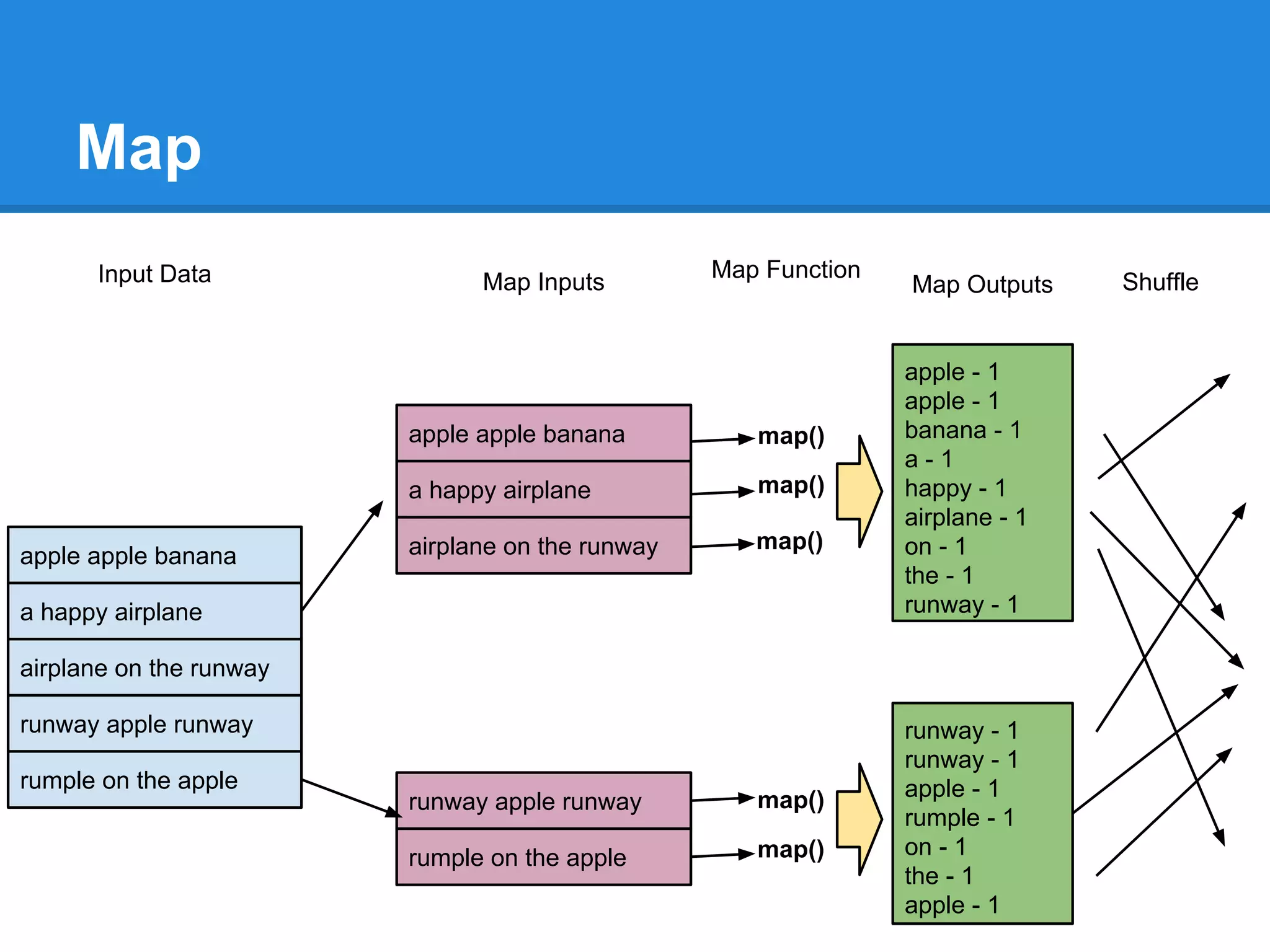
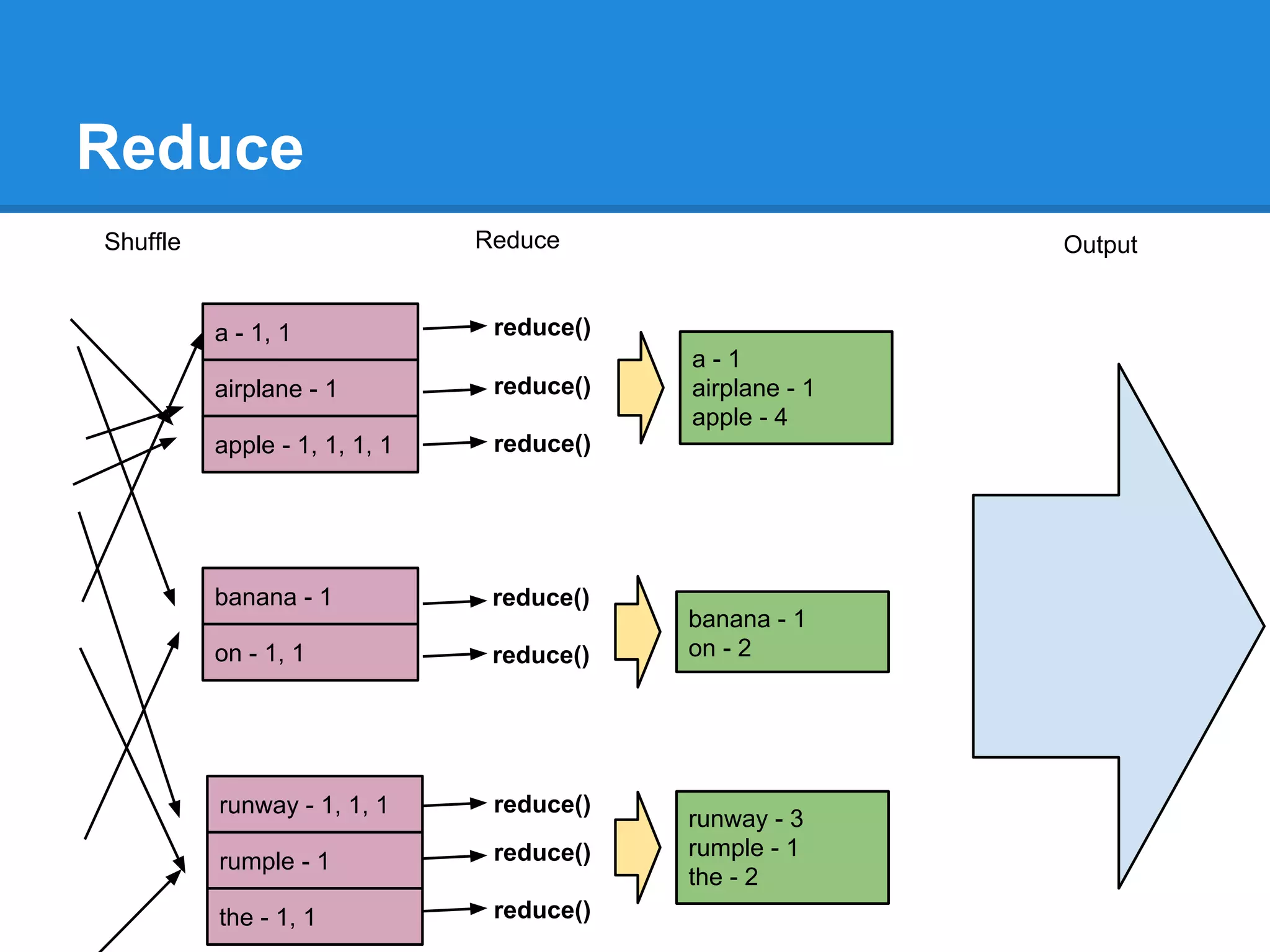
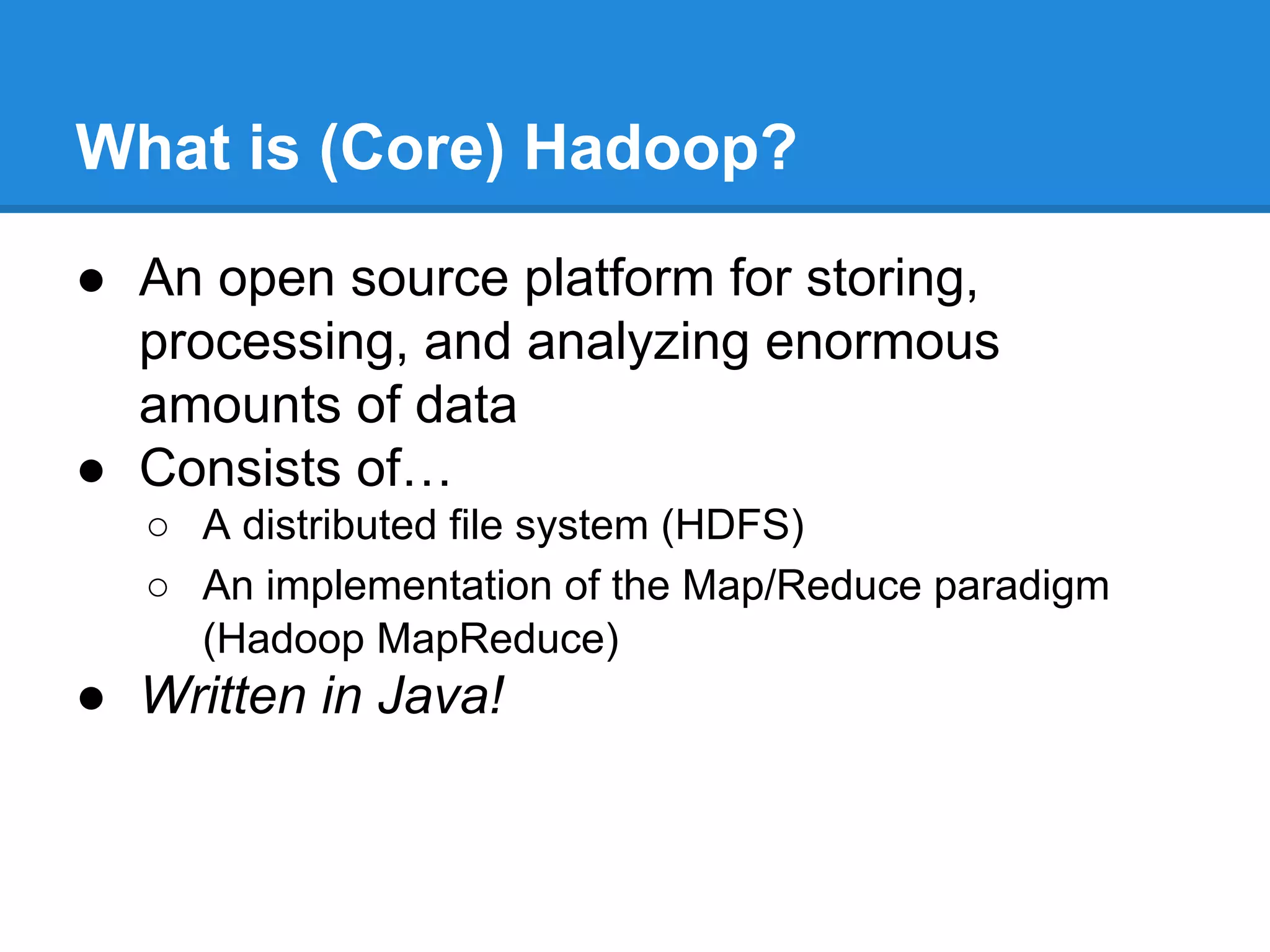
