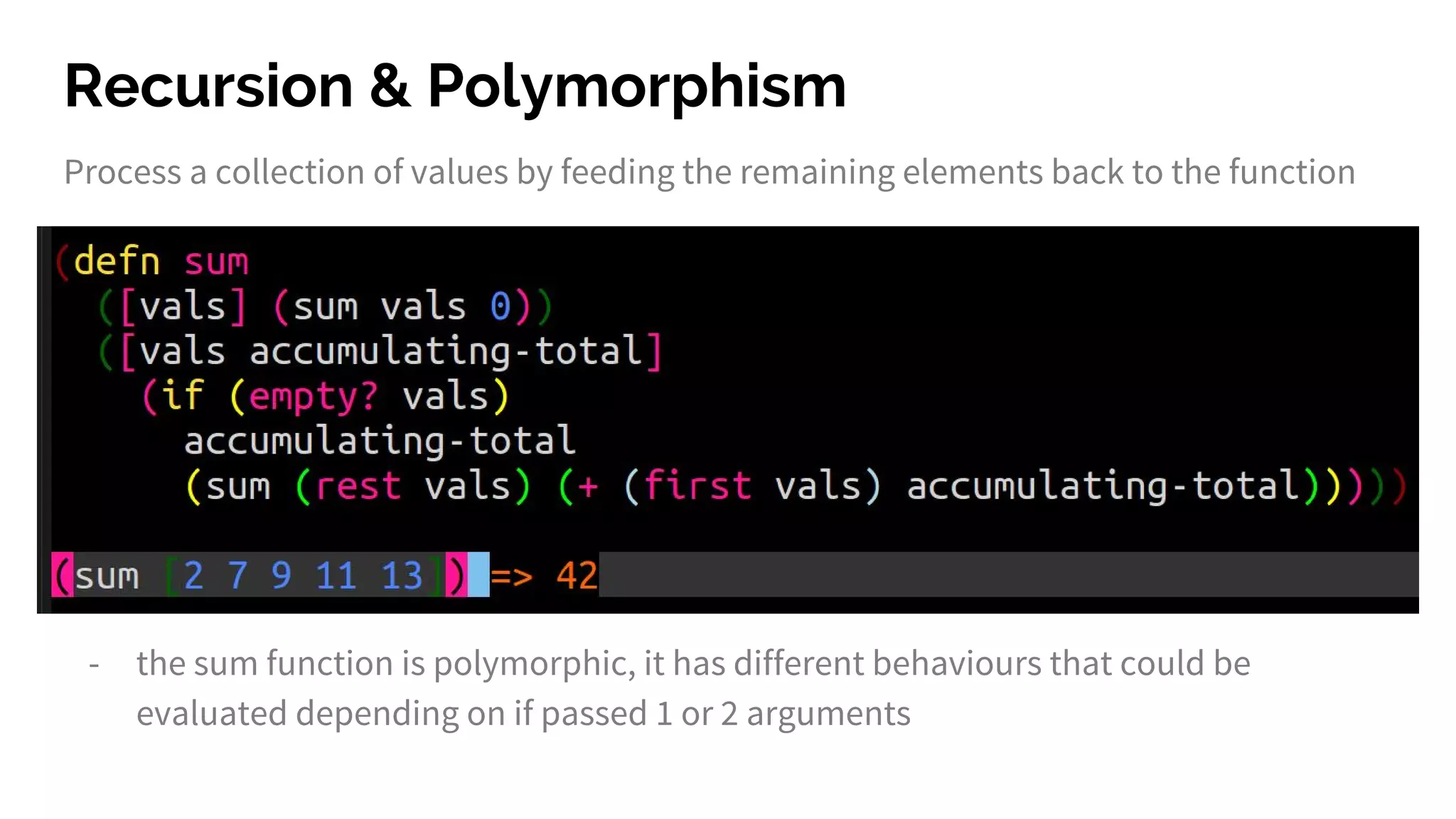
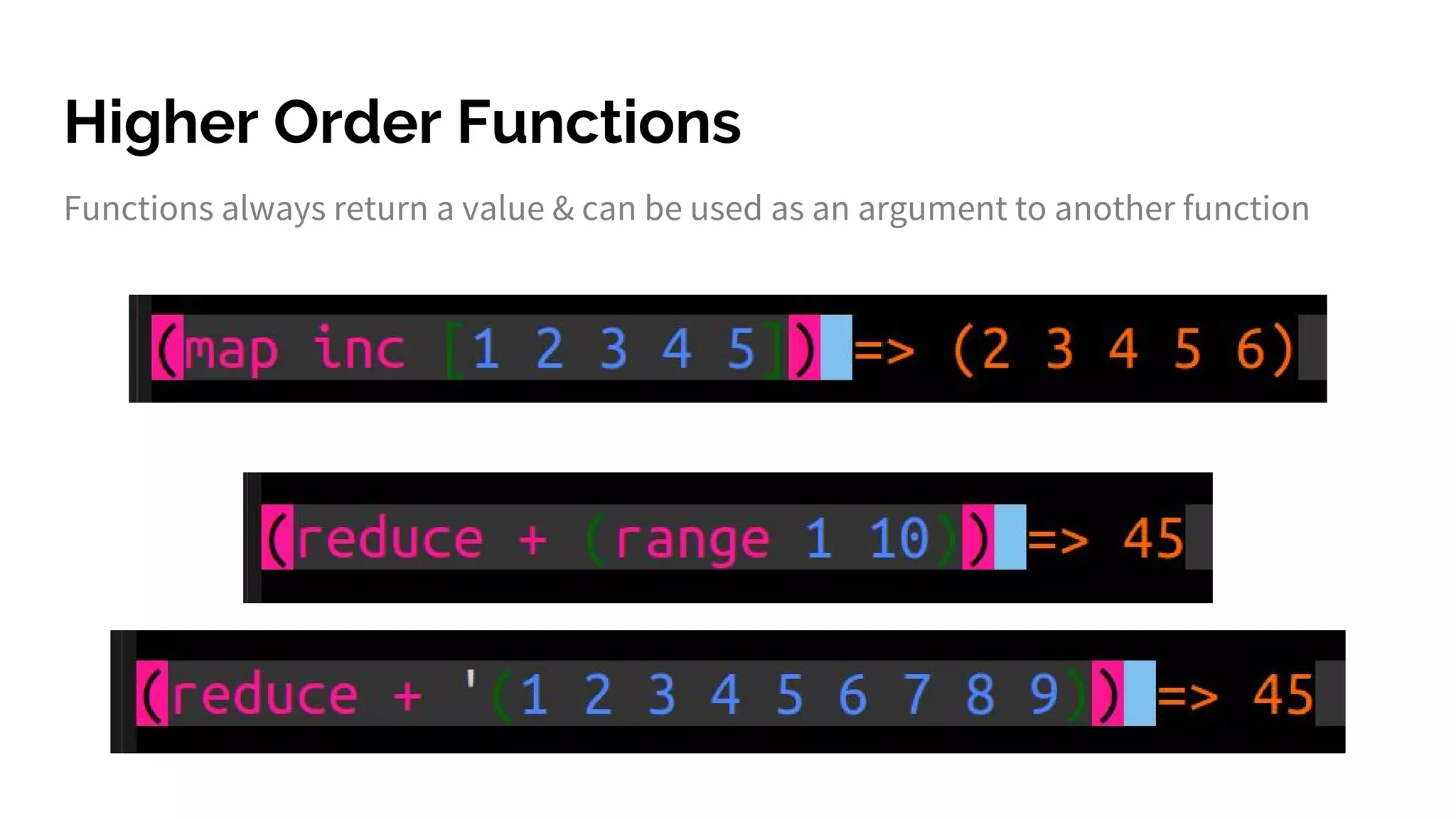
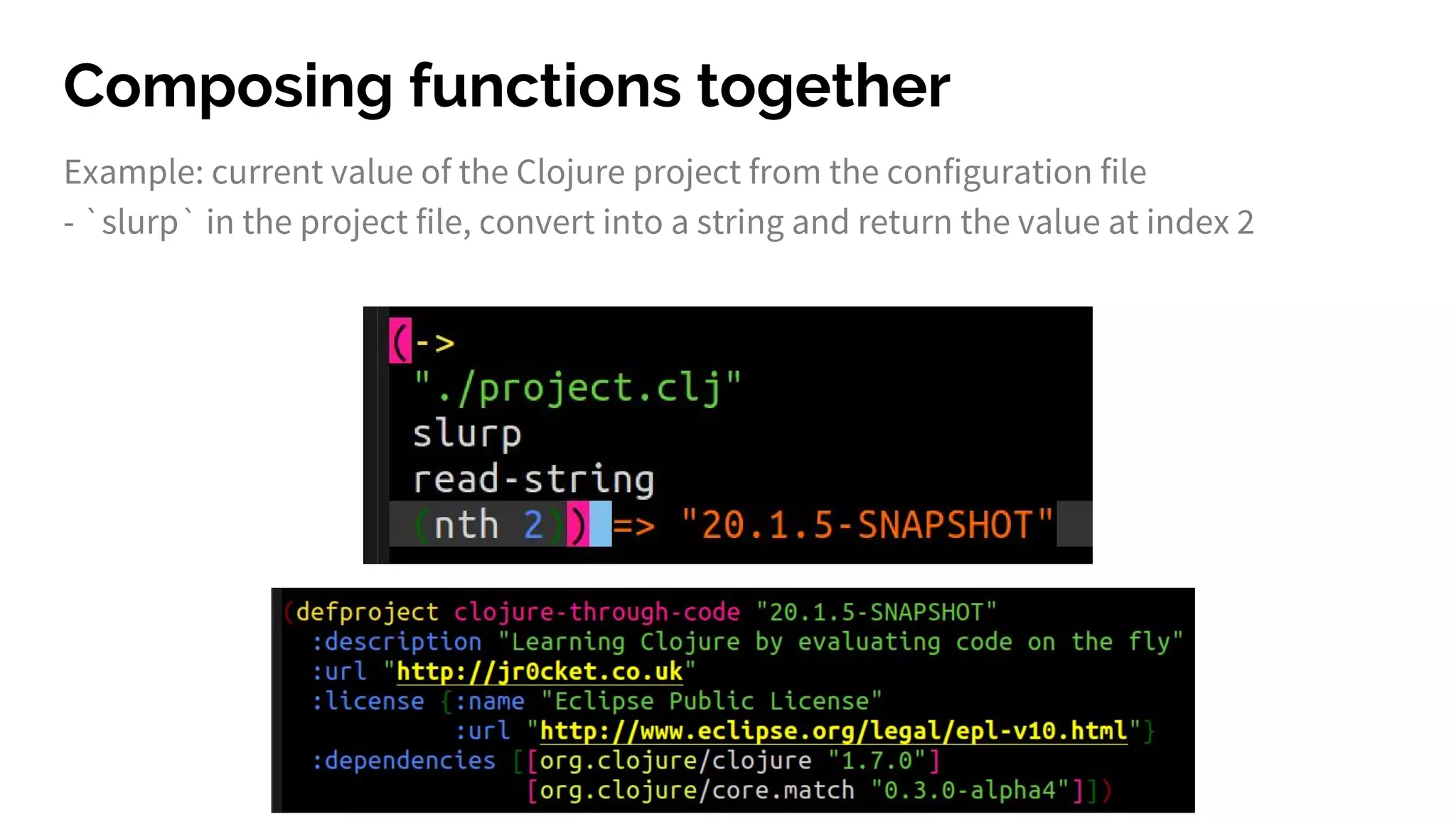
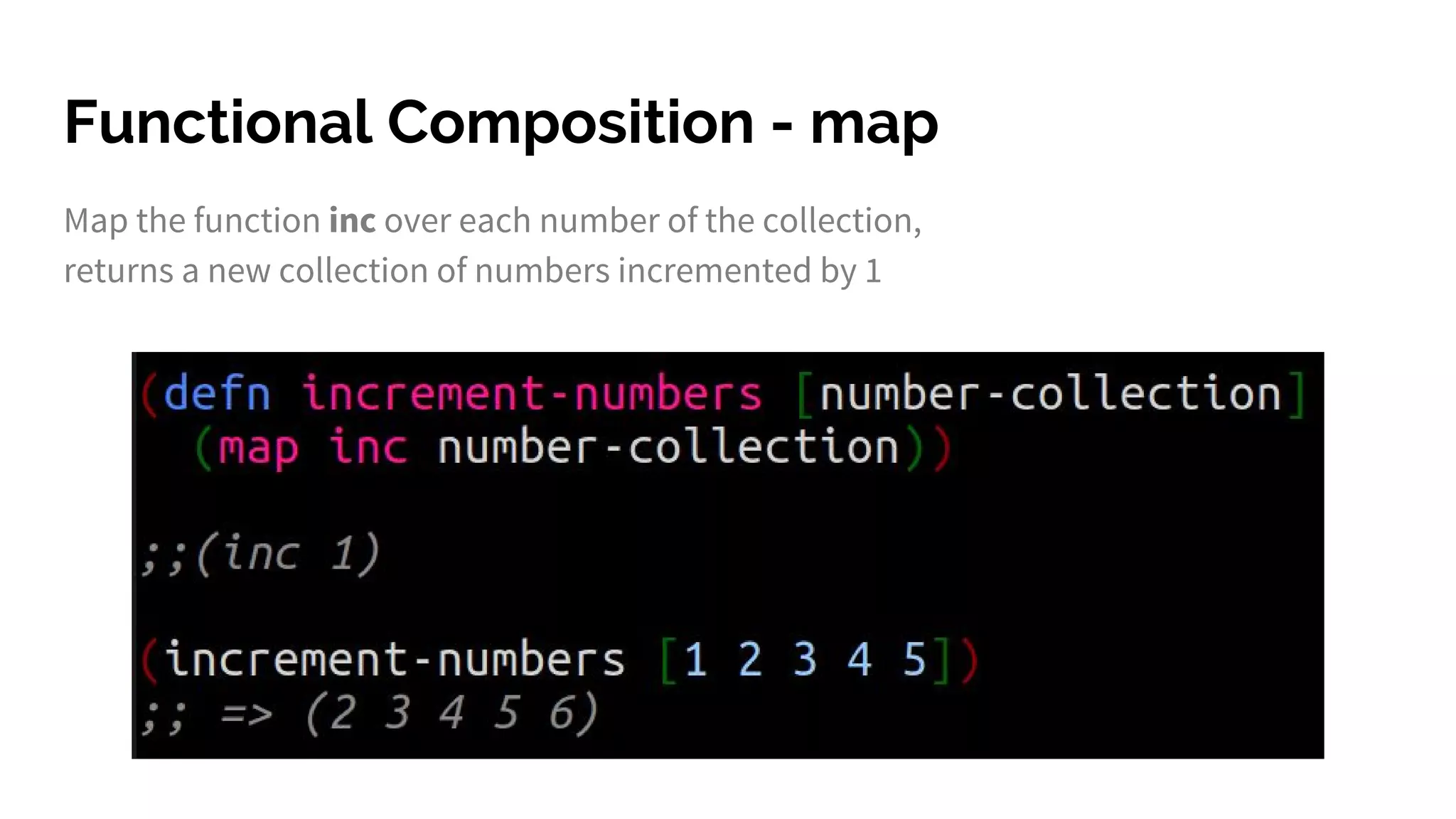
