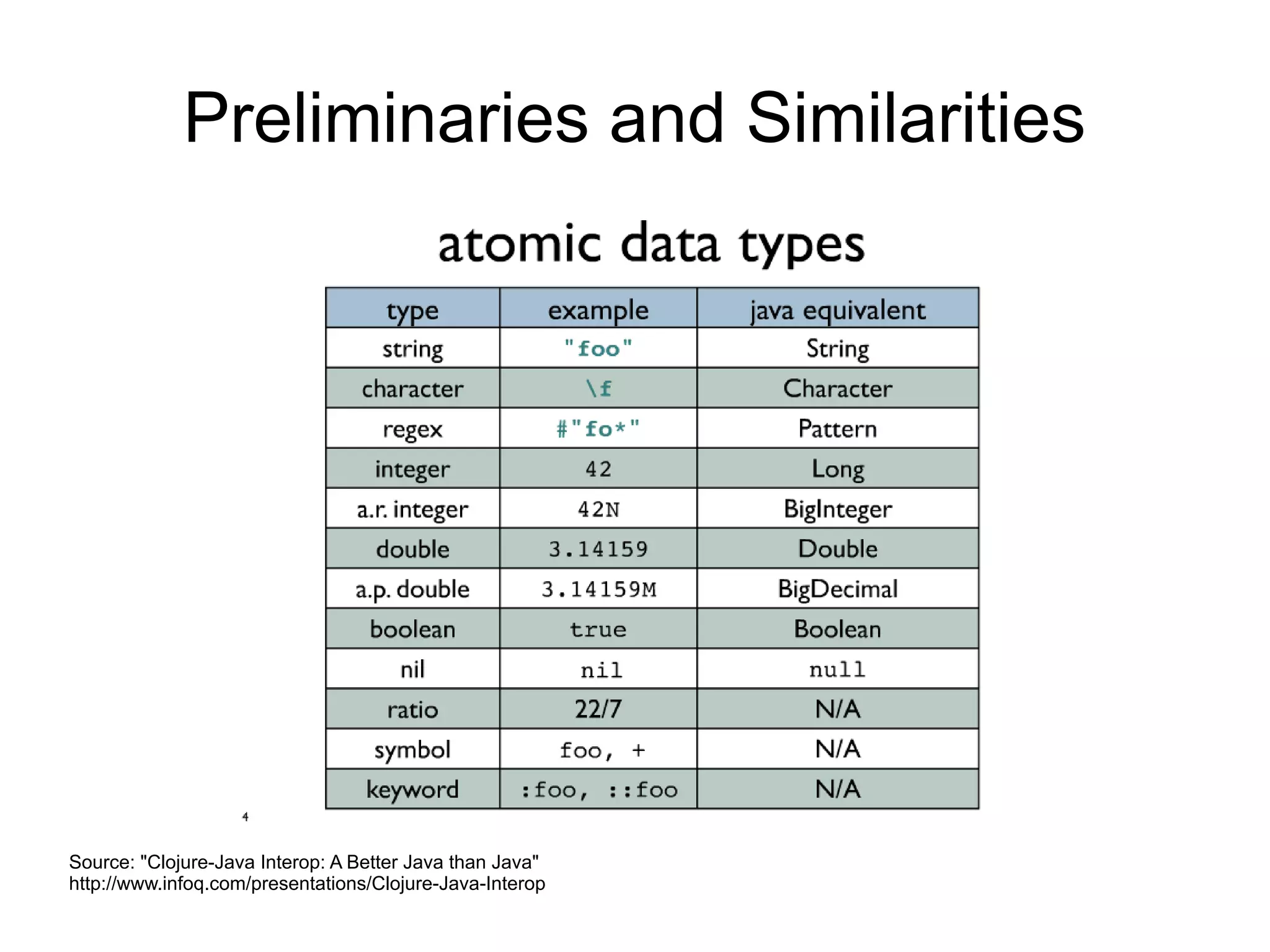
The document introduces Clojure as a powerful JVM language, especially for Java developers, highlighting its advantages such as simplicity and functional programming capabilities. It covers Clojure's features like immutable data structures, concurrency support, and seamless Java interop, along with its unique Lisp characteristics. The author emphasizes the rationale behind Clojure and provides various resources for further exploration.









