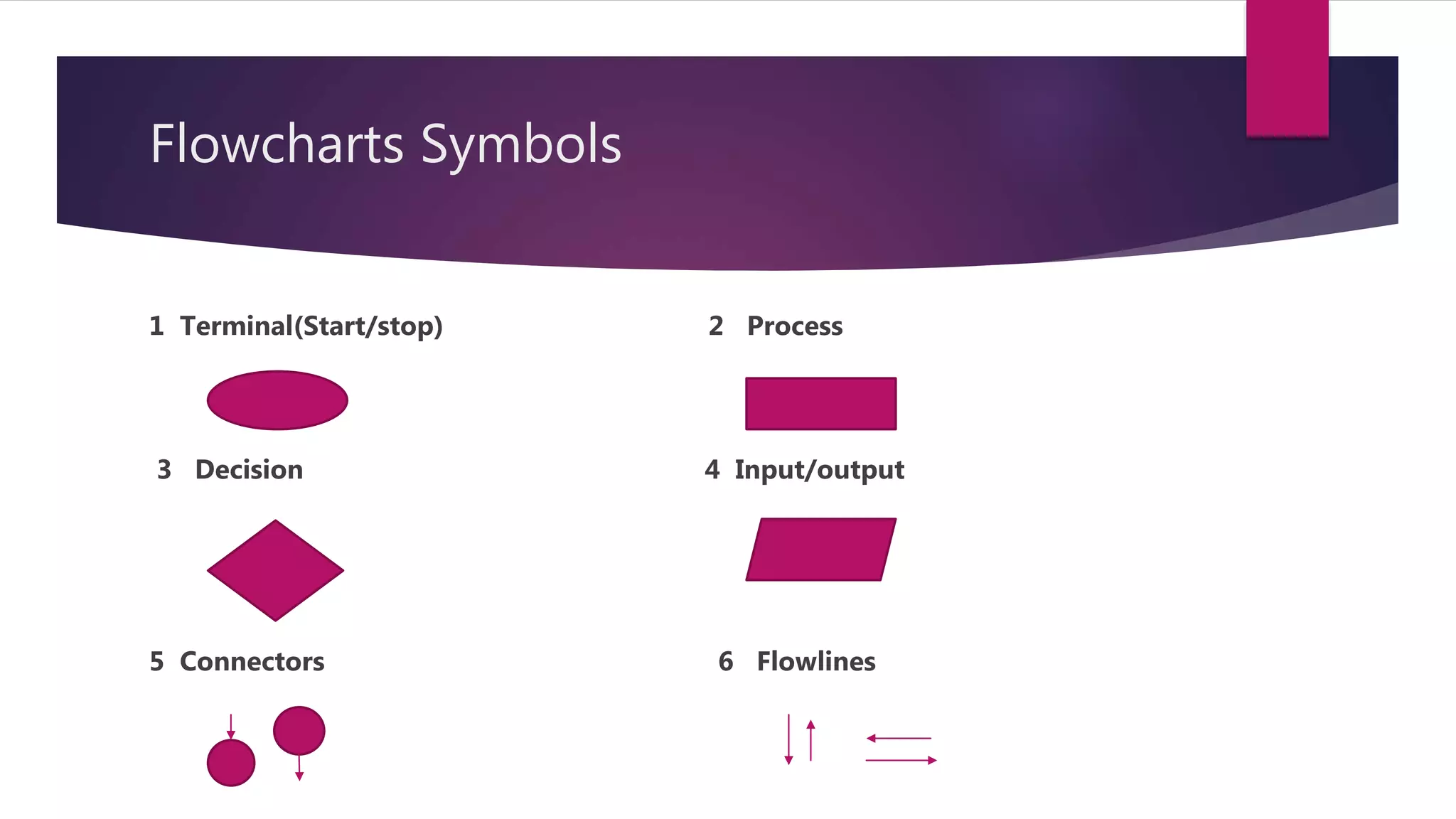
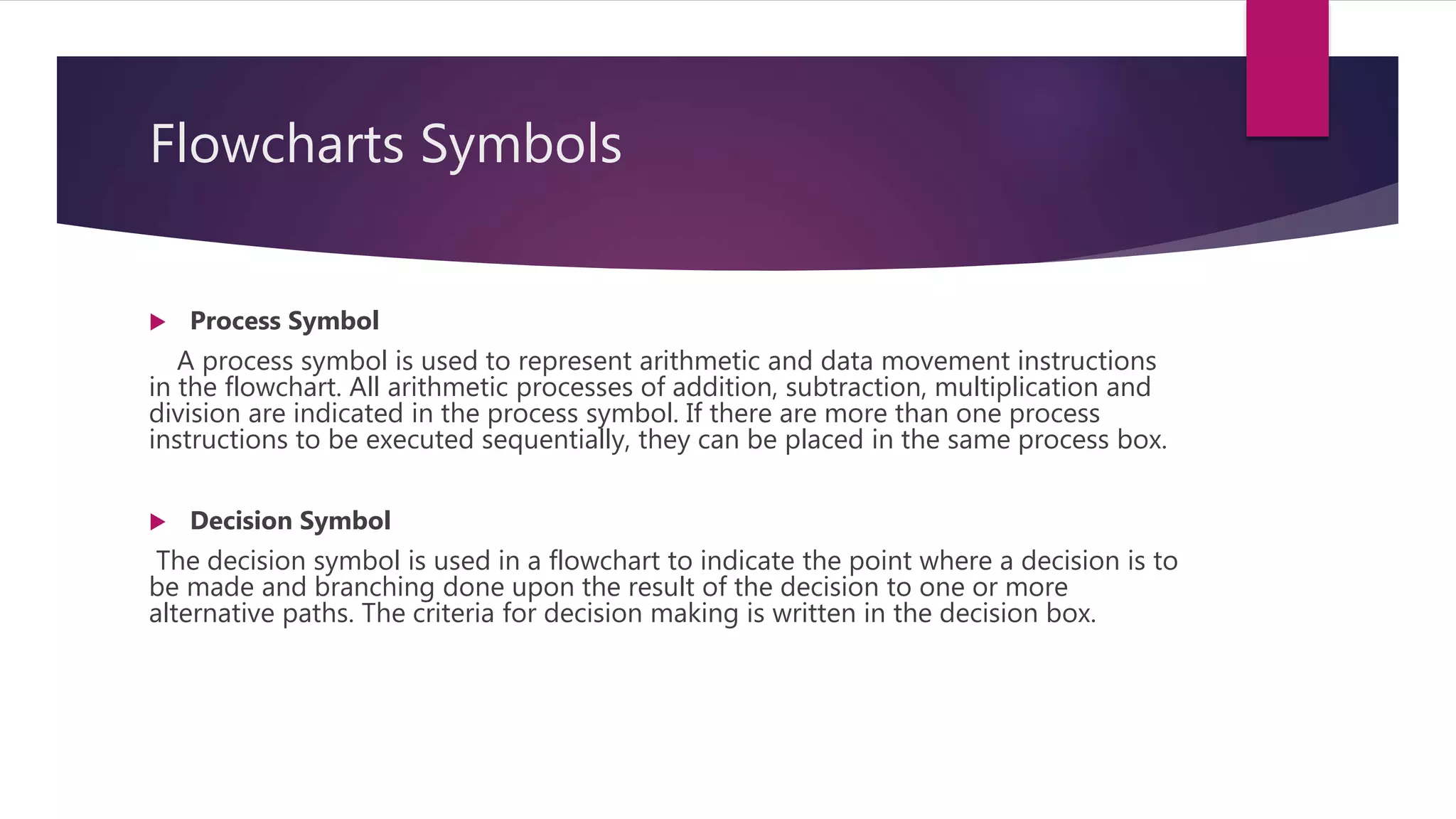
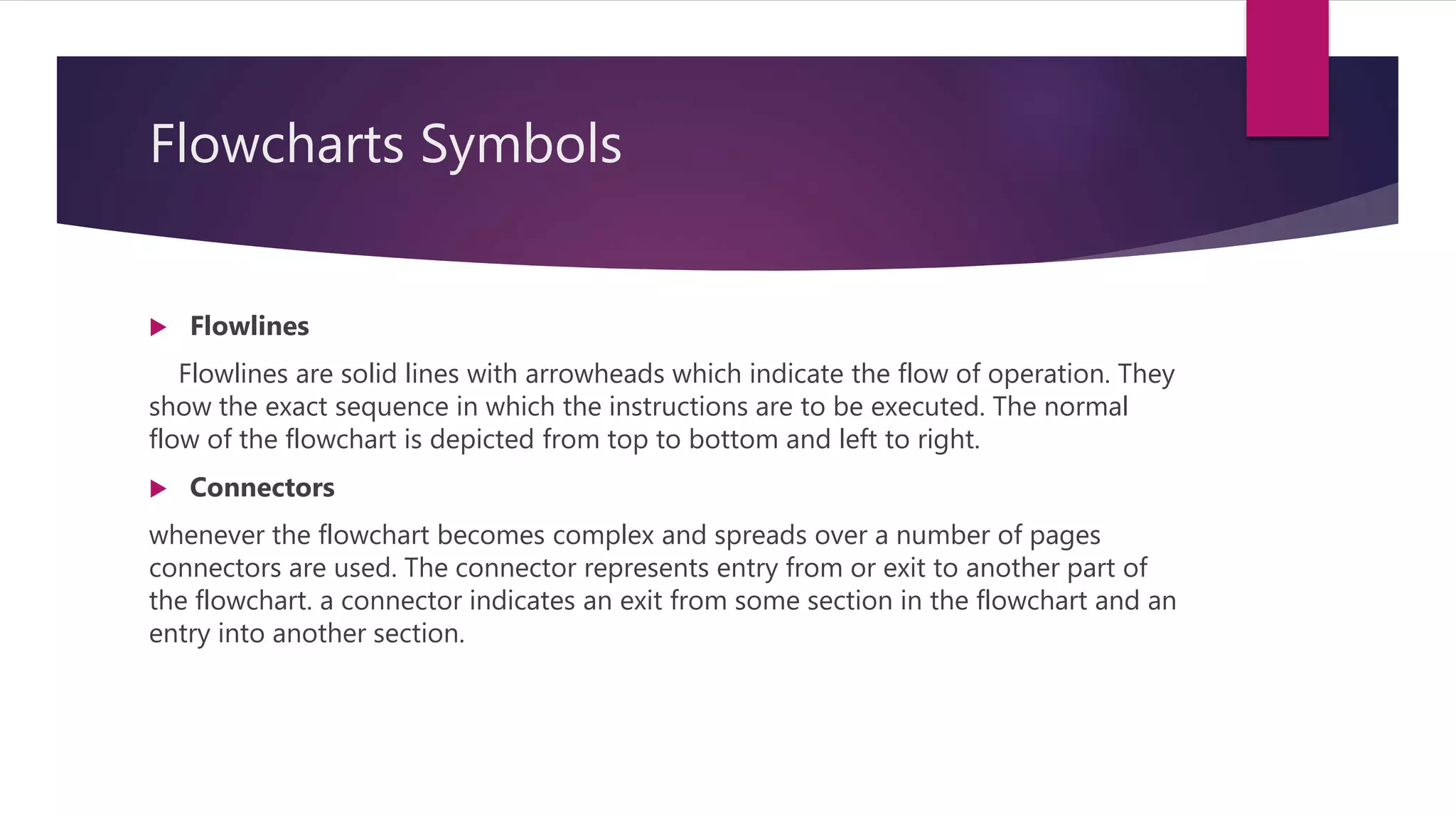
This document discusses fundamentals of algorithms and flowcharts. It begins by defining a flowchart as a diagram that uses boxes and arrows to show the steps and order of an algorithm or process. It then describes the common symbols used in flowcharts including terminals, processes, decisions, inputs/outputs, connectors, and flowlines. The next sections explain each symbol in more detail and the advantages of using flowcharts. Finally, it discusses the main structures that can be represented in a flowchart including sequence, decision, and repetition.