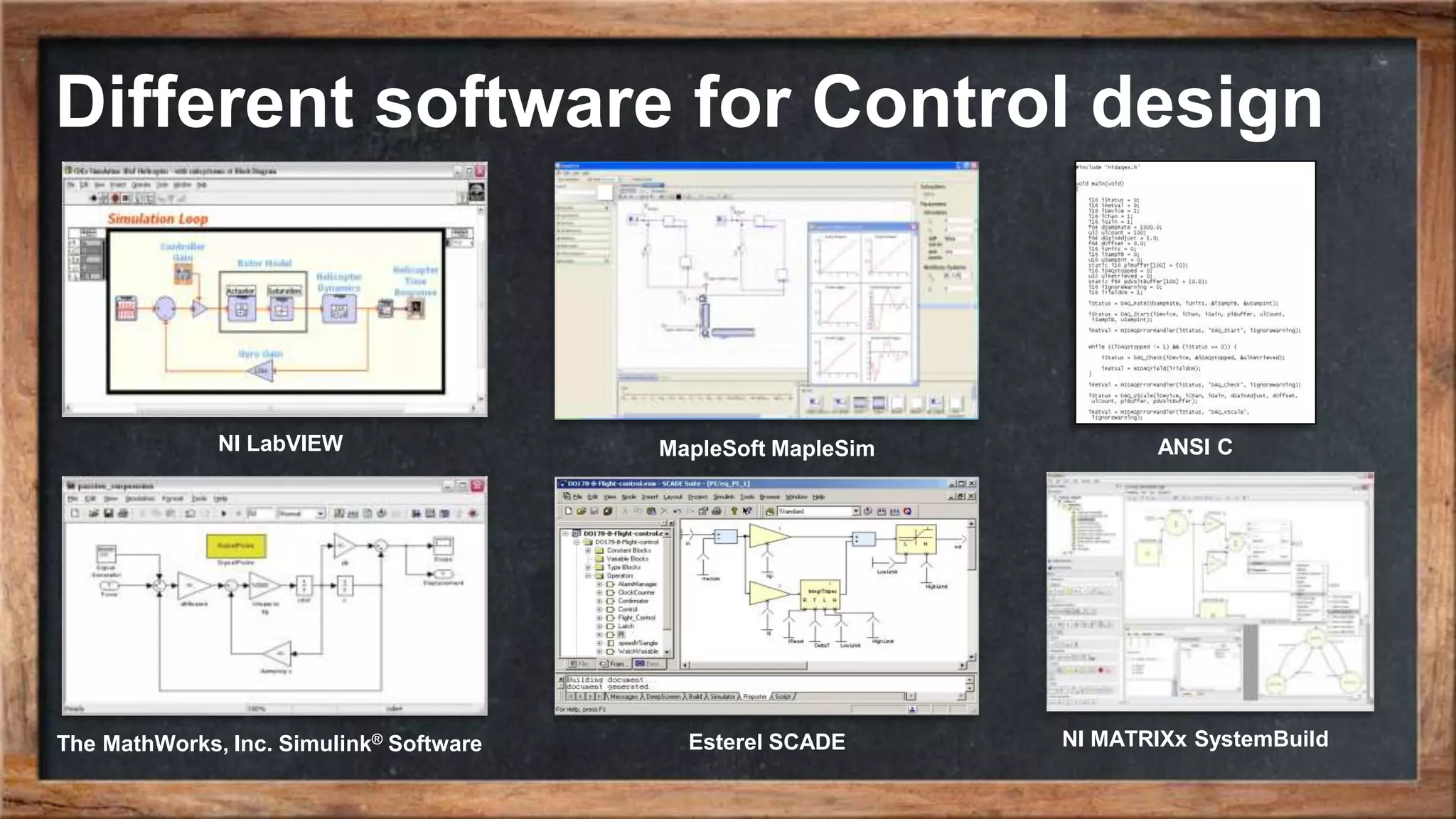
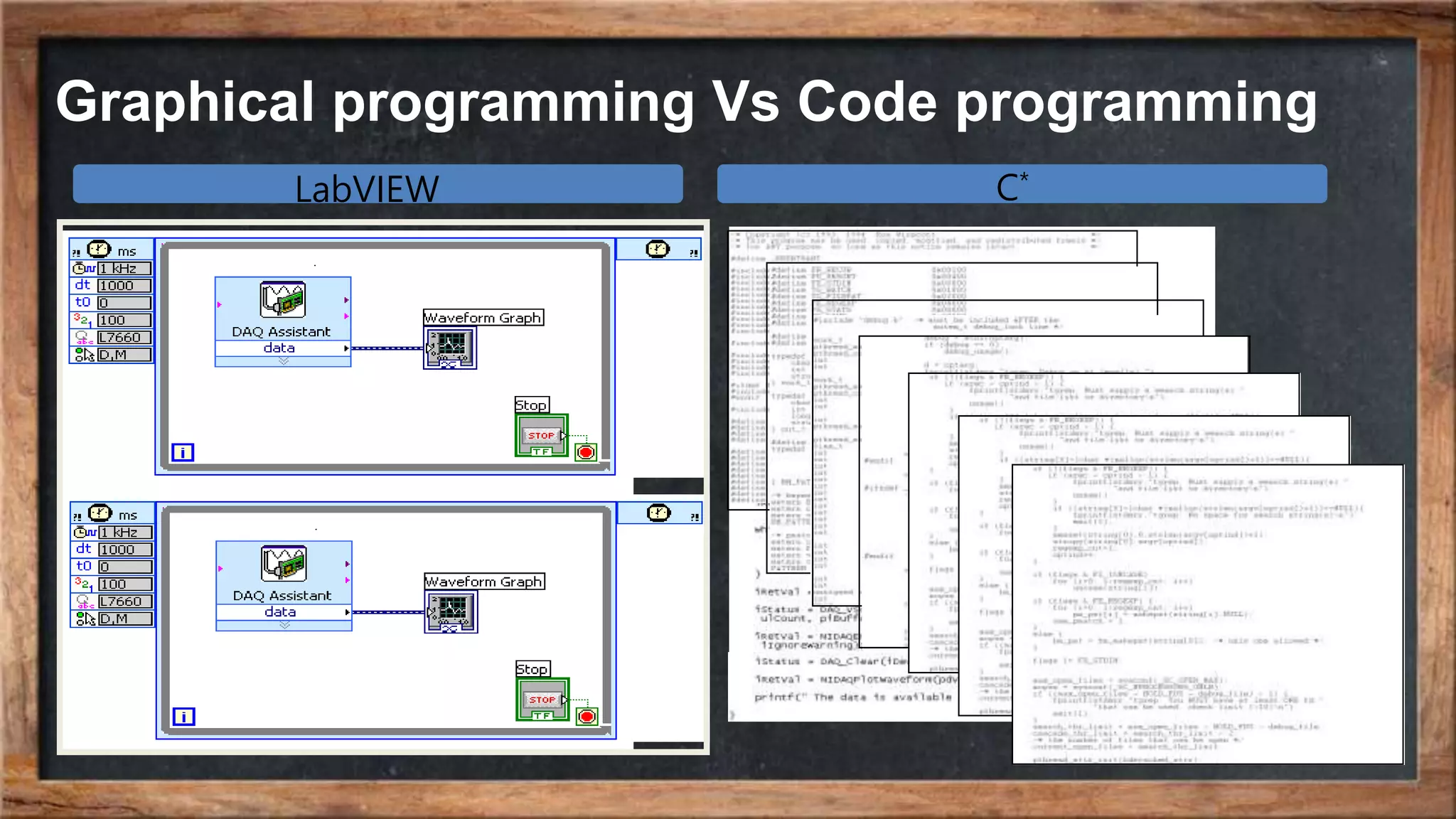
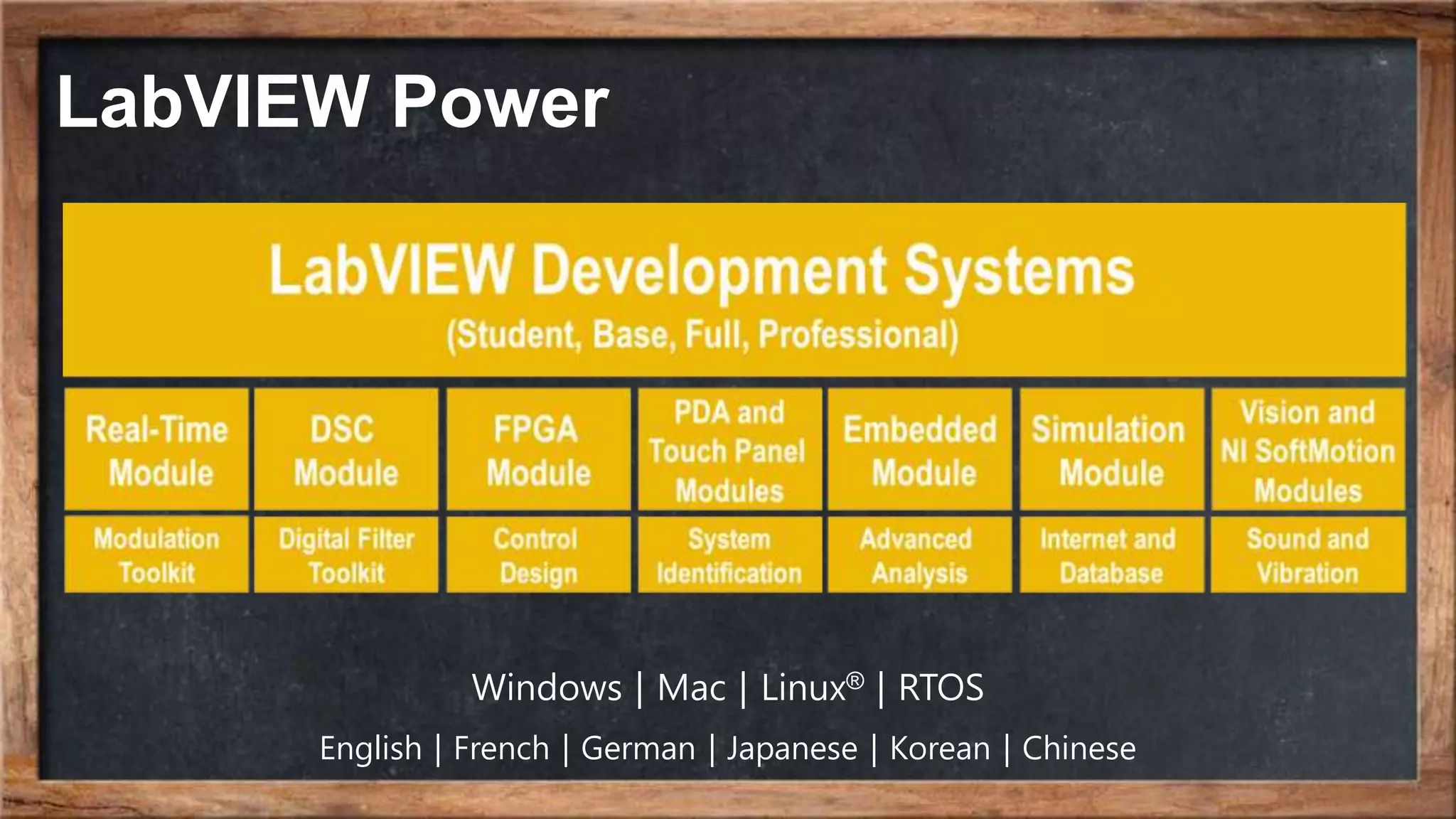
