A linear array is a structured list of elements of the same data type, stored in consecutive memory locations, with its length determined by the range of indices. Arrays can be represented using subscript, bracket, or parenthesis notation and are utilized to manage multiple data items efficiently, though they have limitations such as fixed size and difficulty in insertion or deletion. The address of any array element can be calculated using a specific formula related to its base address and the element's index.

![ARRAY’S LENGTH = UB-LB+1 Example : A(50,5) So, the length is =(50-5+1) =46 Where UB=Upper Bound and LB=Lower Bound Arrays element may be denoted by 3way’s- 1. Subscript notation: A1,A2,A3…………………………………….An 2. Bracket notation: A[1],A[2],A[3]…………………………………….A[n] 3. Parenthesis Notation: A(1),A(2),A(3)…………………………………….A(n)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineararraysinprogramming-241105160050-14be5dd6/75/Linear-Arrays-in-Programming-Array-Length-Benefits-Drawbacks-and-Memory-Layout-Explained-3-2048.jpg)


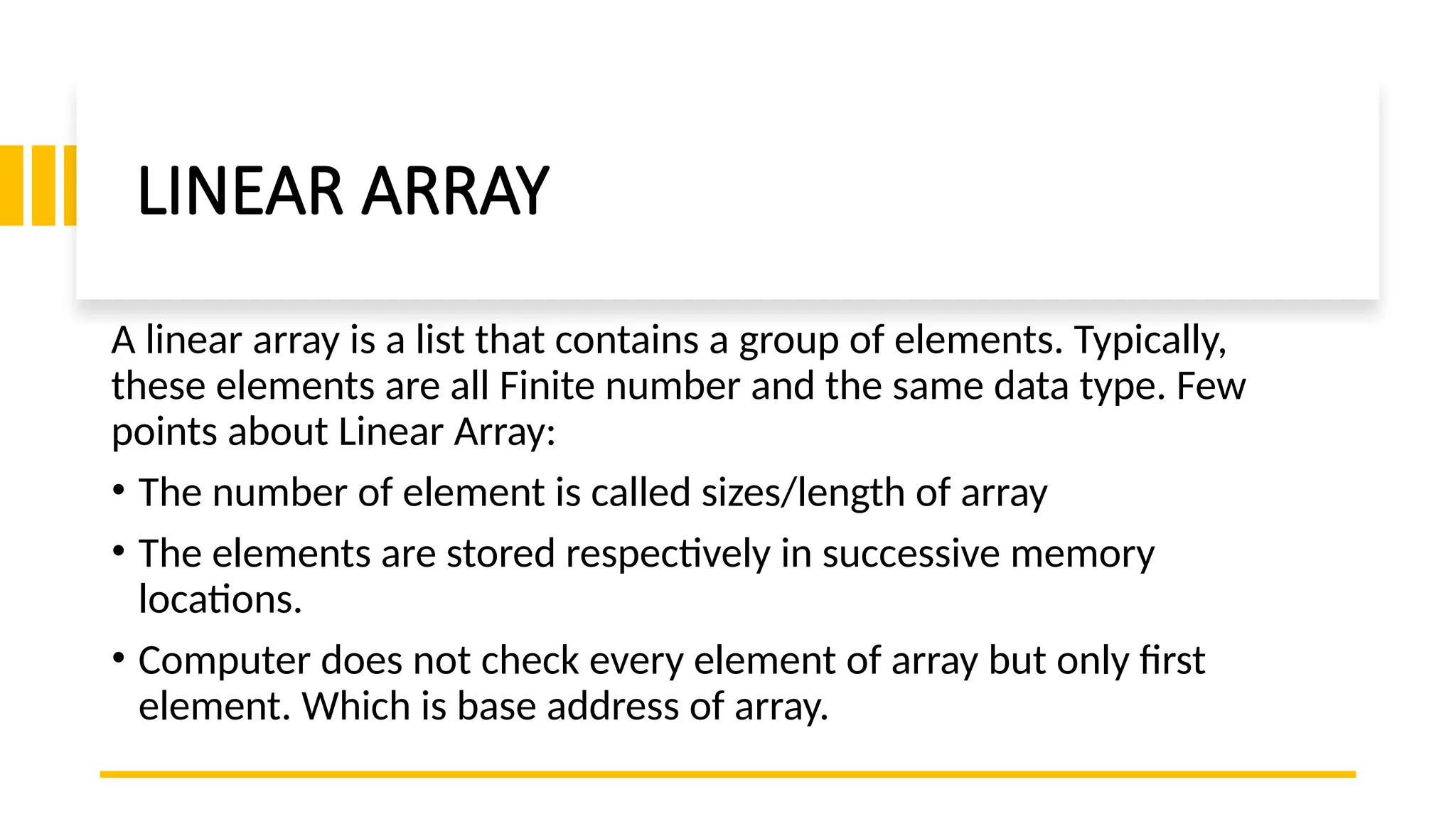
![REPRESENTATION OF LINEAR ARRAYS IN MEMORY: Let LA be a linear array in the memory of the computer. the computer calculates the address of any elements of LA by the following formula: LOC (LA [K]) = Base (LA) + W (K-lower bound) Where LOC (LA [K]) = address of the element LA [K] of the array LA, w is the number of words per memory cell for the array LA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineararraysinprogramming-241105160050-14be5dd6/75/Linear-Arrays-in-Programming-Array-Length-Benefits-Drawbacks-and-Memory-Layout-Explained-6-2048.jpg)
