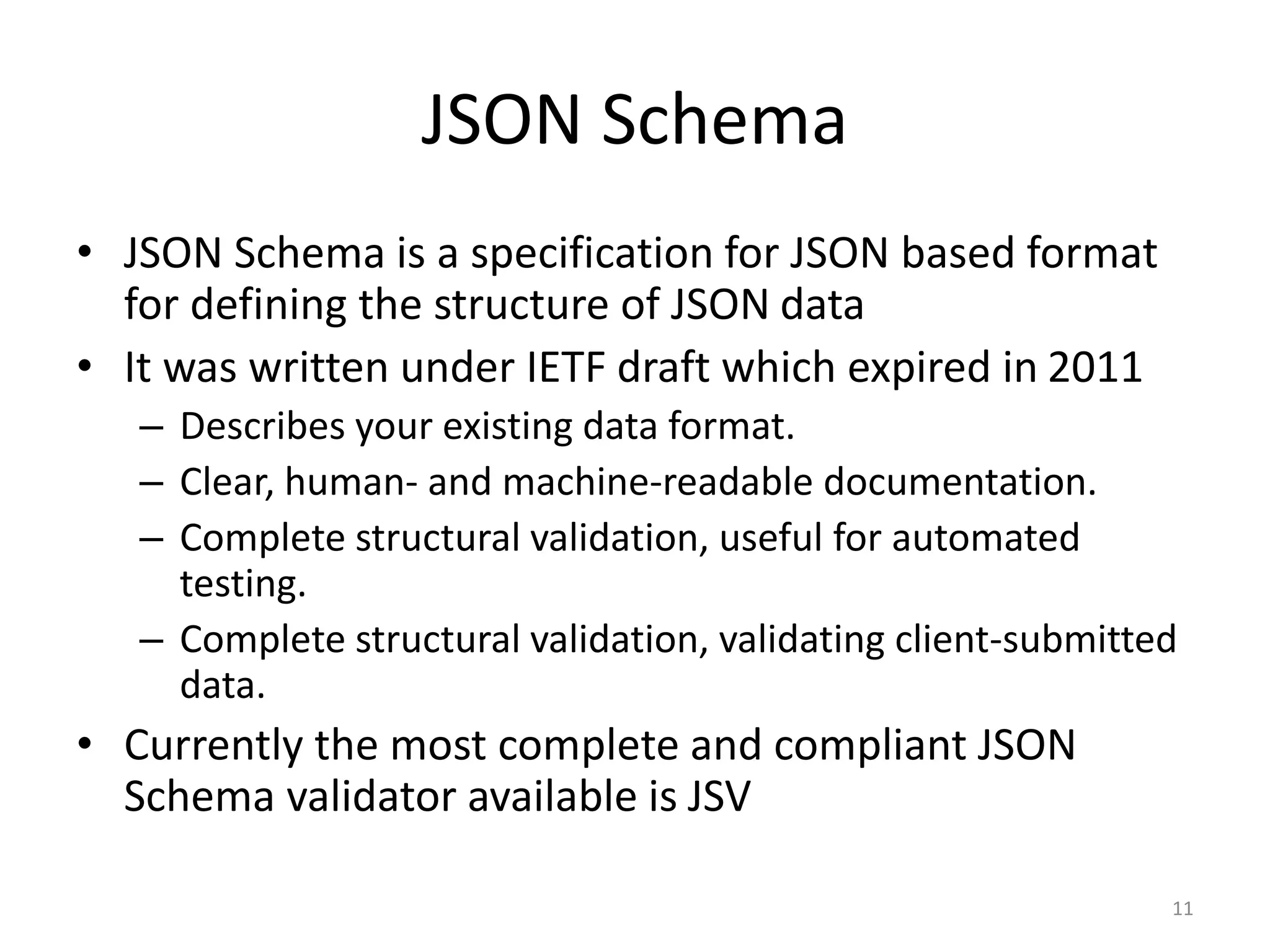
This document provides an overview of JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) and how it can be used with Java and MuleSoft. It introduces JSON syntax and data types, and how JSON can be parsed and generated from Java objects using Jackson annotations and APIs. Key topics covered include JSON parsing and mapping to Java types, Jackson serialization and deserialization annotations, and using JSON in Mule applications.



