The document presents a generic method for detecting code clones in software development, addressing issues caused by duplicate code that impair maintainability and software quality. It introduces a technique capable of identifying four types of clones by segmenting code into modules, using metrics for comparison, and implementing a novel algorithm that leverages ontology schemas. The proposed tool shows better precision and recall values than existing methods, with an effective detection process for various coding languages.
![Generic Code Cloning Method for Detection of Clone Code in Software Development http://www.iaeme.com/IJCET/index.asp 15 editor@iaeme.com common in recent software development by the developers, but it has various drawback[14]. It leads to increase in maintenance cost [16] which also decreases quality of the software in a system [1]. As the code is copied without alternations , there is a chance of increase in bugs in the software, because errors present in one module can be increase the errors in another , when they are linked with modules increase bugs in software system[11][8]. According to review, about 10% to 25% of code in the software development by the developers coping and pasting of code i.e. cloned code, [4] [2] and around 75% of cloned code is tailored clone code i.e. code copied and pasted with some changes like naming, updating or erasing of the instructions to the code[10]. The developers do this process regularly for rapid development of the software which can increase bugs and alter the execution. The developer usually do the process of cloning of code wontedly or unwontedly, A time the code which was written and copied intentionally by the software engineer by adding the code fragments with or without changes, can cause a bug ,a times the code cloning can serve as advantages in reusing the code which was efficiently written, can increase the effectiveness of the software very high. We come across two type of such cloning methods namely semantic and syntactic matching to find similarities. If the word or text of the code matches, then it is syntactic and if the module or procedure matches it is semantic identity. 