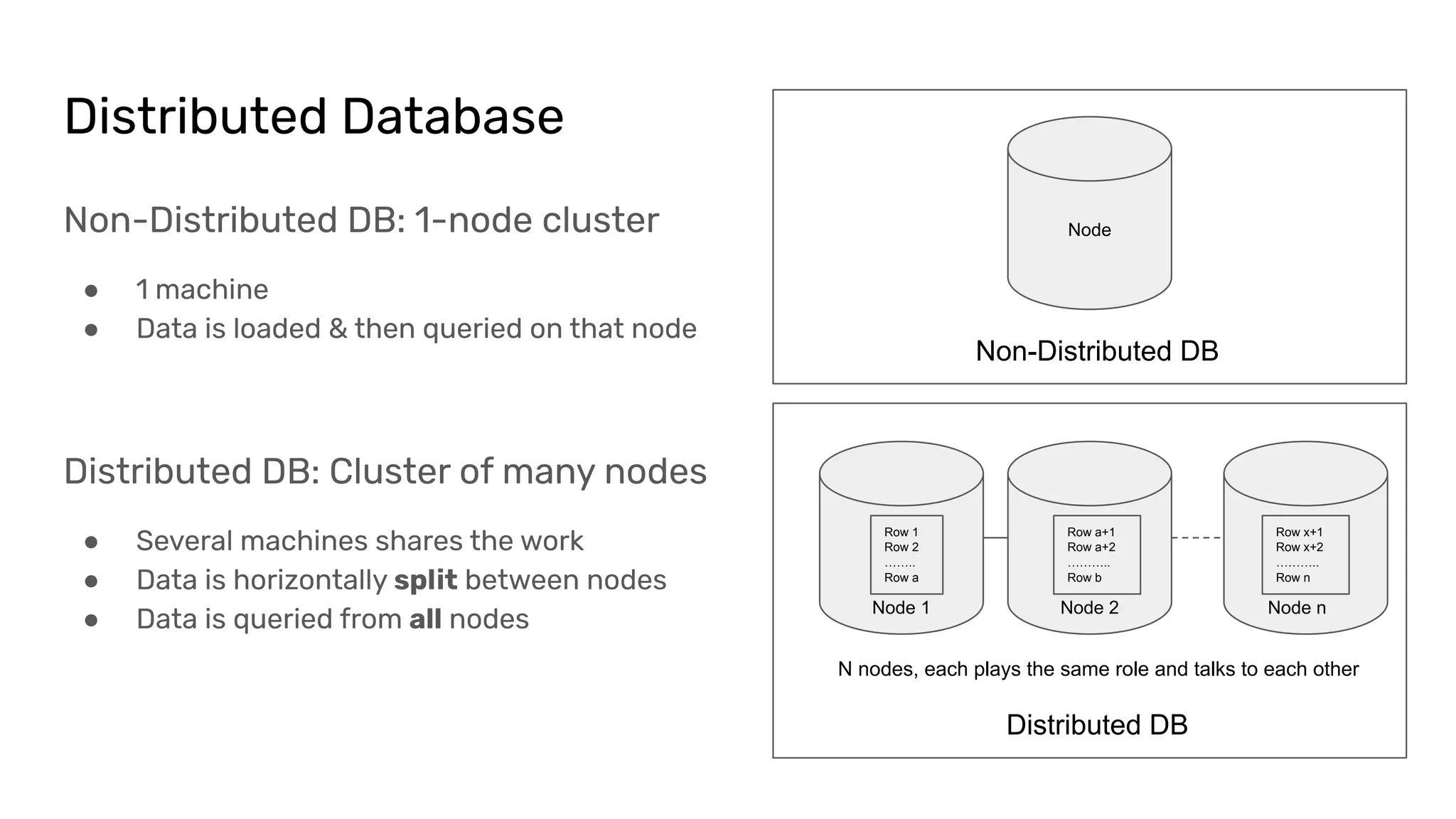
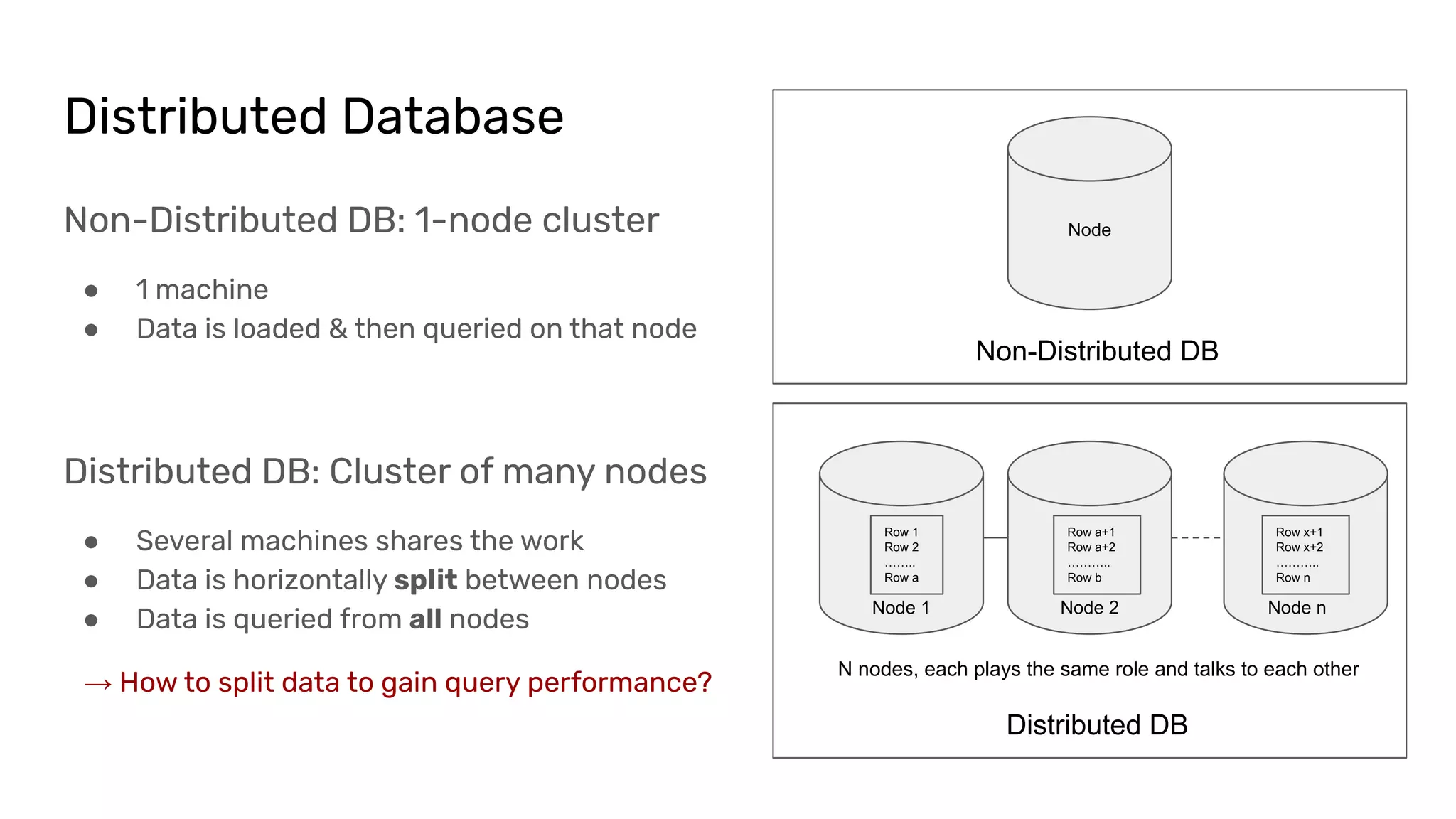
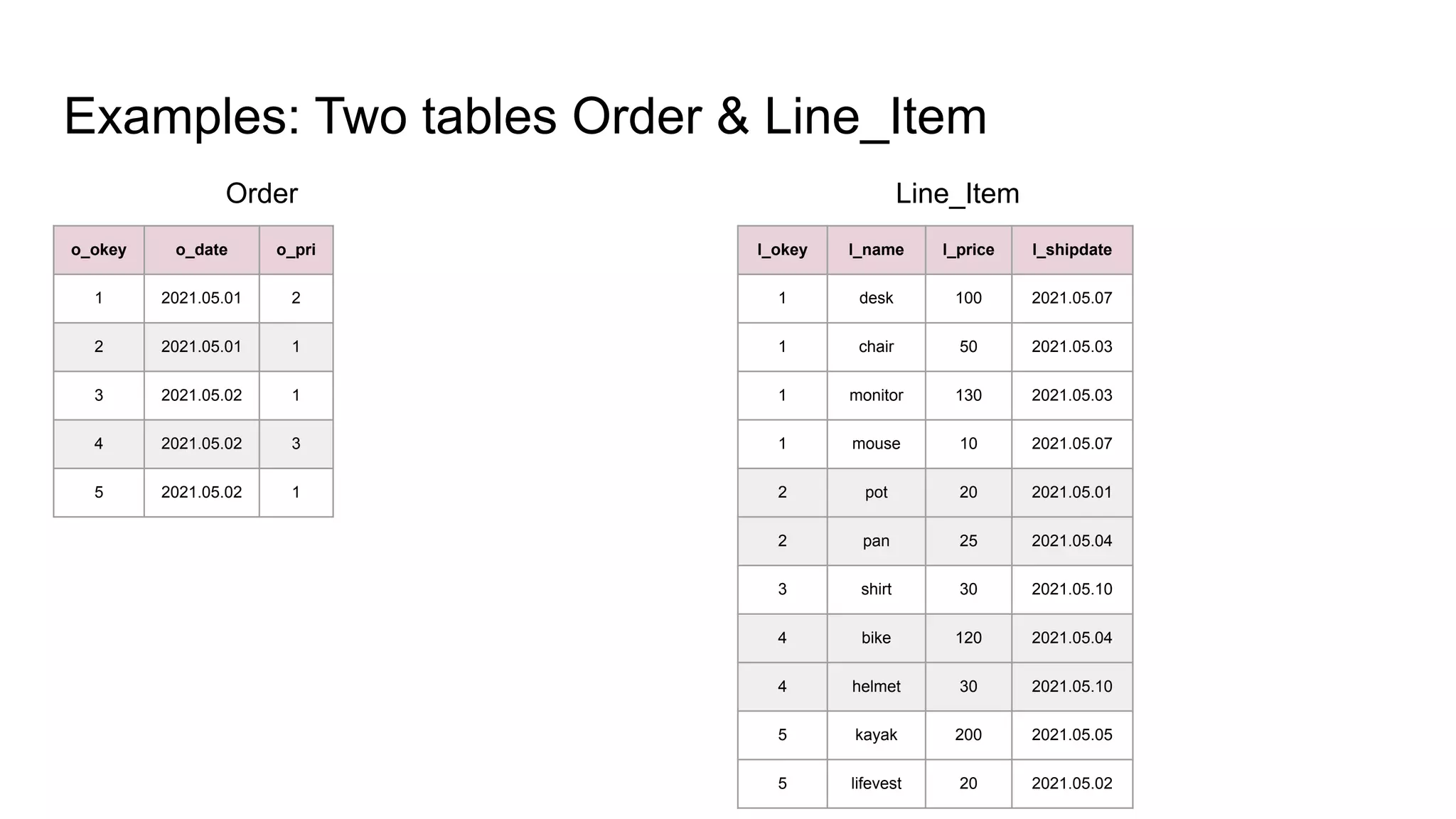
