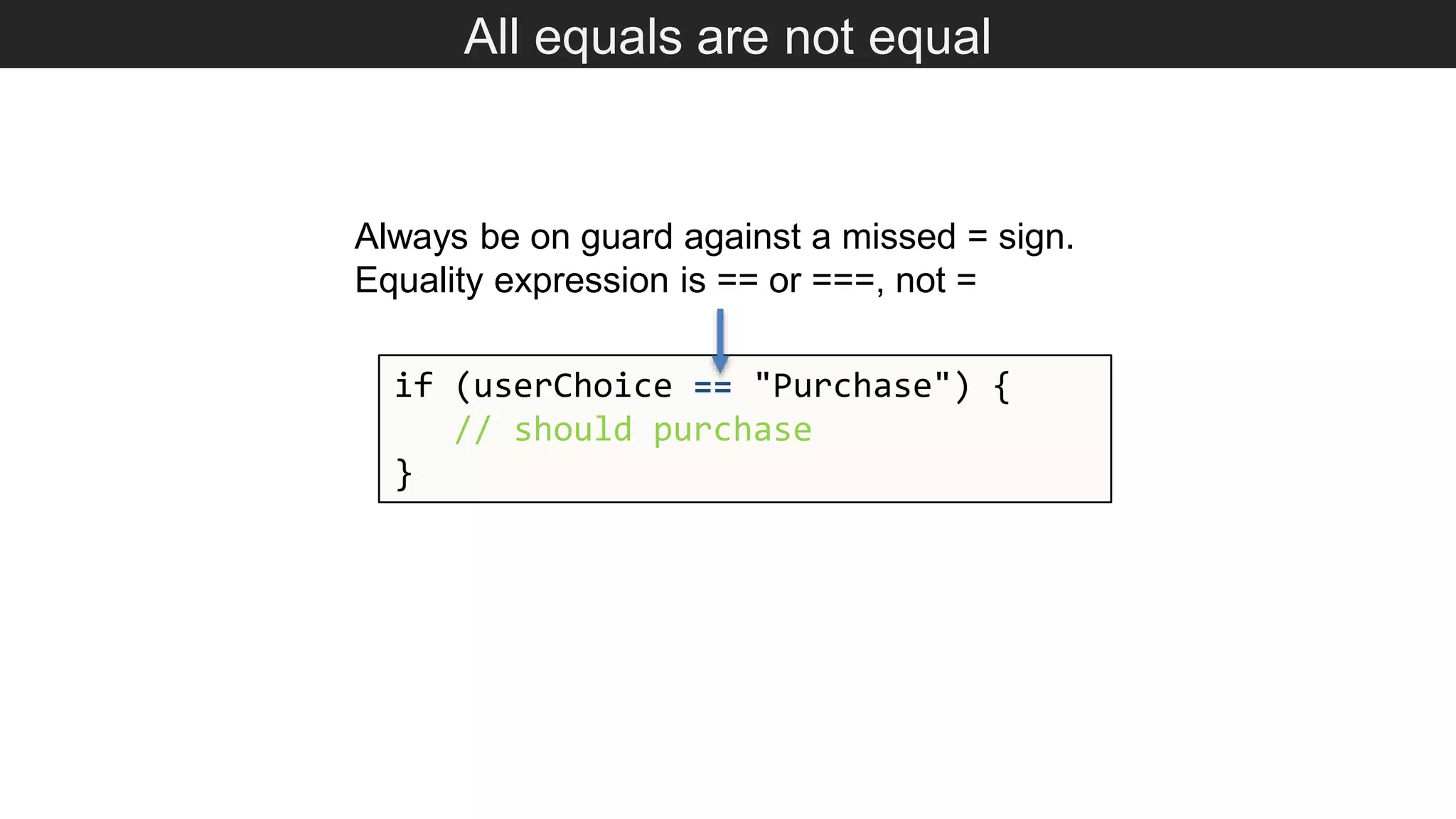
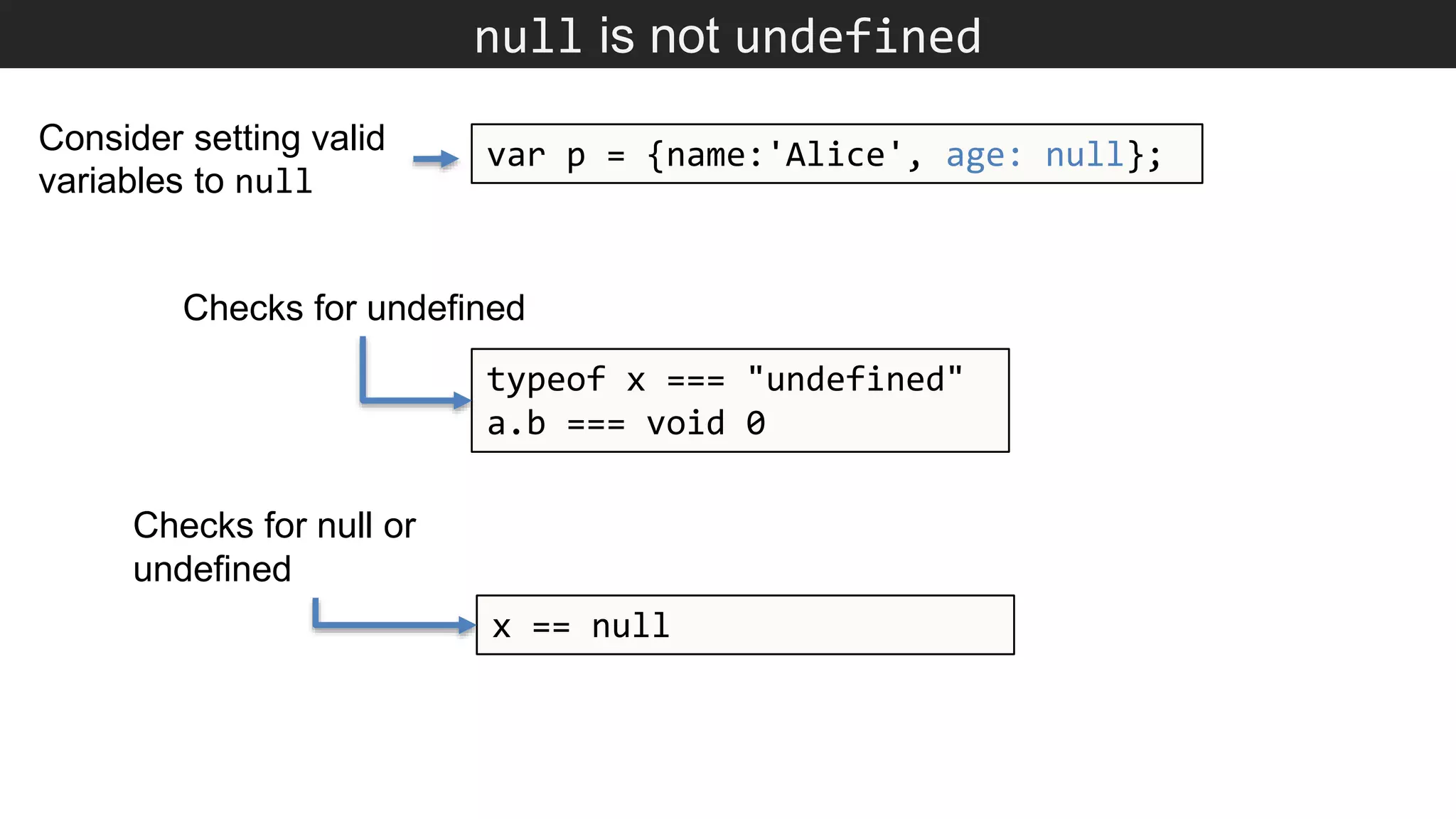
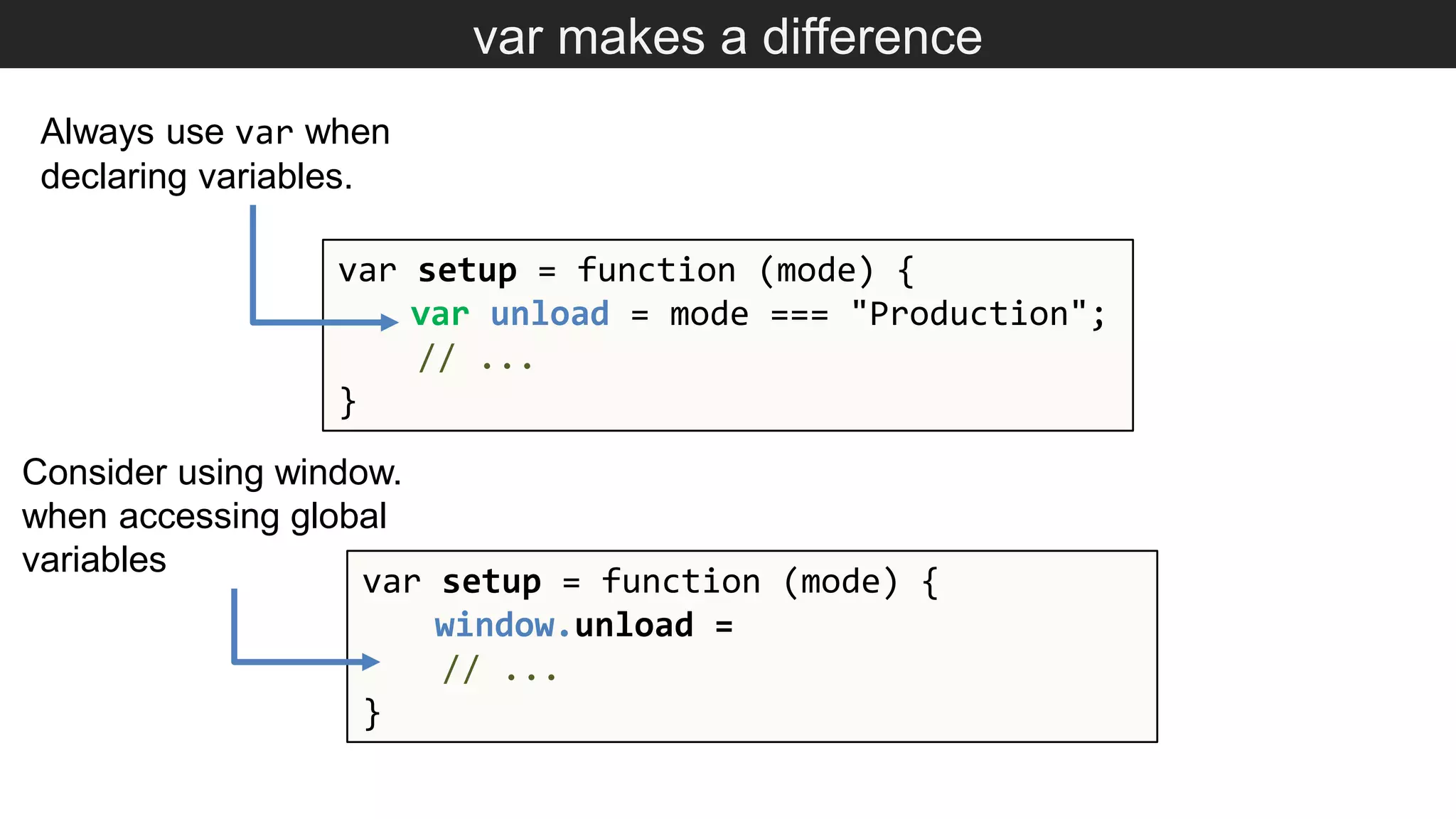
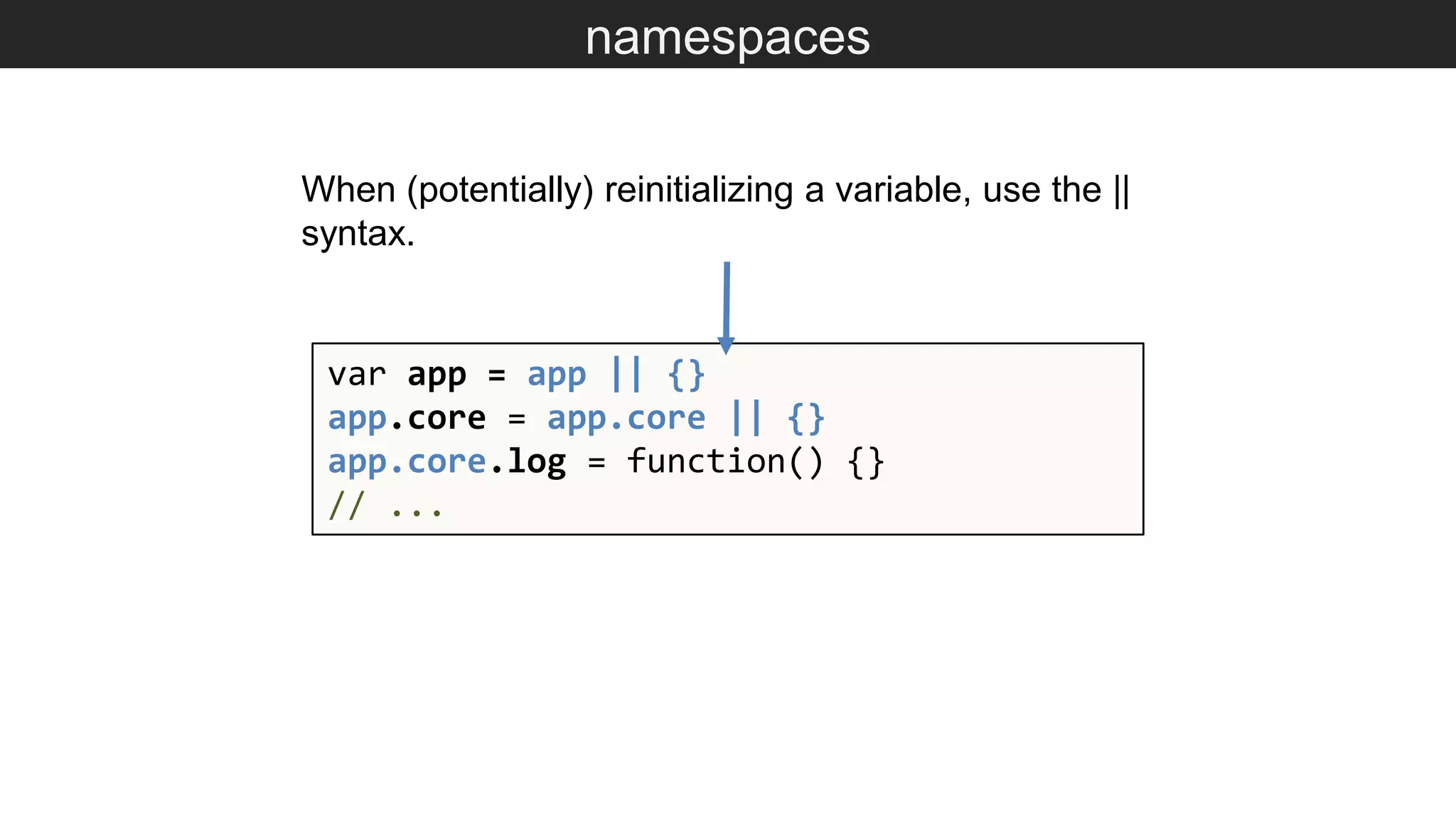
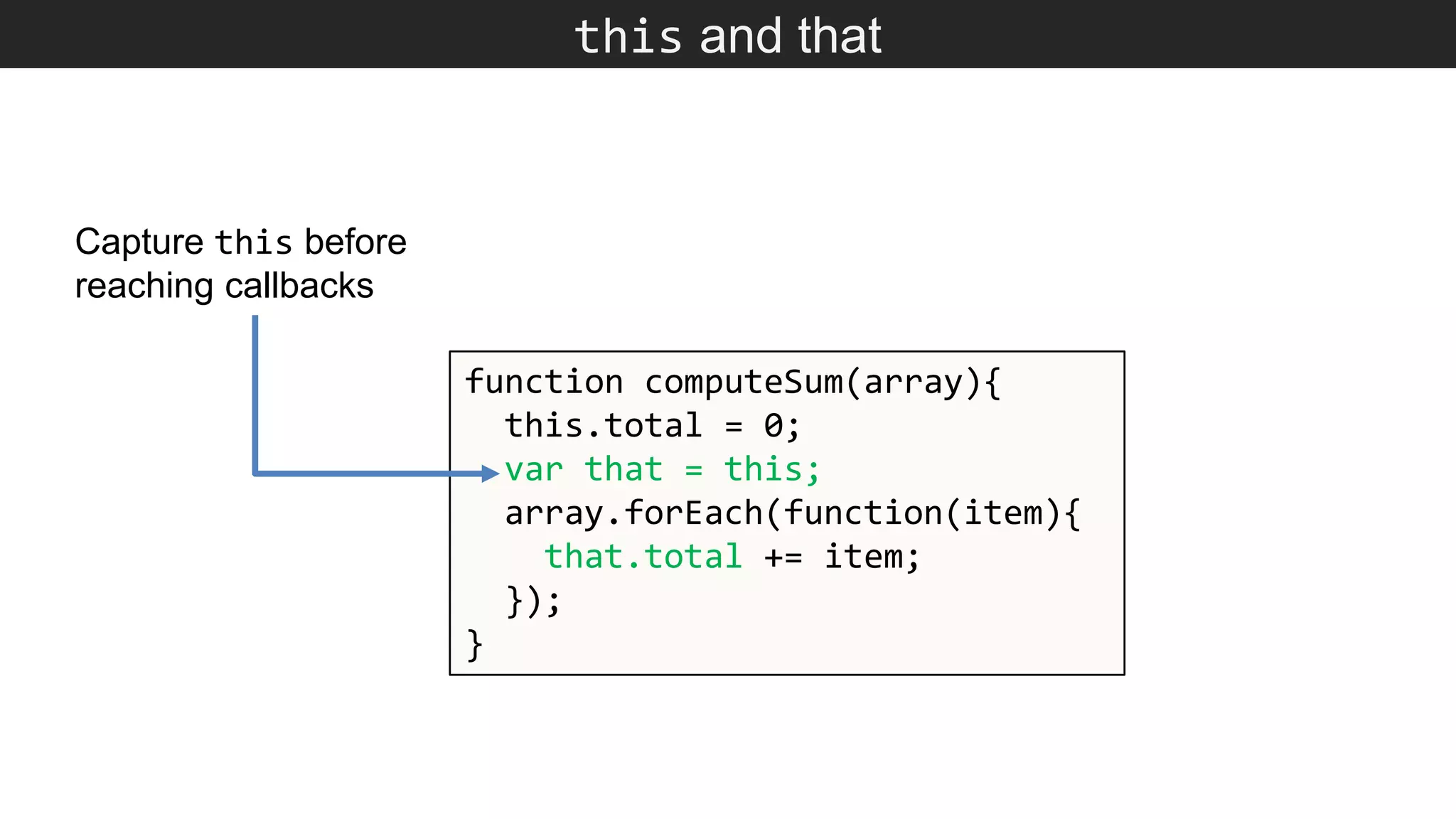
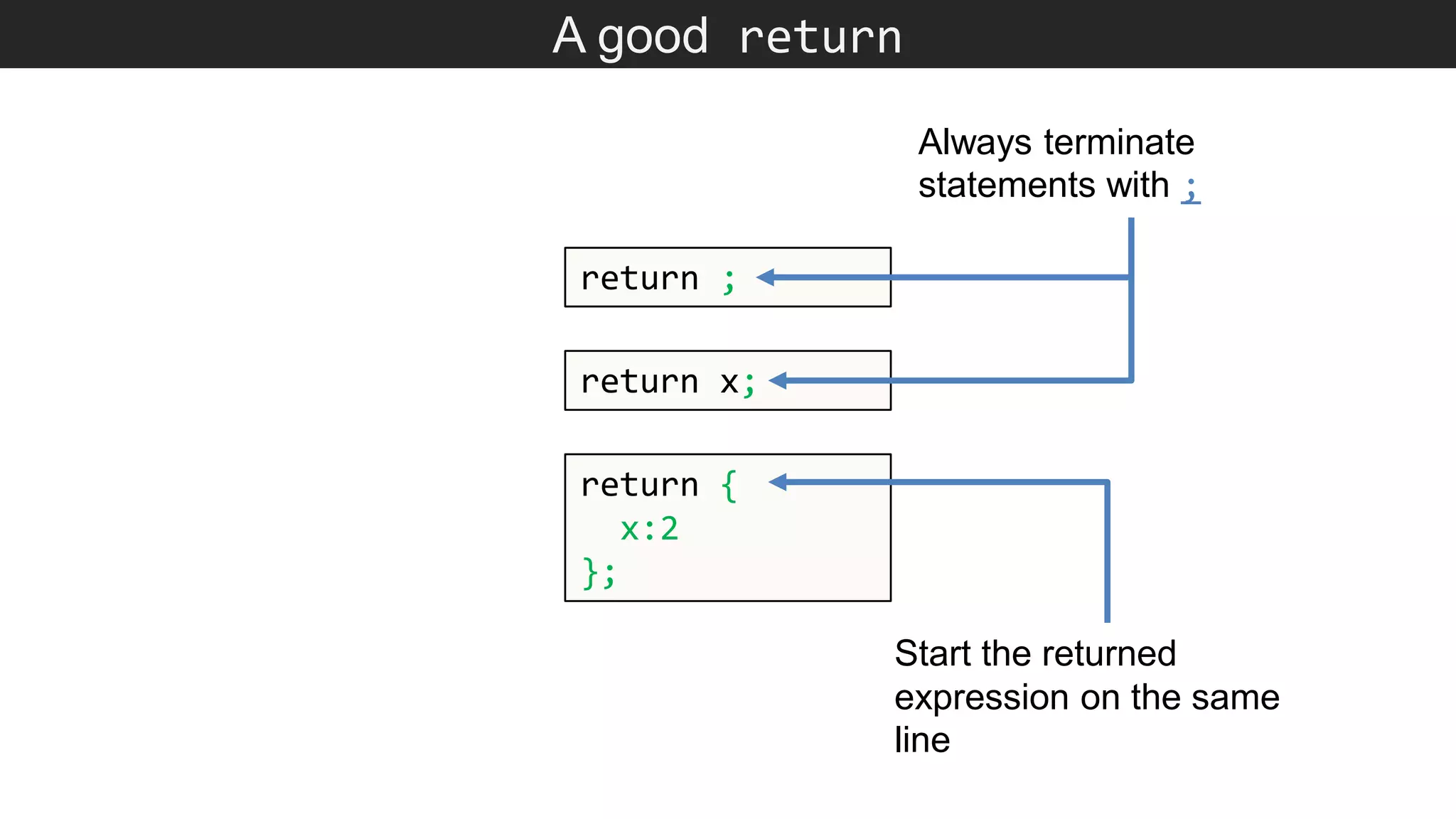
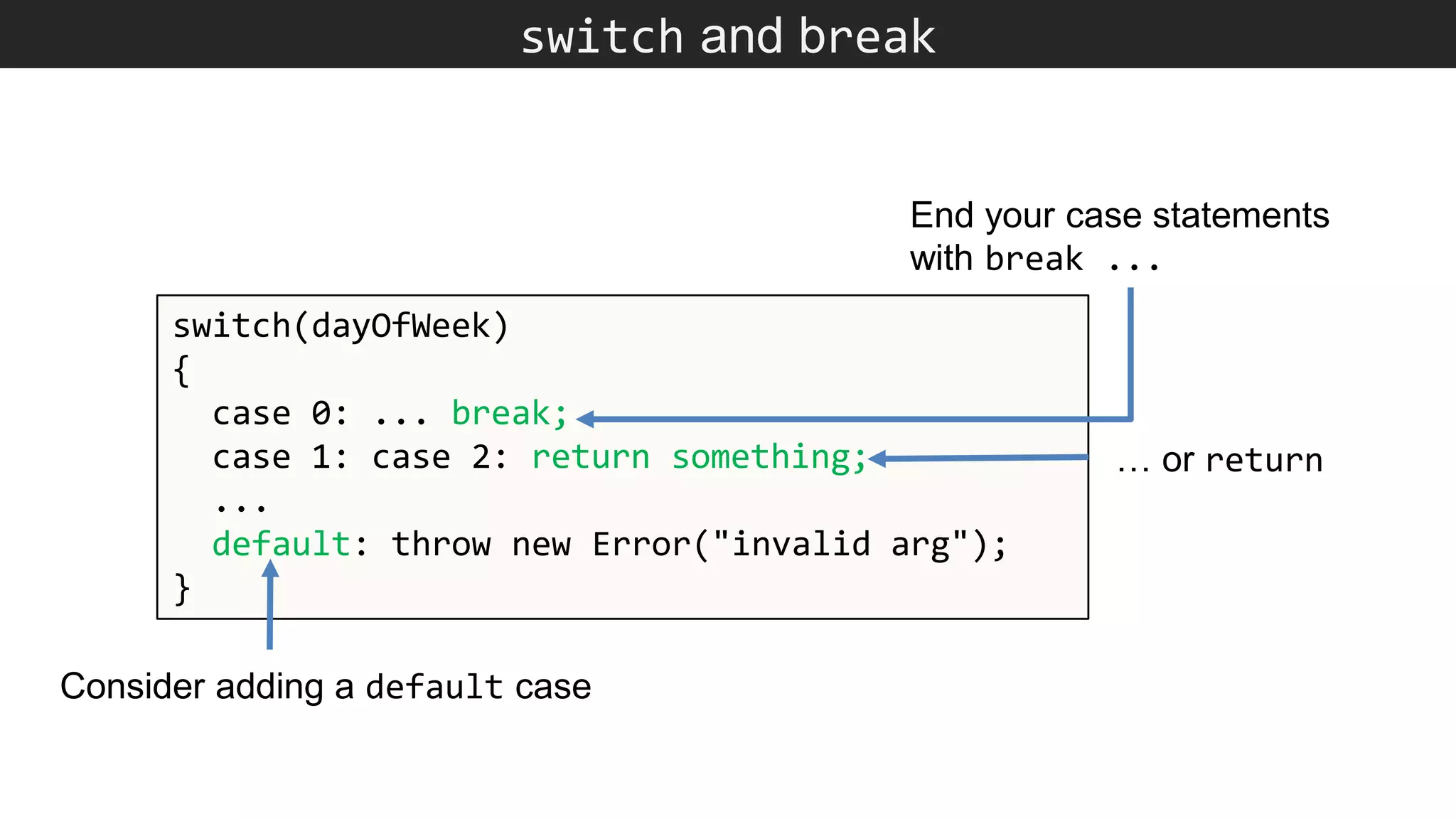
