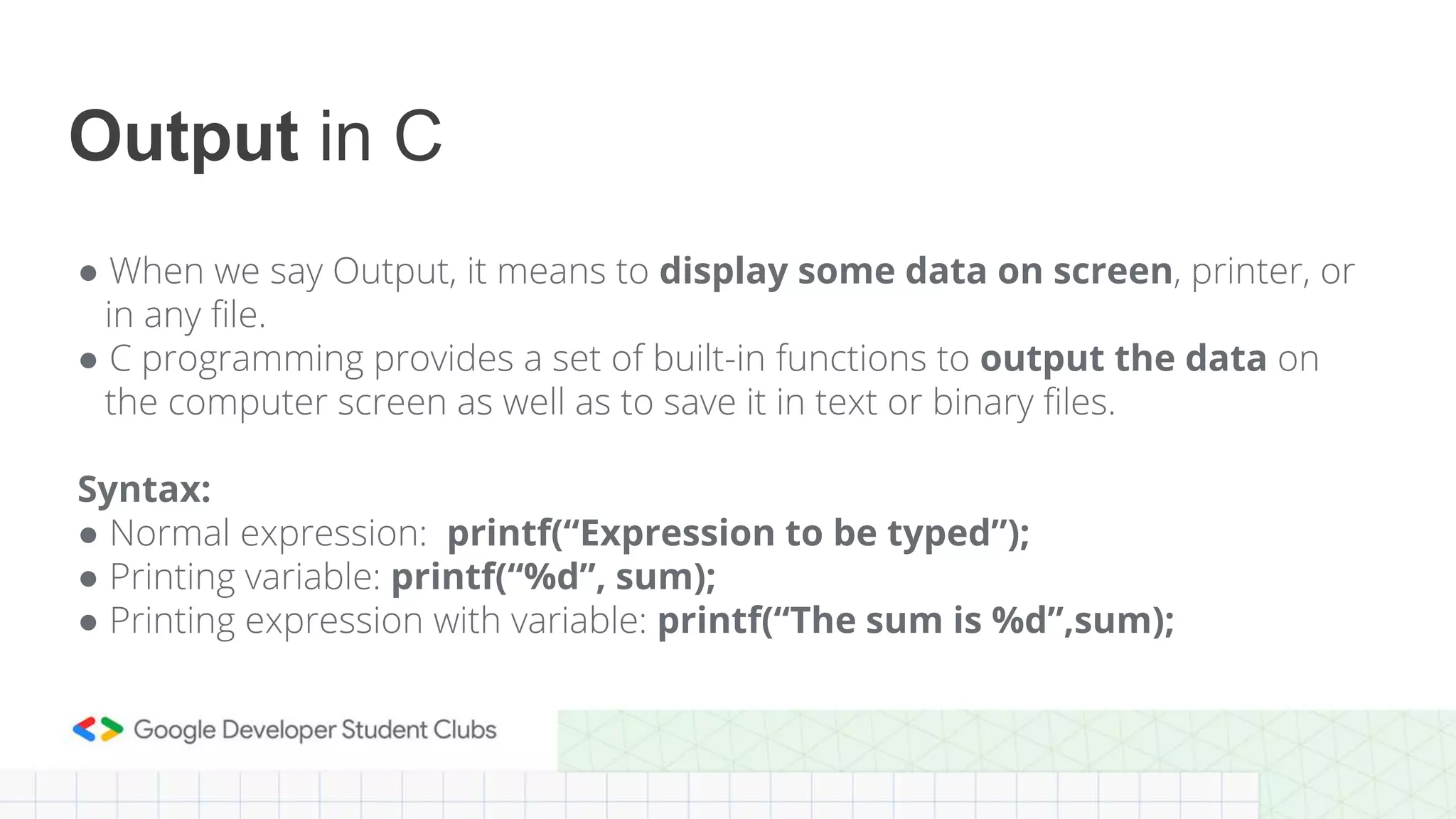
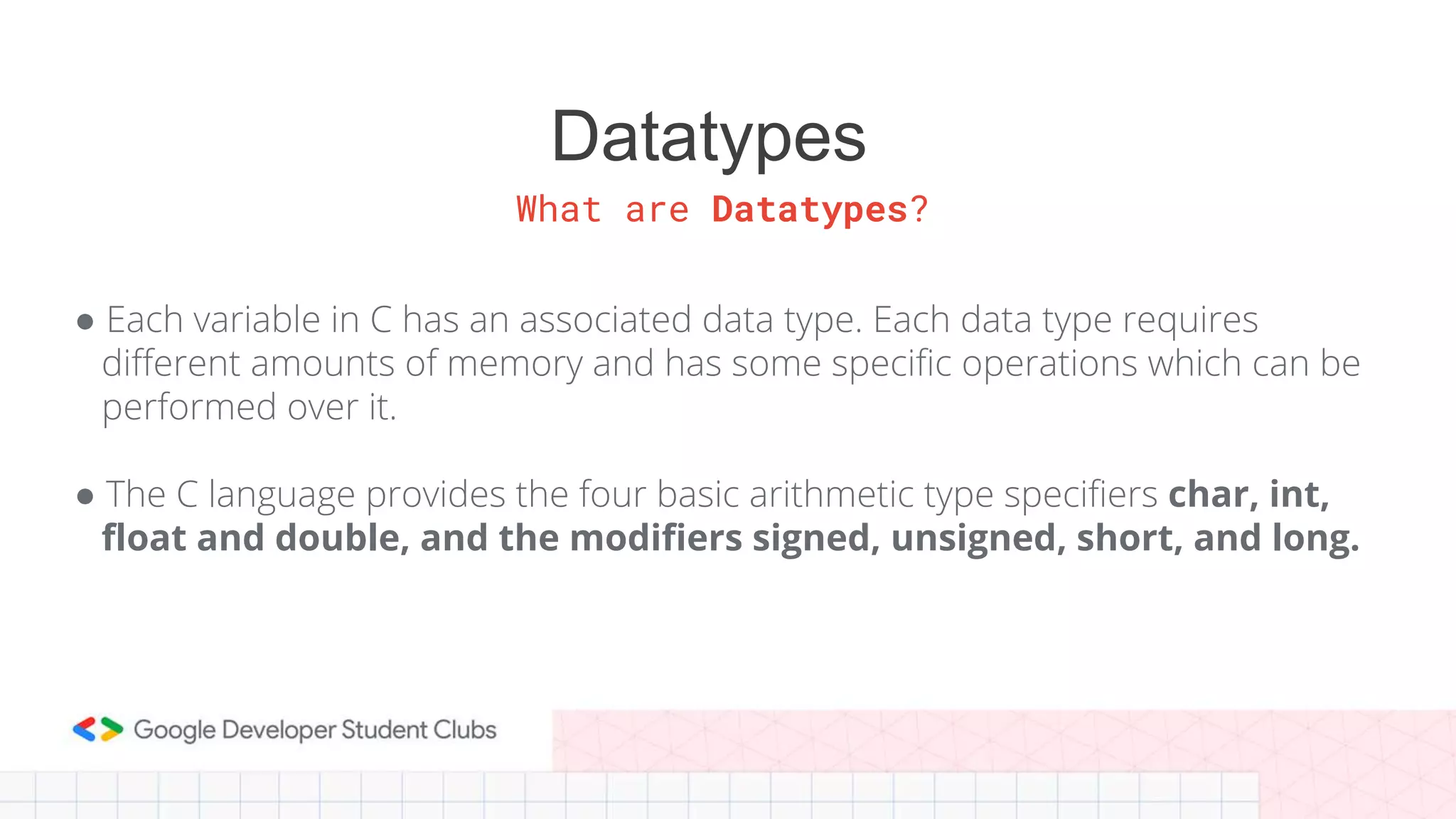
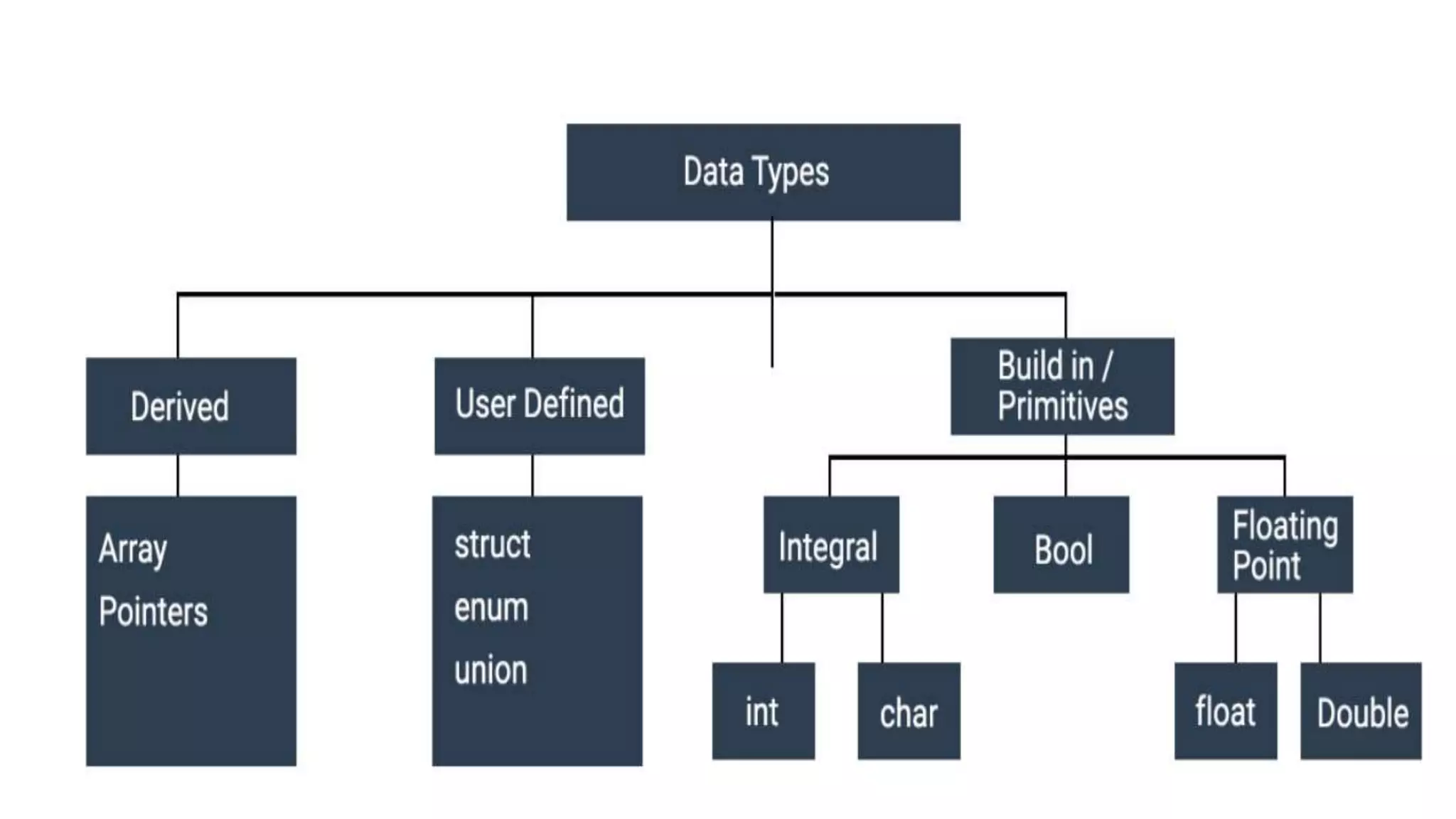
