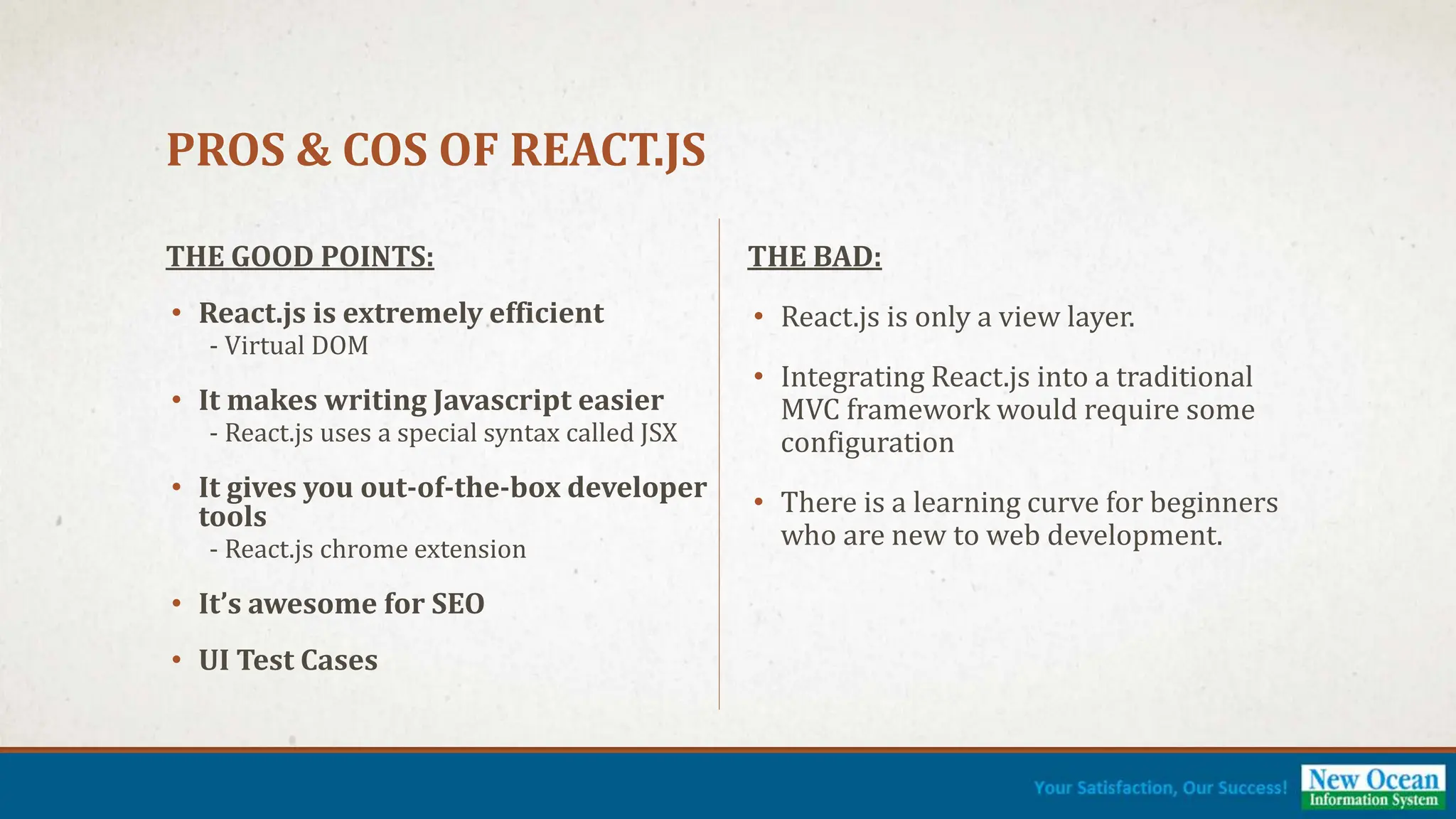
The document provides an introduction to React.js, a JavaScript library for building user interfaces using concepts like components, state, and props, as well as the JSX syntax. It discusses the component lifecycle, advantages such as efficiency and SEO benefits, and challenges like a steep learning curve for beginners. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of React.js for modern web development and its growing demand in the job market.