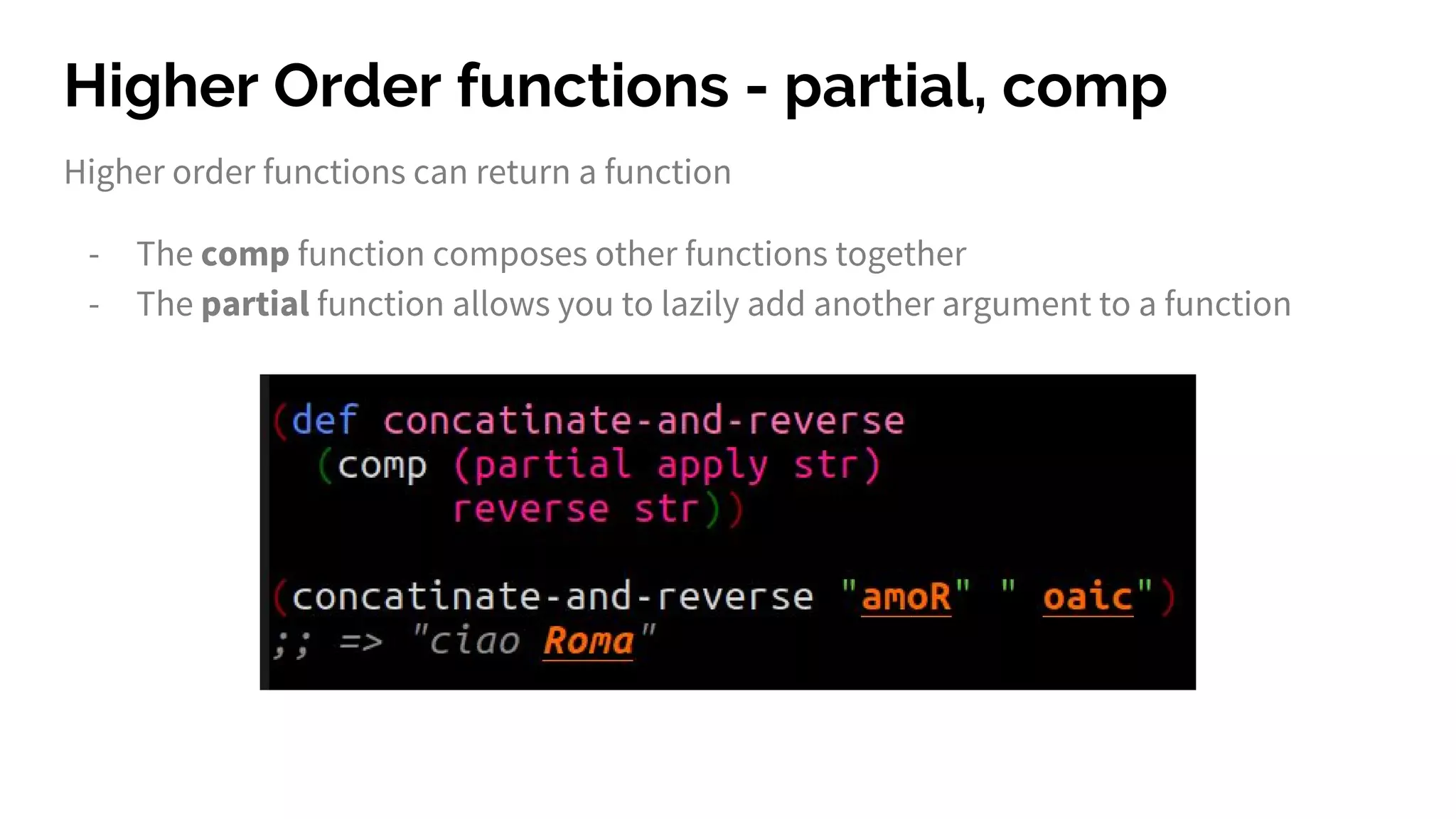
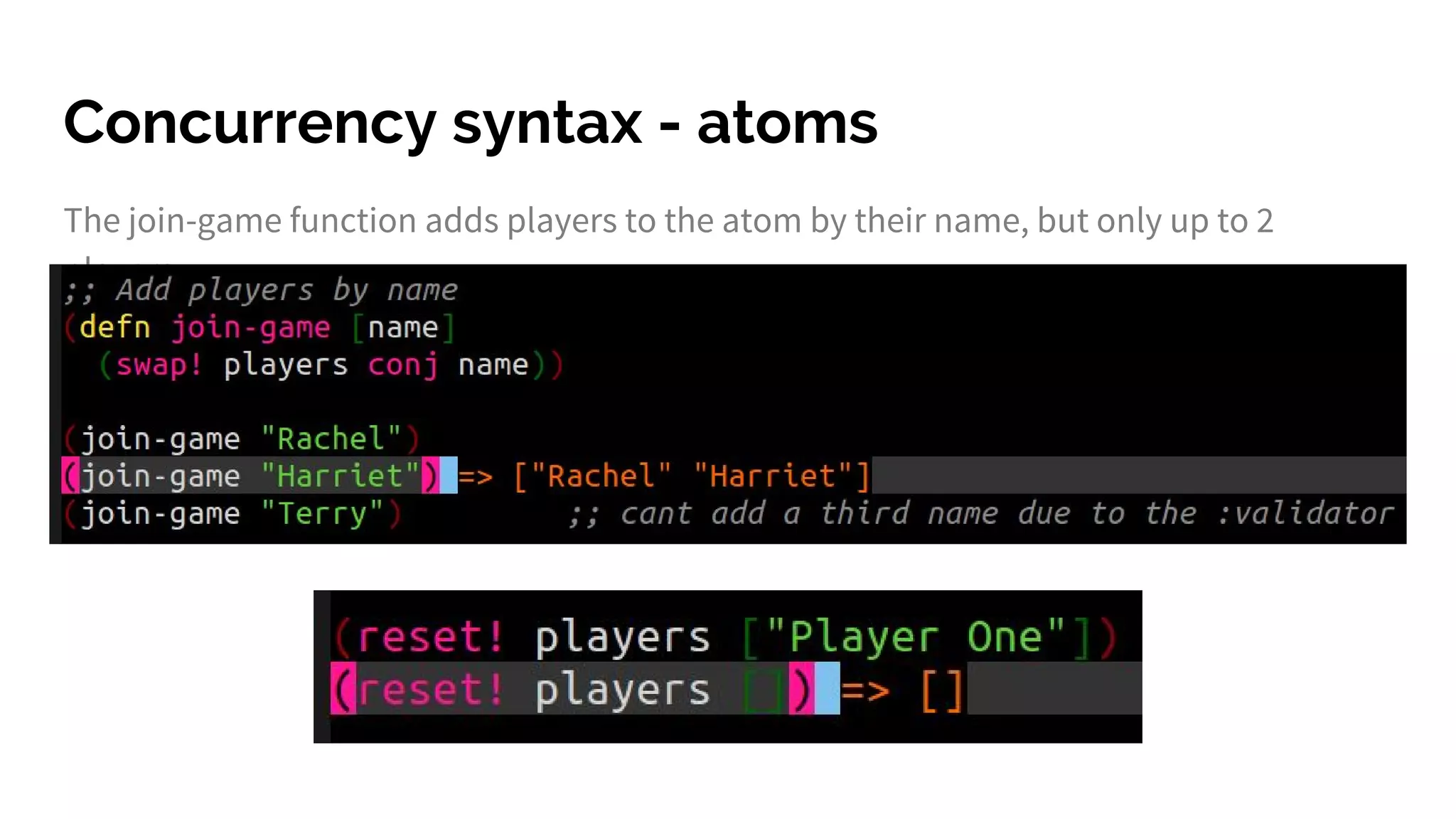
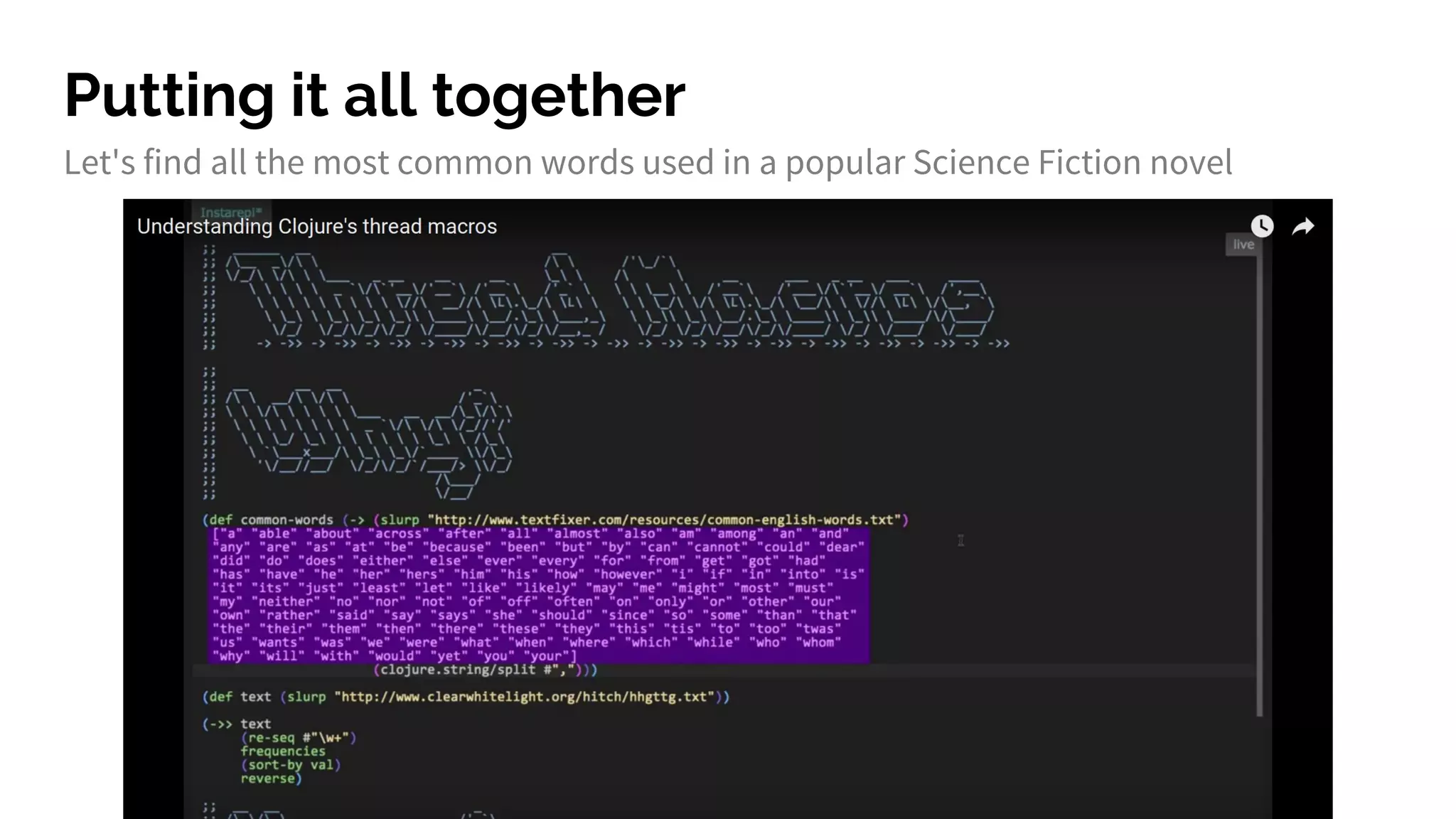
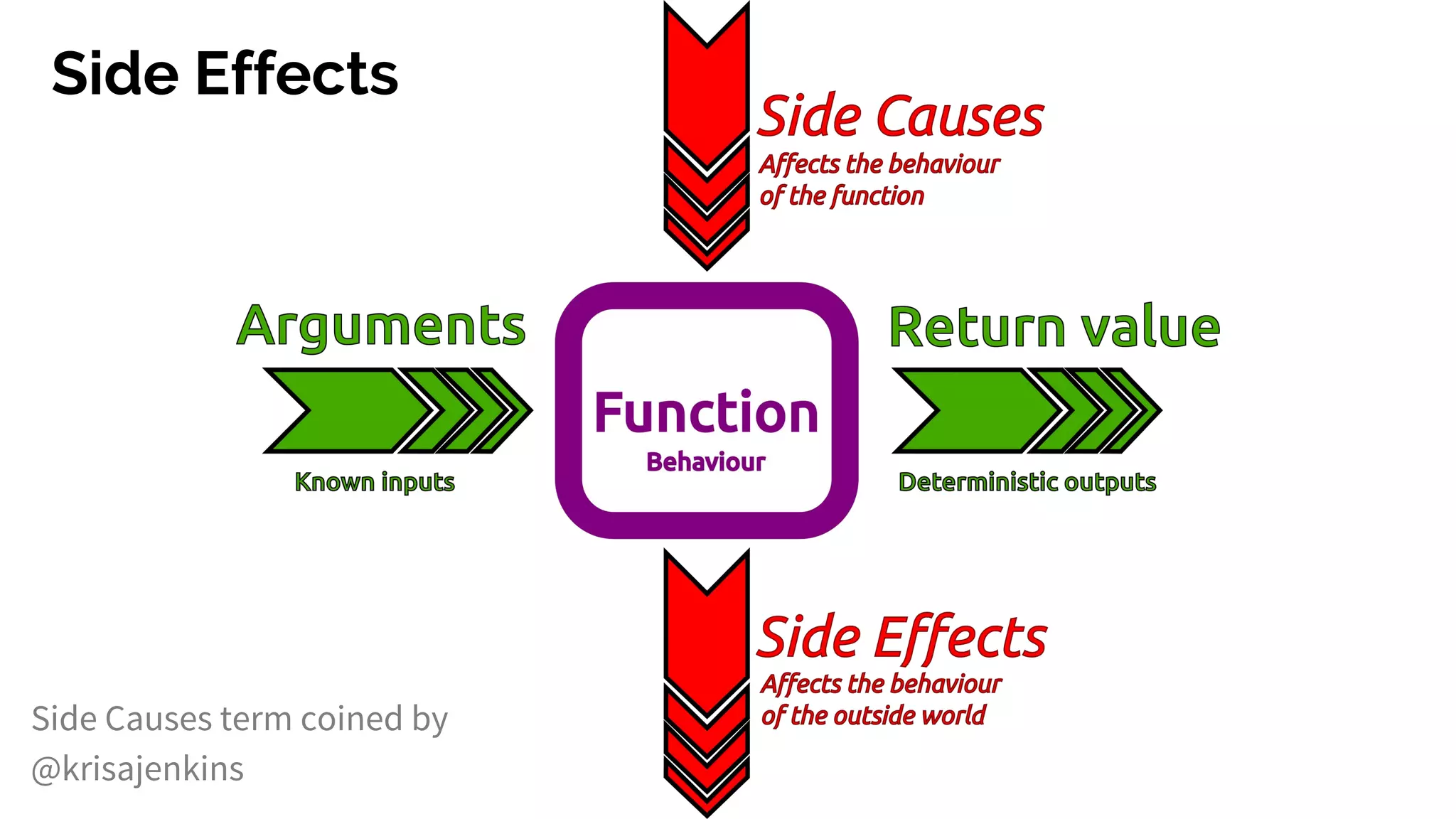
