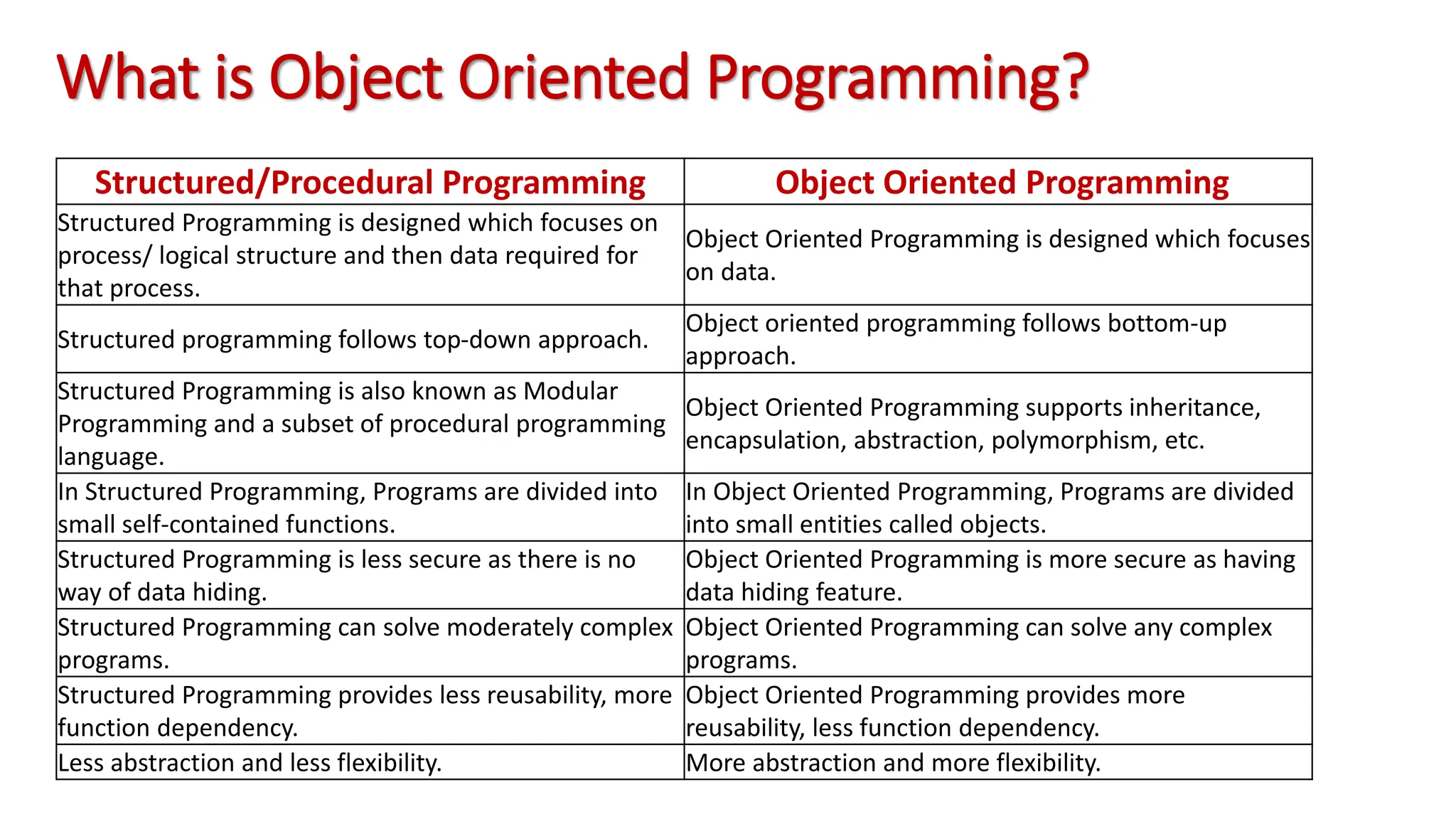
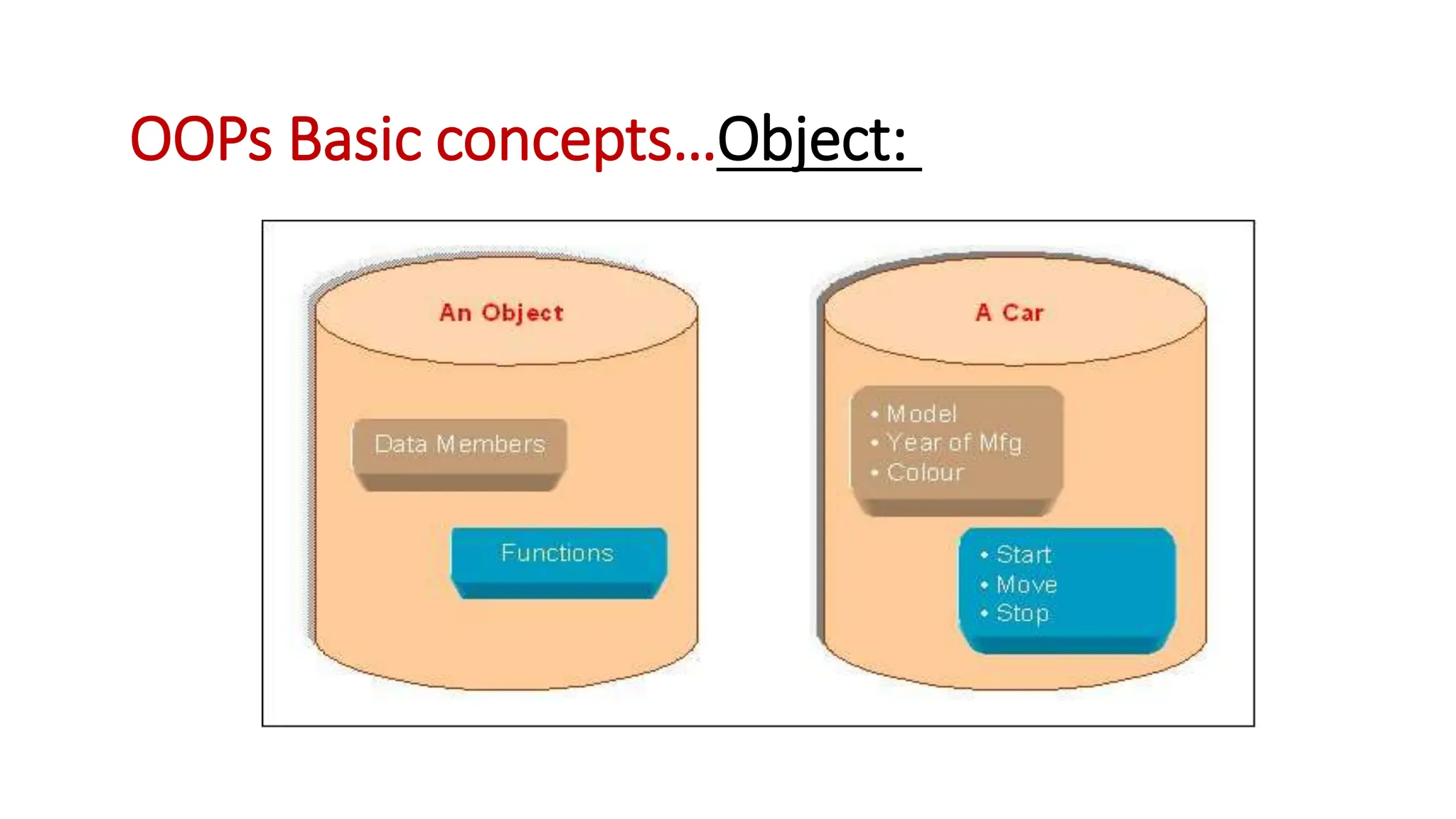
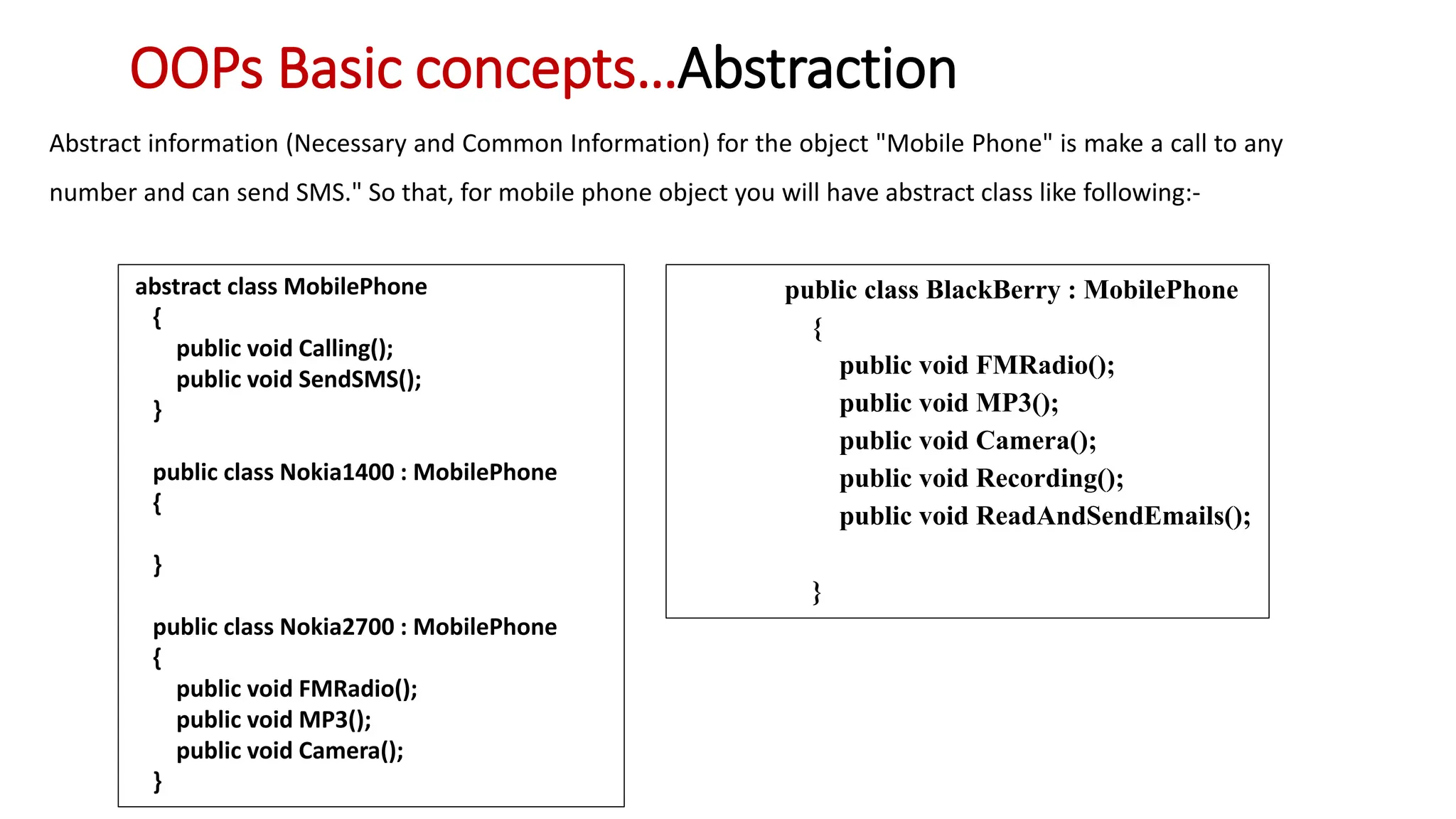
