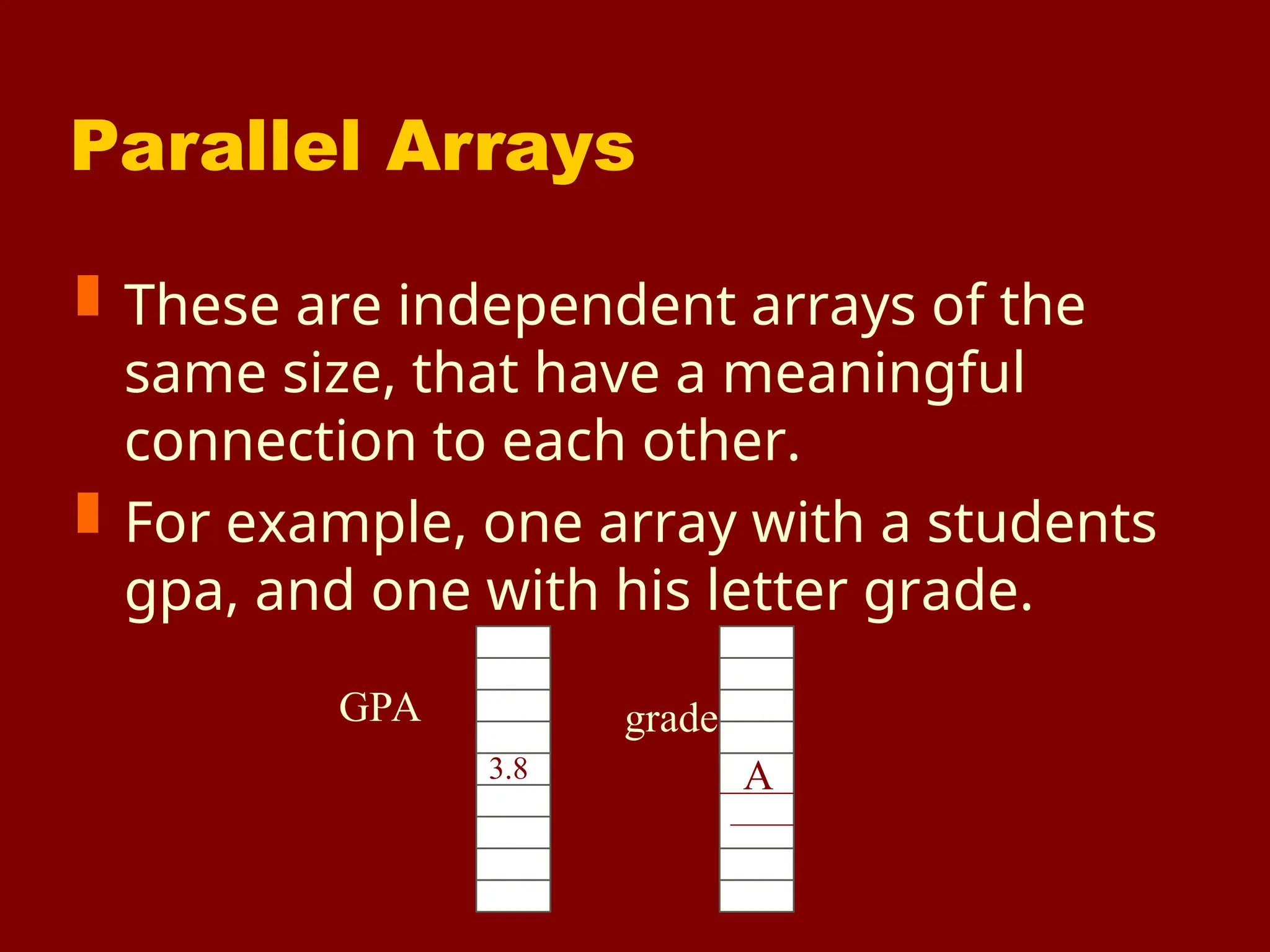
The document provides an extensive overview of arrays in C programming, including their definitions, declarations, and usages. It explains how to initialize arrays, the significance of indexing, and the fundamental operations such as input/output and manipulating array elements. Additionally, it discusses one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays, along with examples illustrating the concepts.


