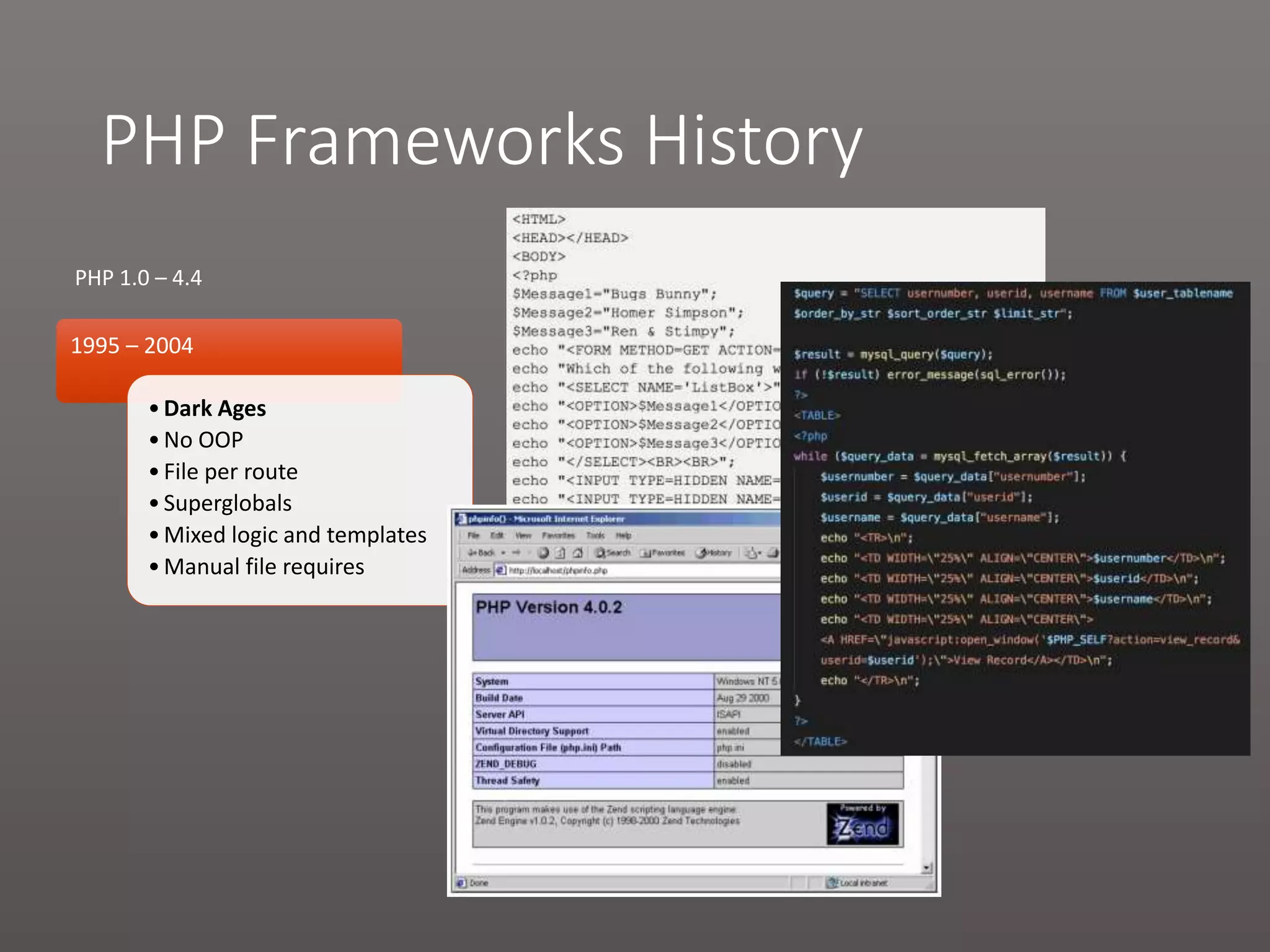
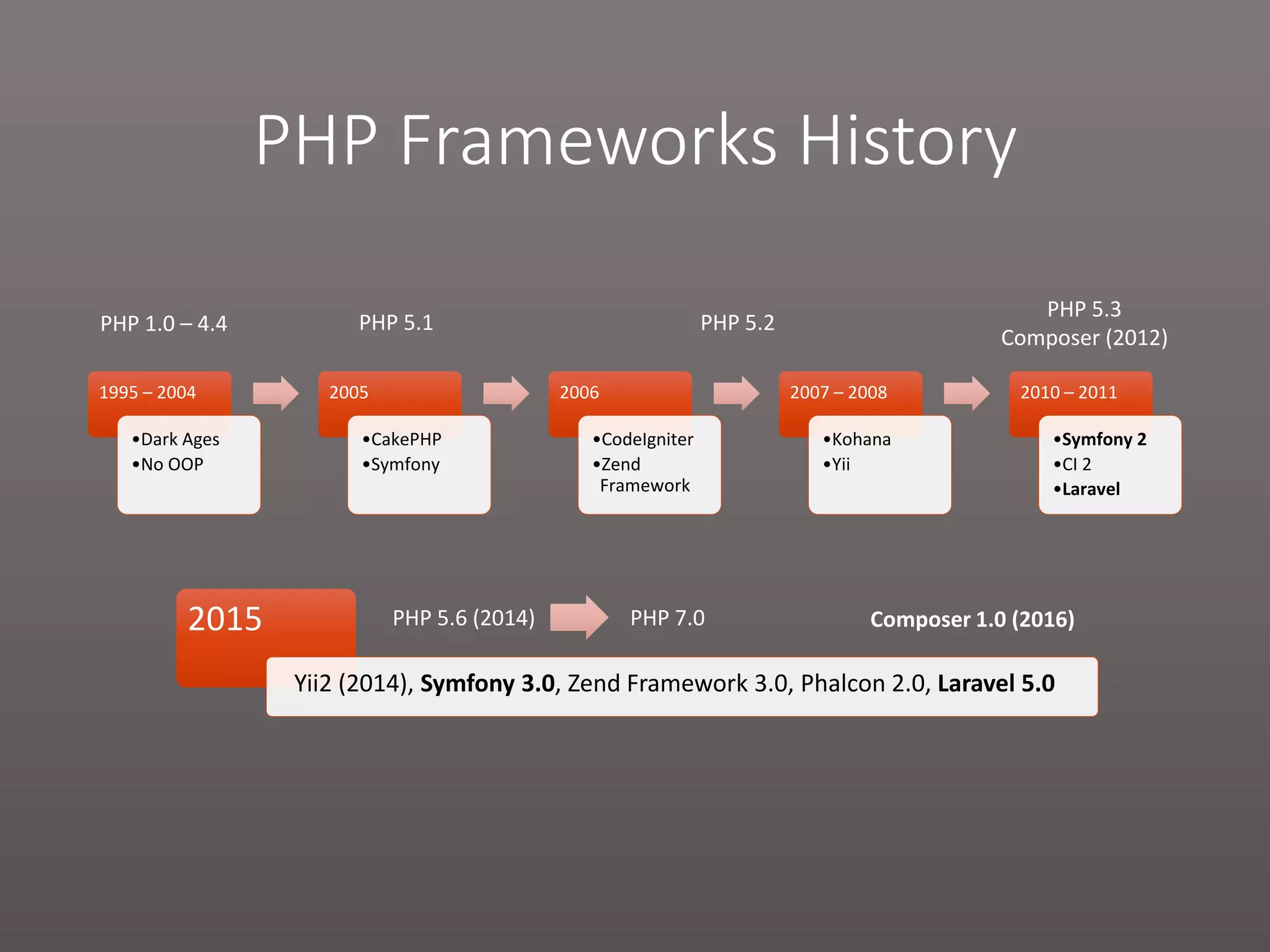
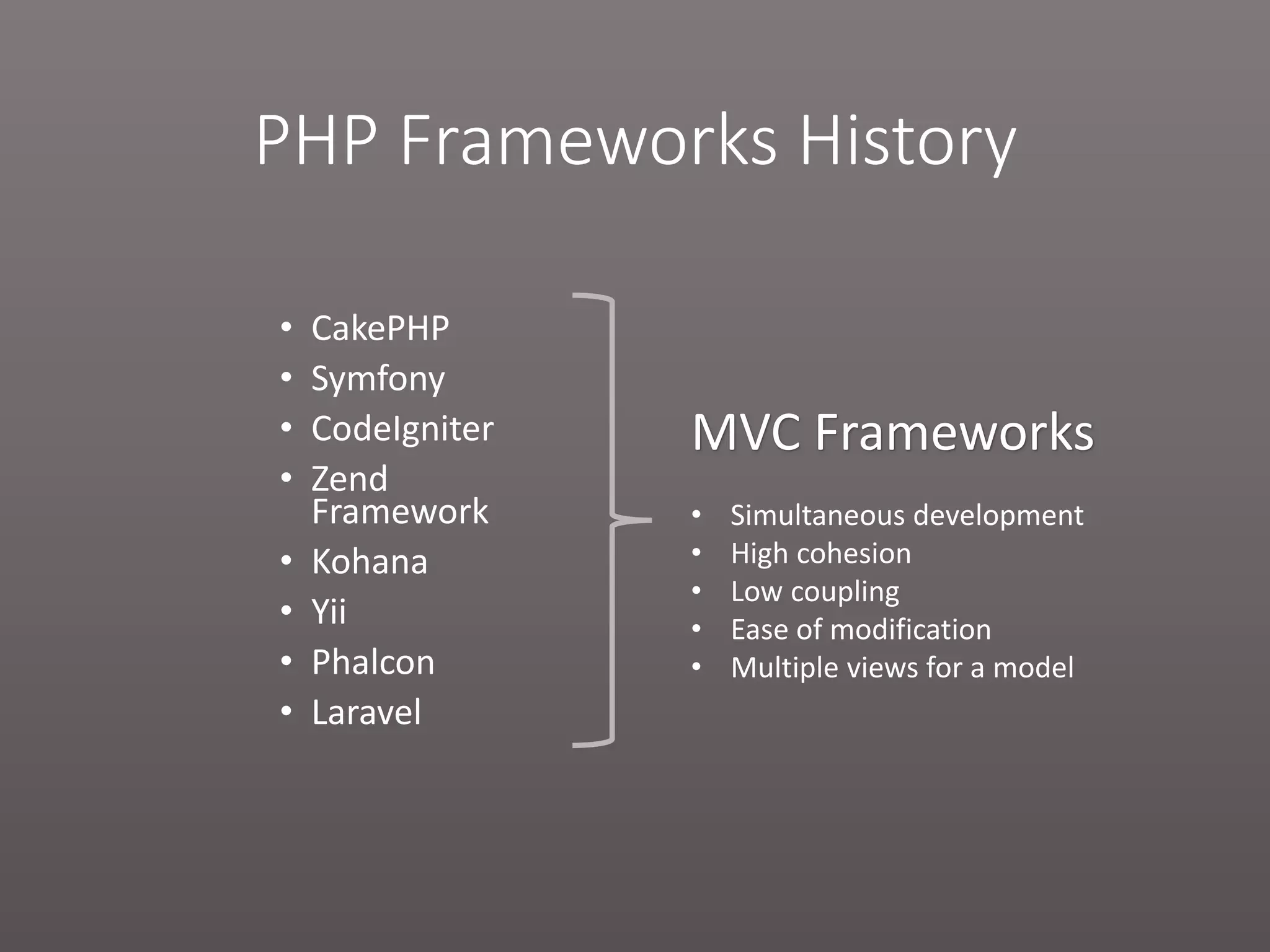