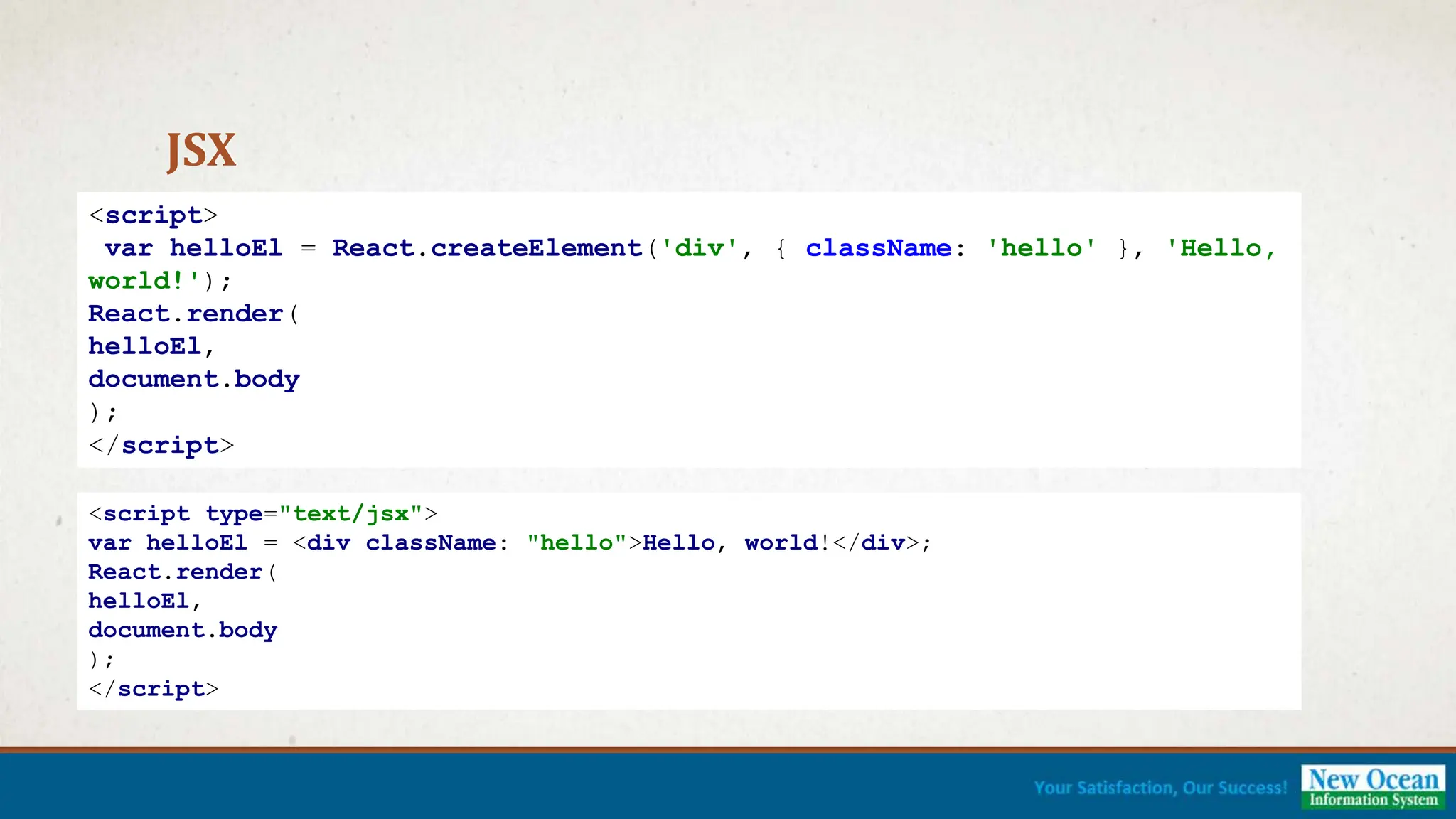
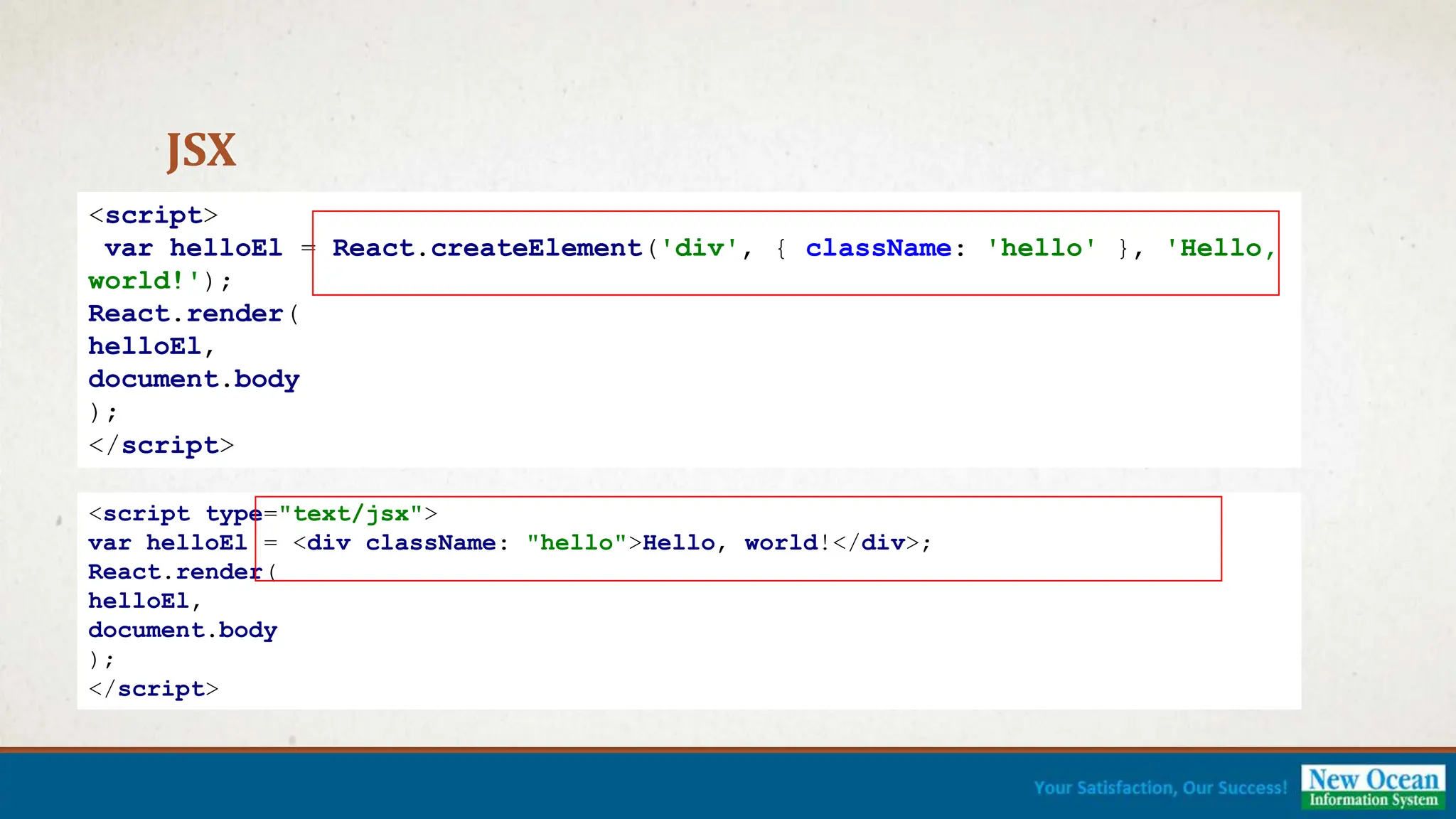