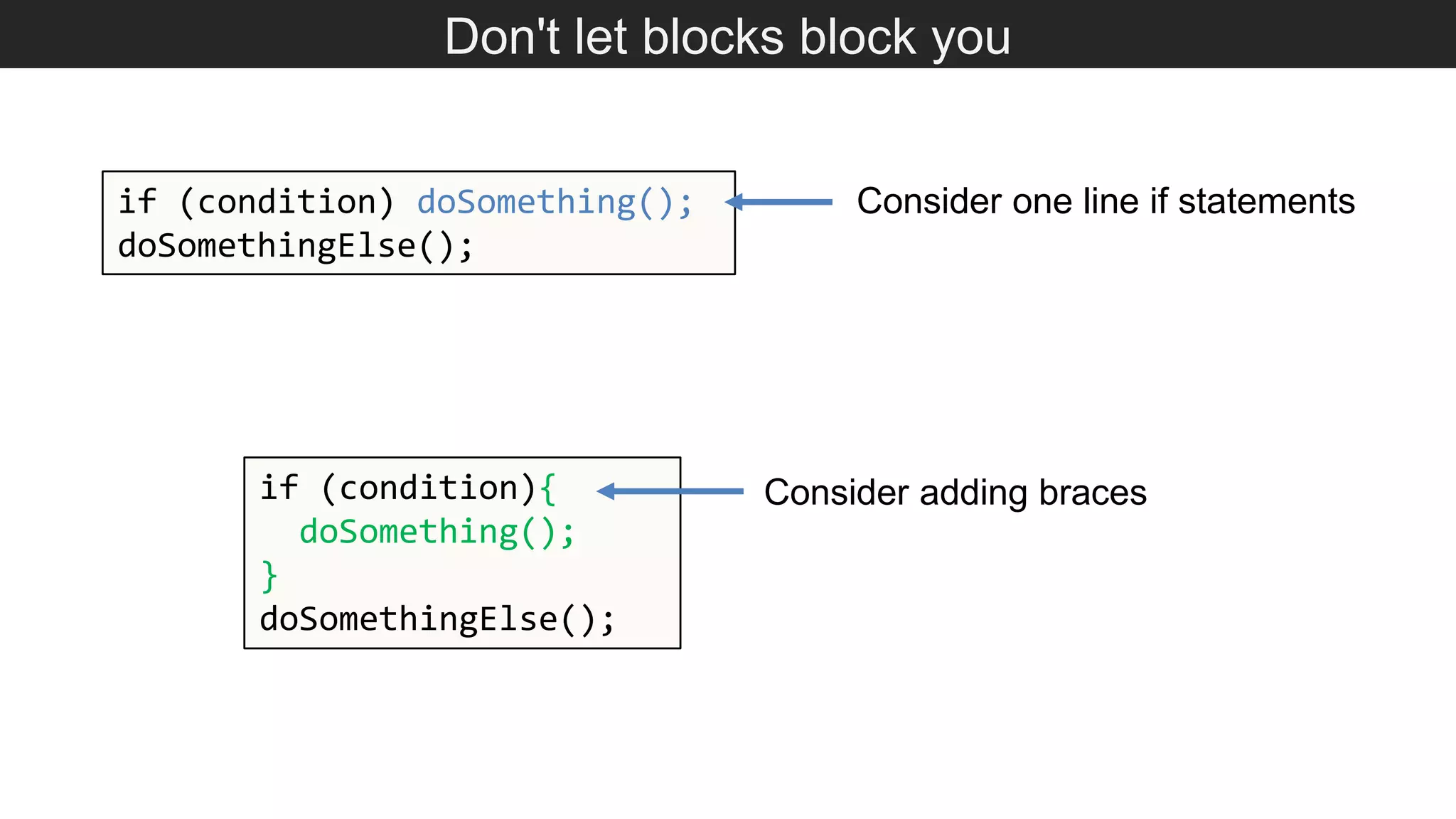
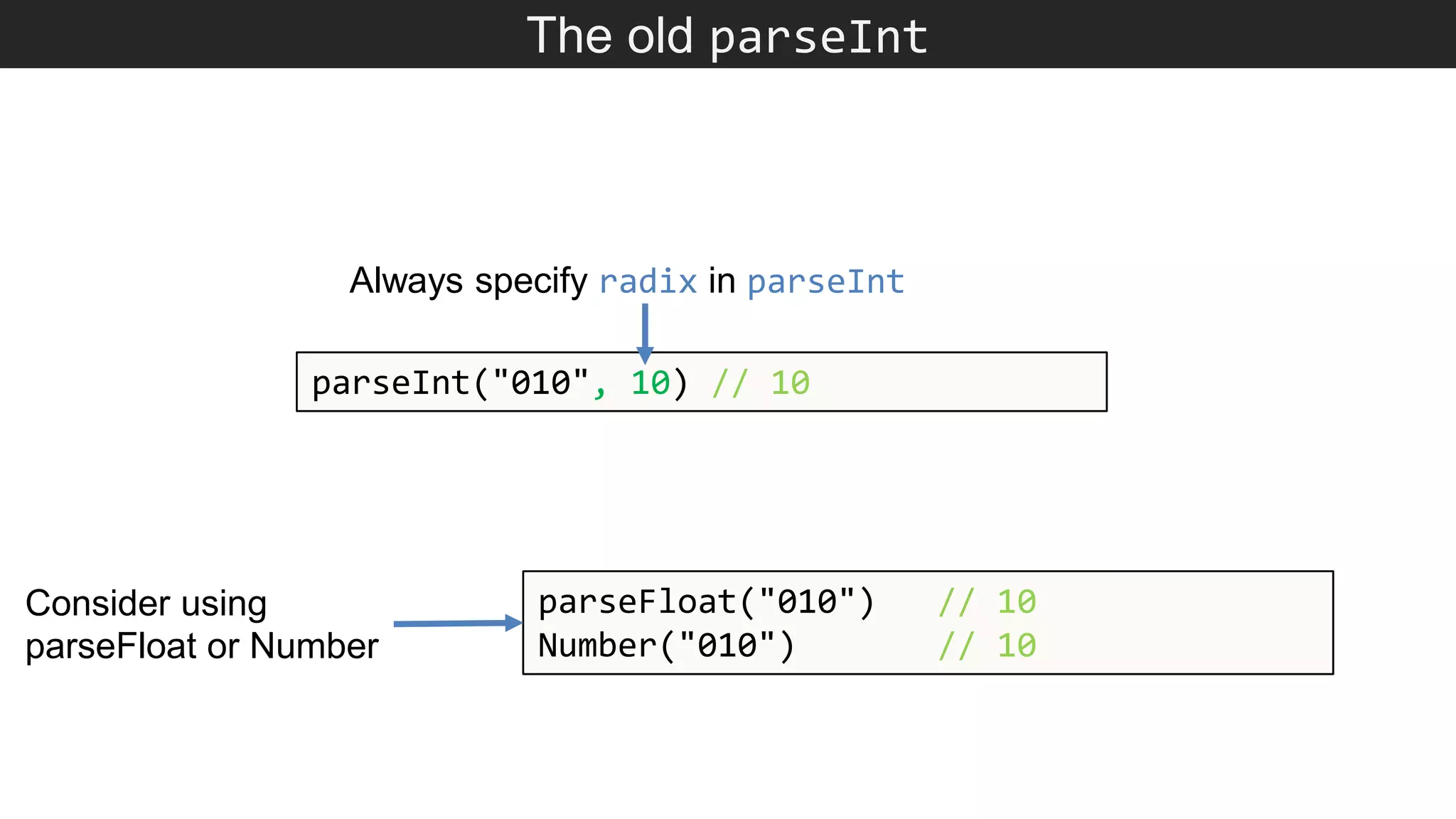
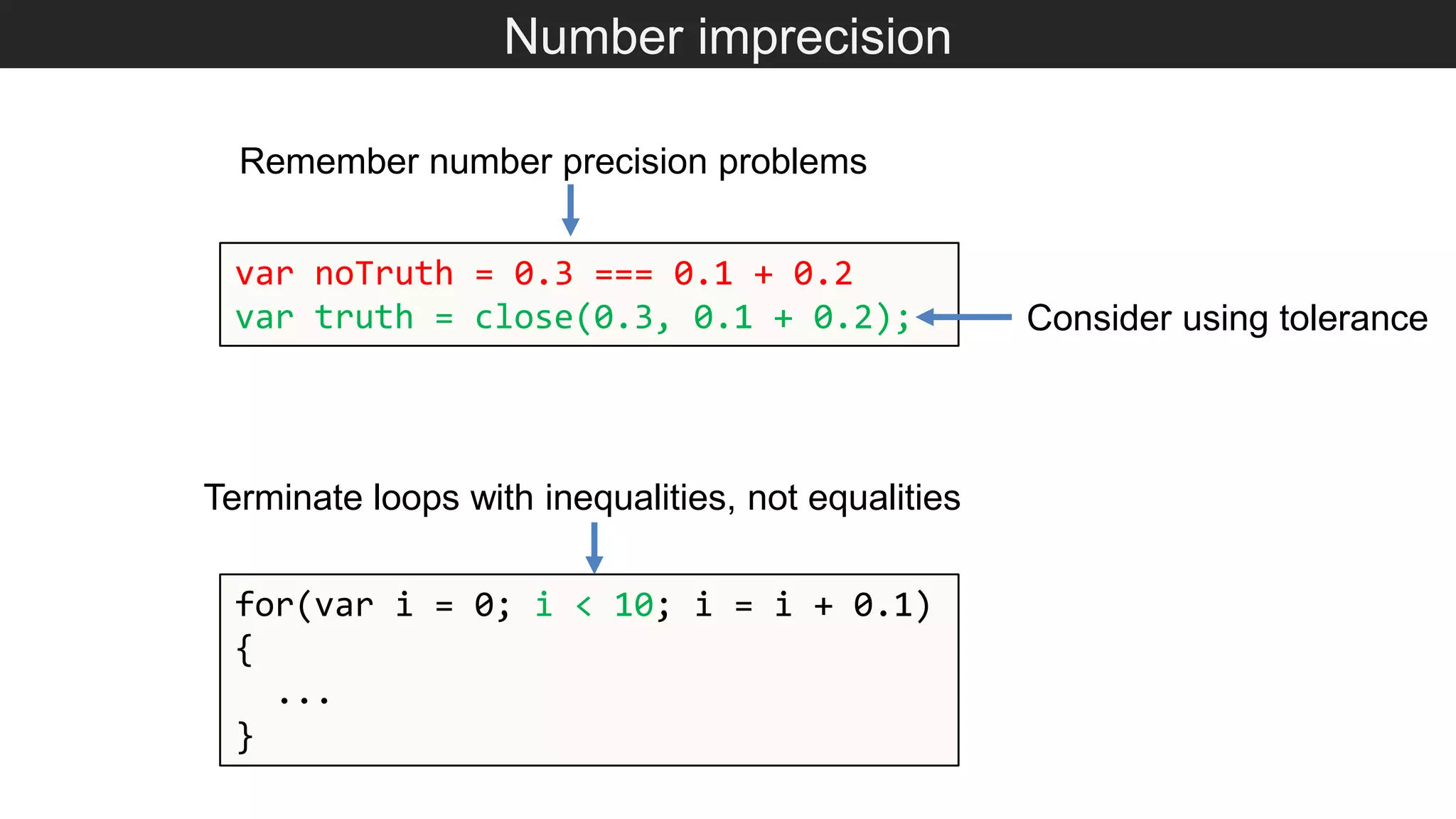
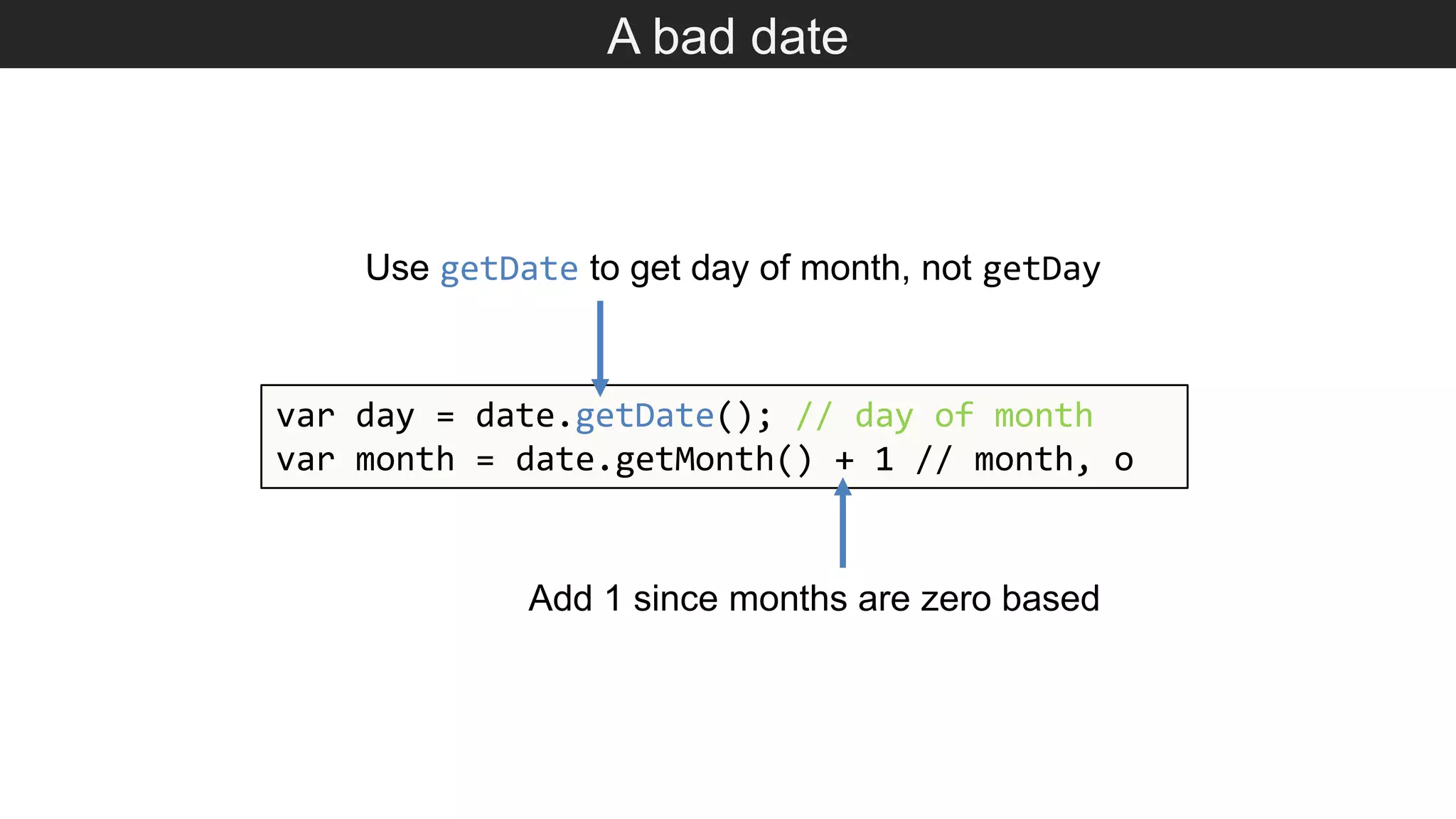
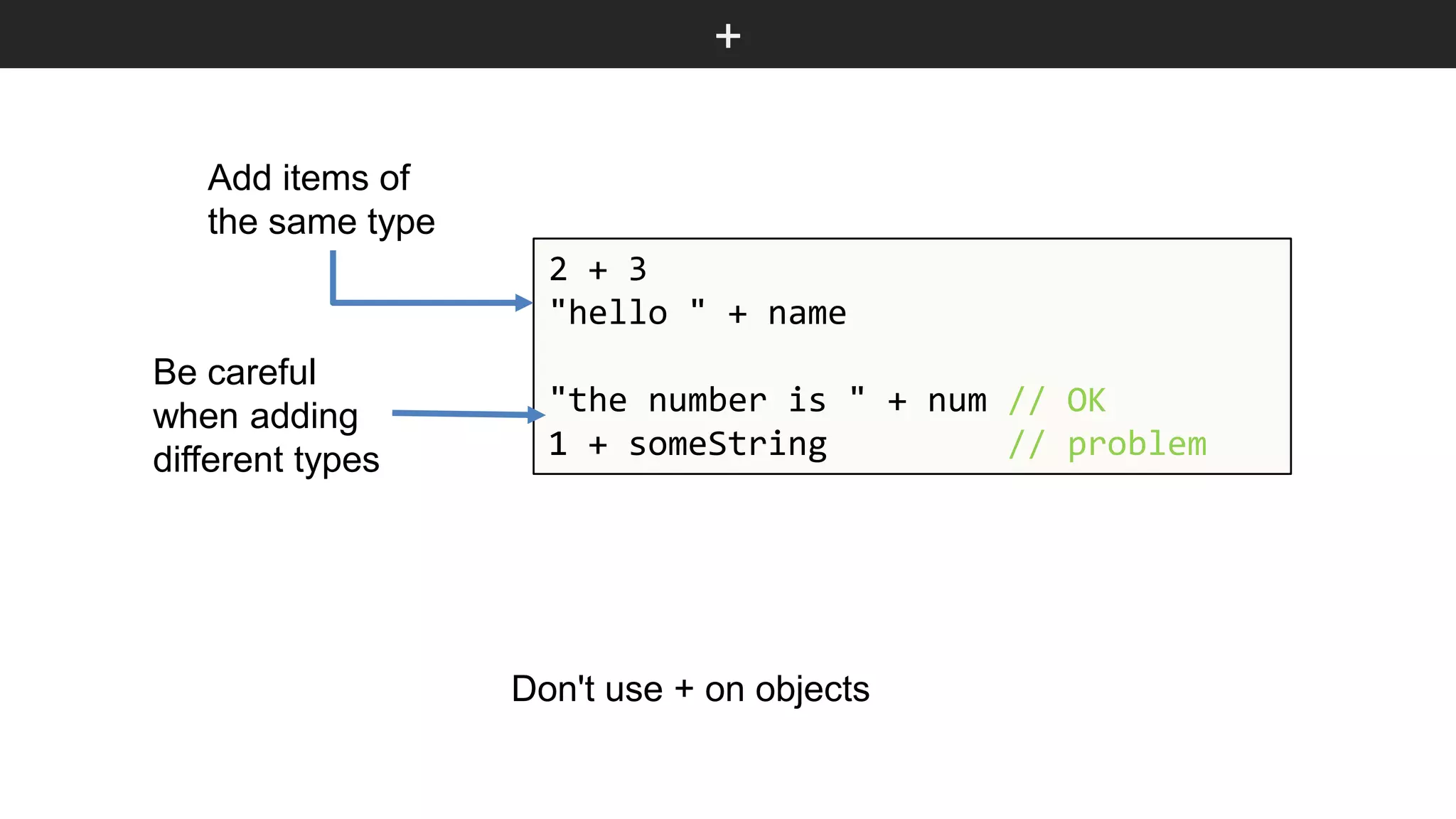
The document outlines various JavaScript coding best practices and common pitfalls, emphasizing proper