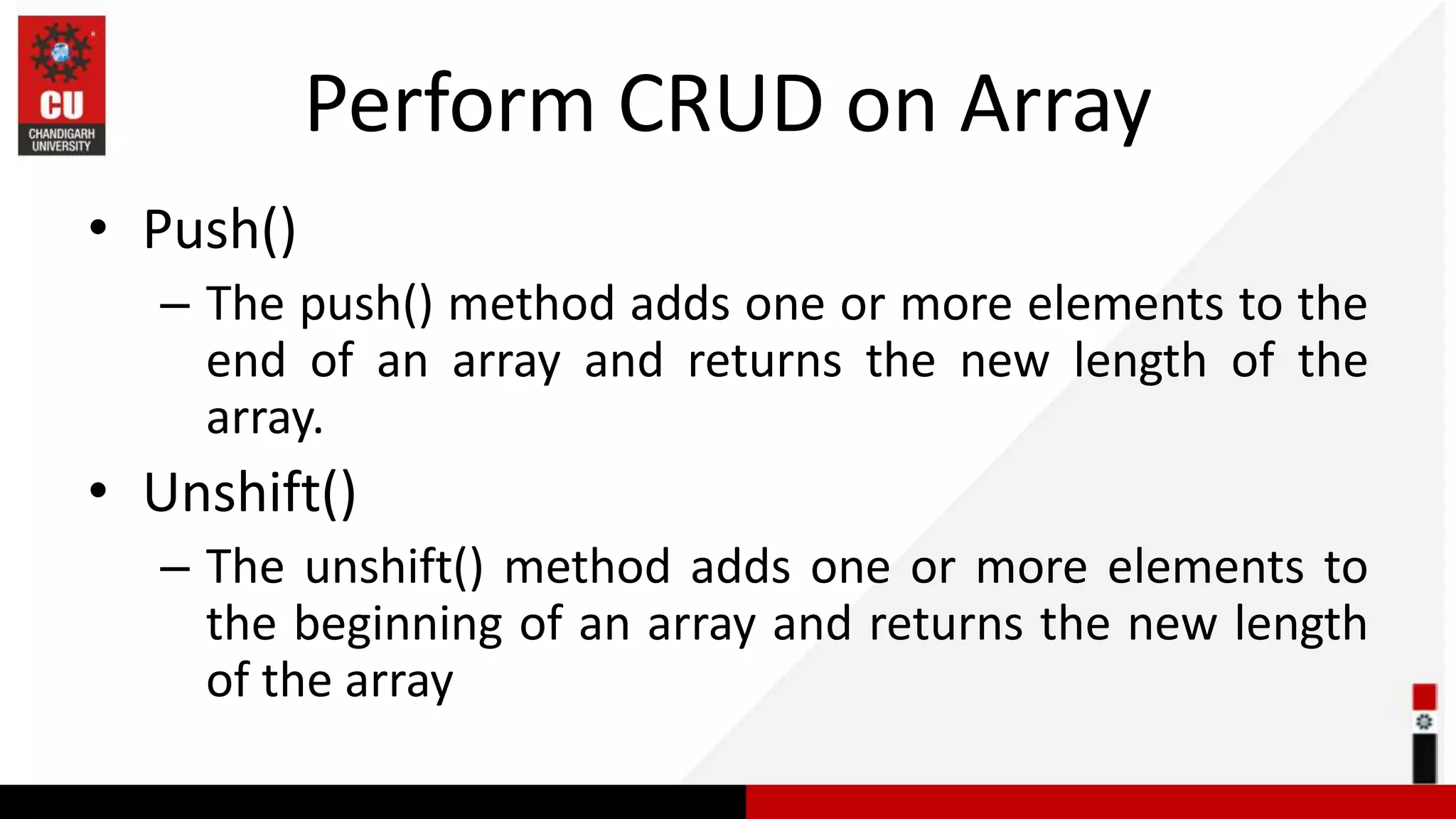
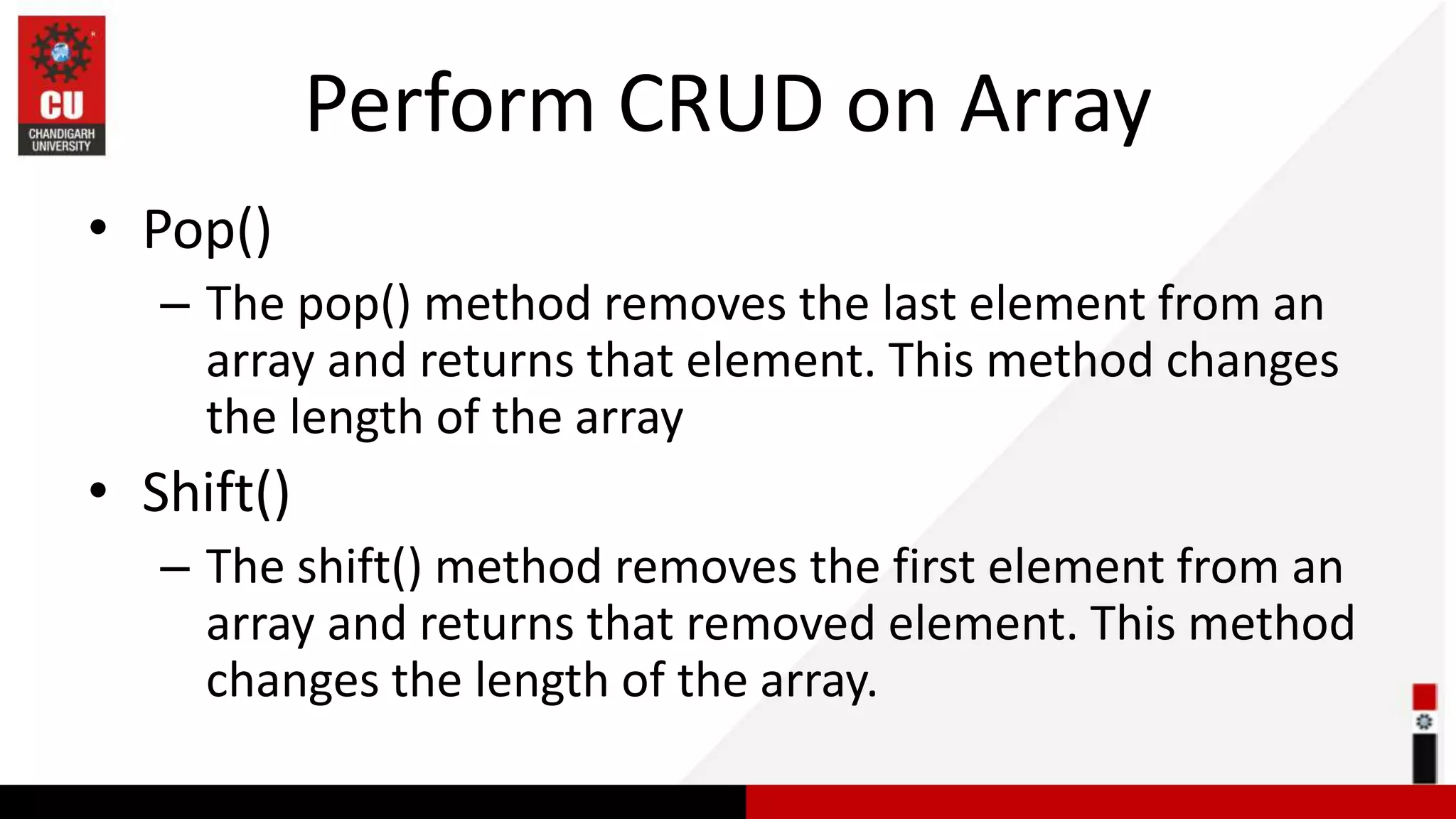
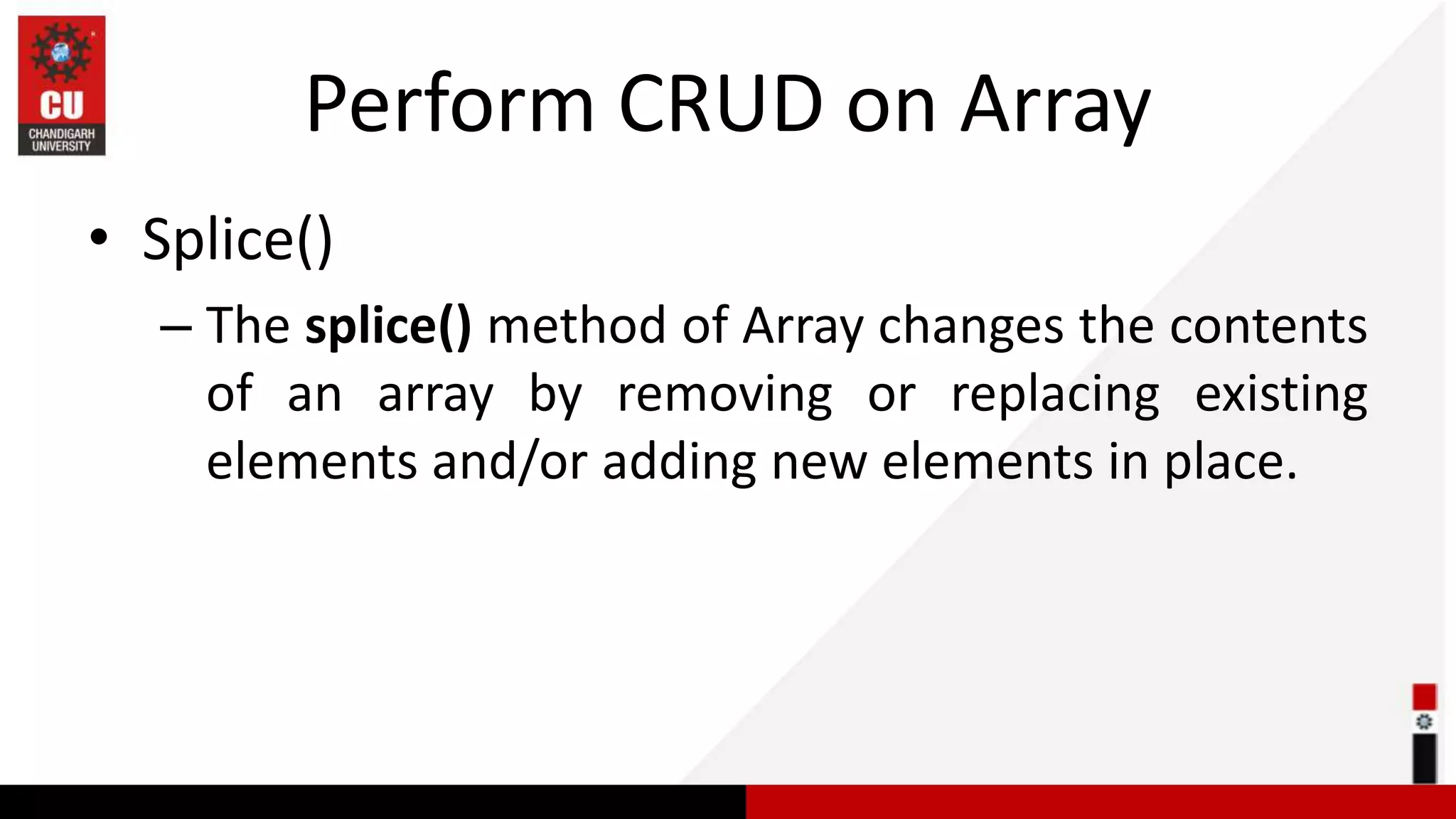
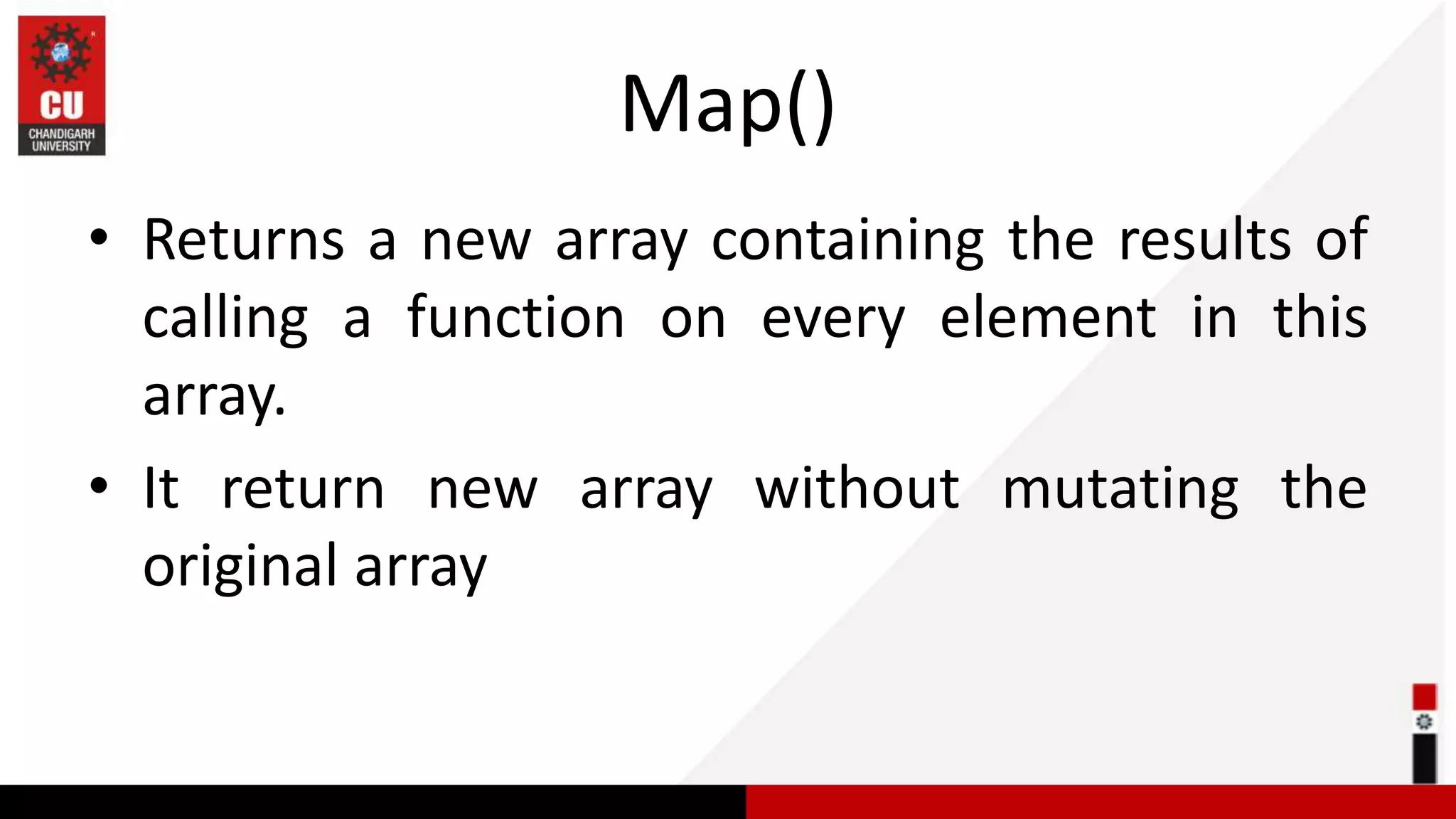