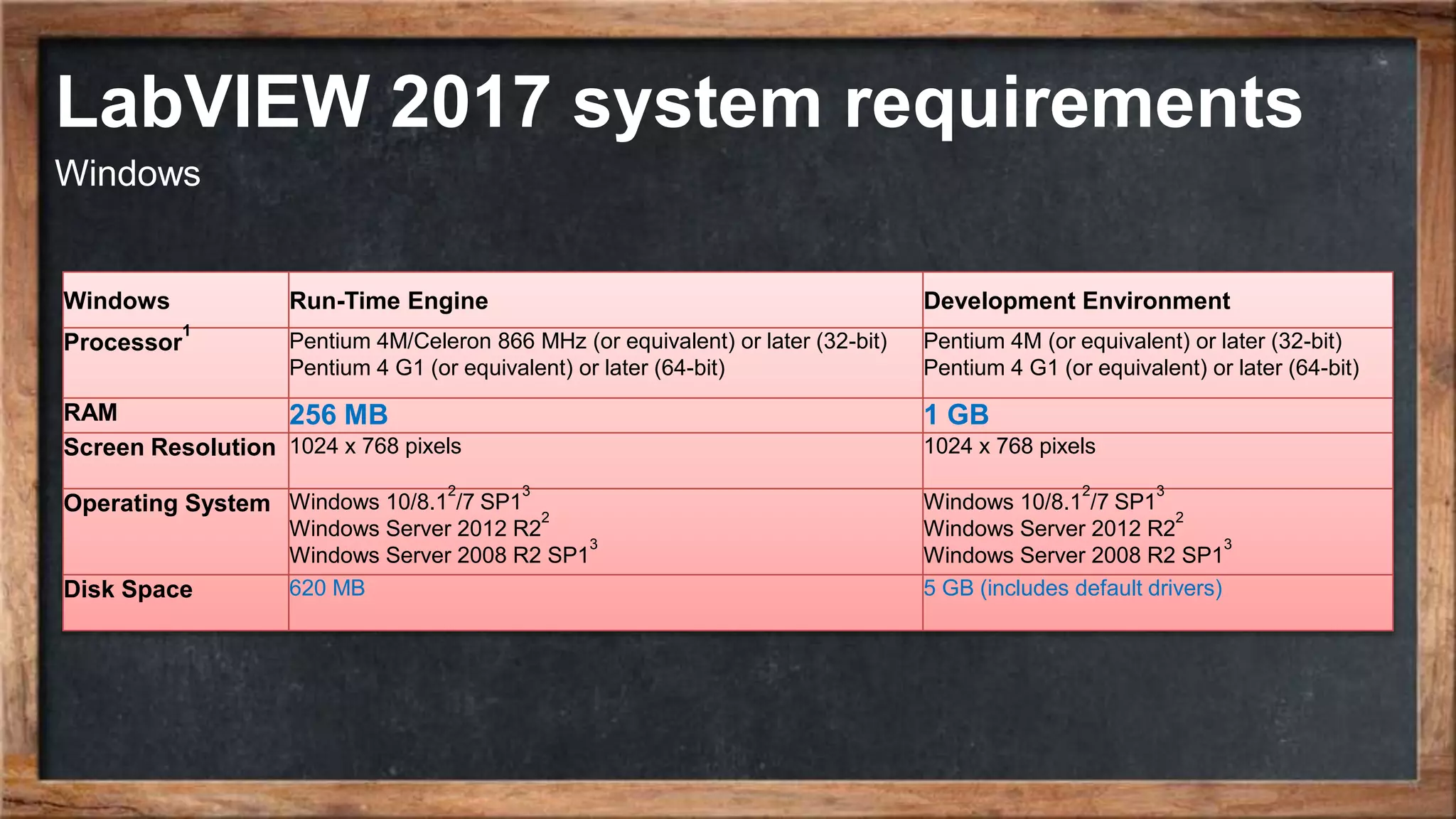
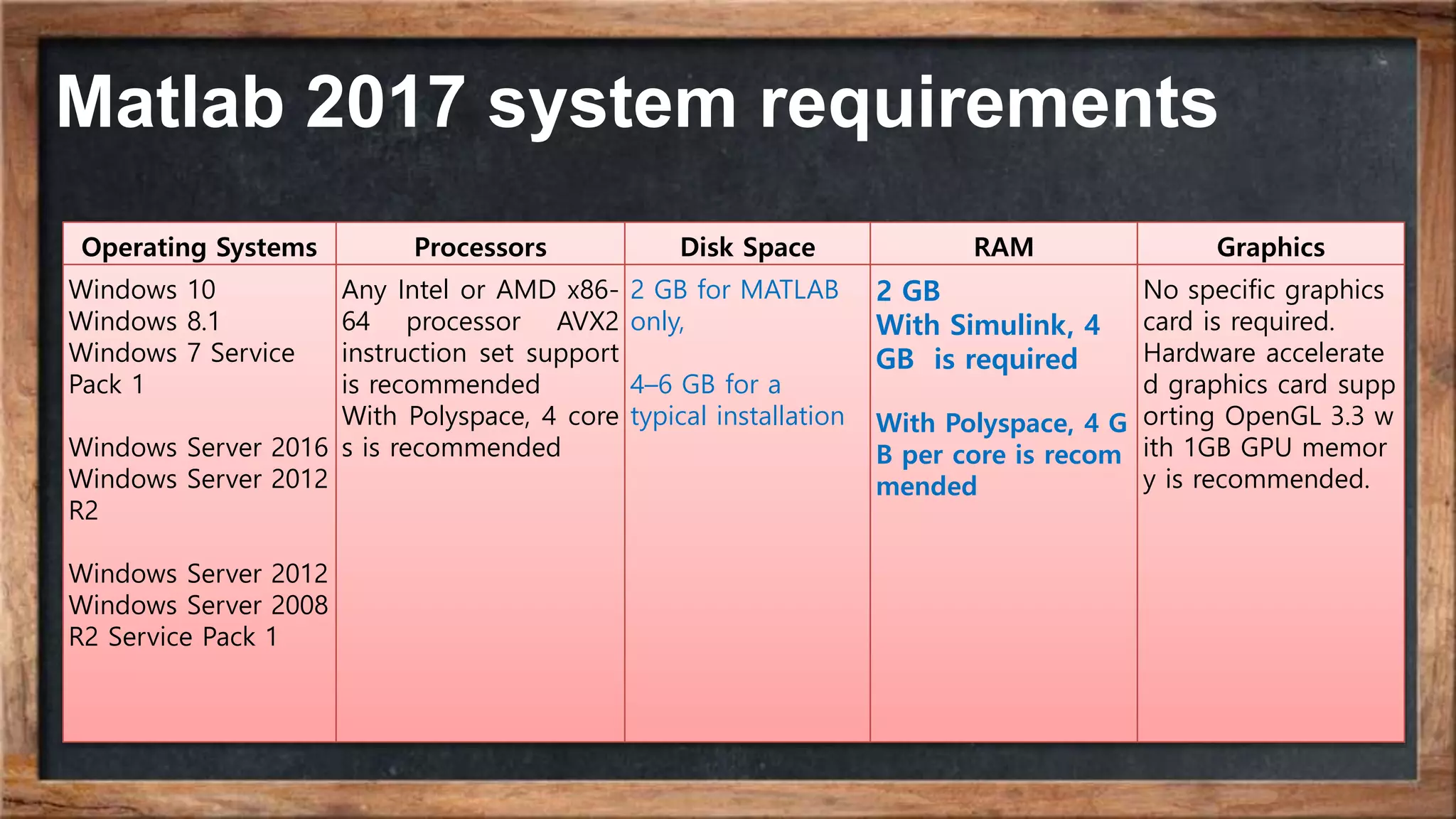
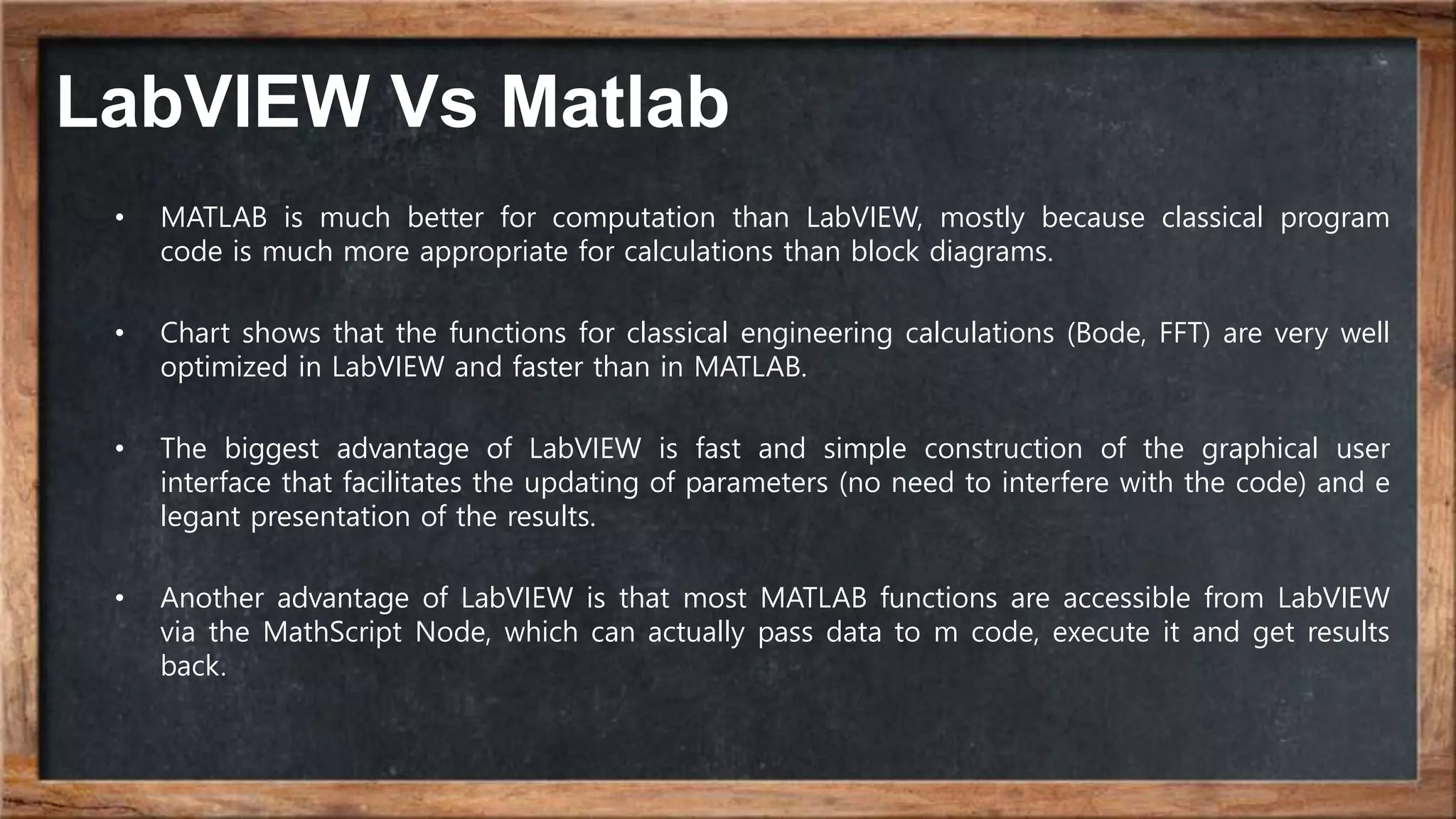