syntax, flow control, and array manipulation. Recommendations include terminating statements with semicolons, using appropriate equality checks, and managing data types correctly. Additionally, it advises on handling numbers with precision issues and provides guidance on using objects and arrays effectively.



![push your array myArray.push(post); if (index < 0 || index >= posts.length) { throw new Error('Invalid index'); } posts[index] = post; Use push to add new items to an array. Verify array bounds before writing to arrays via an index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptgotchas-150222224549-conversion-gate01/75/JavaScript-gotchas-11-2048.jpg)
![splice, don't delete var a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; a.splice(2, 1); // a contains 1,2,4,5 Use array.splice, to remove items from array Do not delete on arrays](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptgotchas-150222224549-conversion-gate01/75/JavaScript-gotchas-12-2048.jpg)
![Sorting out array.sort var numbers = [1, 5, 10]; // [1, 5, 10] numbers.sort(ascending); // [1, 5, 10] var ascending = function(x, y){ if (x > y) return 1; else if (x < y) return -1; return 0; } Use sort functions for sorting arrays You don't have to use a sort function if the array contains only strings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptgotchas-150222224549-conversion-gate01/75/JavaScript-gotchas-13-2048.jpg)
![Arrays vs. dictionaries var dict = {}; dict.name = value1; dict.['age'] = value2; Use empty JavaScript objects for dictionaries, not arrays var array = [1,2,3] ; array[0]; Use only numbers to access array items](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptgotchas-150222224549-conversion-gate01/75/JavaScript-gotchas-14-2048.jpg)