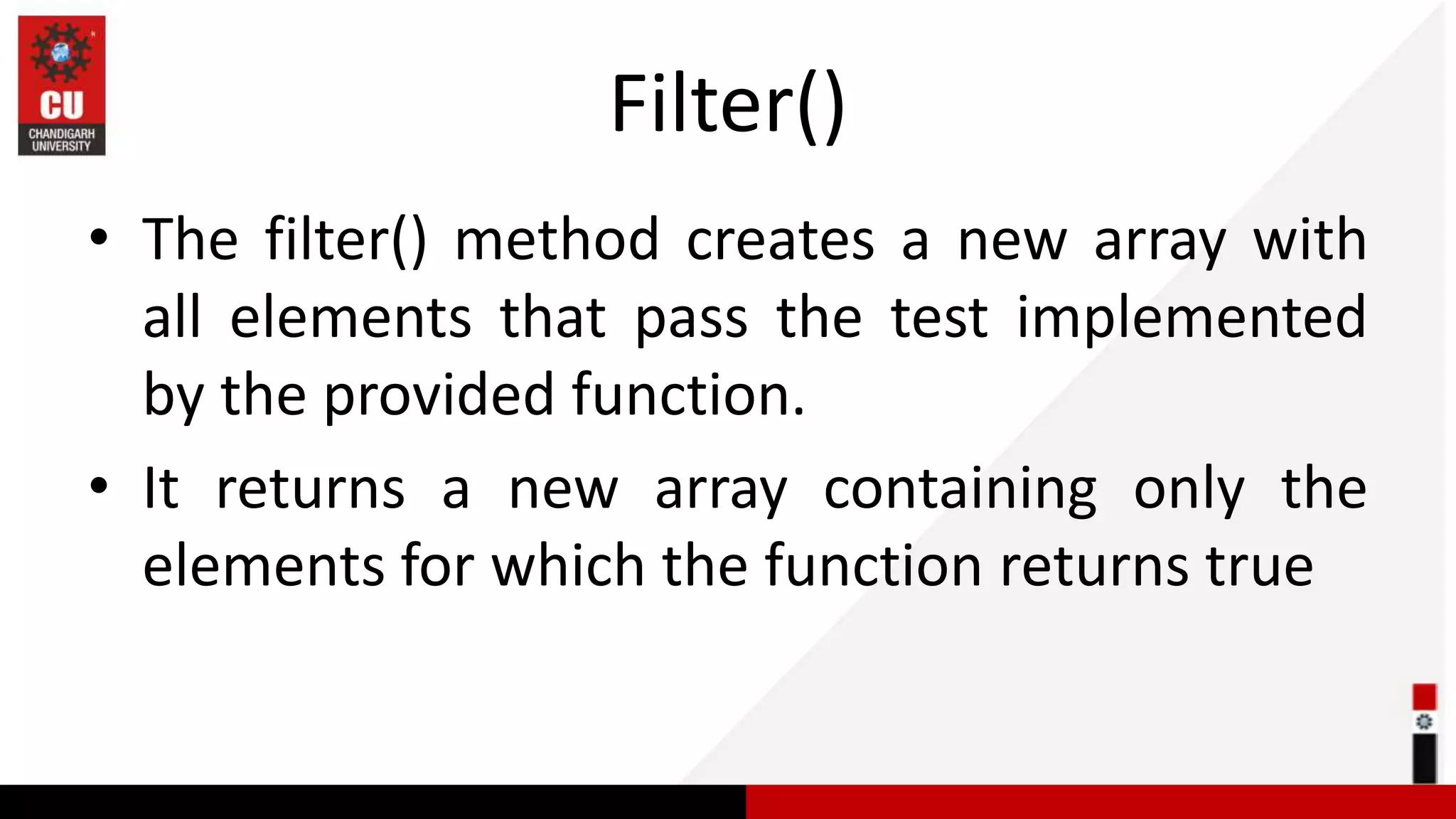
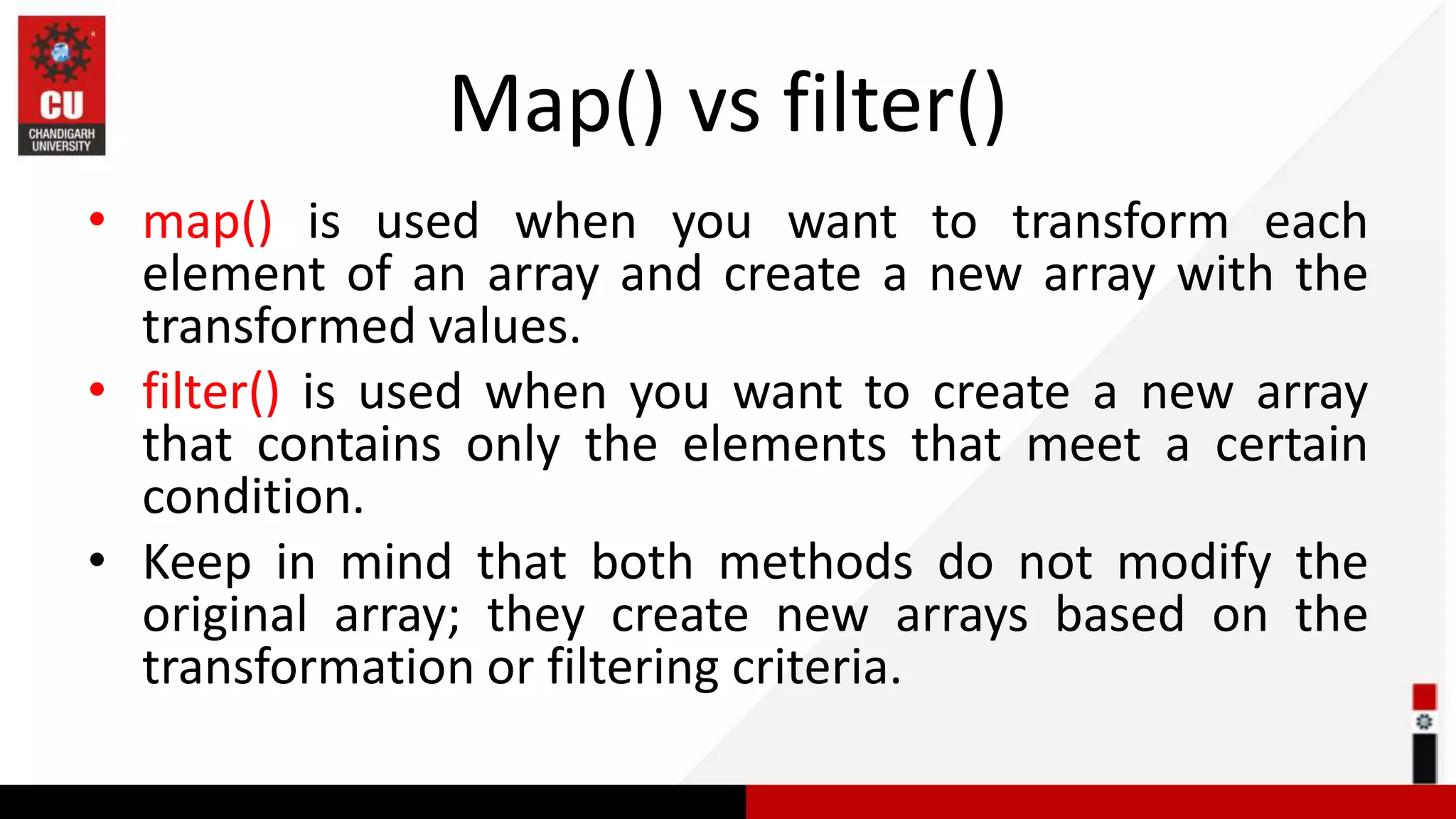
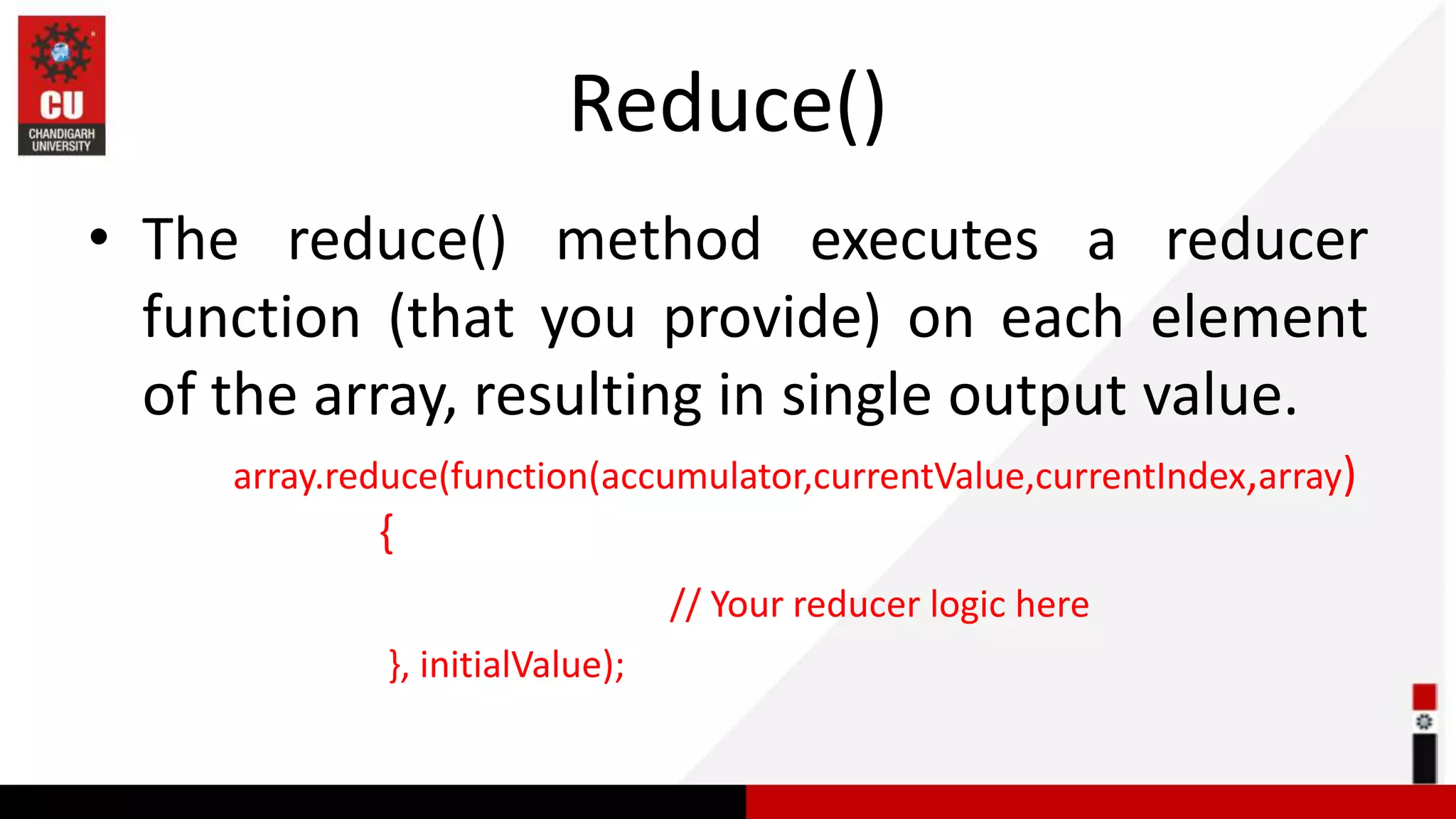
This document provides information on JavaScript arrays. It discusses how arrays allow storing multiple values in a variable, unlike variables declared with var or let which can only store one value. The document covers traversing arrays, and performing CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations on arrays using methods like push(), pop(), splice(), etc. It also explains how to use array methods like map(), filter() and reduce() to transform or filter array elements. Finally, it provides examples of using these methods to process product data from an array of objects.


