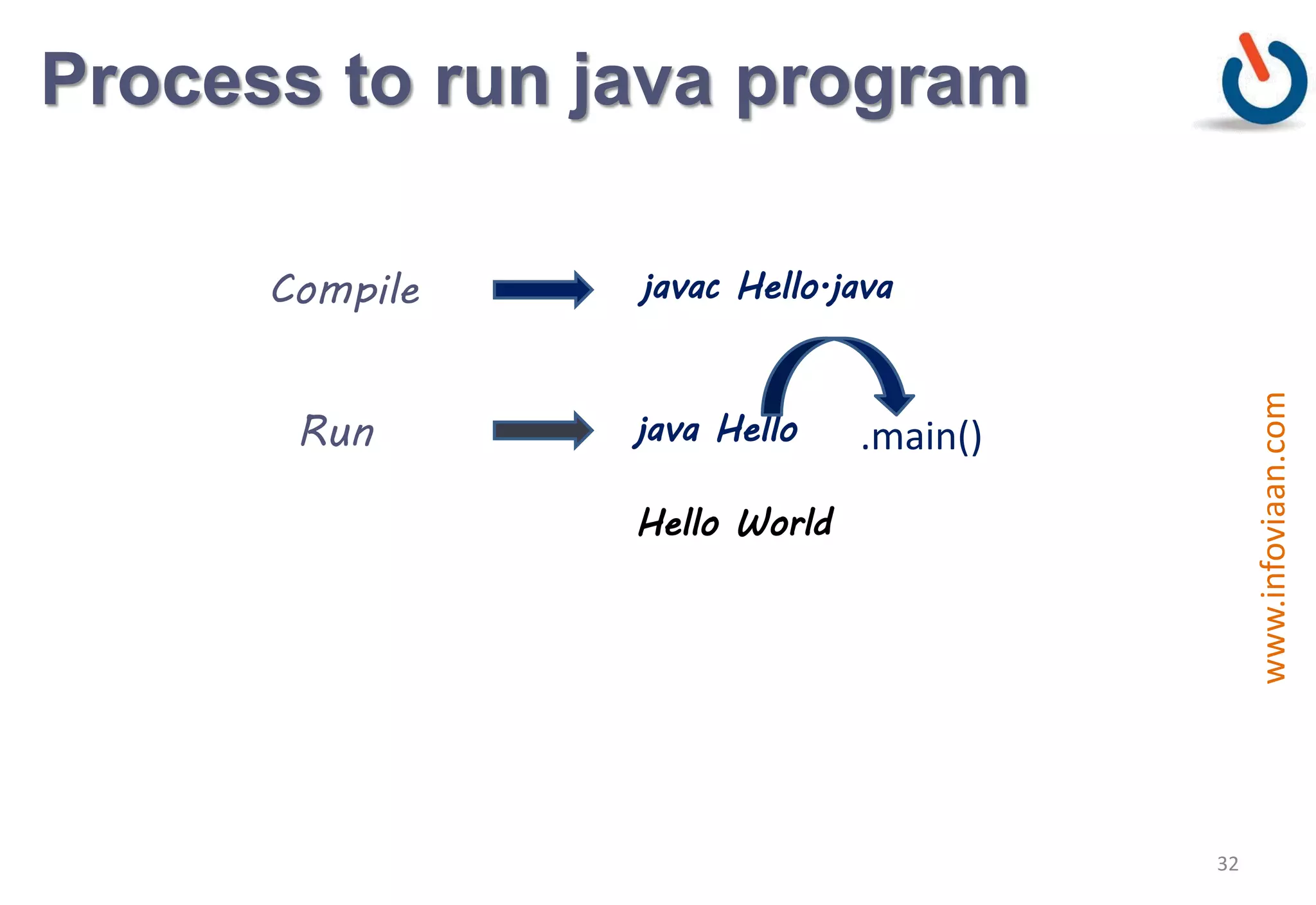
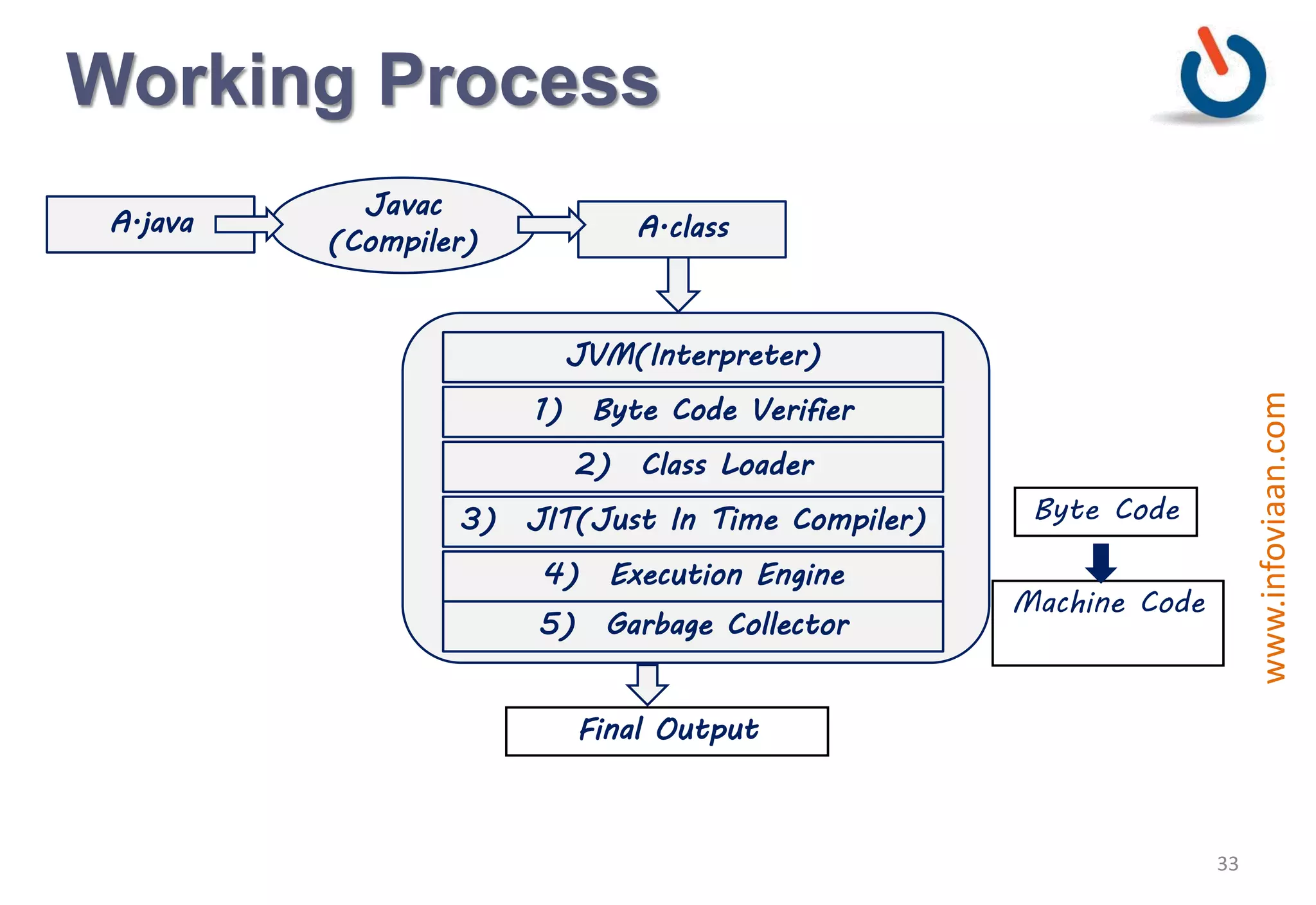
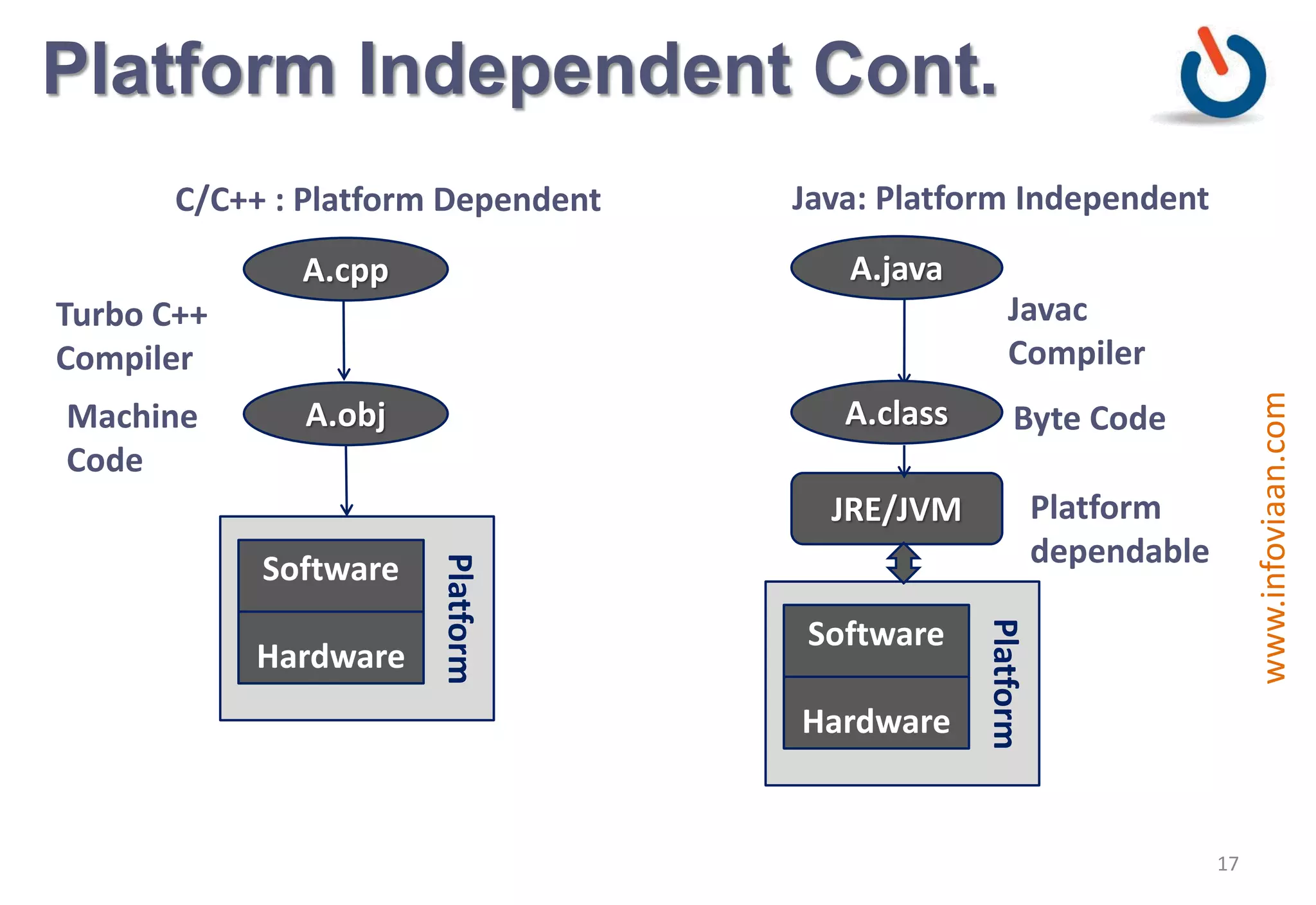
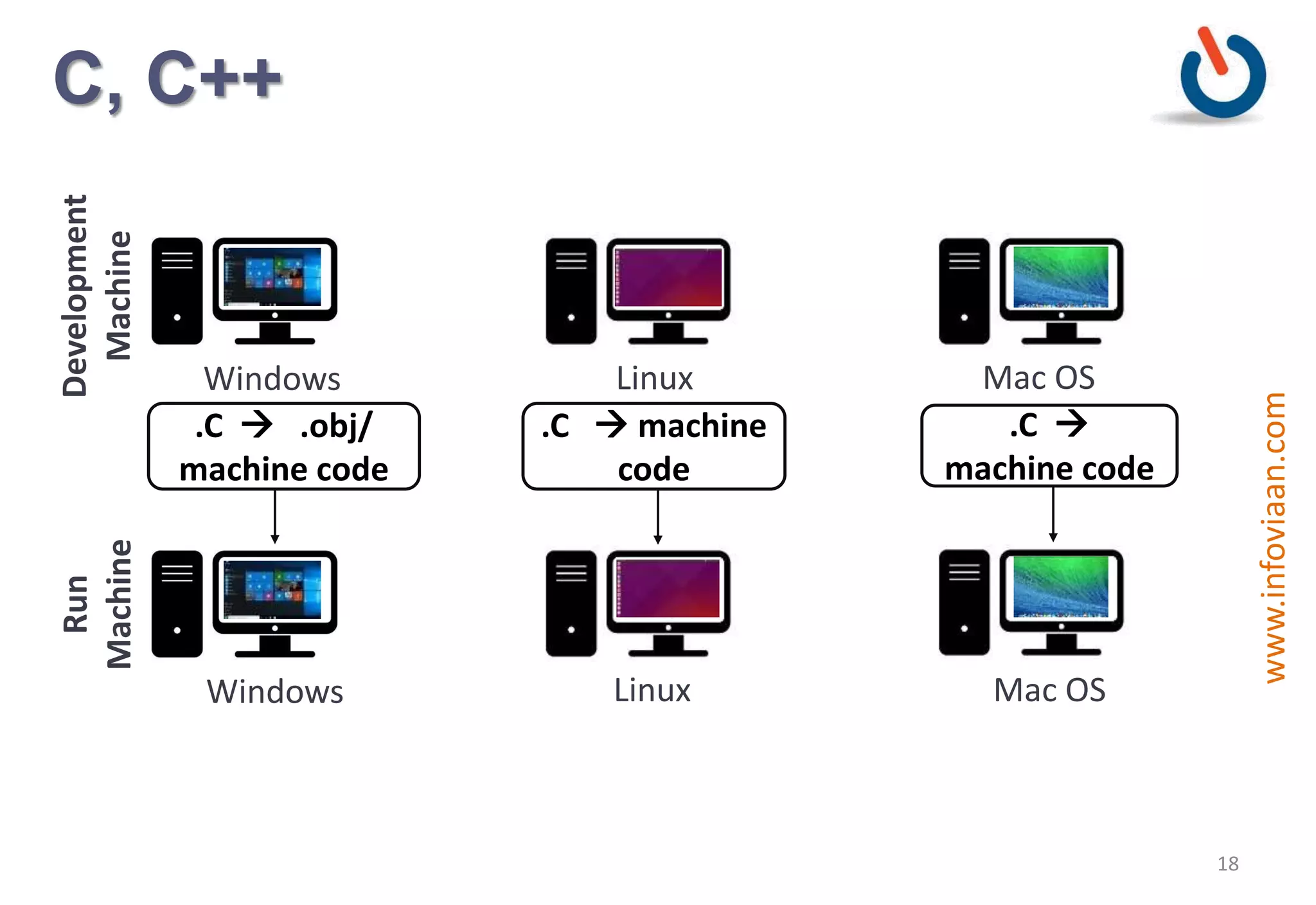
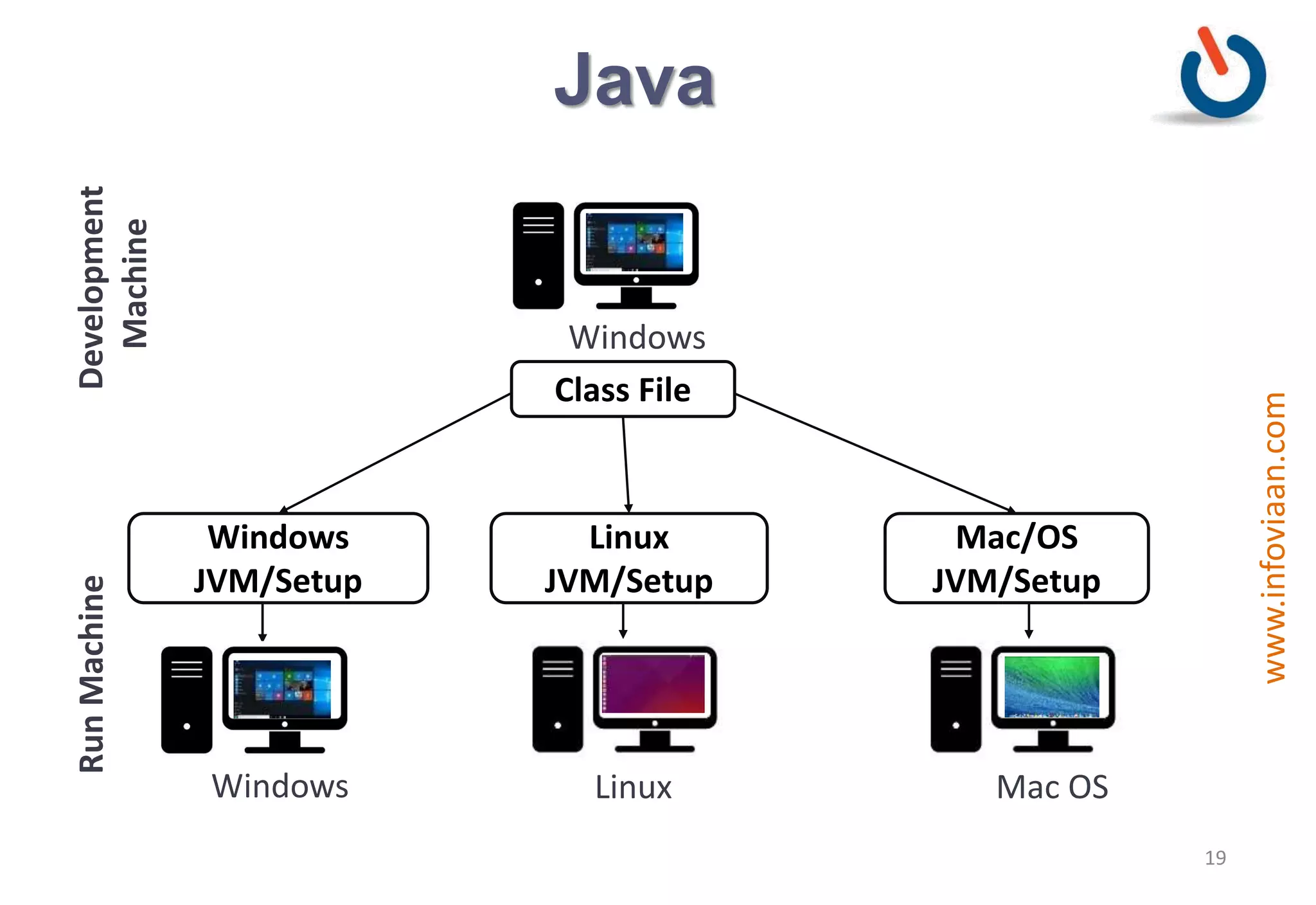
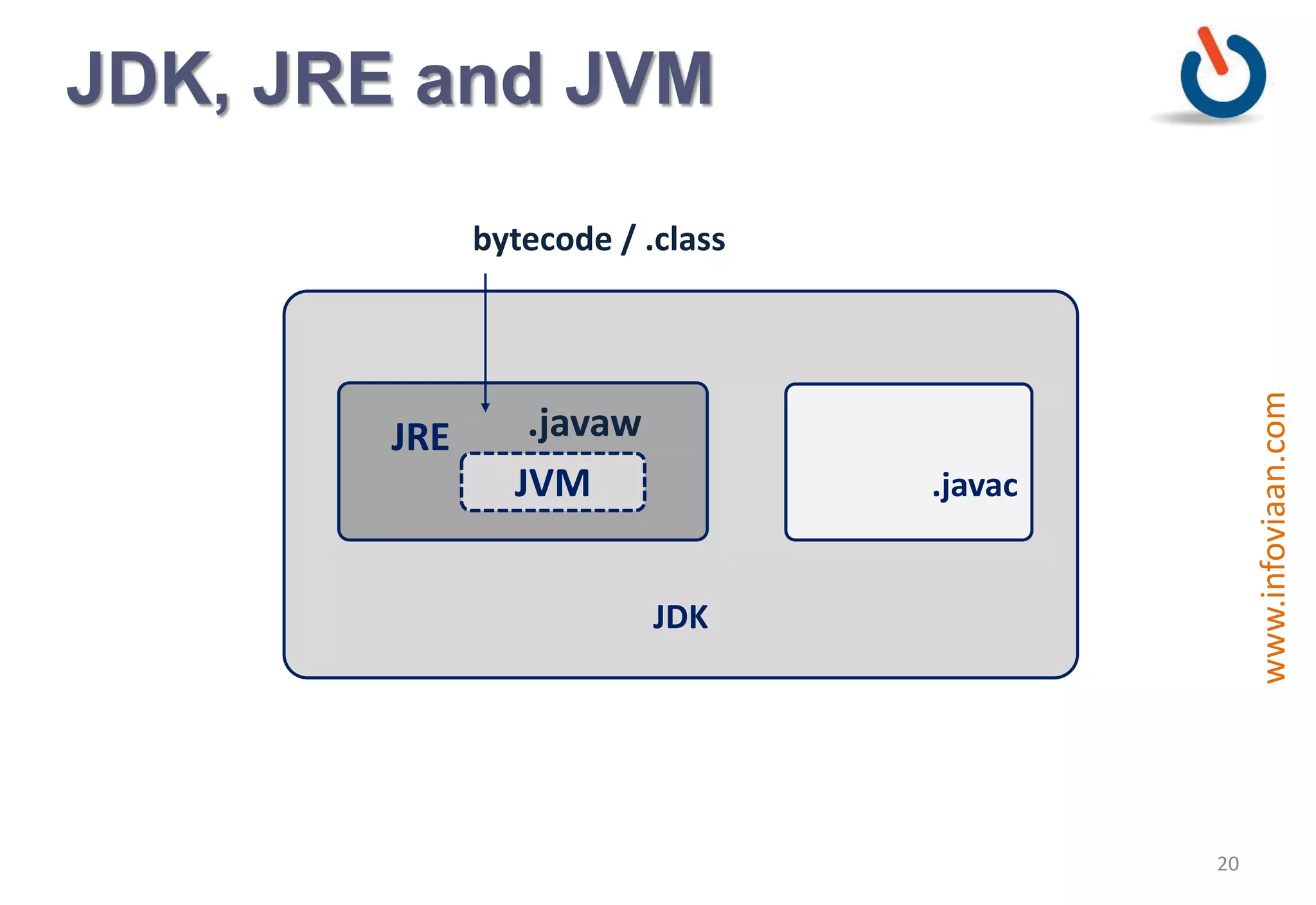
