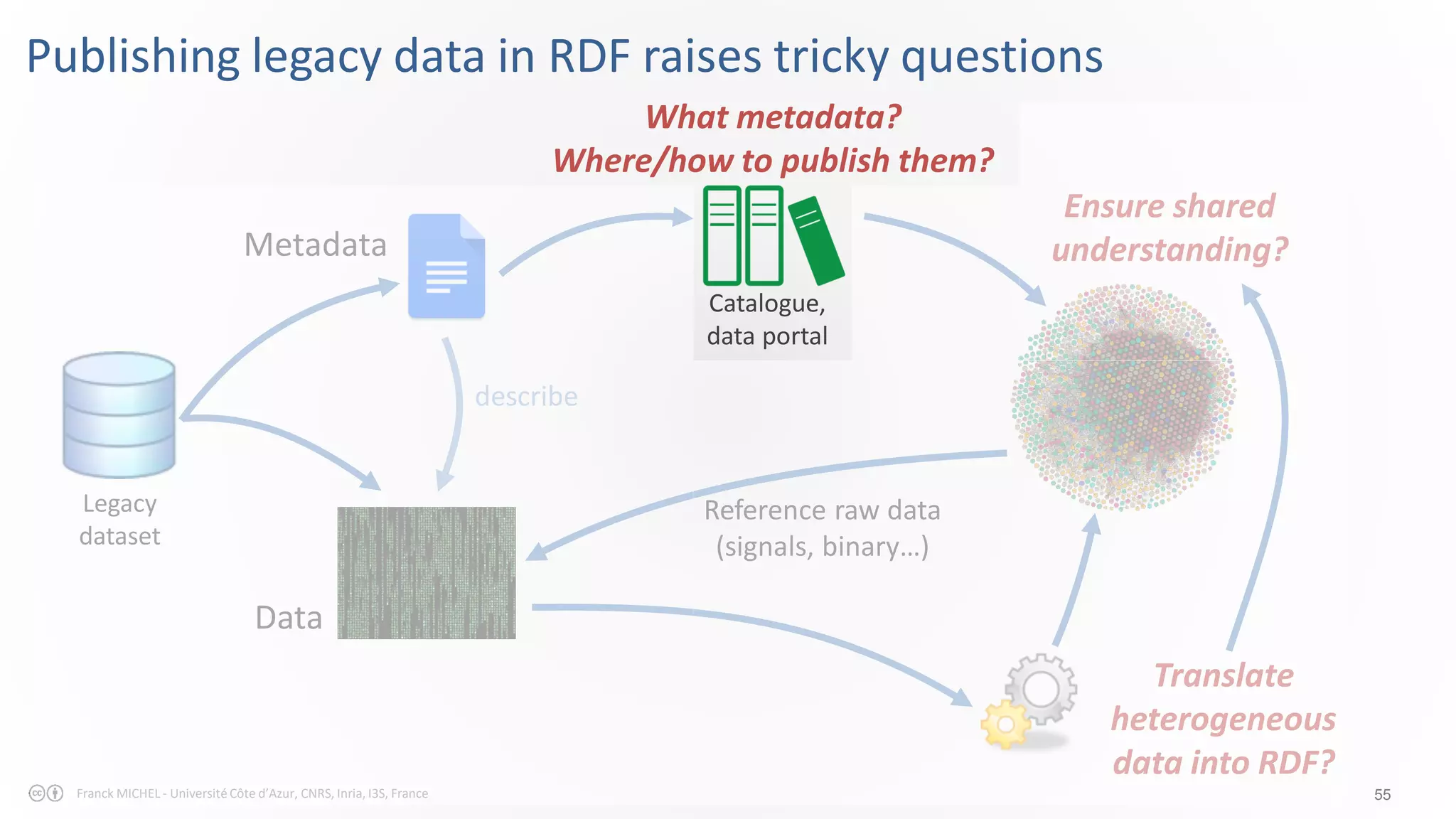
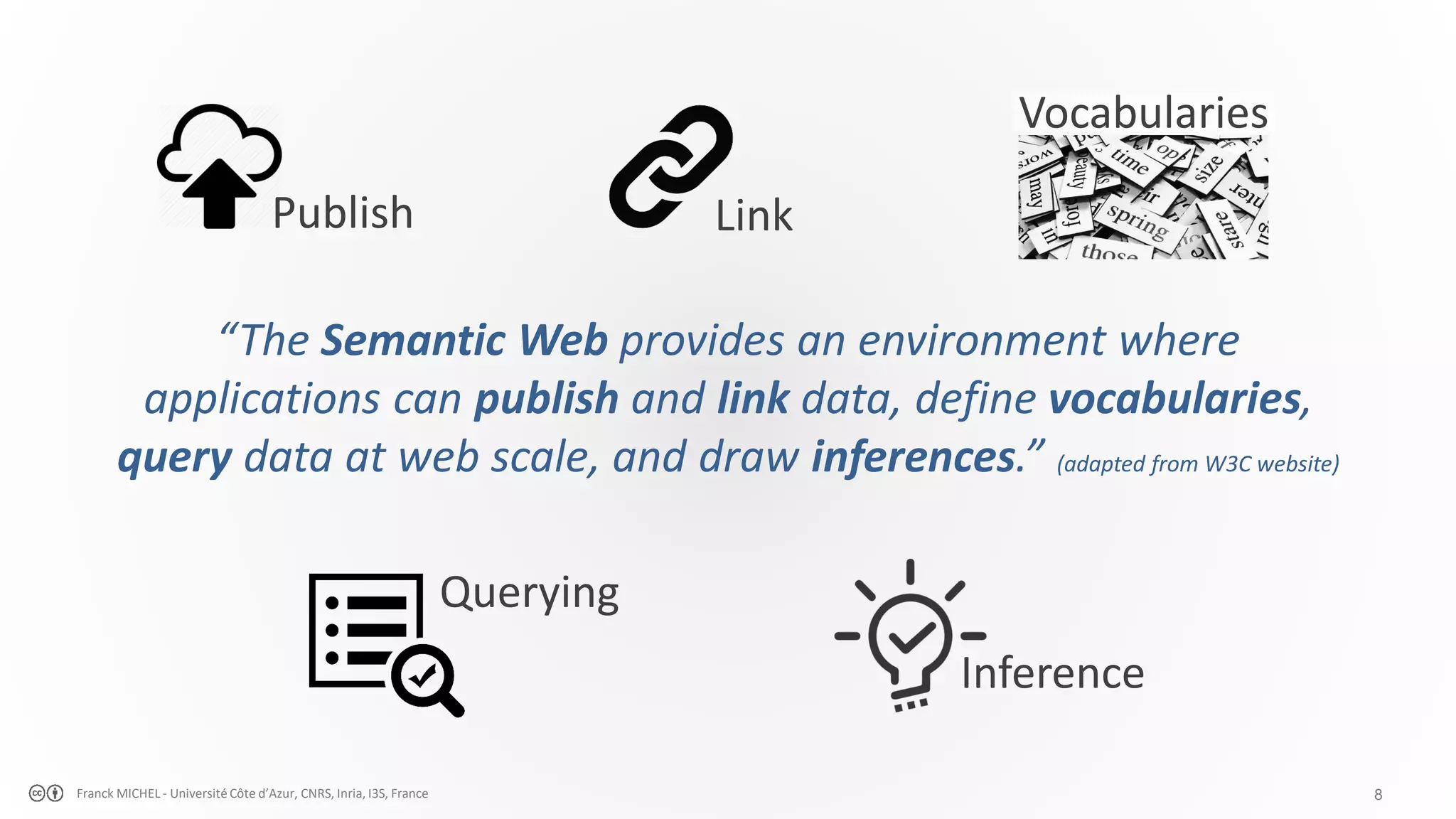
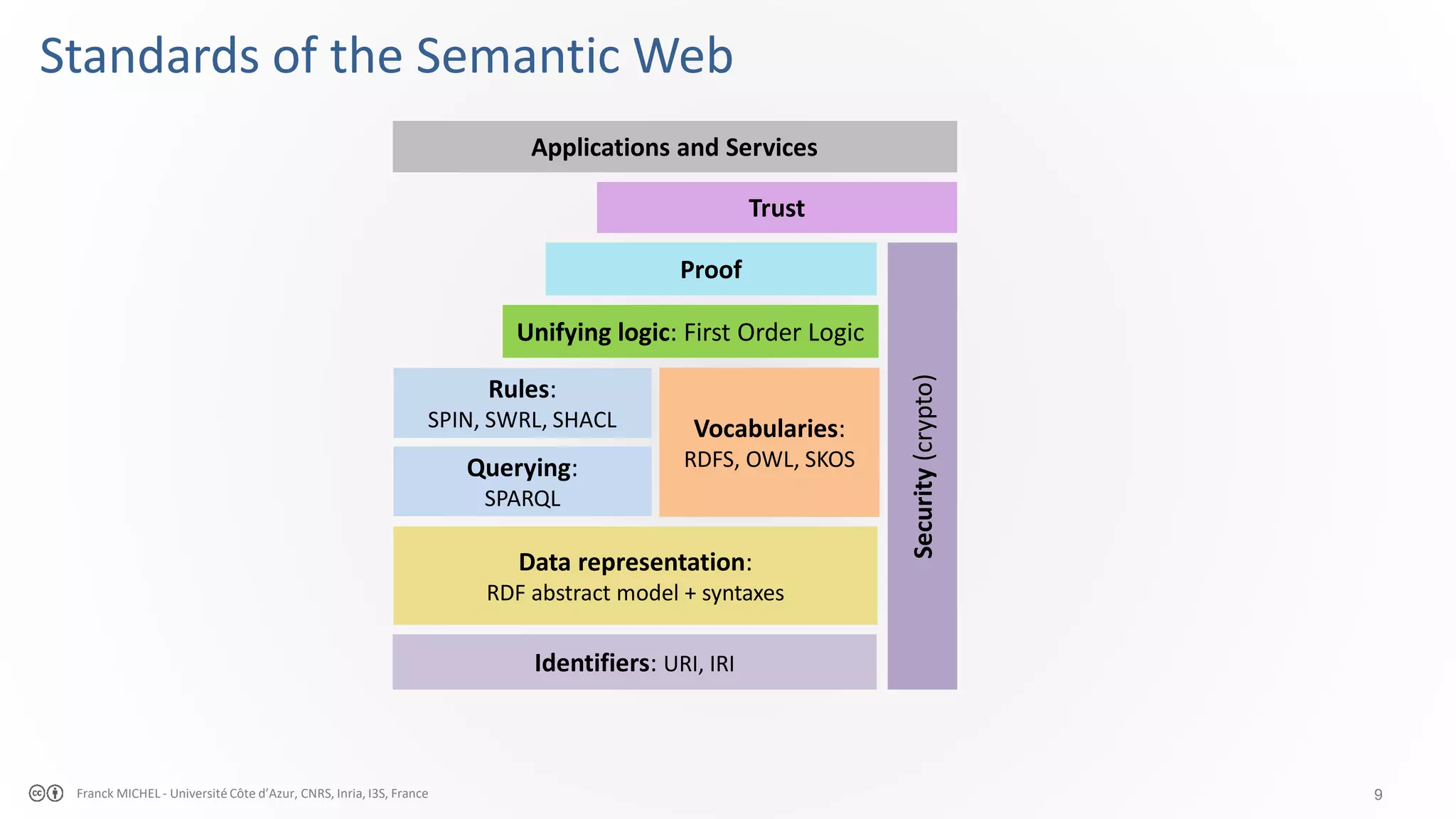
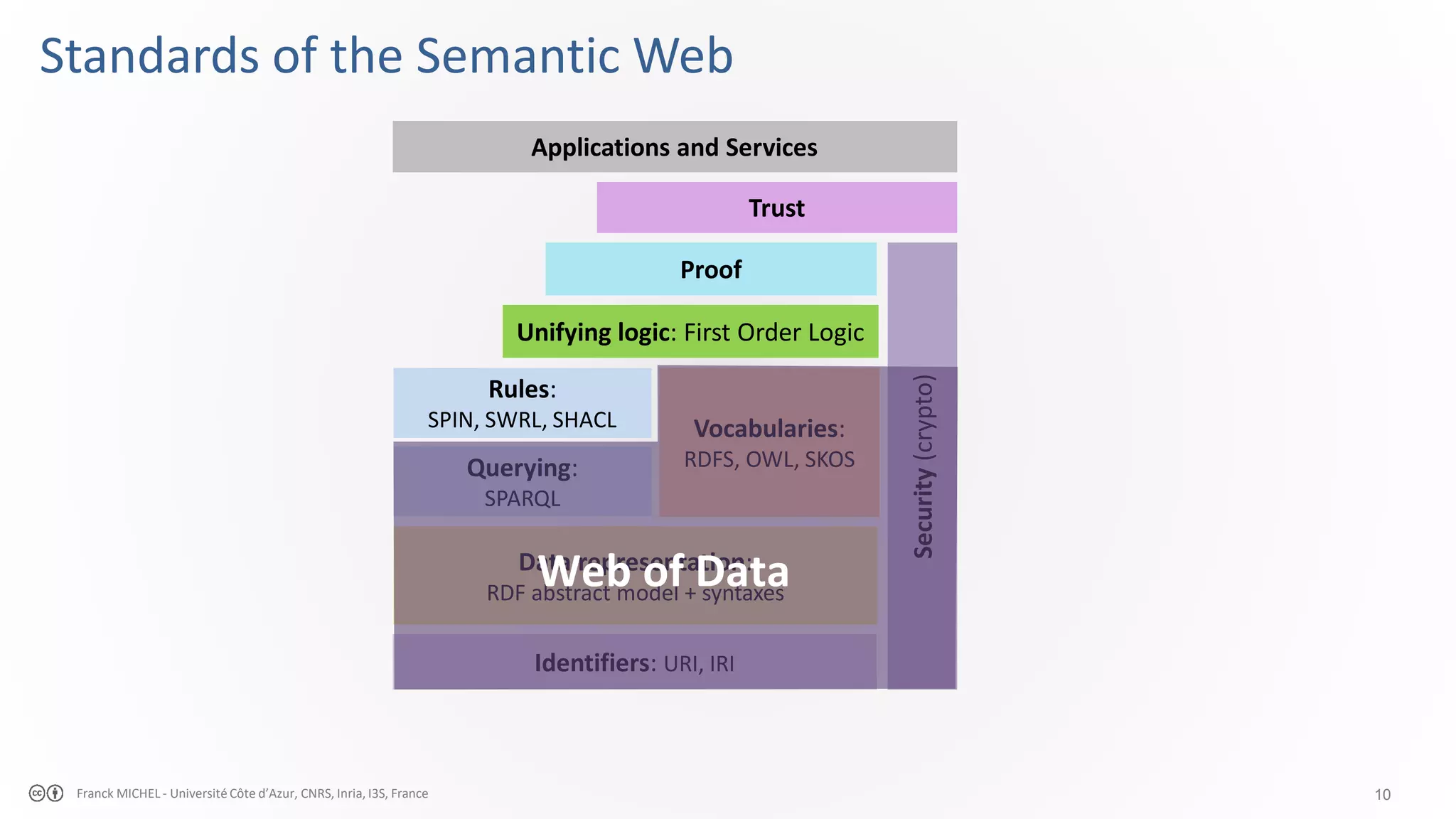
