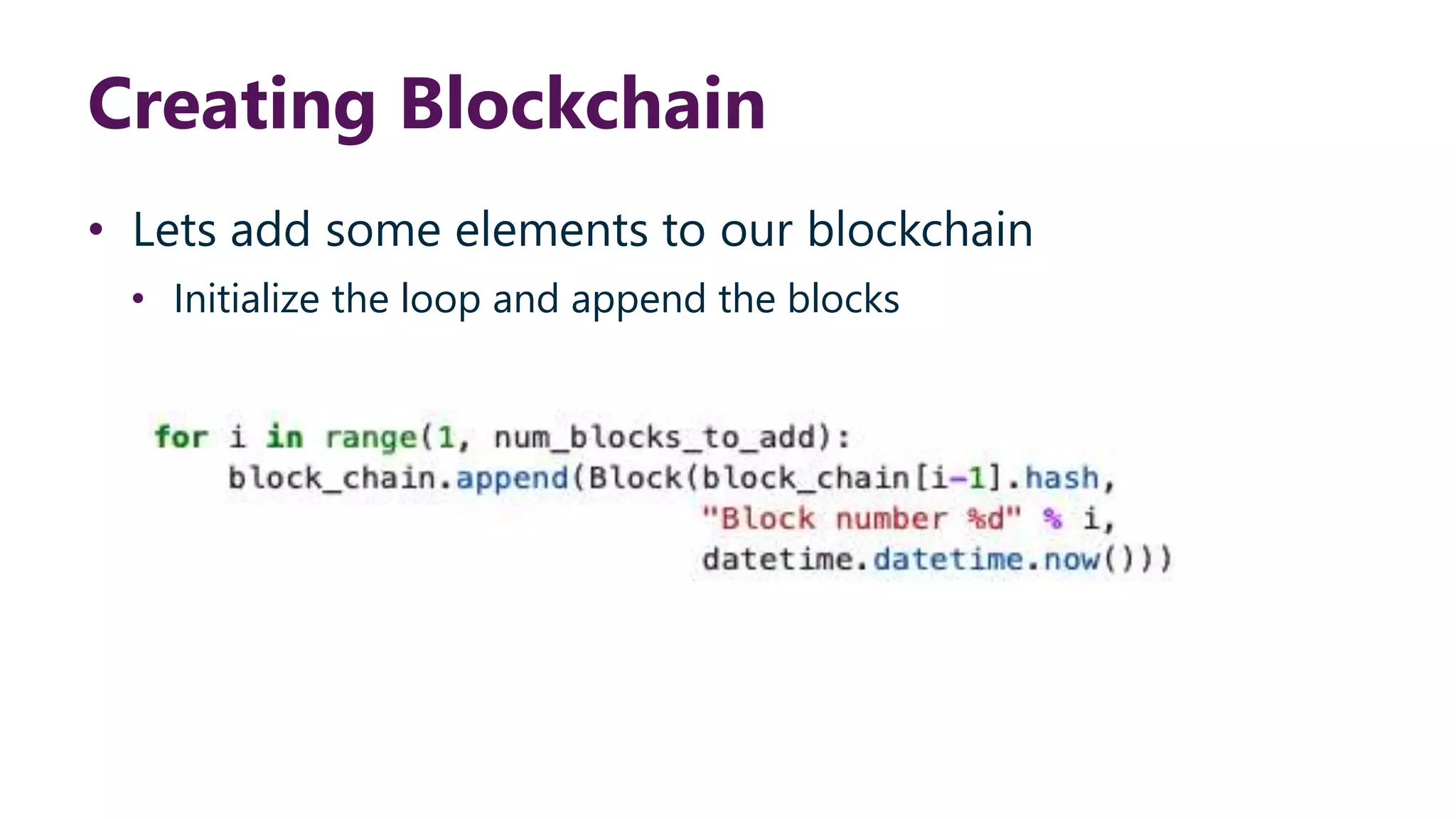
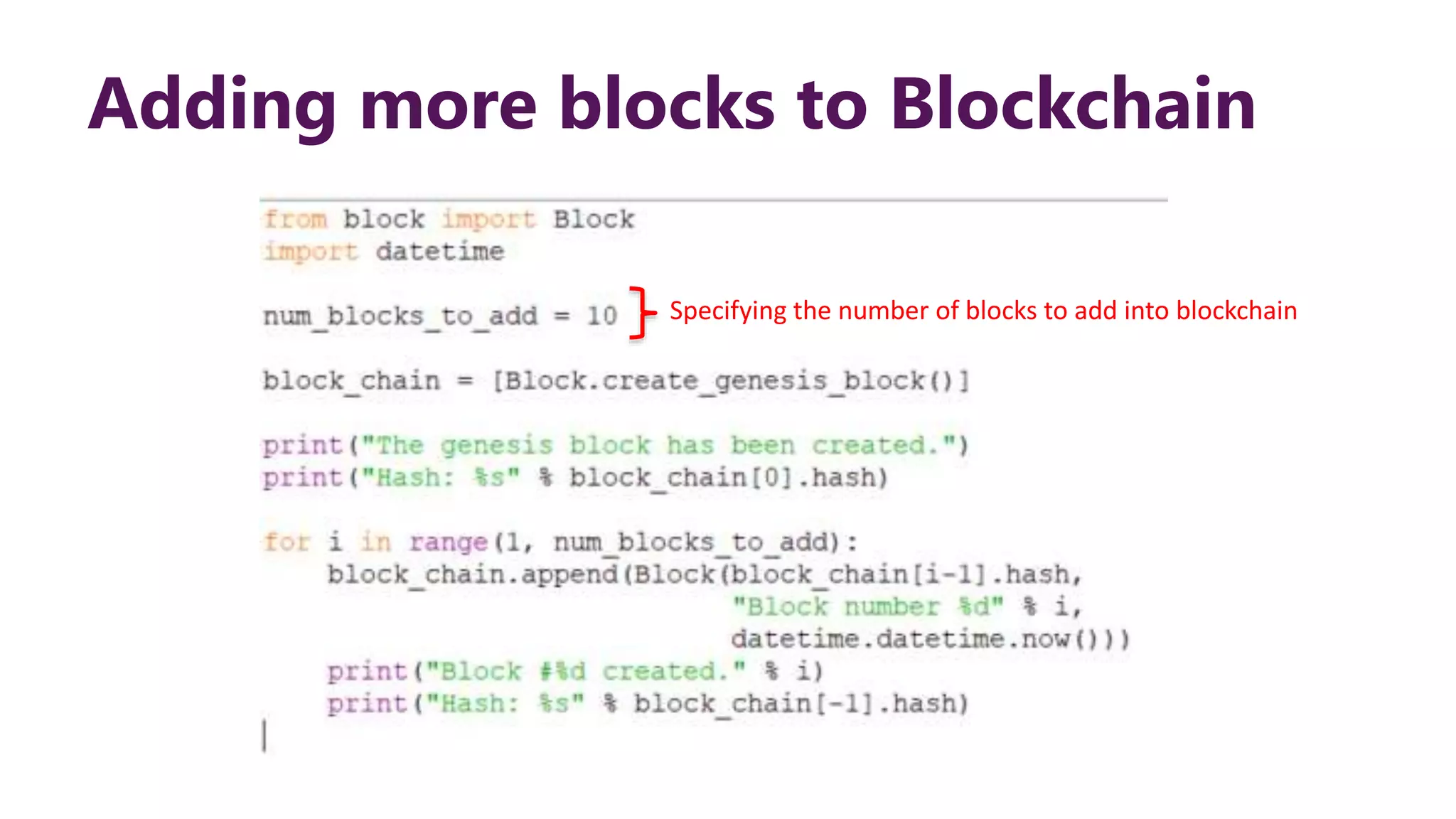
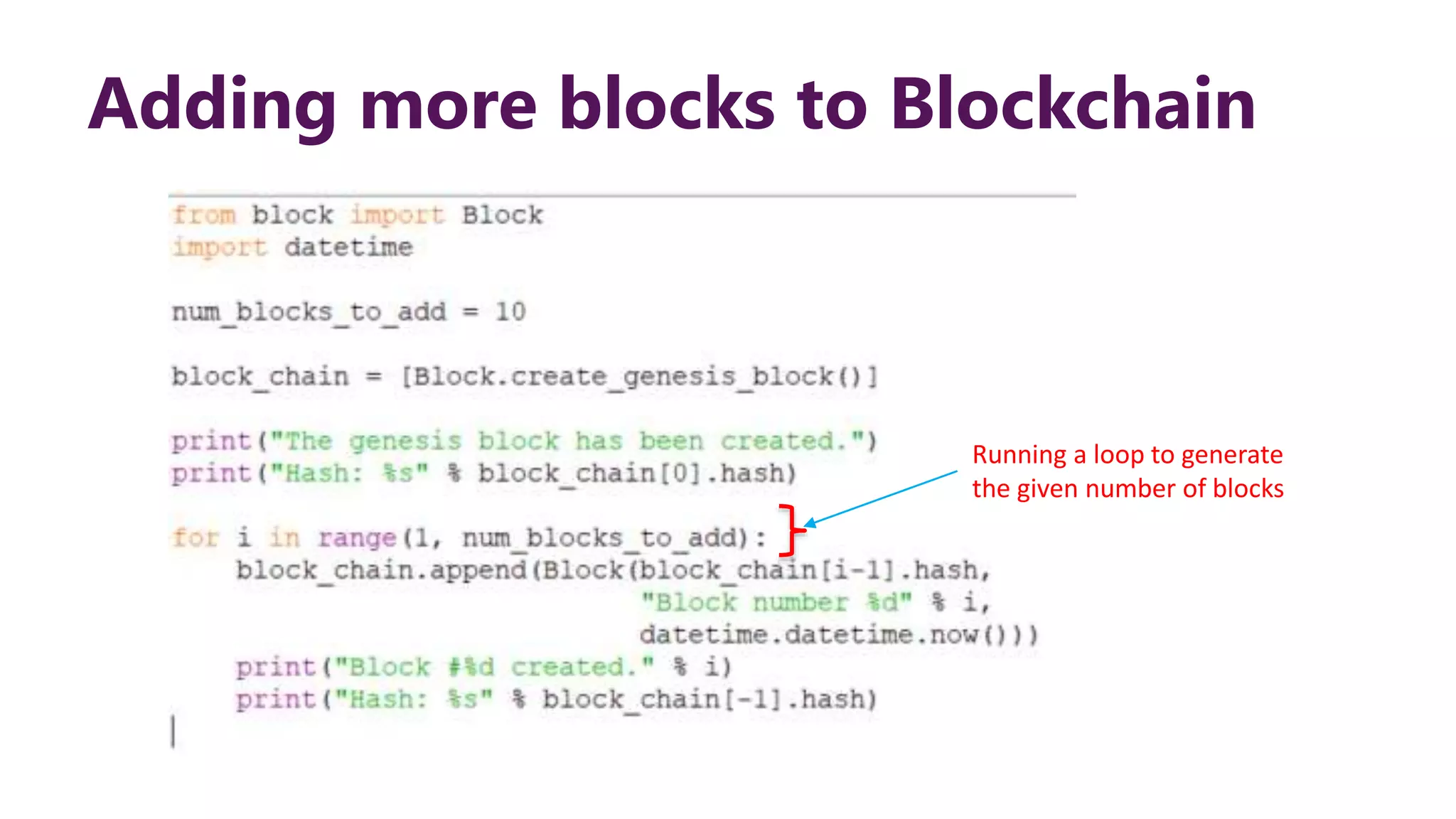
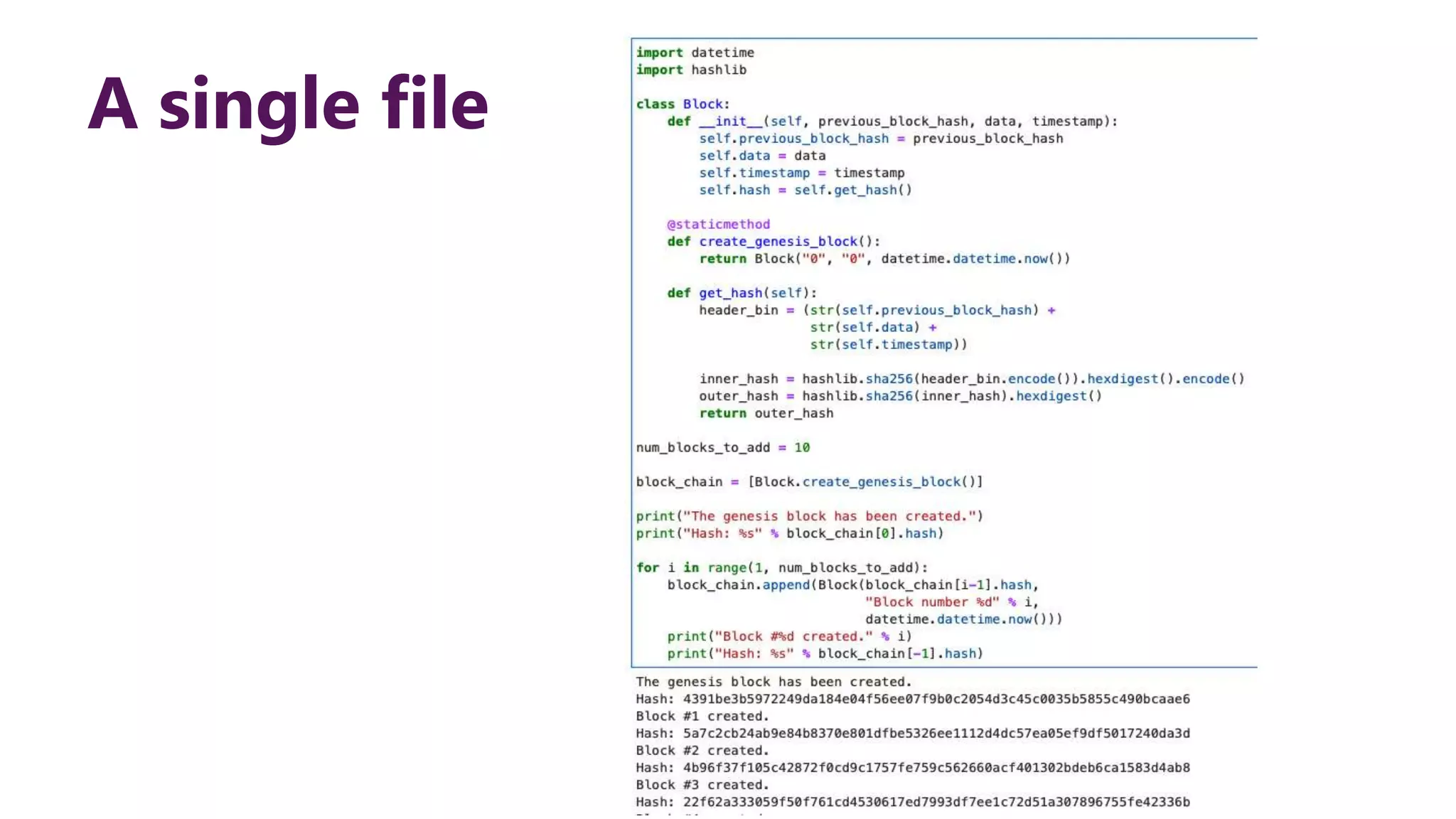
