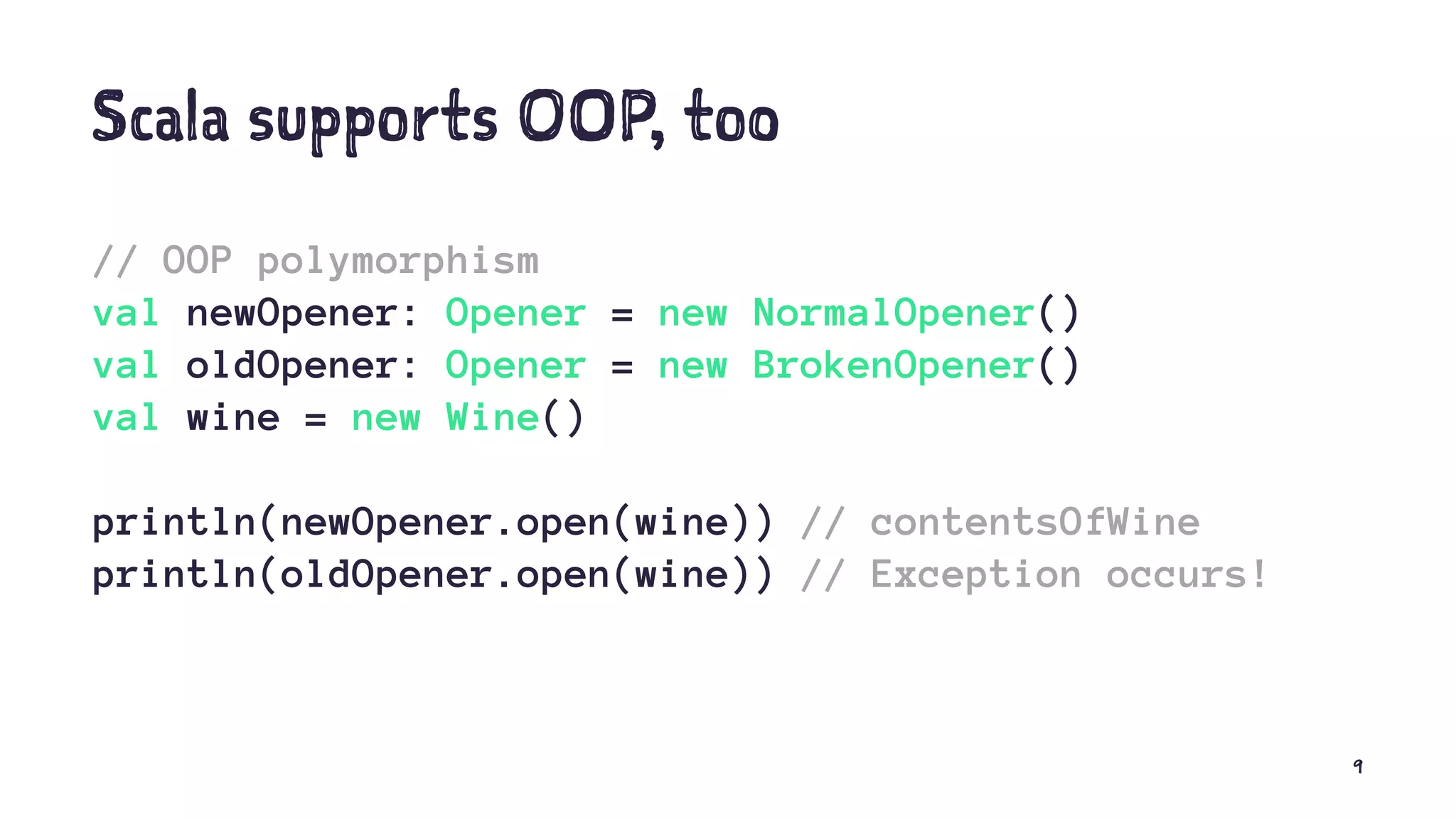
The document discusses functional programming in Scala, highlighting its conciseness and compatibility with Java. It explains key concepts such as immutability, side effects, and the advantages of using functional programming for maintaining elegant code. Additionally, it provides insights on when to adopt functional programming and mentions resources for further learning.





