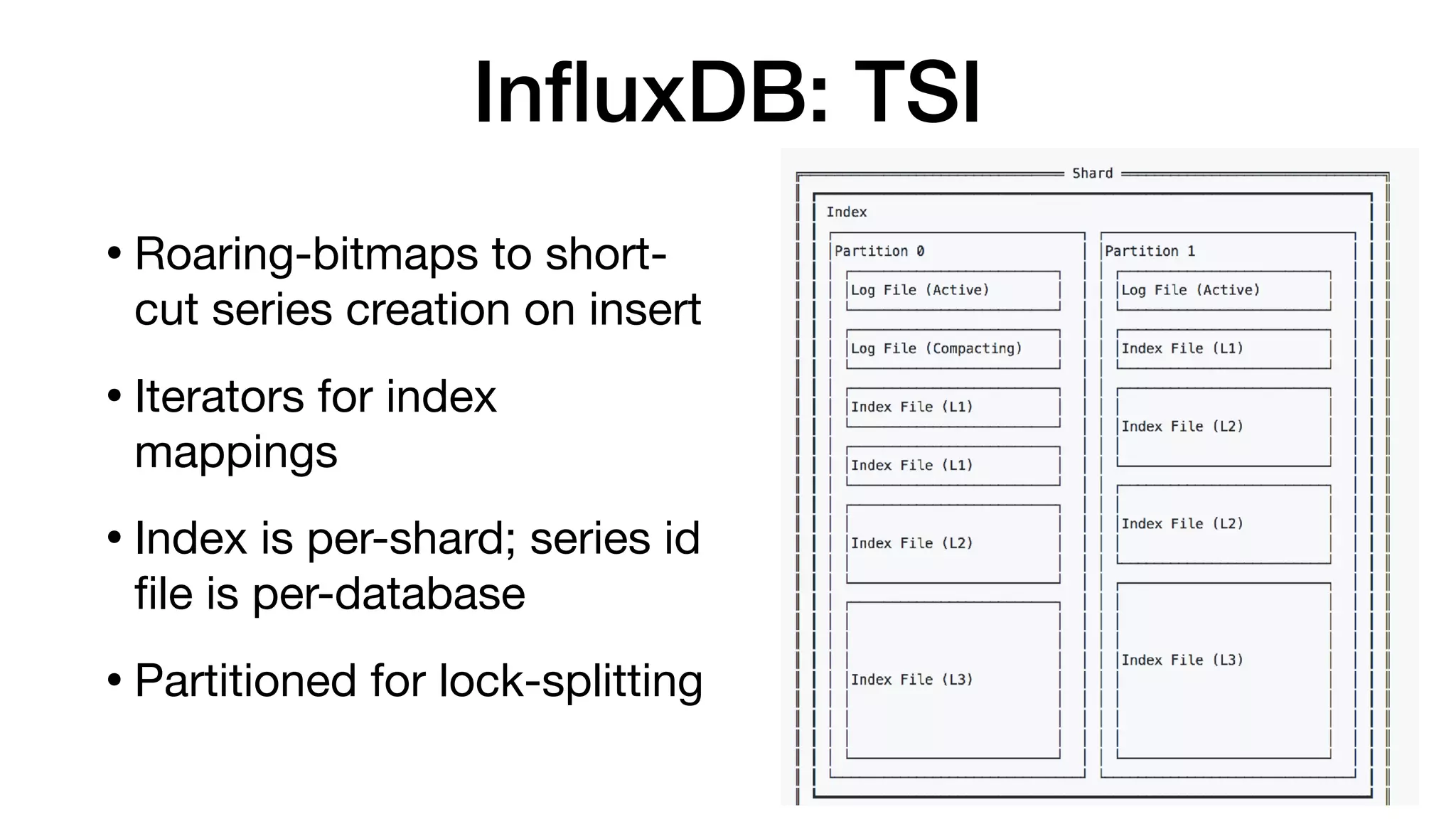
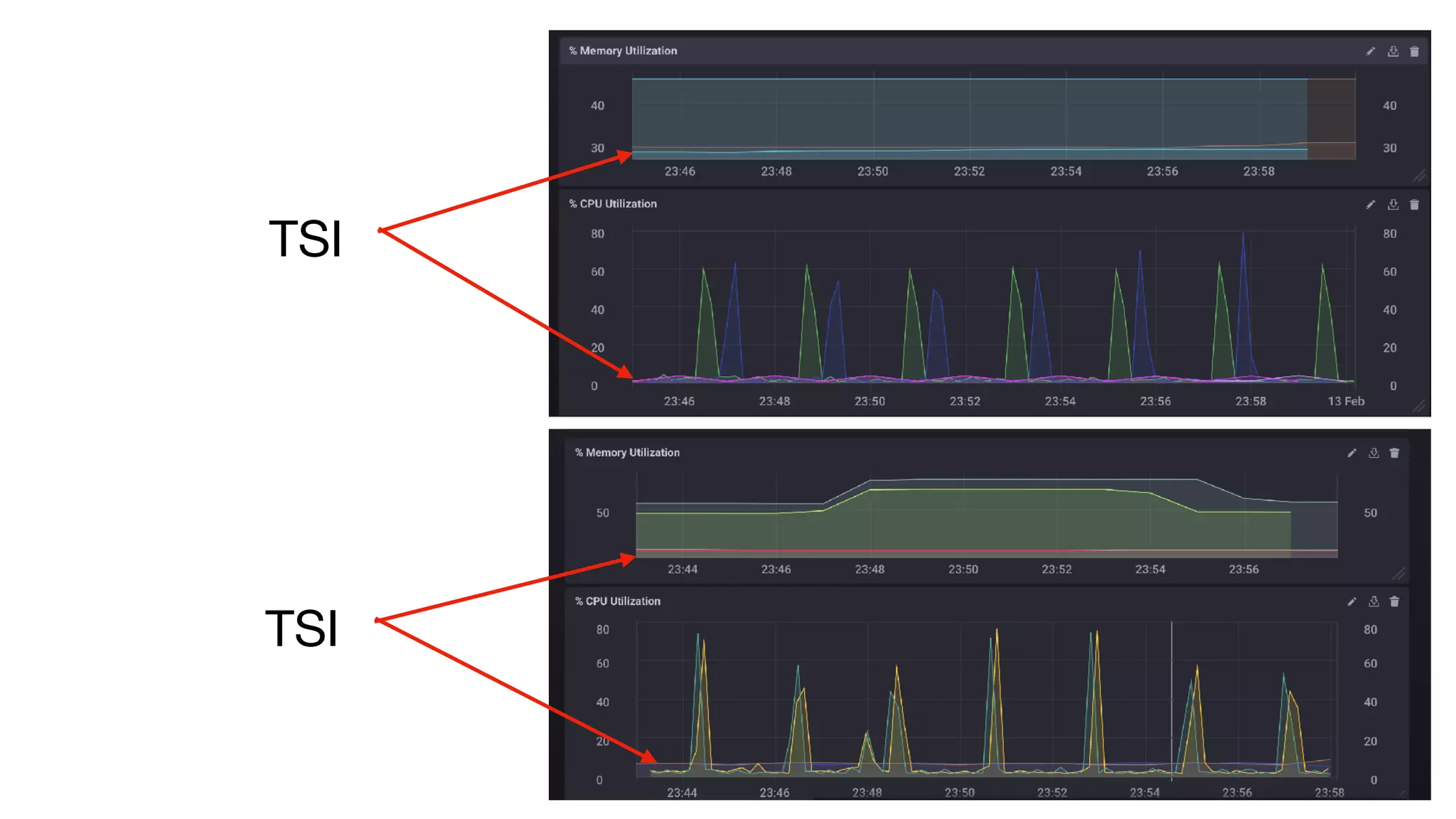
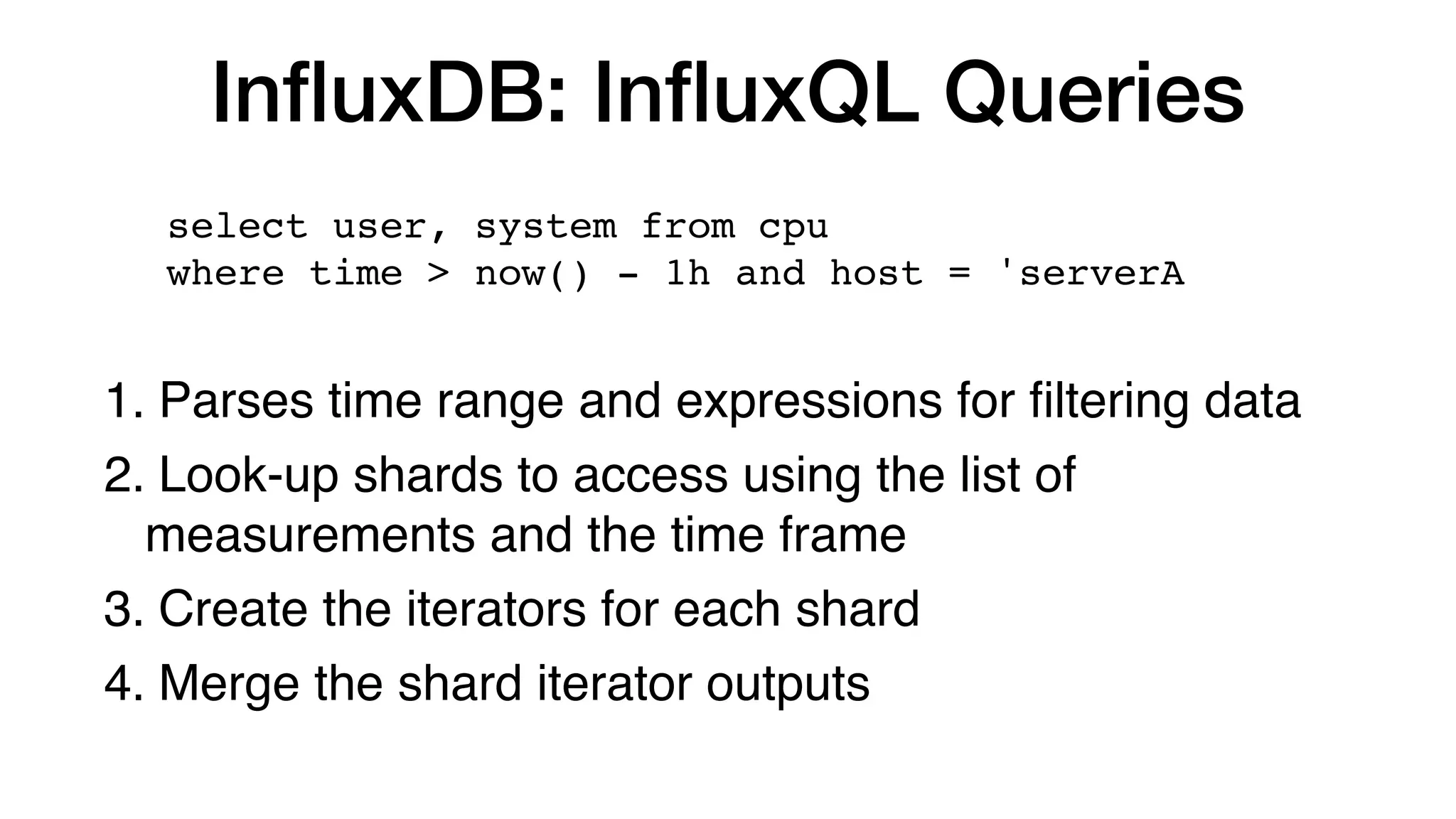