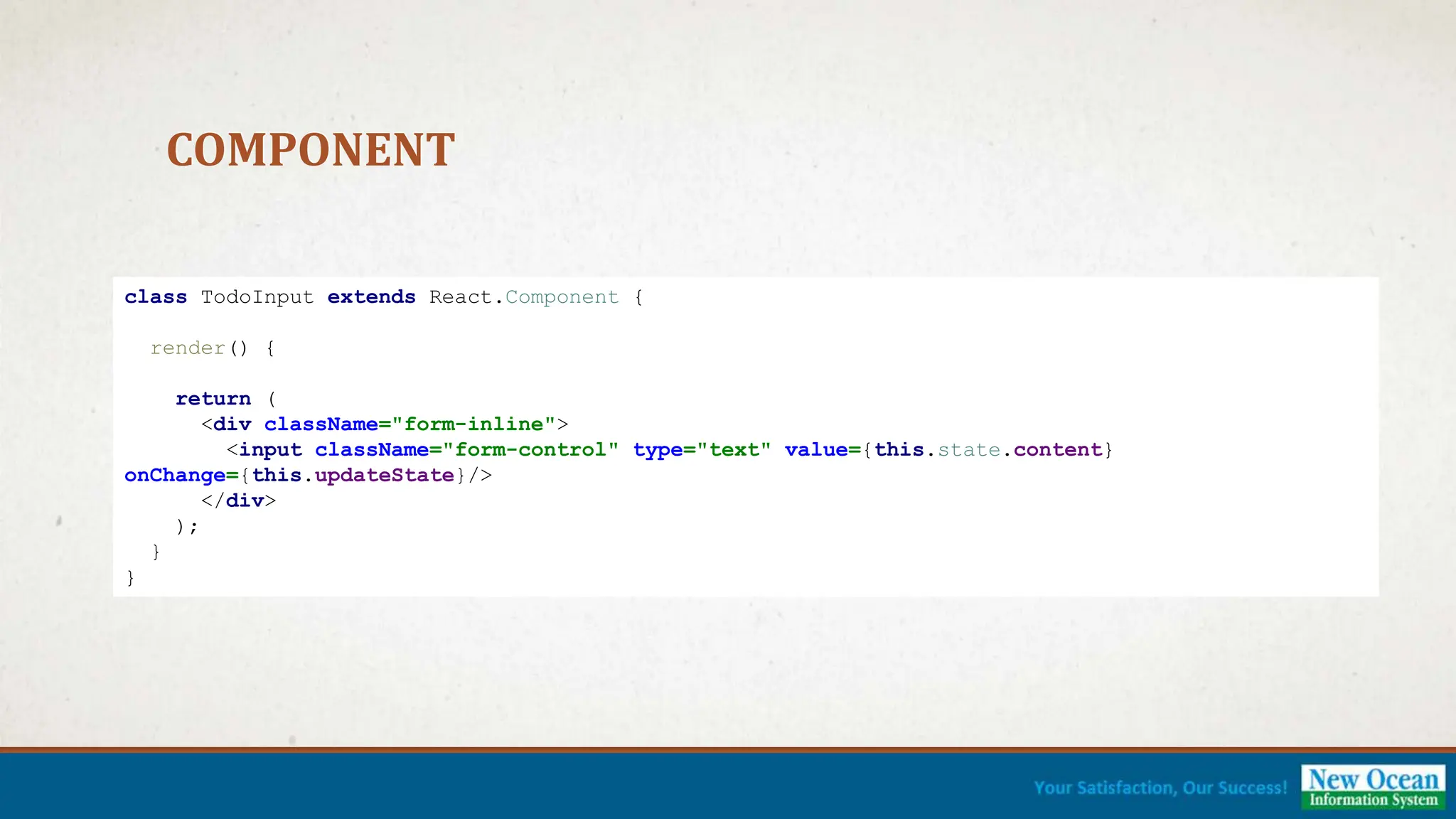

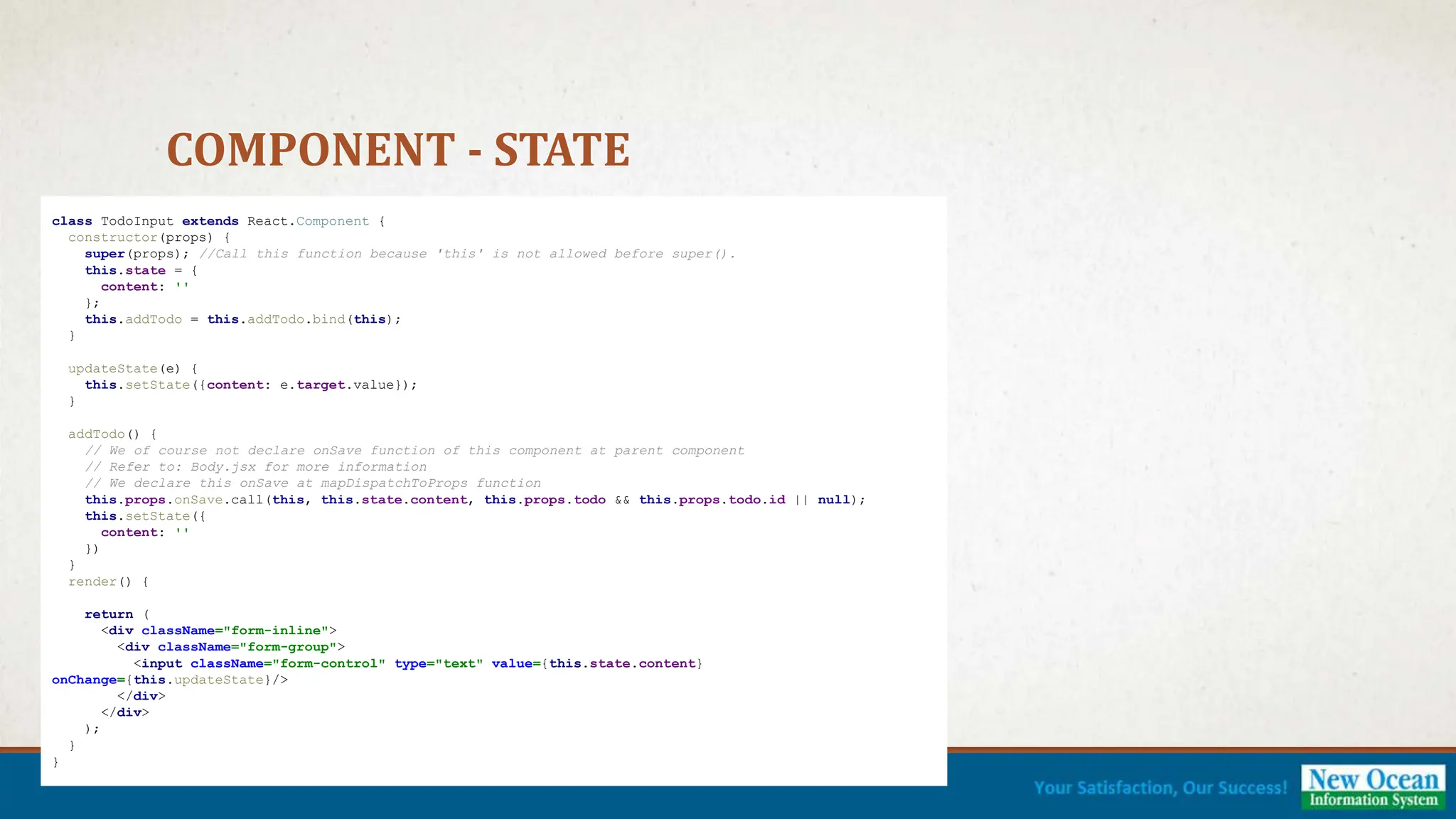
