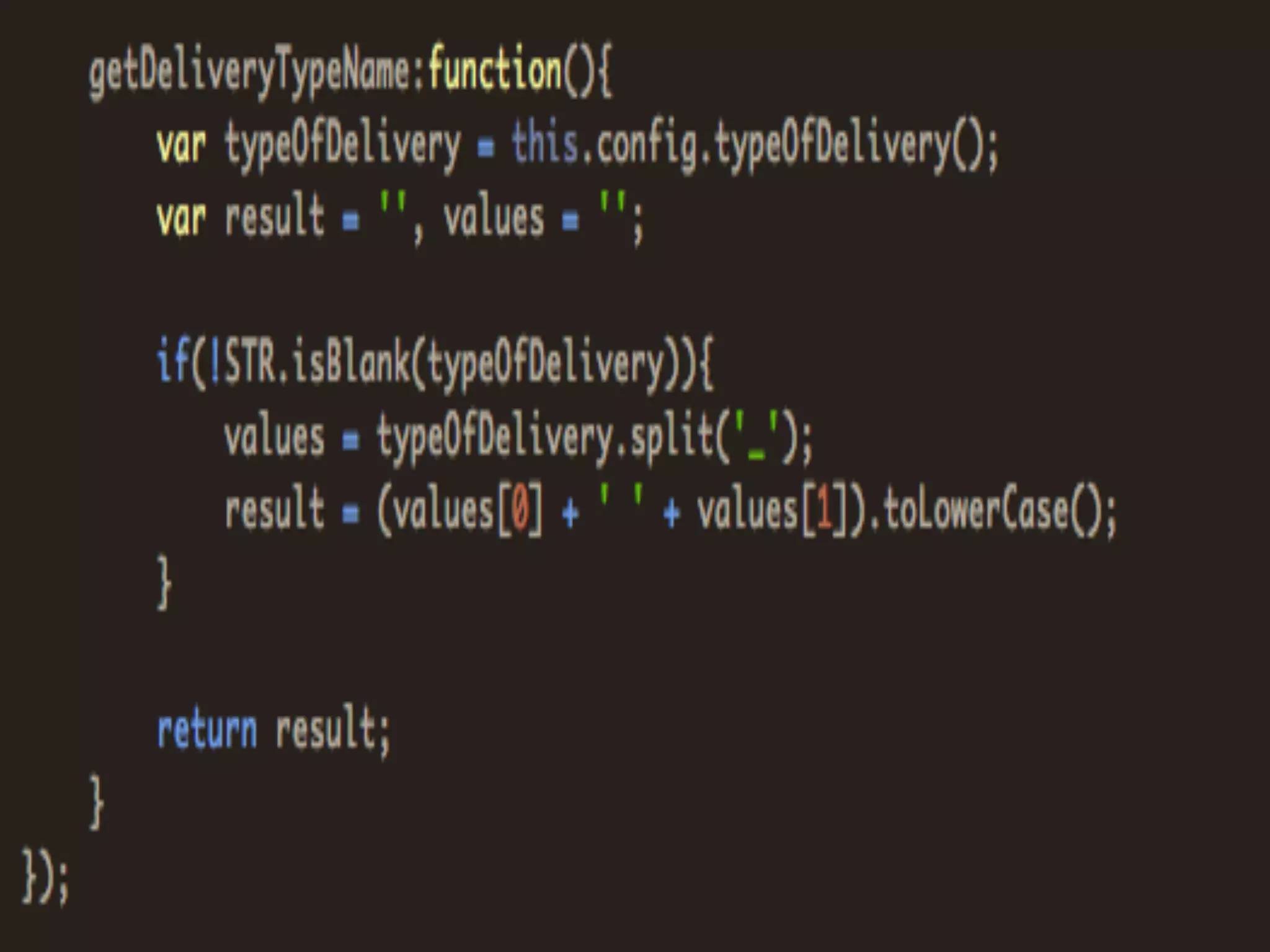
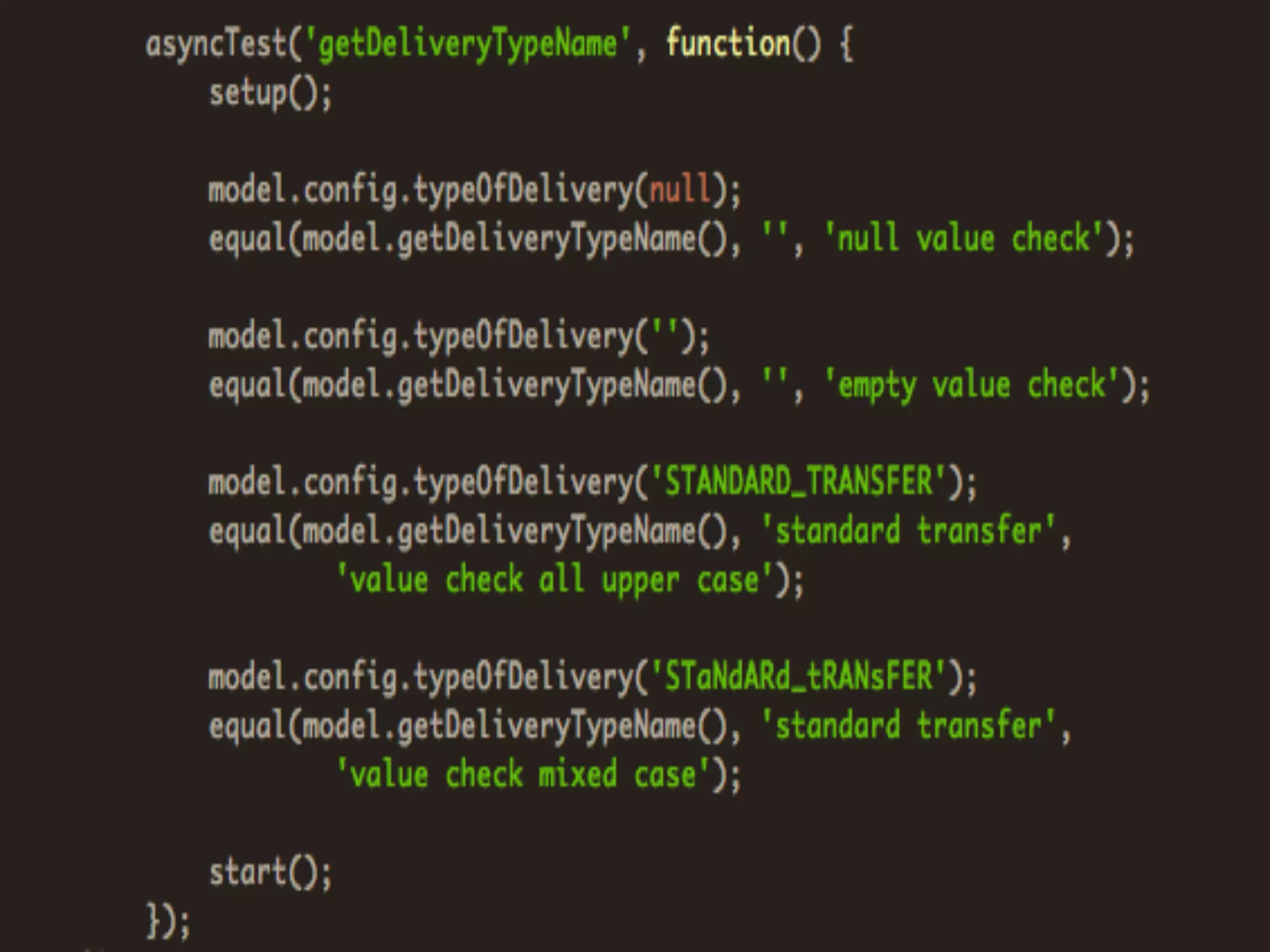
Unit testing verifies specific sections of code by testing individual functions to ensure they work as expected. Qunit is a JavaScript unit testing framework that allows testing code in the browser. It provides assertions like ok(), equal(), and deepEqual() to compare actual and expected results. Unit tests are essential for quality assurance and meeting requirements by confirming code works as intended.







