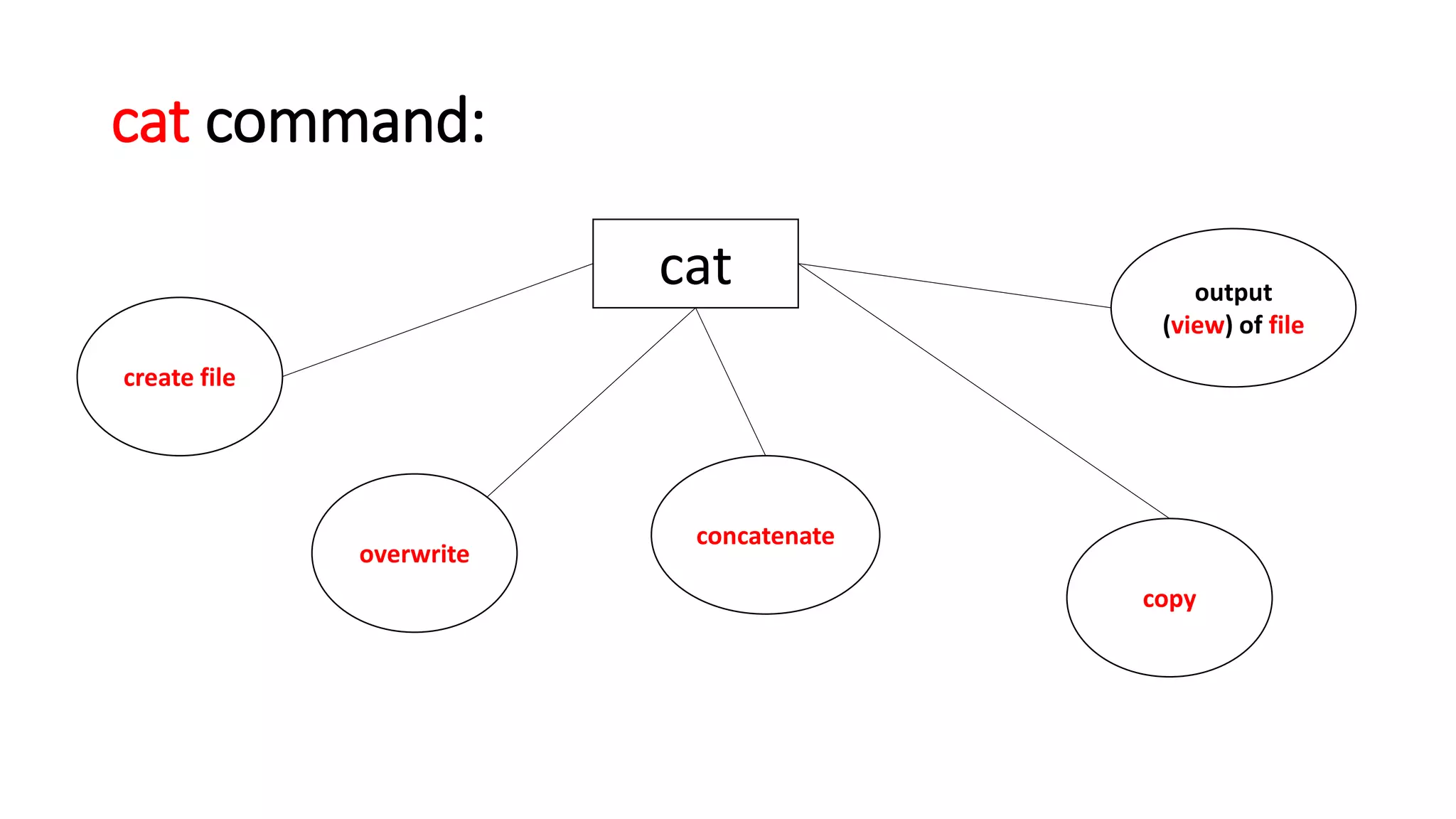
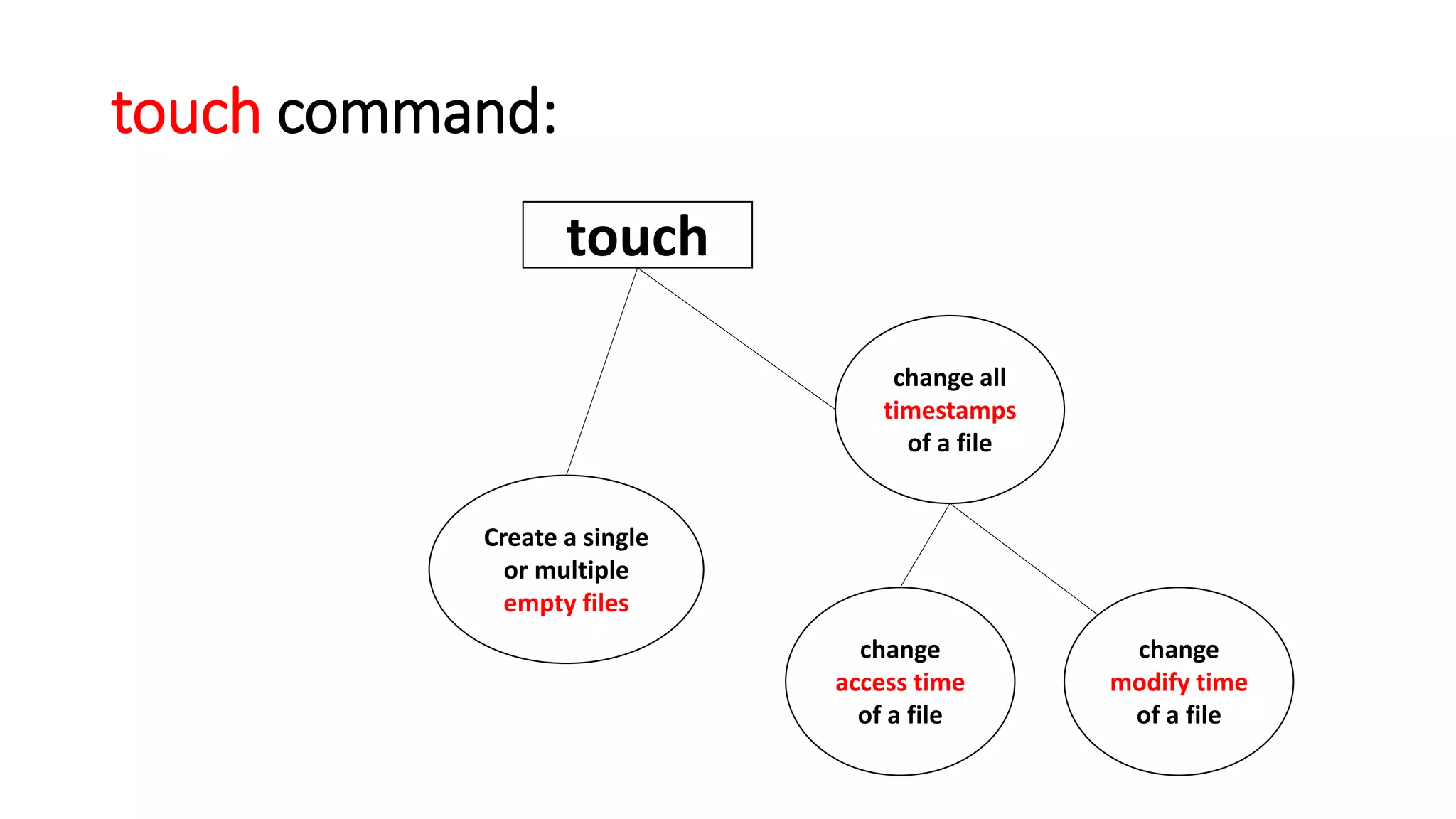
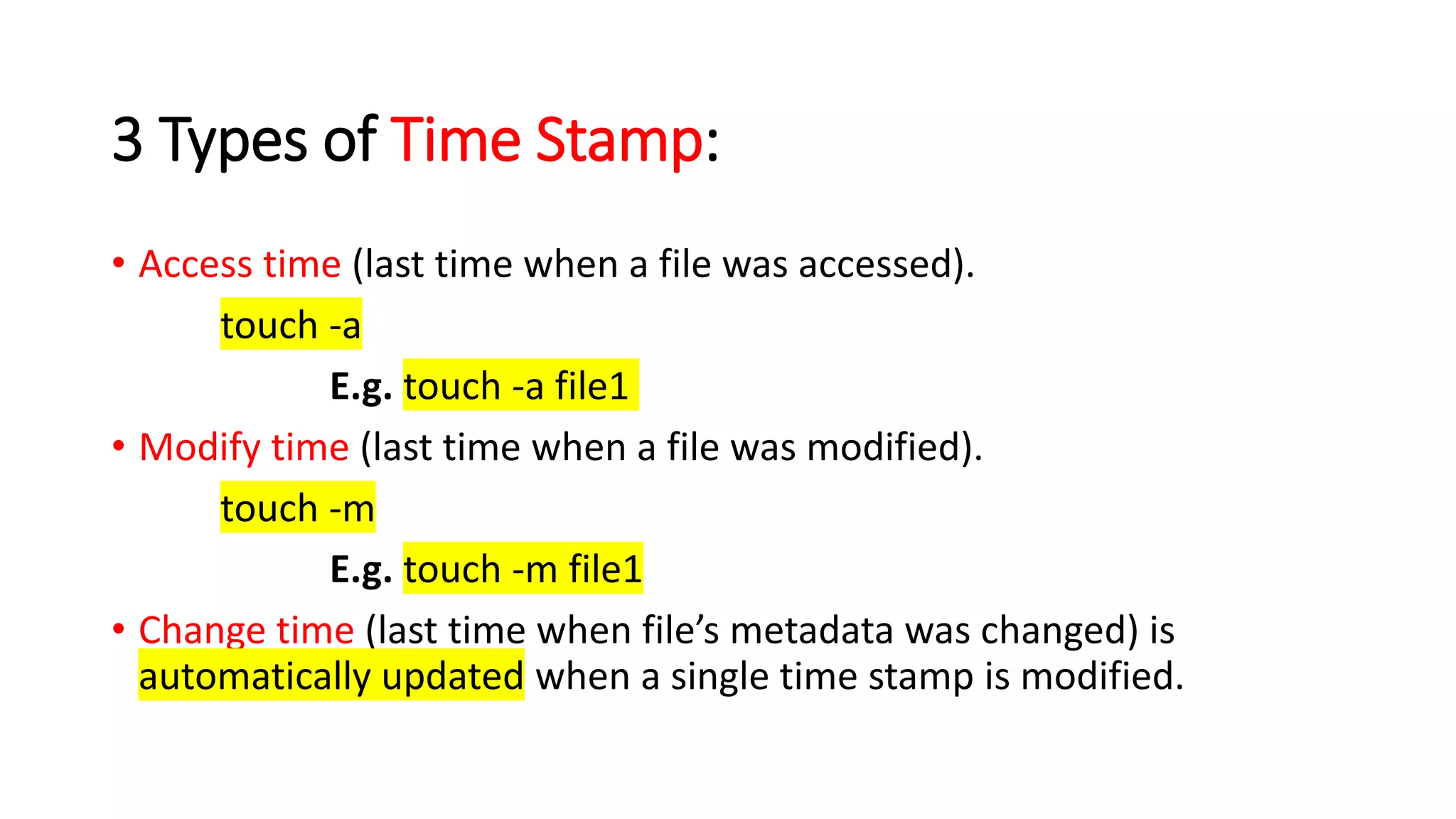