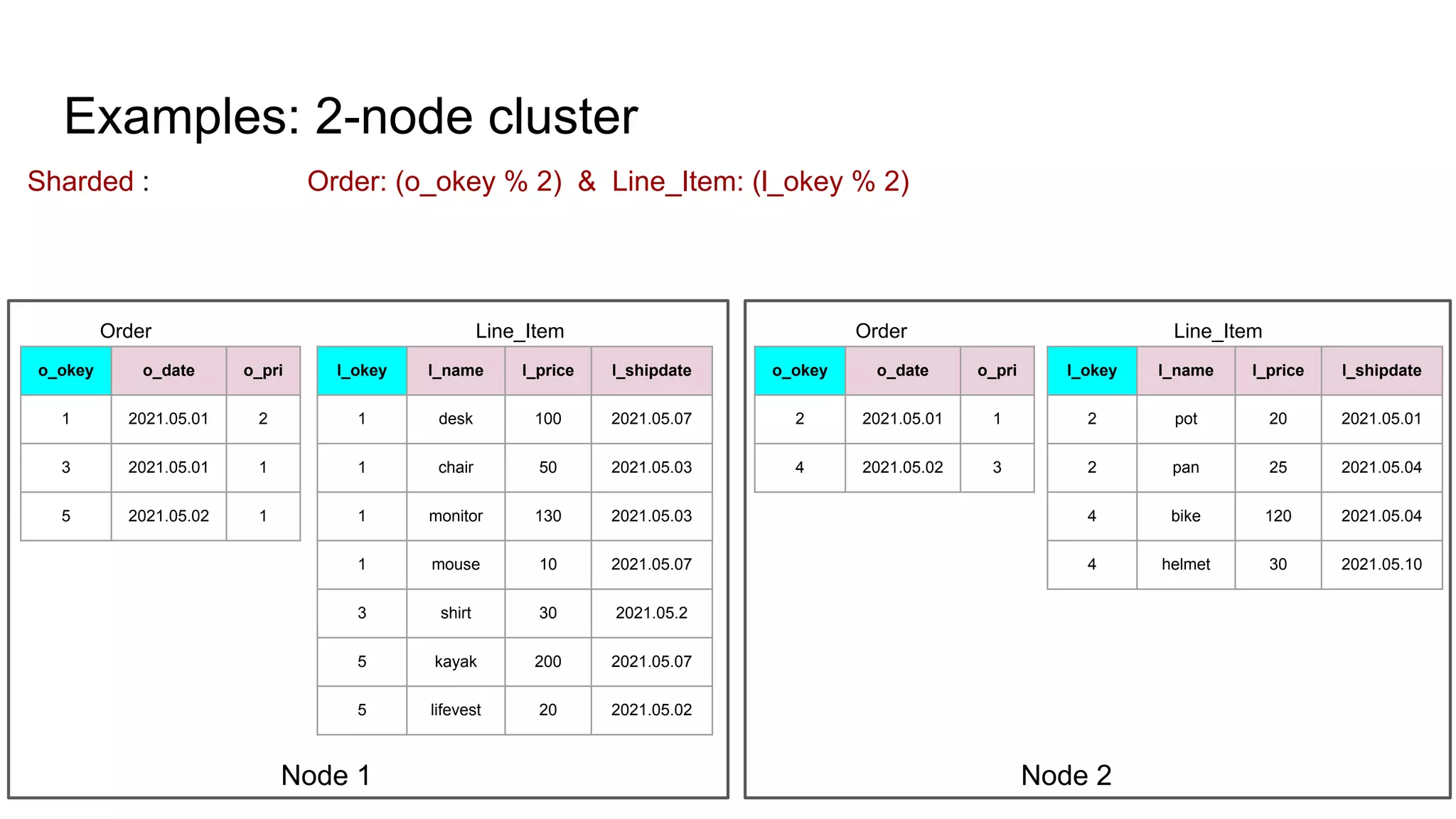
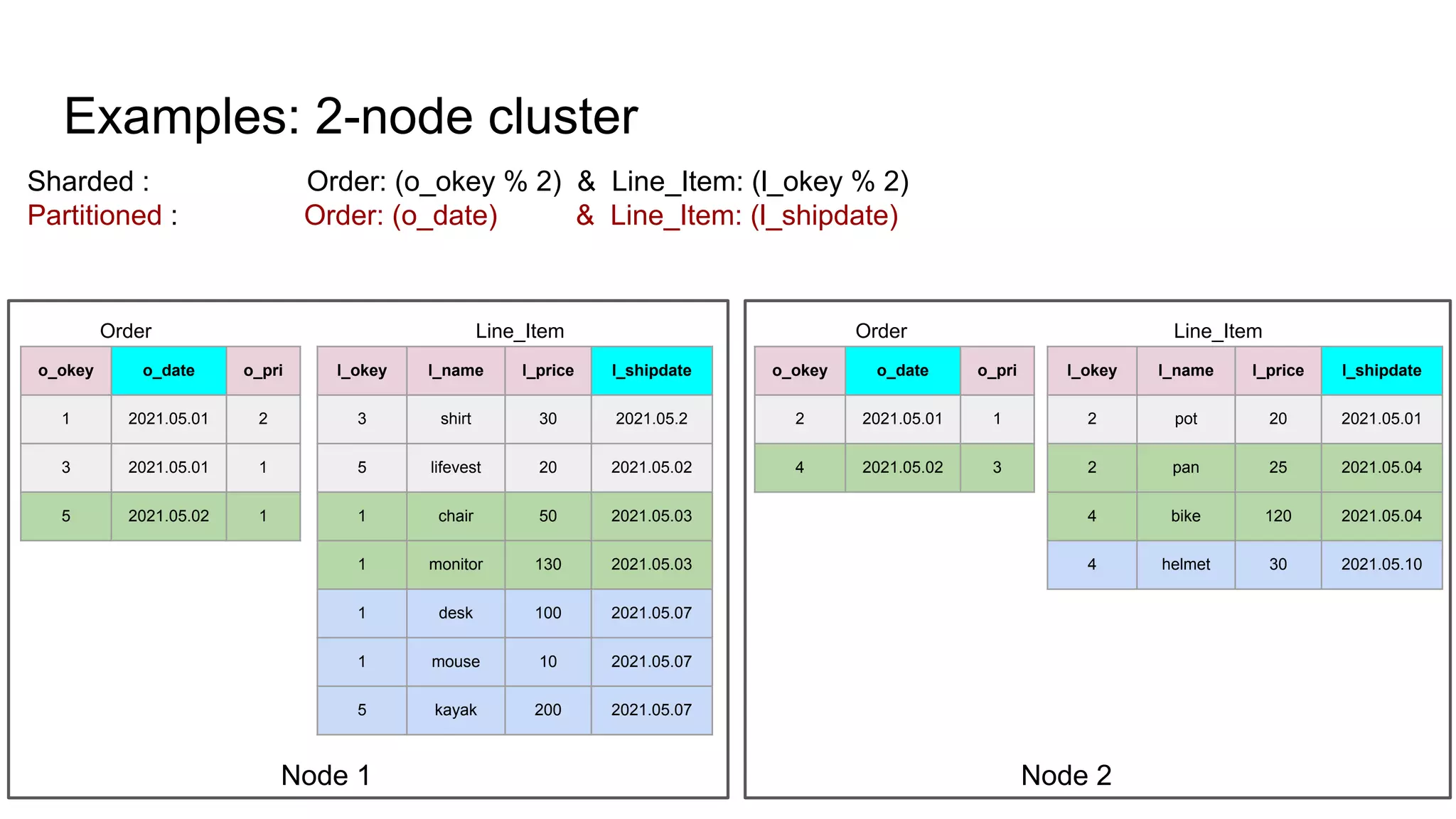
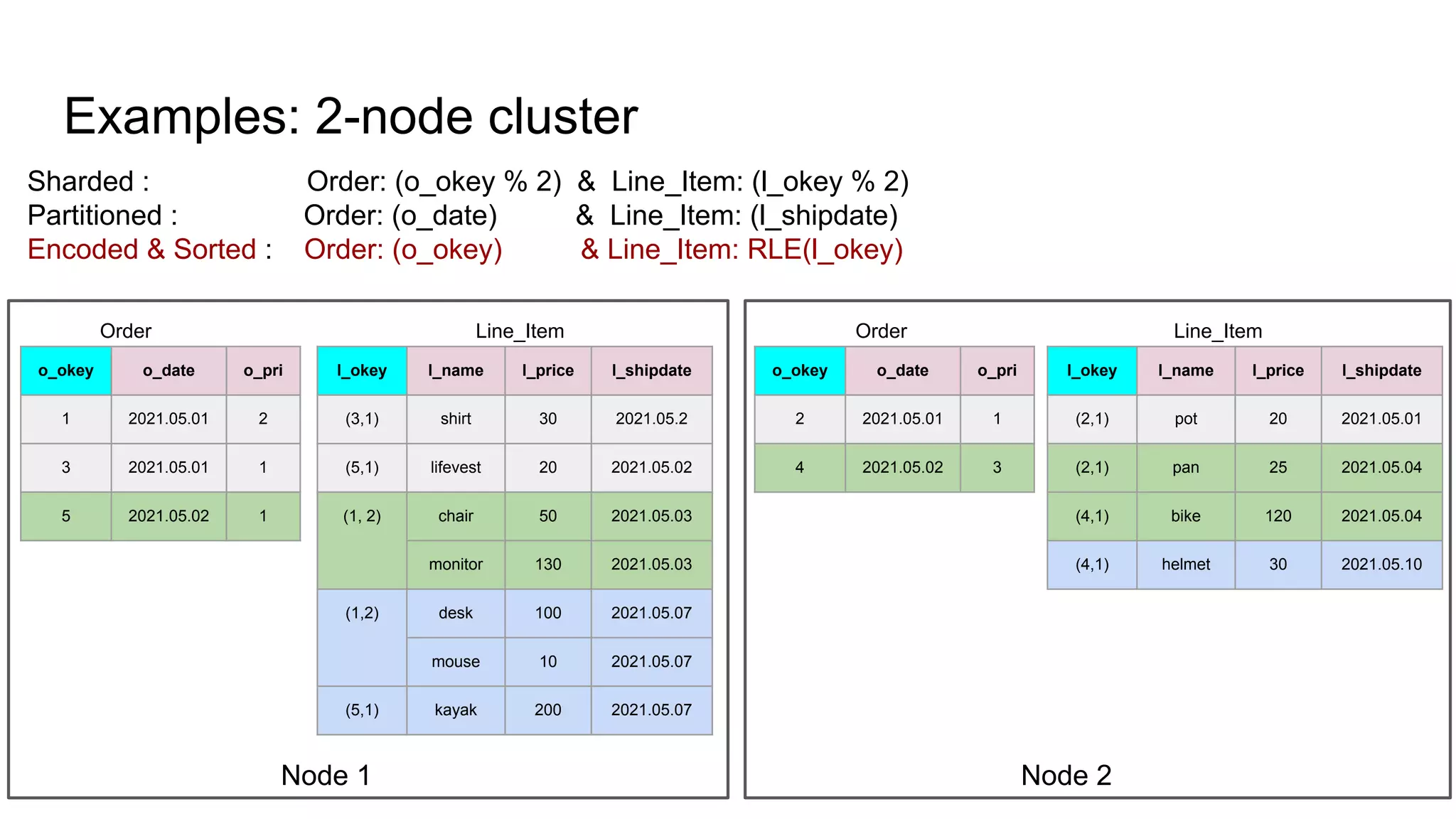