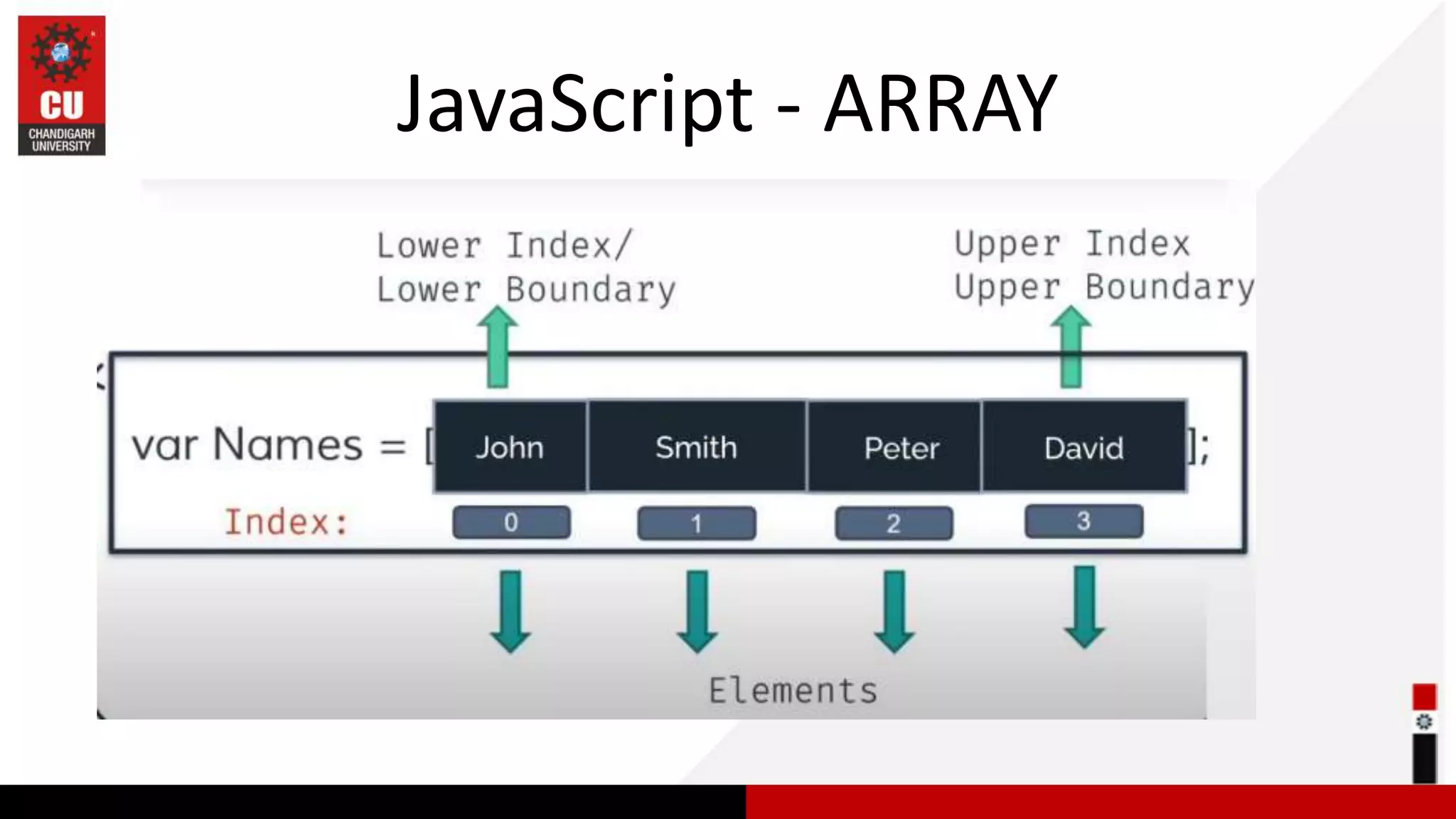
![JavaScript - ARRAY • var Names= [‘John’,’Smith’,’Peter’,’David’]; • First Element of an array known as Lower Index/ Lower Boundary. • Last Element of an array known as Upper Index/ Upper Boundary.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-array-230928051620-99ea72ae/75/javascript-Array-ppsx-3-2048.jpg)

![Traversal in array • if we want to get the single data at a time. arrayVarName[indexNumber] • Traverse the Last Element of an Array arrayVarName[arrayVarName.length-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-array-230928051620-99ea72ae/75/javascript-Array-ppsx-6-2048.jpg)

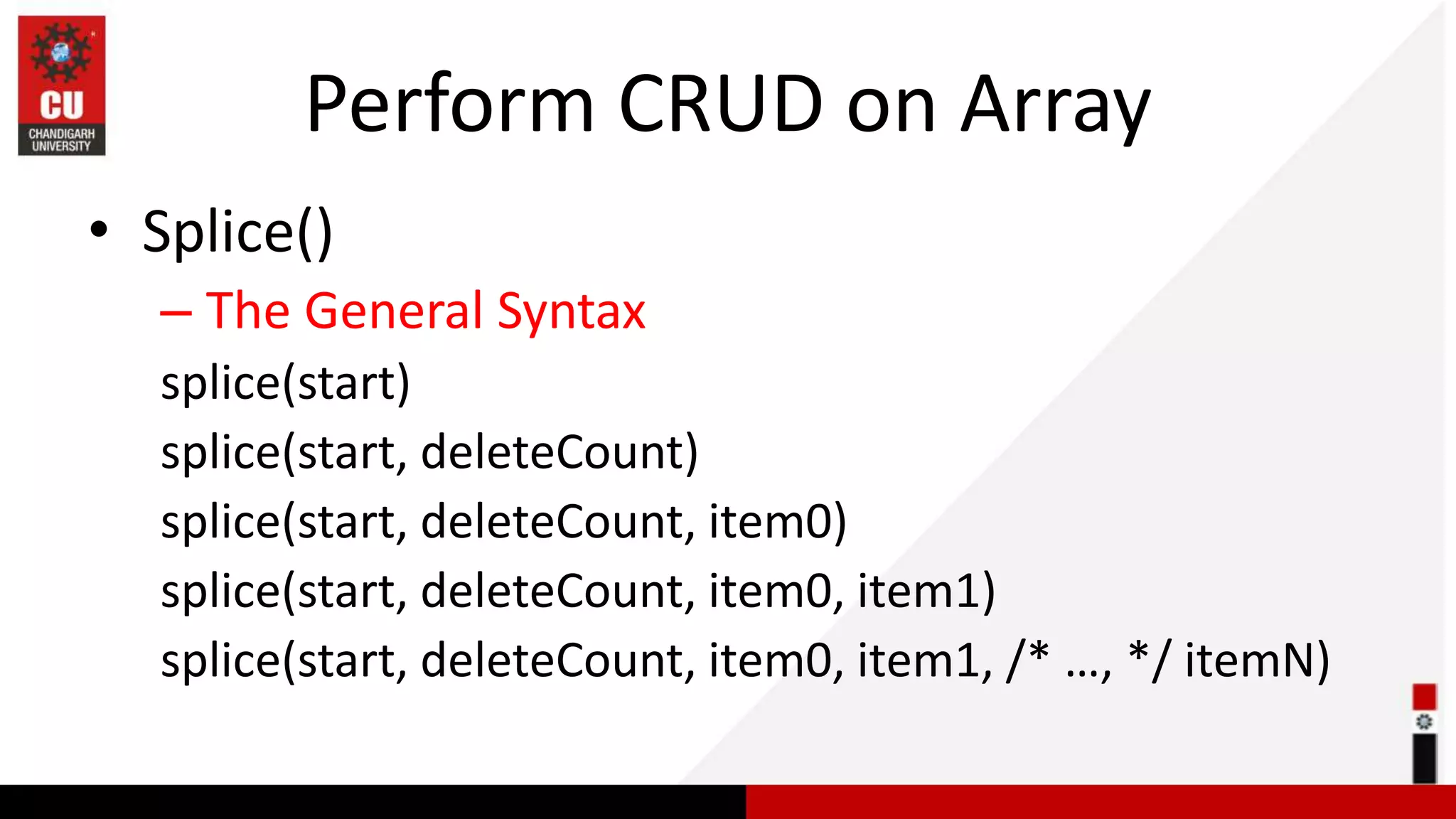
