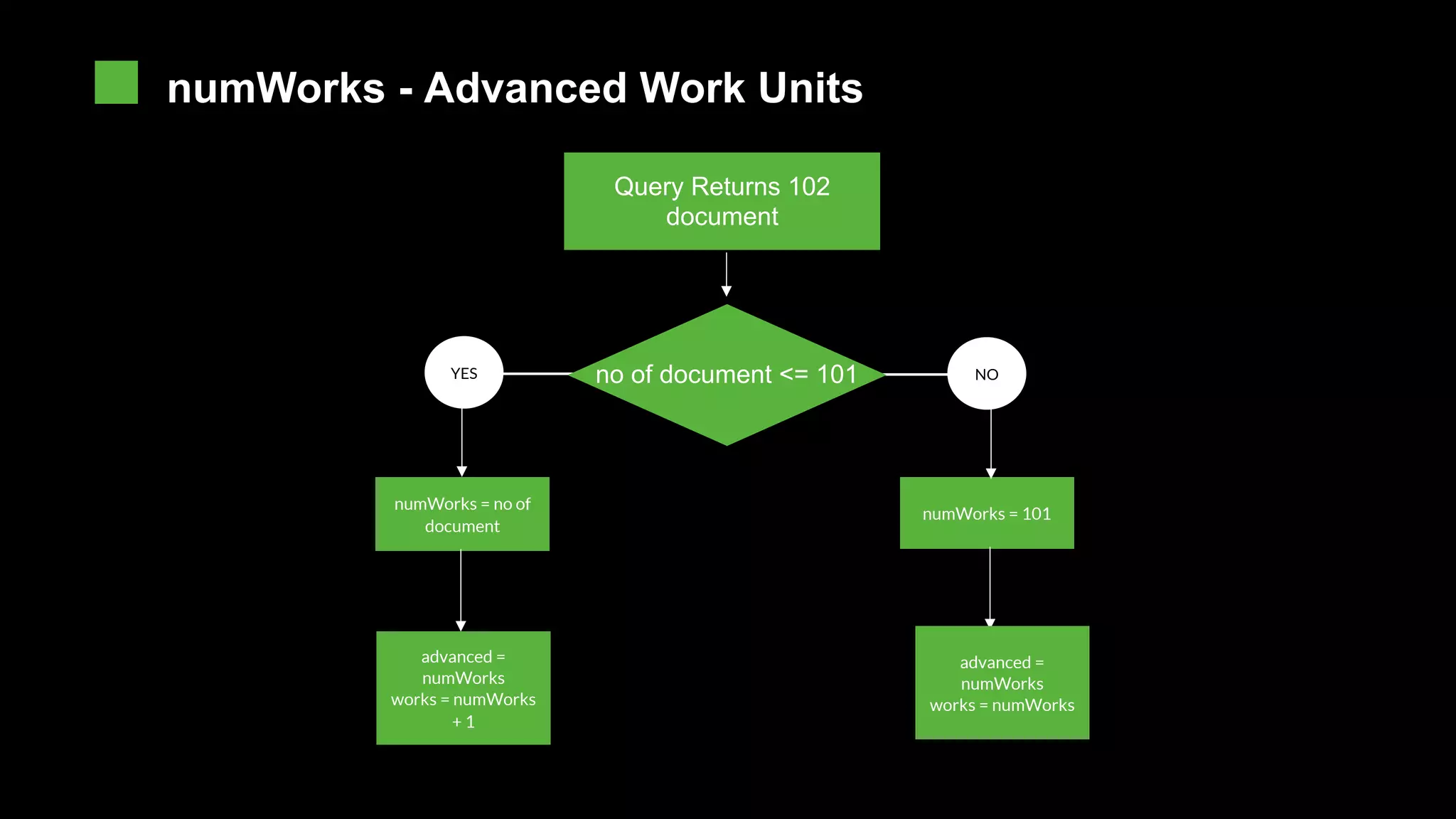
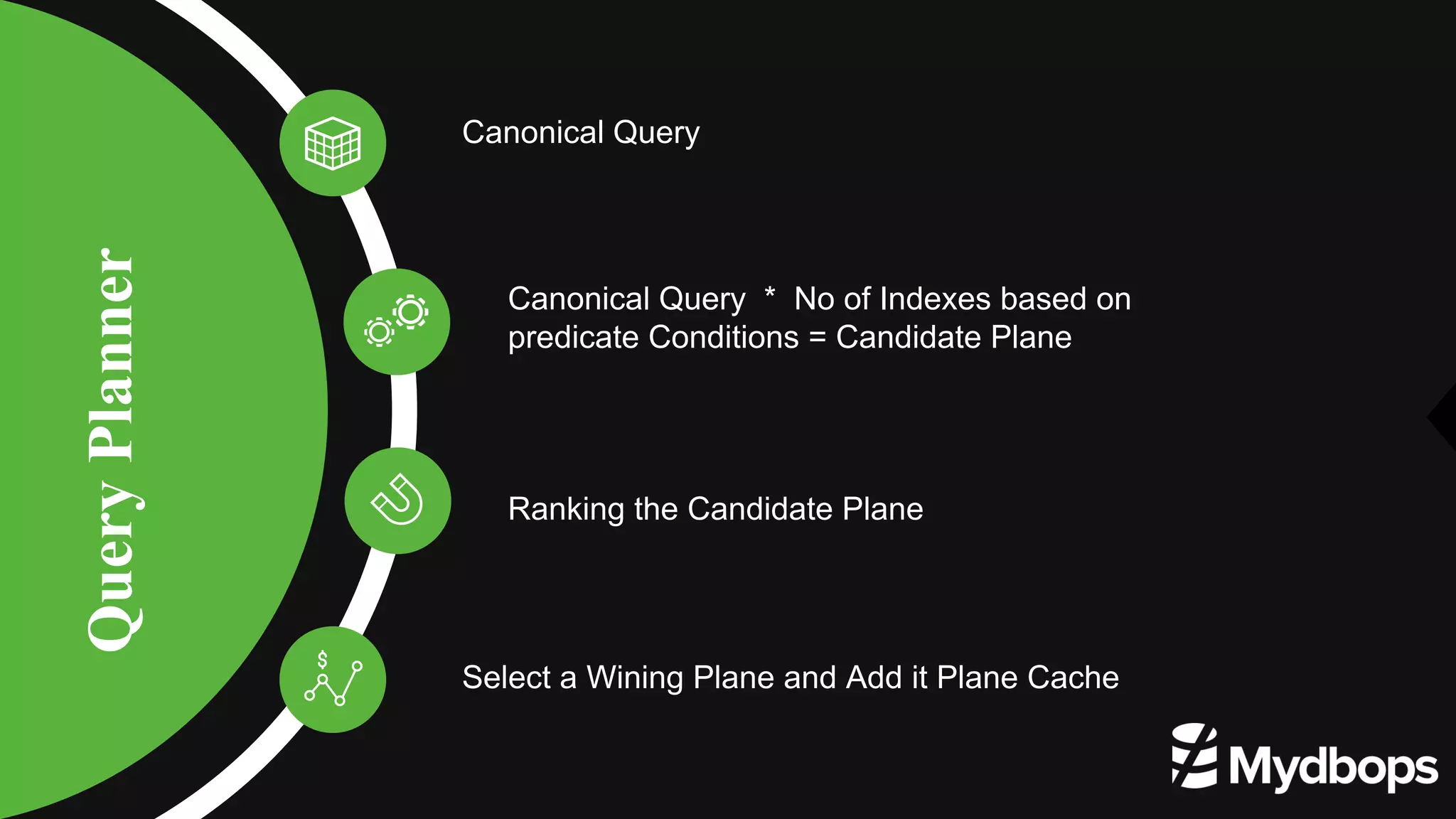
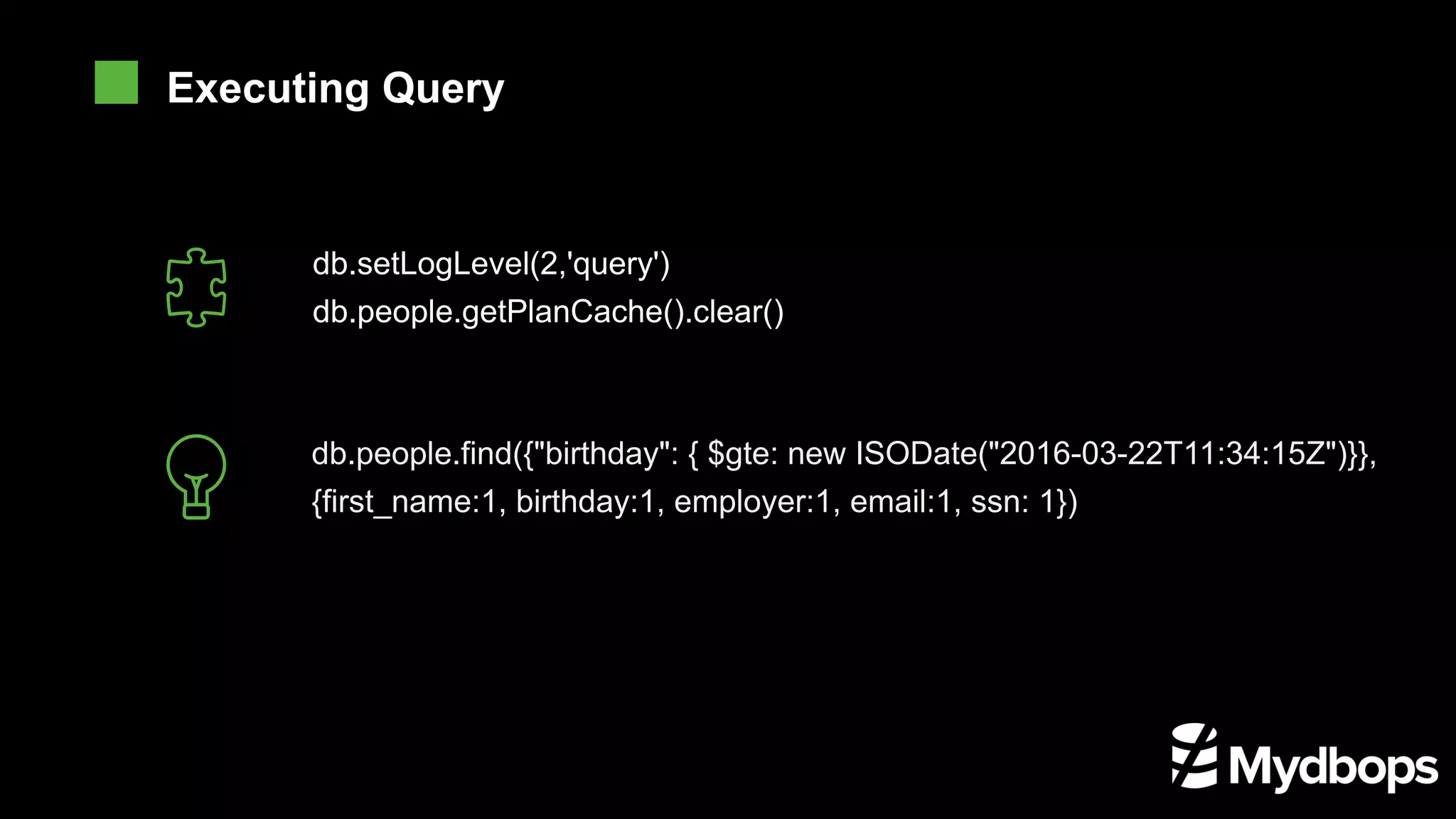
The document provides an overview of MongoDB's execution plans and optimizers, including how queries are processed and analyzed during execution. It explains various modes of the `explain()` function, detailing the process of query planning, execution stages, and metrics for analyzing performance. Additionally, the document discusses plan caching and its impacts on efficiency when executing queries in MongoDB.




