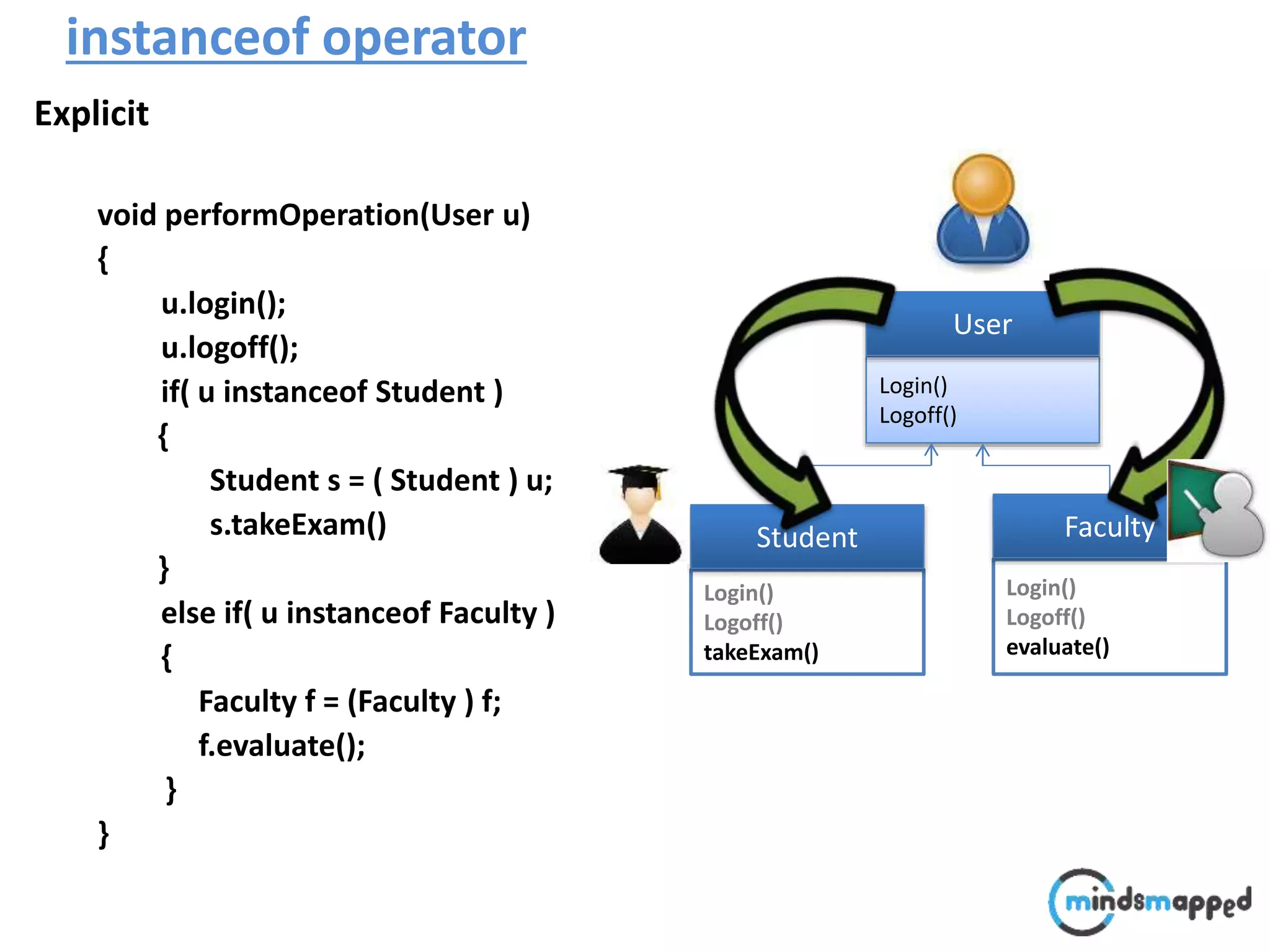
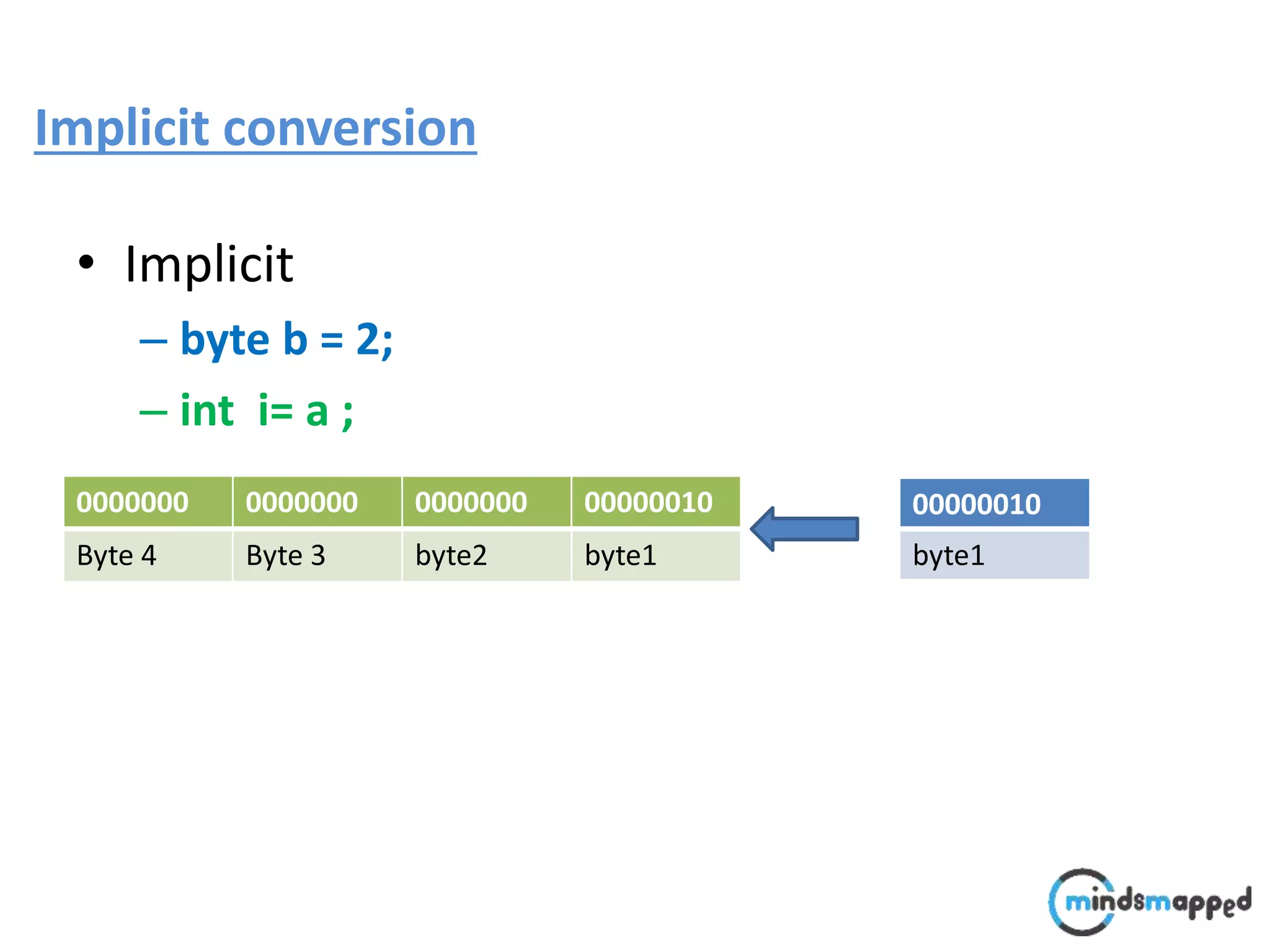
The document provides an overview of type casting in Java, explaining both implicit and explicit conversions between data types. It illustrates how to implement inheritance and polymorphism using classes like 'Shape', 'Rectangle', and 'Triangle', emphasizing method invocation based on object reference types at runtime. Additionally, it introduces the 'instanceof' operator to check an object's type before performing operations, thus avoiding class cast exceptions.