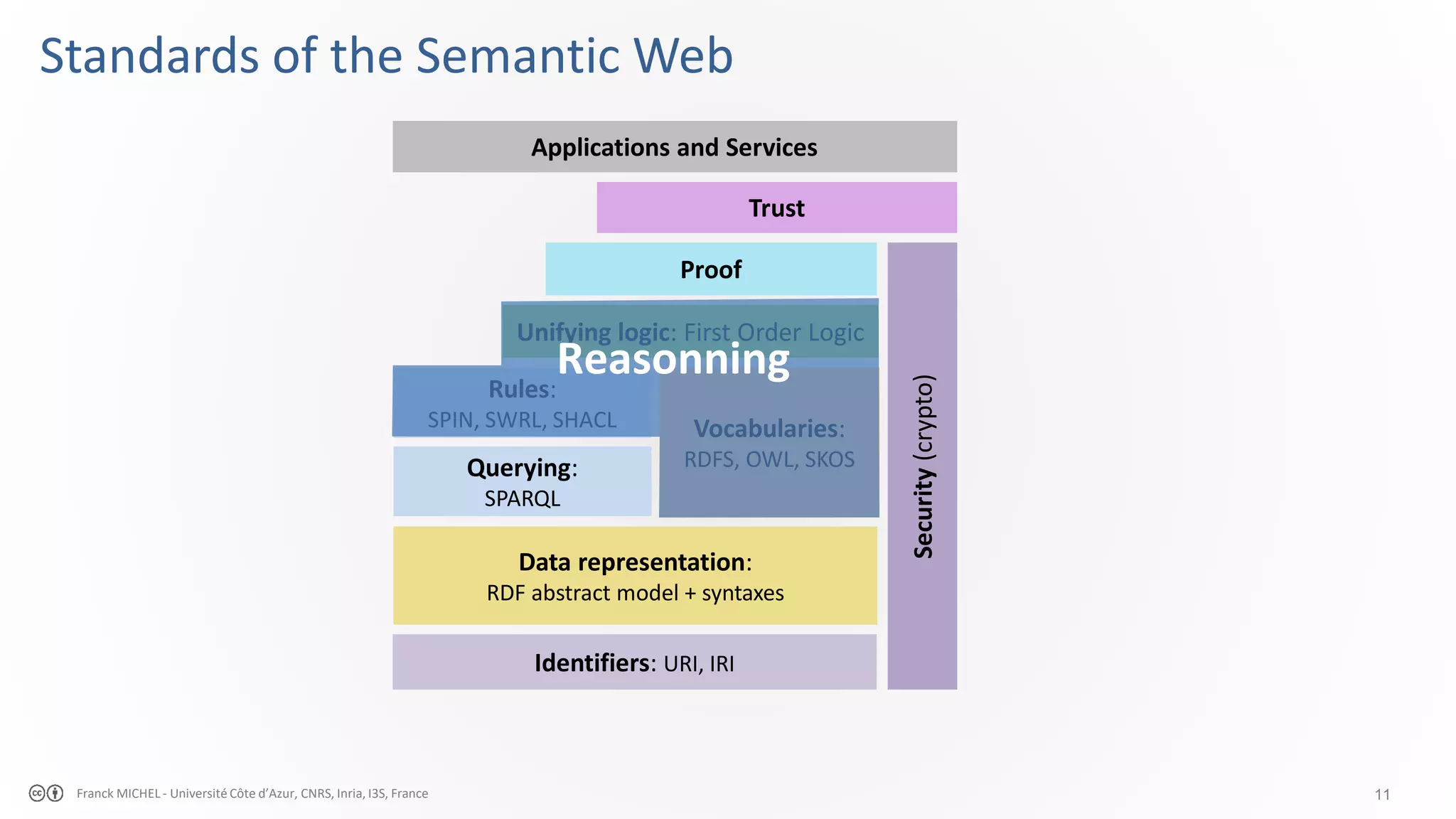
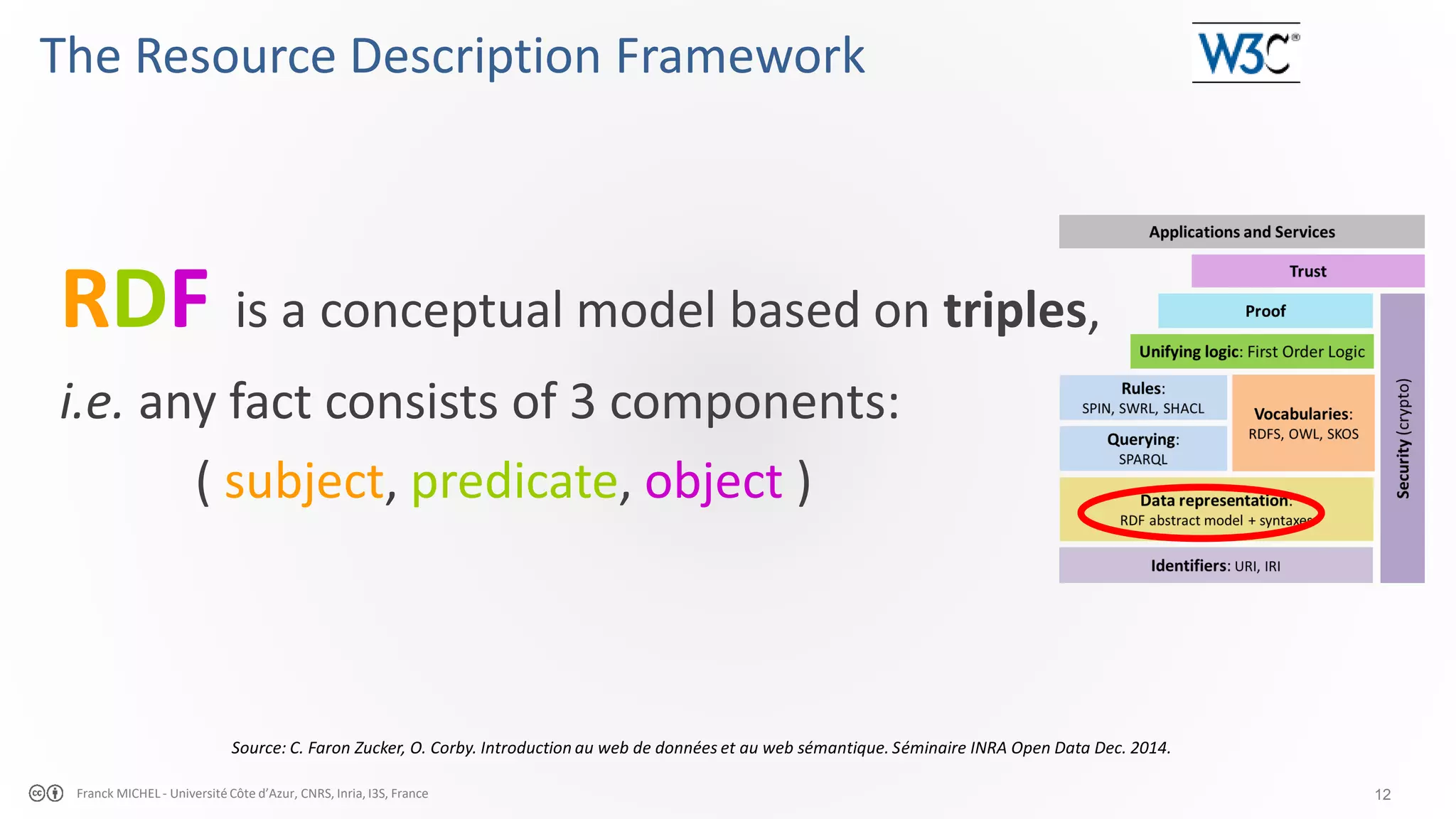
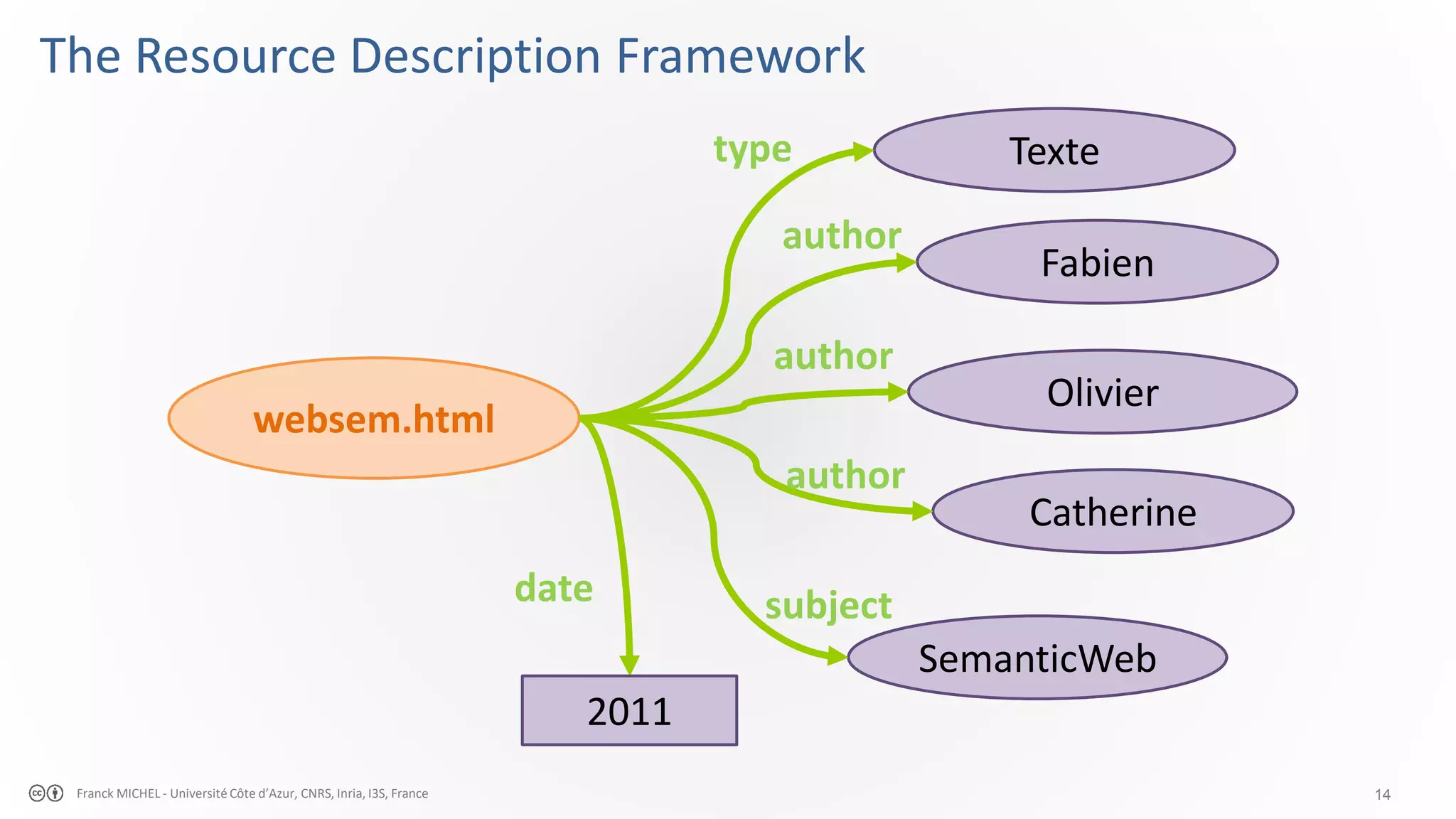
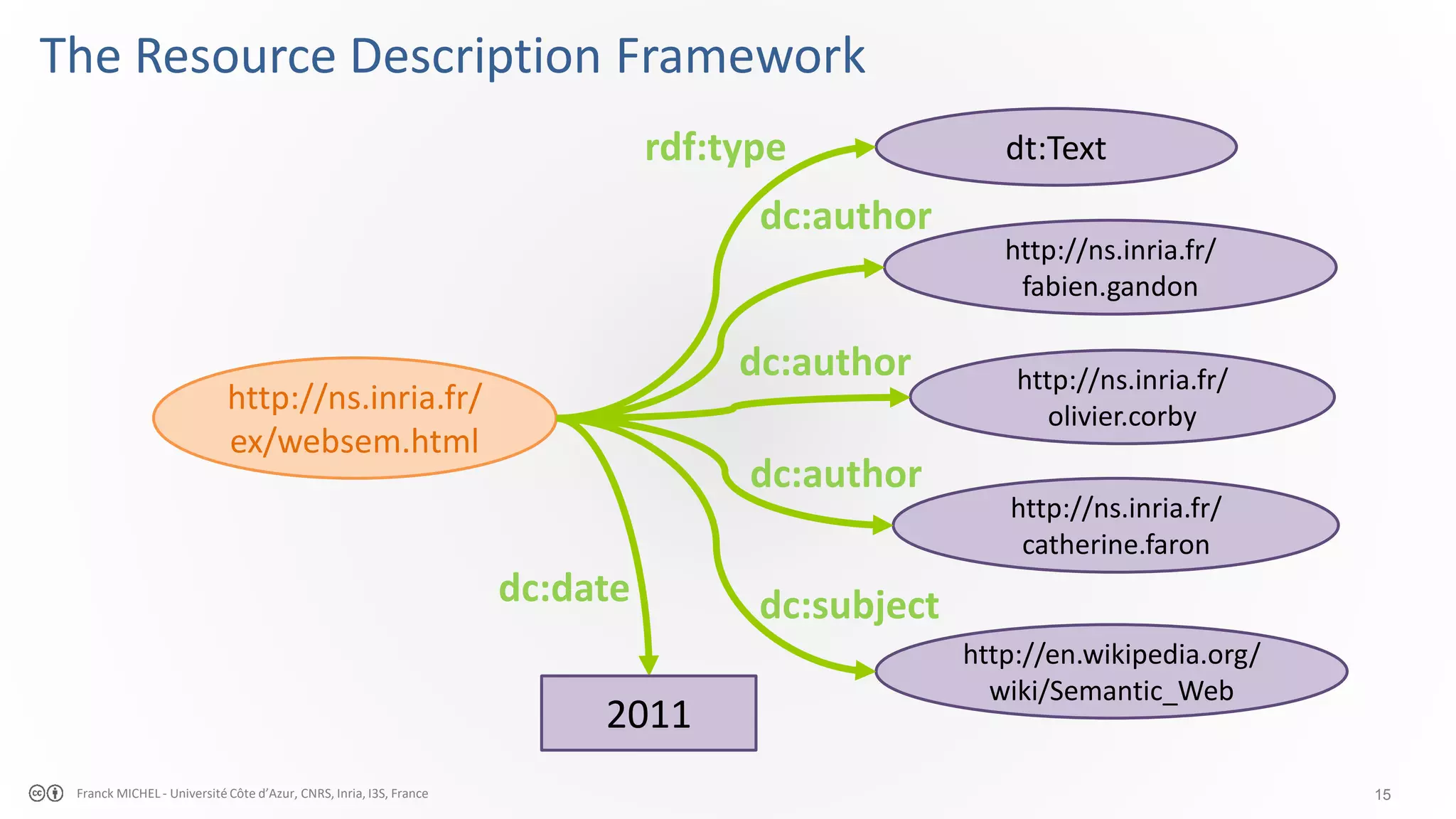