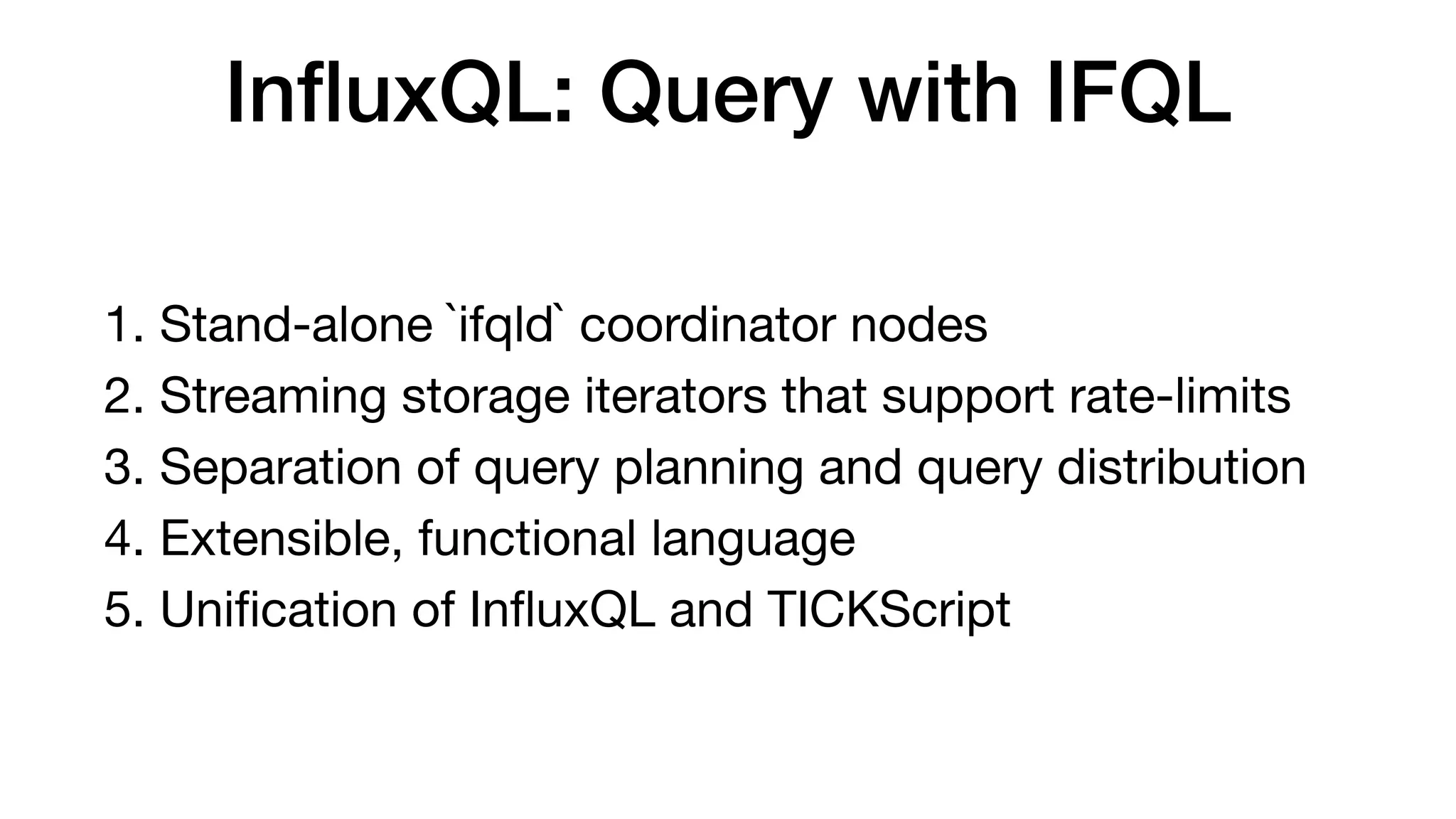
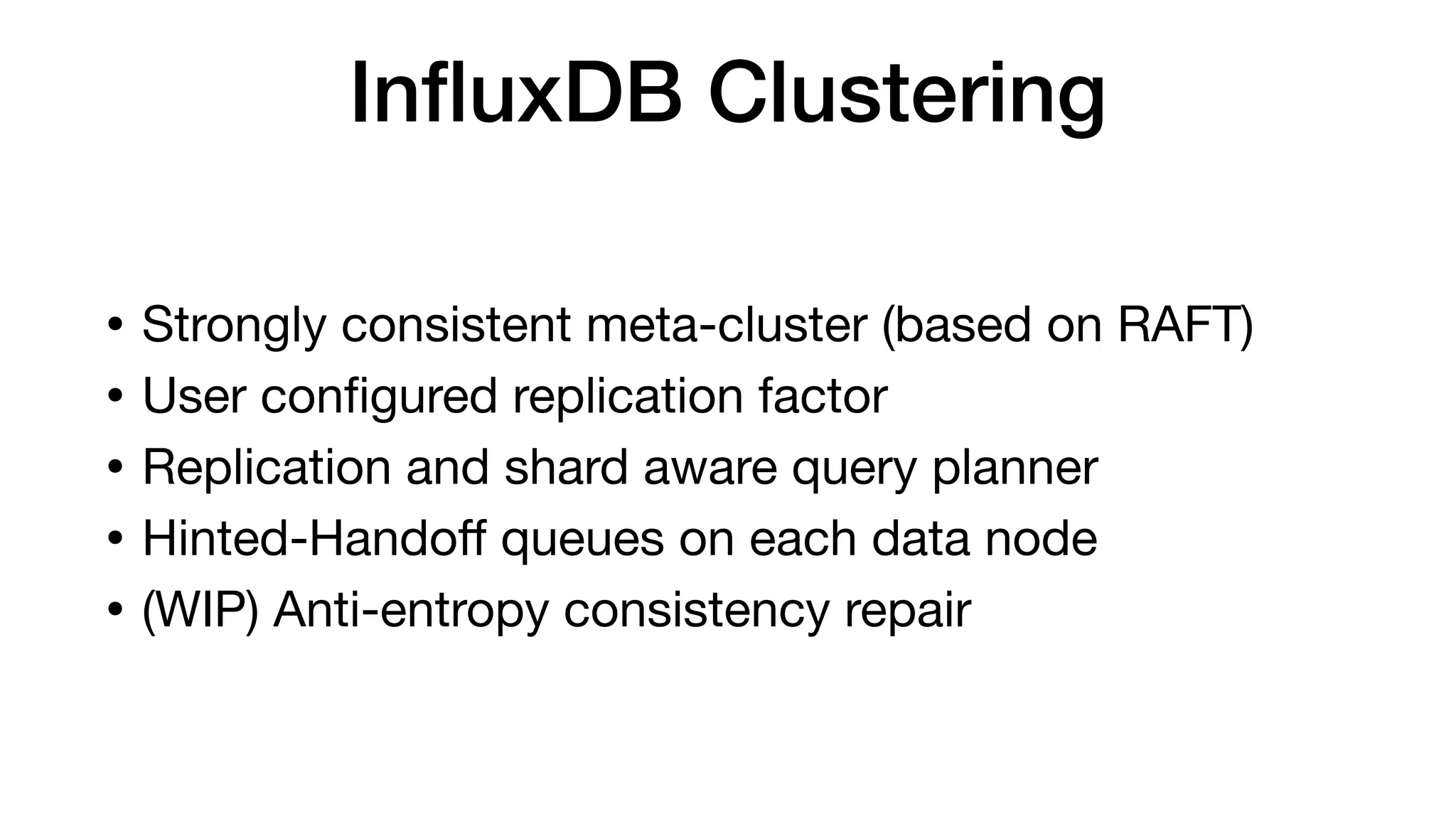
The document discusses the internals of InfluxDB, focusing on its design as a time series database. It highlights the unique requirements of time series data, including high throughput ingestion, fast queries, and special storage needs. Key advancements in InfluxDB, such as TSI for cardinality management and IFQL for improved query execution, are also outlined.