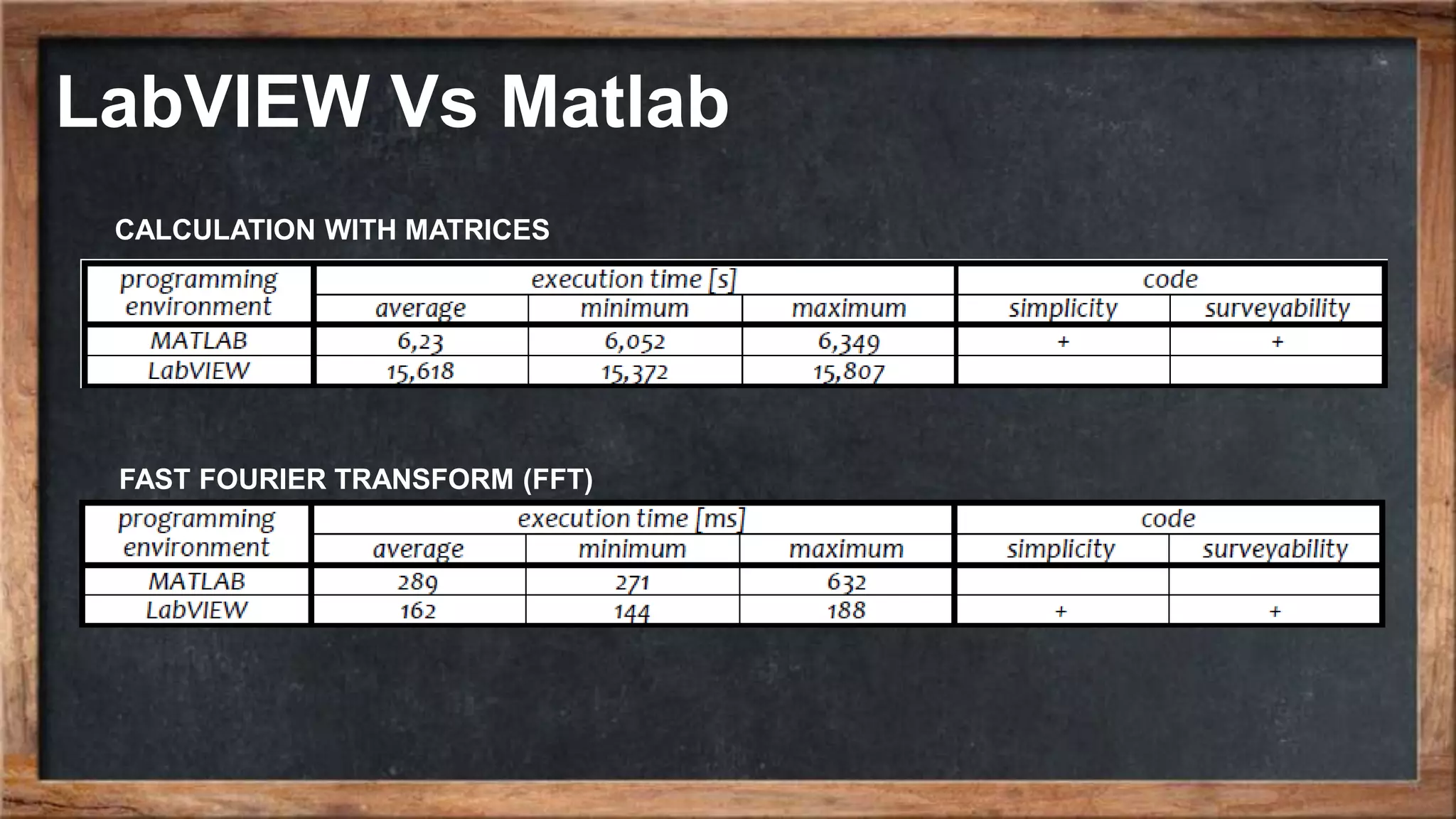
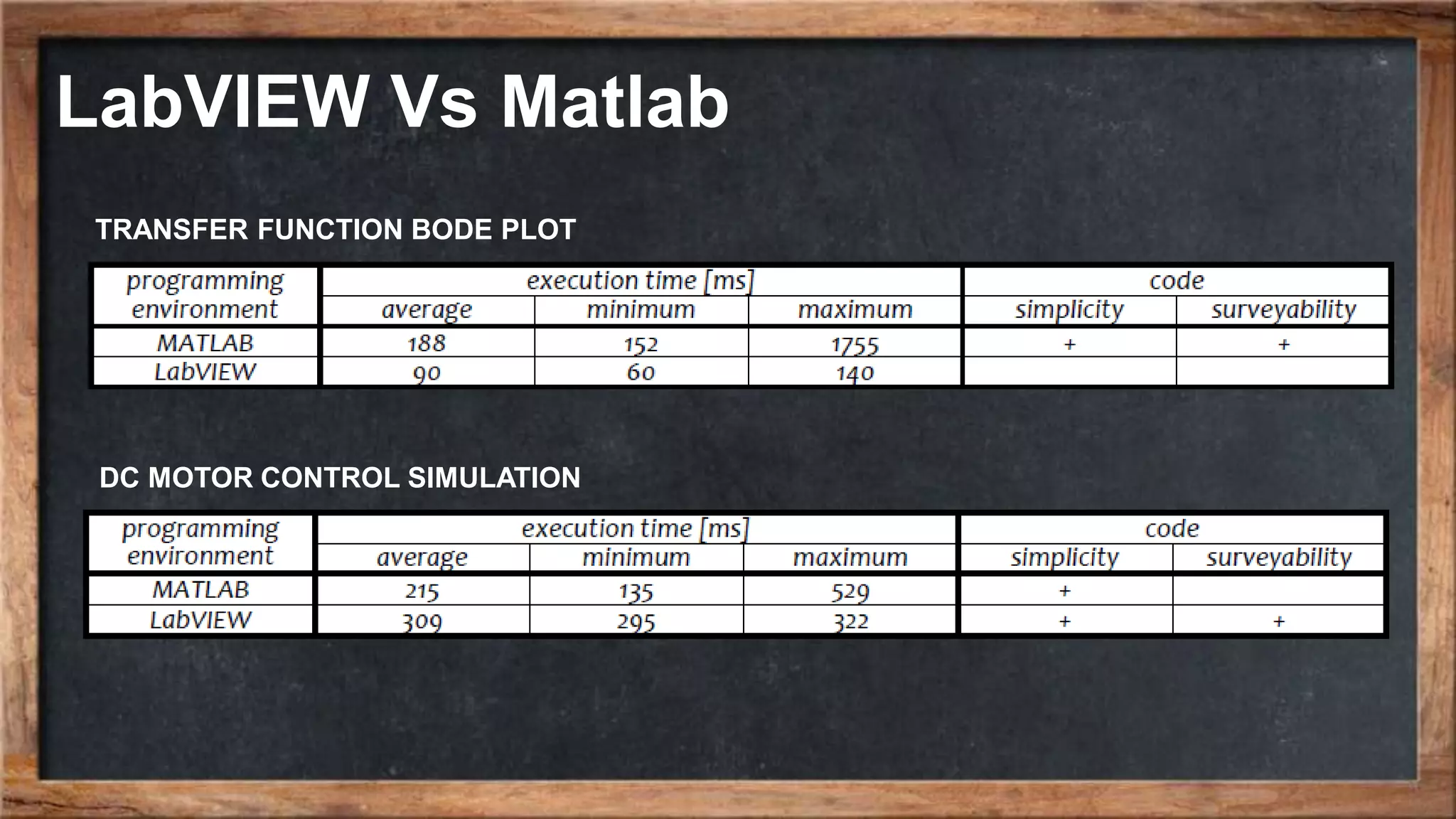
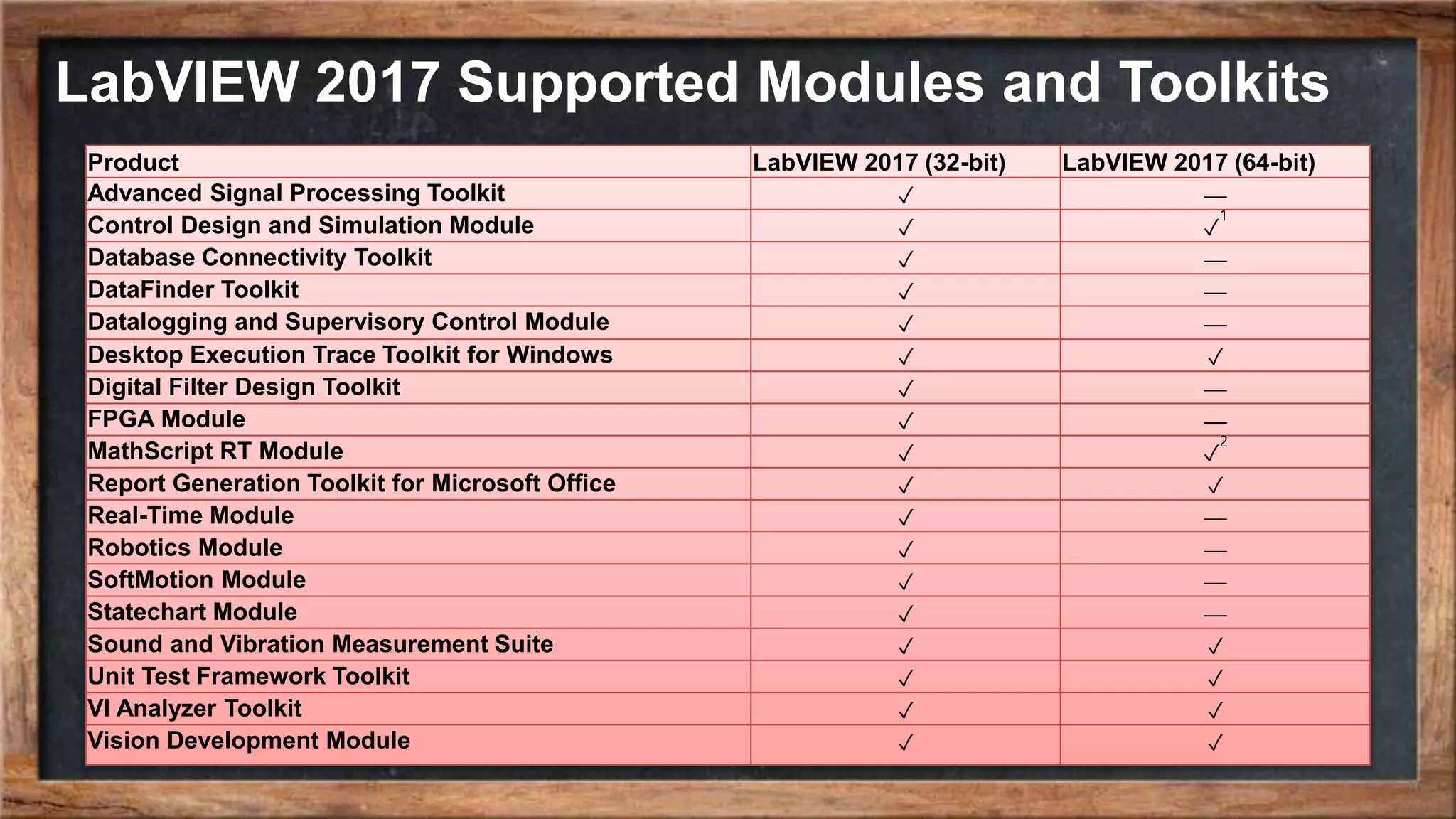