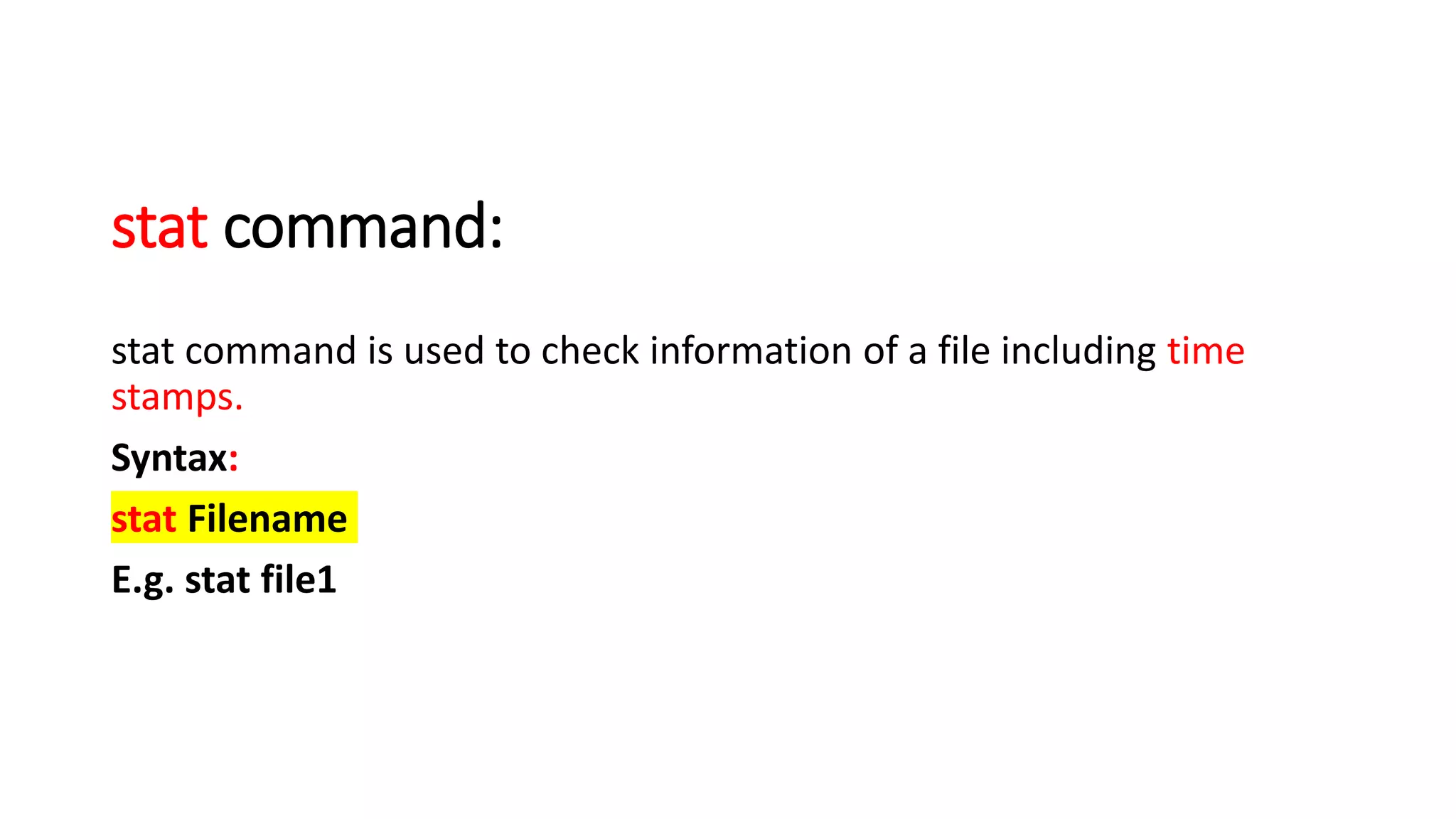
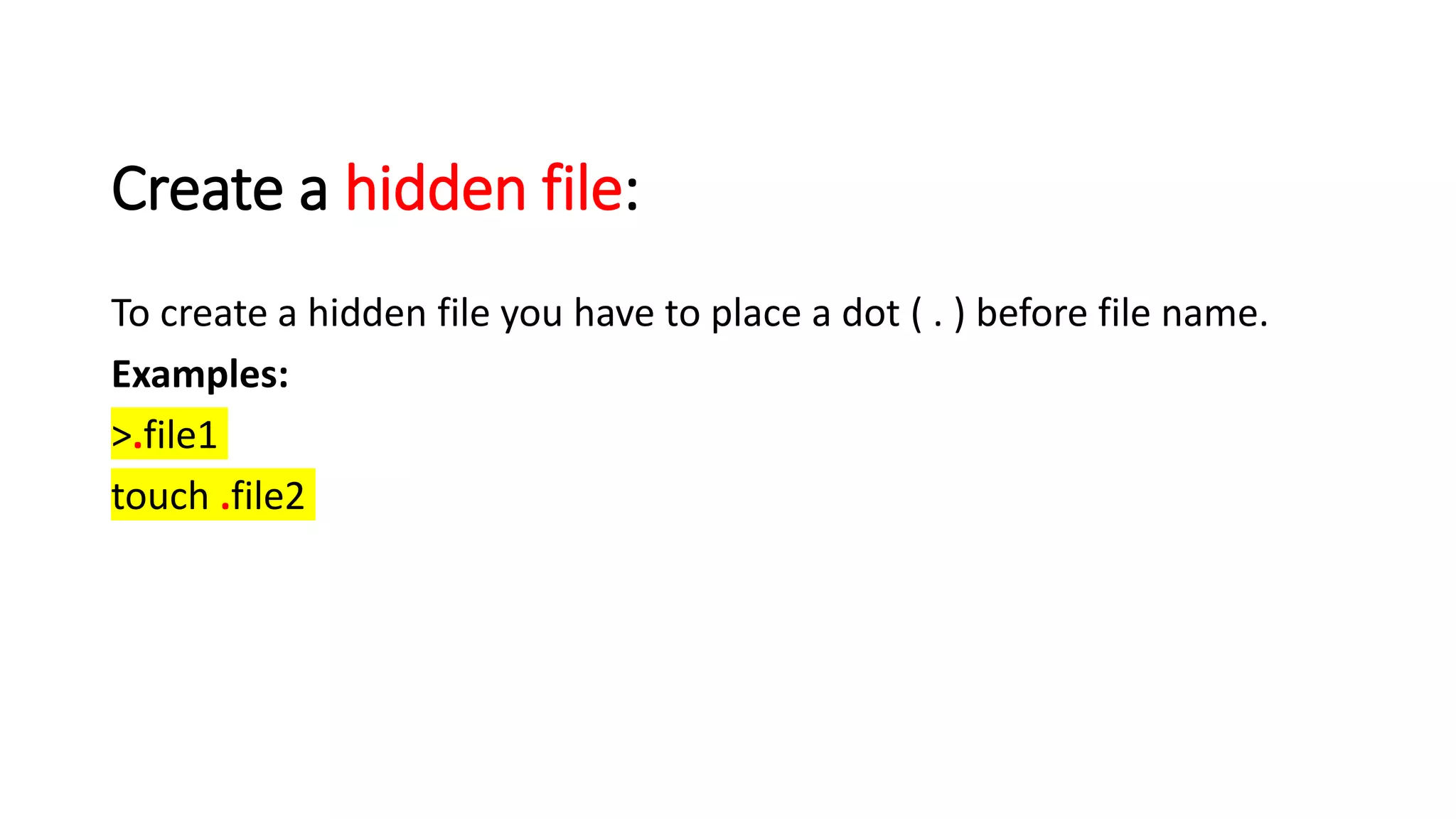
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various Linux commands for file creation, including 'cat', 'touch', 'vi', 'nano', 'echo', and 'printf'. It explains how to create, overwrite, and concatenate files using these commands, along with details on working with text editors such as 'vi' and 'nano'. Additionally, the document introduces file timestamps and the use of the 'stat' command to check file information.