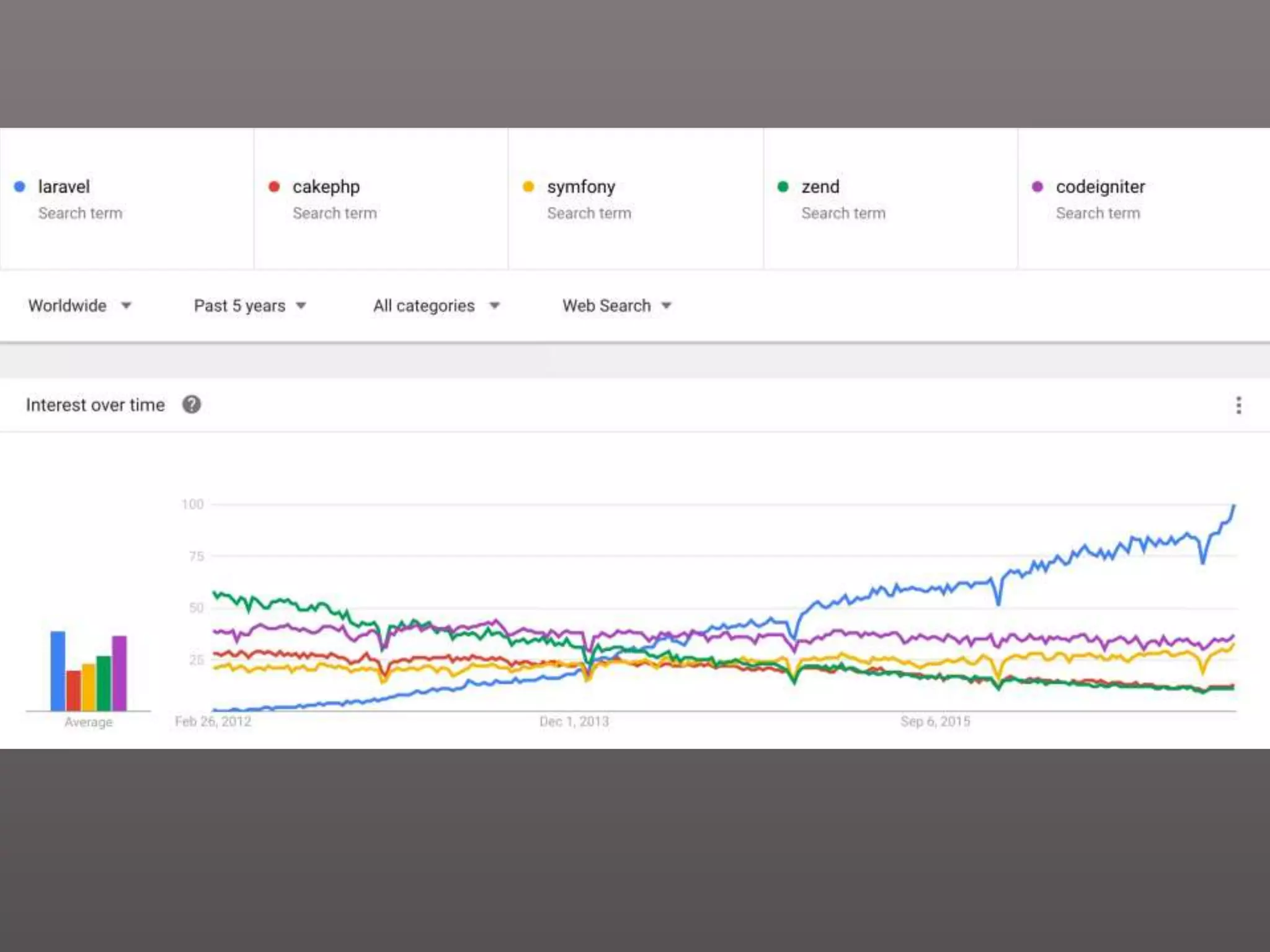
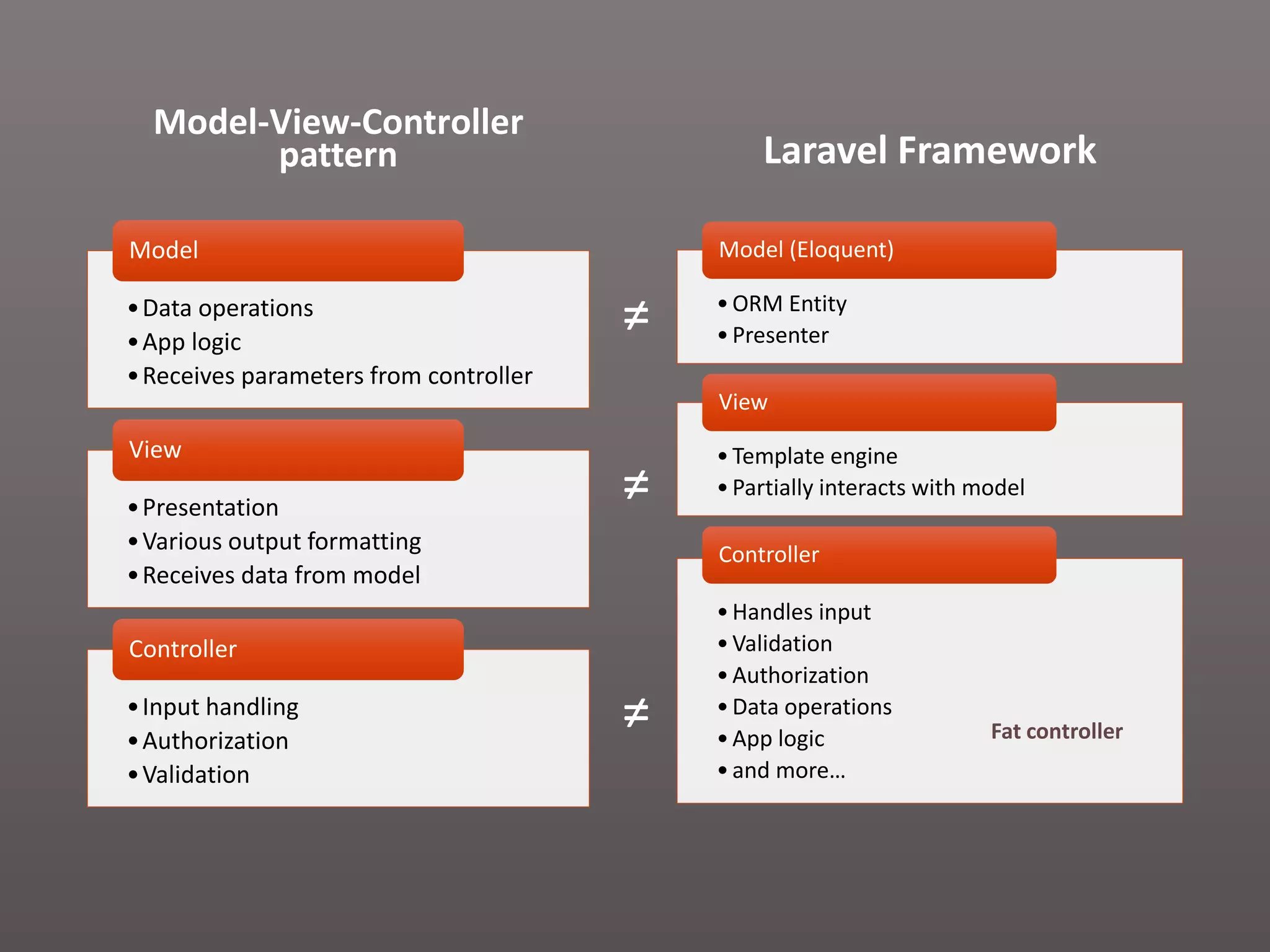
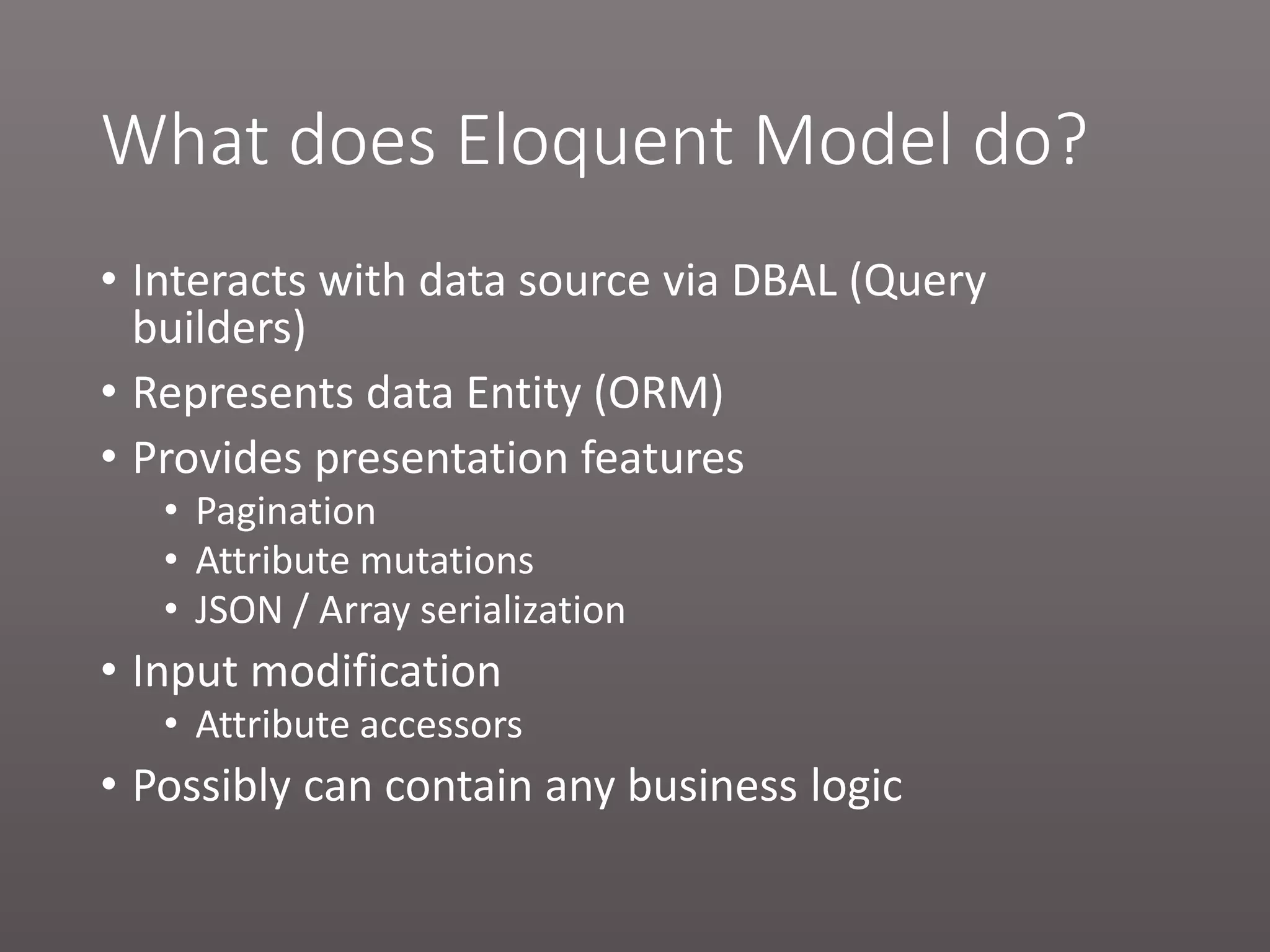
