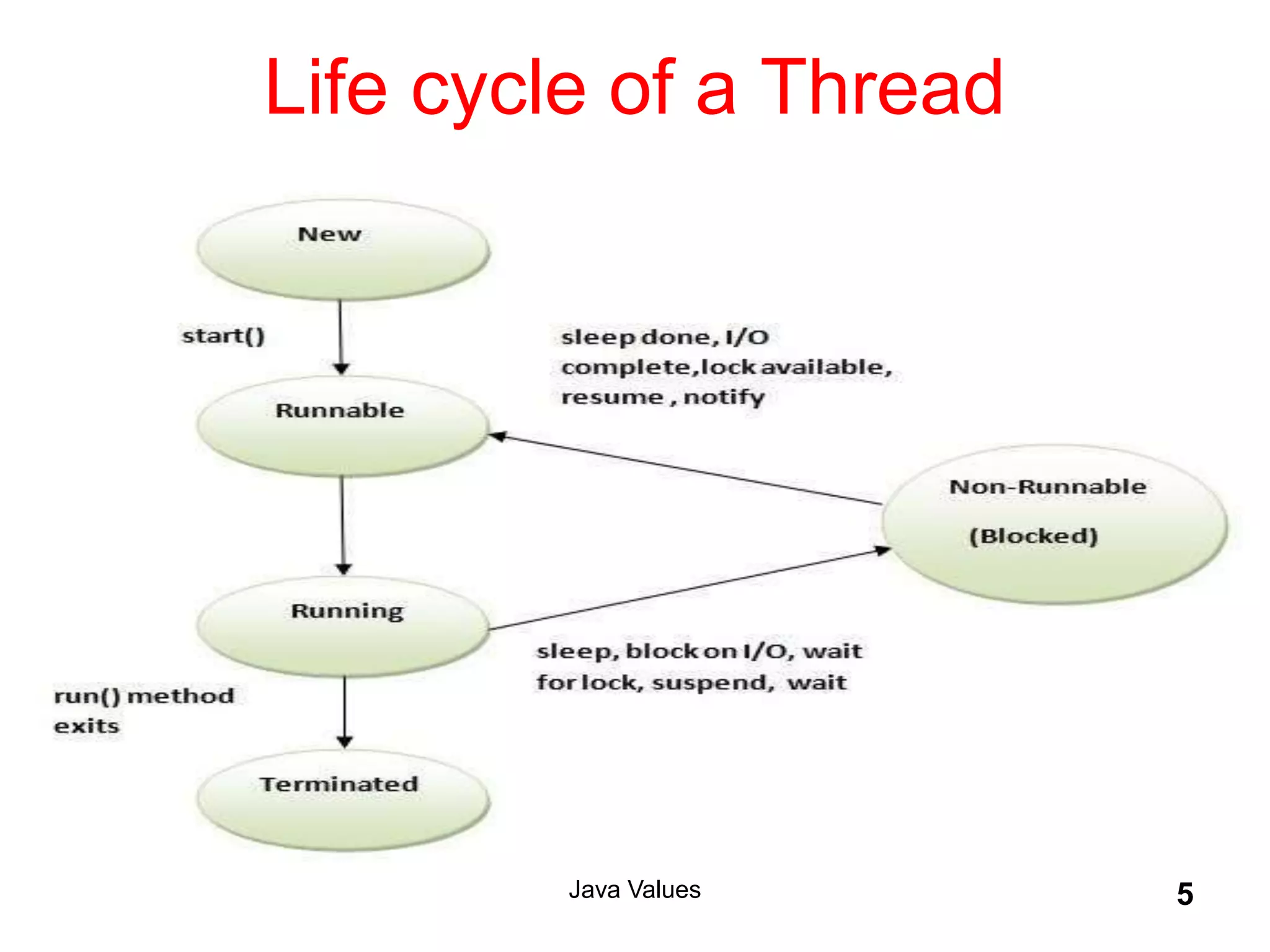
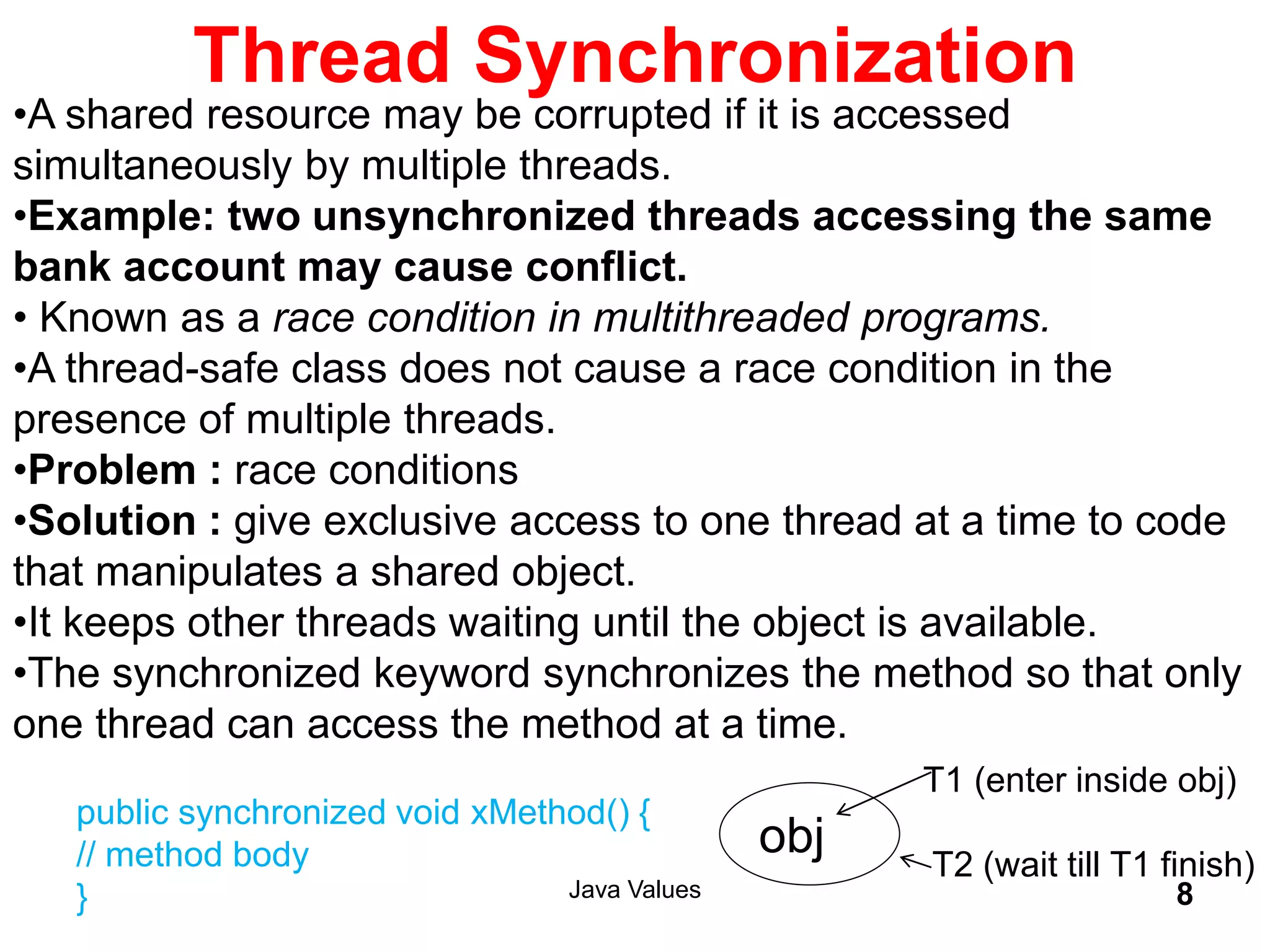
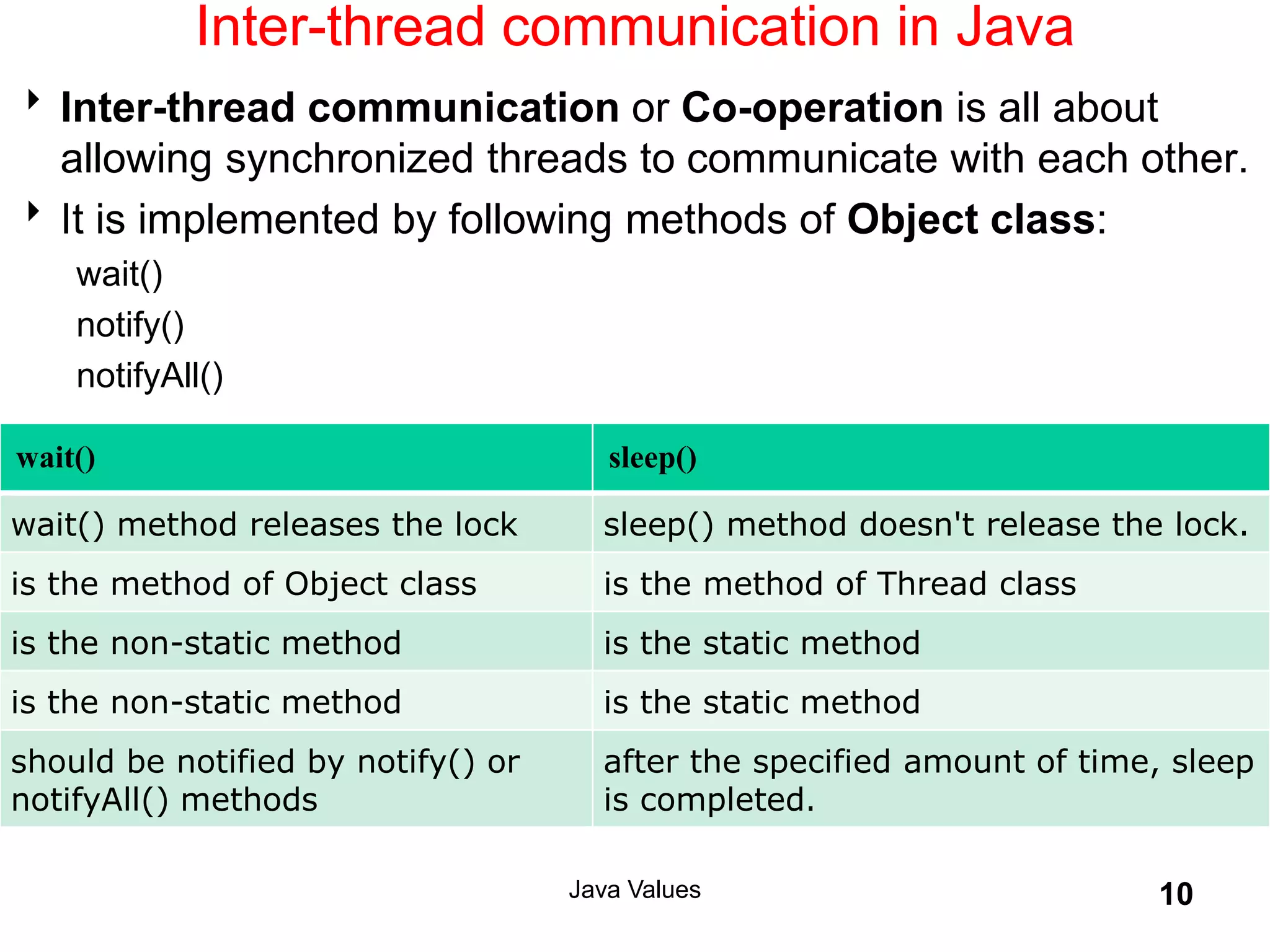
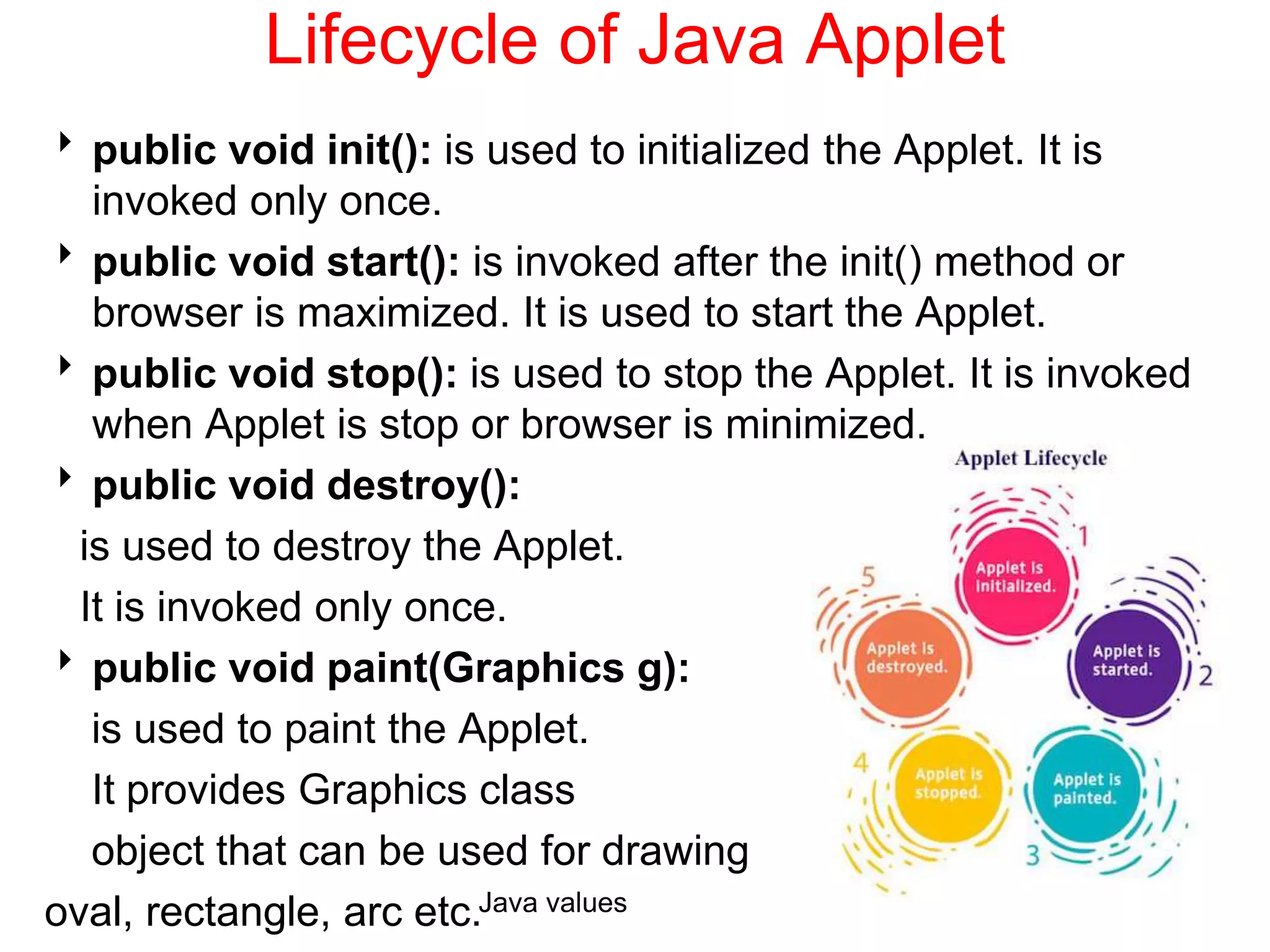
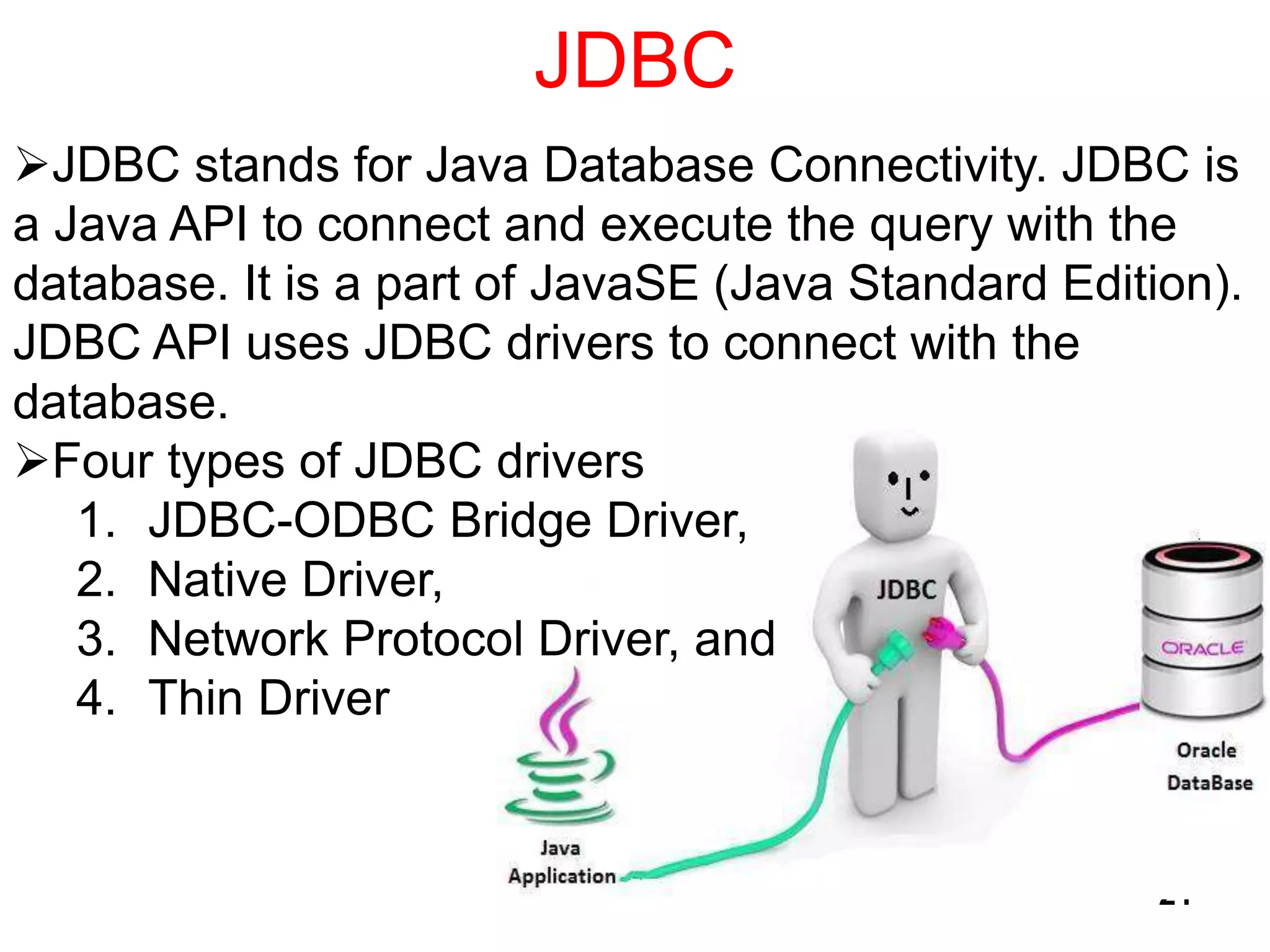
The document explains key concepts of Java programming including threads, applets, Swing GUI components, JDBC, and access modifiers. It discusses the lifecycle of threads, thread synchronization, applet lifecycle, and JDBC operations. Additionally, it covers various aspects such as thread priorities, deadlocks, inter-thread communication, and the differences between statement types in JDBC.