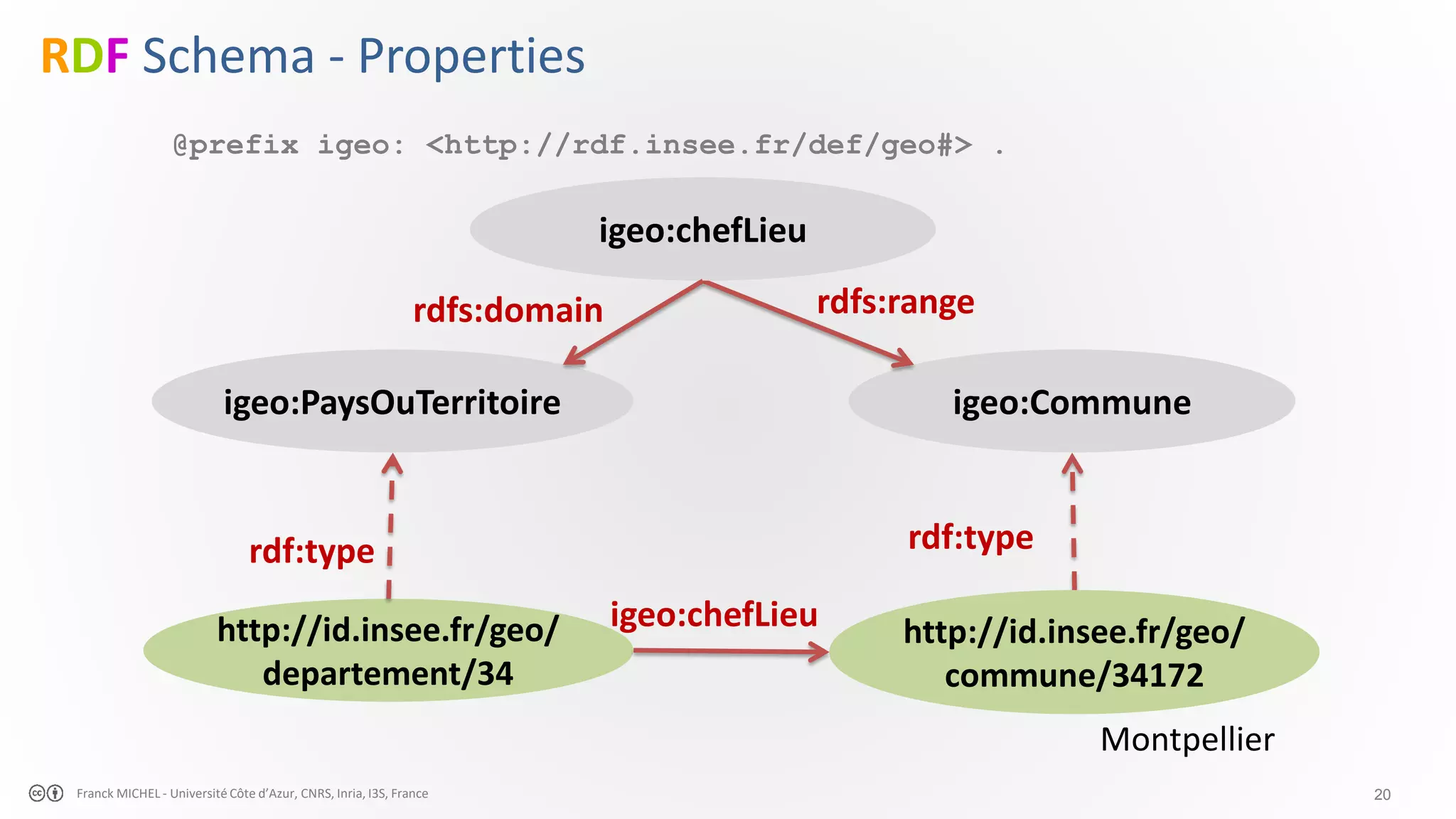
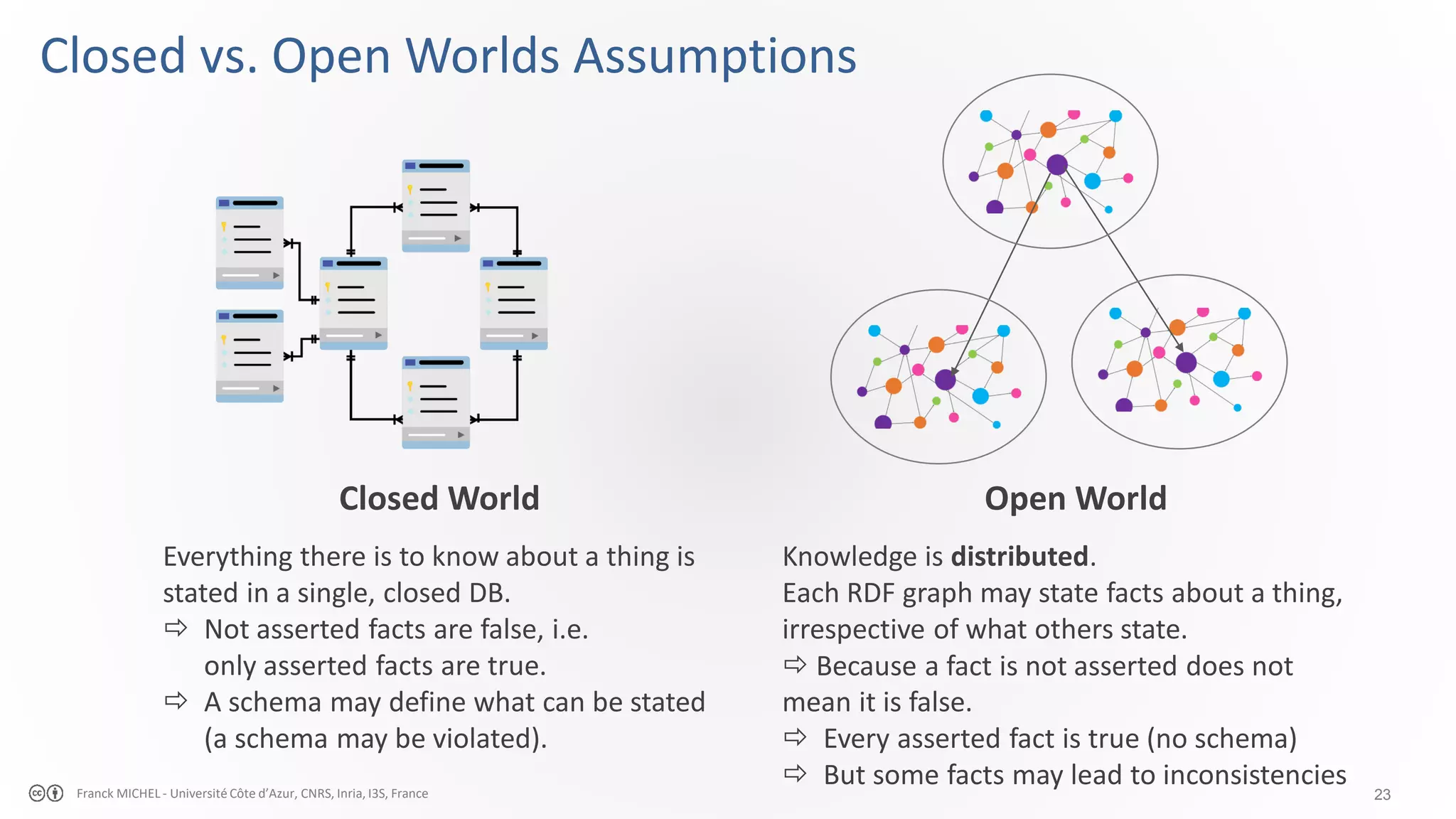
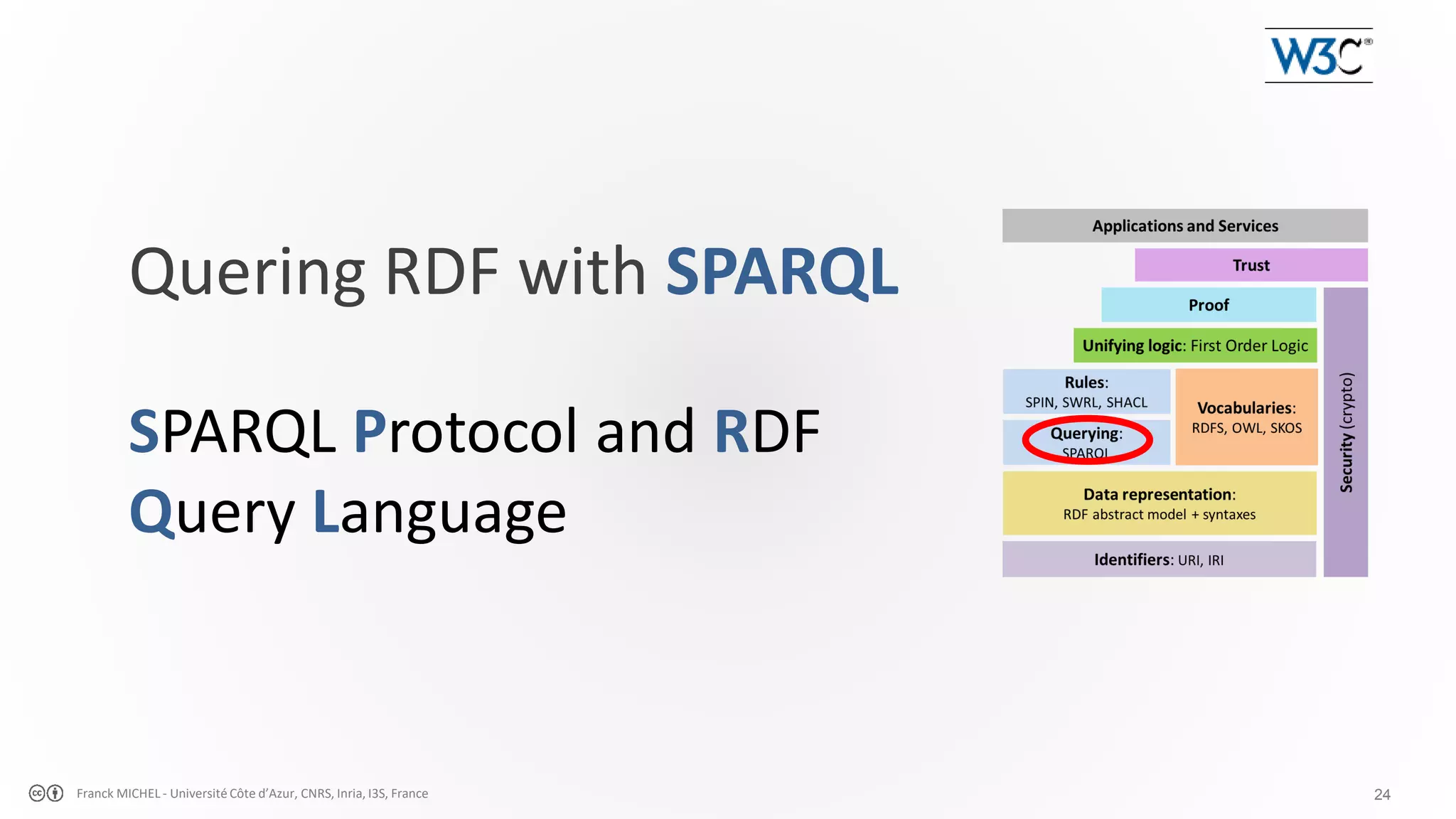
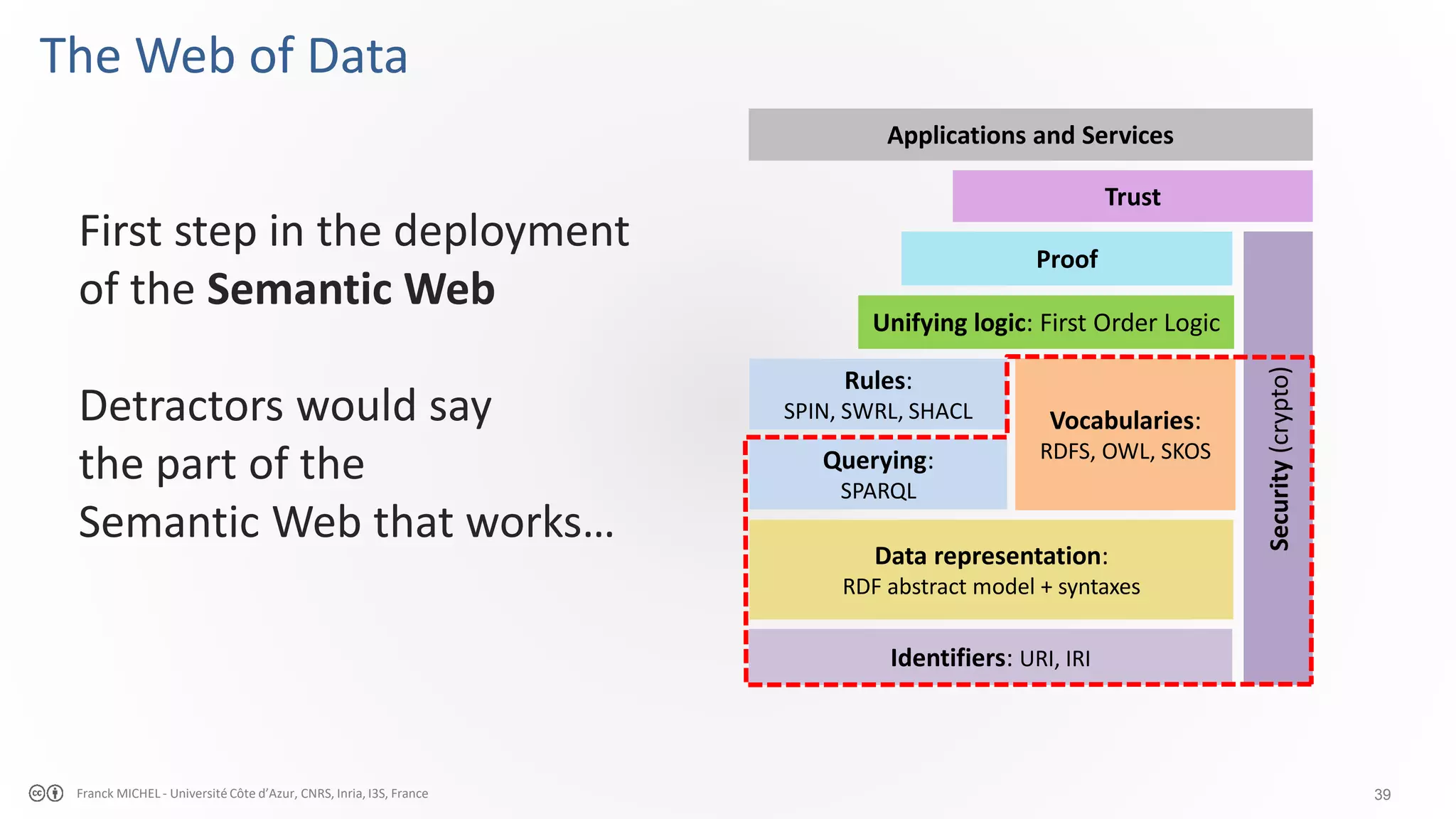
