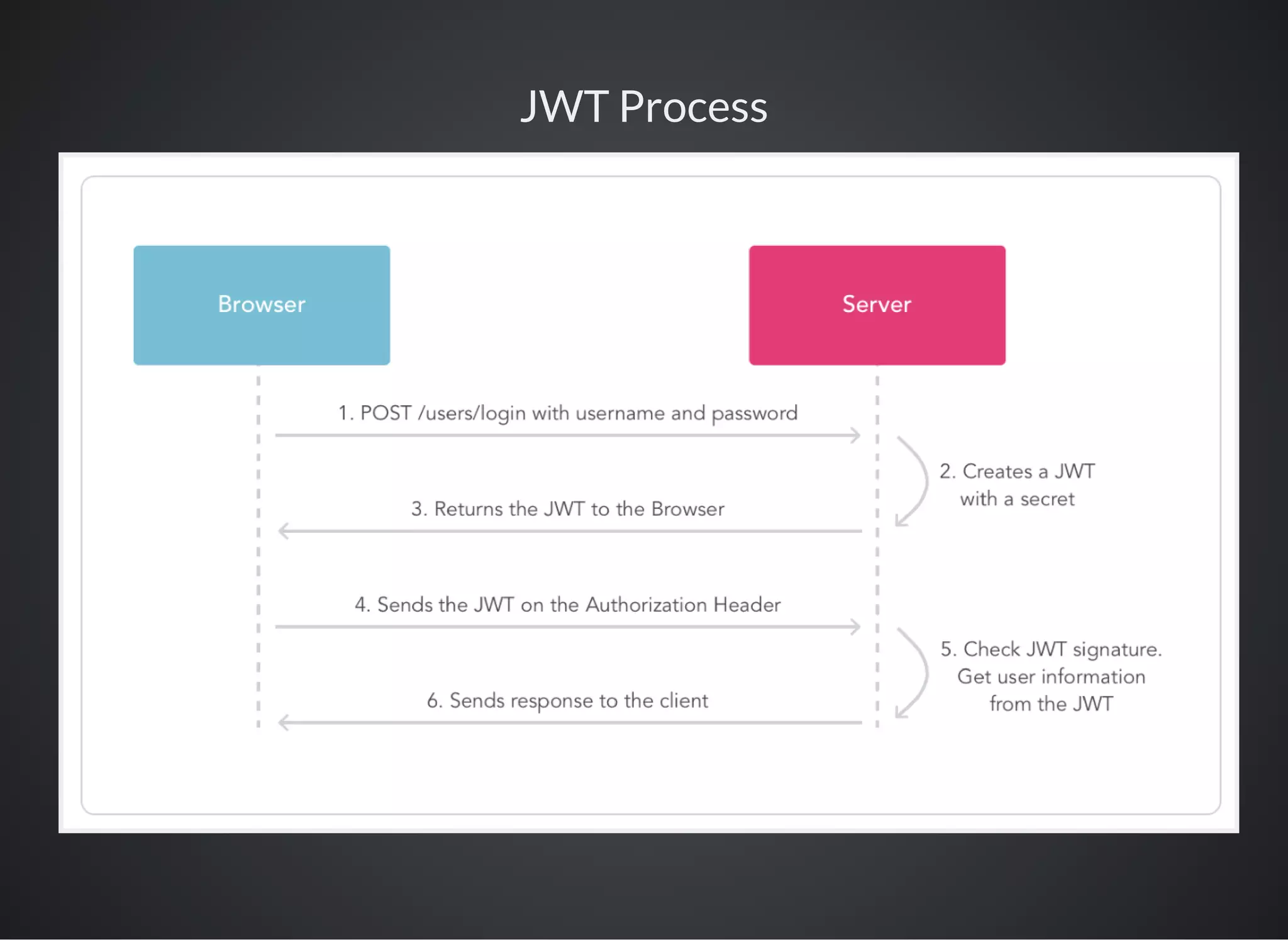
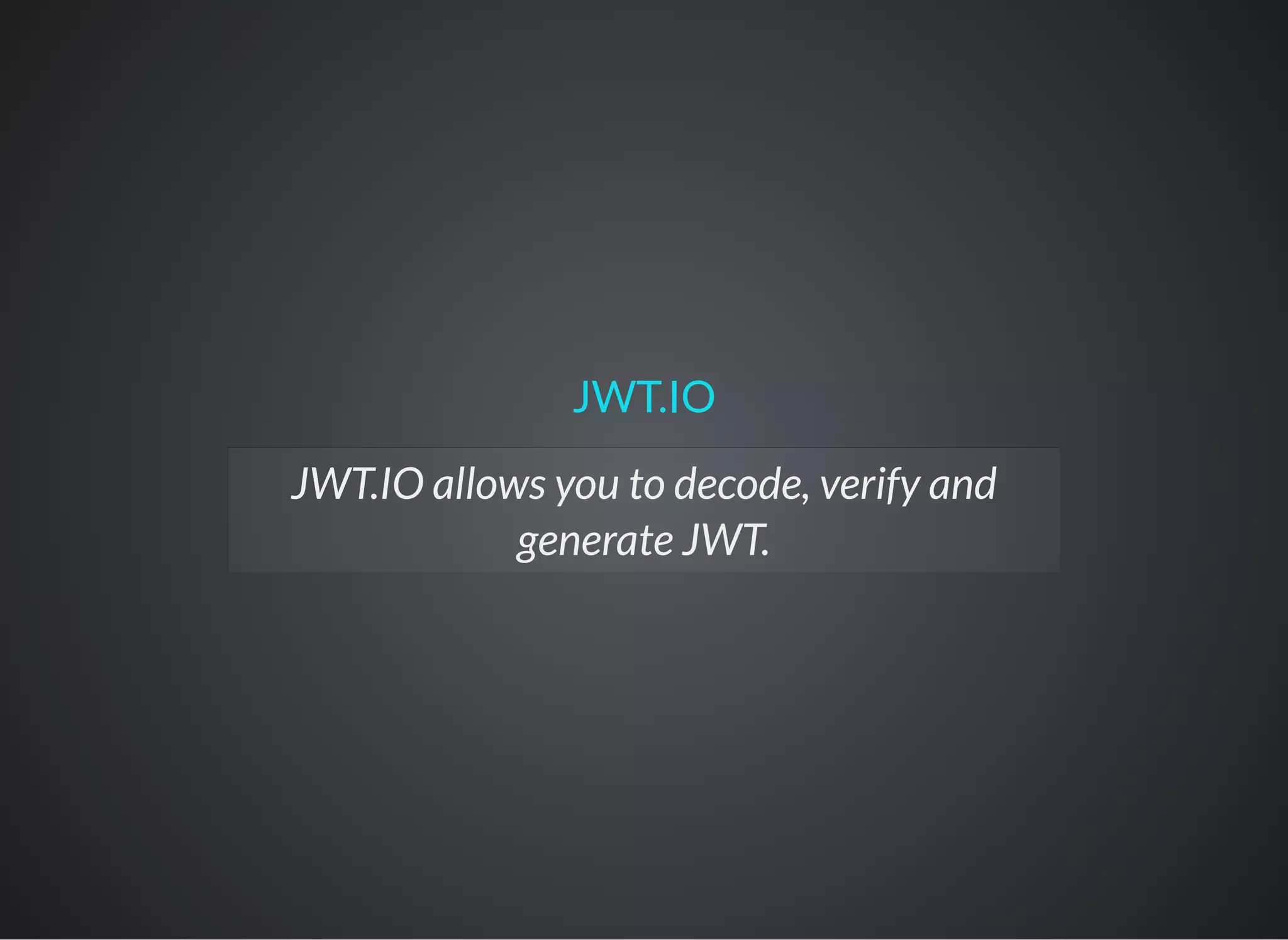
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are a secure method for representing claims between two parties, allowing for digital signing and encryption. They are primarily used for authentication and information exchange, enabling features like single sign-on and secure communication. JWTs consist of a header, payload, and signature, offering scalability and security against certain attacks.