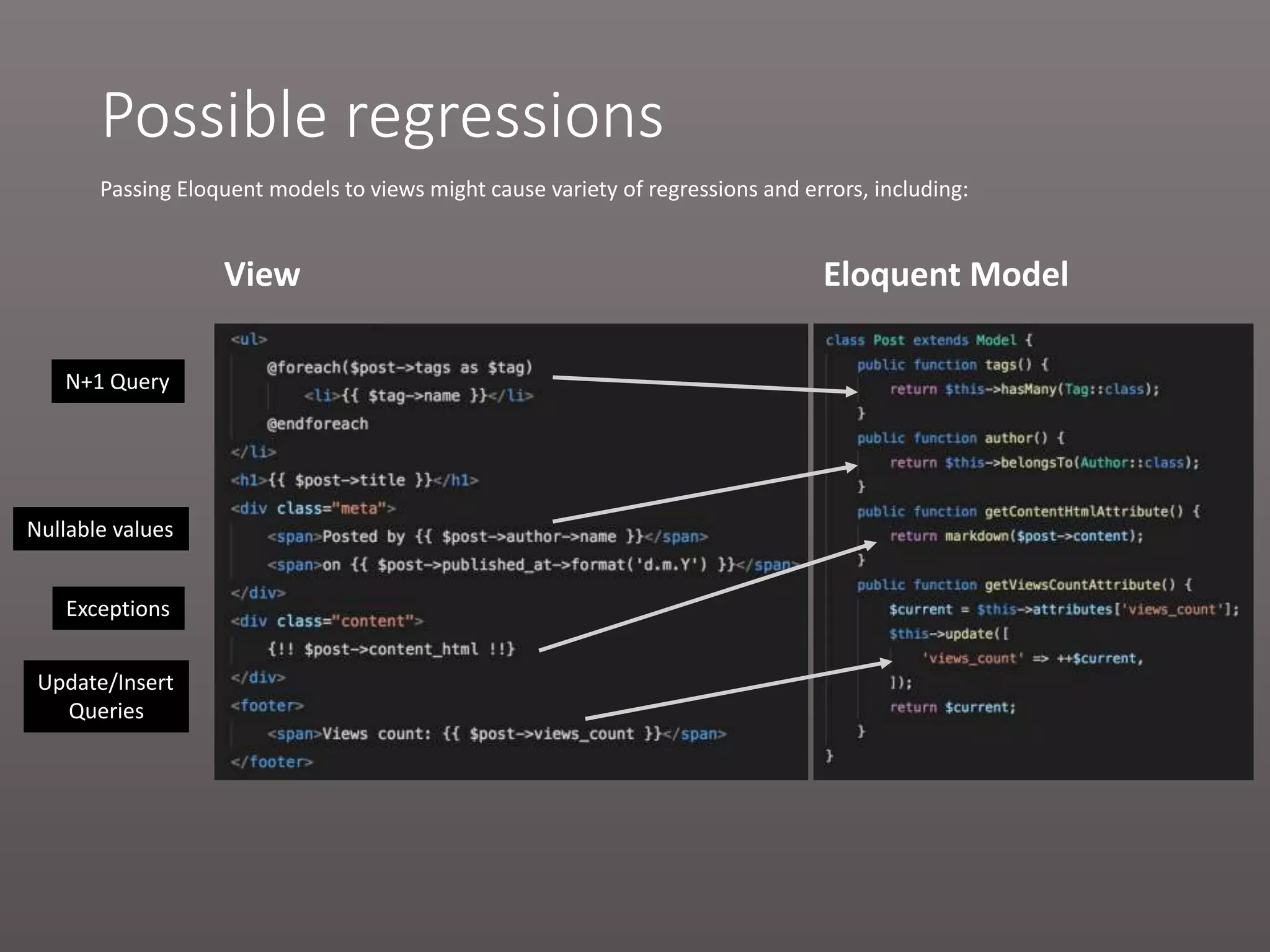
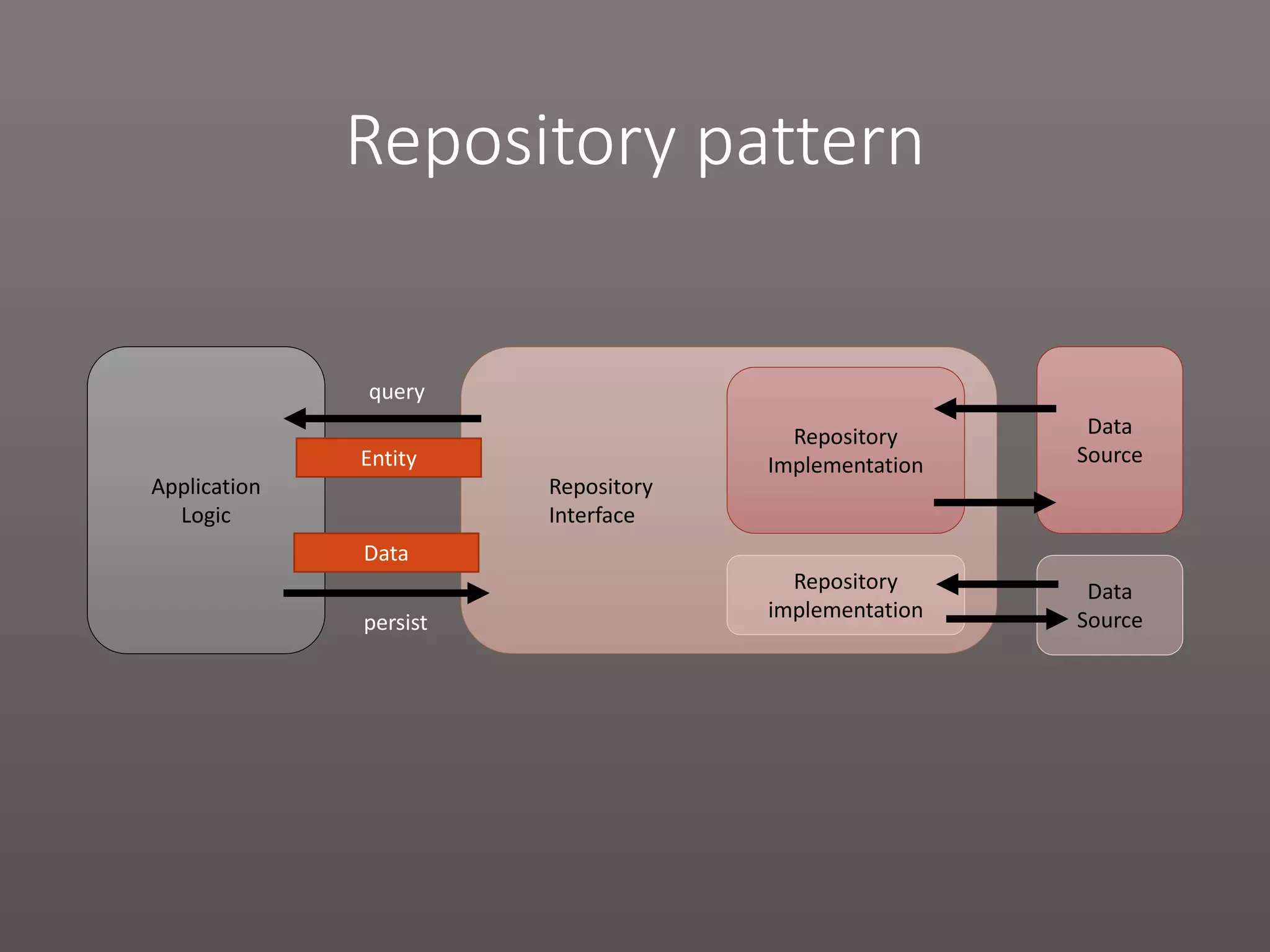
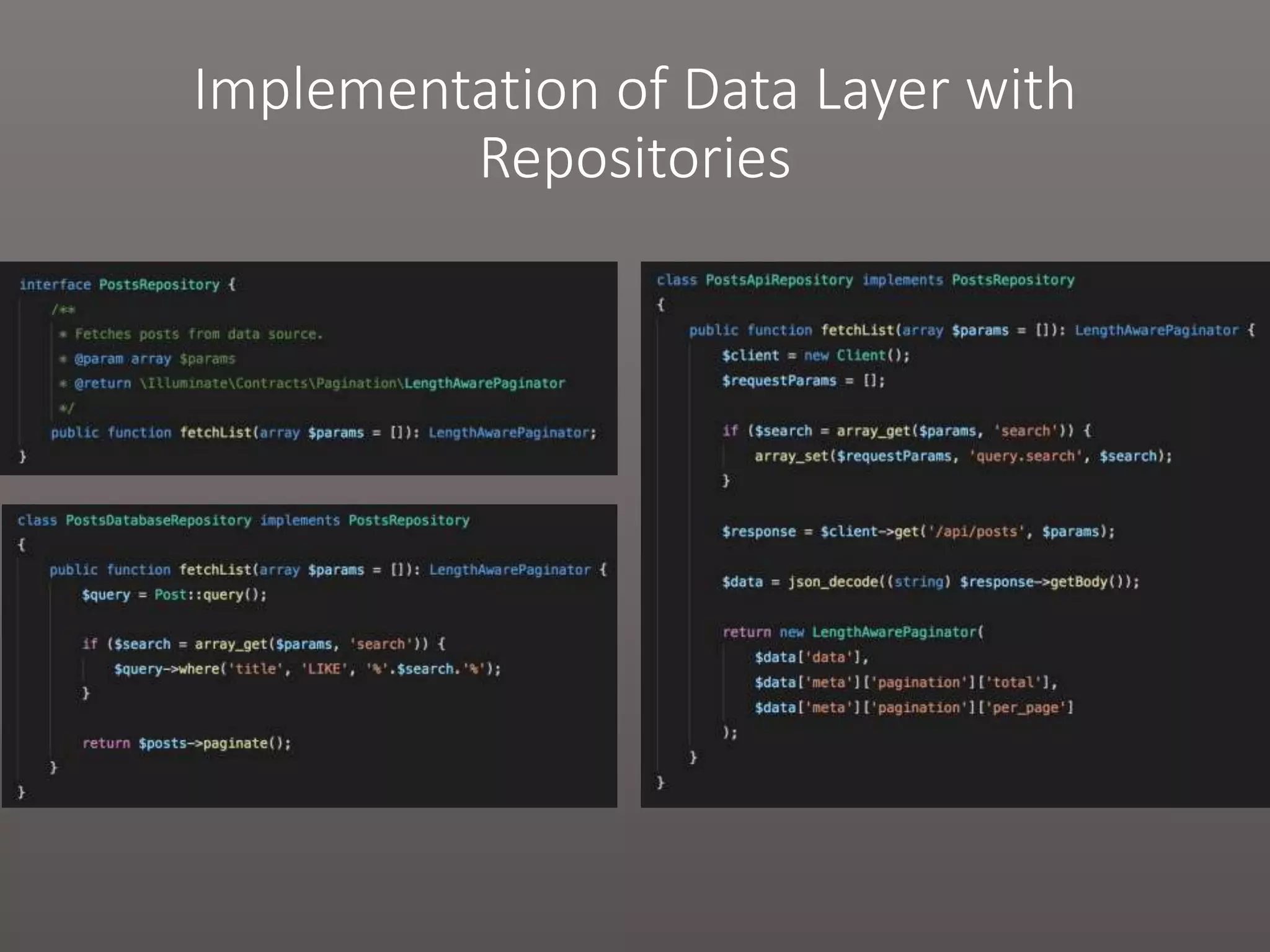