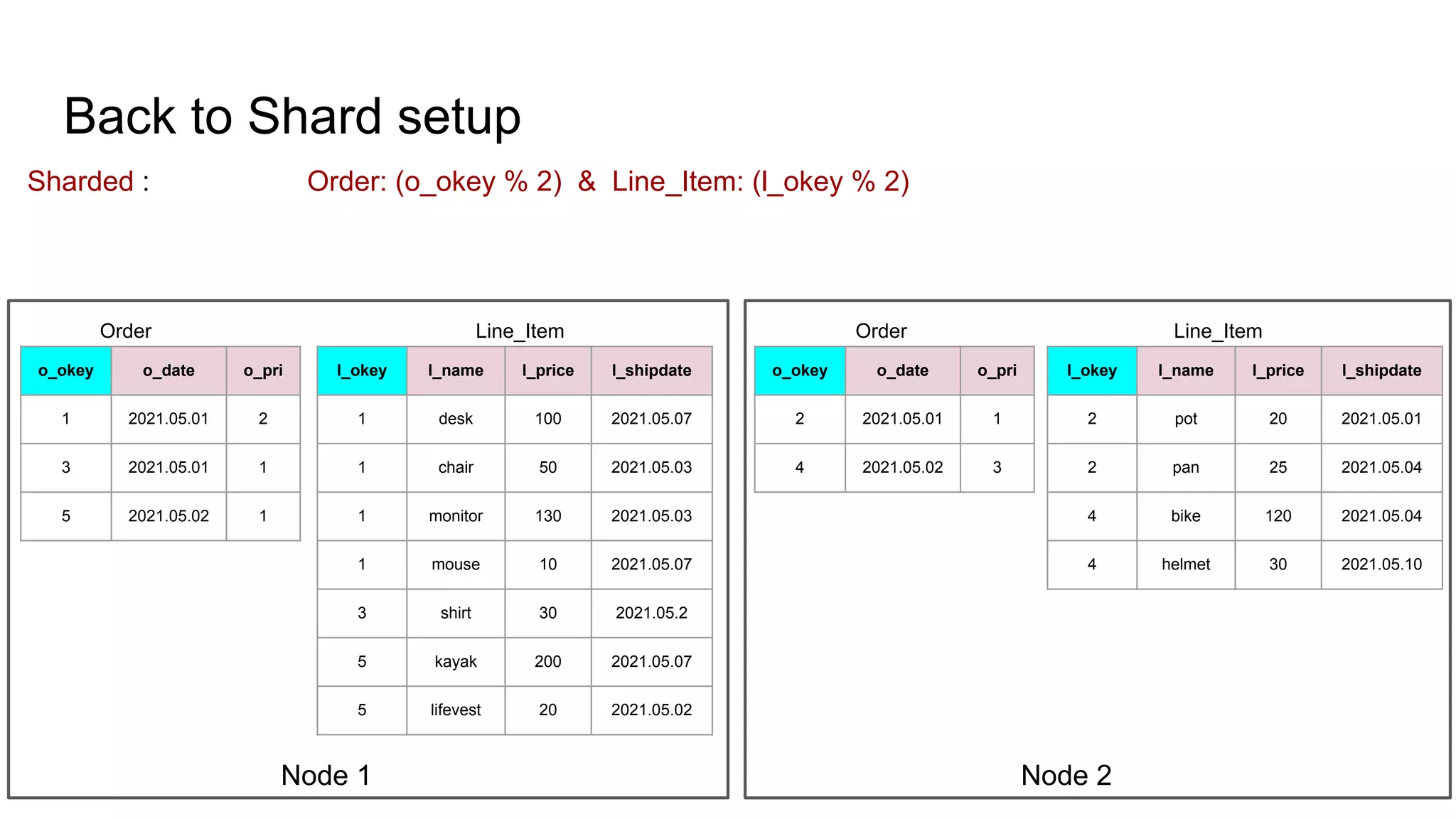
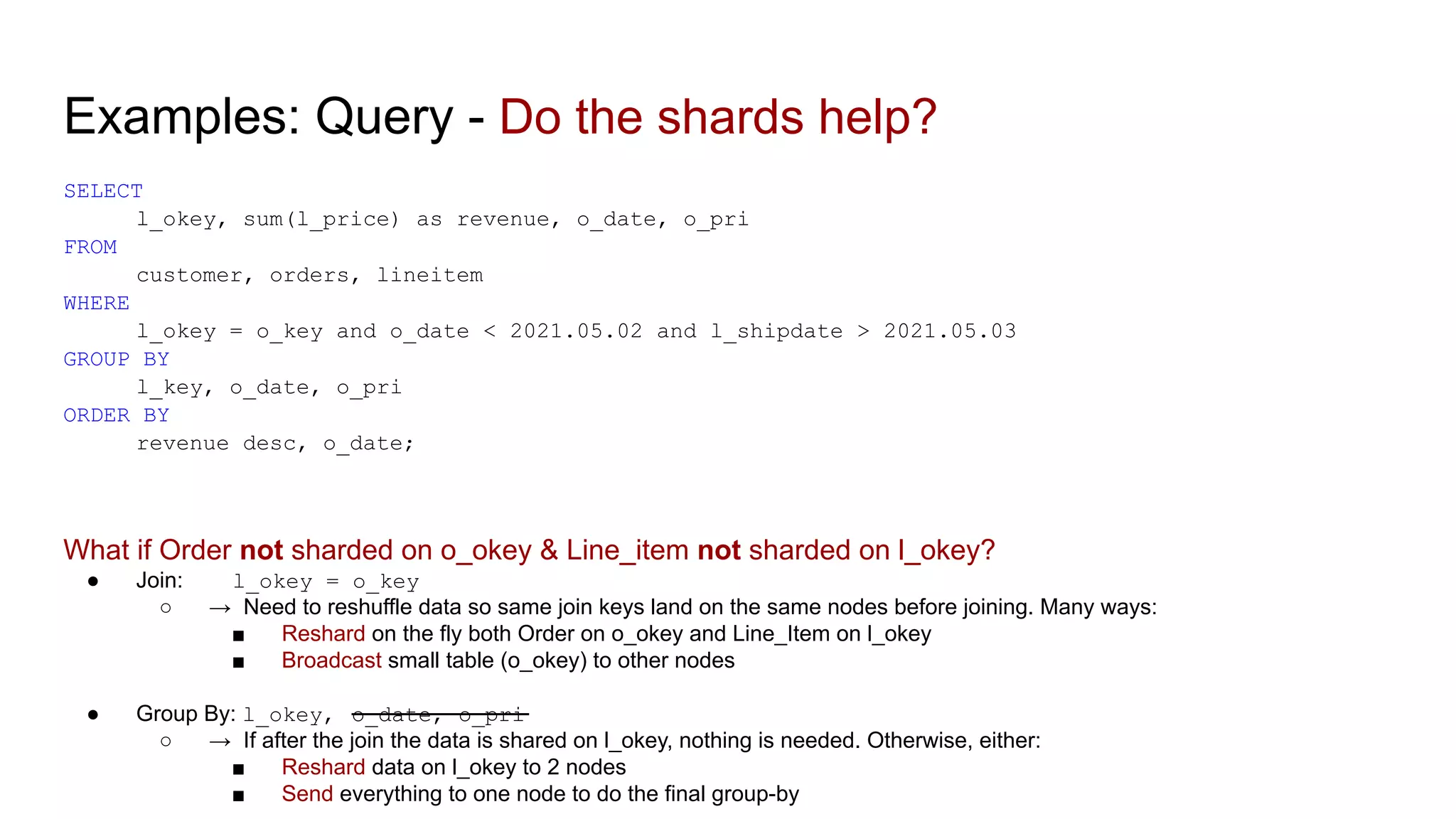
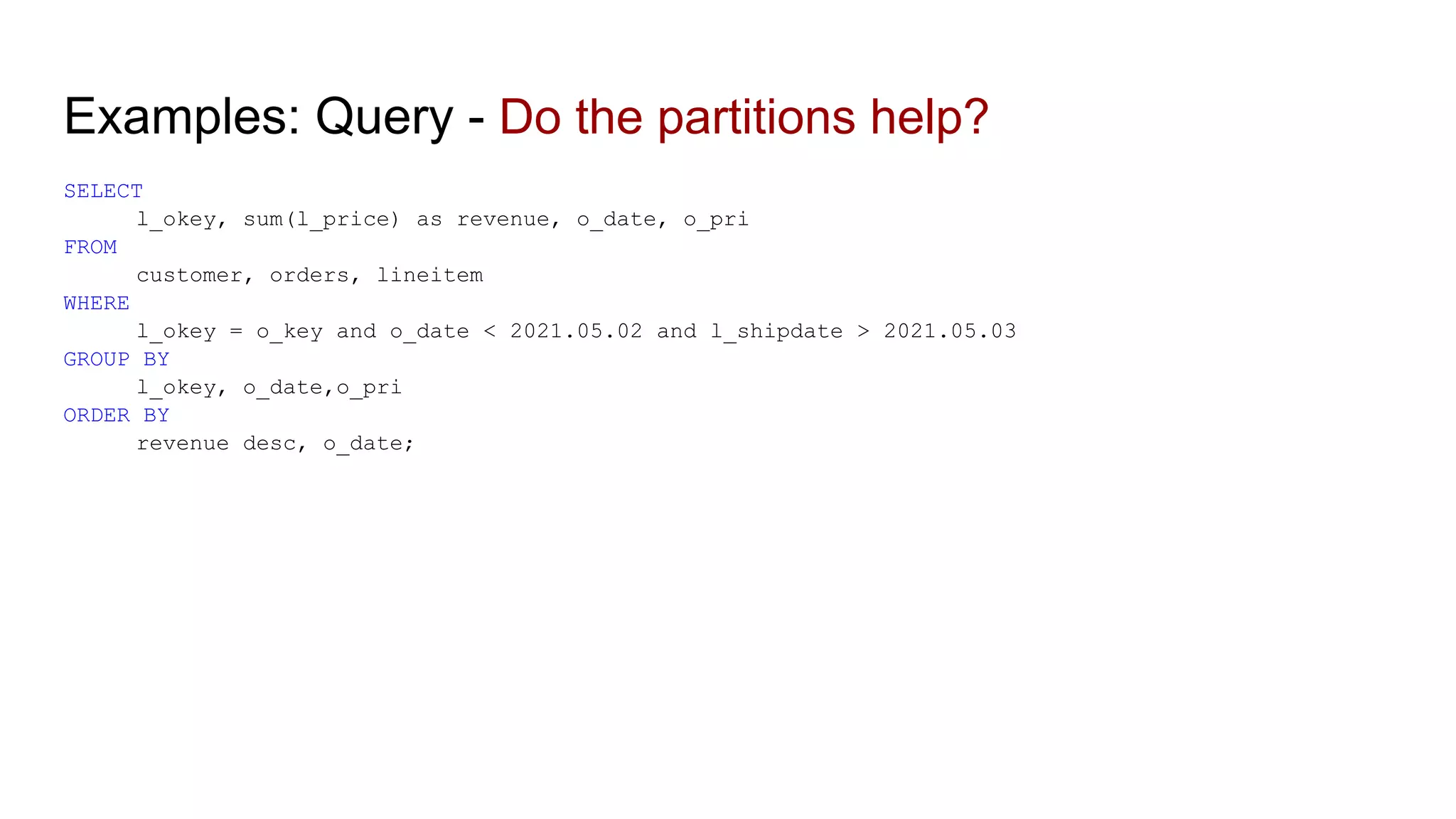