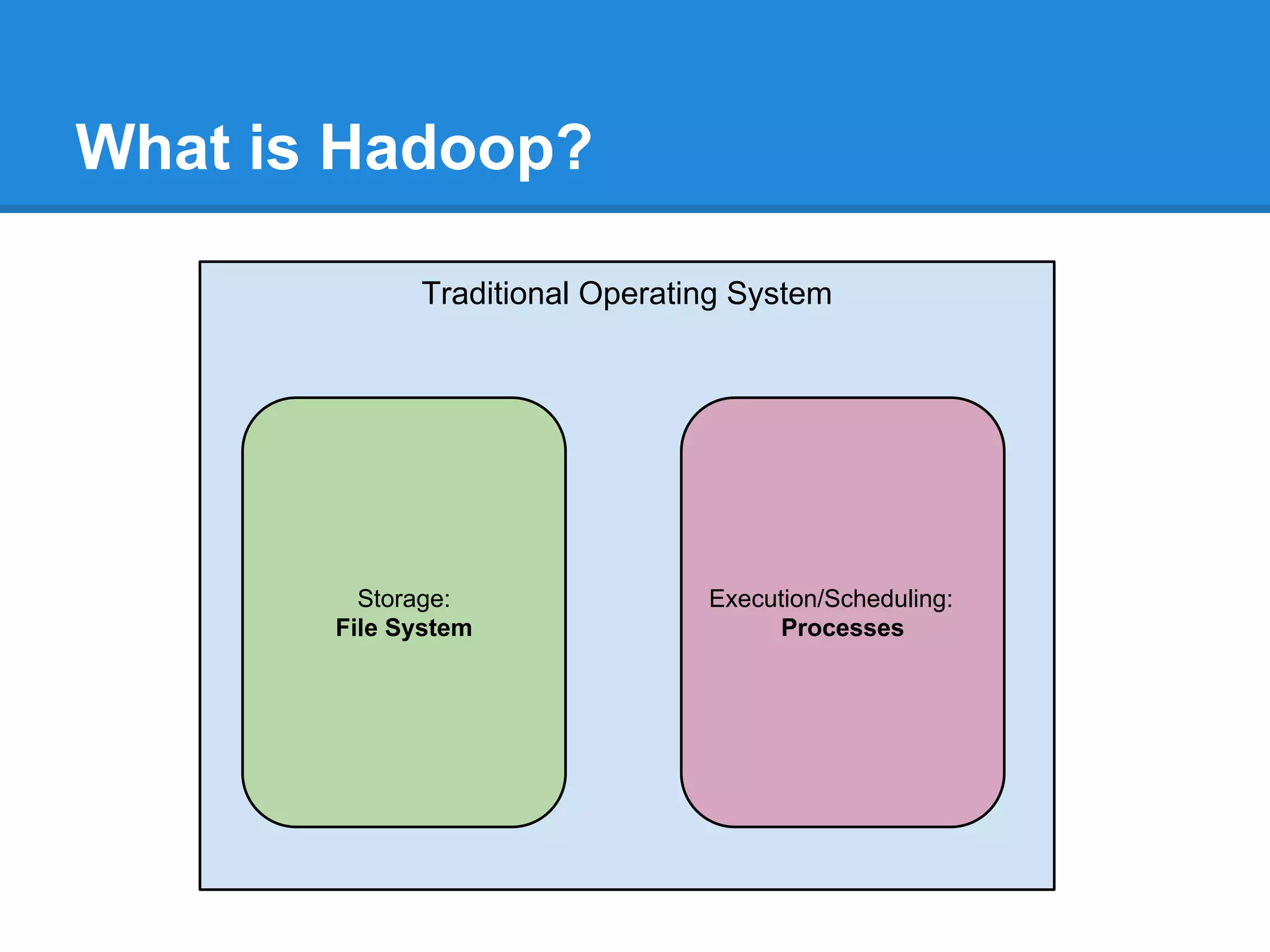
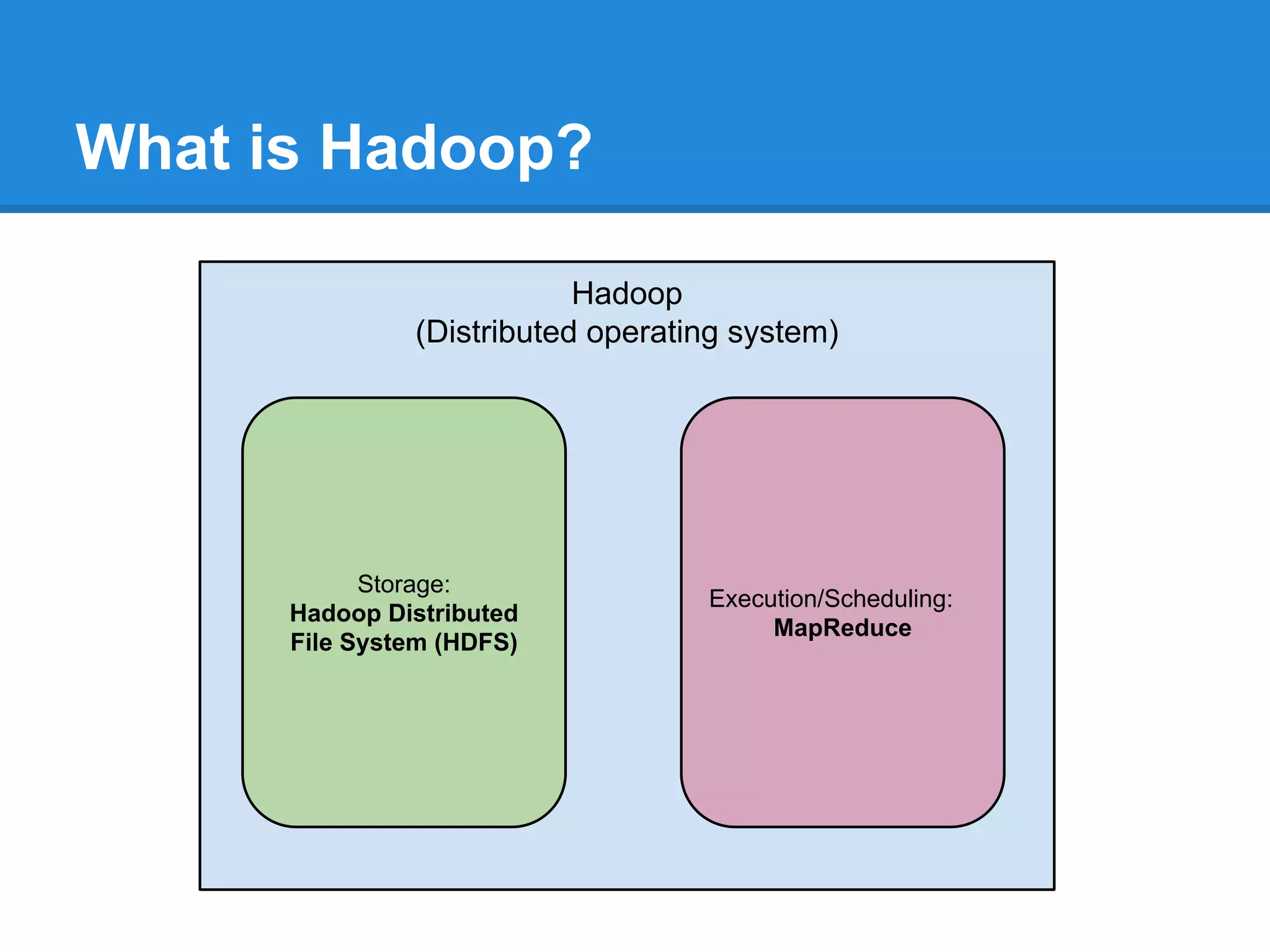
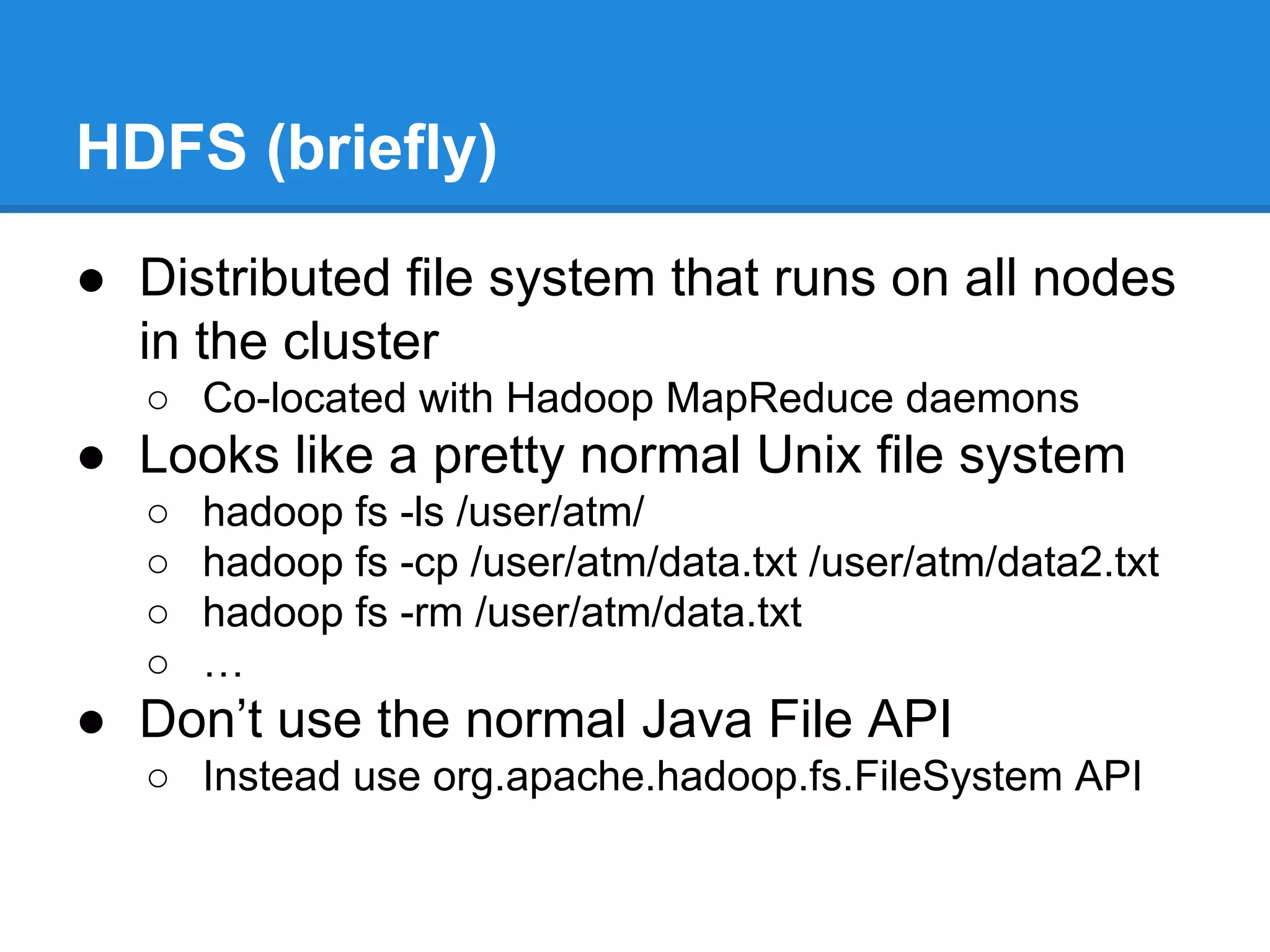
Aaron Myers introduces MapReduce and Hadoop. MapReduce is a distributed programming paradigm that allows processing of large datasets across clusters. It works by splitting data, distributing it across nodes, processing it in parallel using map and reduce functions, and collecting the results. Hadoop is an open source software framework for distributed storage and processing of big data using MapReduce. It includes HDFS for storage and Hadoop MapReduce for distributed computing. Developers write MapReduce jobs in Java by implementing map and reduce functions.