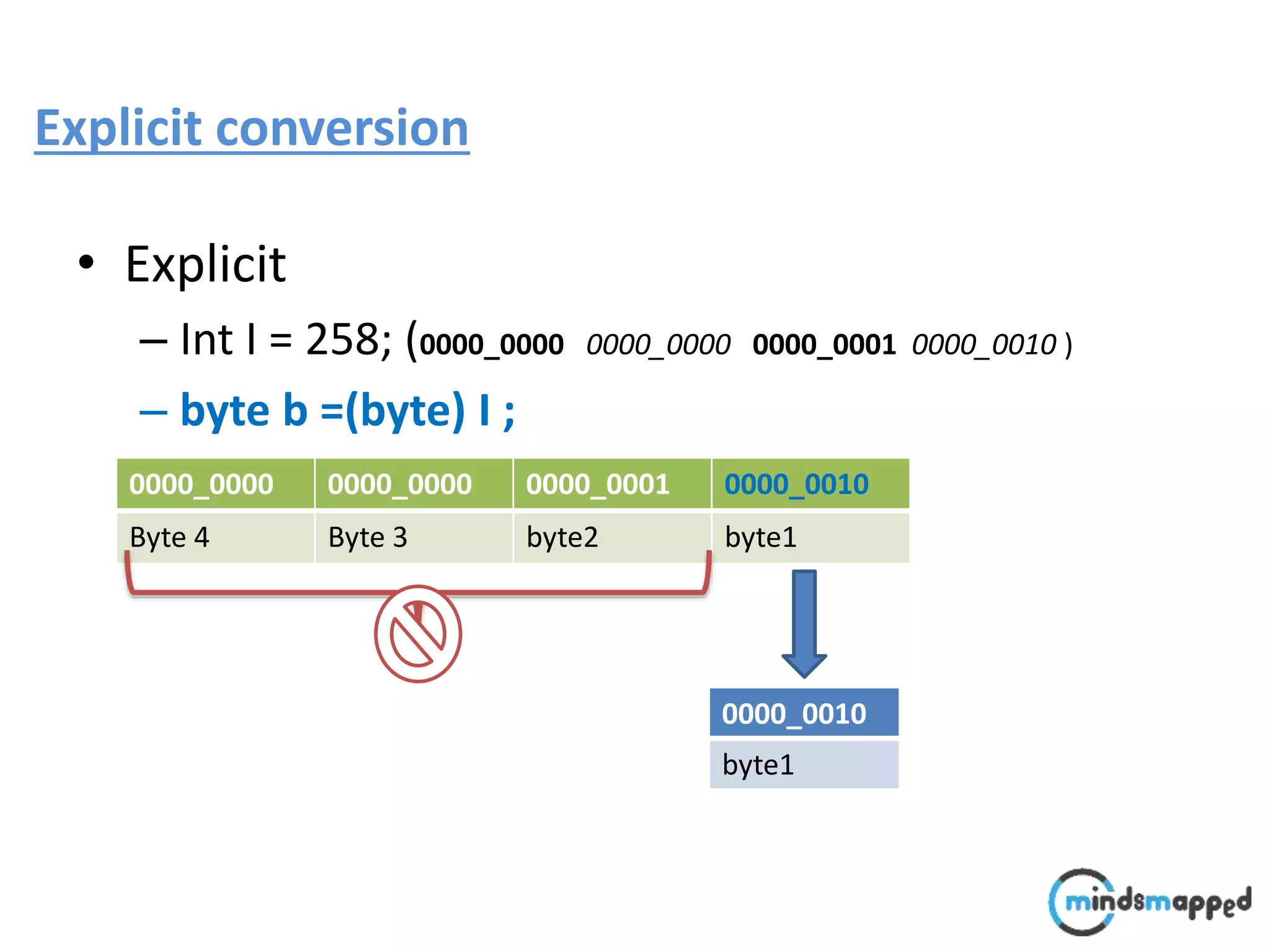
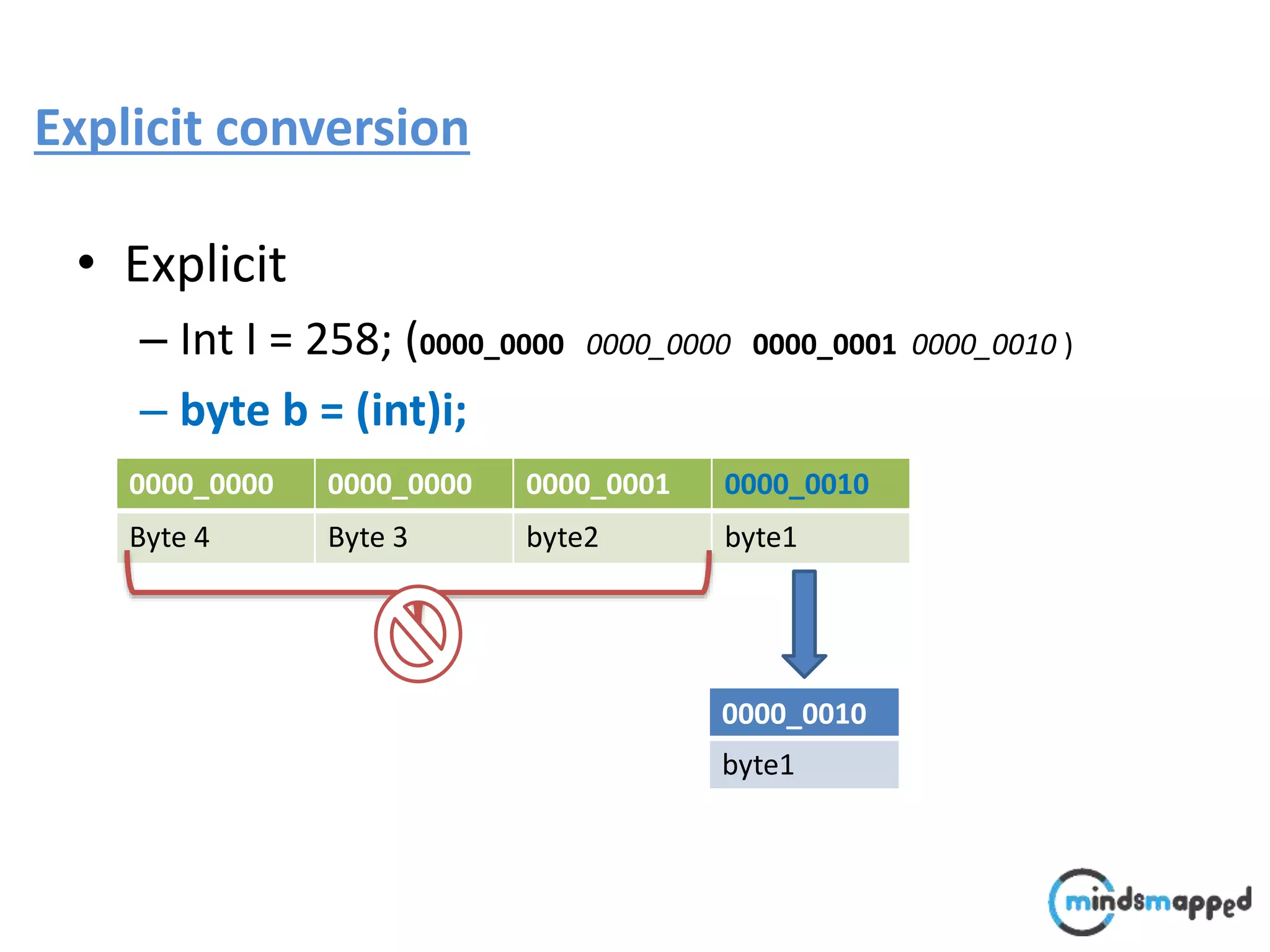
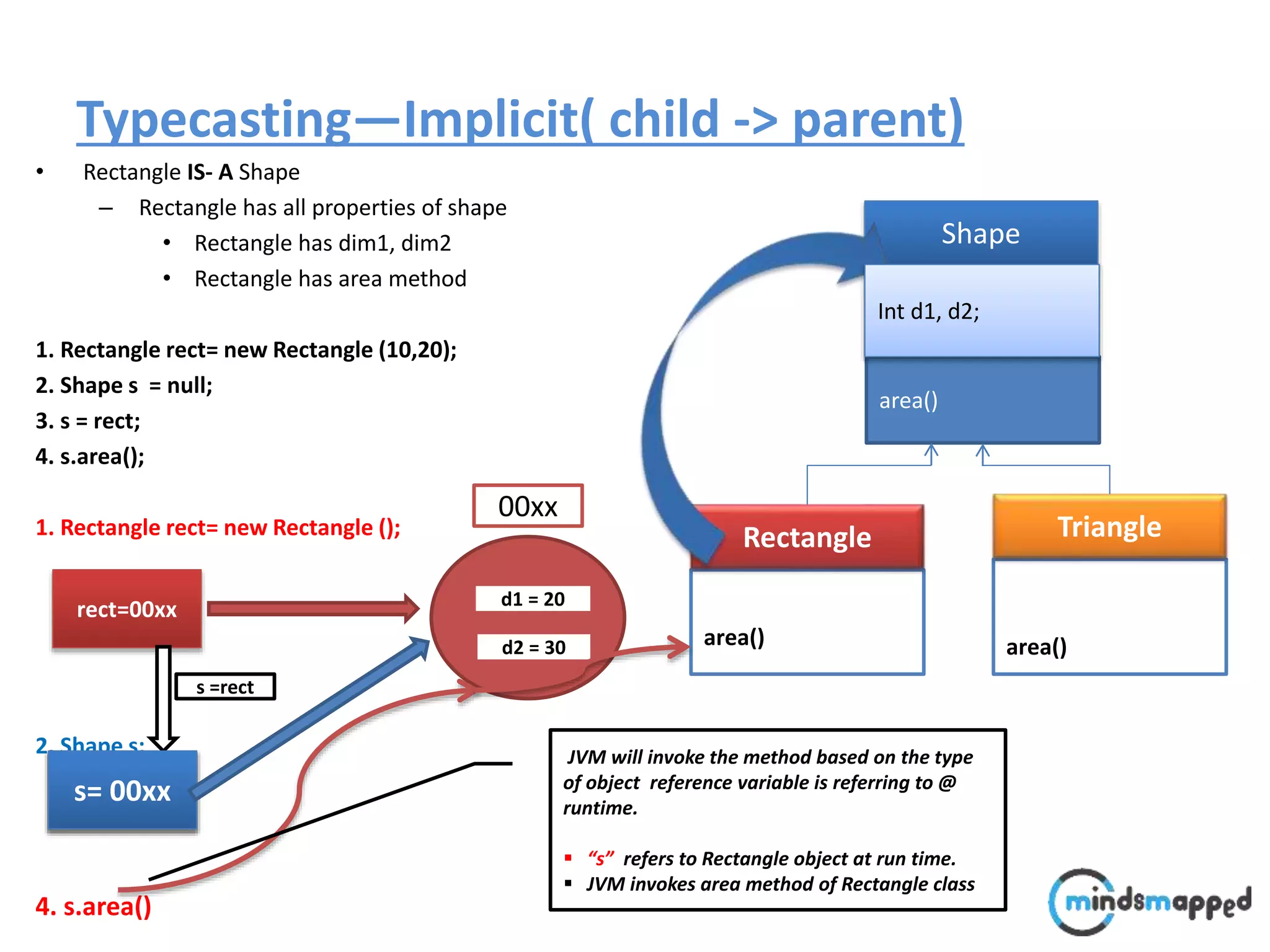