![... in Elegant Functional Programming Way val openerO = Some(Opener) val wineO = Some(Wine(vintage = 1997)) val contentsO = for { opener ← openerO wine ← wineO } yield opener.open(wine) // contentsO: Option[Contents] = Some(contentsOfWine) // no null, no NullPointerException 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetup-why-scala-180220215458/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-7-2048.jpg)
![... in Elegant Functional Programming Way val openerO = Some(Opener) val wineO = None val contentsO = for { opener ← openerO wine ← wineO } yield opener.open(wine) // contentsO: Option[Contents] = None // no null, no NullPointerException 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetup-why-scala-180220215458/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-8-2048.jpg)

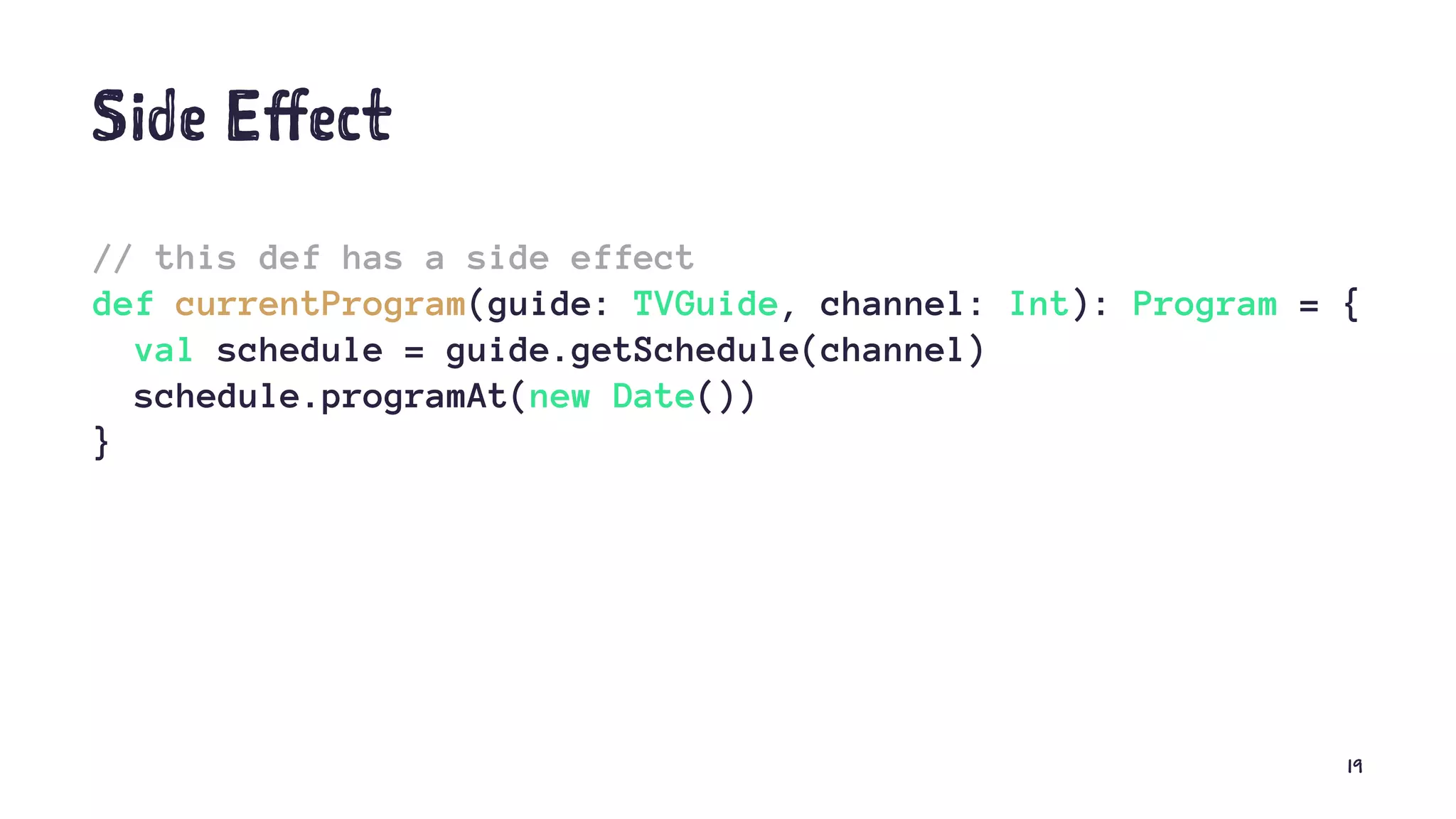