![Parts of Arrays Elements Refers to the number of individual items represented by the array Index (or more formally, Subscript) Refers to one particular element in the array The first position in an array is represented by an index, or subscript of 0 (zero). For example, • arrStudentGrades[ 0 ] The second position is referred to by • arrStudentGrades[ 1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-4-2048.jpg)

![Arrays A particular value in an array is referenced using the array name followed by the index in brackets For example, the expression scores[2] refers to the value 94 (the 3rd value in the array) That expression represents a place to store a single integer and can be used wherever an integer variable can be used](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-6-2048.jpg)
![Arrays For example, an array element can be assigned a value, printed, or used in a calculation: scores[2] = 89; scores[first] = scores[first] + 2; mean = (scores[0] + scores[1])/2; printf ("Top = %d”, scores[5]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-7-2048.jpg)

![Declaring an array The declaration is similar to the declaration of other variables (except for the brackets and number of elements): int iMyFirstArray[ 15 ], iMySecondArray[ 20 ]; You can use a #define constant to set the size of the array #define GRID_ROWS_MAX 8 int arrGridRows[ GRID_ROWS_MAX ] ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-9-2048.jpg)
![Declaring Arrays The scores array could be declared as follows: int scores[10] ; The type of the variable scores is an array of integers The variable scores is set to a new blank array that can hold 10 integers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-10-2048.jpg)
![Declaring Arrays Some examples of array declarations: double prices[500] ; int factor[12] , age[6]; char codes[30] ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-11-2048.jpg)
![Initializing an Array You can initialize an array when you declare it, as you do with other variables Syntax is slightly different, as you are now initializing more than one element at a time One way at declaration, using initializers: int iMyFirstArray[ 5 ] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; Note the braces around the initial zeroes which themselves are separated by commas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-12-2048.jpg)
![Initializing an Array (cont’d) If you specify fewer initializing values than you have elements, all the rest are initialized to a value of 0. For example: int iMyFirstArray[ 5 ] = { 0 }; would set all elements to 0 int iMyFirstArray[ 5 ] = { 4 }; would set the zeroth element to 4 and the rest to 0!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-13-2048.jpg)
