Here are the key points about object equality in Java: - The == operator checks if the objects are the same instance - The equals() method checks if the objects have the same value - By default, equals() only returns true if comparing the same instance - Classes should override equals() to check for value equality instead of reference equality So in this case: - jack1 == jack2 will print false as they are different instances - jack1.equals(jack2) will print false by default, as equals() isn't overridden










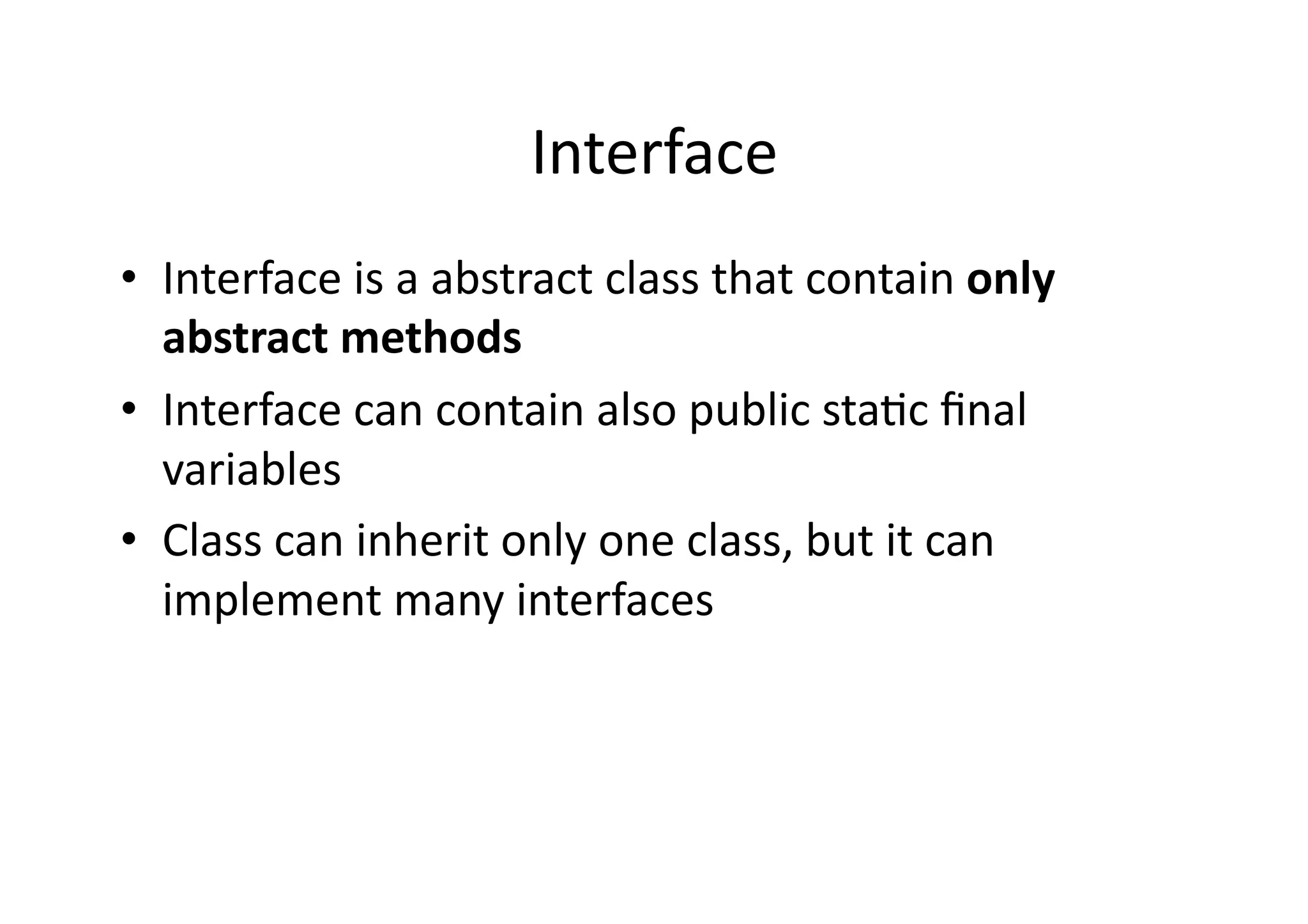
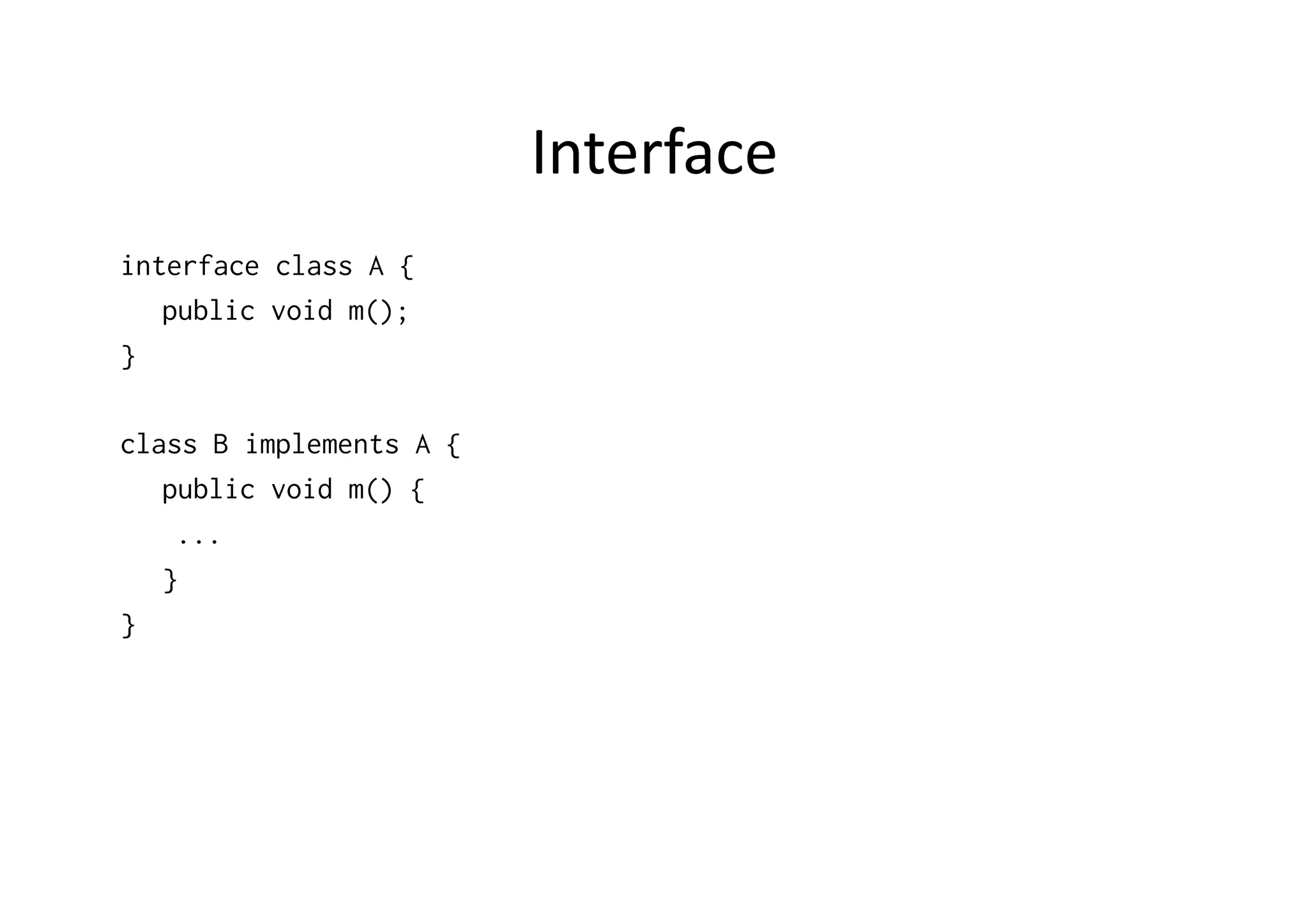
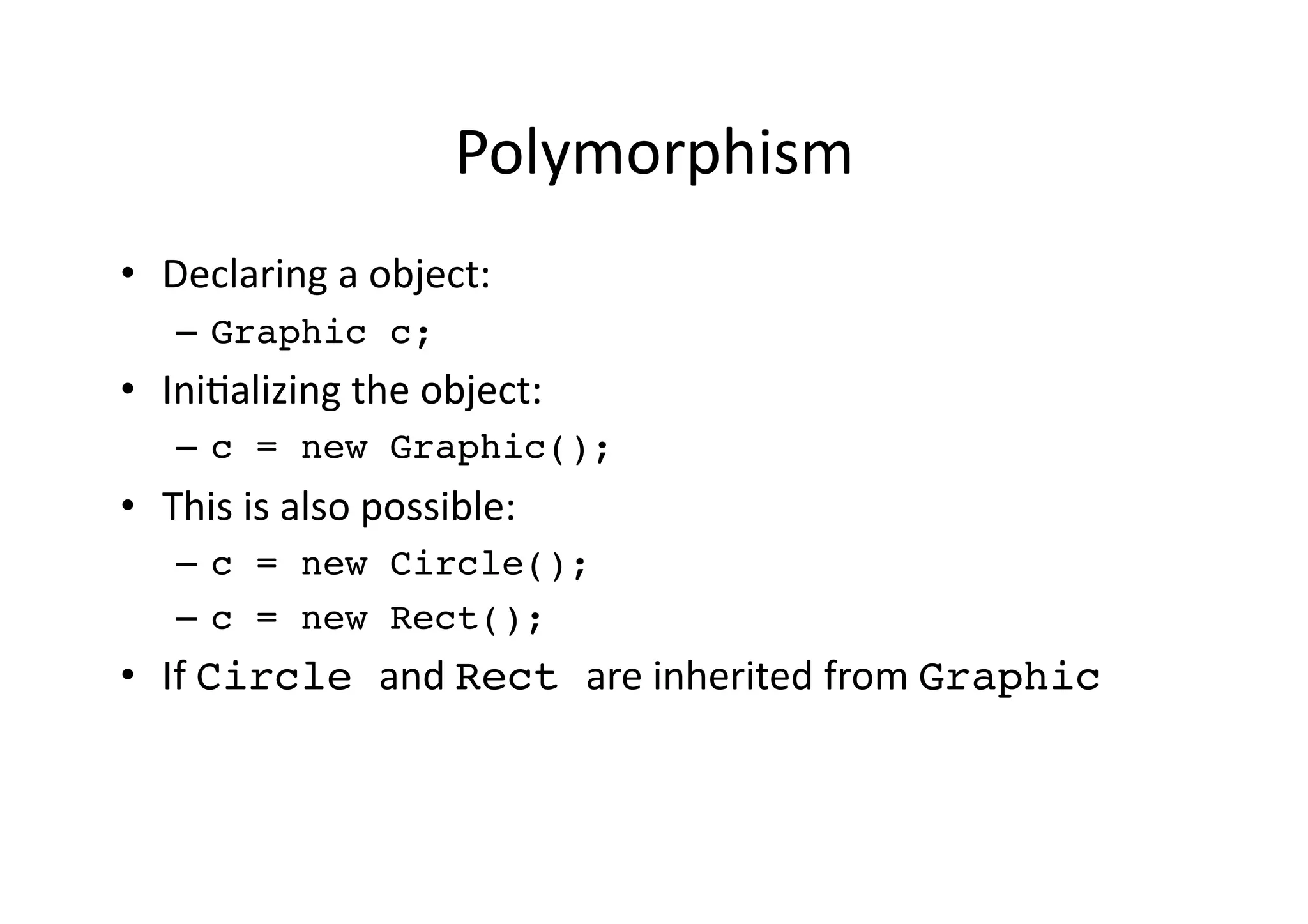
![Polymorphism class Polymorphism { public static void main(String [] args) { // What are the possible objects to be passed? method(??) } public static void method(Graphic c) { ... } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/00oorevisited-1218053794137089-8/75/Java-OO-Revisited-18-2048.jpg)
![Polymorphism interface R { ... } class Polymorphism { public static void main(String [] args) { // What are the possible objects to be passed? method(??) } public static void method(R r) { ... } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/00oorevisited-1218053794137089-8/75/Java-OO-Revisited-19-2048.jpg)

