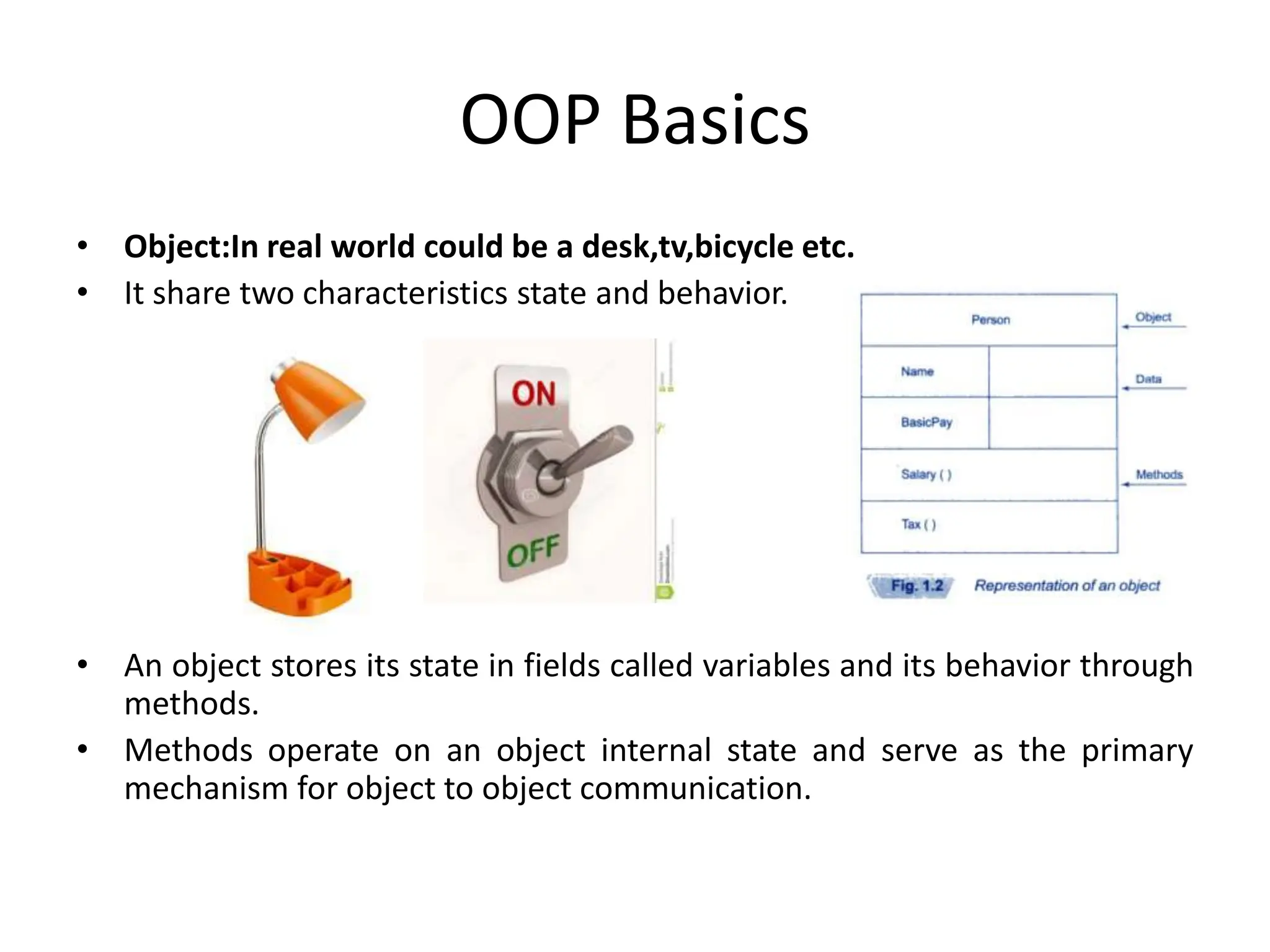
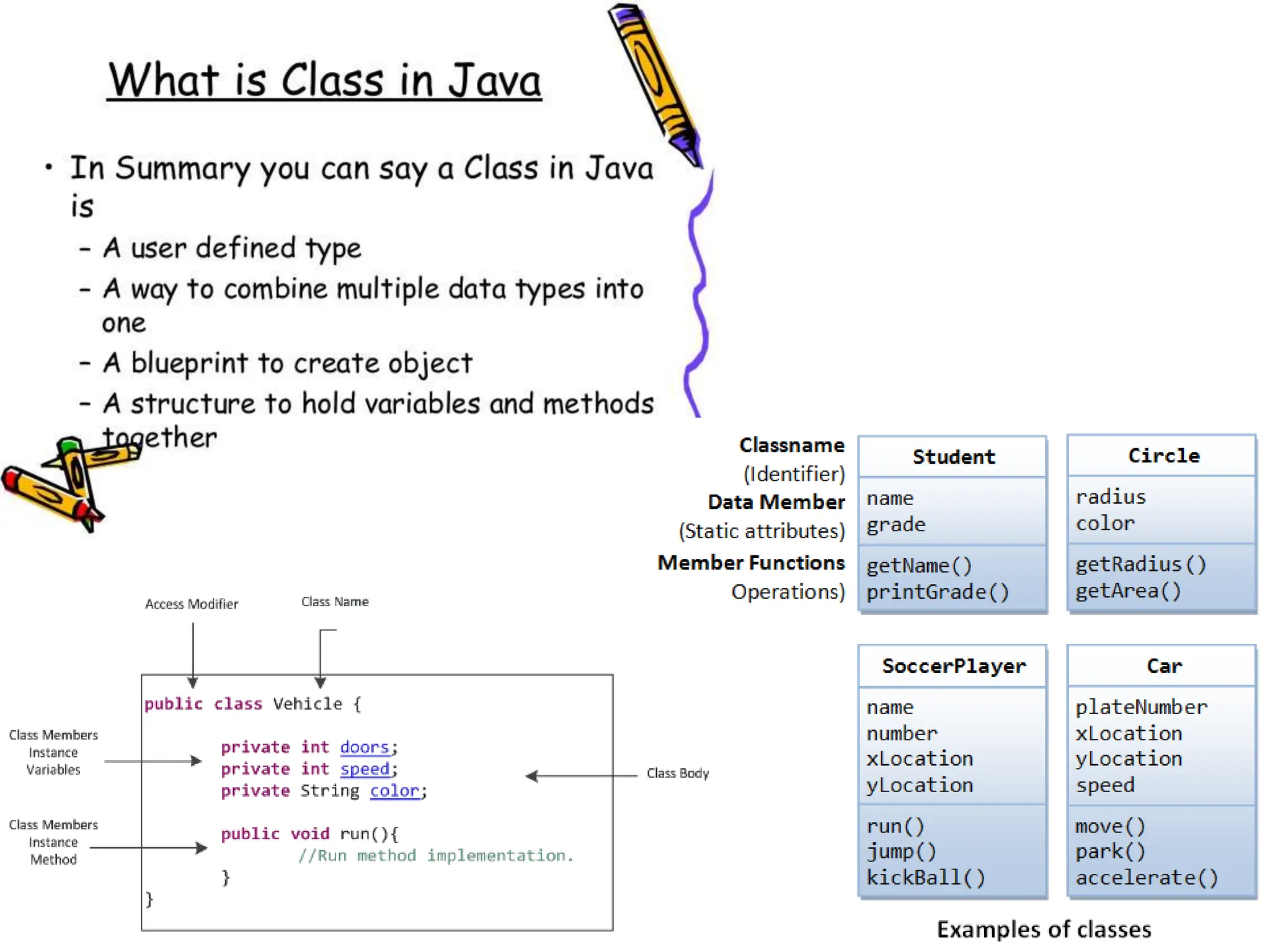
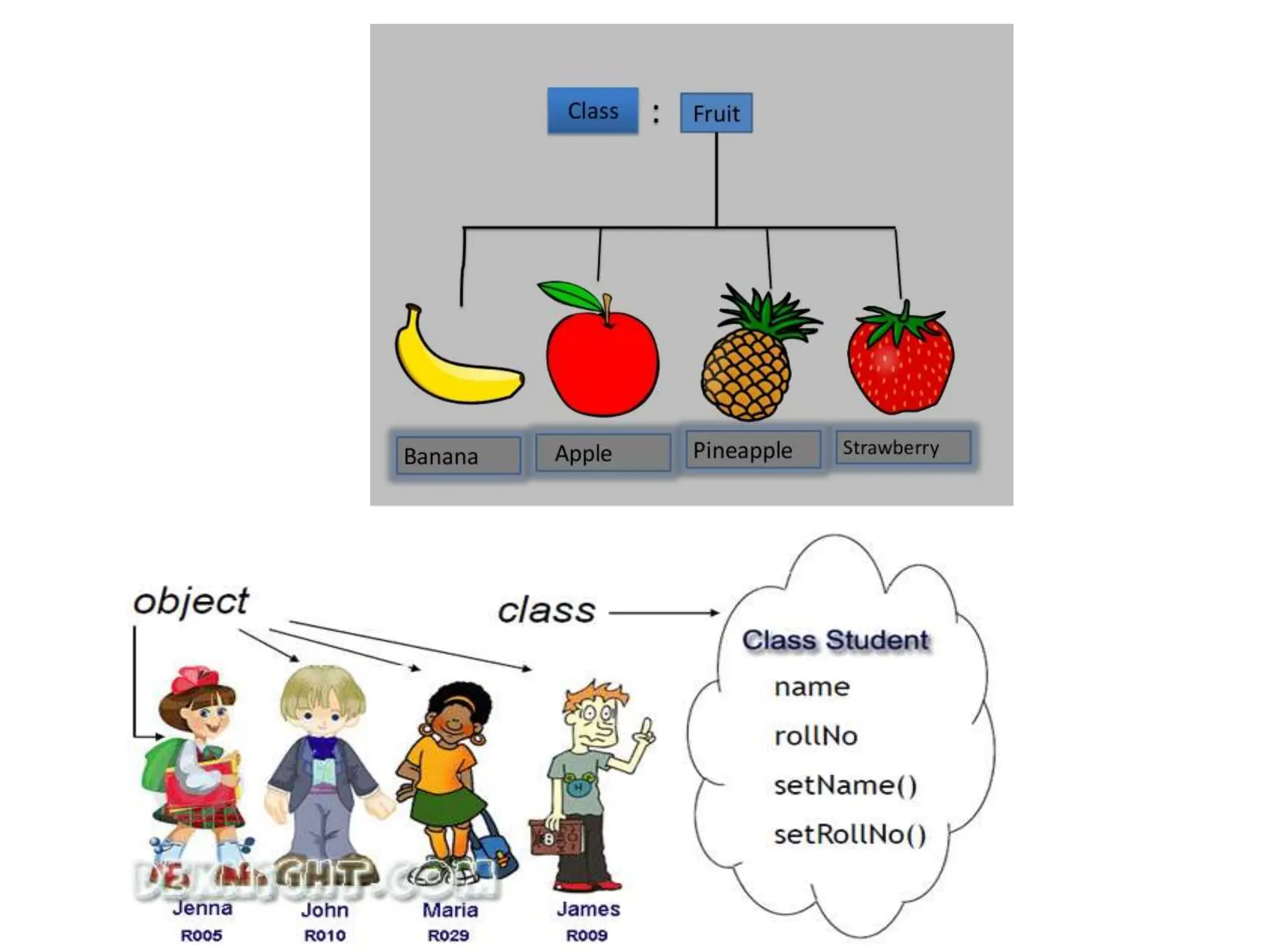