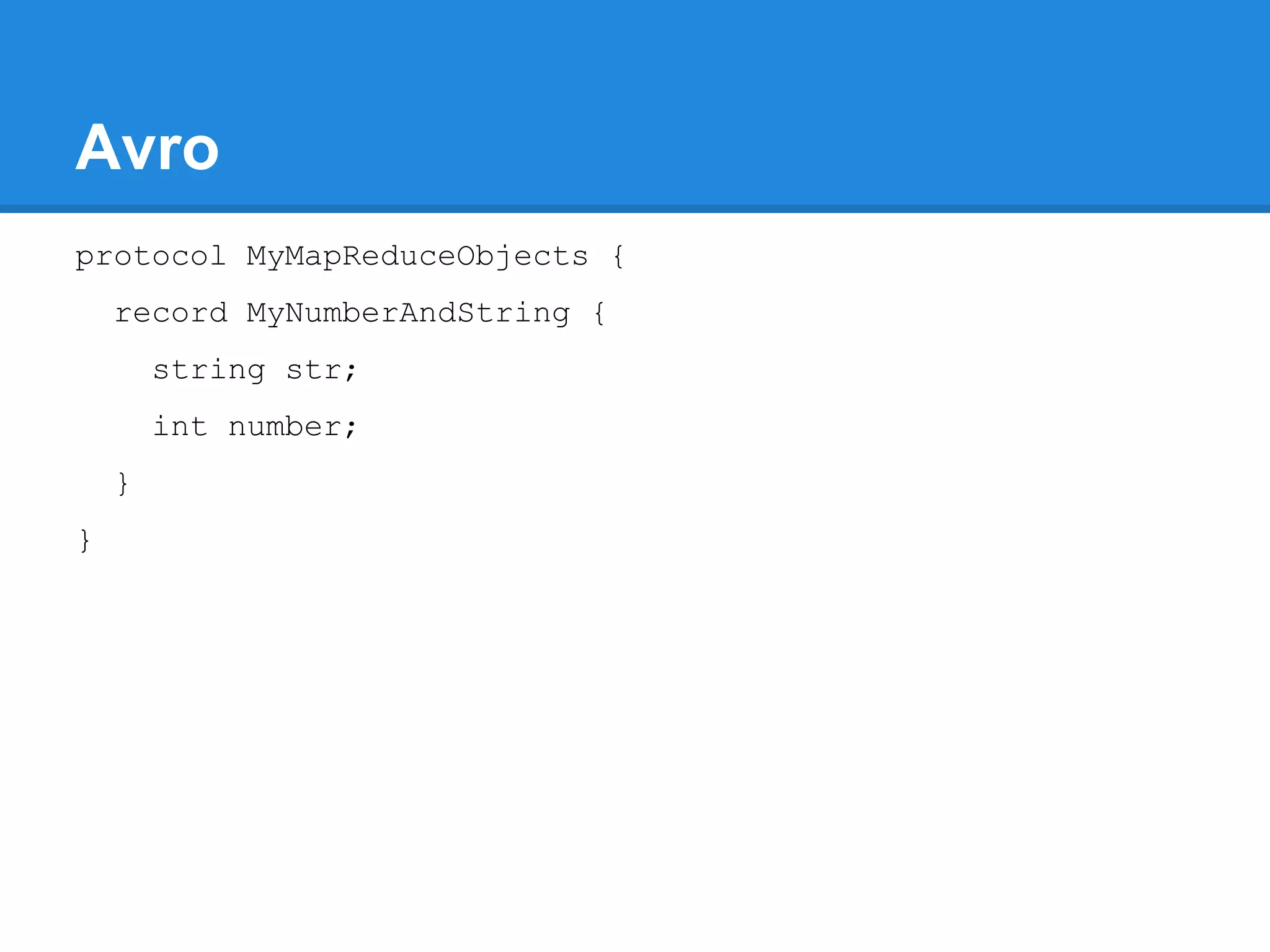




![Crunch public class WordCount { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Pipeline pipeline = new MRPipeline(WordCount.class); PCollection<String> lines = pipeline.readTextFile(args[0]); PCollection<String> words = lines.parallelDo("my splitter", new DoFn<String, String>() { public void process(String line, Emitter<String> emitter) { for (String word : line.split("s+")) { emitter.emit(word); } } }, Writables.strings()); PTable<String, Long> counts= Aggregate.count(words); pipeline.writeTextFile(counts, args[1]); pipeline.run(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20140412introductiontomapreduceprogramming-hdfs-140412075206-phpapp02/75/Hadoop-Introduction-to-map-reduce-programming-Reuniao-12-04-2014-34-2048.jpg)