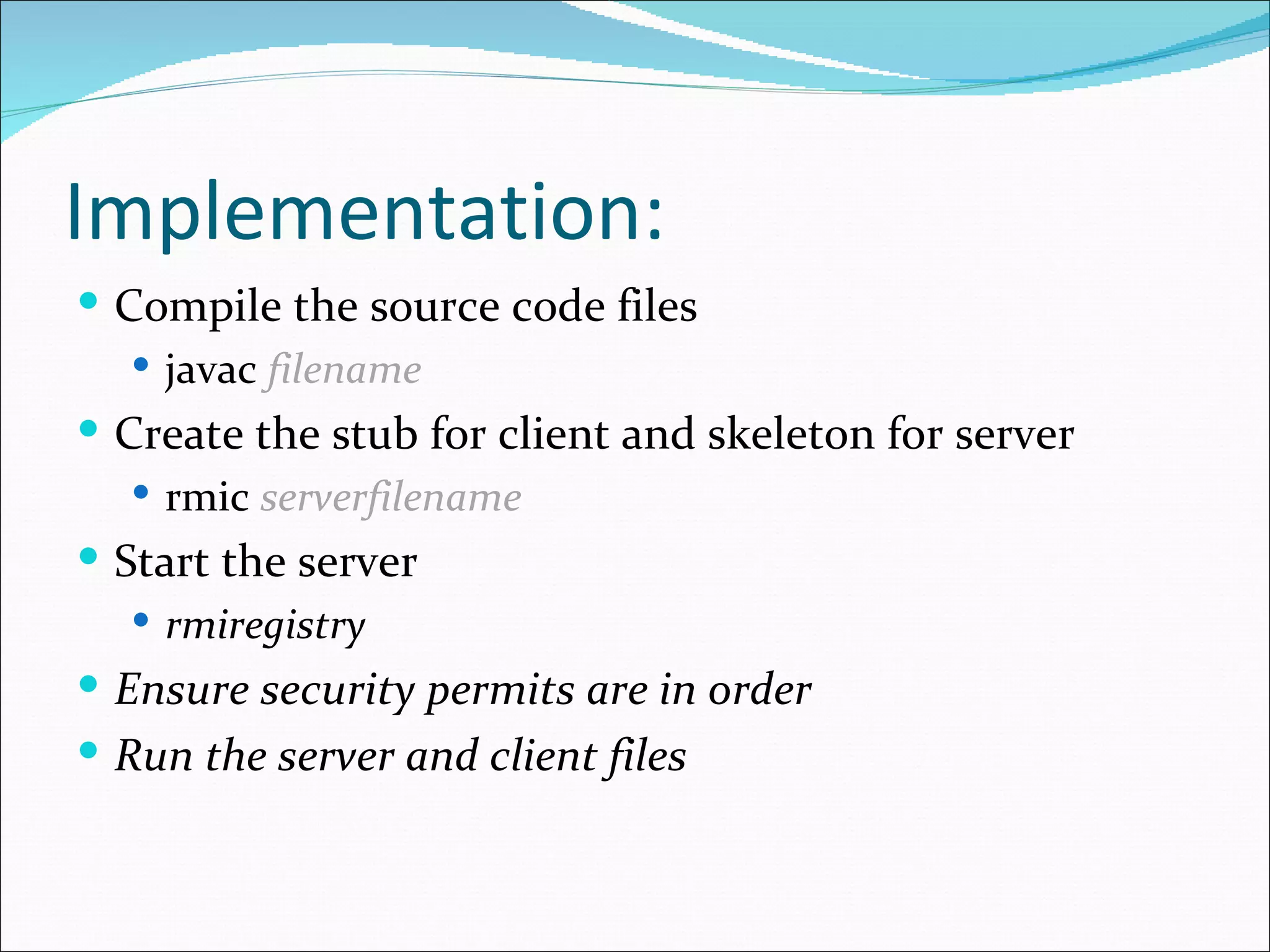
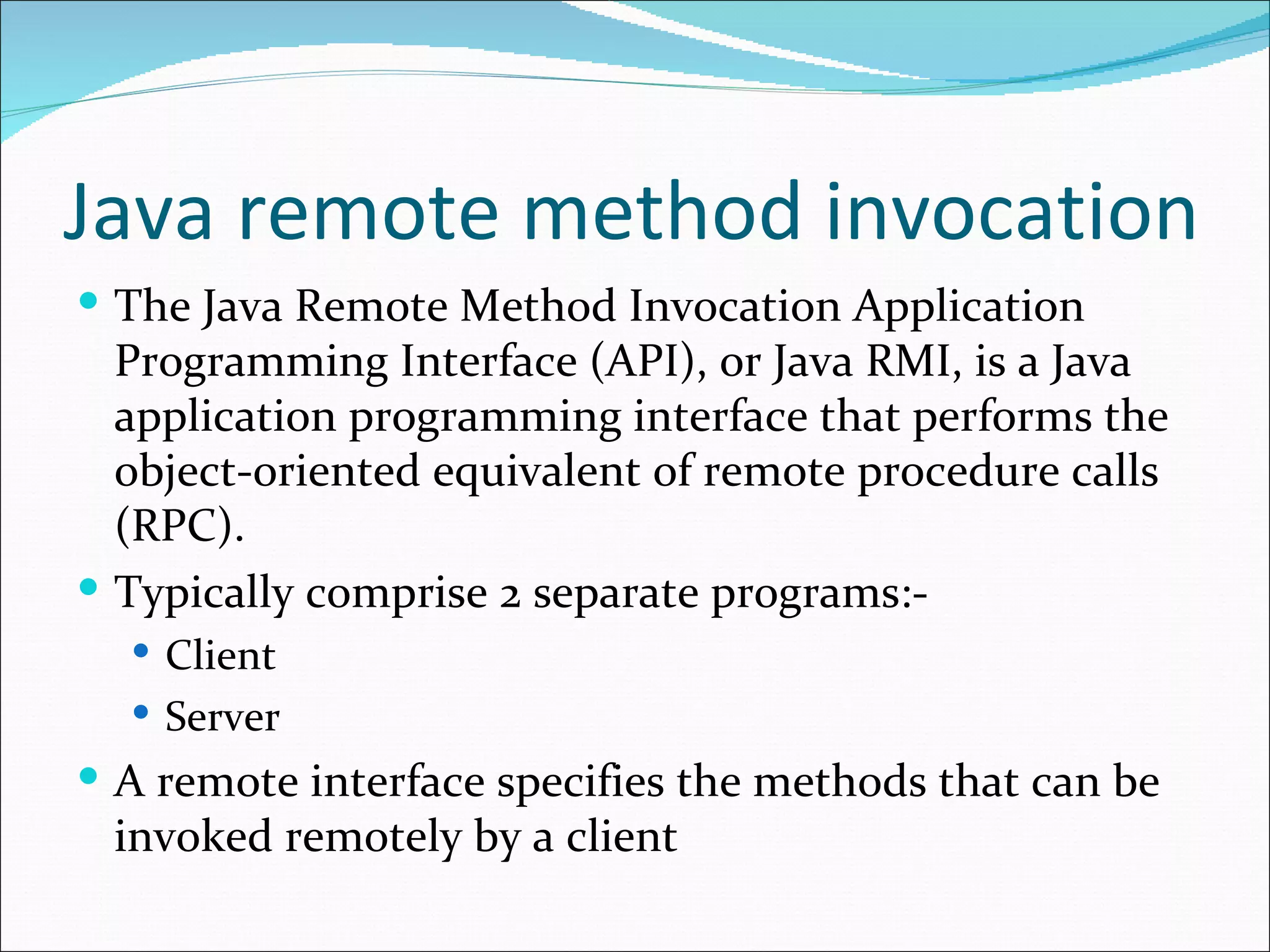
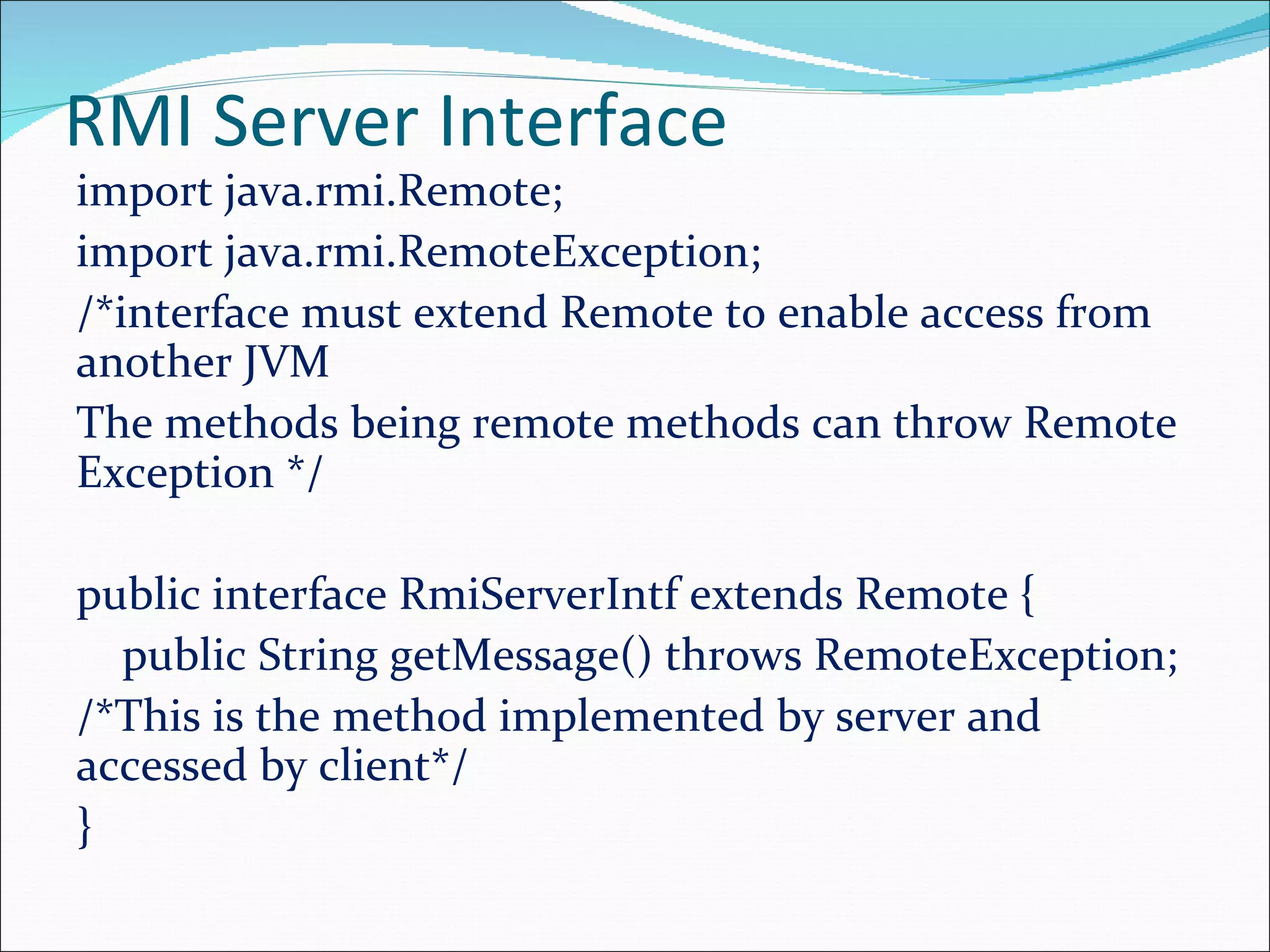
This document discusses Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI), which allows Java objects to invoke methods on other Java objects running in another Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It describes how RMI works using a client-server model, with an interface defining remote methods, an implementation class on the server exporting objects, and clients looking them up by name. It provides code examples of an RMI server interface, implementation class, and client class, along with steps for compiling, running the rmiregistry, and potential error sources.