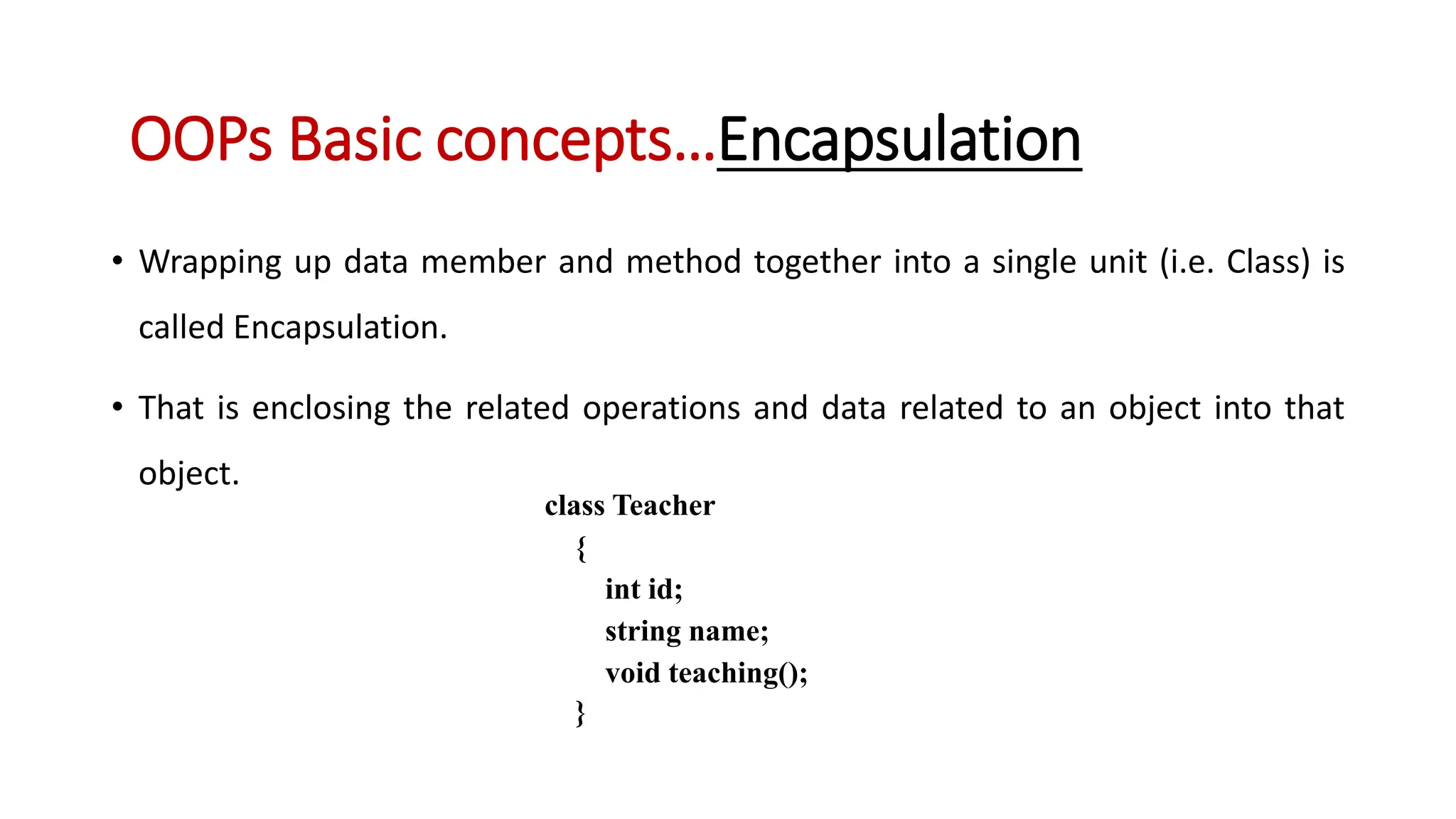
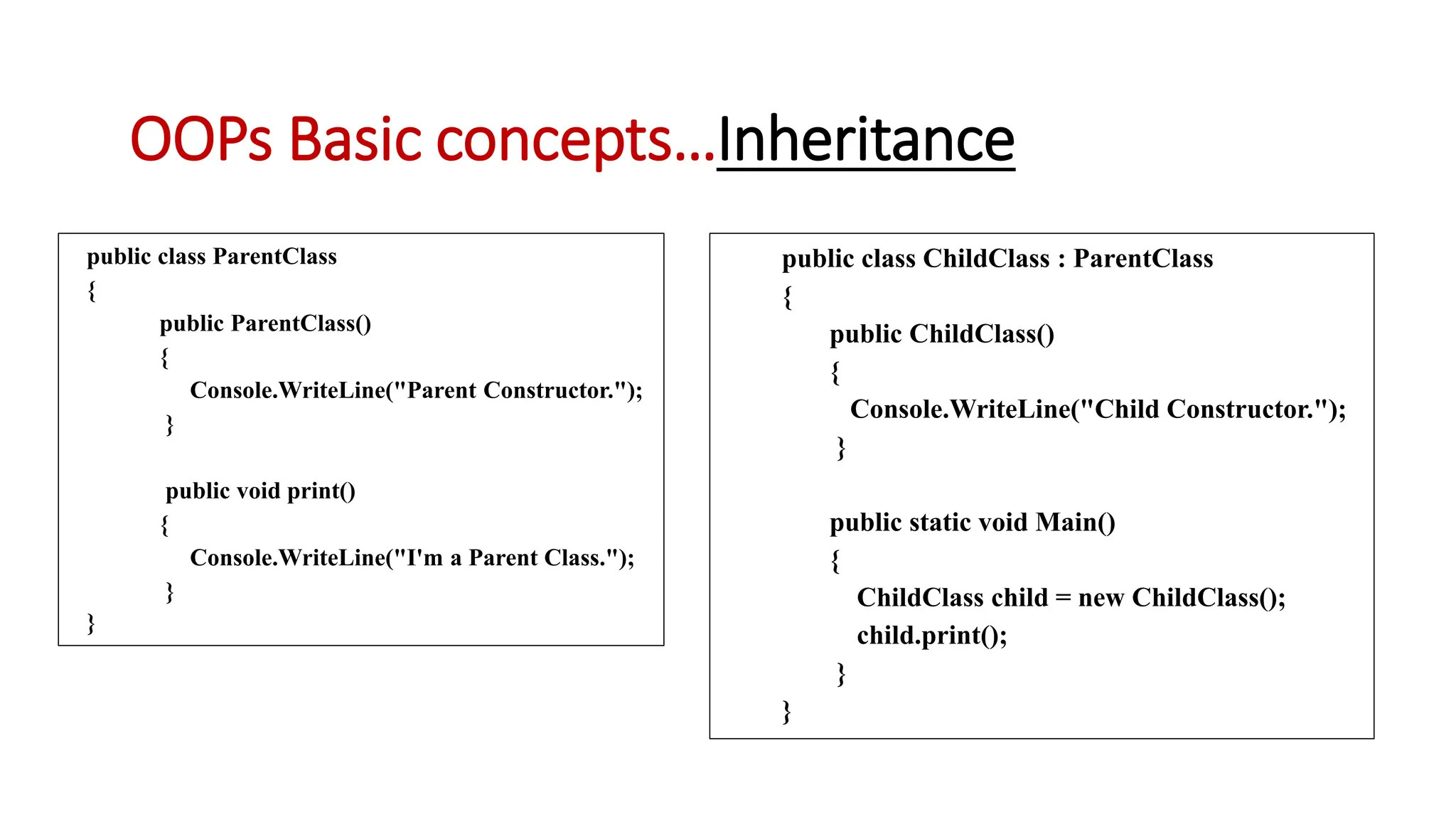
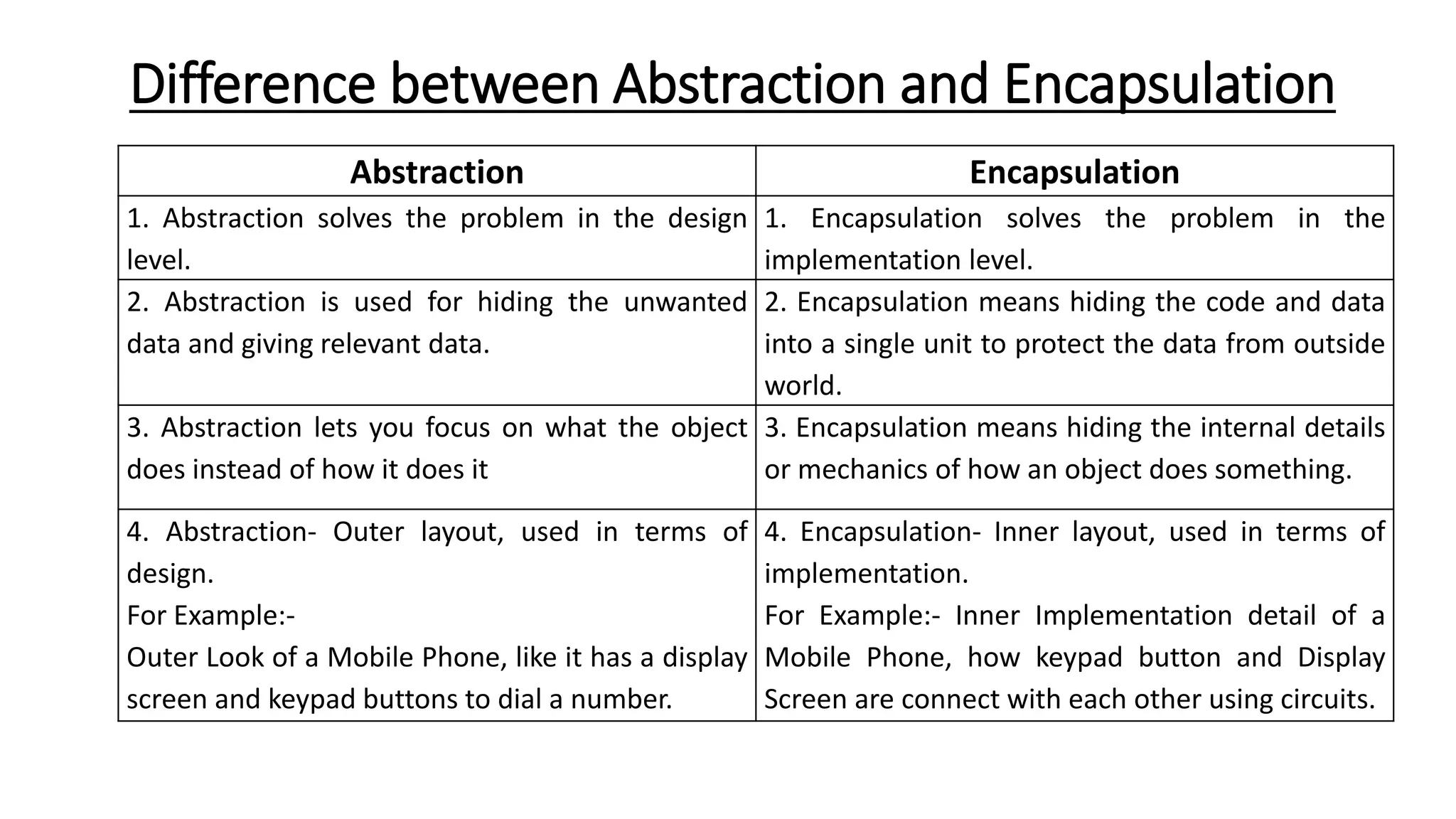
Object oriented programming (OOP) represents problems using real-world objects and their interactions. This chapter introduces OOP concepts including classes, objects, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It contrasts OOP with structured programming, which organizes programs in a logical structure rather than representing real-world entities. The chapter defines key OOP terms and provides examples to illustrate abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.