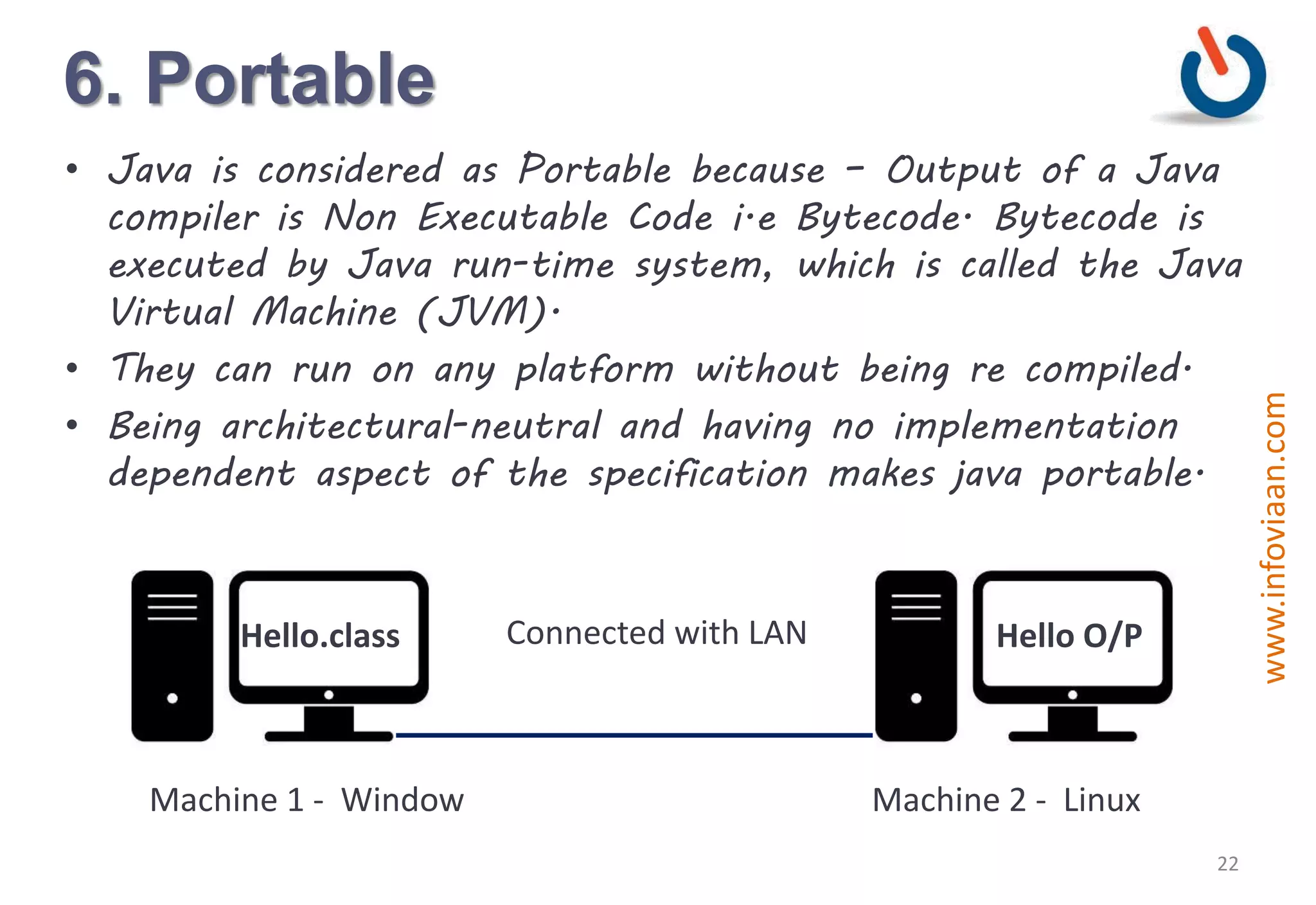
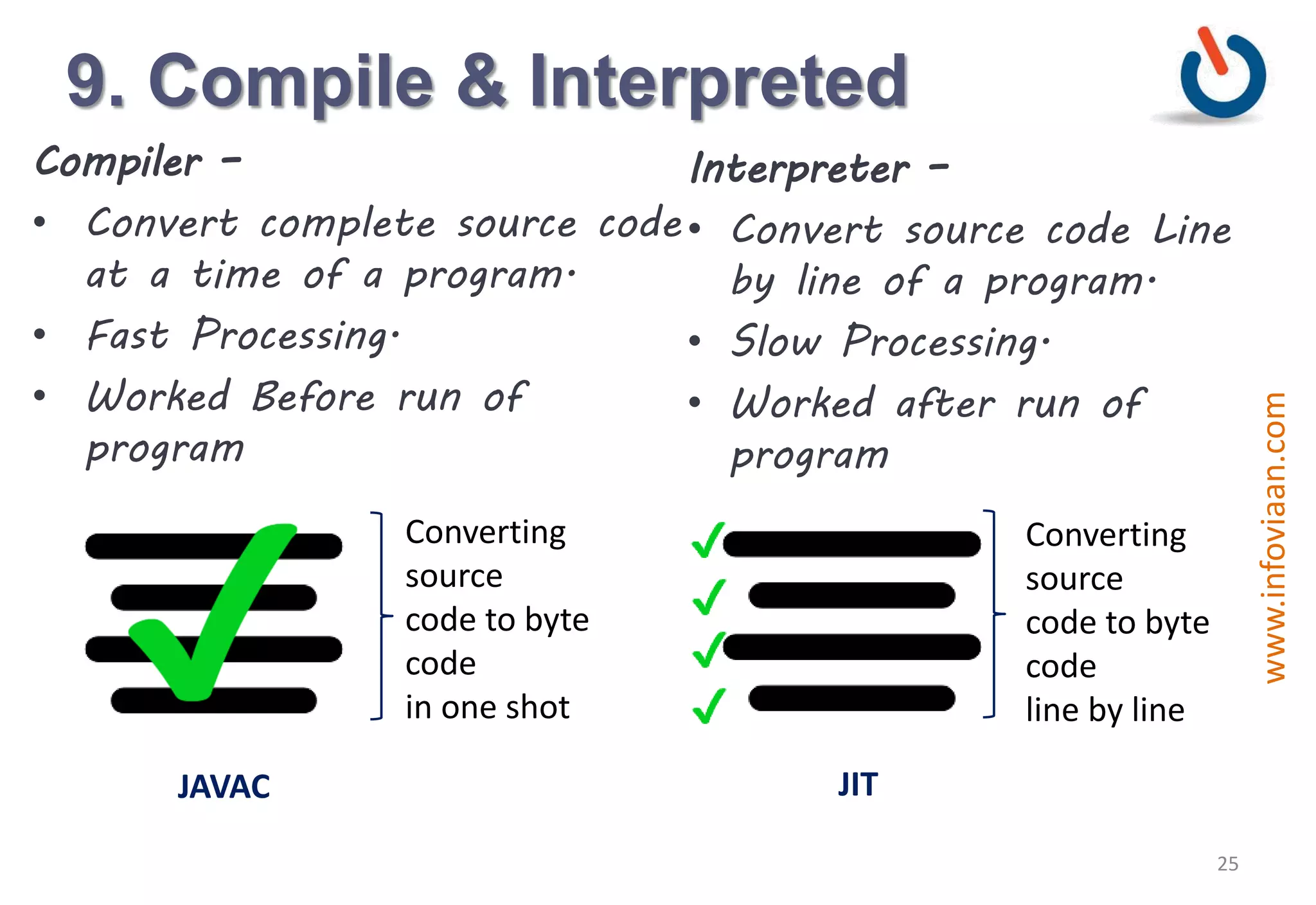
Java is an object-oriented programming language that is high-level, robust, secure, portable and multi-threaded. It was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s. Java code is compiled into bytecode that runs on a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) making Java platform independent. The JVM interprets the bytecode and performs tasks like memory management and security.









![Hello Program Explanation public class HelloProgram { public static void main(String args[]) { String name = “Infoviaan”; System.out.println(“Hello This is ”+name); } } public, class, static, and void are keywords, Keywords are always written in small letters in java. Class Name Keyword Method Variable Object reference 30 www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java1-introhelloprogram-200311181841/75/JAVA-INTRODUCTION-1-30-2048.jpg)
![Program Explanation Cont. public – Access modifier, shows accessibility of a class or variable or method to other java classes. class - used to define a class. static - is used to assigned memory once in life. void - is null return type of main method. String name = “Infoviaan”; is variable that store a value. System.out.println(“Hello This is ”+ name); is method, which display “Hello This is Infoviaan” at console output. here + is used for concatenate string. main – method is the entry point of program execution. it means program execution start from here. String args[] – Command line arguments 31 www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java1-introhelloprogram-200311181841/75/JAVA-INTRODUCTION-1-31-2048.jpg)