1-Type: find the syntactic similarities, these allow only certain information’s like spaces and remarks 2-Type: These are naming changing clones with same syntactic, in this only changes is allowed in variable, constant, type of data type, spaces and remarks. 3-Type: clones with identical syntactic similarities, in this clone variation are allowed to rename literal, identifier and addition or deletion of statement to code. 4-Type: These are semantic clone with semantic similarities; these clones are semantically same but syntactically differenti. e. computation is same but implement by different syntactic variants. 2. CLONE DETECTION PRADIAGMS Text Based Approach- In this method the duplicate or copied code is detected line by line in the form of group of characters [4]. The approach is very easy to write, this approach only solves 1-type clone. Token Based Approach: In this method, the code source has to be transformed into smaller tokens by using lexer or parser[15]. The comparison is done line by line, but in the form of tokens[4]. This approach only detects 1-type and 2-type clones [15]. ASTB Approach: In this method first the code source is converted into Syntax tree using parsing [1][8]. The comparison in this approach is done using sub-tree of syntax tree. This approach is very difficult to write, it can detect only 1-type, 2-type and 3-type clones. Implementation of the ASTB is very tedious because to convert a source code into tree is difficult. PDG Approach: In this method when applied, converts code sources into direct graph structure. This methods solves only 1-type, 2-type and 3-type, Implementation of PDG is very difficult. Metric Based Approach: In the method, the code source is transformed into another form. After conversion it metric values are evaluated from the code, like number of classes, number of objects, number of lines, number of function calls, number of branching statements, number of loops, number of comments etc. Then the metrics of two source codes are](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijcet0802003-170313104143/75/GENERIC-CODE-CLONING-METHOD-FOR-DETECTION-OF-CLONE-CODE-IN-SOFTWARE-DEVELOPMENT-2-2048.jpg)
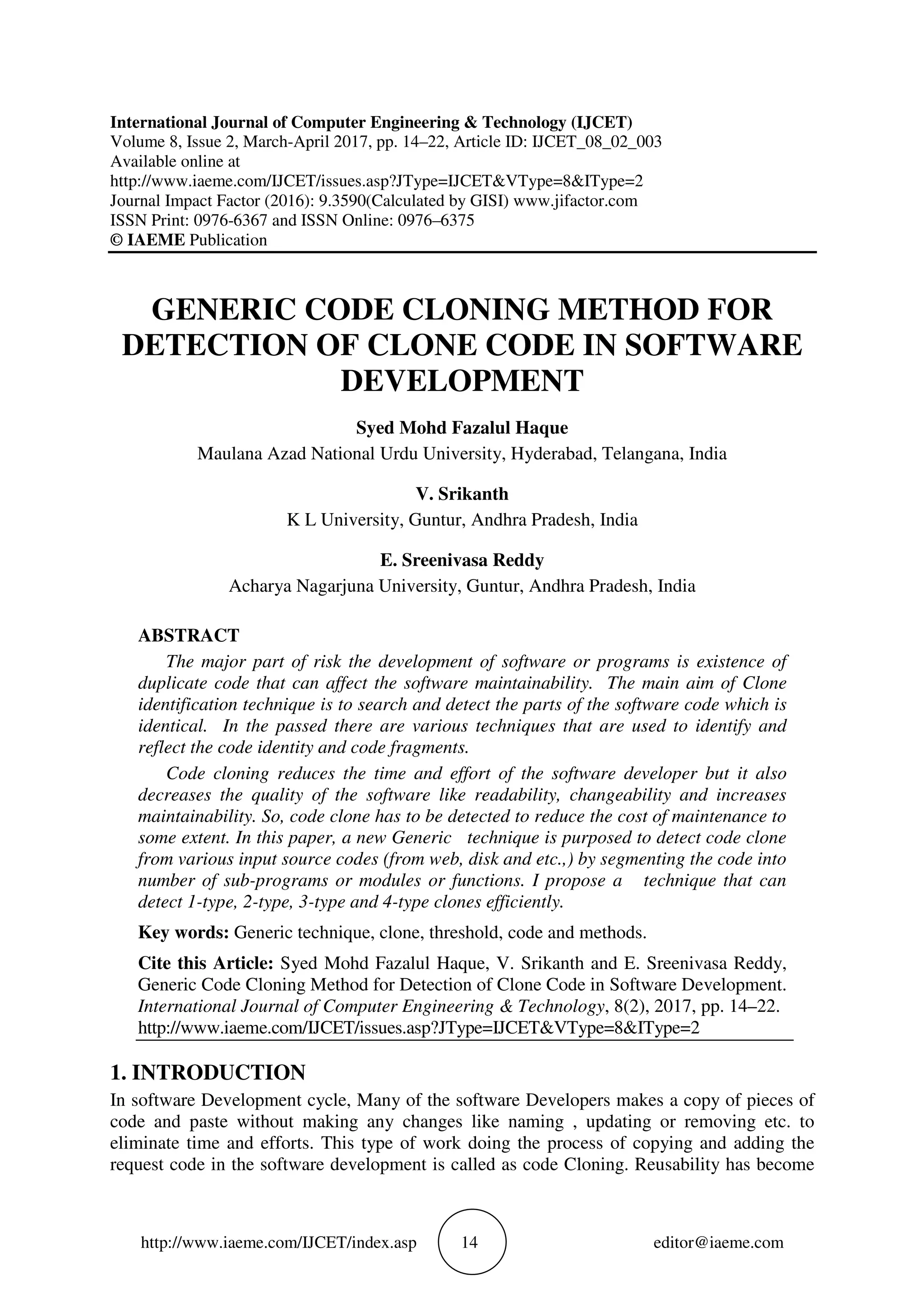