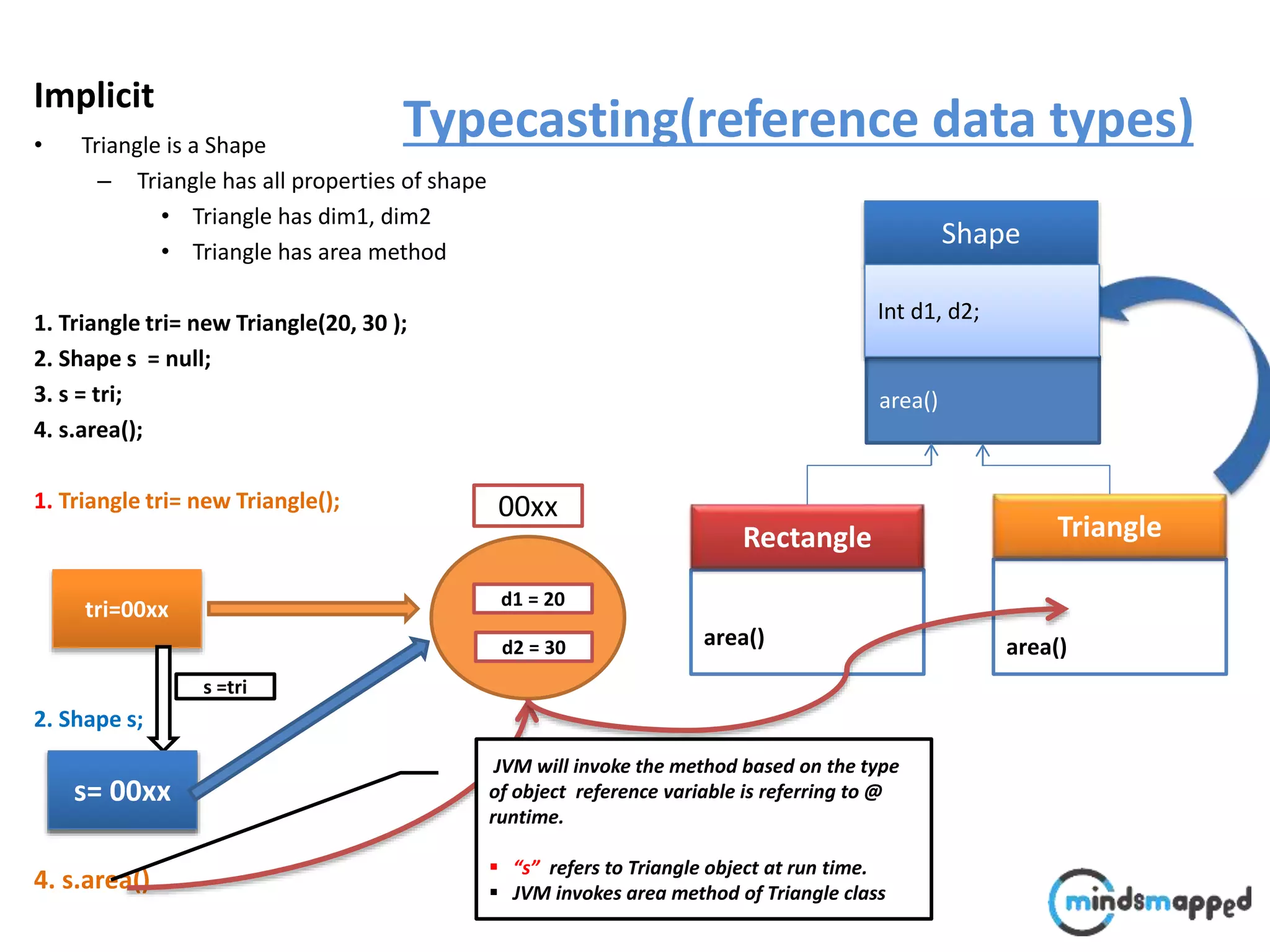
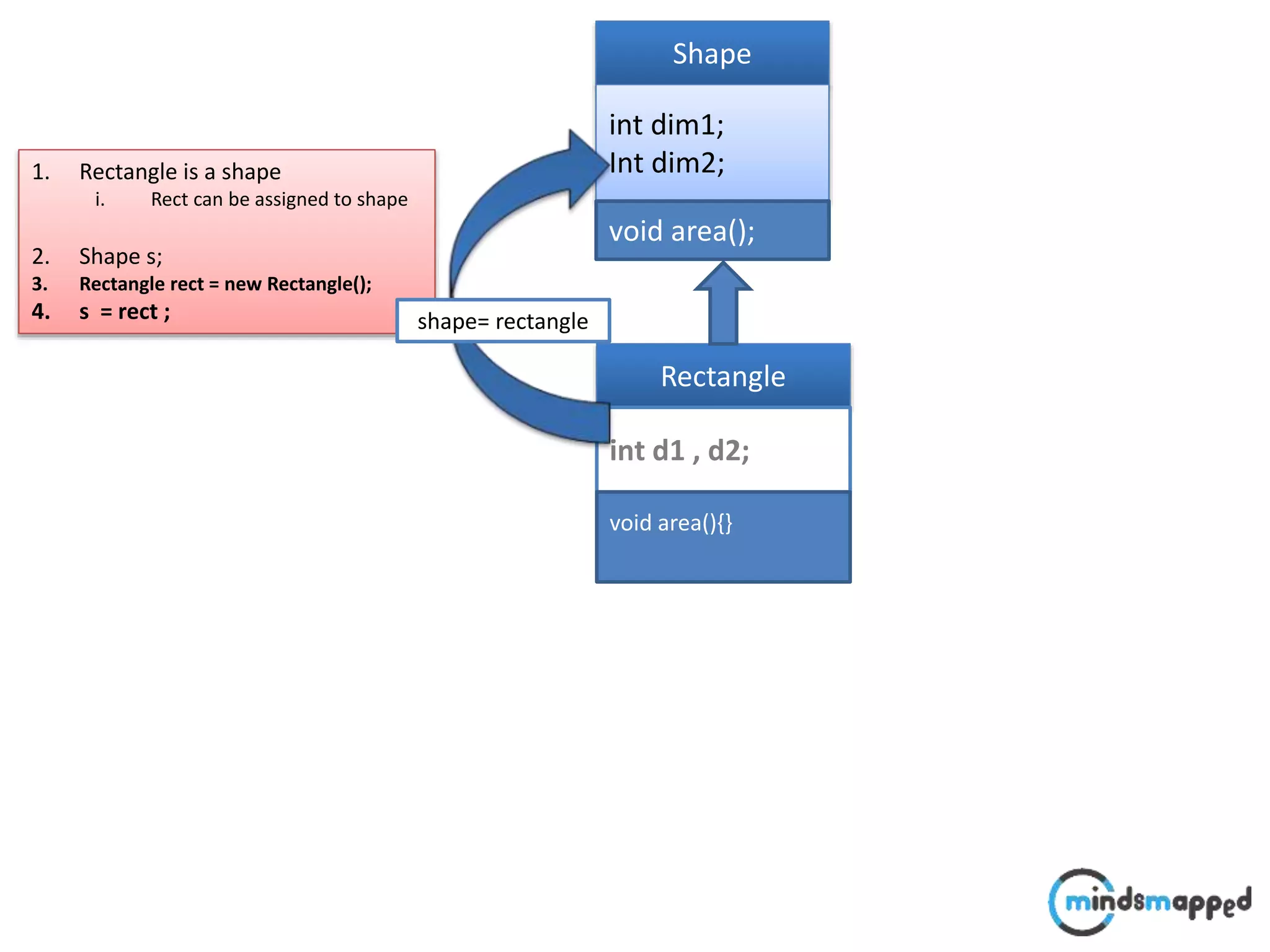
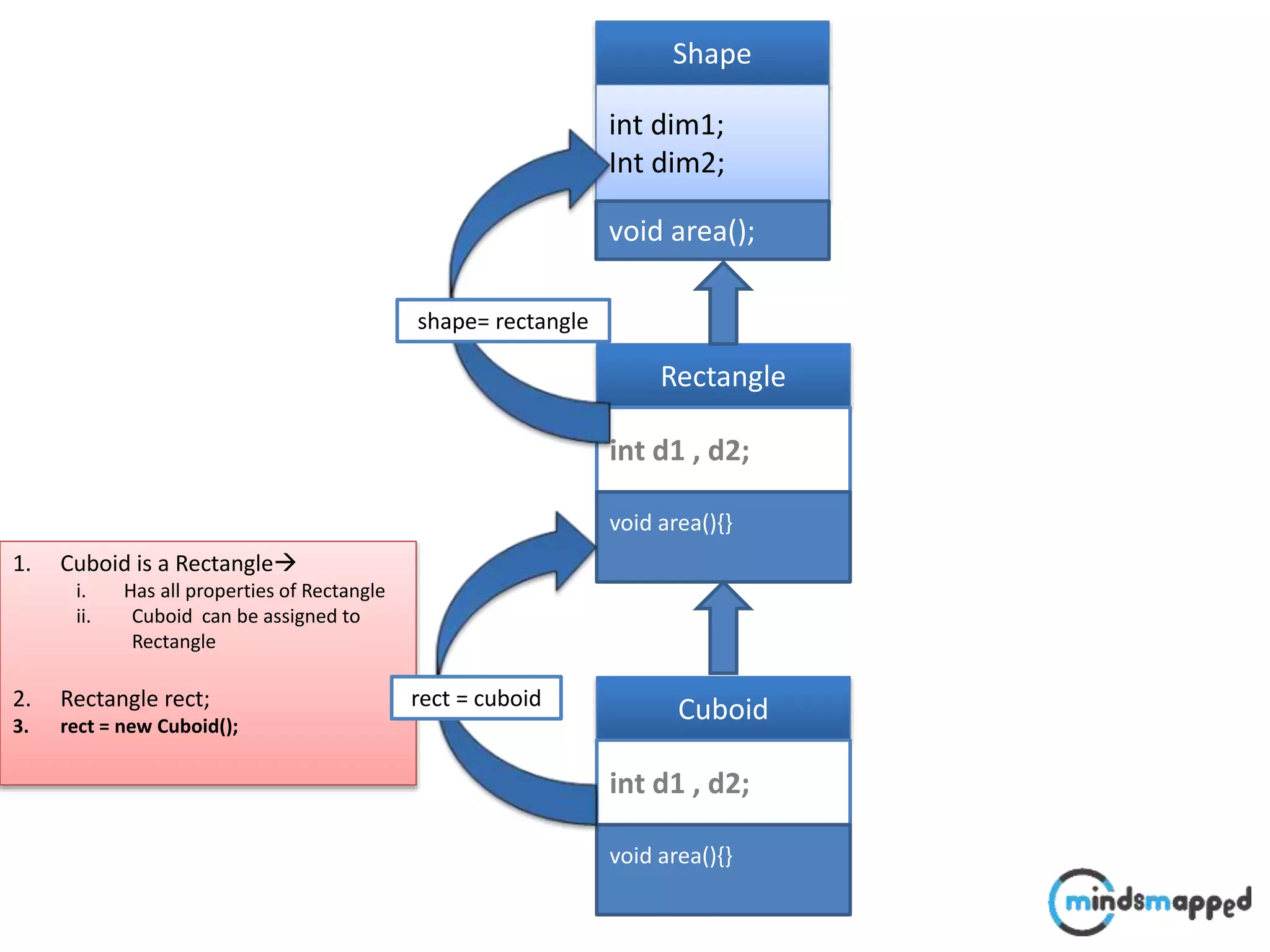