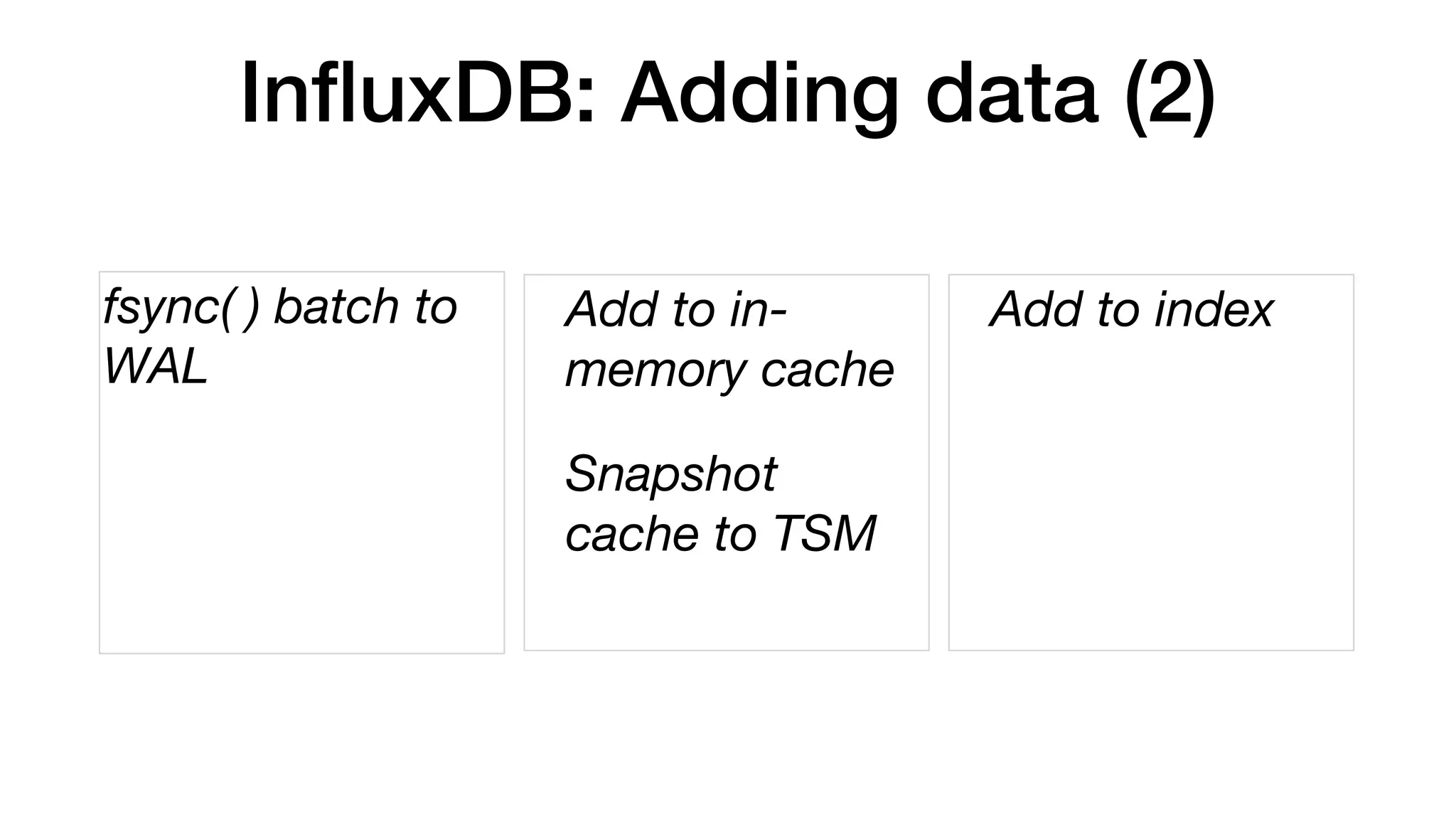
![InfluxDB: on-disk (filesystem) CREATE RETENTION POLICY <retention_policy_name> ON <database_name> DURATION <duration> REPLICATION <n> [SHARD DURATION <duration>] [DEFAULT] Database directory /db Retention Policy directory /db/rp Shard Group (time bounded) (Logical) Shard directory (db/rp/Id#) TSM0001.tsm (data file) TSM0002.tsm (data file)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ryanbetts-180215155933/75/InfluxDB-Internals-13-2048.jpg)