![Syed Mohd Fazalul Haque, V. Srikanth and E. Sreenivasa Reddy http://www.iaeme.com/IJCET/index.asp 16 editor@iaeme.com compared and clone will be detected [10]. This method is easy to write but very difficult when they are complex. 3. PROPOSED METHOD AND IMPLEMENTATION Proposed work is divided into two categories 1. Prepare an ontology Schema 2. Develop a Generic algorithm for Clone Detection using Ontology 3.1. Ontology Schema Table 1 Showing the Ontology used in Code Cloning We build a model table 1.Of ontology which captures clones, clone objects, clone sets like program variables, relationship between variables. The ontology elements include class instance, interface, functions, methods, variables and fields. The type of relationship provided between variables are implements, extends, declare and data types, association, aggregation , generalization , In added to the schema , there are other 3 specific clone type relations namely diffuse, reside in and contain. These associations describe the relationship between clones and clone fragments. Using the above ontology, code objects are detected and cloning relationship is found very easily. The figure 1. shows the Ontology Schemes relationship between cloned objects, objects sets, program variables, class instance, interface, functions, methods, variables, for loop, while, aggregation, associations and generalizations. 3.2. Ontology Schema Structure Ontology is a specification of a conceptualization that is designed for reuse across multiple applications and implementations. …a specification of a conceptualization is a written, formal description of a set of concepts and relationships in a domain of interest. It guides in forming relationship between the objects, clone objects and object sets. 3.3. Working of Ontology Schemas It helps to guide to form relations, associations, aggregation and generalization between objects and object sets in code Subject Relation Object Clone set Contain Clone instance Clone instant Reside_in Method Clone instance Diff_use Function, field, variable, class, interface, Clone instance Common_use Variable, loop, functions, class, interface Class Extend Class Class Implement Interface Class Declared_in Class Interface Extend