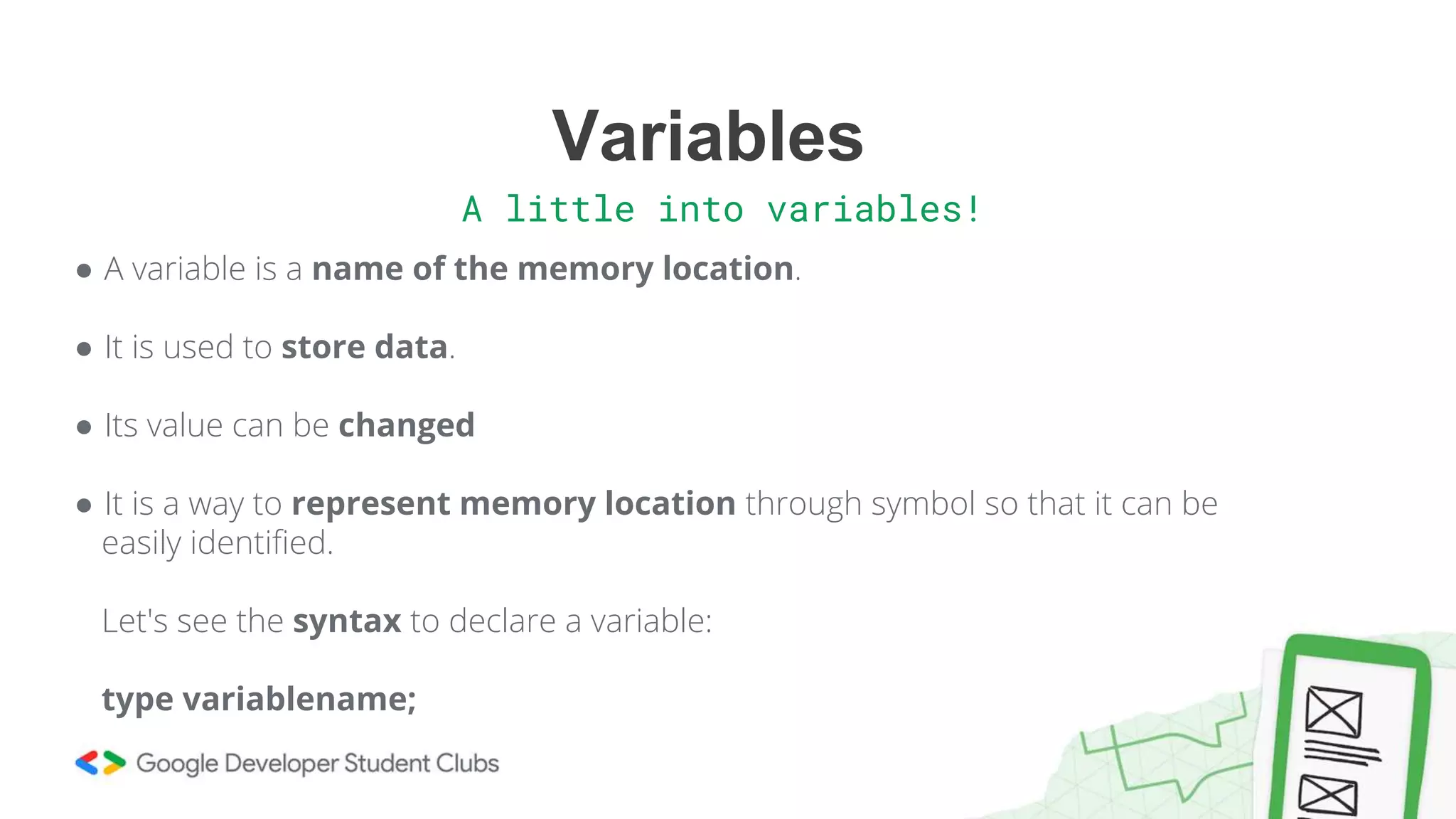
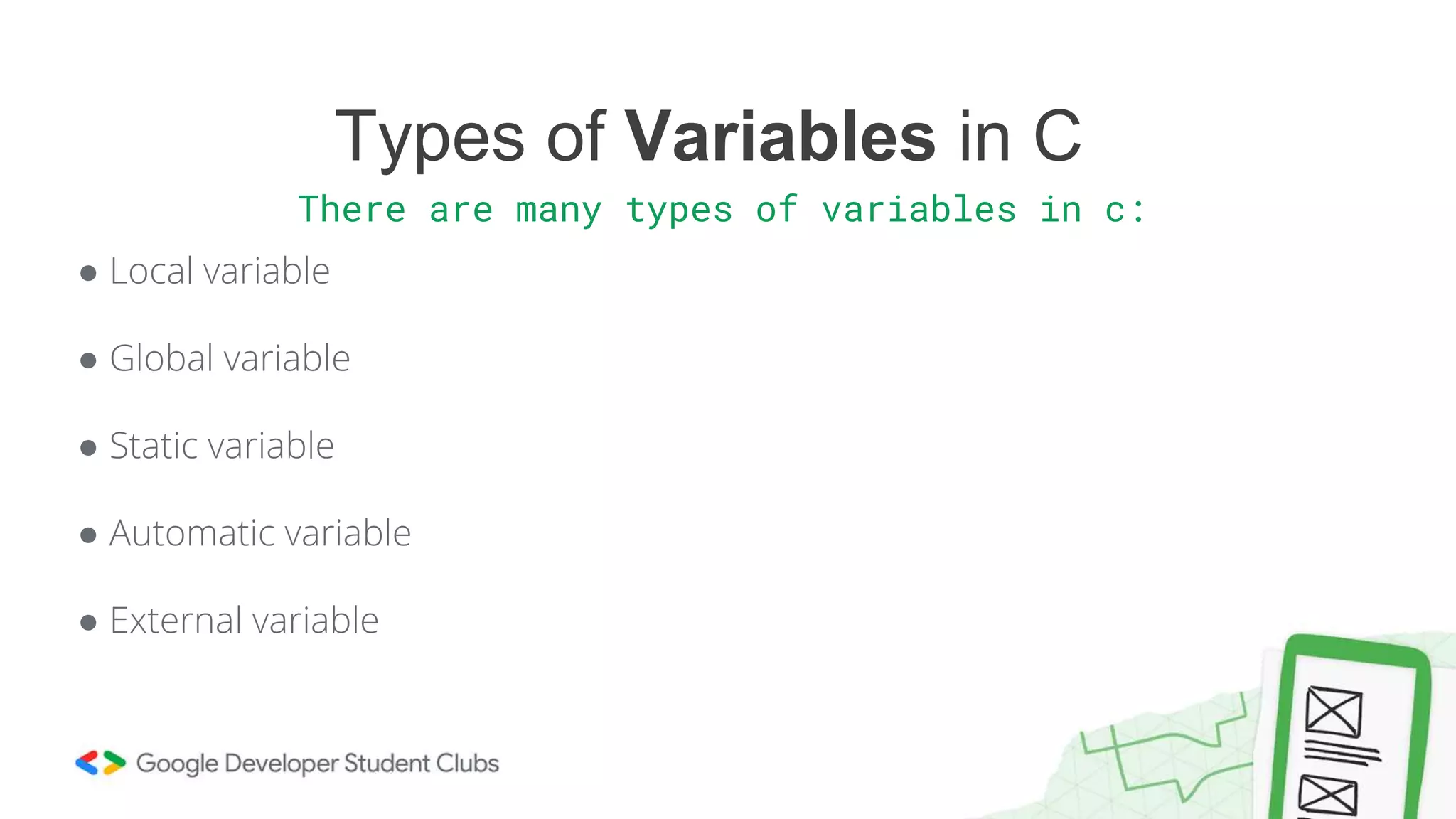