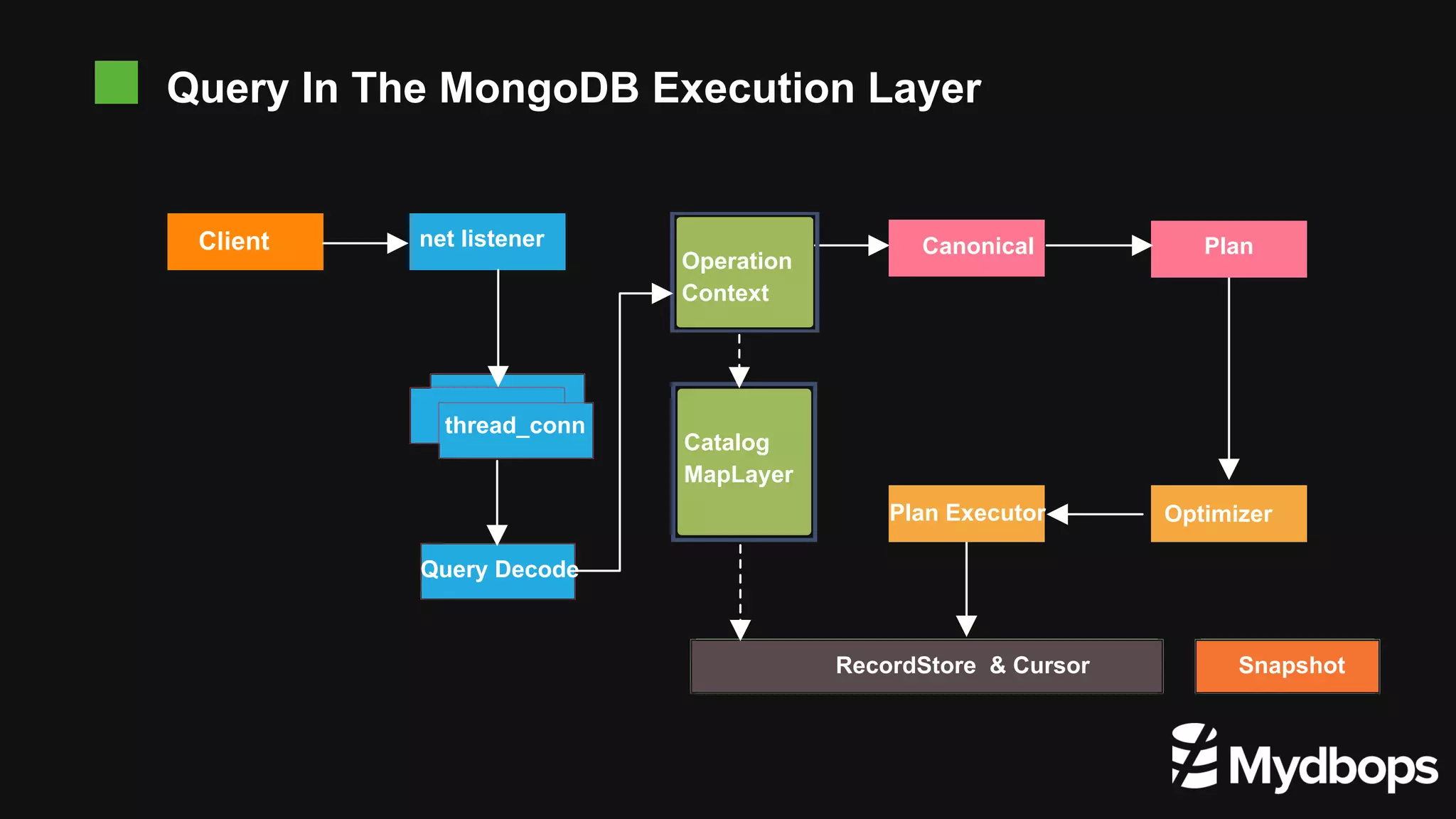


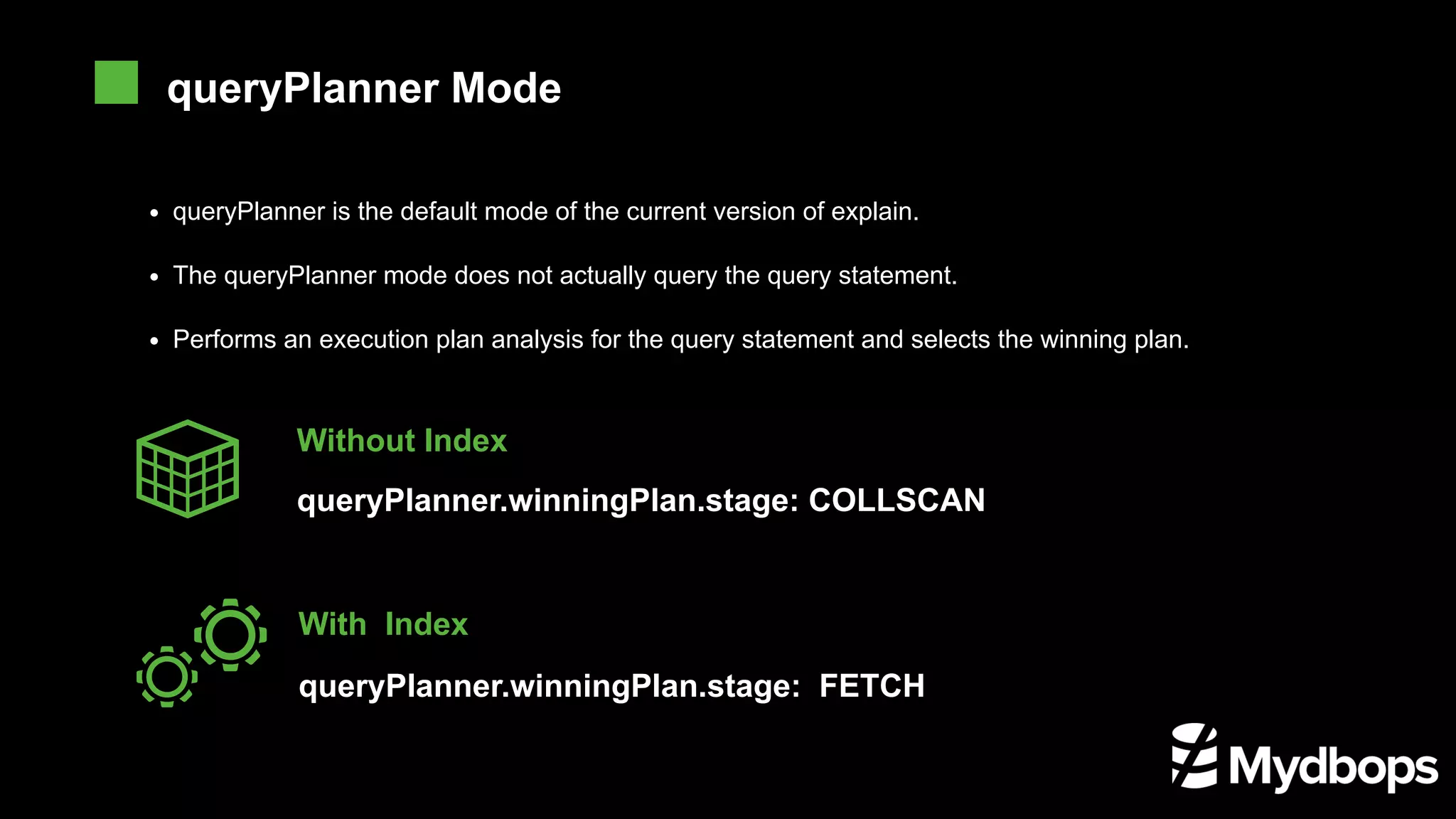
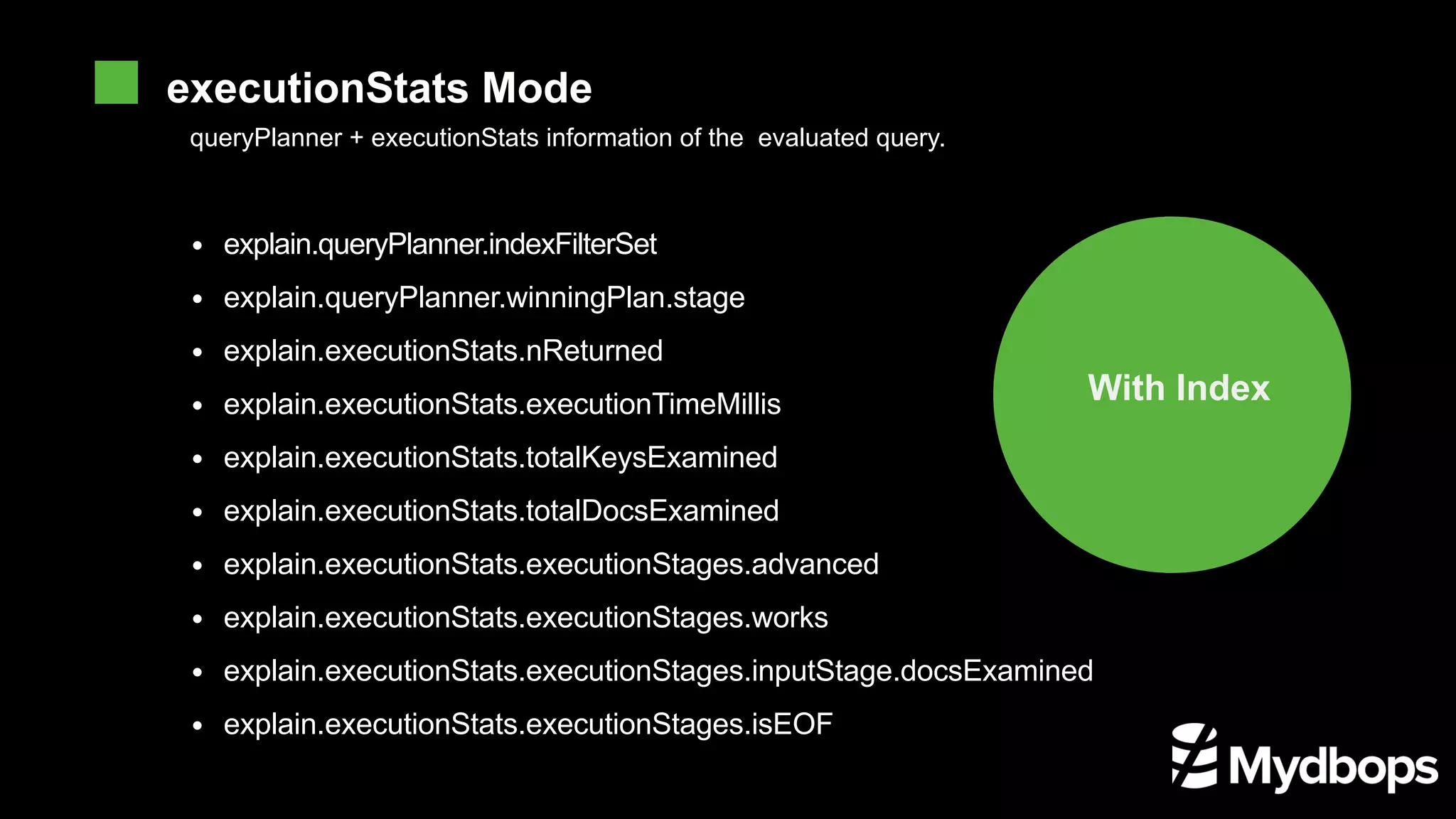
![EX db.runCommand( { planCacheSetFilter: "orders", query: { status: "A" }, indexes: [ { cust_id: 1, status: 1 }, { status: 1, order_date: -1 } ] } ) IndexFilter determines how the query optimizer will use index for a type of query. Thquery optimizer will ignore the index set by the 1. explain.queryPlanner.indexFilterSet The stage of the optimal execution plan 2. explain.queryPlanner.winningPlan.stage COLLSCAN: Full table scan IXSCAN: Index scan FETCH: Retrieve the specified document based on the indexEmpty text SHARD_MERGE: Return each fragment to the data for merge SORT: Indicates that sorting is done in memor LIMIT: Use limit to limit the number of returns