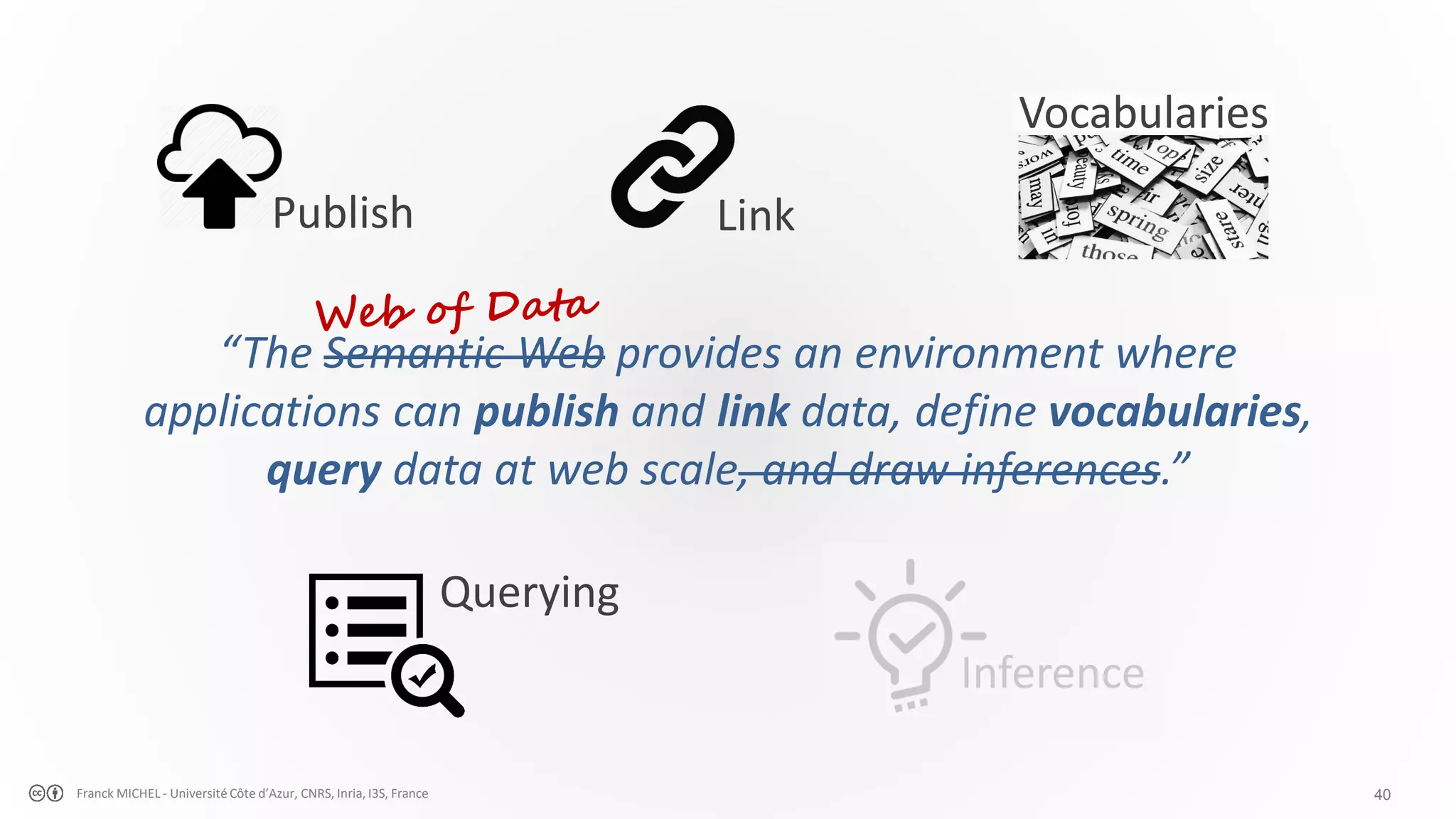
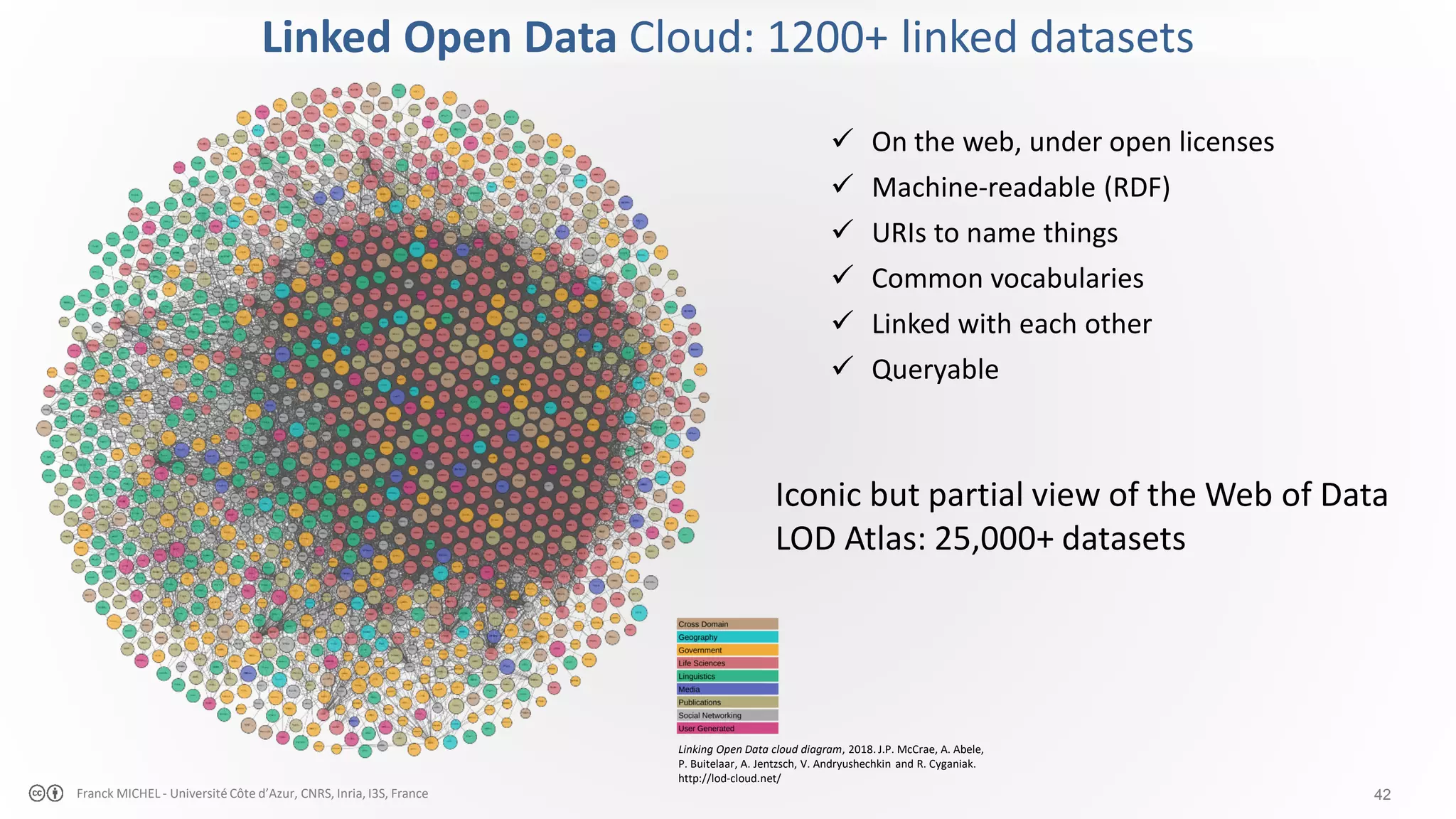
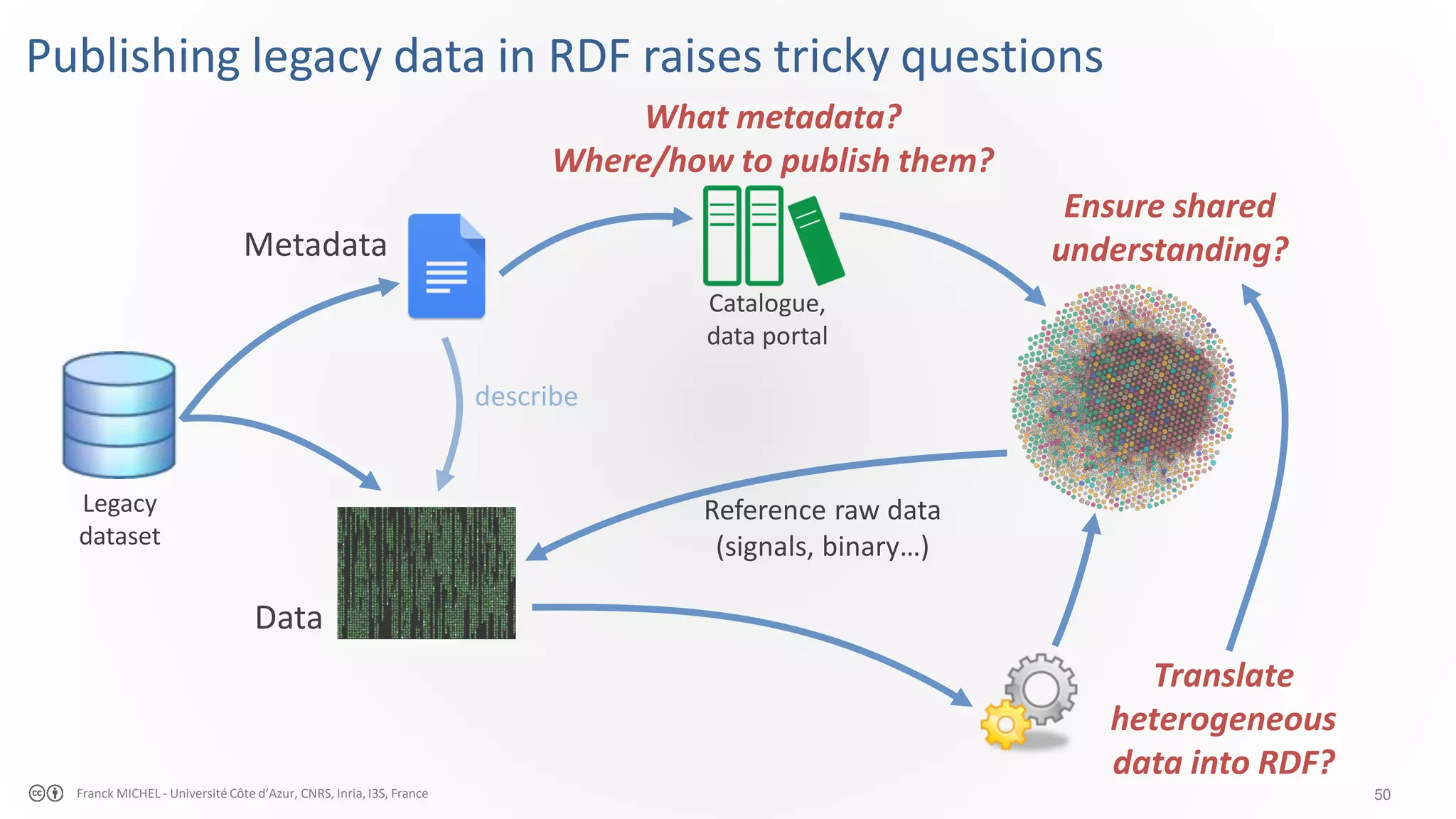
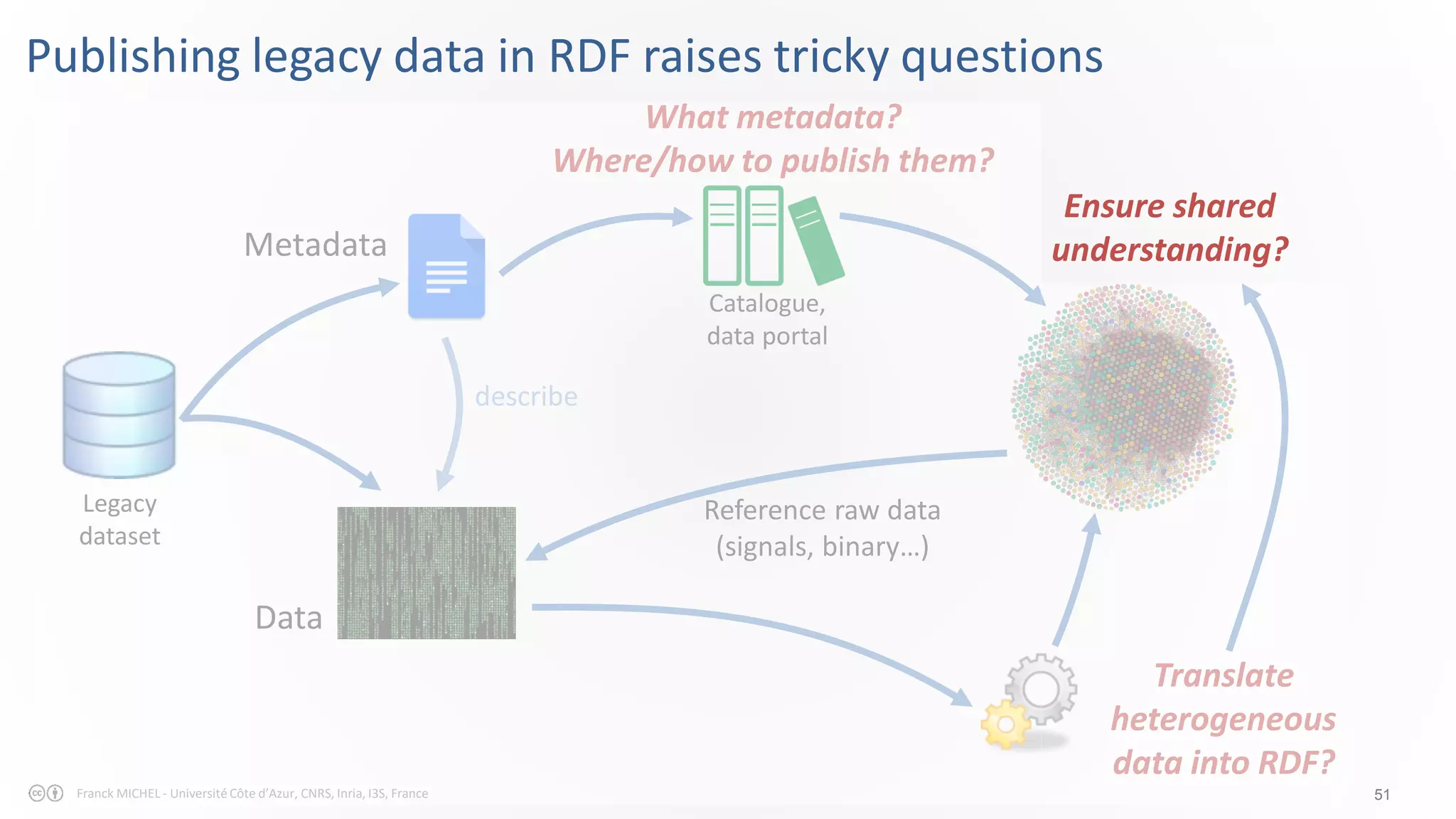