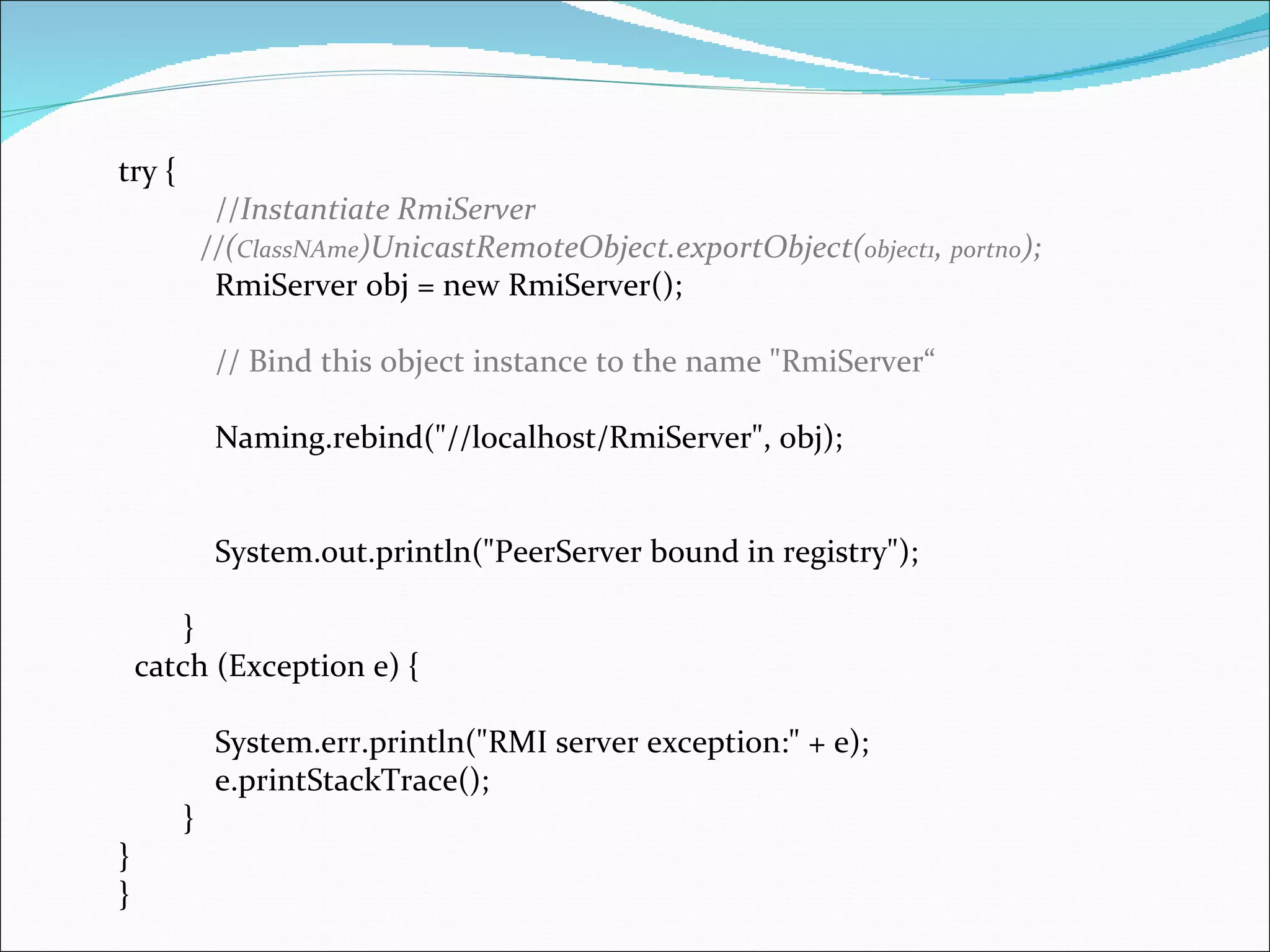
![public static void main(String args[]) { //main method is used to create an instance and make it available to clients. //Write the todo code here System.out.println("RMI server started"); // Create and install a security manager if (System.getSecurityManager() == null) { System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager()); System.out.println("Security manager installed."); } else { System.out.println("Security manager already exists."); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaremotemethodinvocation-120318064355-phpapp01/75/Java-remote-method-invocation-6-2048.jpg)


![public static void main(String args[]) { // Create and install a security manager if (System.getSecurityManager() == null) { System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager()); } RmiClient cli = new RmiClient(); System.out.println(cli.getMessage()); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaremotemethodinvocation-120318064355-phpapp01/75/Java-remote-method-invocation-10-2048.jpg)