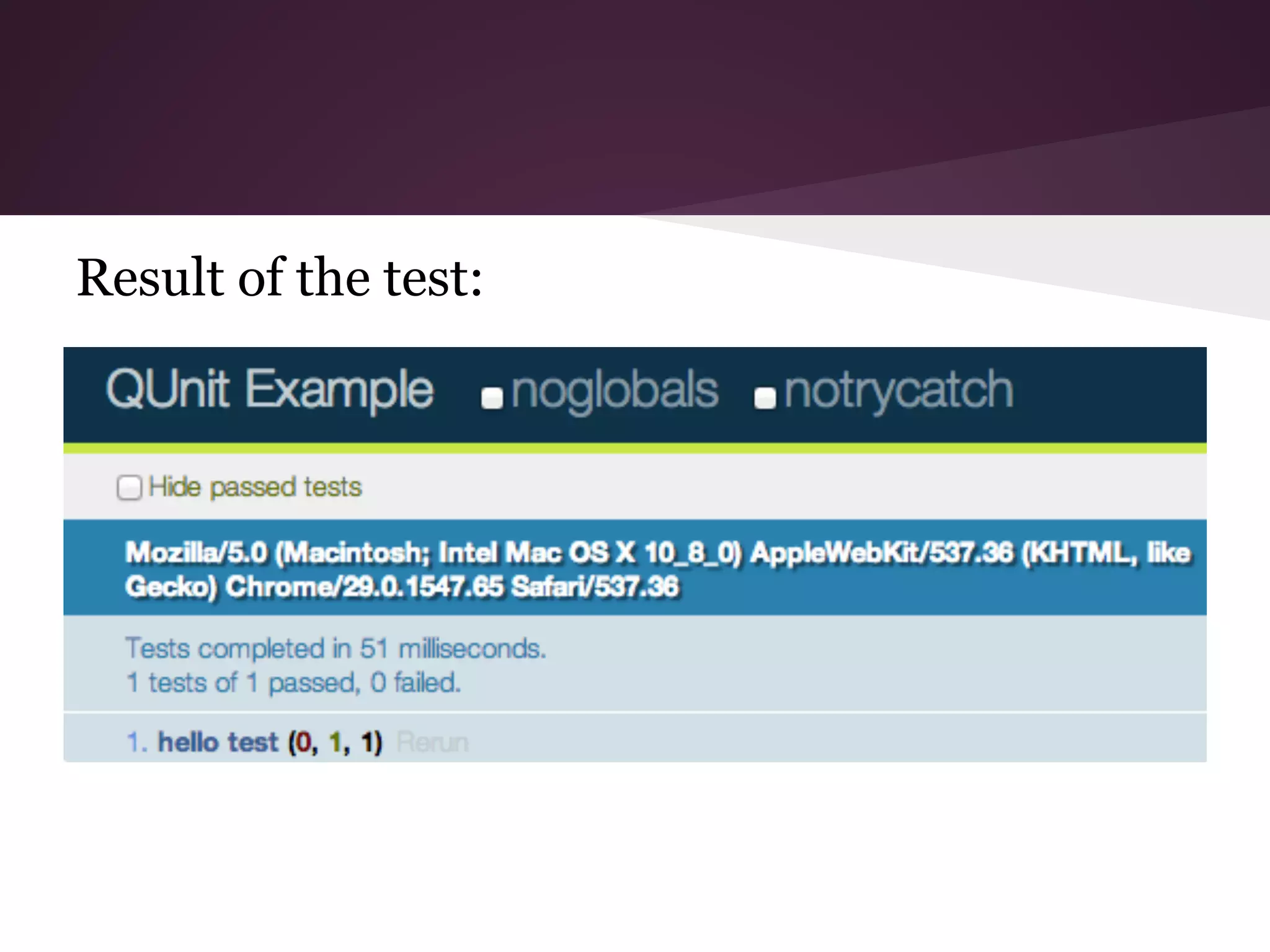

![ok() ● ok(truthy,[message]) ● most basic assertion ● requires only one argument, in addition you can send a string to show as a message examples: ok(true,”true succeeds”); ok(1==1,”test passed”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copyofmidsempresentation-131120035949-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Unit-Testing-using-QUnit-13-2048.jpg)
![equal() ● equal(actual,expected,[message]); ● compares your expected value with the actual value examples: equal(1,1,”1 equals 1, test passes”); equal(“”,0,”zero equals empty, test passes”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copyofmidsempresentation-131120035949-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Unit-Testing-using-QUnit-14-2048.jpg)
![deepEqual() ● deepEqual(actual,expected,[message]); ● can be used just like equal, is a better choice ● uses more accurate comparison operator (===) instead of simple (==) examples: deepEqual(0,””,”test fails, zero not equal to empty”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copyofmidsempresentation-131120035949-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Unit-Testing-using-QUnit-15-2048.jpg)