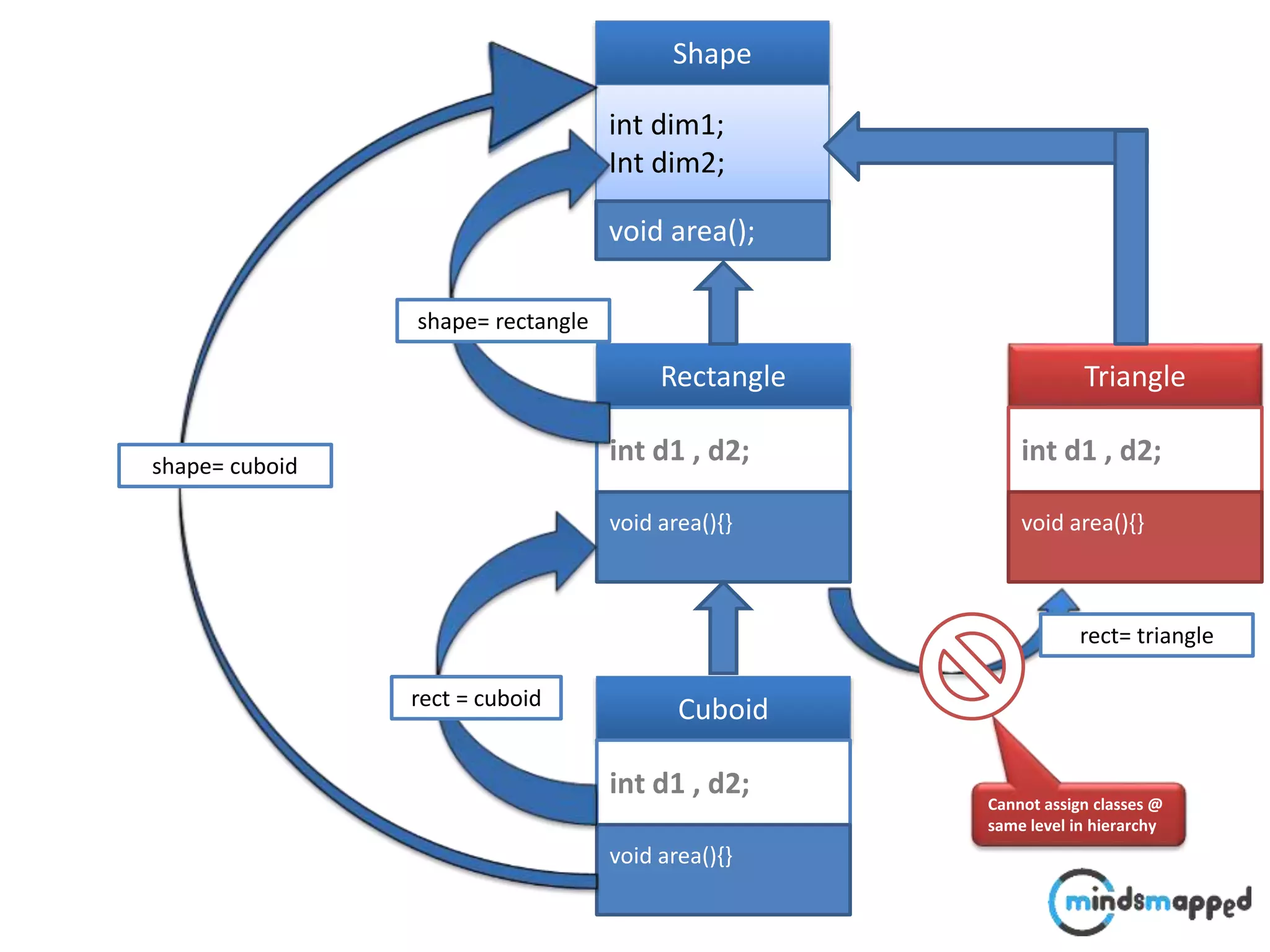
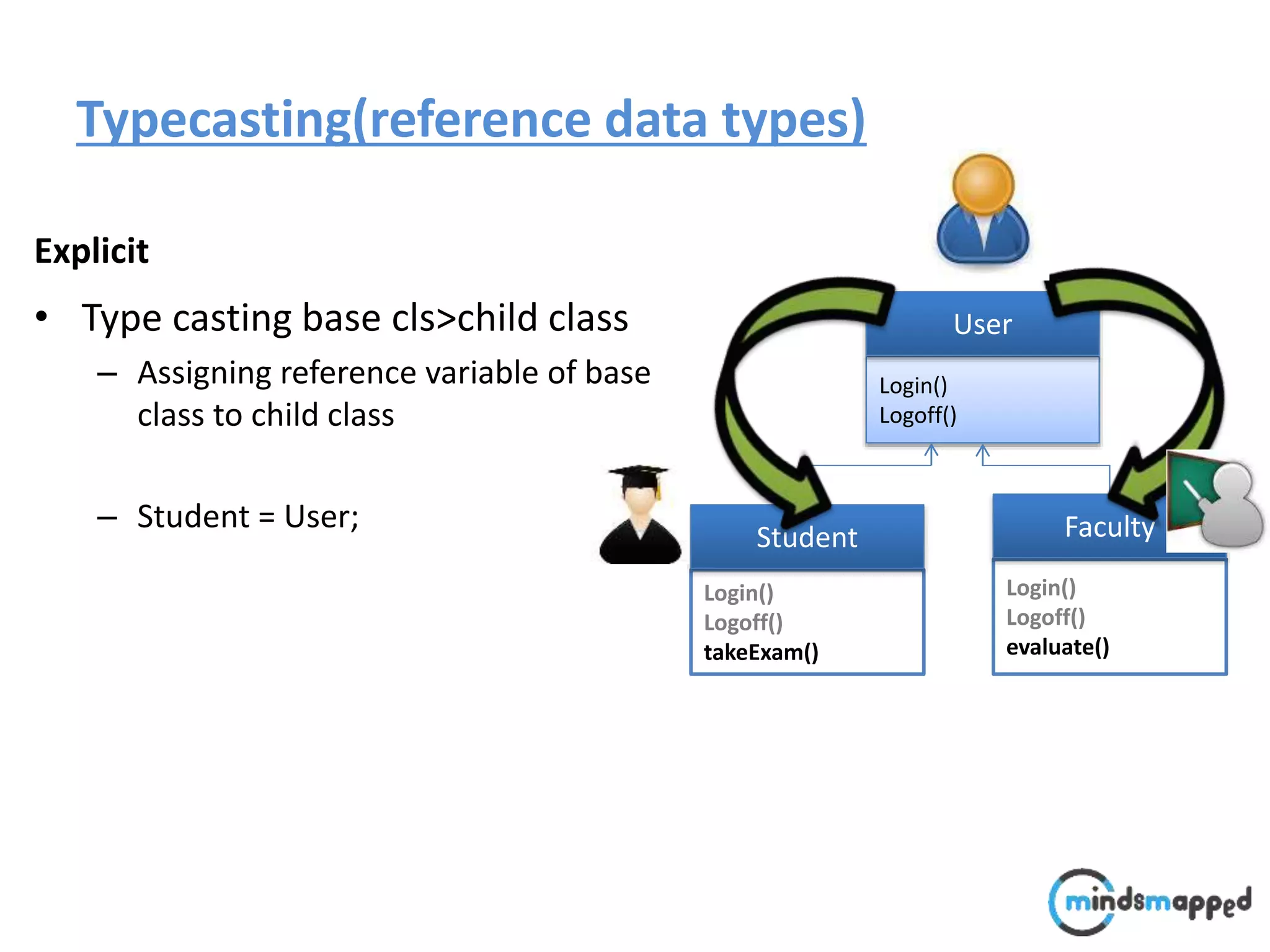
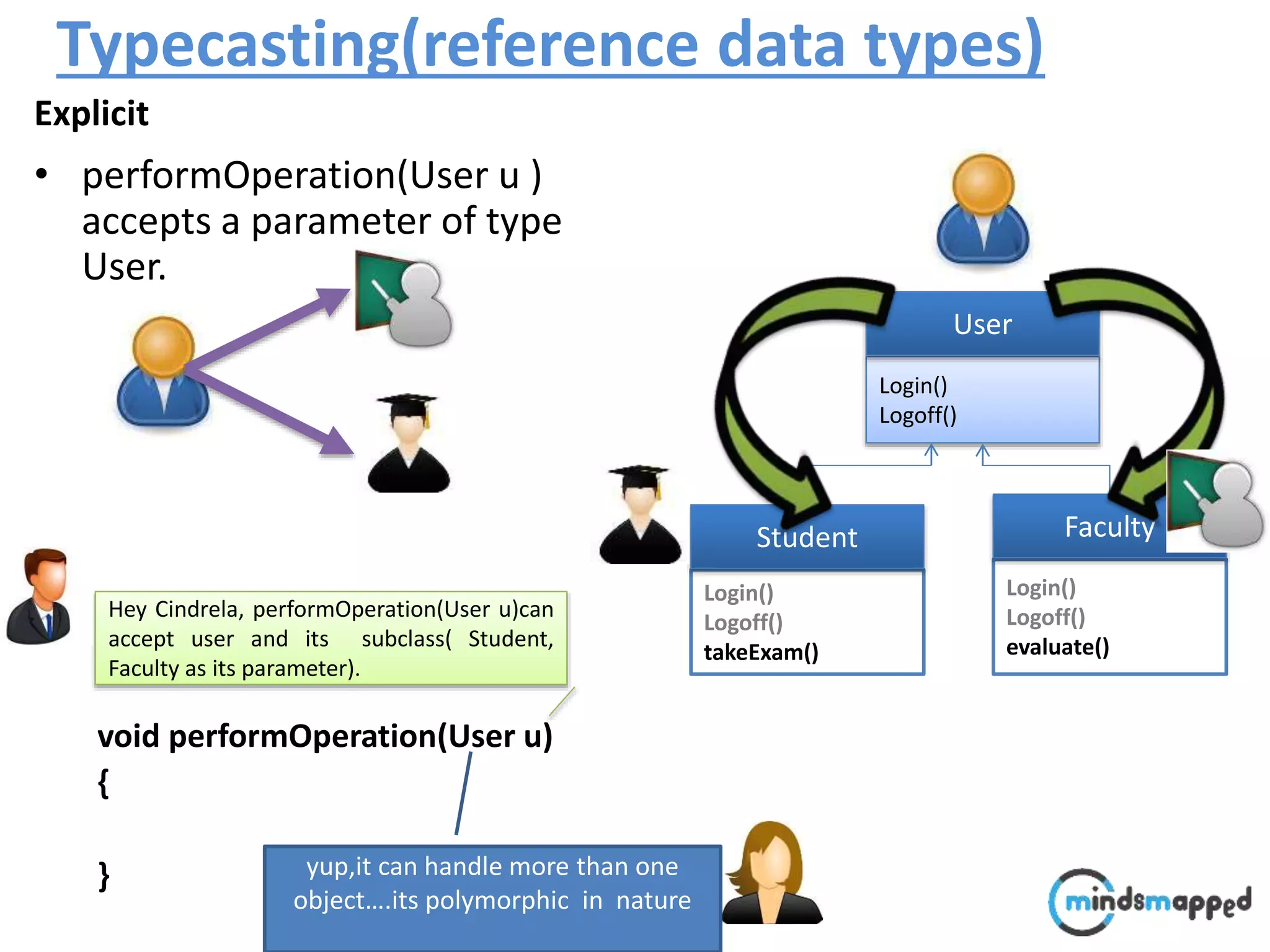

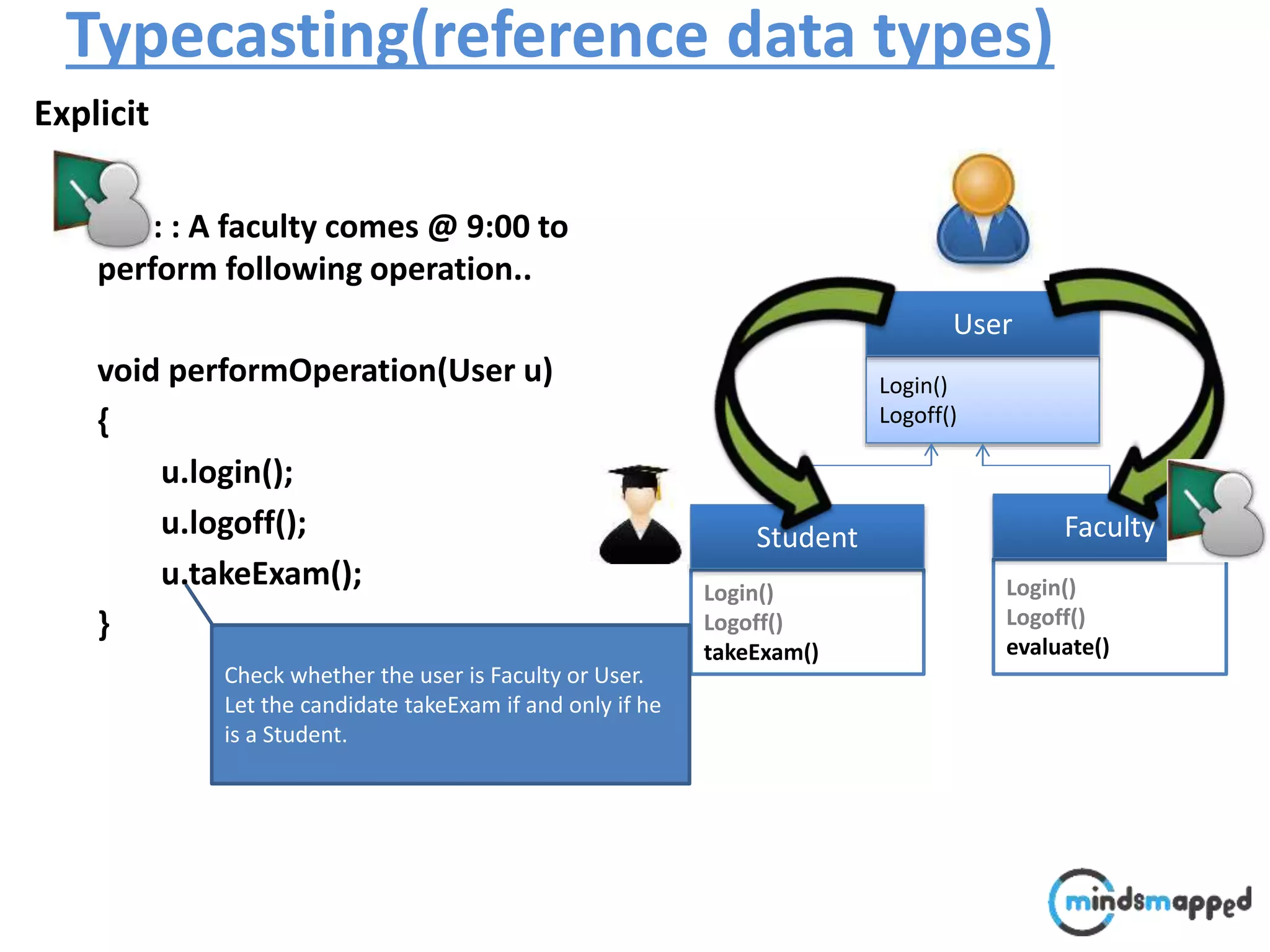