Class Method Declared_in Interface Method has_return_type Class/interface Field Has_type Interface Field Has_type Class/interface Field Has_type Method, for, while , class, interface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijcet0802003-170313104143/75/GENERIC-CODE-CLONING-METHOD-FOR-DETECTION-OF-CLONE-CODE-IN-SOFTWARE-DEVELOPMENT-3-2048.jpg)
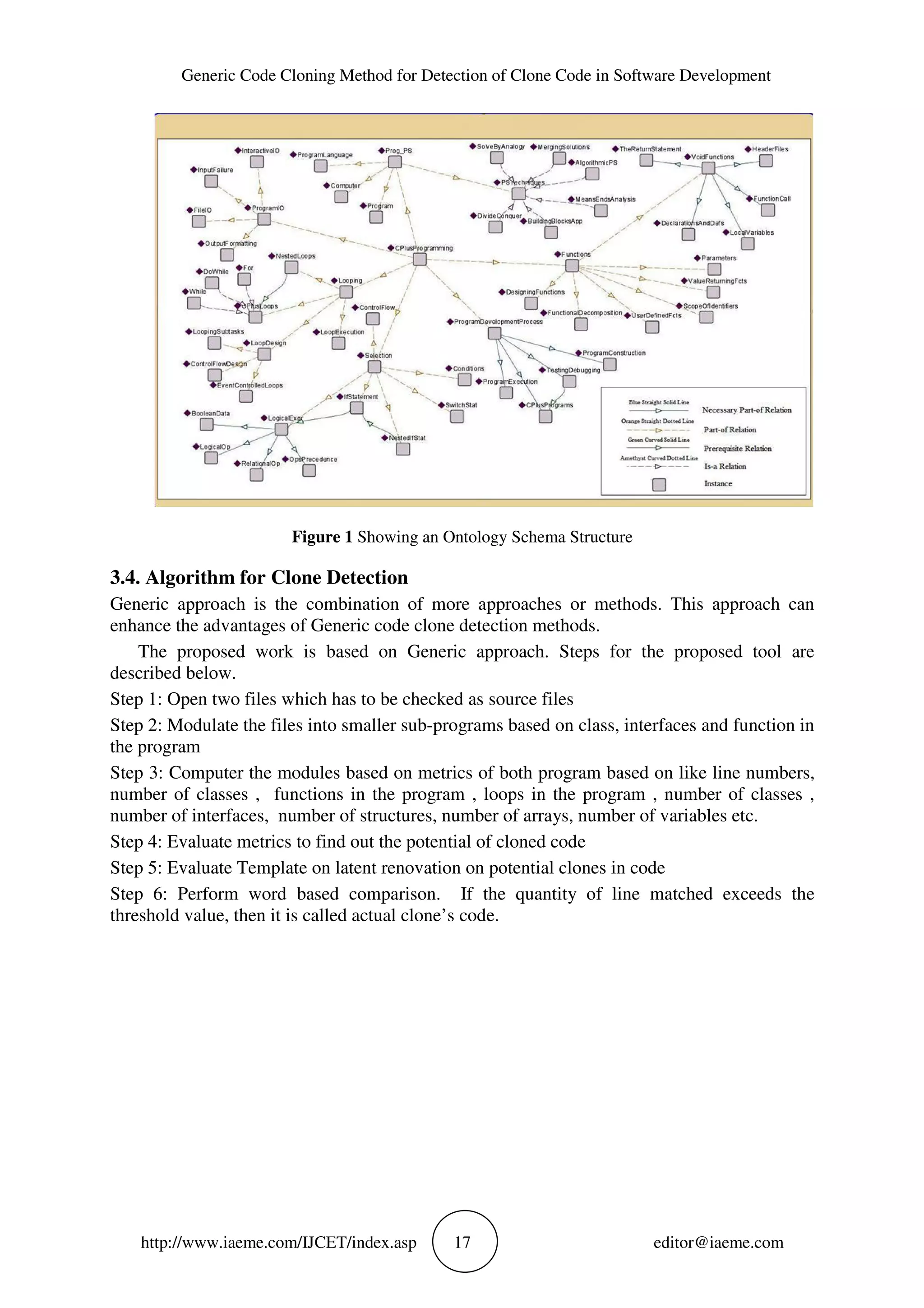

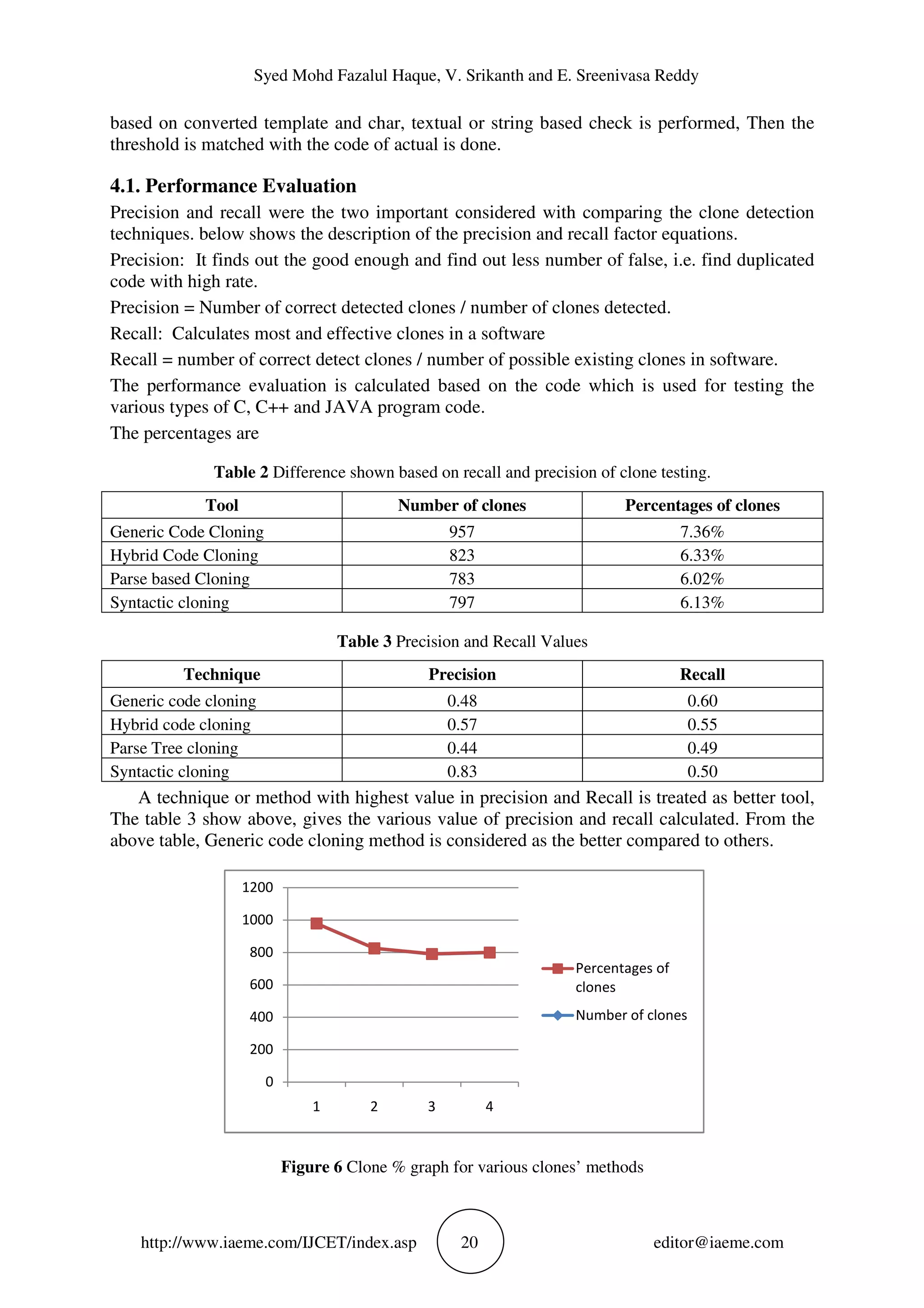
![Generic Code Cloning Method for Detection of Clone Code in Software Development http://www.iaeme.com/IJCET/index.asp 21 editor@iaeme.com The above figure 6. Shows the various techniques used of program code detect with percentage are show, from all the above , the height clones that can be detected accurately and efficiently is the Generic cloning techniques which can detect 1-type , 2 –type , 3-type and 4- type clones based on the syntax, semantic and etc. Figure 7 Show the precision and recall values of methods 5. CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE SCOPE The method that has been developed used Generic method which combines various techniques for mapping and matching the code from source with respect to other. The developed tool can detect 1-type, 2-type, 3-type and 4-type very efficiently. This tool can be further can be further enhanced for better complexity and efficient detection. REFERENCES [1] Rajkumar Tekchandani, Rajesh Kumar Bhatia and Maninder Singh, “Semantic Code Clone Detection Using Parse Trees and Grammar Recovery”, pp.41-46, IEEE, 2013. [2] AmandeepKaur and Balraj Singh, “Study on Metrics Based Approach for Detecting Software Code Clones”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, Volume 4, Issue 1,January 2014. [3] KanikaRaheja, RajkumarTekchandani, “An Efficient Code Clone Detection model on java byte code using hybrid approach”,Page 16-21, IEEE, SEPT 2013. [4] Geetika, Rajkumar Tekchandani, “Detection of Potential Clones from Software using Metrics”, IJARCSSE, Volume 4, Issue 4, April 2014. [5] Deepak sethi, Manishasehrawat and Bharat BhushanNaib, “Detection of code clones using datasets”IJARCSSE, Volume 2, Issue 7, july 2012. [6] Yoshiki Higo, Yasushi Ueda, Minoru Nishino, Shinji Kusumoto, “Incremental