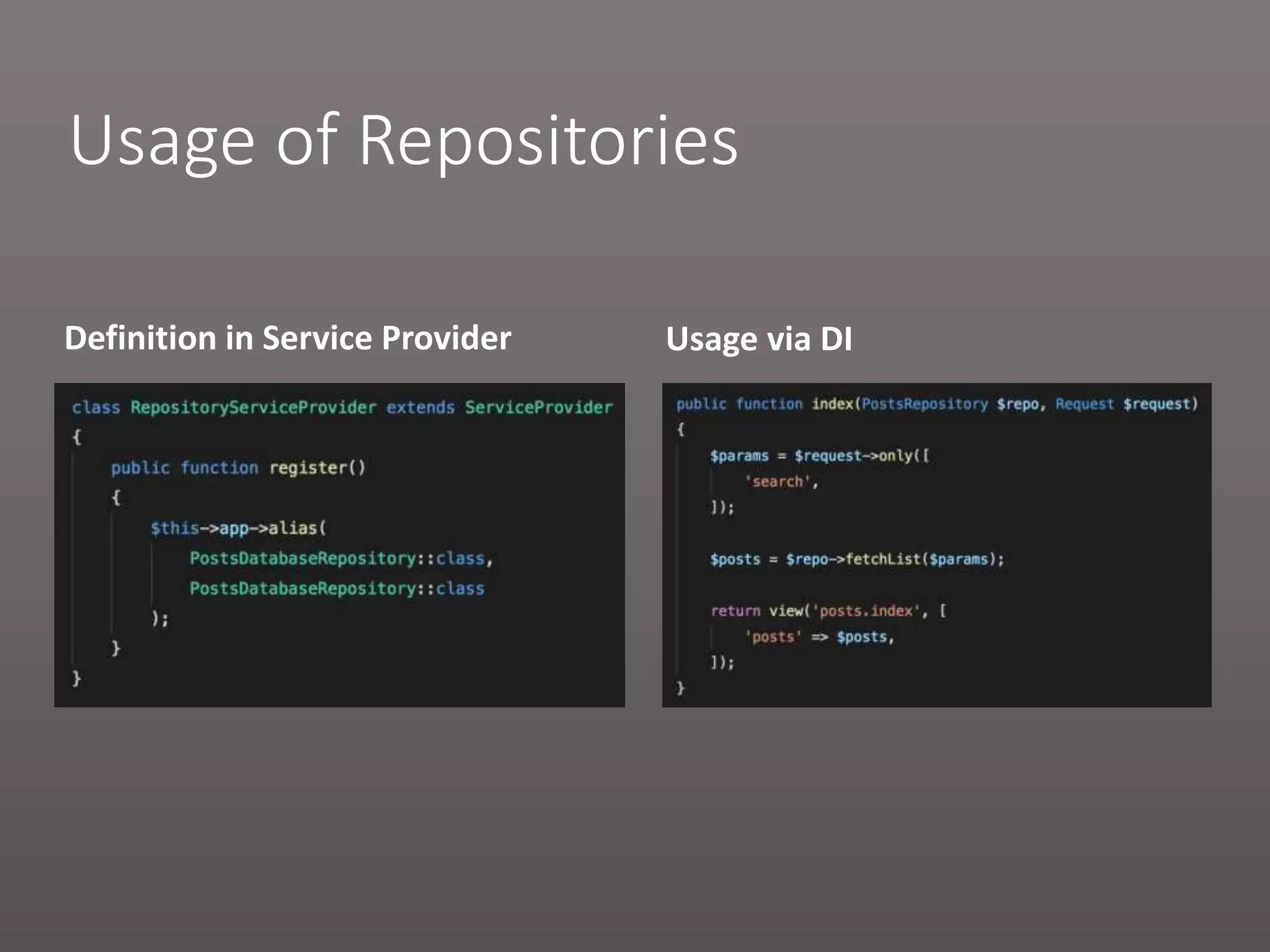
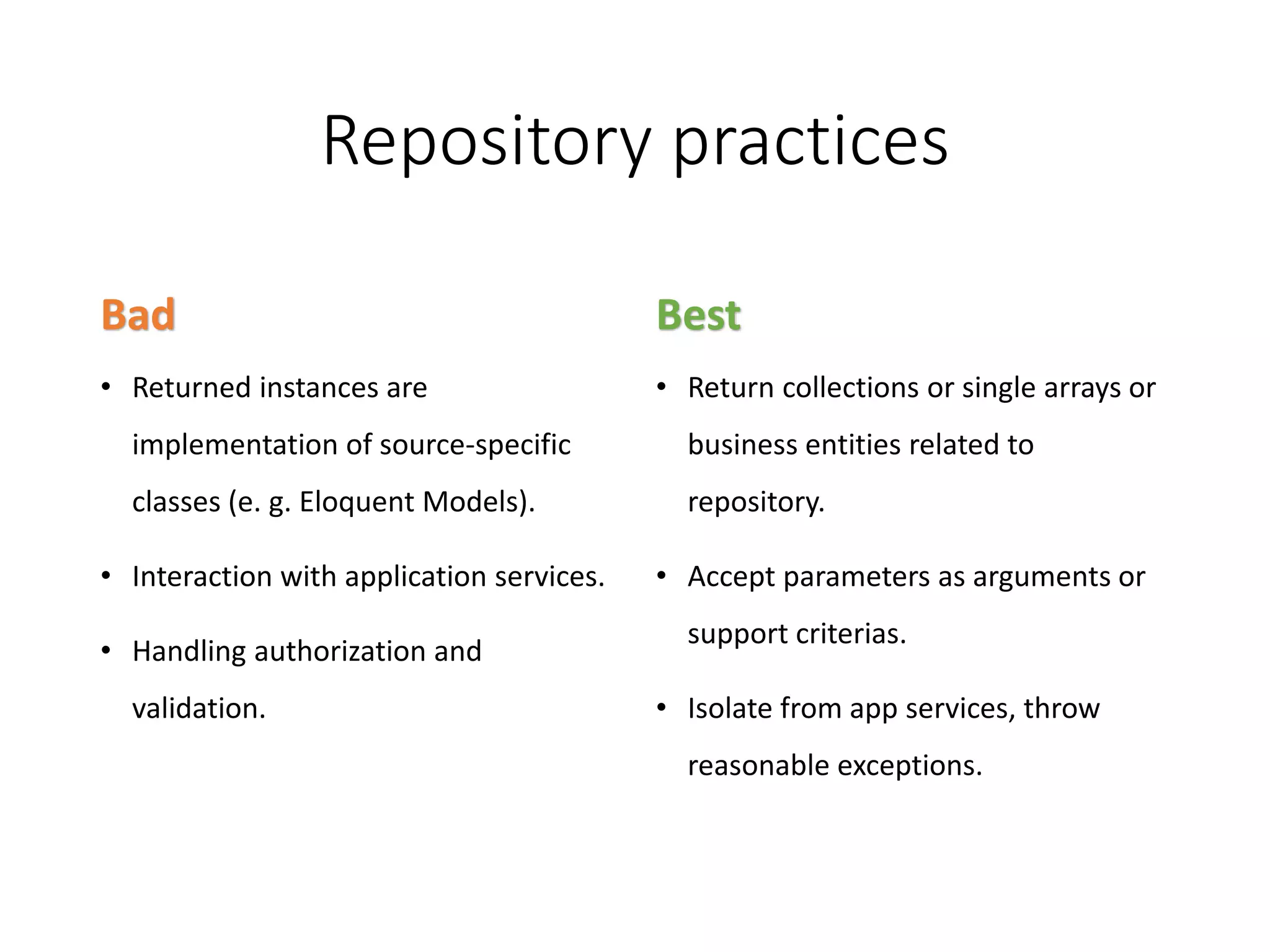
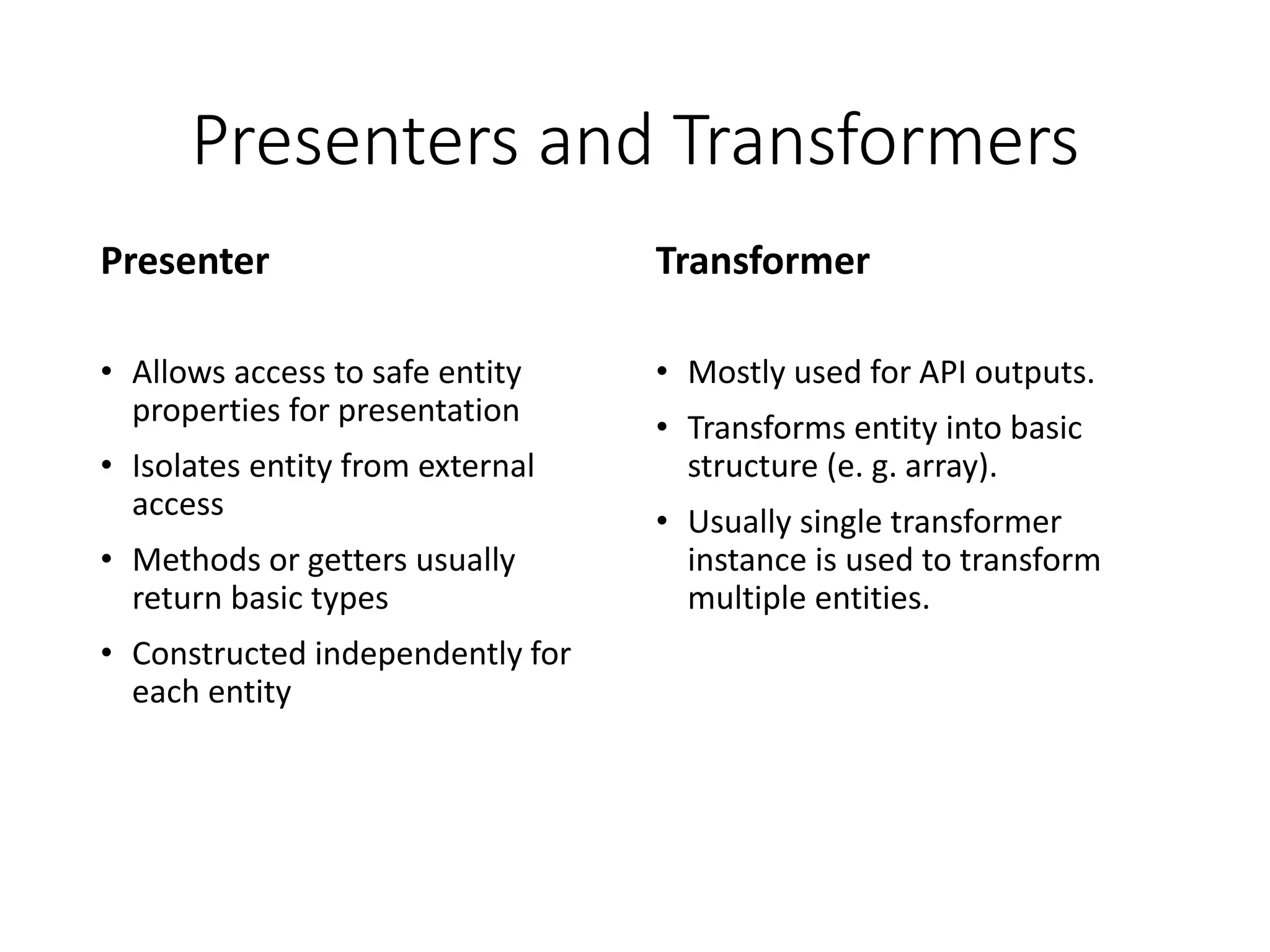
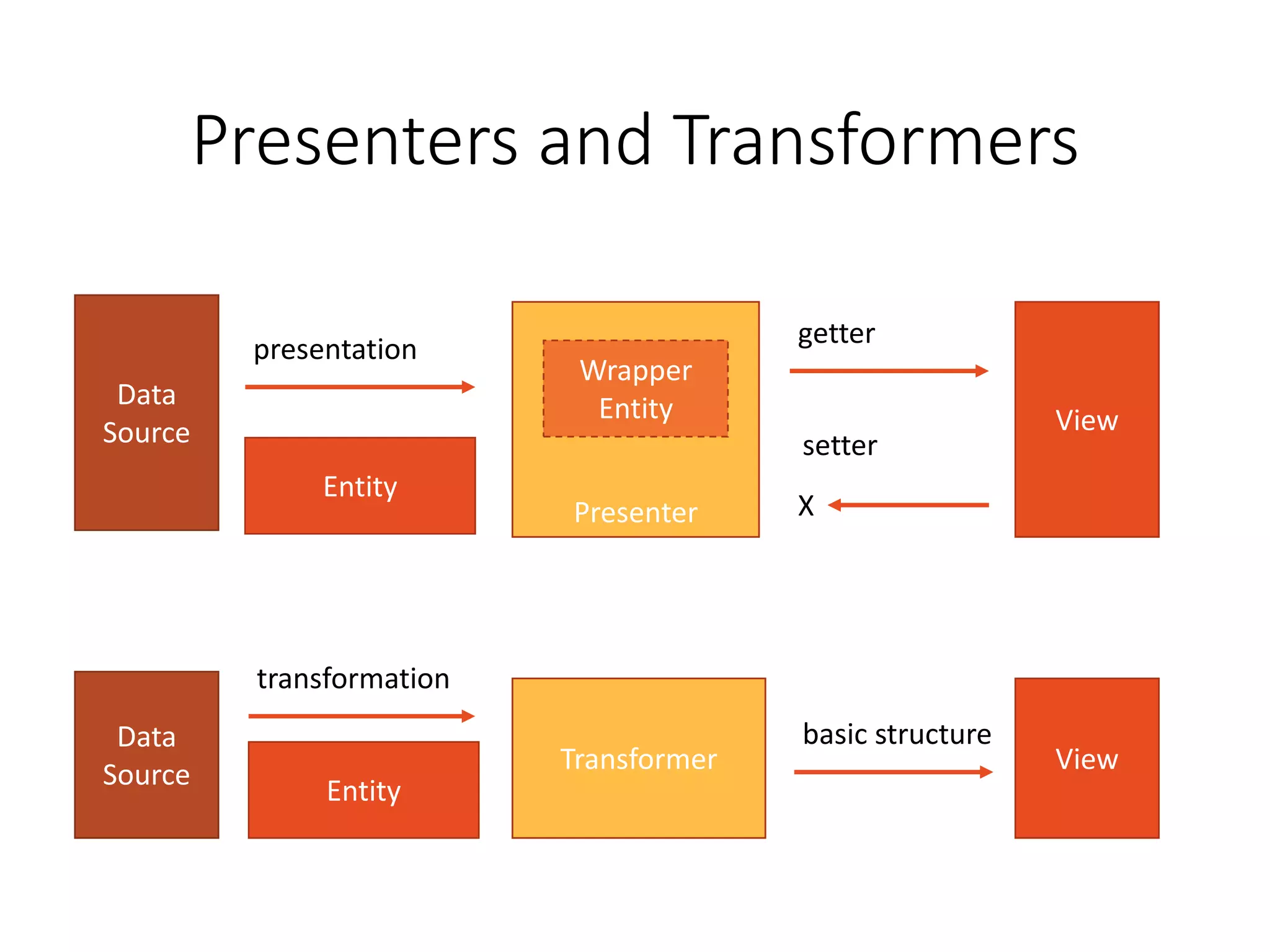