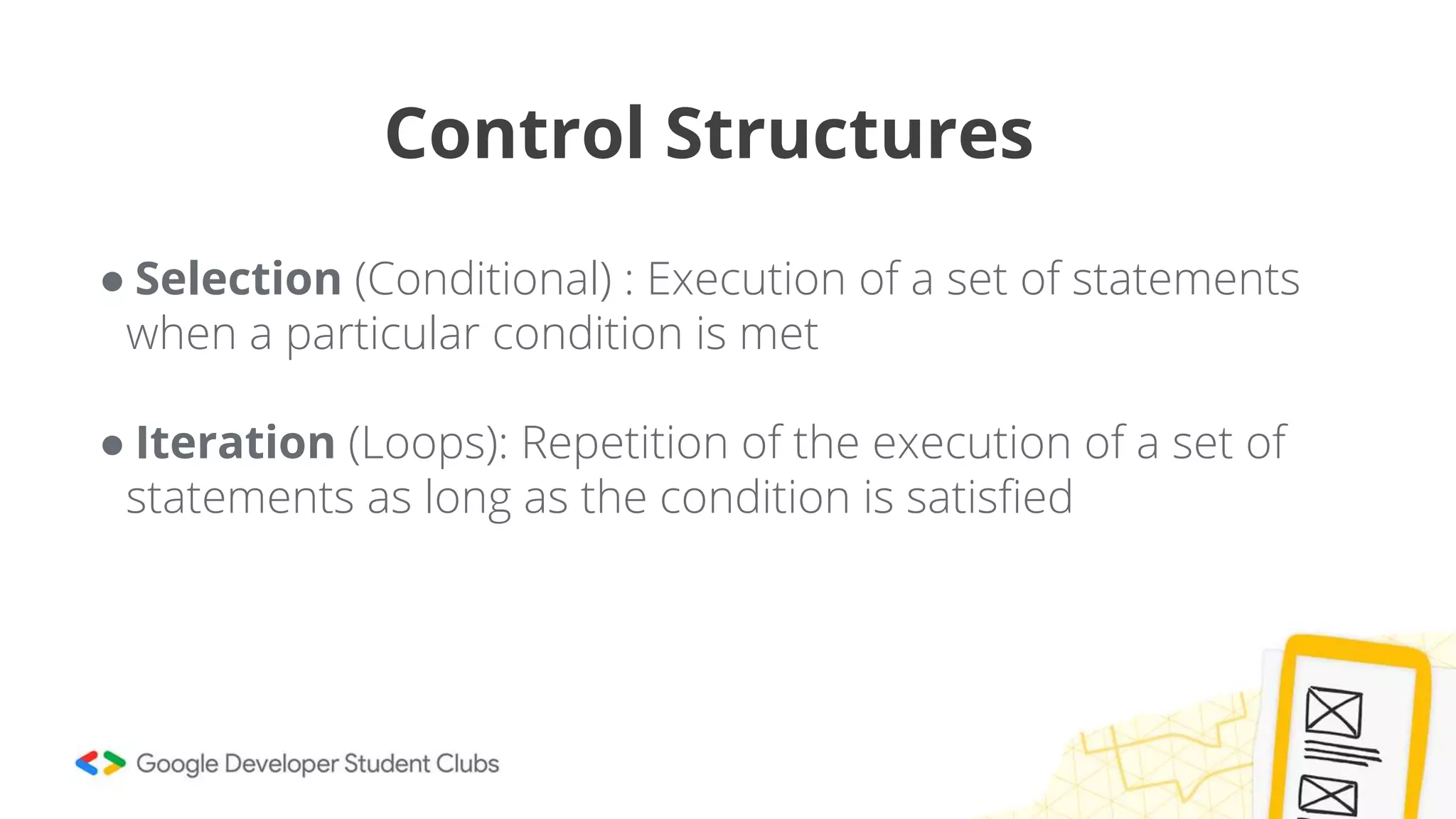
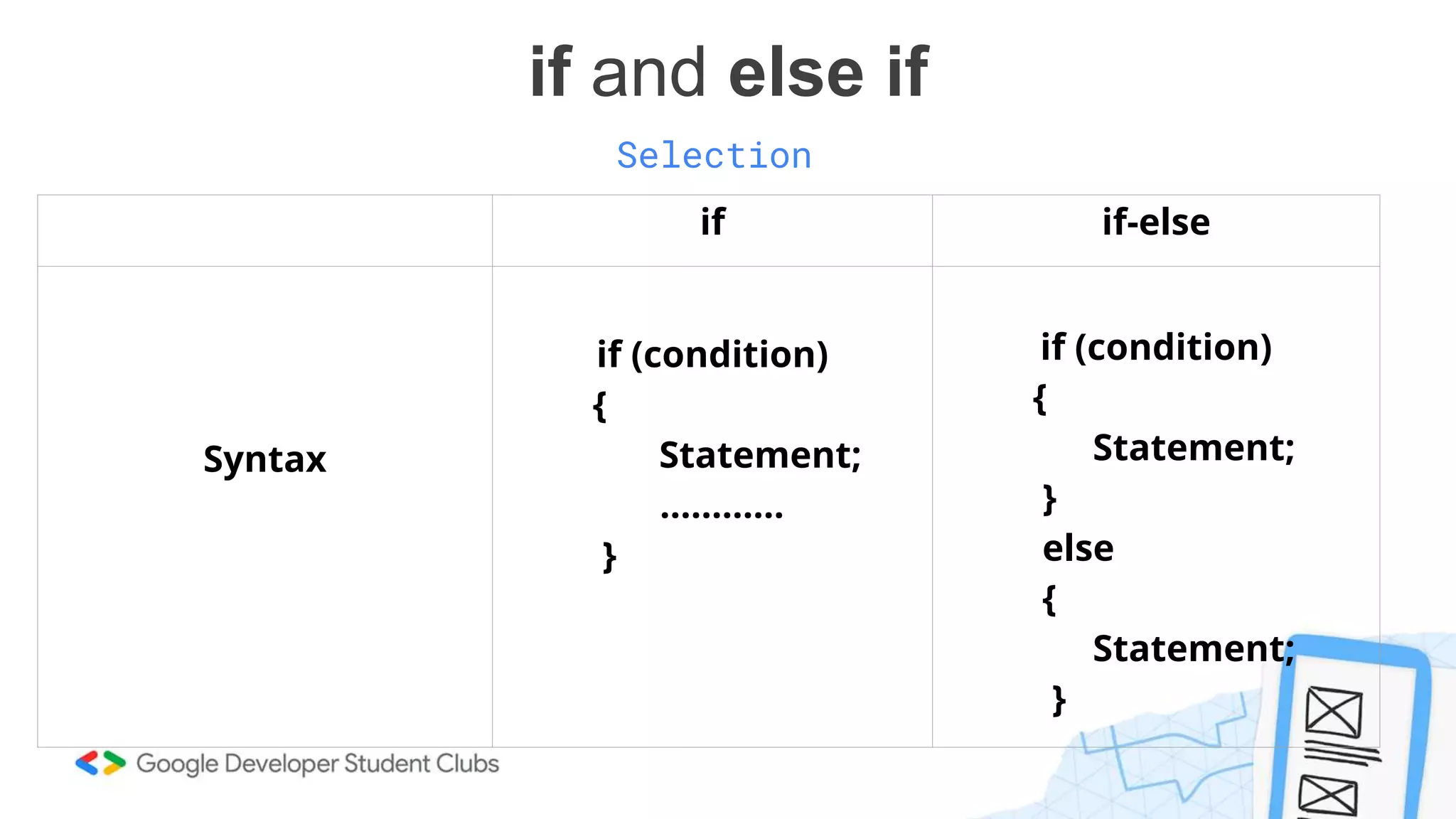
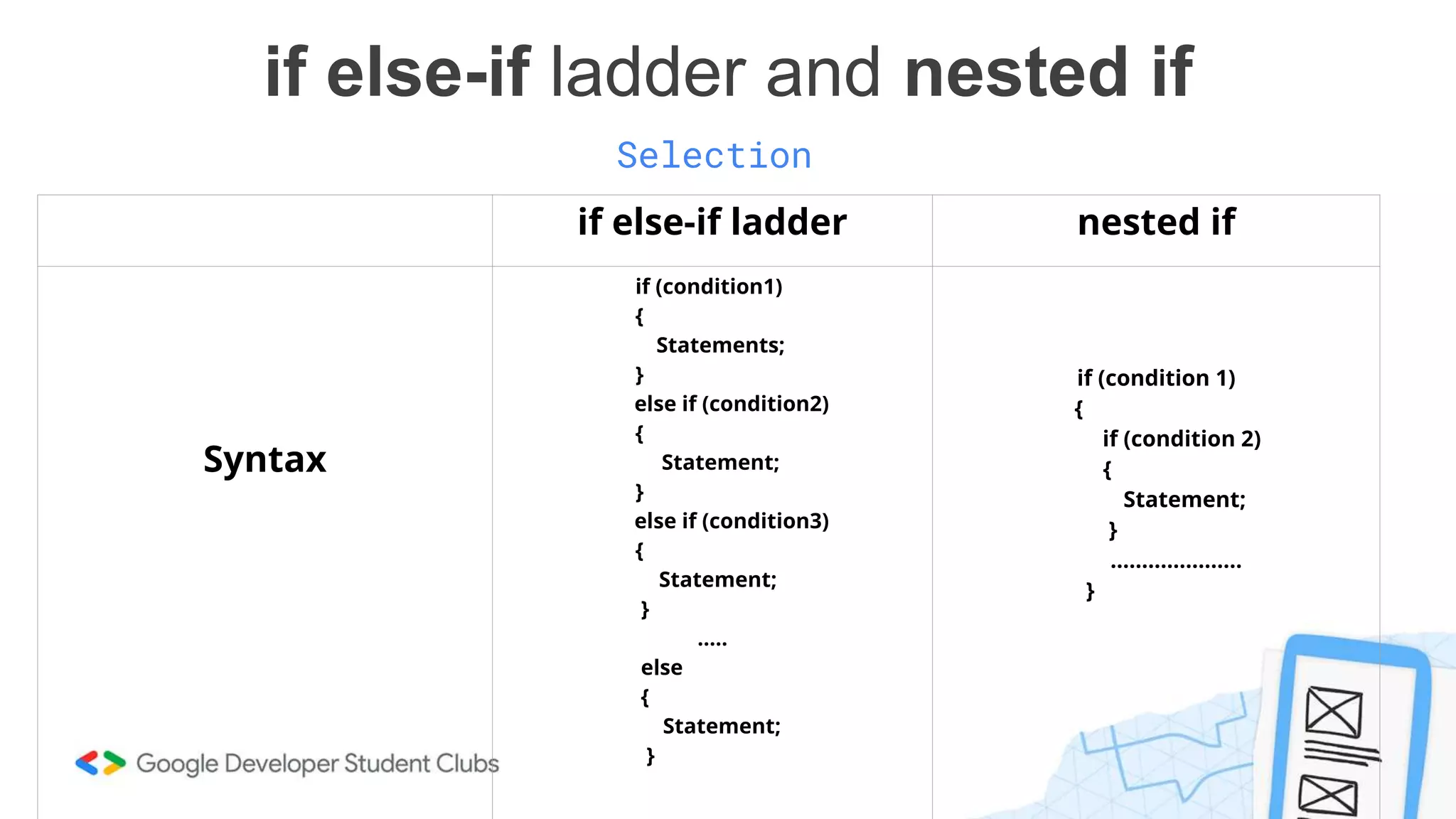