![Java Class 6 “Don't worry if it doesn't work right [when coding]. If everything did, you'd be out of a job.” Agenda •Threads in Java •Applets •Swing GUI •JDBC •Access Modifiers in Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day5-200809190135/75/Java-Class-6-Java-Class-6-Threads-in-Java-Applets-Swing-GUI-JDBC-Access-Modifiers-in-Java-Java-Program-1-2048.jpg)
![Java Values 3 Main Thread Default Thread in any Java Program JVM uses to execute program statements Program To Find the Main Thread Class Current { public static void main(String args[]) { Thread t=Thread.currentThread(); System.out.println(“Current Thread: “+t); System.out.println(“Name is: “+t.getName()); } } Output??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day5-200809190135/75/Java-Class-6-Java-Class-6-Threads-in-Java-Applets-Swing-GUI-JDBC-Access-Modifiers-in-Java-Java-Program-3-2048.jpg)







![Java Database Connectivity with 5 Steps import java.sql.*; class OracleCon{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ //step1 load the driver class Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //step2 create the connection object Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sonoo","root","root"); //step3 create the statement object Statement stmt=con.createStatement(); //step4 execute query ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery("select * from emp"); while(rs.next()) System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2)+" "+rs.getString(3)); //step5 close the connection object con.close(); }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e);} } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day5-200809190135/75/Java-Class-6-Java-Class-6-Threads-in-Java-Applets-Swing-GUI-JDBC-Access-Modifiers-in-Java-Java-Program-23-2048.jpg)
![Statement interface Java Values 24 1) public ResultSet executeQuery(String sql): is used to execute SELECT query. It returns the object of ResultSet. 2) public int executeUpdate(String sql): is used to execute specified query, it may be create, drop, insert, update, delete etc. 3) public boolean execute(String sql): is used to execute queries that may return multiple results. 4) public int[] executeBatch(): is used to execute batch of commands. •The Statement interface provides methods to execute queries with the database. •The statement interface is a factory of ResultSet i.e. it provides factory method to get the object of ResultSet. •Commonly used methods of Statement interface:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day5-200809190135/75/Java-Class-6-Java-Class-6-Threads-in-Java-Applets-Swing-GUI-JDBC-Access-Modifiers-in-Java-Java-Program-24-2048.jpg)