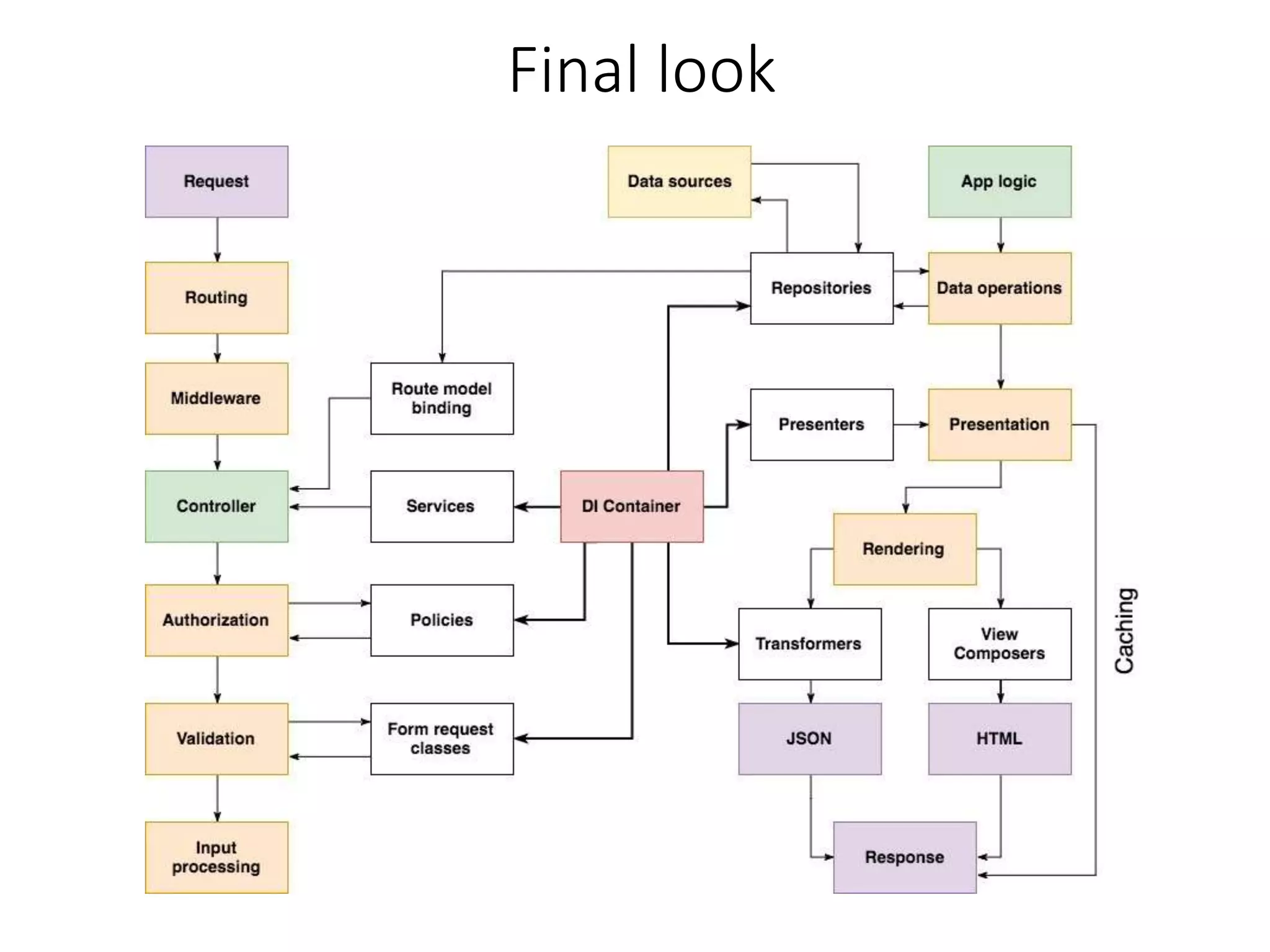
The document provides a historical overview of PHP frameworks from 1995 to 2017, detailing their evolution and key components such as MVC architecture and Eloquent ORM. It discusses common issues with fat controllers and mixed logic, as well as best practices for using repositories and presenters to improve code quality and maintainability. Additionally, it highlights offerings in Laravel 5.5, including transformers and auto presenters for data handling.