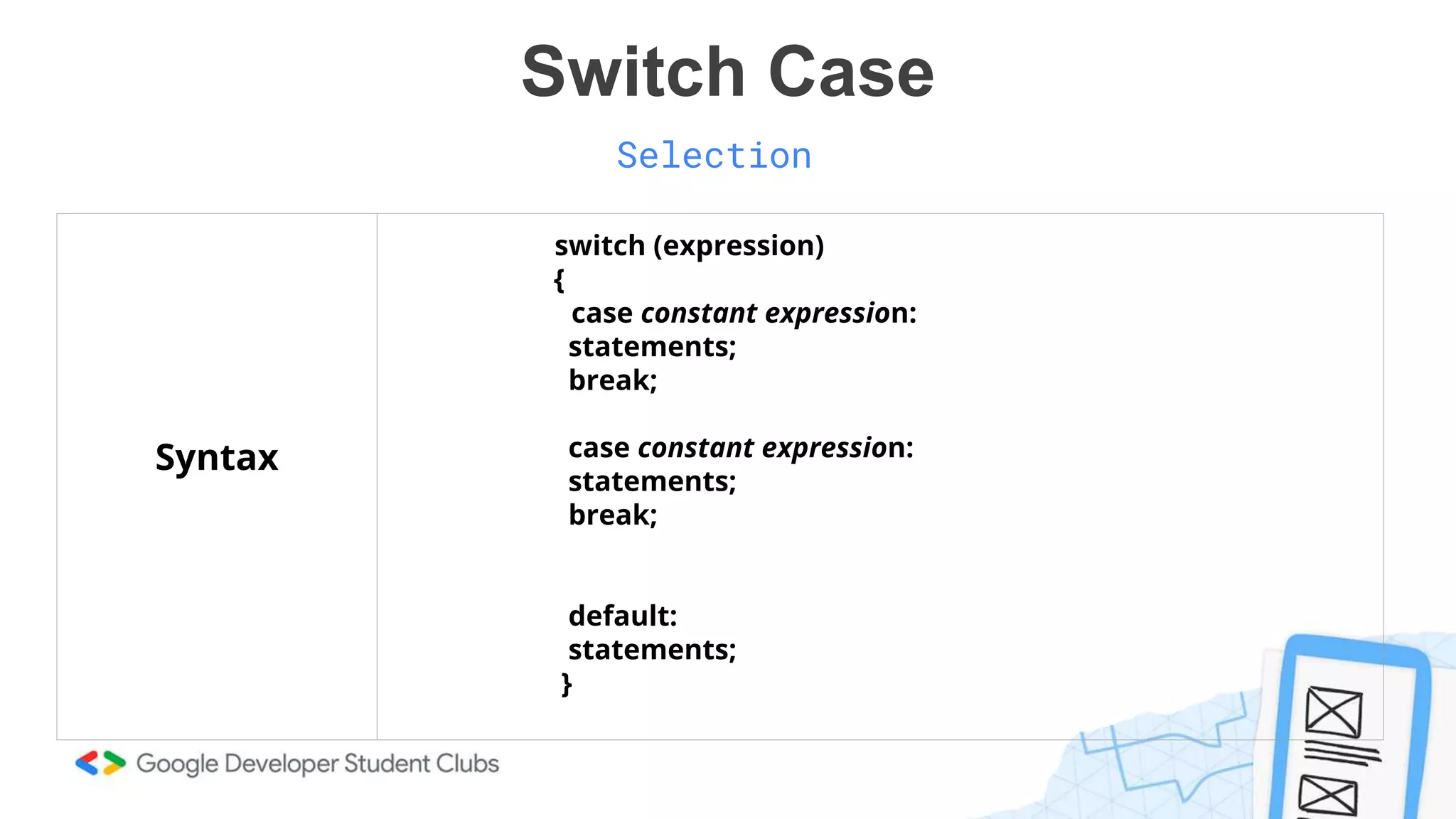
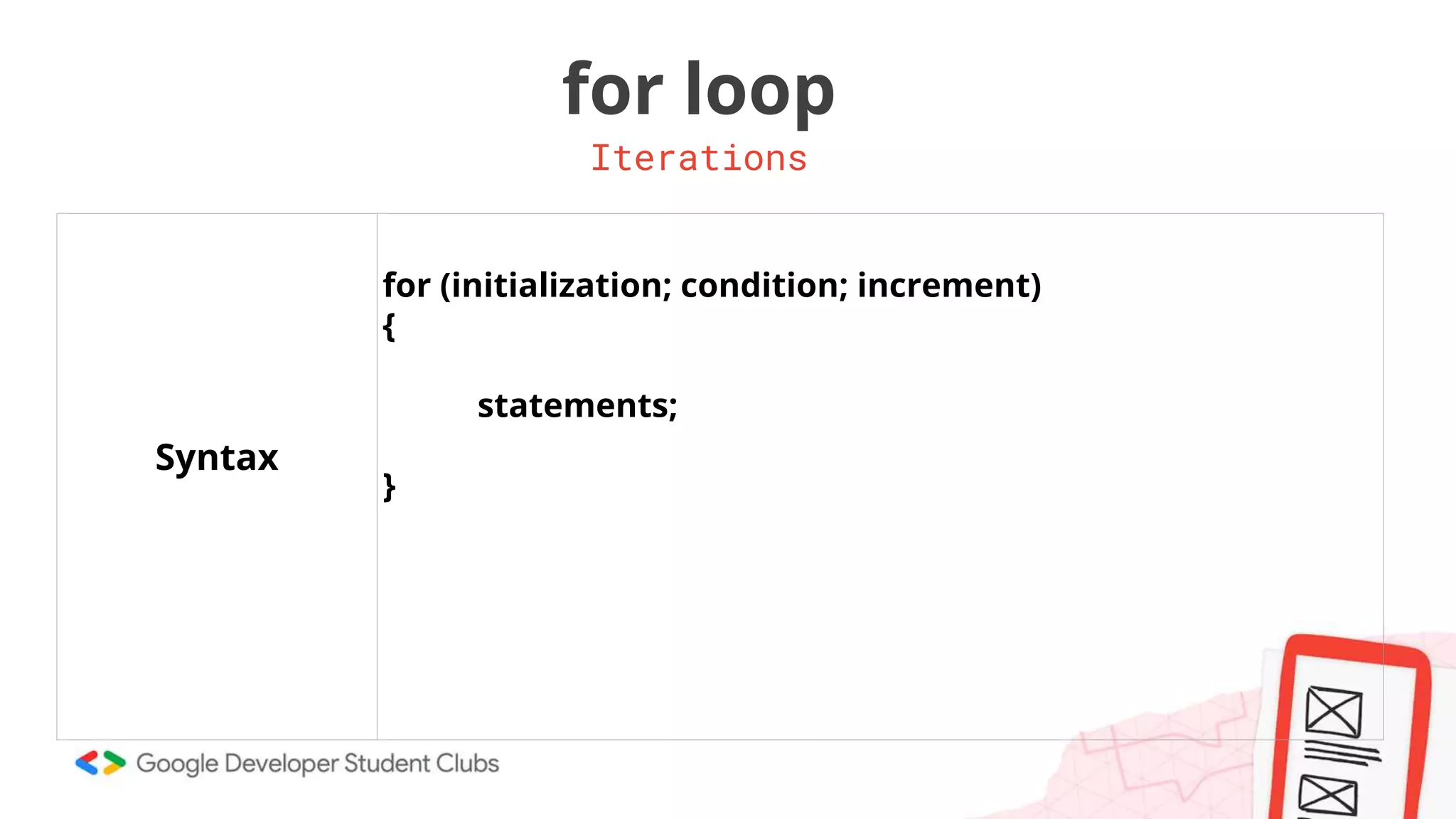
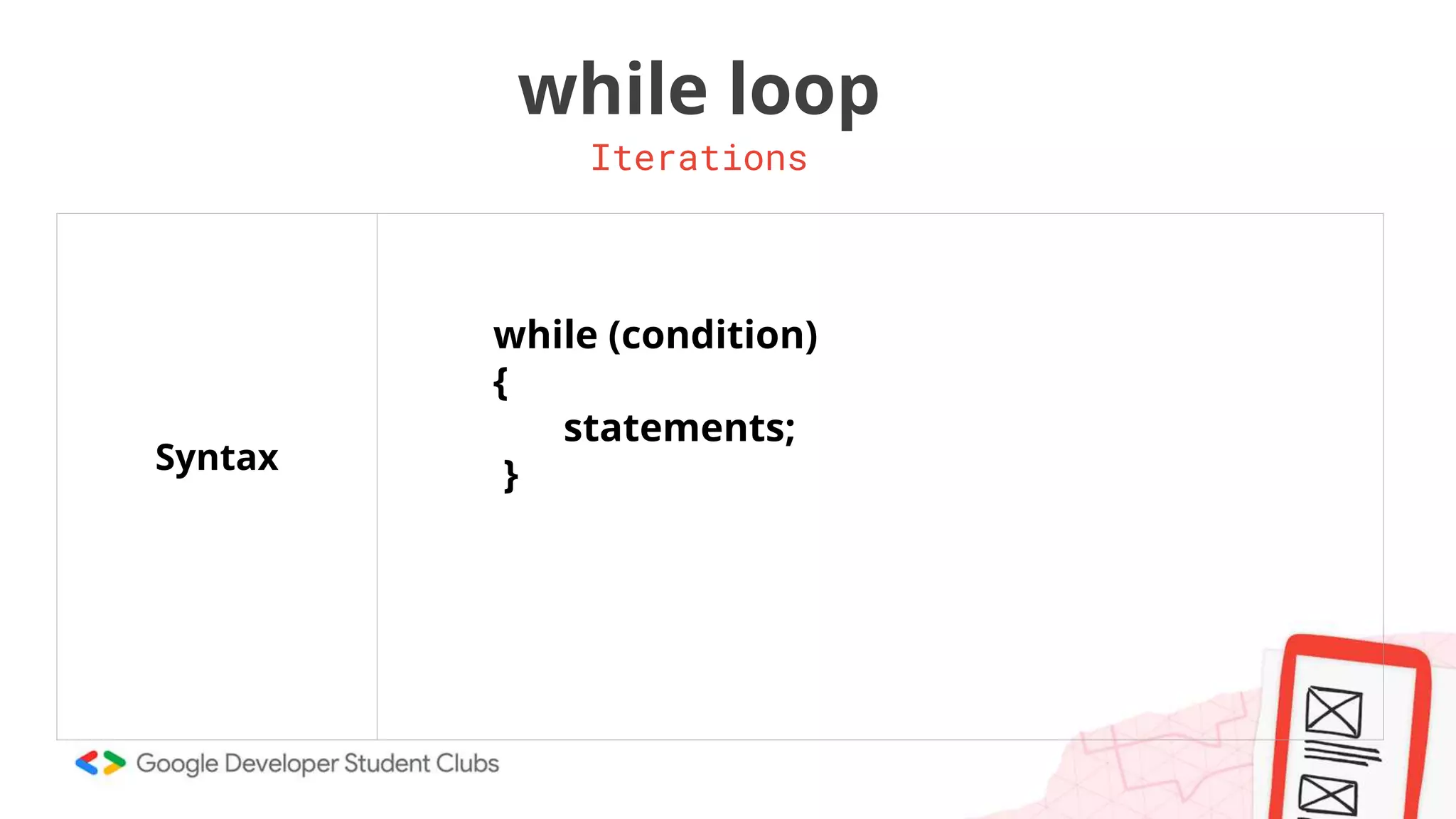