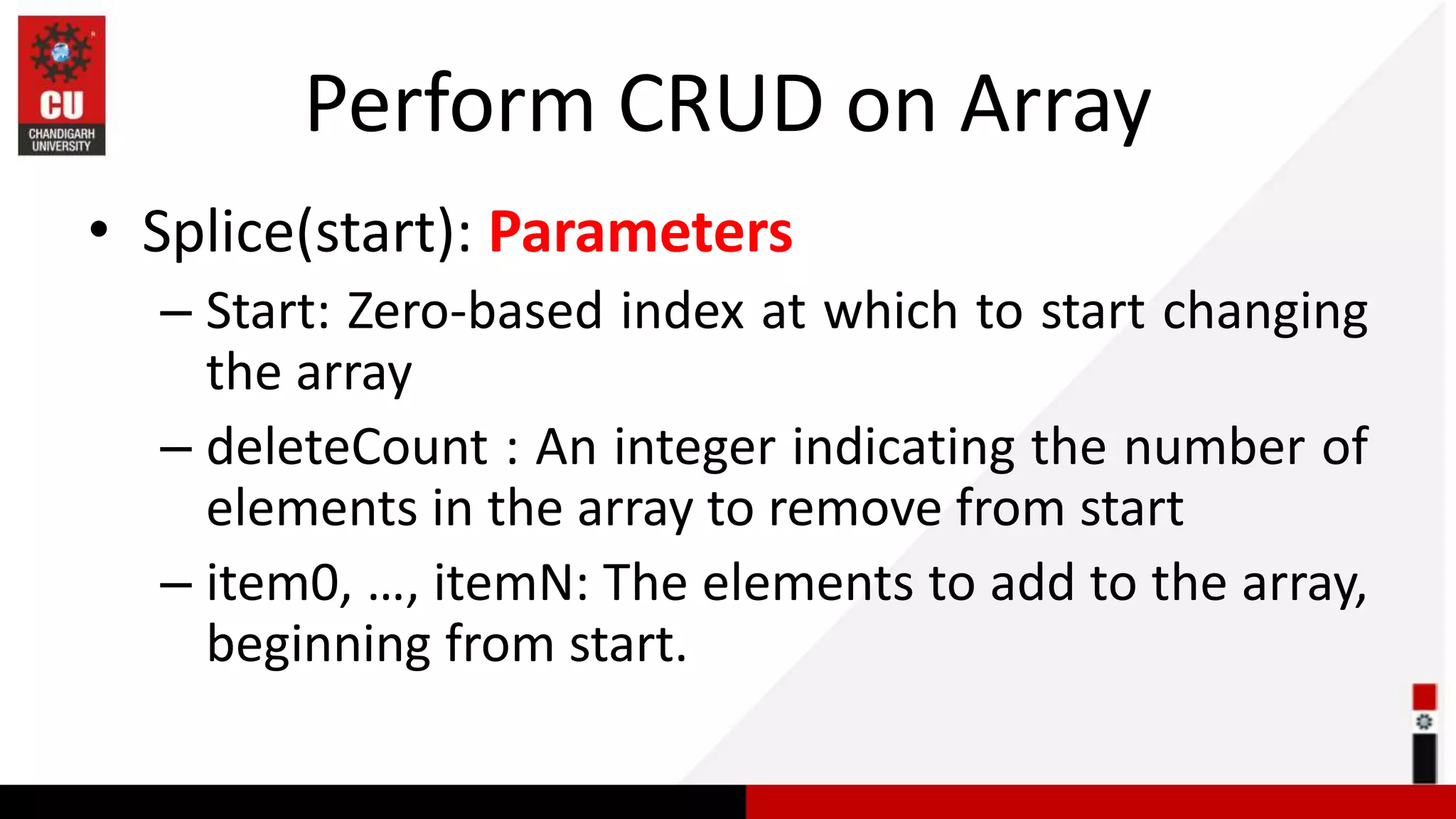
![Task of the Day 1. Add Dec at the end of an array? 2. What is the return value of splice method? 3. update march to March (update)? 4. Delete June from an array? const months = ['Jan', 'march', 'April', 'June', 'July'];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-array-230928051620-99ea72ae/75/javascript-Array-ppsx-13-2048.jpg)
![Example • Find the square root of each element in an array? let arr = [25, 36, 49, 64, 81]; • Multiply each element by 2 and return only those elements which are greater than 10? let arr = [2, 3, 4, 6, 8];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-array-230928051620-99ea72ae/75/javascript-Array-ppsx-16-2048.jpg)