![… and Vice Versa // scala code object Person { val MALE = "m"; } // java code public class App { public static void main(String argv[]) { Person$ person = Person$.MODULE$; System.out.println(person.MALE()); } } 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetup-why-scala-180220215458/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-11-2048.jpg)



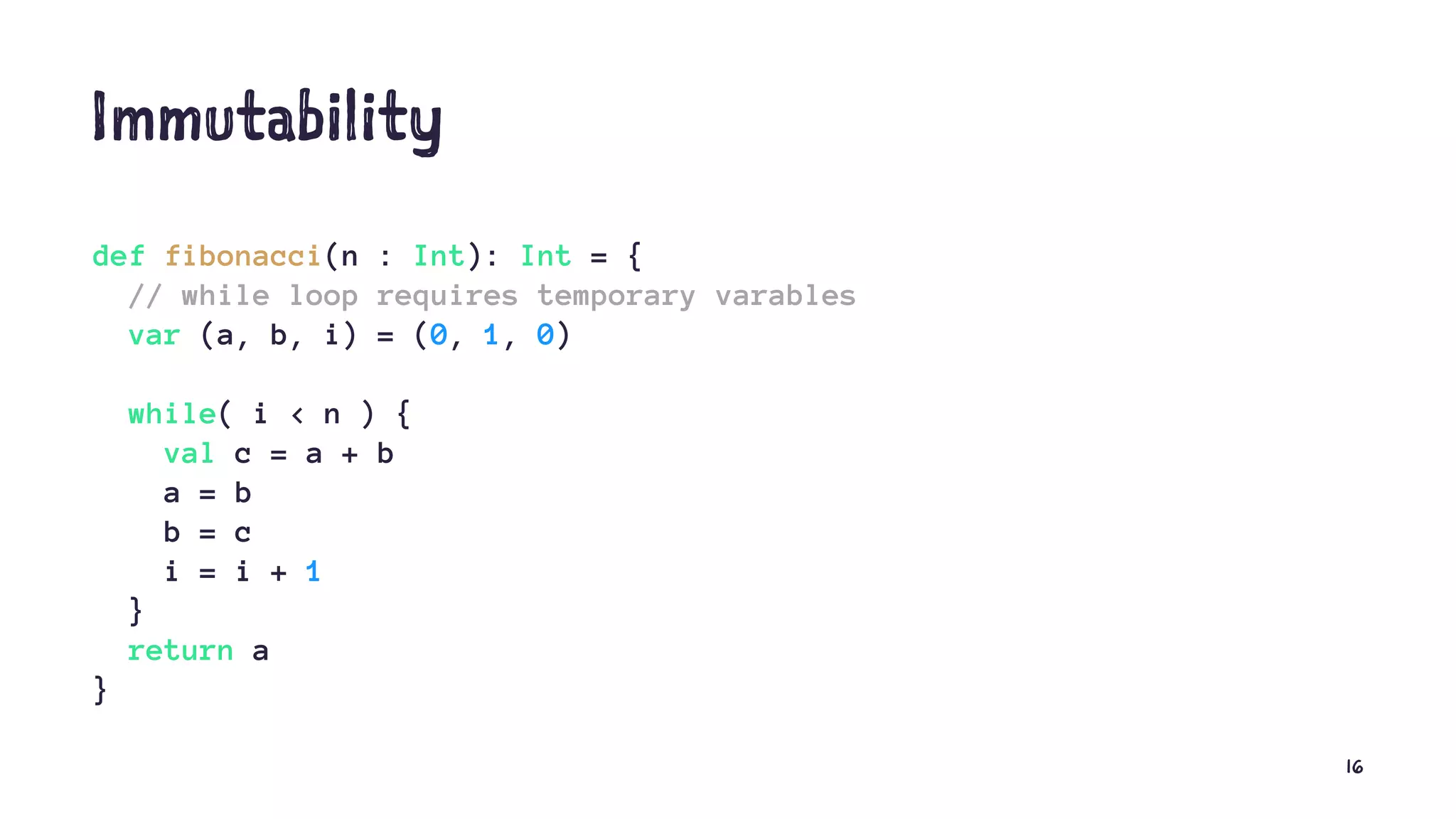
![Immutability // value, not variable val a = 1 a = 2 // error: reassignment to val // list val ints1: List[Int] = 1 :: 2 :: Nil val ints2: List[Int] = ints1 :+ 3 println(ints1) // List(1, 2) println(ints2) // List(1, 2, 3) println(ints2 == 1 :: 2 :: 3 :: Nil) // true 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetup-why-scala-180220215458/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-15-2048.jpg)