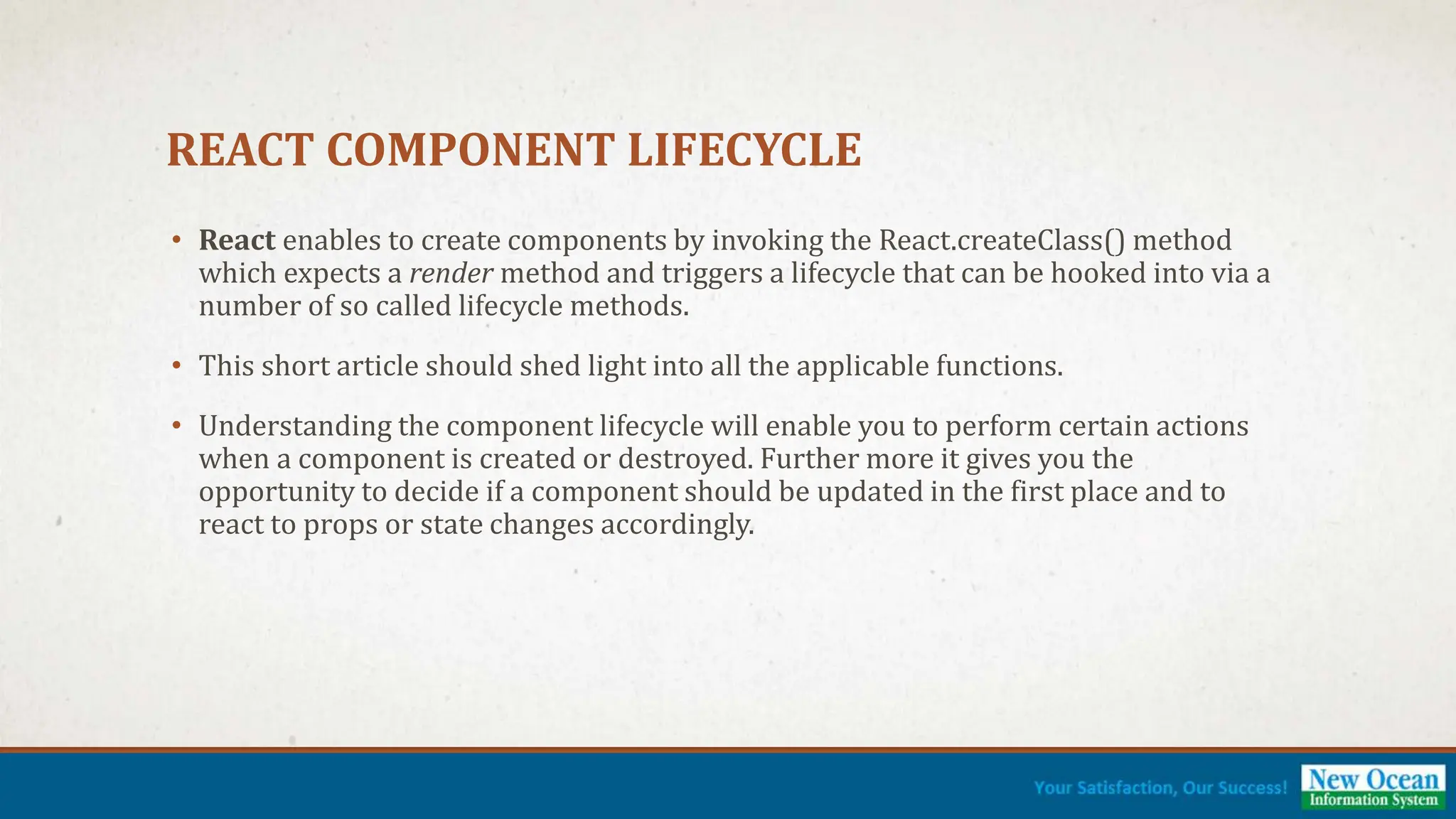
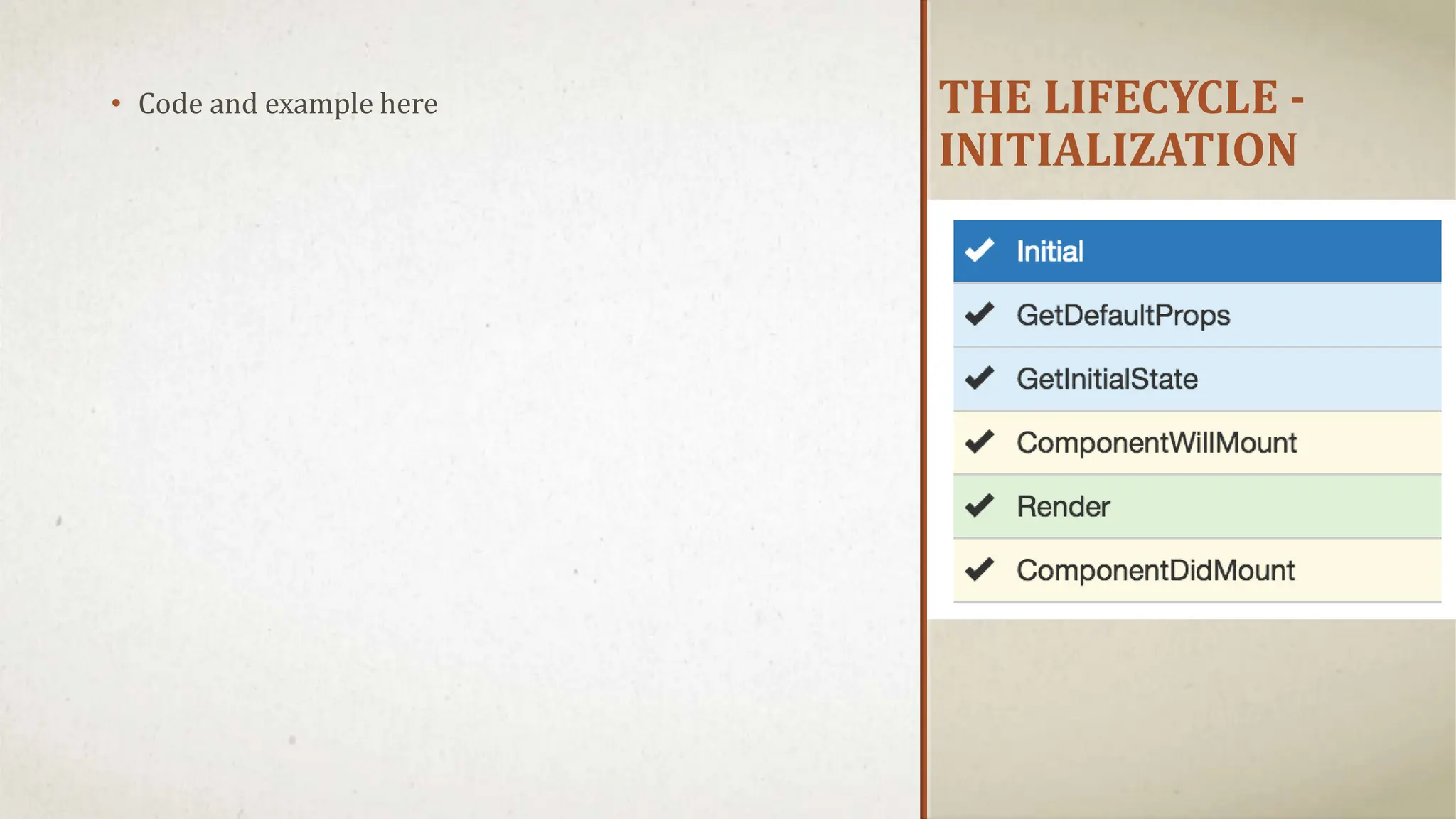