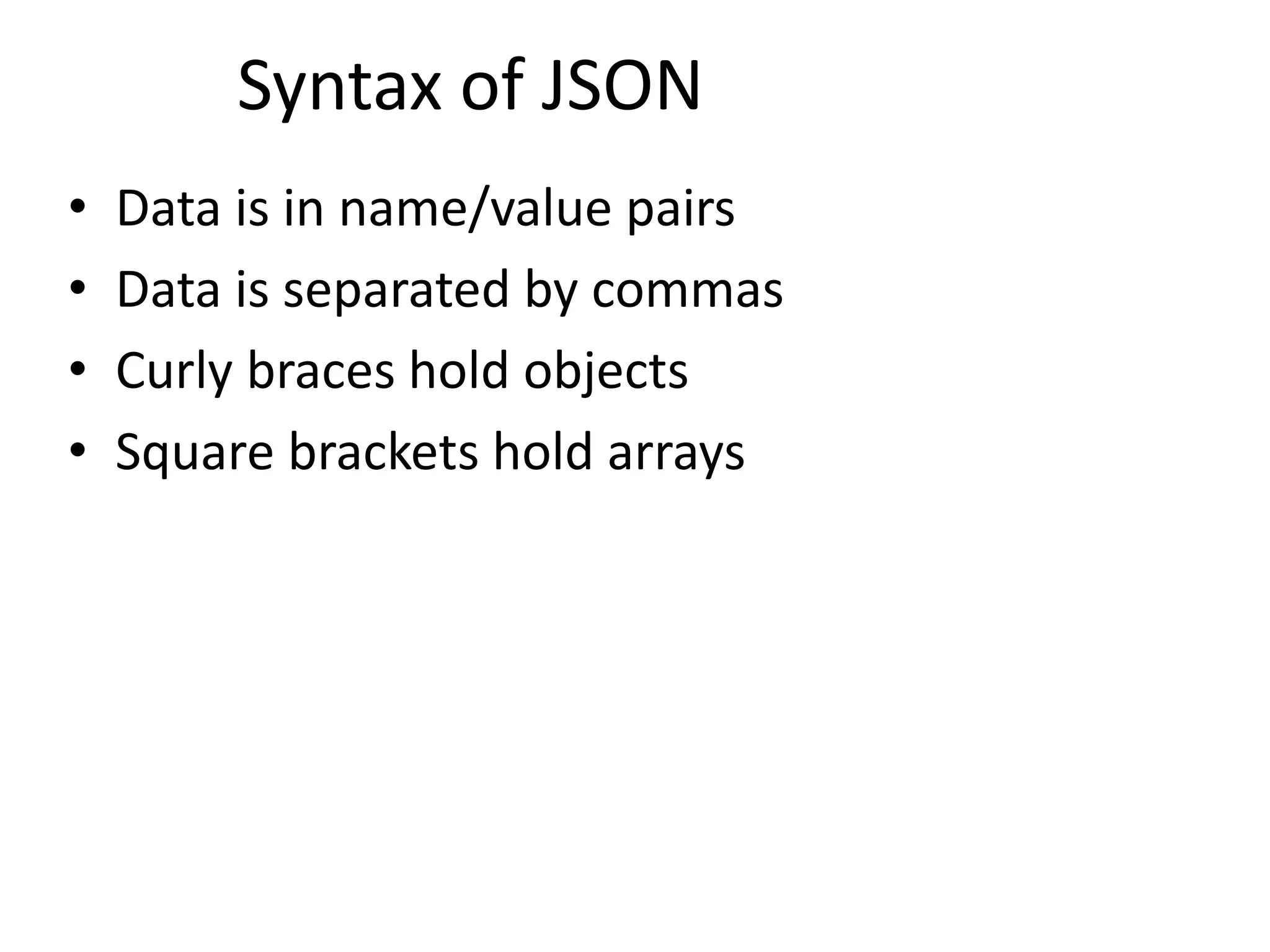
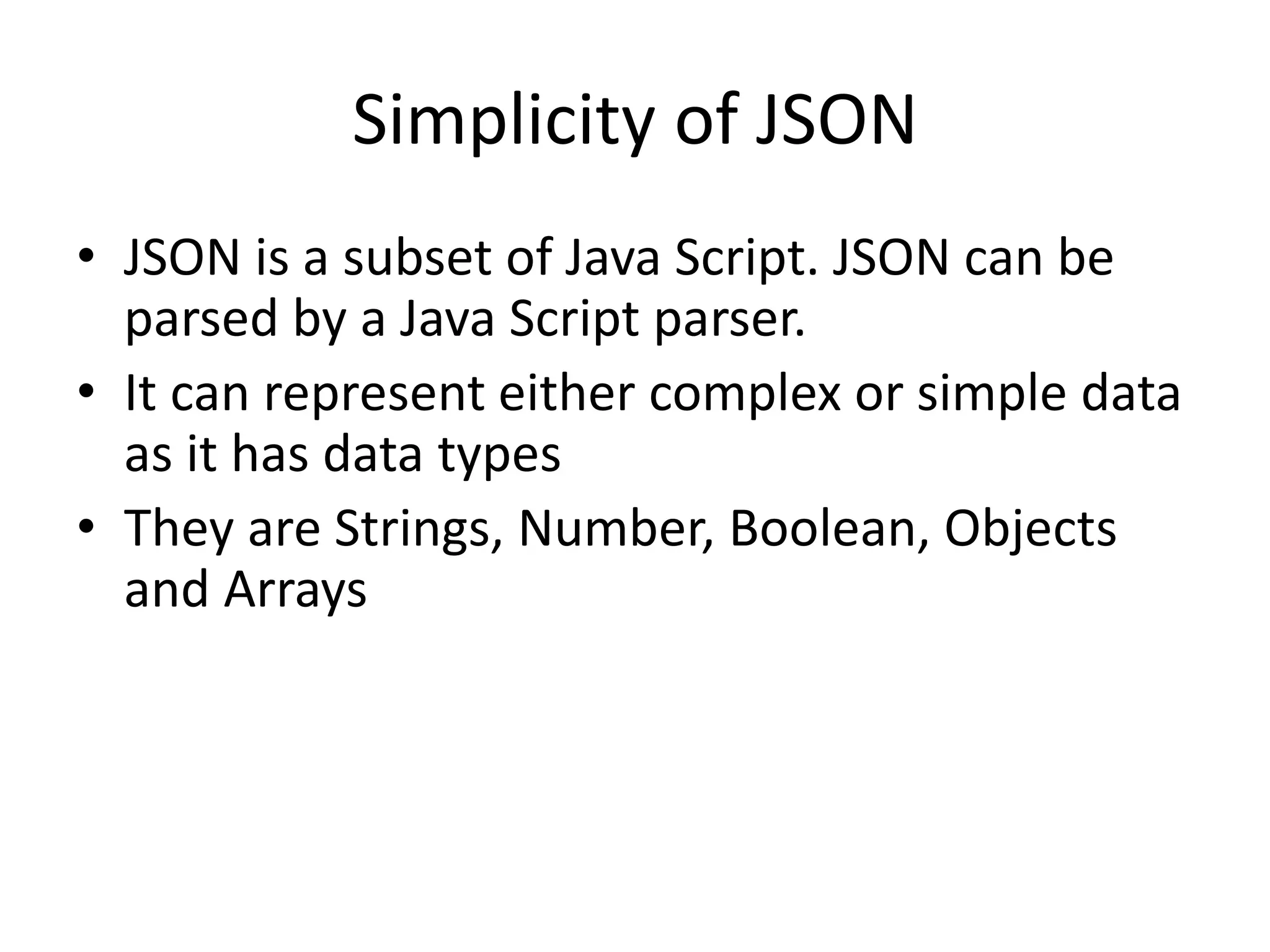
![• Array – ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday“] – "employees":[ {"firstName":"John", "lastName":"Doe"}, {"firstName":"Anna", "lastName":"Smith"}, {"firstName":"Peter","lastName":"Jones"} ] • Object – { “firstname": “Santhosh ", “lastname": “Gowd”} All data types are intuitive and similar to other programming languages • Also compatible with other languages like C, C++, C#, ColdFusion, Python and many more. 6 JSON Compatibility](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whishworks-json-151216062820/75/JSON-Processing-and-mule-6-2048.jpg)