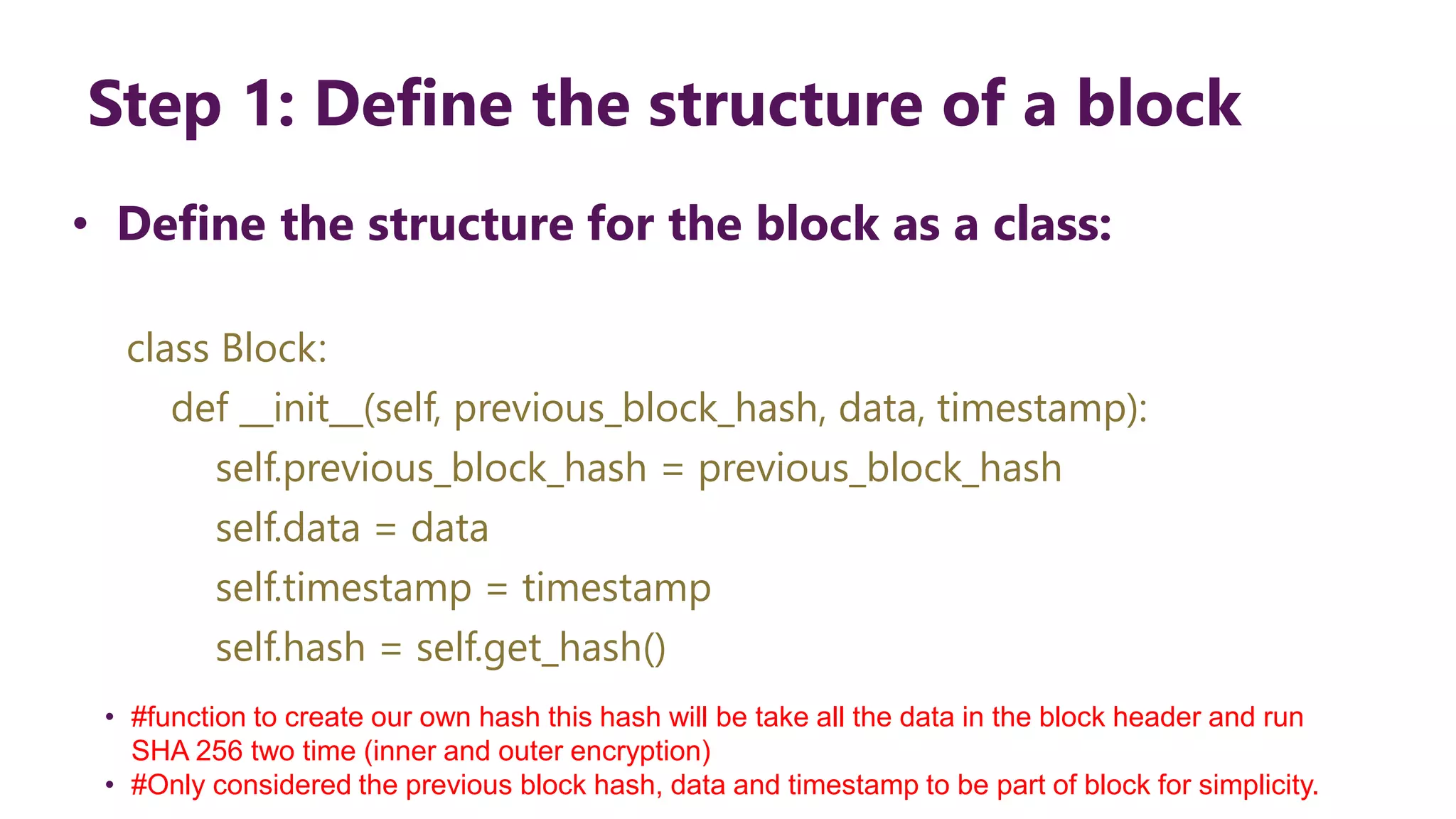
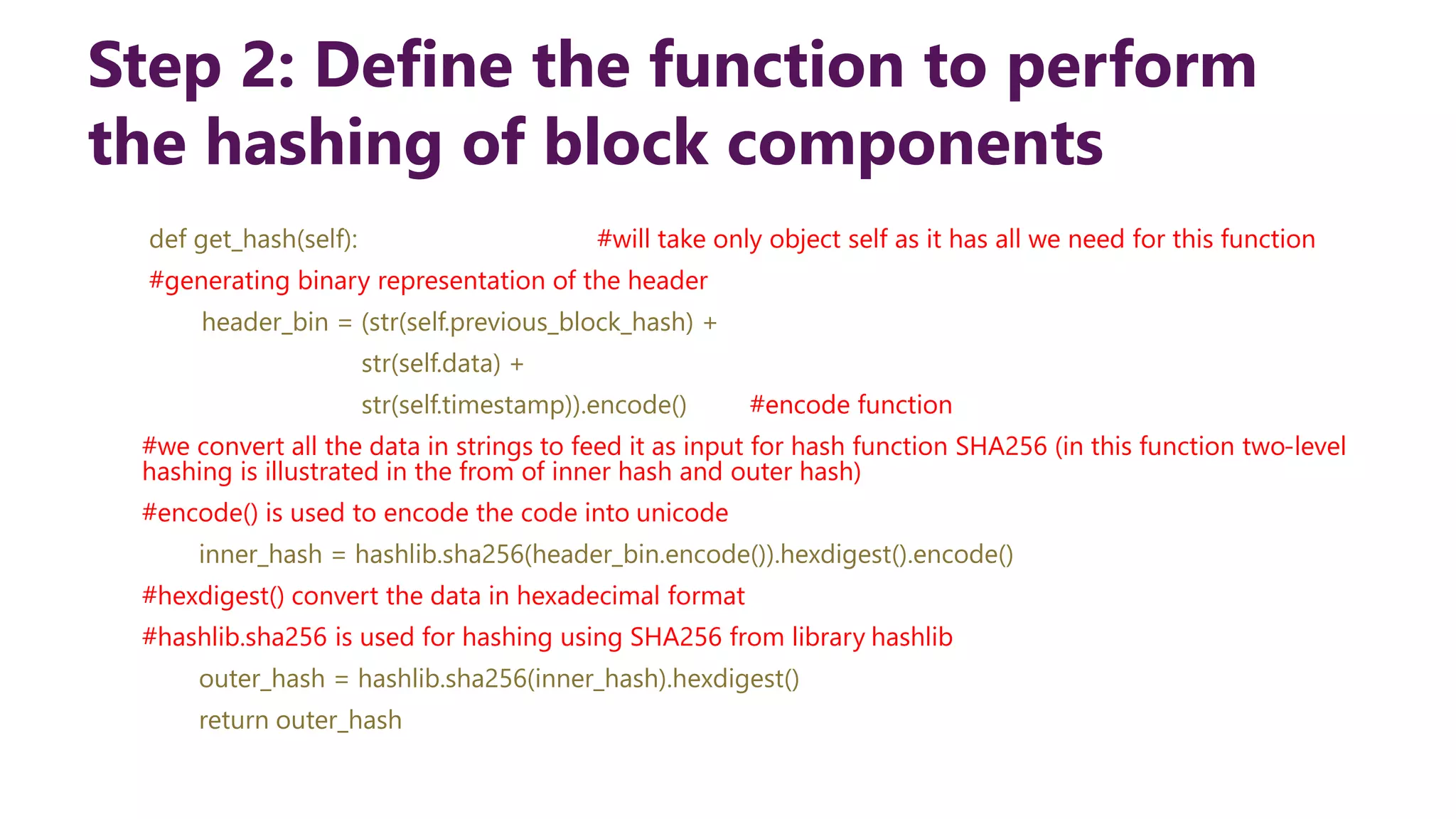
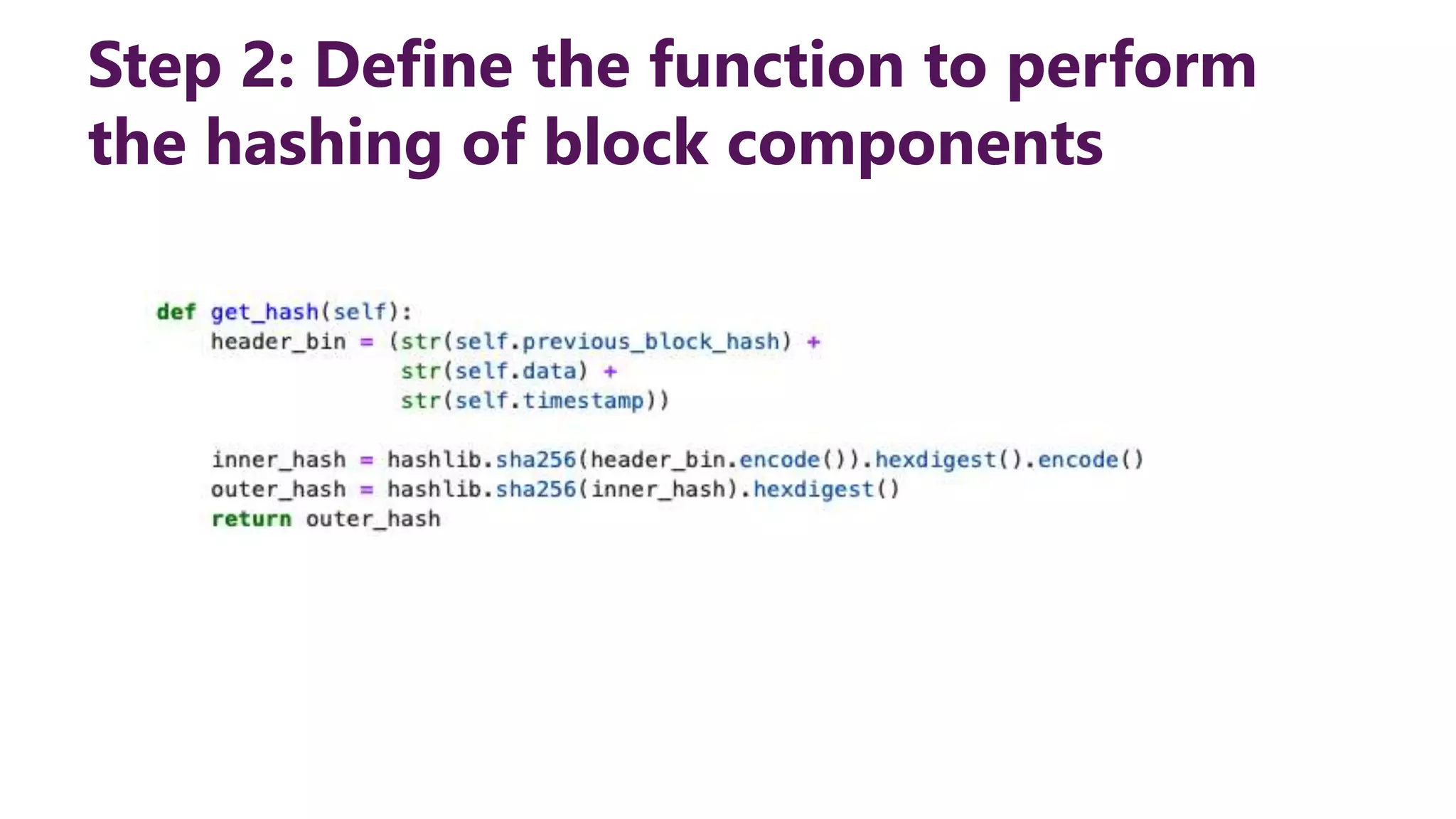
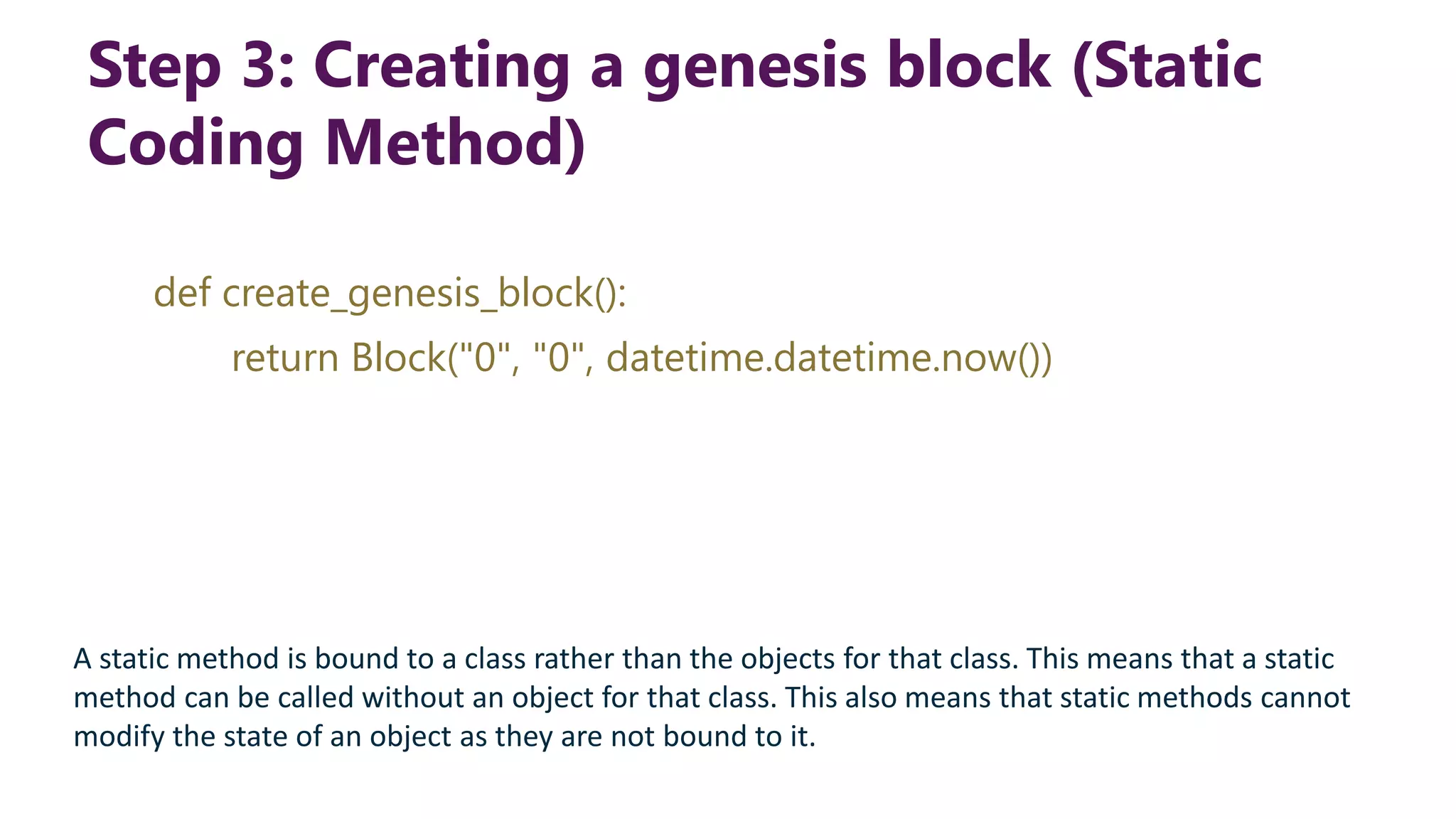
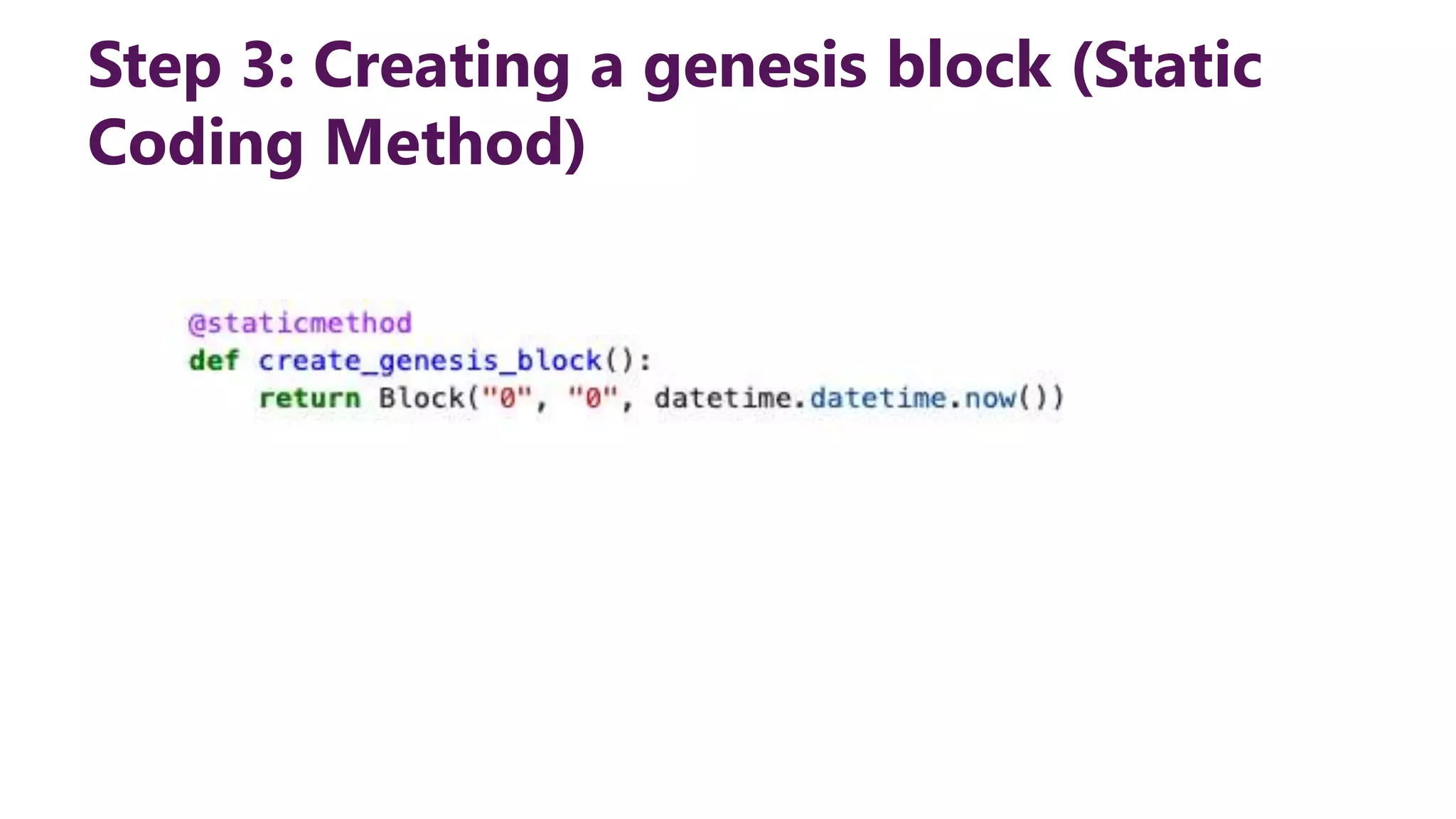
