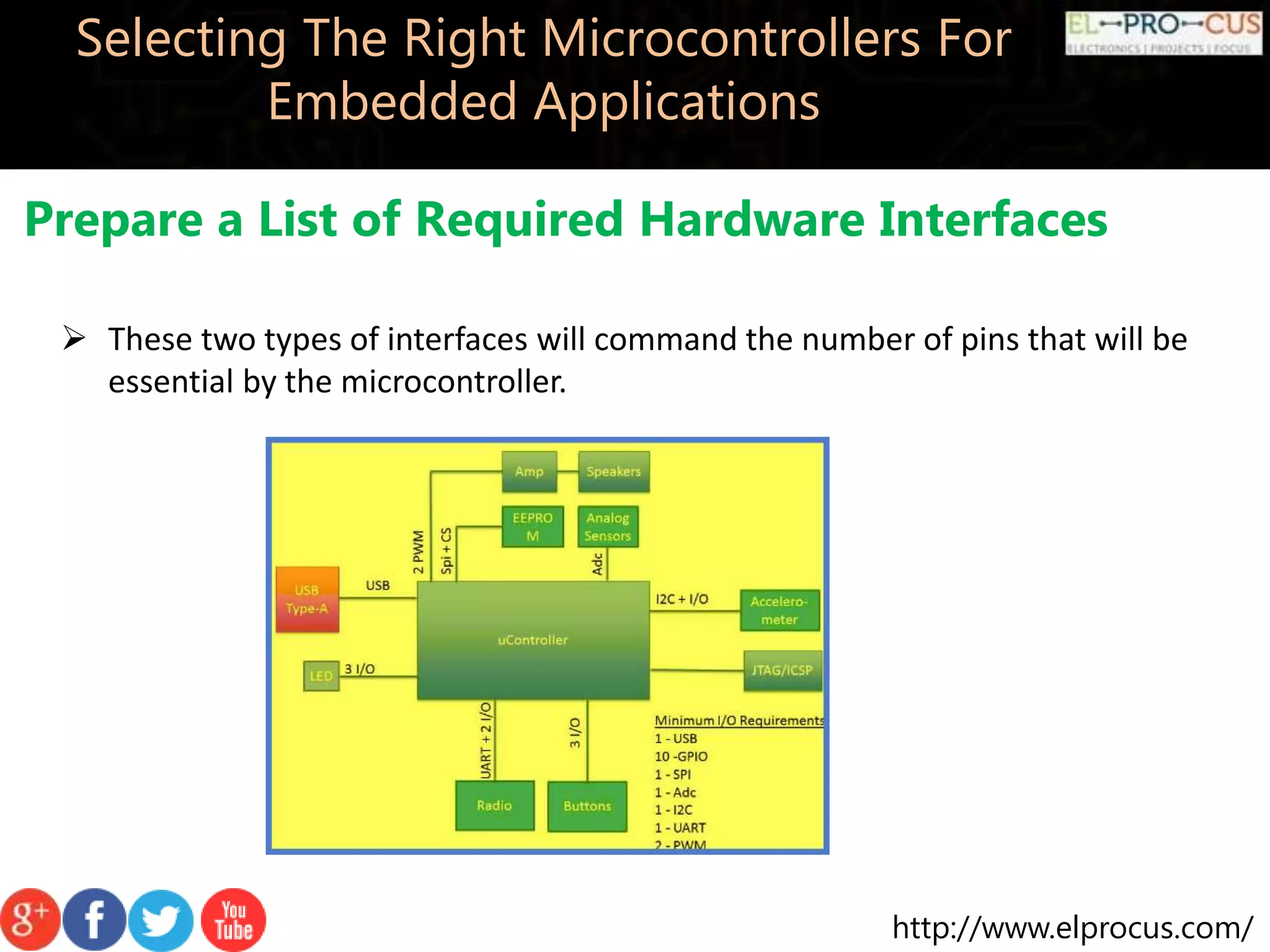
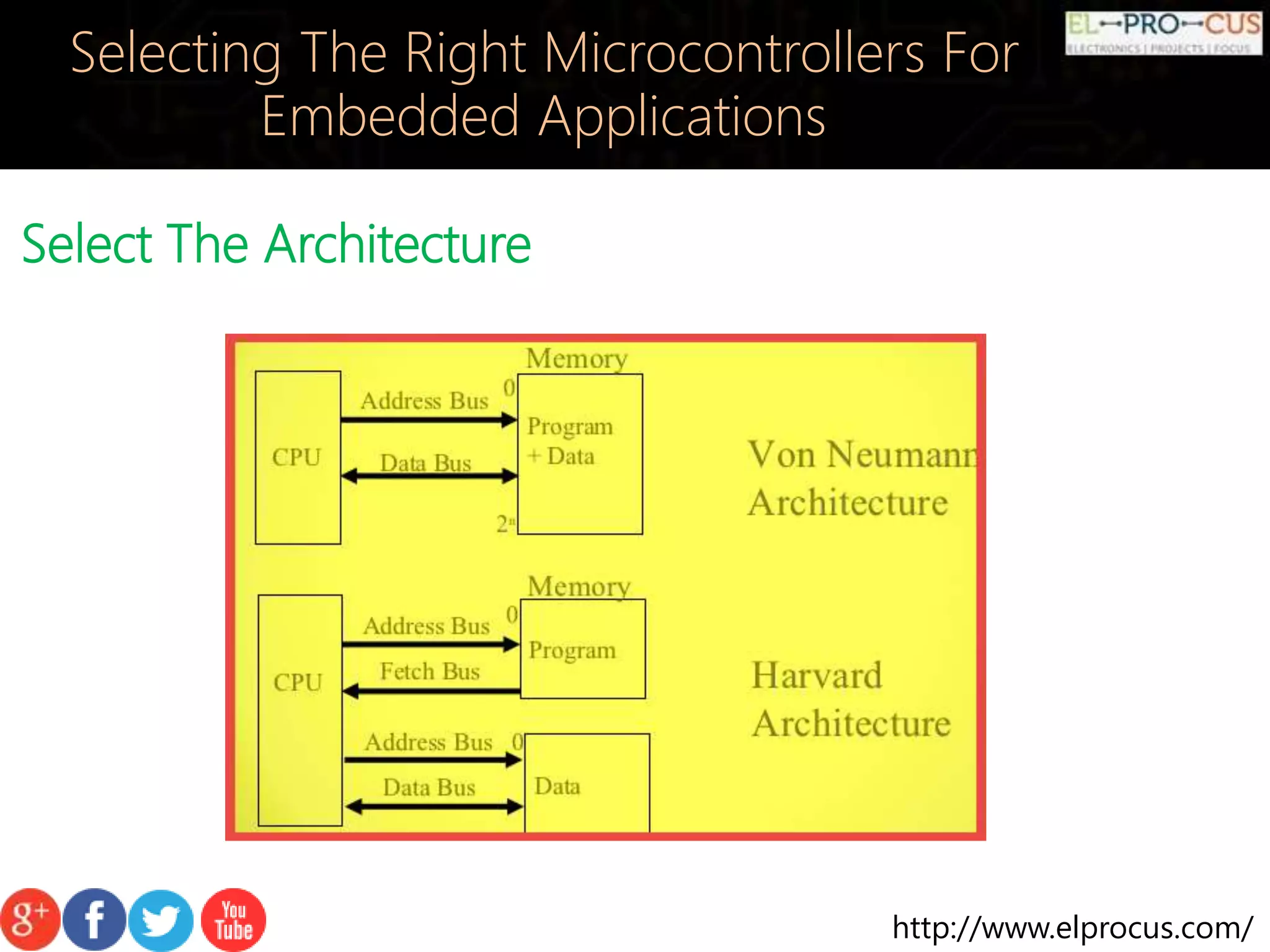
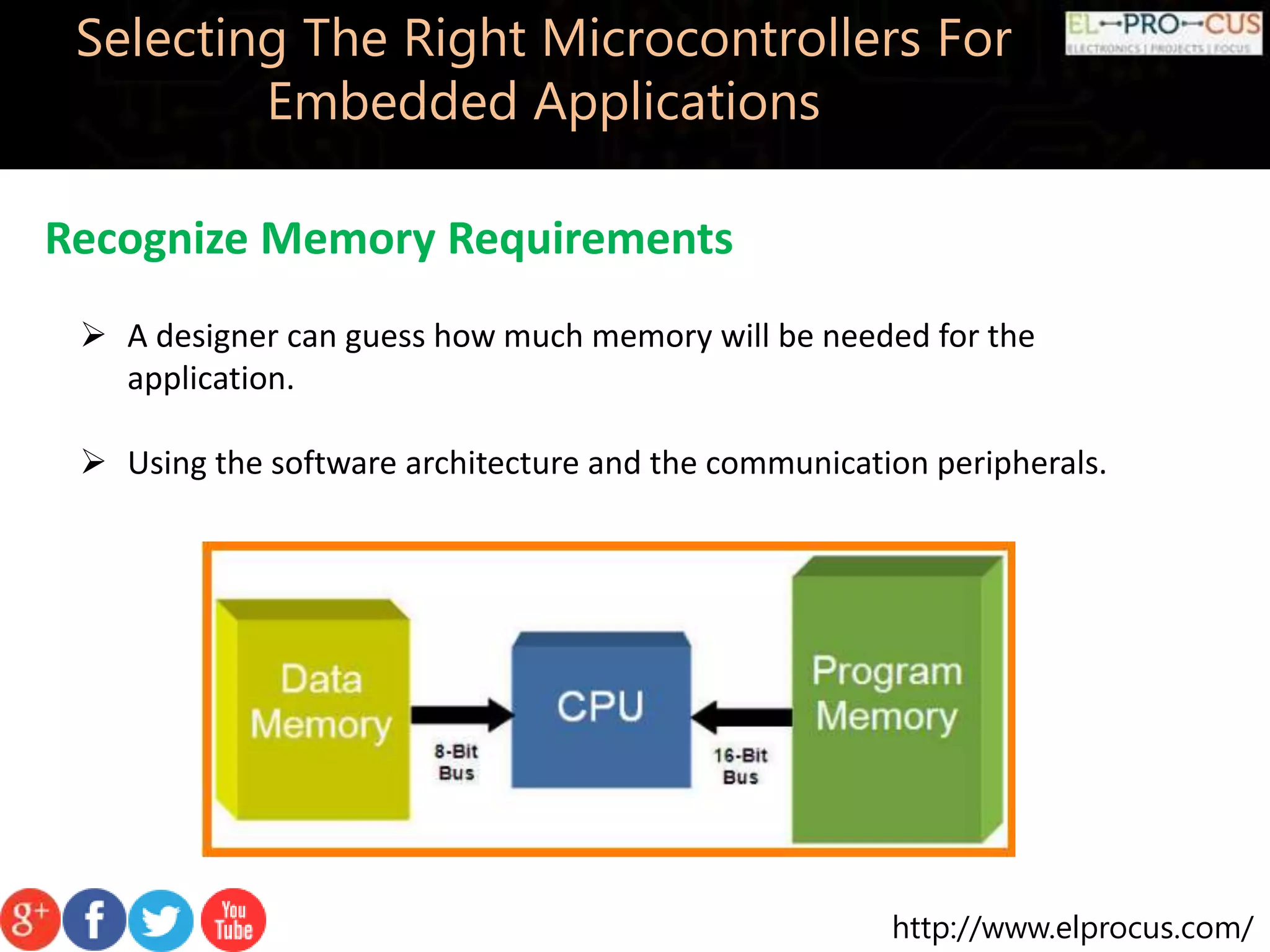
This document discusses how to select the right microcontrollers for embedded applications. Key factors to consider include preparing a list of required hardware interfaces, selecting an appropriate architecture, recognizing memory requirements, observing cost and power limitations, and picking a development kit. Selecting the right microcontroller is an iterative process that requires evaluating technical specifications and tradeoffs.