Code Clone Detection: A PDG-based Approach”, Page 3-12, IEEE, 2011. [7] Mai Iwamoto, Shunsuke Oshima, Takuo Nakashima, “Token-based Code Clone Detection Technique in a Student’s Programming Exercise”, Page 650-655,,IEEE, 2012. [8] TahiraKhatoon, Priyansha Singh, ShikhaShukla” Abstract Syntax Tree Based Clone Detection for Java Projects” IOSR Journal of Engineering,Volume 2,Issue12,Dec 2012 [9] MikkelJonsson Thomsen, Fritz Henglein,”Clone Detection using Rolling Hashing, Suffix Trees and Dagnification:A Case Study.”IEEE,2012. 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1 2 3 4 Recall Precision](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijcet0802003-170313104143/75/GENERIC-CODE-CLONING-METHOD-FOR-DETECTION-OF-CLONE-CODE-IN-SOFTWARE-DEVELOPMENT-8-2048.jpg)
![Syed Mohd Fazalul Haque, V. Srikanth and E. Sreenivasa Reddy http://www.iaeme.com/IJCET/index.asp 22 editor@iaeme.com [10] PriyankaBatta, Miss Himanshi, “Hybrid Technique for software code clone detection” IJCT, Volume 2 no. 2 April 2012. [11] Kiranpreet, SushilGarg, “Detection and measuring similarity in code clone using ripley’s function Approach.”,IJAST,Volume 2,issue 4,dec 2014. [12] RubalaSivakumar,Kodhai.E, ”Code clone detection in website using approach ”, IJCA, Volume 48-No. 13,June 2012. [13] Balwinder Kumar, Dr. Satwinder Singh, “Code clone detection and Analysis using Software Metrics and Neural Network- A Literature Review”,IJCST, ,Volume 3,issue 2, mar-apr 2015. [14] Prajila Prem, ”A Review on code clone analsis and code clone detection ”, IJEIT , Volume 2, issue 12, june2013. [15] G. Anil kumar, Dr. C.R.K.Reddy, Dr. A. Govardhan, An Efficient Method-Level Code Clone Detection Scheme through Textual Analysis Using Metrics. International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET).3 (1), 2012, pp. 273-288. [16] Prof. Deepika Shukla and Apurva Desai, Review on Generic Object Recognition Techniques: Challenges and Opportunities. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology, 6 (12), 2015, pp. 104-133](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijcet0802003-170313104143/75/GENERIC-CODE-CLONING-METHOD-FOR-DETECTION-OF-CLONE-CODE-IN-SOFTWARE-DEVELOPMENT-9-2048.jpg)