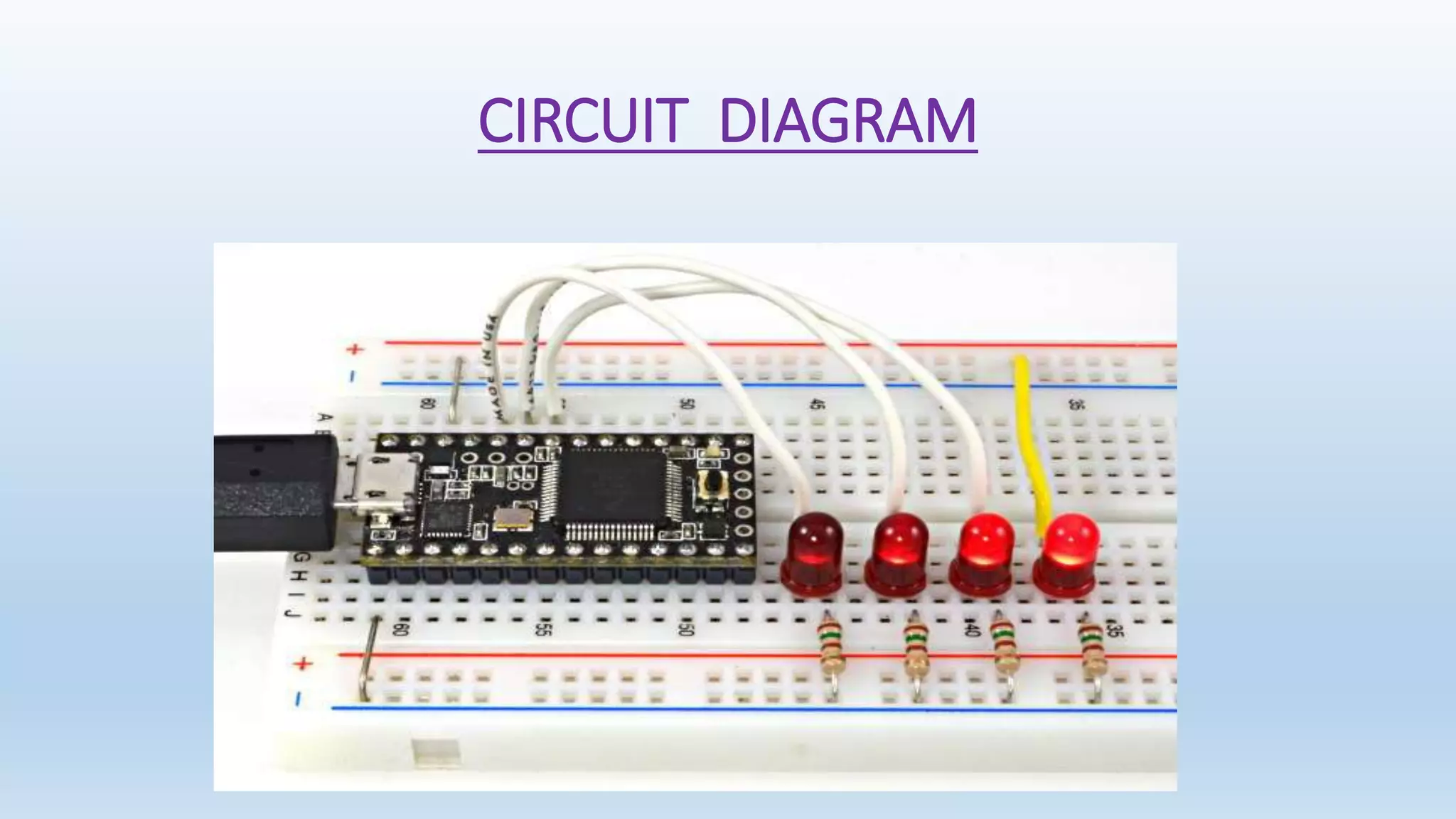
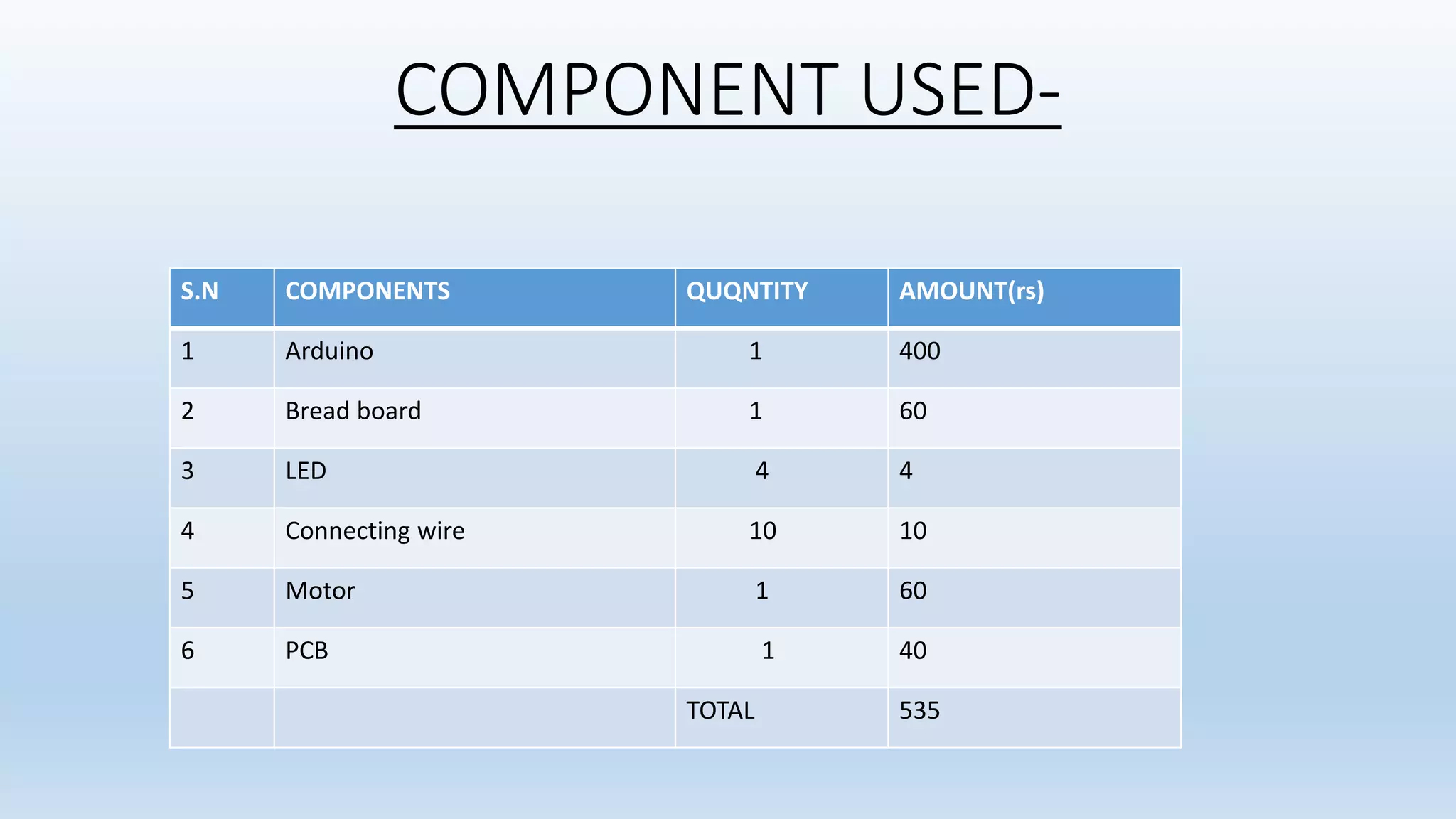
The document summarizes a minor project on generating PWM signals of various duty cycles using an Arduino. It discusses how PWM works by rapidly switching a signal on and off to simulate variable voltages. The project uses an Arduino to generate PWM signals at 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% duty cycles that control the brightness of an LED. The circuit diagram and components used are listed, along with advantages of PWM like low power loss and applications like dimming LEDs and controlling motor speed.