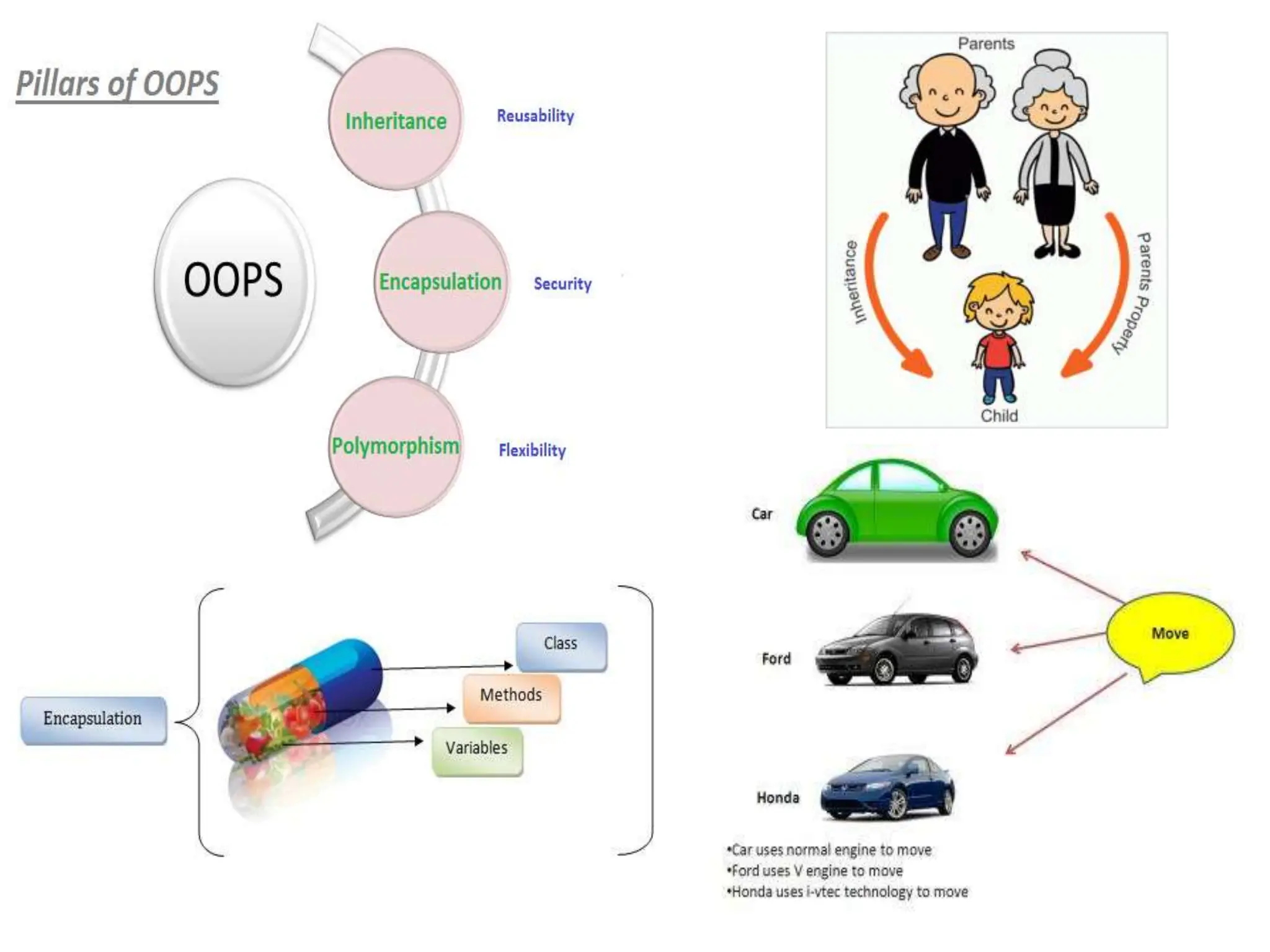
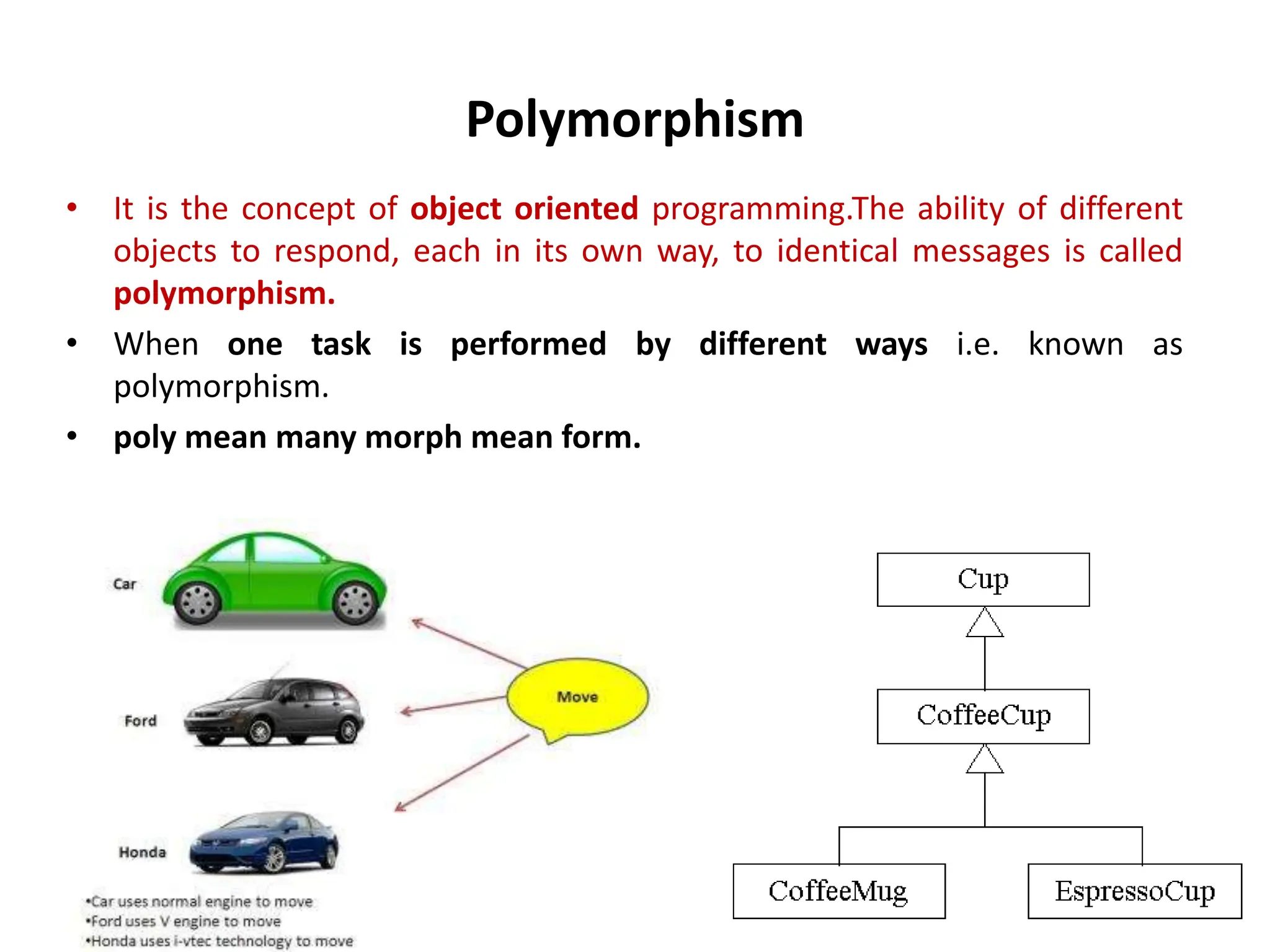
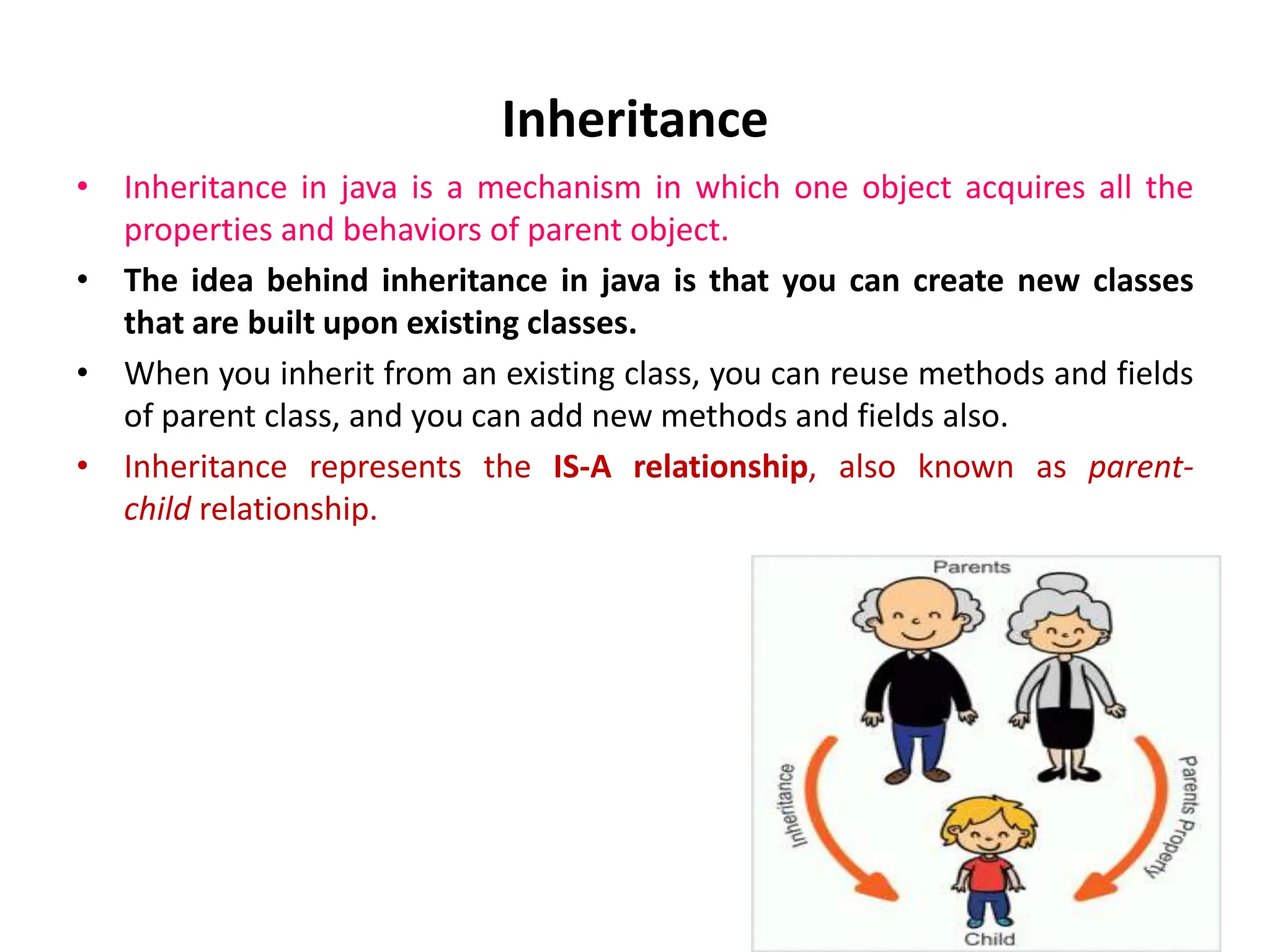