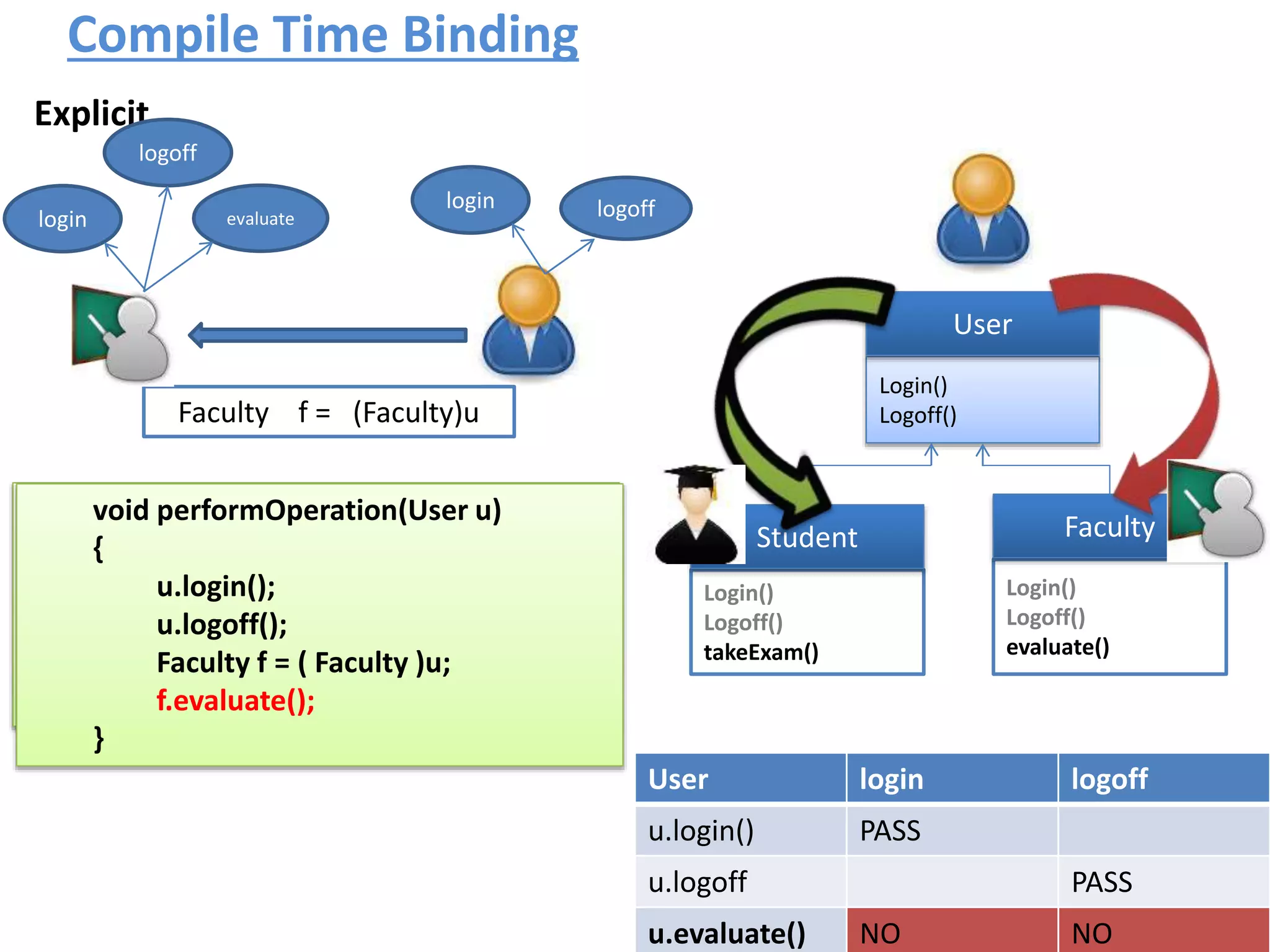
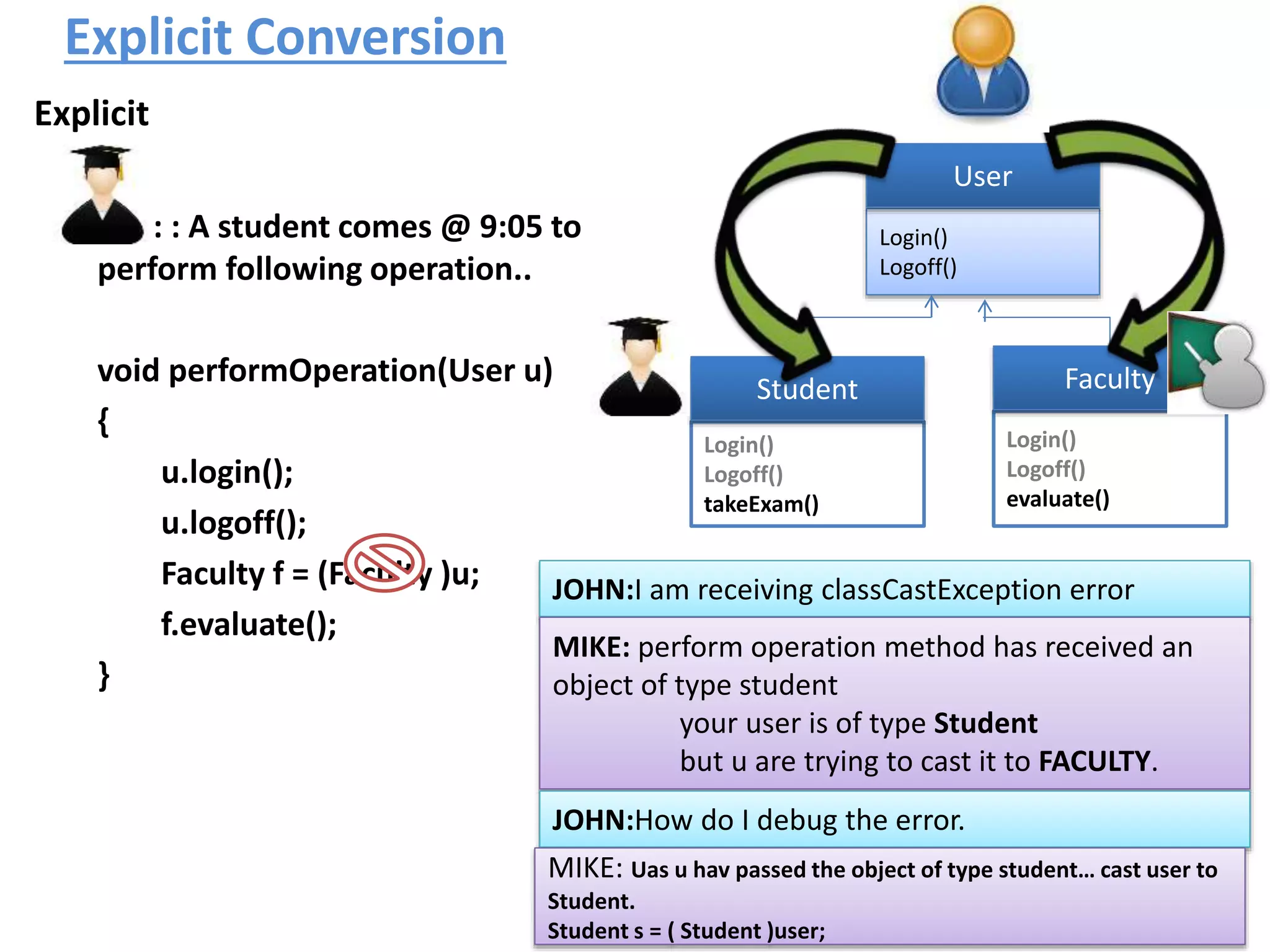
![Typecasting Explicit : : A faculty comes @ 9:00 to perform following operation.. void performOperation(User u) { u.login(); u.logoff(); Faculty f = (Faculty )u; f.evaluate(); } Login() Logoff() User Login() Logoff() takeExam() Student Login() Logoff() evaluate() Faculty student..?/] ????](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typecastingprimitivedatatype1-180728195342/75/Java-Type-Casting-16-2048.jpg)