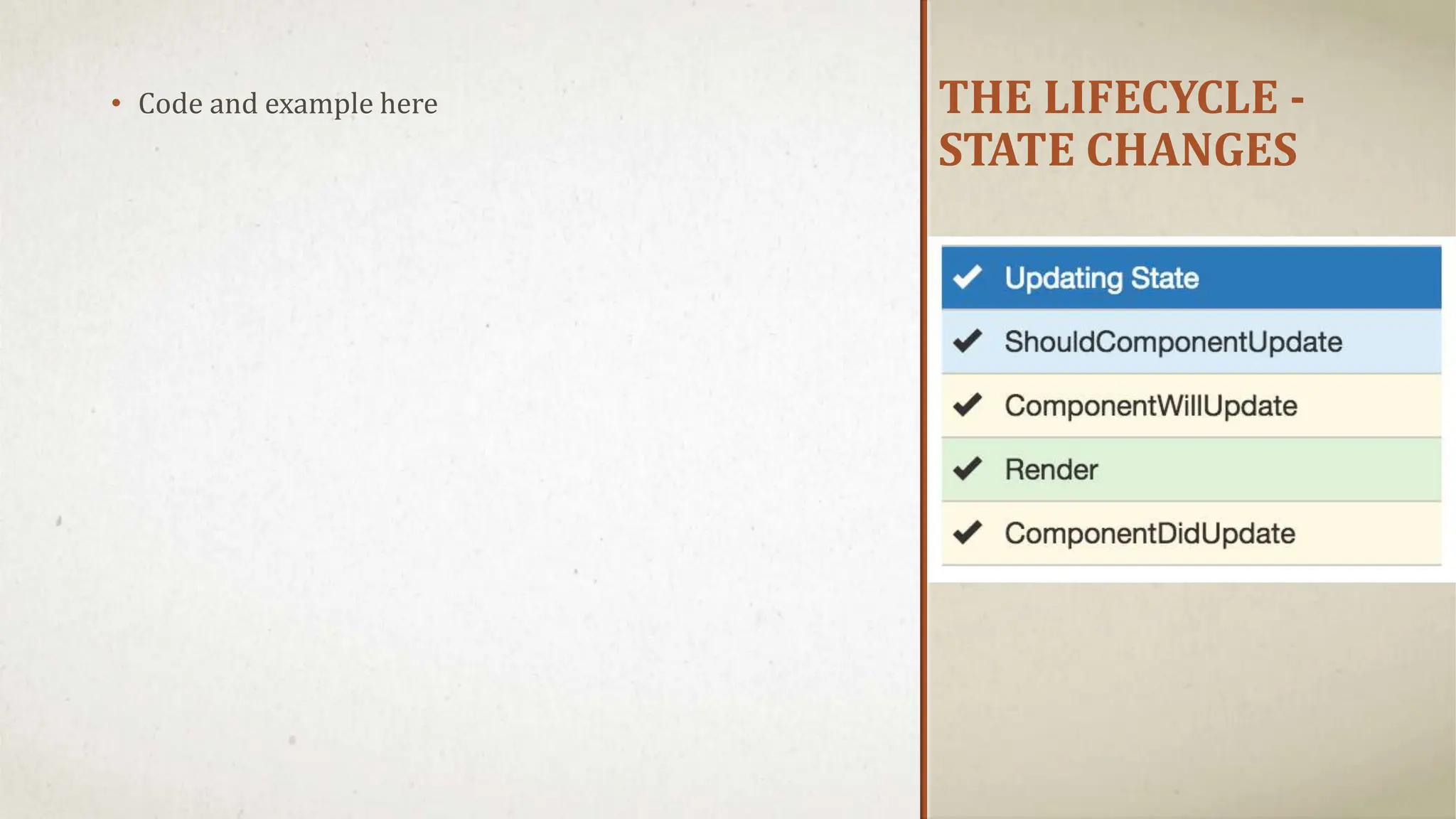