![Initializing an array without specifying size You can also initialize and set the number of elements with the same step: int iMyFirstArray[ ] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; Note: there is NO size specified; C automatically makes it 5 elements since you gave five initial values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-14-2048.jpg)
![Initializer Lists Examples: int units[ ] = {147, 323, 89, 933, 540, 269, 97, 114, 298, 476}; char letterGrades[ ] = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', ’F'}; Note that an initializer list can only be used in the array declaration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-15-2048.jpg)
![Initializing array with a for loop After declaring an array, you can initialize it in the body of your program by using a for loop: int i = 0, iMyFirstArray[ 5 ] ; /* size is 5*/ for ( i = 0 ; i <= 4 ; i++ ) { iMyFirstArray[ i ] = 0 ; } /* end for i */ Note the upper bound is 4, not 5. That is, you loop through 0 to 4 to initialize an array with 5 elements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-16-2048.jpg)

![Bounds Checking For example, if the array codes can hold 100 values, it can be indexed using only the numbers 0 to 99 If count has the value 100, then the following reference will cause a problem: for (int index=0; index <= 100; index++) codes[index] = index*50 + epsilon; problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-18-2048.jpg)
![Array Input/ Output We typically use for loops for any kind of array processing. To input an array, one by one: for (i=0; i<10 ; i++ ) { printf(“ Enter element %d : “, i ); scanf ( “ %d “, &scores[i] ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-19-2048.jpg)
![Array Output To display an array, one element per line: for (i=0; i<10 ; i++ ) { printf(“ scores [%d] : %dn“, i , scores[i] ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-20-2048.jpg)
![#define SIZE 10 int main() { int myFirstArray[SIZE], i; for (i=0; i<=SIZE-1; i++) { myFirstArray[i] = i * 2; printf("myFirstArray with subscript of %d holds the value %dn", i, myFirstArray[i]); } return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-21-2048.jpg)
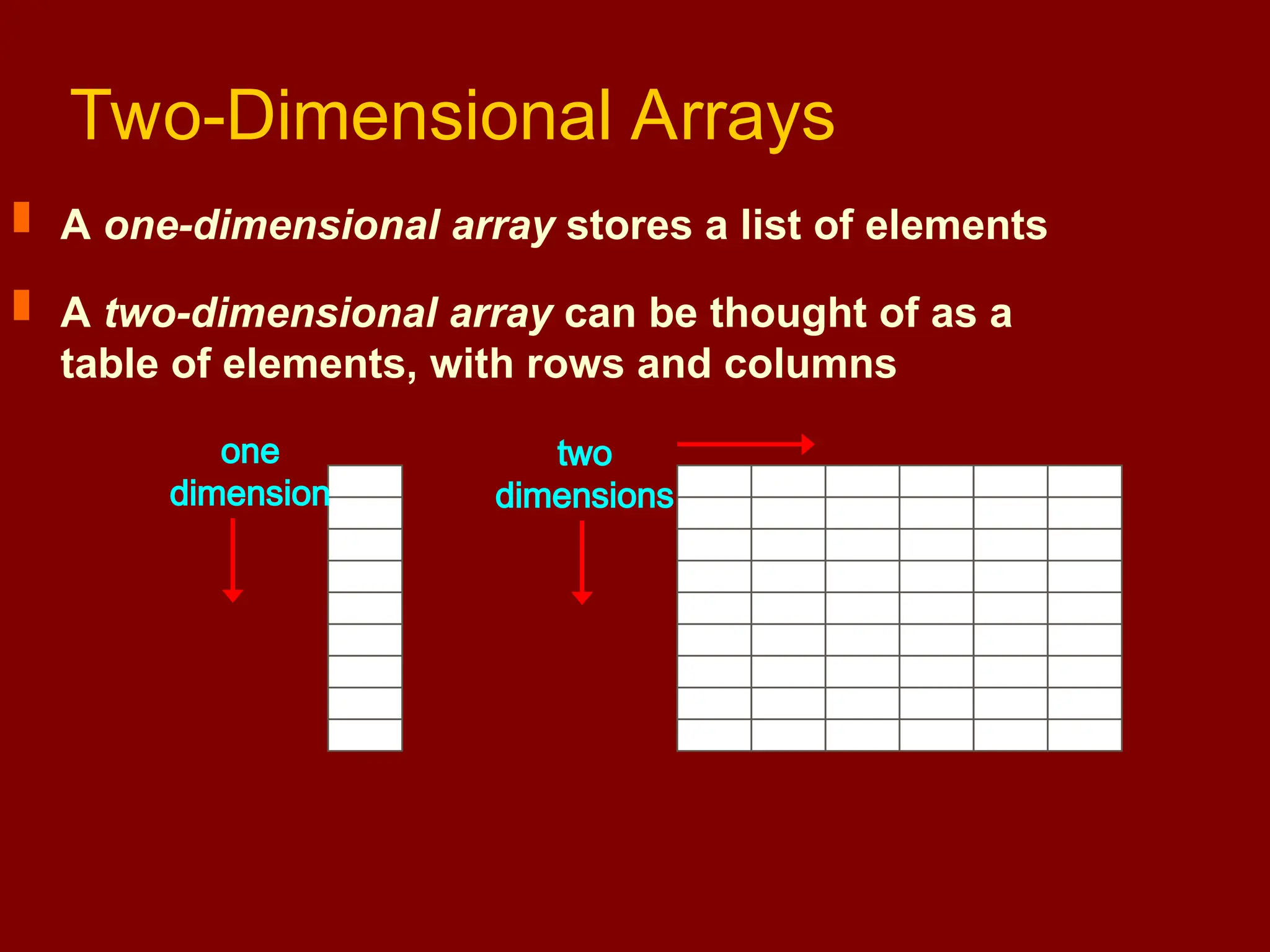
![Two Dimensional Arrays Declaration: int arr[5][5]; Traversed using two nested for loops: for (i = 0; i<=4 ; i++) for (j = 0; j<=4; j++) arr[i][j] = i * j;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-23-2048.jpg)
![Multi dimensional arrays Arrays can be 3 dimensional, 4 dimensional, or of n dimensions. int arr[3][3][3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15arrays-250211100250-8953b2c8/75/Lecture-15-Arrays-with-C-programming-ppt-24-2048.jpg)