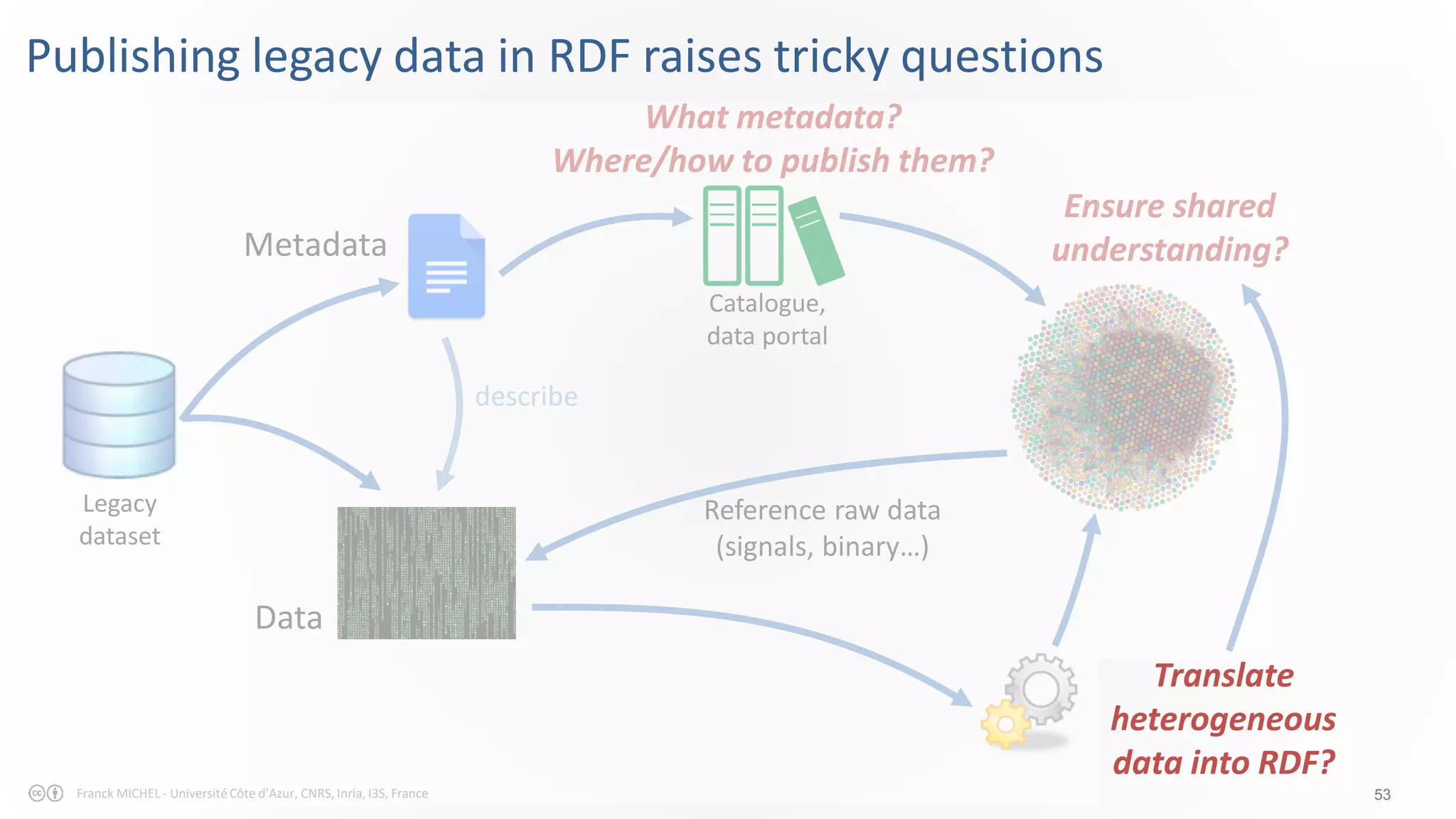
The document discusses the semantic web and linked data, outlining its purpose to facilitate data publication, querying, and interoperability across diverse data sources. It details the standards, including RDF for data representation, SPARQL for querying, and the principles of linked data that emphasize the use of URIs. Challenges such as semantic and structural heterogeneity in data management are also highlighted.