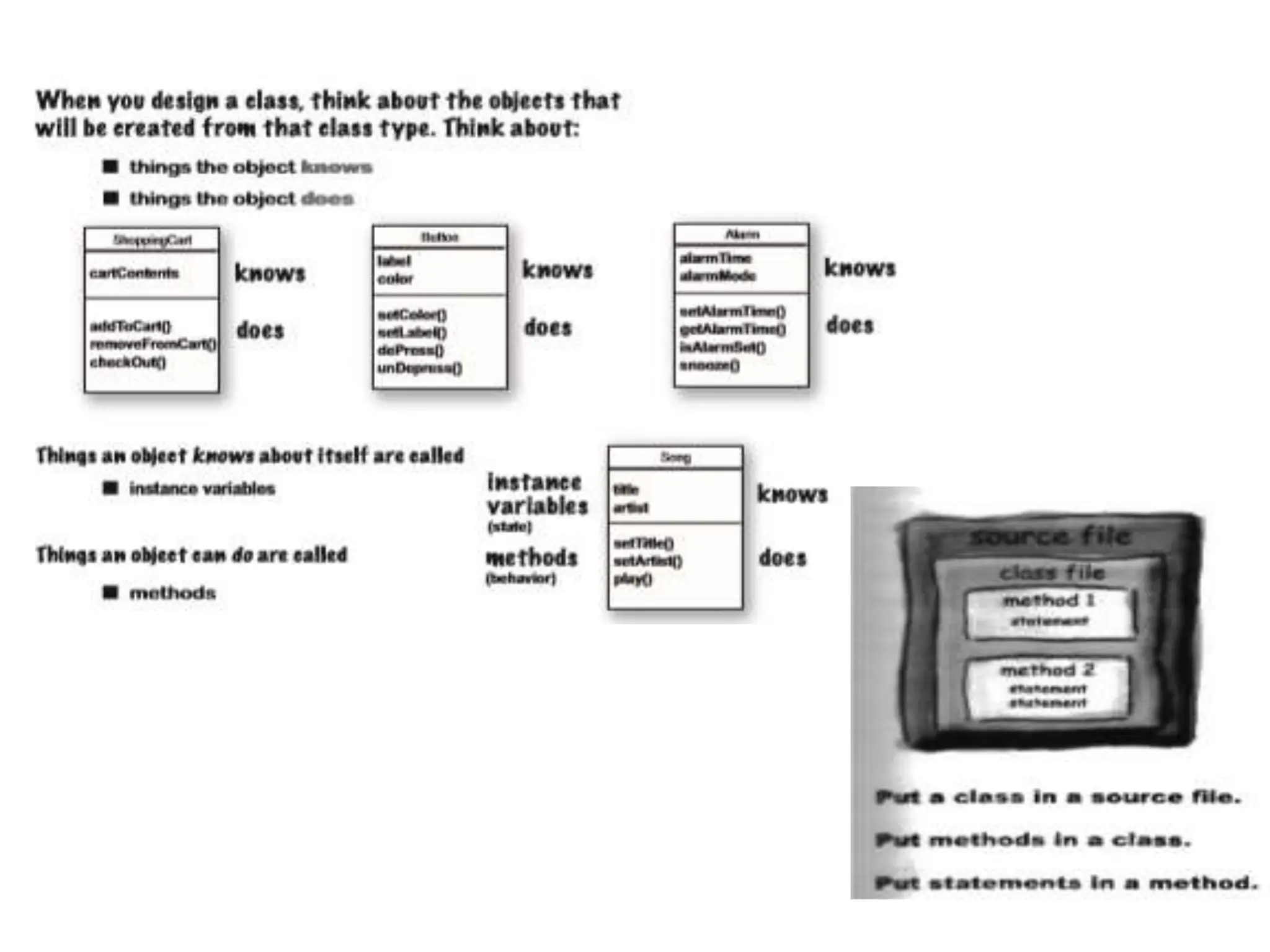
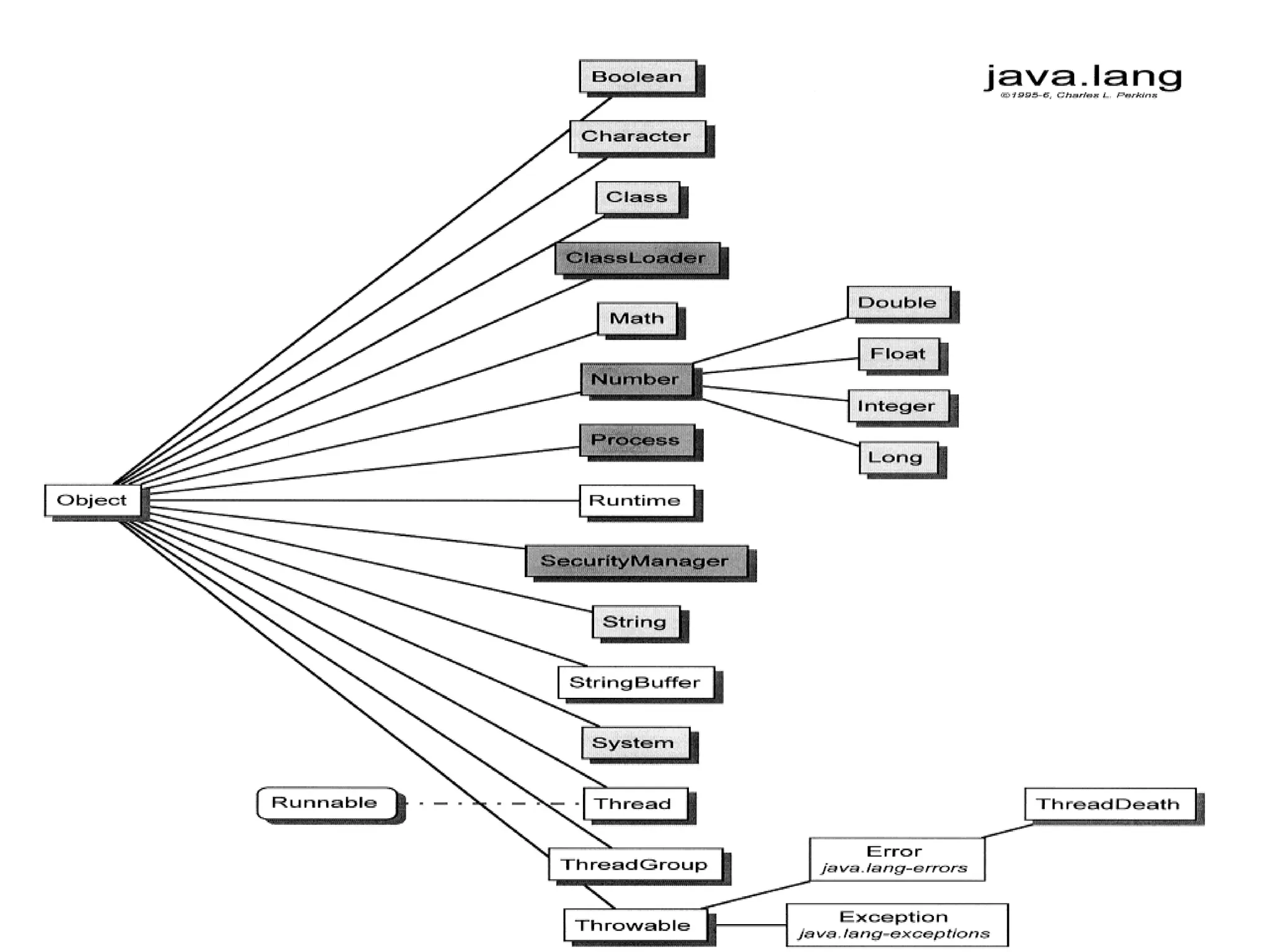
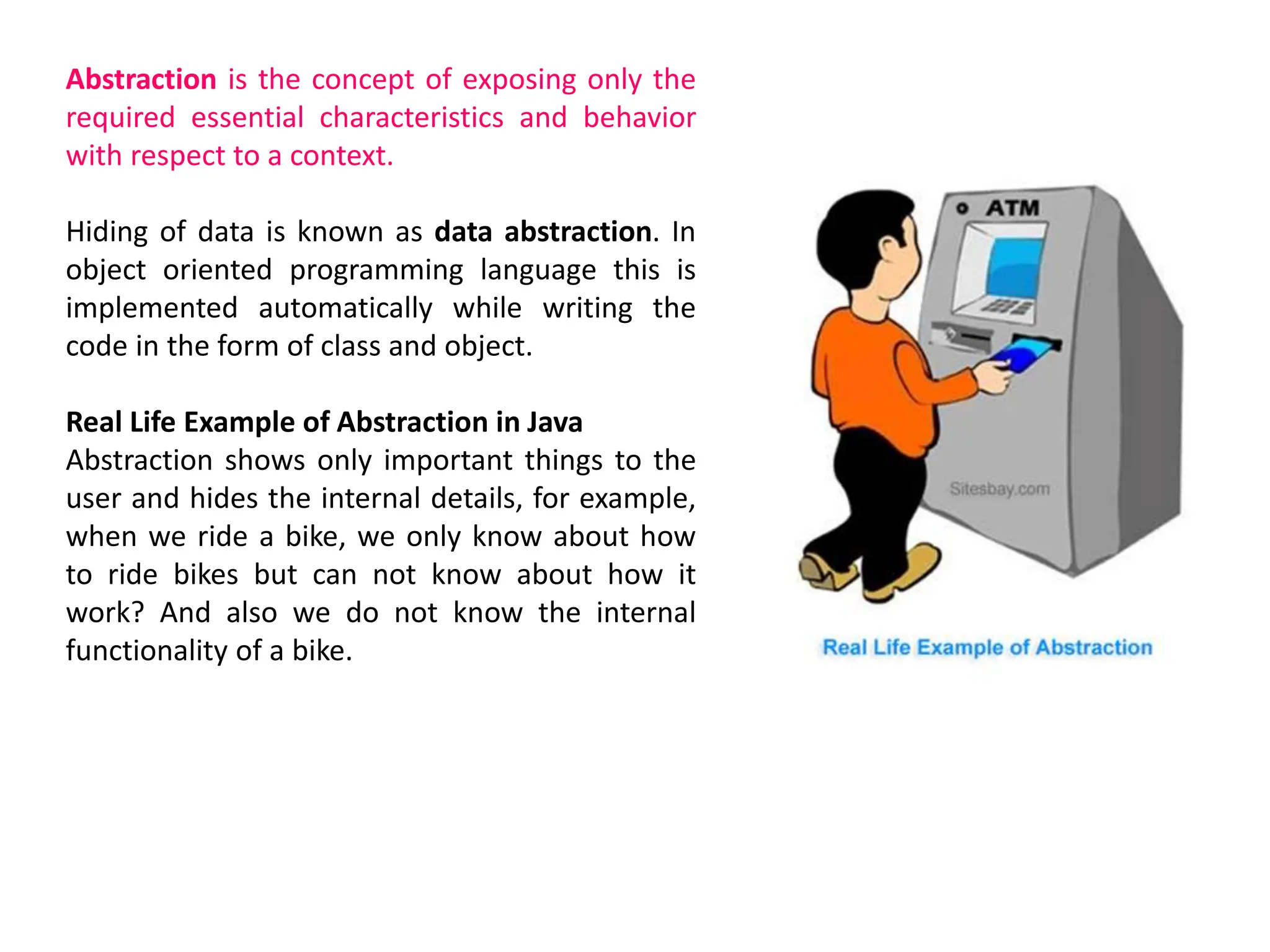
The document compares structured programming languages, like C, with object-oriented programming (OOP) languages, such as Java and Python, highlighting the modular approach of structured programming versus the object-focused methodology of OOP. Key OOP concepts such as encapsulation, polymorphism, and inheritance are explained, emphasizing how they allow for the manipulation of objects and code reuse. Additionally, it discusses the process of program creation, the differences between high-level and low-level languages, and the concept of abstraction in programming.