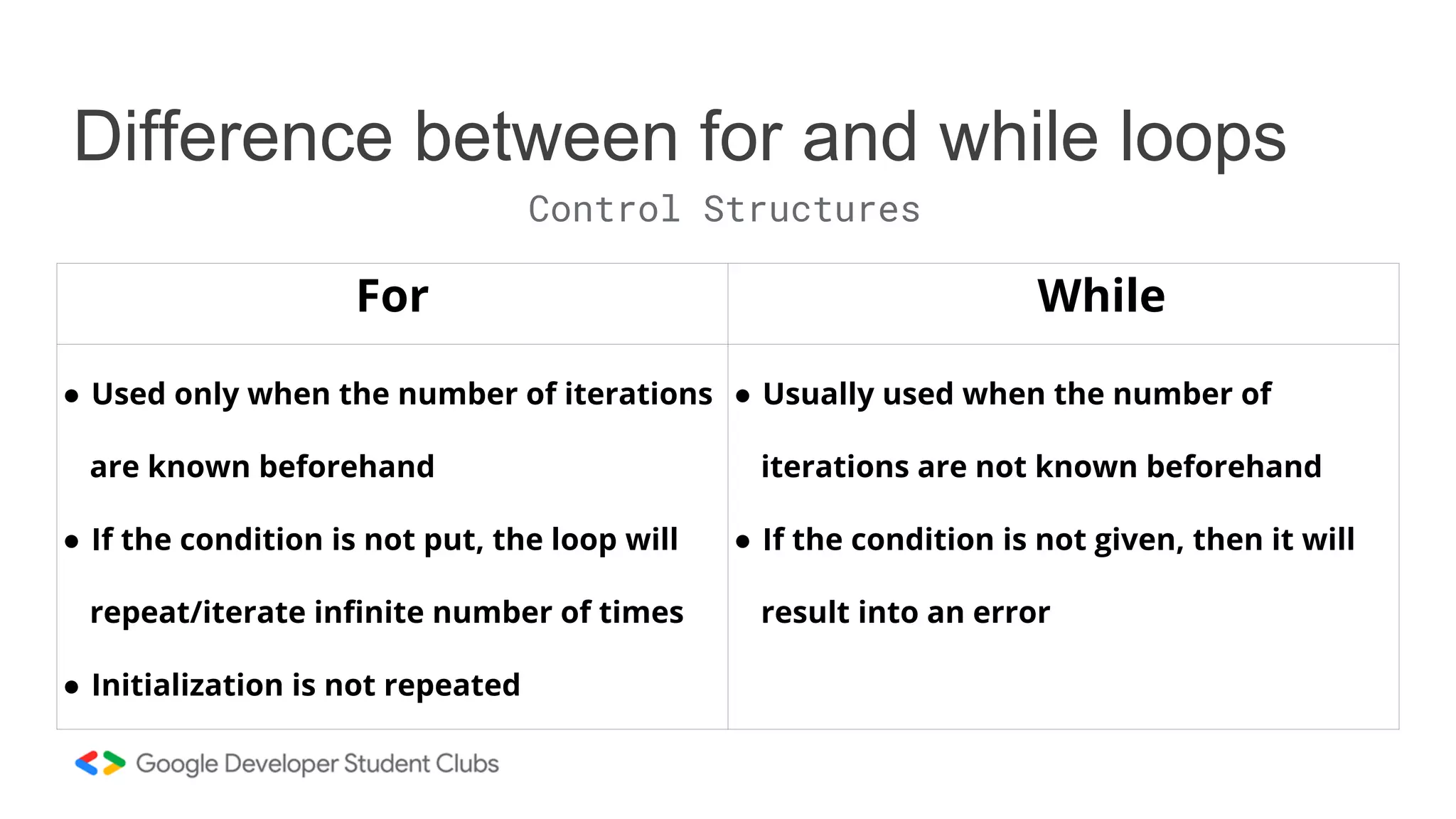
This document provides an introduction to coding, specifically focusing on the C programming language. It outlines key concepts such as the purpose of coding, types of variables, data types, control structures, and the syntax used for various programming functions. The content emphasizes the importance of coding in problem-solving and creativity, while also detailing practical coding examples.