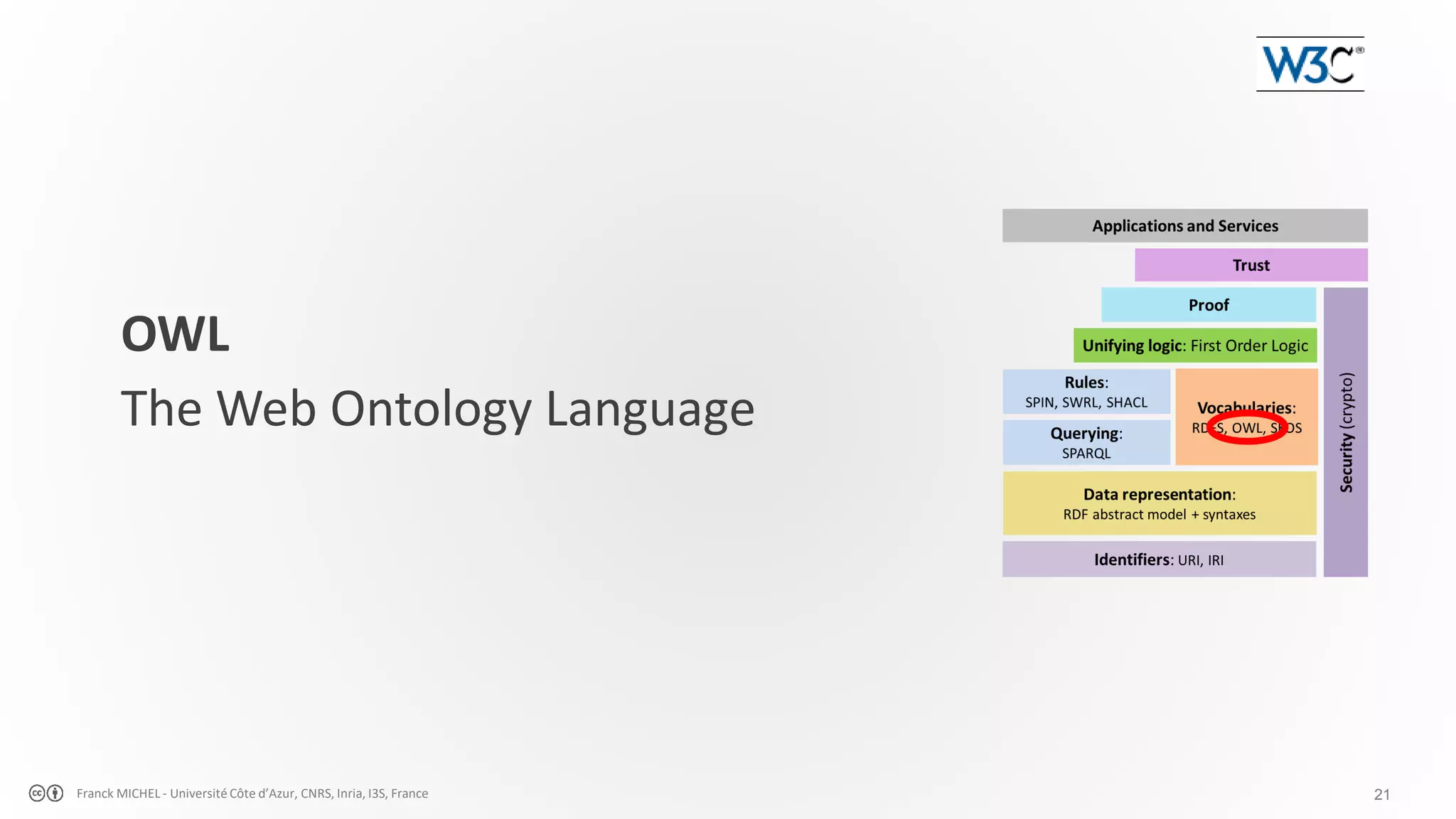
![22Franck MICHEL - Université Côte d’Azur, CNRS, Inria, I3S, France def. by enumeration def. by intersection def. by union def. by complement class disjunction def. by restriction def. by cardinality def. by equivalence ! 1..1 [>=18] def. by value restrict. … OWL in one slide… (a)symetric prop. prop. disjunction cardinality1..1 ! indiv. prop. negation chained prop. (irr)reflexive prop. transitive prop. inverse prop.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20181113apsem-introsw-copie-190825014119/75/Knowledge-Engineering-Semantic-web-web-of-data-linked-data-22-2048.jpg)





![33Franck MICHEL - Université Côte d’Azur, CNRS, Inria, I3S, France SPARQL JSON results { "head": { "vars": [ "student" ] }, "results": { "bindings: [ {"student": { "type": "uri", "value": "http//www.mit.edu/data.rdf#joe" } }, { "student": { "type": "uri", "value": "http//www.mit.edu/abcdef" } } ] } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20181113apsem-introsw-copie-190825014119/75/Knowledge-Engineering-Semantic-web-web-of-data-linked-data-33-2048.jpg)



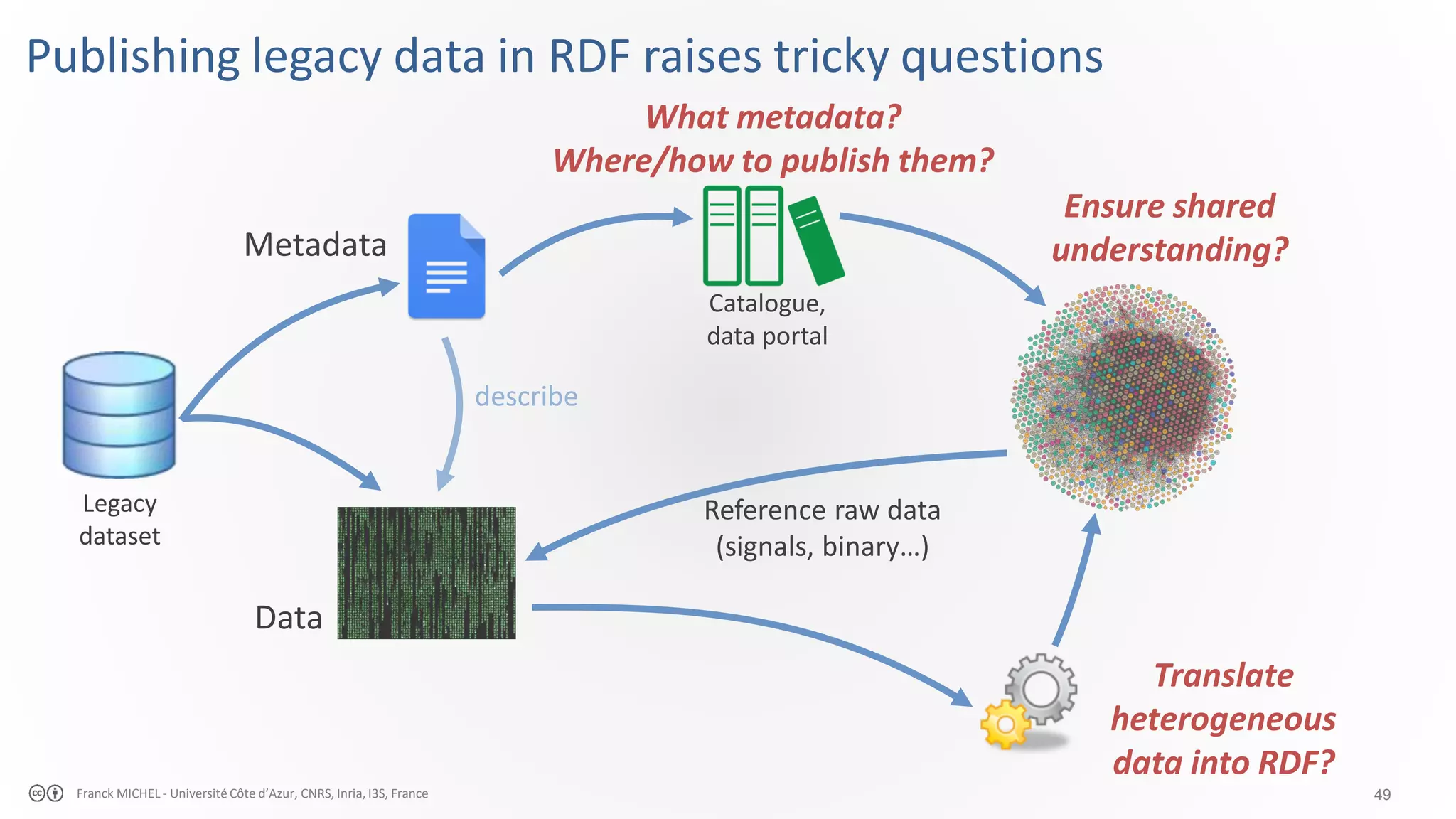

![54Franck MICHEL - Université Côte d’Azur, CNRS, Inria, I3S, France Many methods for many types of data sources AstroGrid-D, SPARQL2XQuery, XSPARQL XML XLWrap, Linked CSV, CSVW, RML CSV/TSV/Spreadsheets D2RQ, R2O, Ultrawrap, Triplify, SM R2RML: Morph-RDB, ontop, Virtuoso Relational Databases RML, TARQL, Apache Any23, DataLift, SPARQL-Generate Multiple formats RDFa, Microformats HTML TARQL, JSON-LD, RML JSON xR2RML (MongoDB), ontop (MongoDB), [Mugnier et al, 2016] (key-value stores) NoSQL M.L. Mugnier, M.C. Rousset, and F. Ulliana. “Ontology-Mediated Queries for NOSQL Databases.” In Proc. AAAI. 2016. SPARQL Micro-services, Linked REST APIs Web APIs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20181113apsem-introsw-copie-190825014119/75/Knowledge-Engineering-Semantic-web-web-of-data-linked-data-54-2048.jpg)