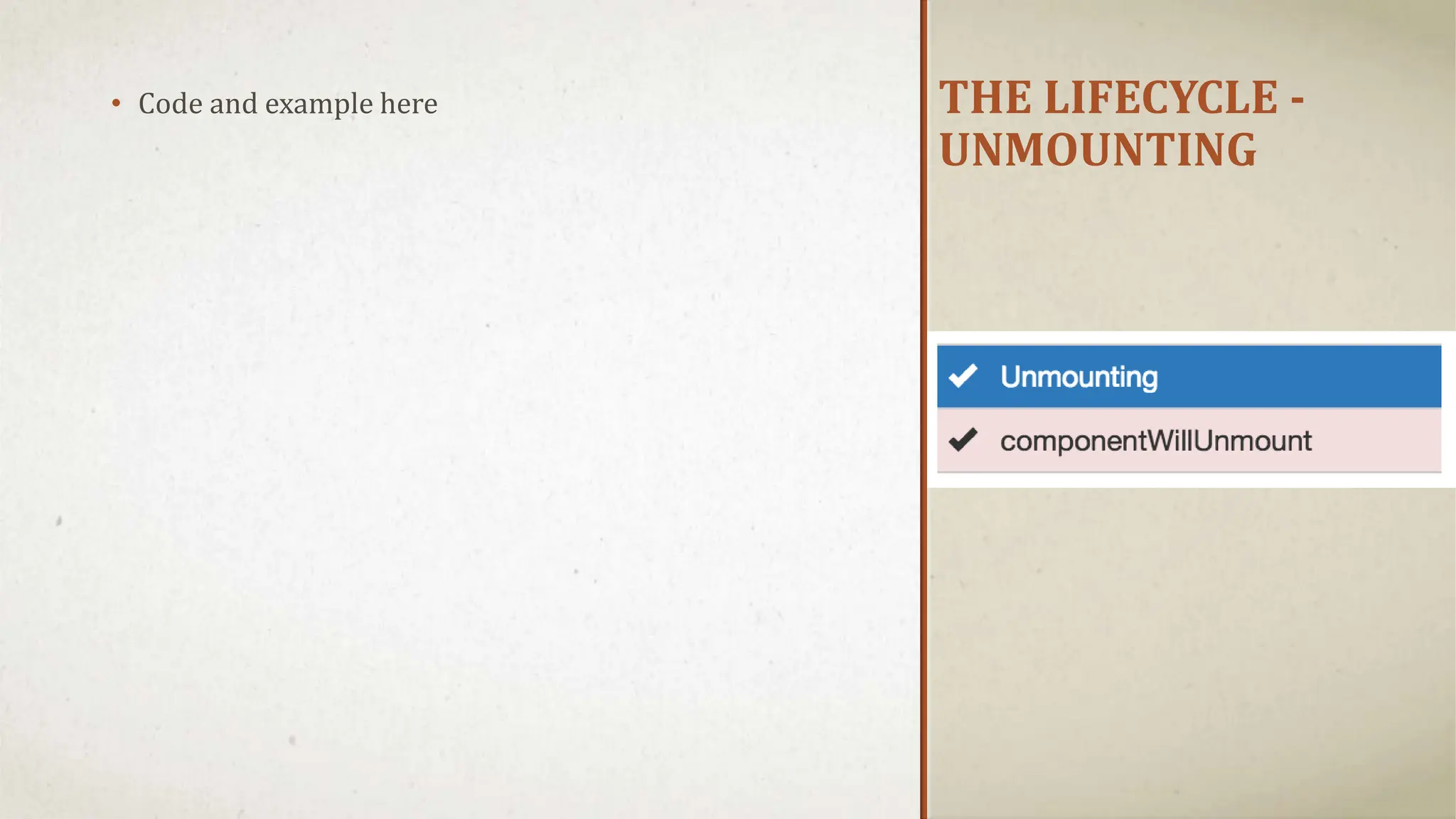


![DEMONSTRATION [Complete Demo]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactjspresentation-230512081854-82f9aa1e-240701060735-c47f5b3b/75/Introduction-Web-Development-using-ReactJS-21-2048.jpg)