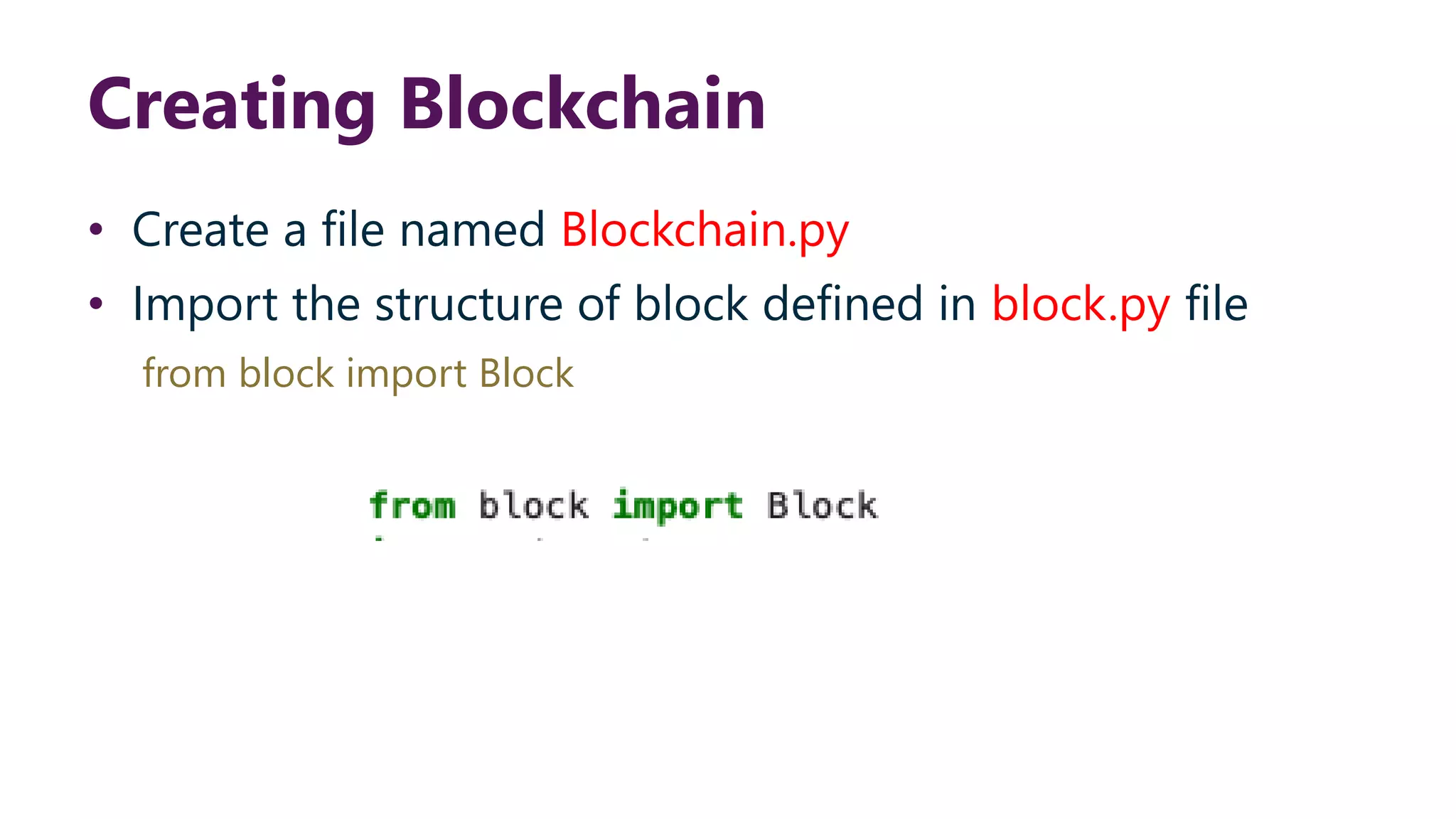
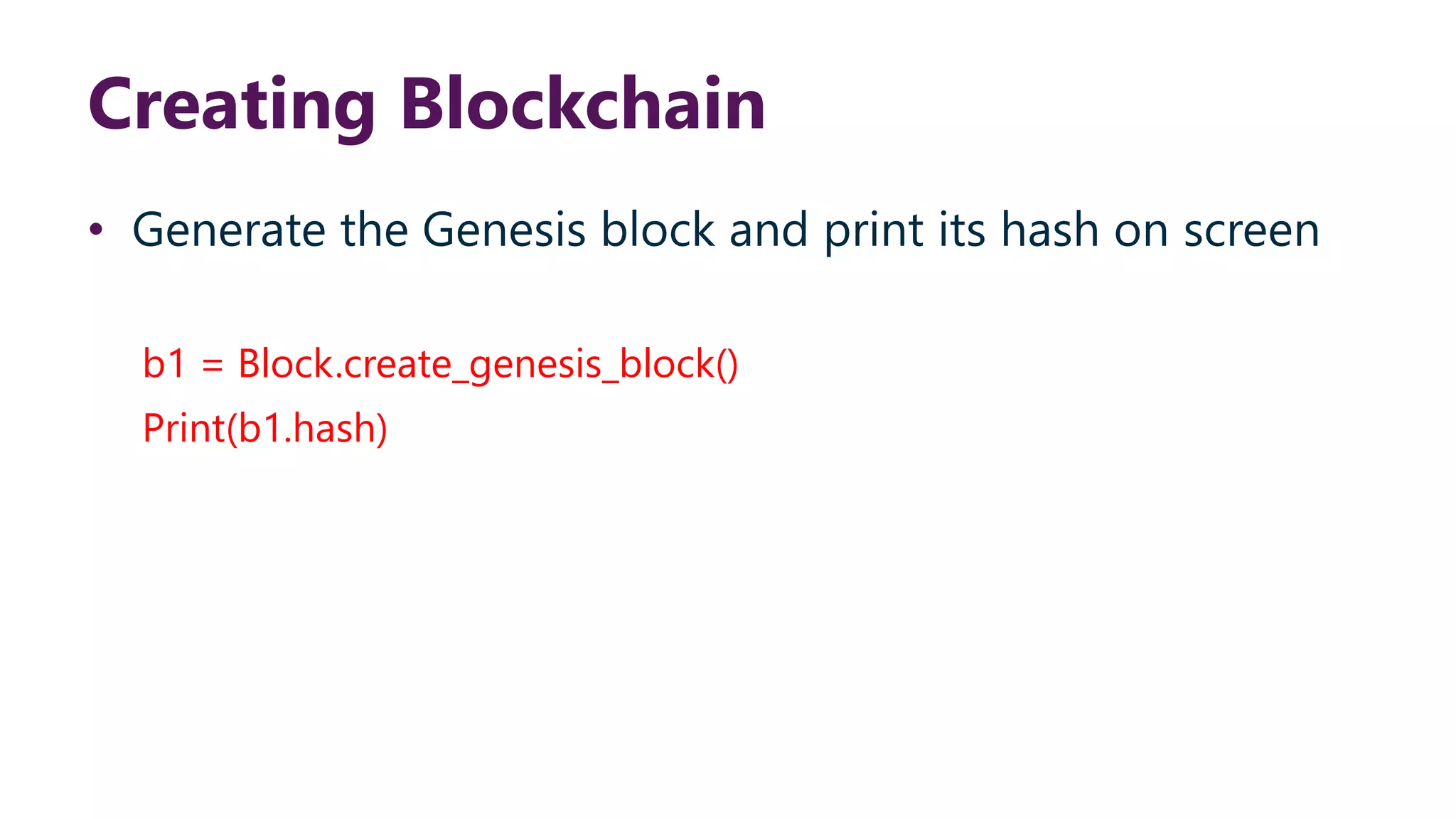
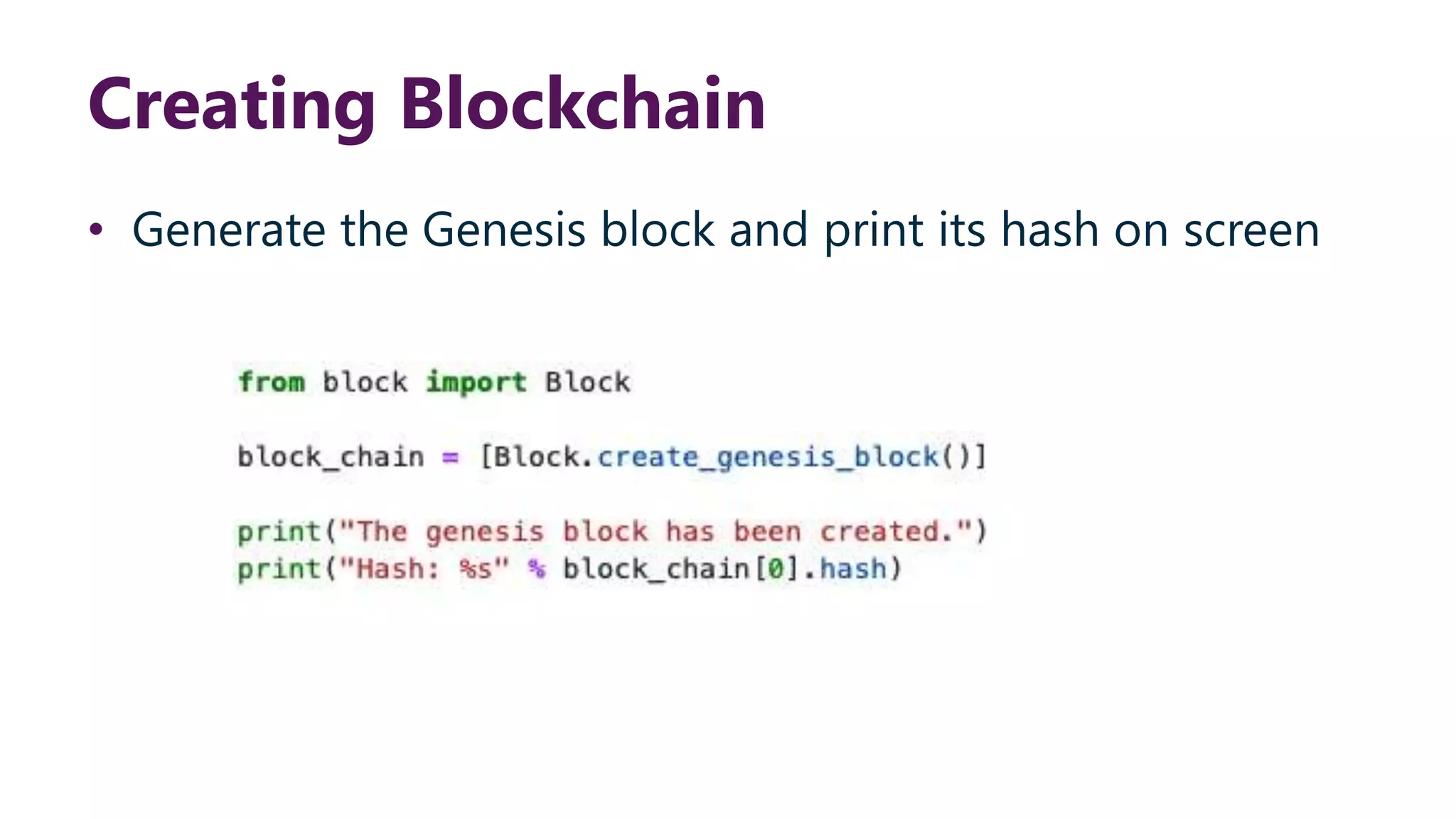
This document provides steps to develop a custom blockchain in Python. It describes defining a Block class to structure each block, including the previous hash, data, and timestamp. It defines a get_hash() method to hash block contents and return the hash. A create_genesis_block() static method is used to generate the first block. The Blockchain.py file imports the Block class and generates the genesis block. It then runs a loop to add a fixed number of blocks by hashing the prior block and appending new blocks to the blockchain list.







![Creating Blockchain • Lets add some elements to our blockchain • Initialize the loop and append the blocks for i in range(1, num_blocks_to_add): block_chain.append(Block(block_chain[i-1].hash, "Block number %d" % i, datetime.datetime.now()))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture17blockchainimplementationusingpython-221122174625-d47b3ca9/75/Lecture-17-Blockchain-Implementation-using-Python-pptx-16-2048.jpg)