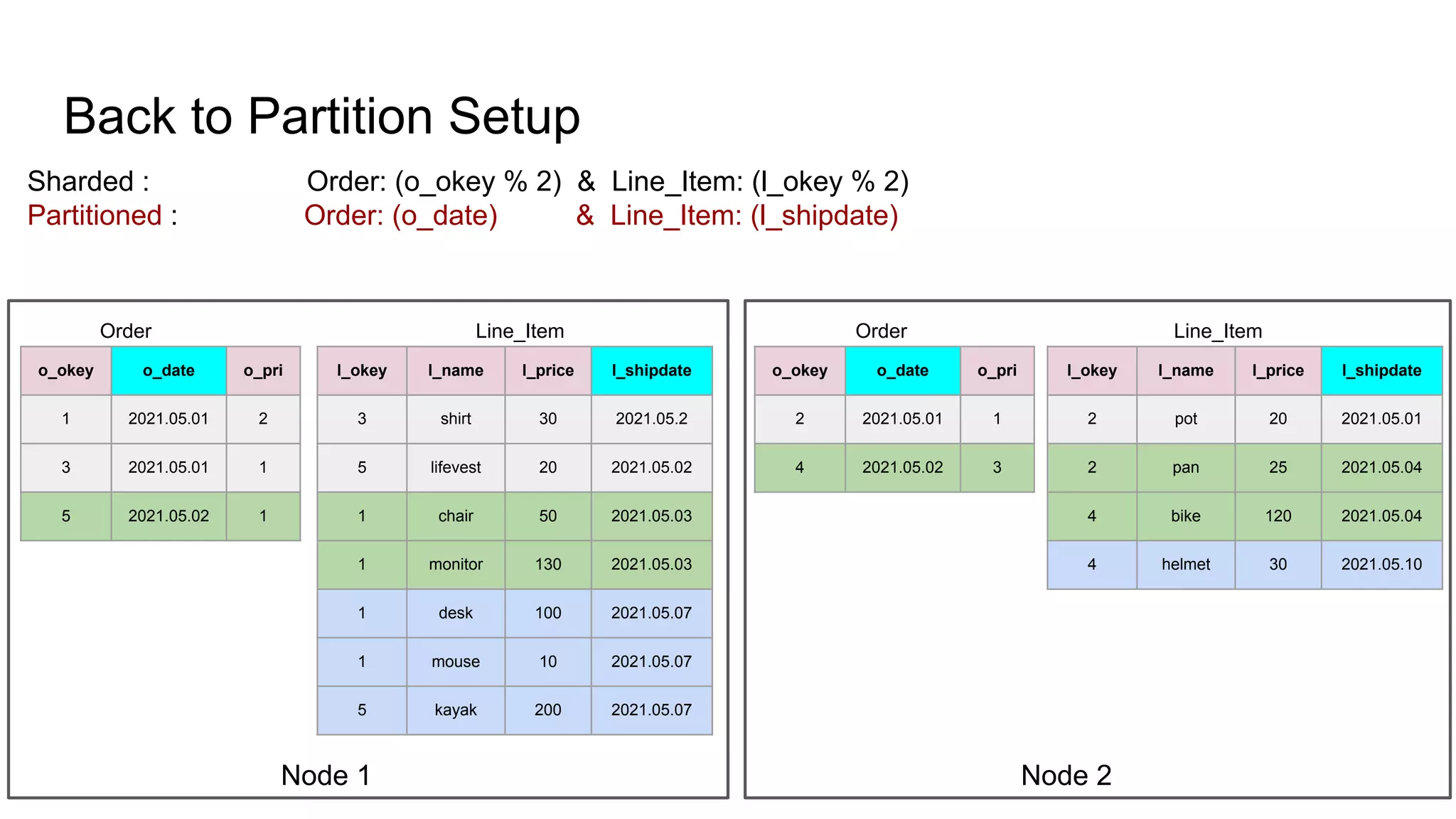
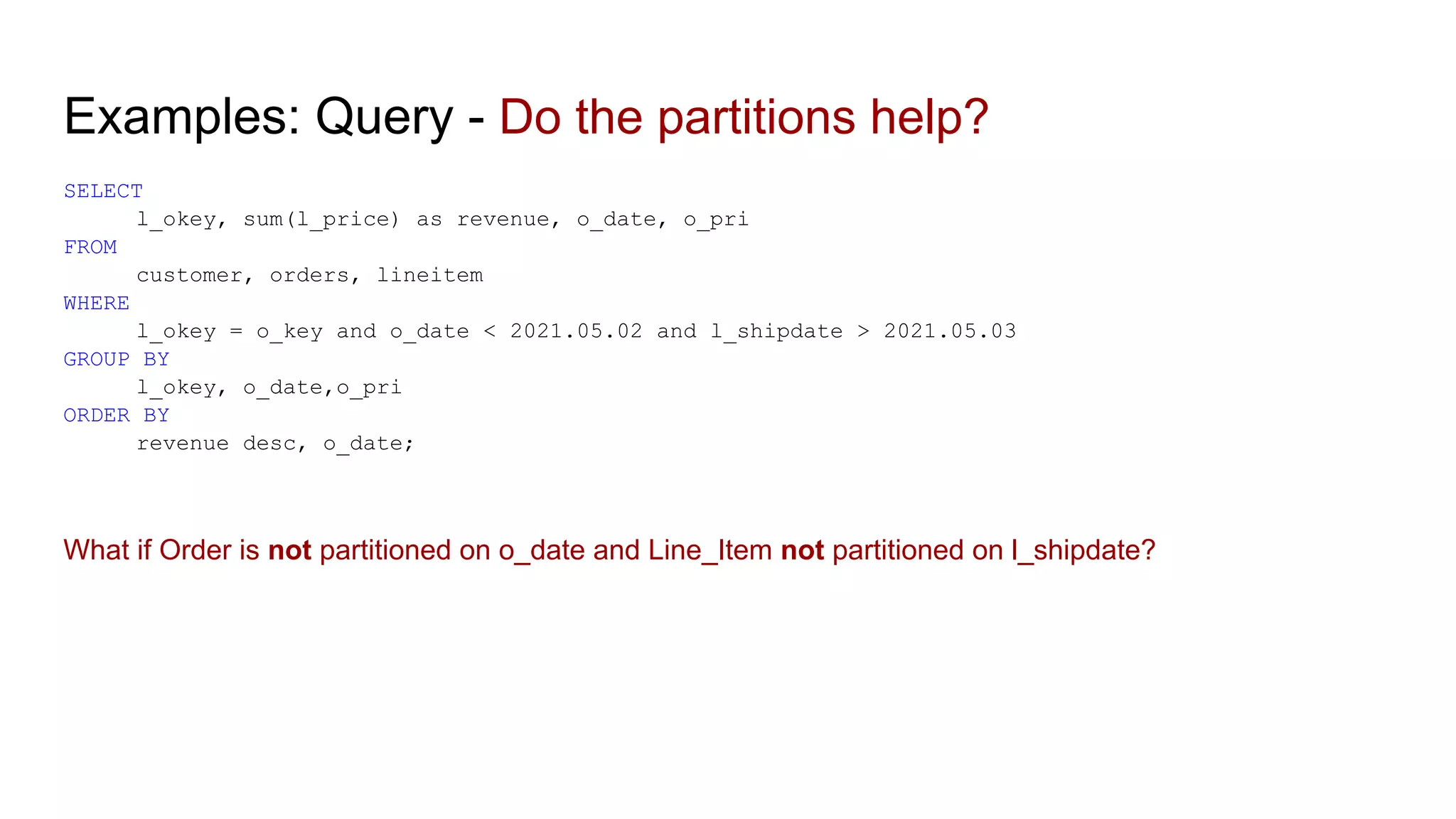
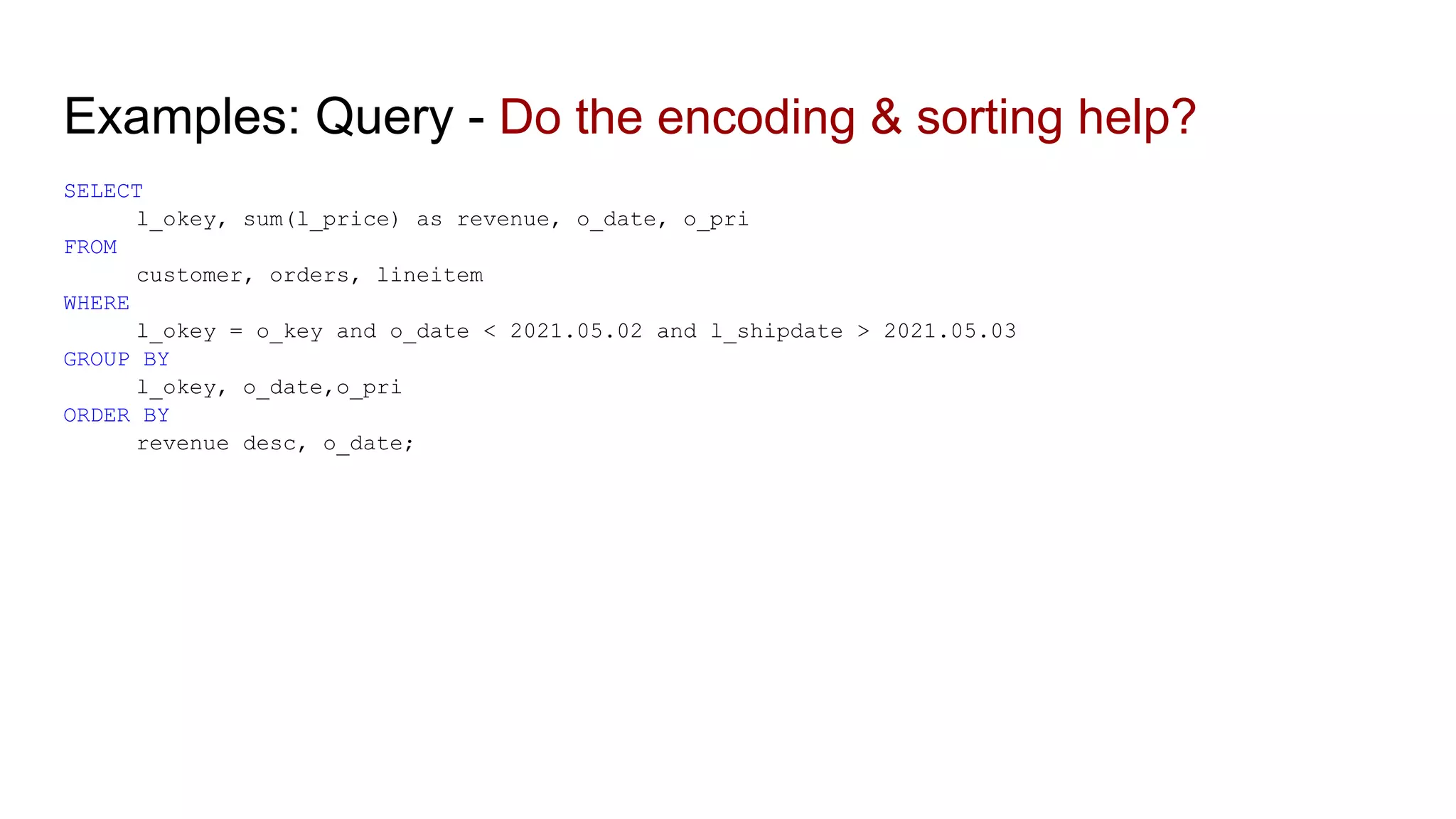