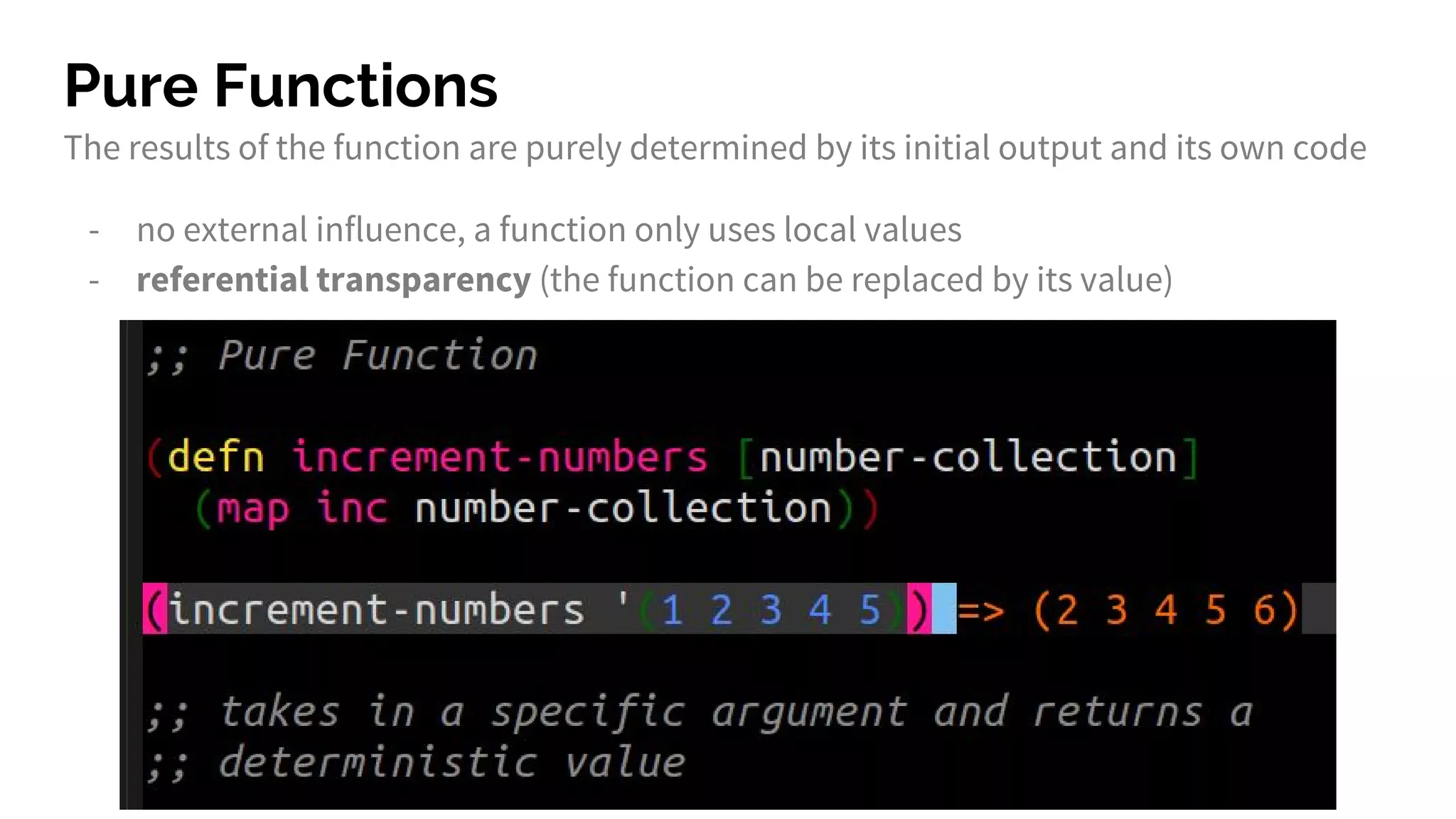
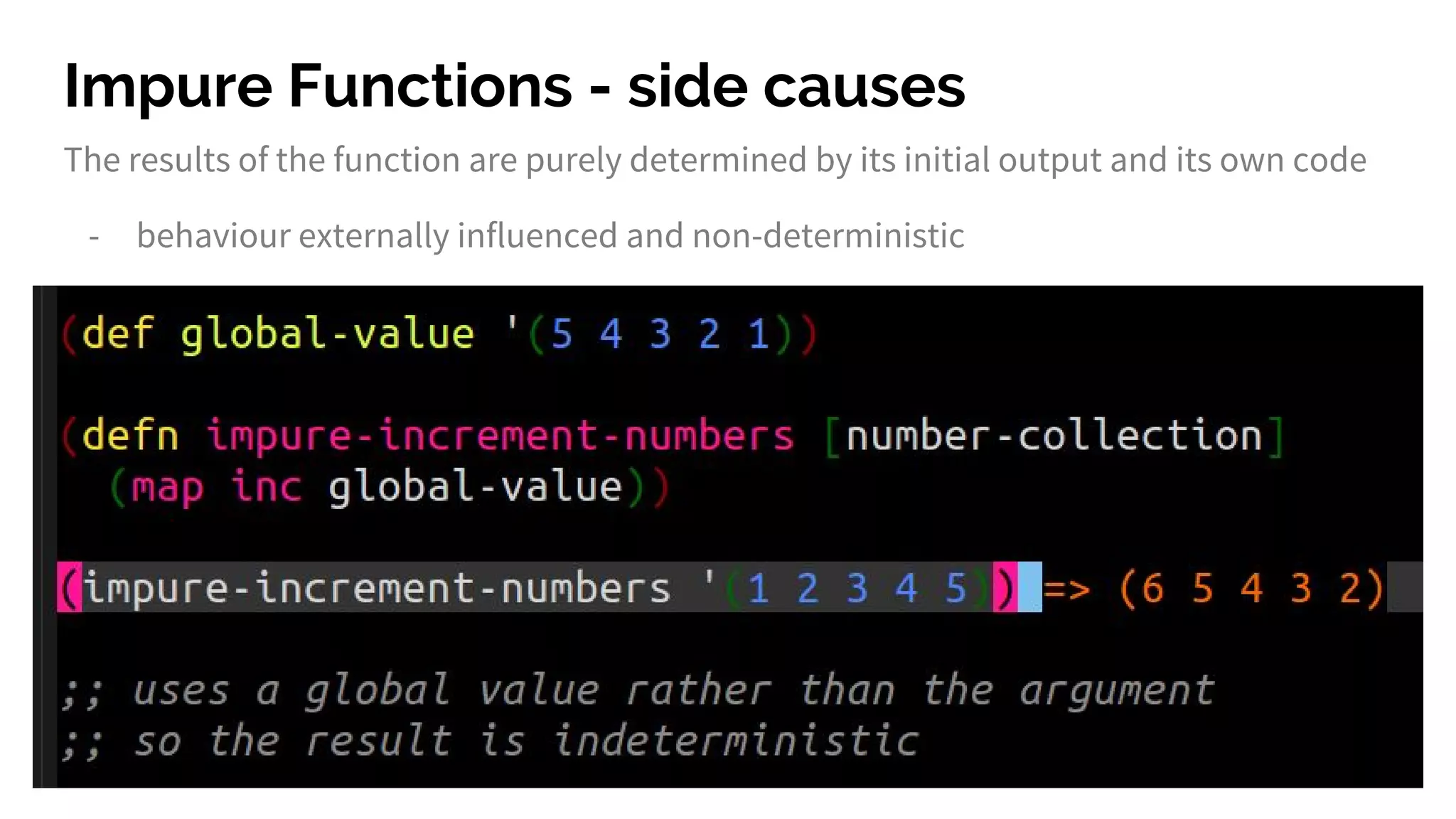
The document discusses functional programming principles using Clojure, focusing on the importance of eliminating side effects and using pure functions. It highlights key features such as immutability, persistent data structures, and concurrency management while providing insights into Clojure's syntax and design idioms. The content encourages learning through practical examples and community engagement to enhance understanding of Clojure.









![List, Vector, Map & Set Clojure’s built-in data structures are all immutable - returning a new data structure when a function is applied (list 1 2 3 4 5) ‘(“fish” “chips” 42) (vec ‘(1 2 3 4)) [1 2 3 4] {:key “value”} {:name “John” :skill “conferencing”} (set ‘(1 2 3 4 4)) #{1 2 3 4}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/getintofunctionalprogrammingwithclojure2-170325091900/75/Thinking-Functionally-with-Clojure-14-2048.jpg)