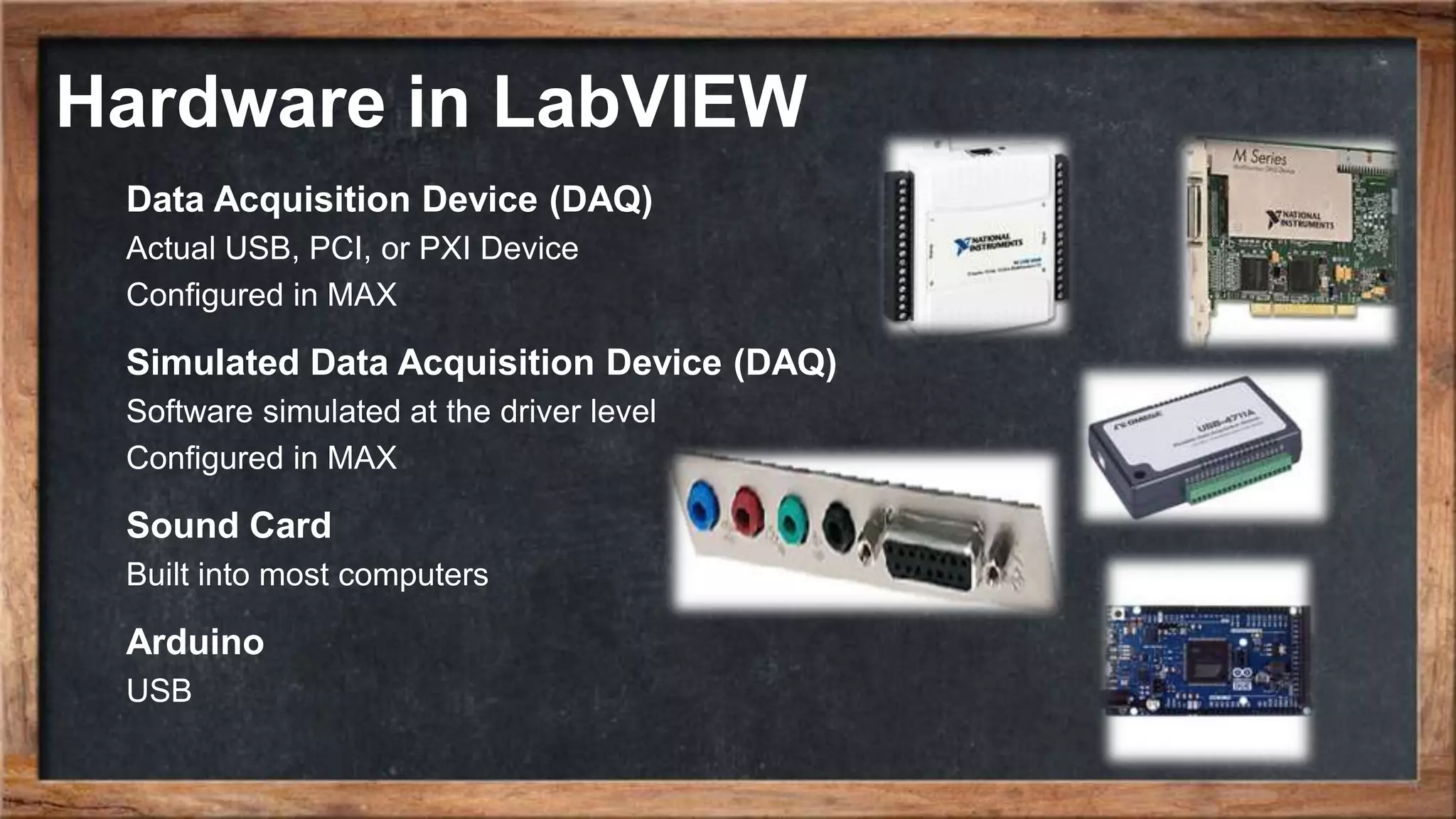
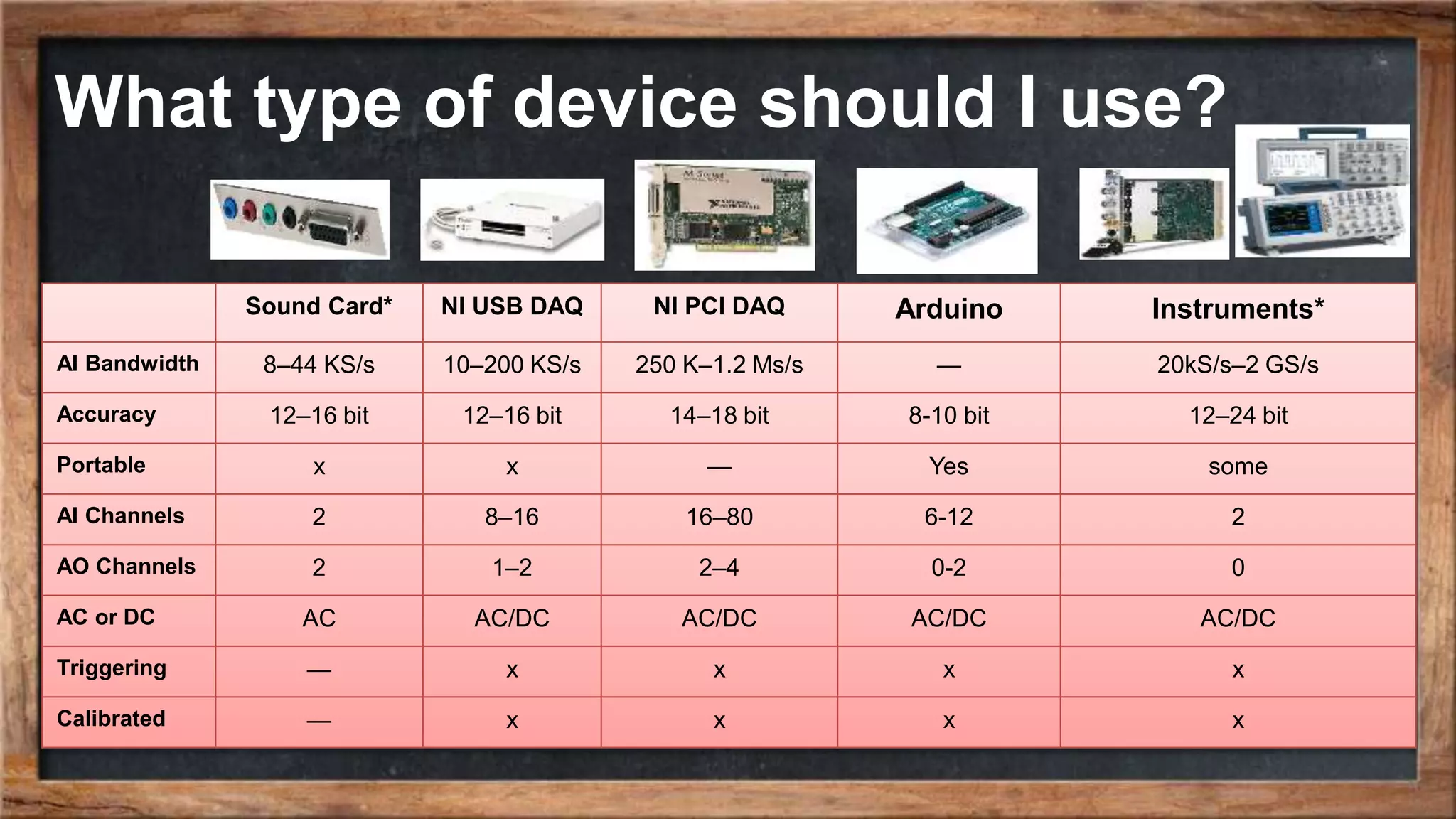
The document outlines the course overview for control and robotics applications at Shiraz University, covering various software tools such as LabVIEW and MATLAB, along with their functionalities and system requirements. It details project deadlines and scoring criteria for assignments, emphasizing the use of graphical programming in LabVIEW compared to MATLAB's computational strengths. Additionally, the document highlights the features and supported modules of LabVIEW in various applications, including control design, measurements, and hardware integration.