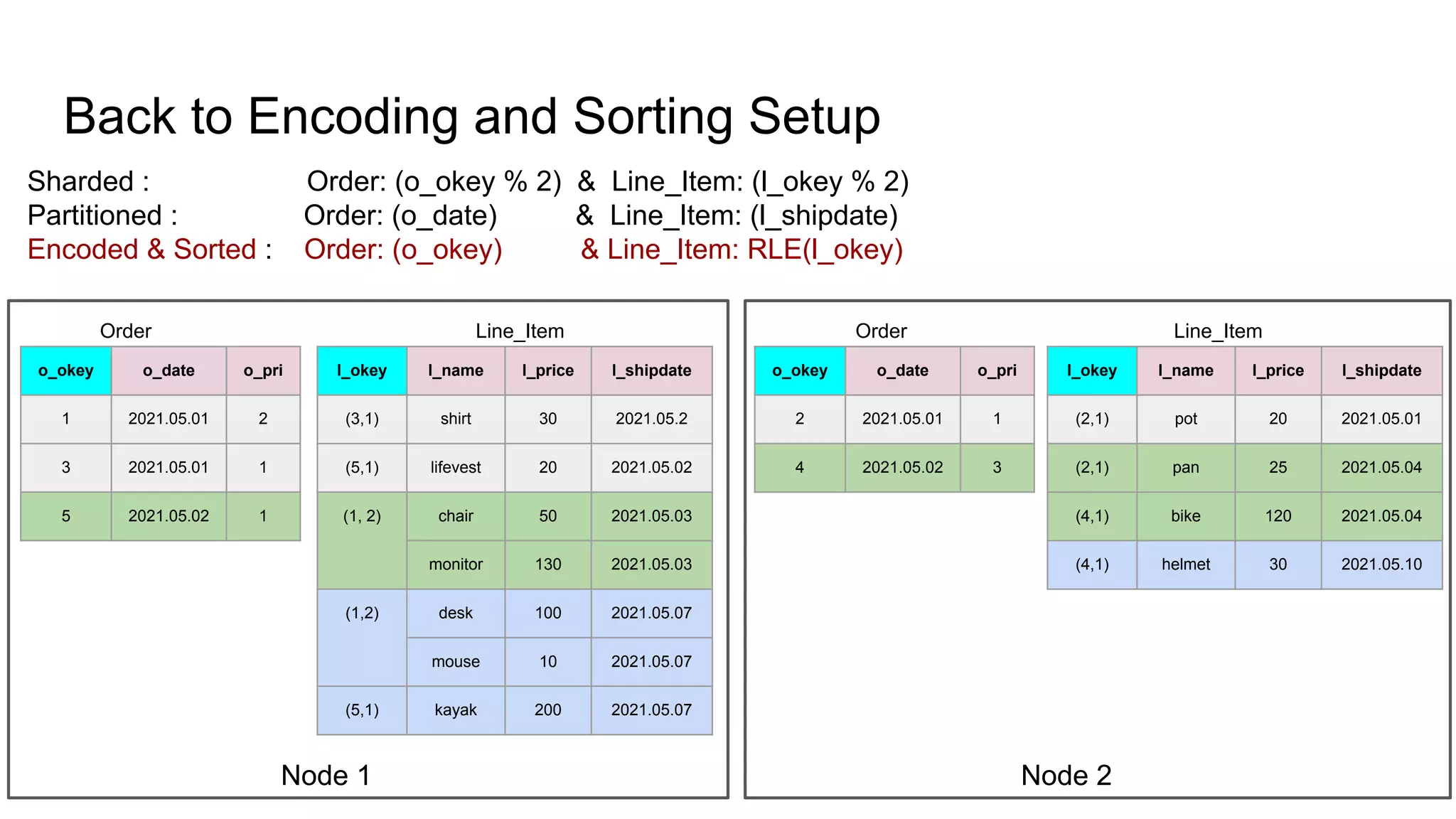
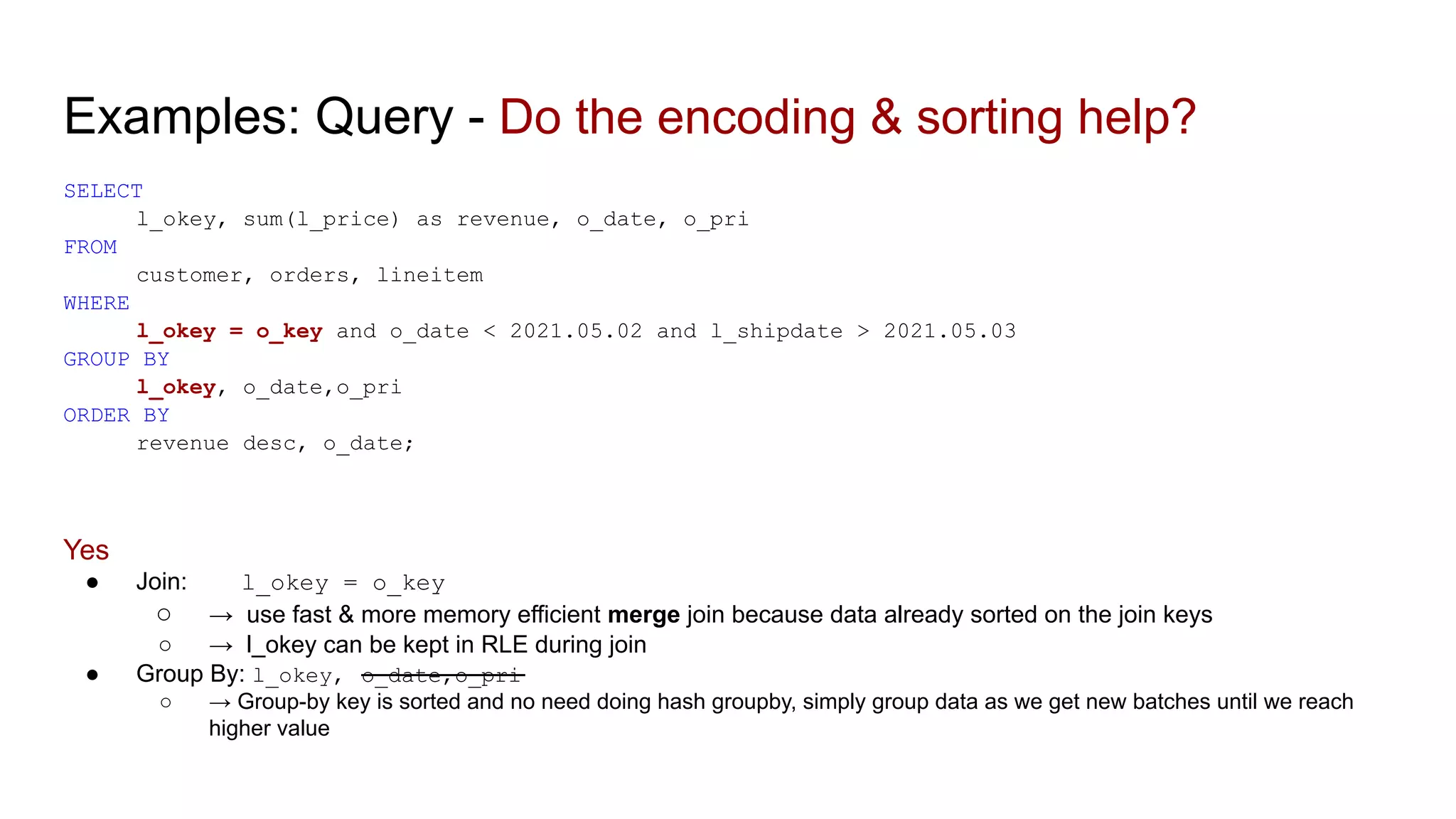
The document discusses the impacts of sharding, partitioning, encoding, and sorting on query performance in distributed databases compared to non-distributed databases. It highlights how different data setups can optimize query performance through techniques like data splitting, filtering, and local parallelism. The analysis includes practical examples to illustrate how these techniques affect processing efficiency and data retrieval scenarios.