SKIP: Skip using skip IDHACK: Query for _id SHARDING_FILTER: Querying fragmented data by mongos COUNT: Count operation using db.coll.explain().count() COUNTSCAN: Count does not use the stage return when using Count for index COUNT_SCAN: Count uses the stage to return when the index is counted SUBPLA: Stage return of $or query not used to index TEXT: Stage return when using full-text index for queryPROJECTION: The return of the stage when the return field is qualified STAGE executionStats Metrics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-mongodb-execution-plan-optimizer-final-191115020708/75/Introduction-to-Mongodb-execution-plan-and-optimizer-11-2048.jpg)


![The planner ask plan each time for the next document via call to work() If the plan can give supply document it respond with document, Otherwise the plan respond with needTime If all the all the document have been retrieved then isEOF = 1 Work - Advanced - isEOF [ Algorithm ] "works": 18667 "advanced": 18666 "needTime": 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-mongodb-execution-plan-optimizer-final-191115020708/75/Introduction-to-Mongodb-execution-plan-and-optimizer-14-2048.jpg)
![WorkingSet workingSet; PlanStage* rootStage = makeQueryPlan(&workingSet, ...); while (!rootStage->isEOF()) { WorkingSetID result; switch(rootStage->work(&result)) { case PlanStage::ADVANCED: // do something with result WorkingSetMember* member = workingSet.get(result); cout << "Result: " << member->obj << std::endl; break; case PlanStage::IS_EOF: // All done. Will fall out of while loop. break; Work - Advanced - isEOF [ Code ] Cont . . case PlanStage::NEED_TIME: // Need more time. break; case PlanStage::FAILURE: // Throw exception or return error. break; } if (shouldYield) { // Occasionally yield. stage->saveState(); stage->restoreState(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-mongodb-execution-plan-optimizer-final-191115020708/75/Introduction-to-Mongodb-execution-plan-and-optimizer-15-2048.jpg)



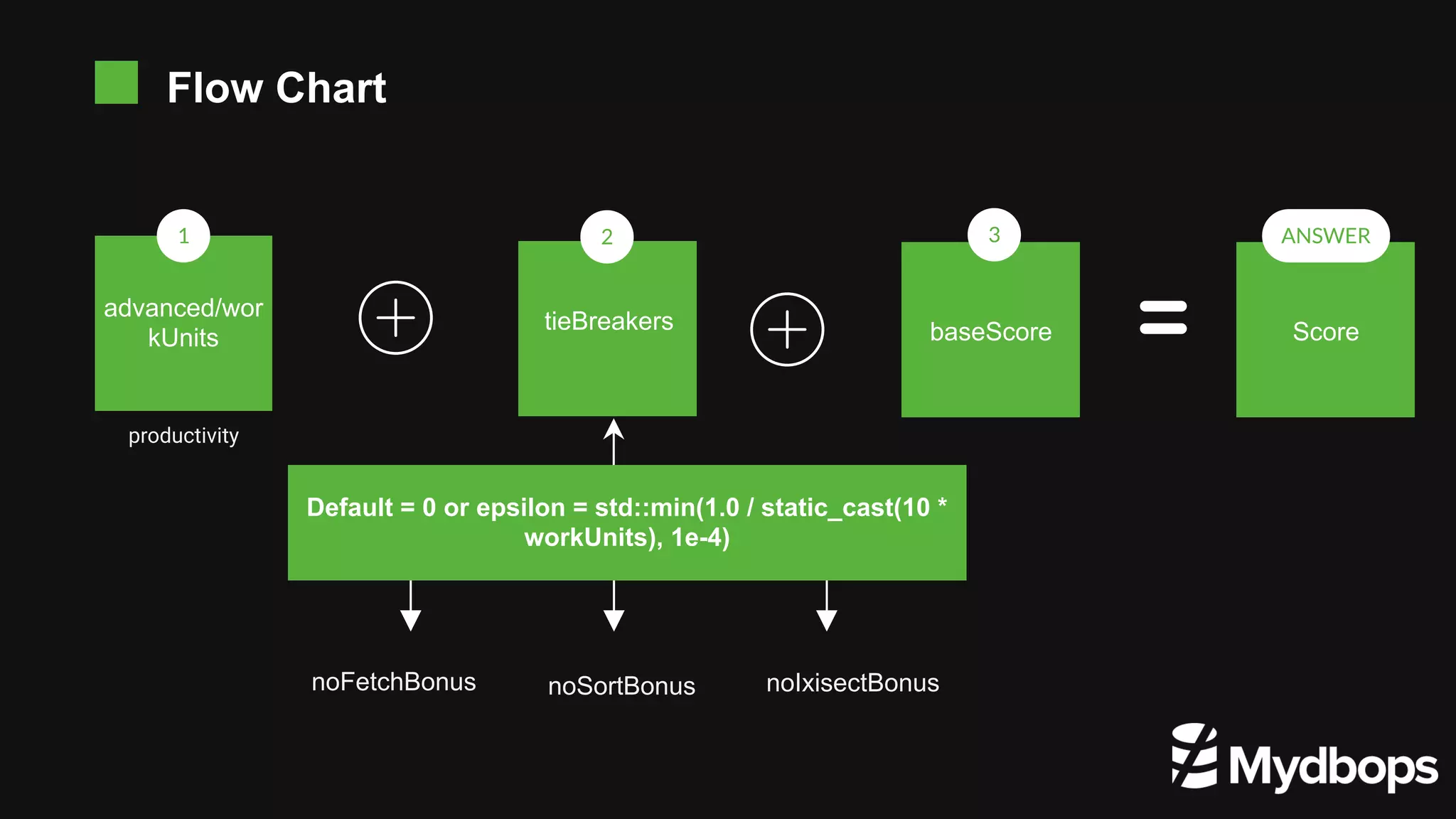
![numWorks baseScore common.advanced workUnits productivity(Plan Produce range[0, 1]) noFetchBonus noSortBonus noIxisectBonus epsilon tieBreakers Scorea MongoDB Plan Ranking Terms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-mongodb-execution-plan-optimizer-final-191115020708/75/Introduction-to-Mongodb-execution-plan-and-optimizer-22-2048.jpg)