![Clojure Data Structures ● Lists '( 1 2 3 4 ) ● new insertions go to the front ● Vectors [ 1 2 3 4 ] ● new insertions go to the back ● Maps { :a 1 :b 2 :c 3 :d 4} ● Sets #{ :a :b :c :d } ● implemented as k/v where k=v.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avramaelony-slides-121004103224-phpapp02/75/I-know-Java-why-should-I-consider-Clojure-12-2048.jpg)





















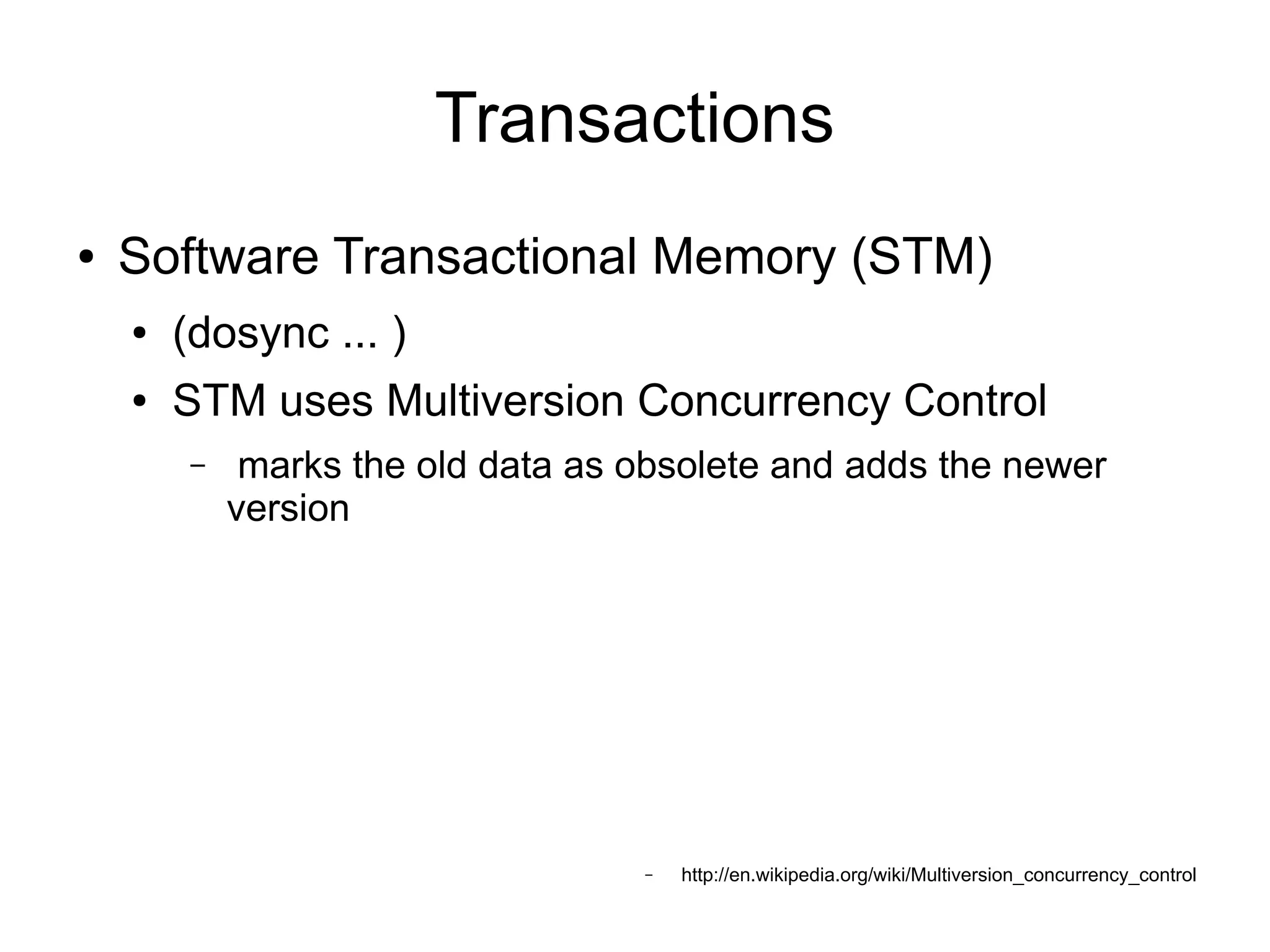







![REPL via Leiningen ] lein new clj-excel && cd clj-excel now edit file “project.clj” ] lein deps && lein repl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avramaelony-slides-121004103224-phpapp02/75/I-know-Java-why-should-I-consider-Clojure-54-2048.jpg)
![REPL via Leiningen ] lein deps ] lein repl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avramaelony-slides-121004103224-phpapp02/75/I-know-Java-why-should-I-consider-Clojure-55-2048.jpg)