![Example • In the following array return only those elements which are greater than 5? const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-array-230928051620-99ea72ae/75/javascript-Array-ppsx-18-2048.jpg)
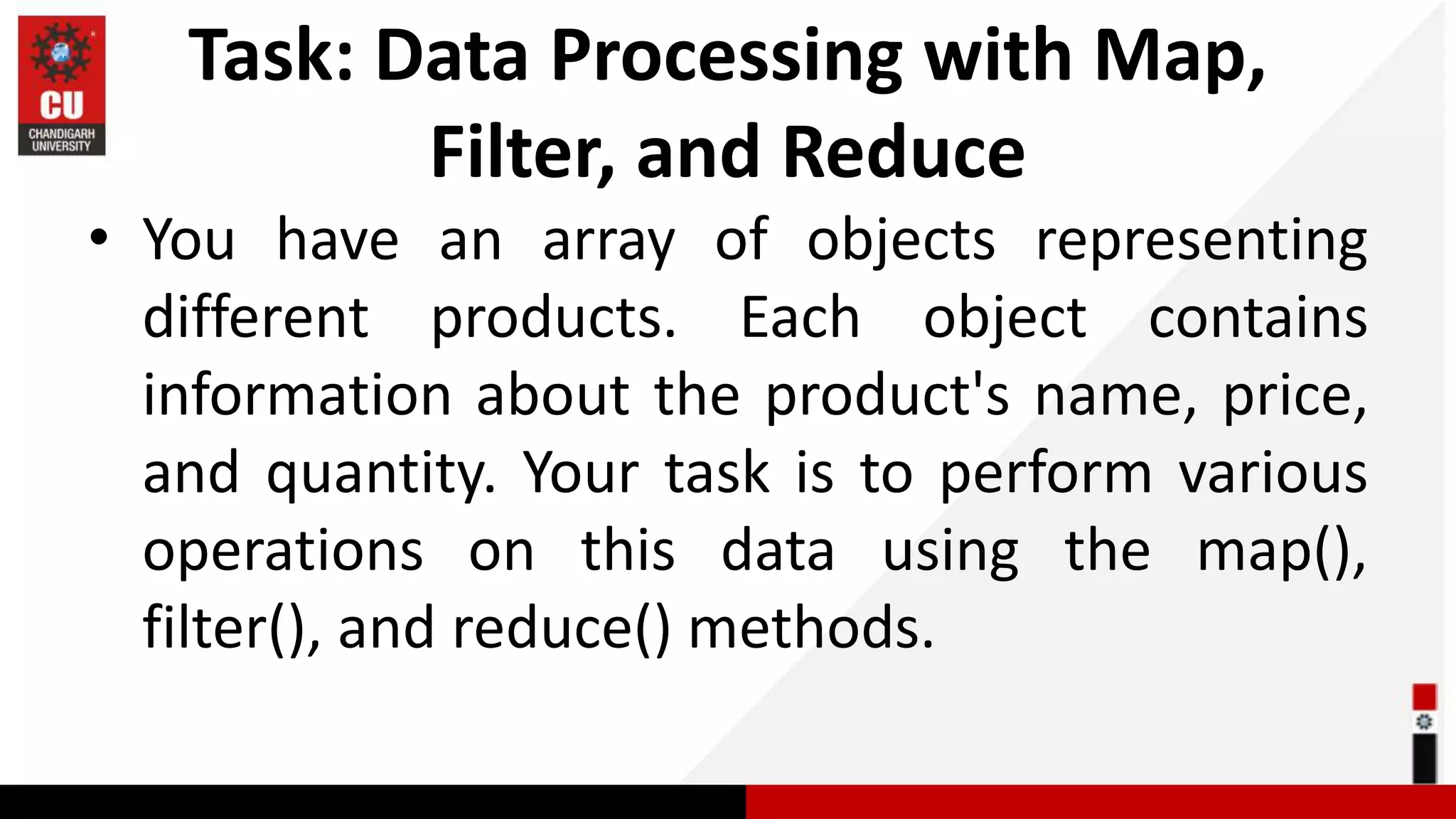
![Array of an Object const products = [ { name: 'Laptop', price: 1000, quantity: 5 }, { name: 'Phone', price: 600, quantity: 10 }, { name: 'Tablet', price: 300, quantity: 7 }, { name: 'Headphones', price: 150, quantity: 20 }, { name: 'Monitor', price: 300, quantity: 3 } ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-array-230928051620-99ea72ae/75/javascript-Array-ppsx-22-2048.jpg)

