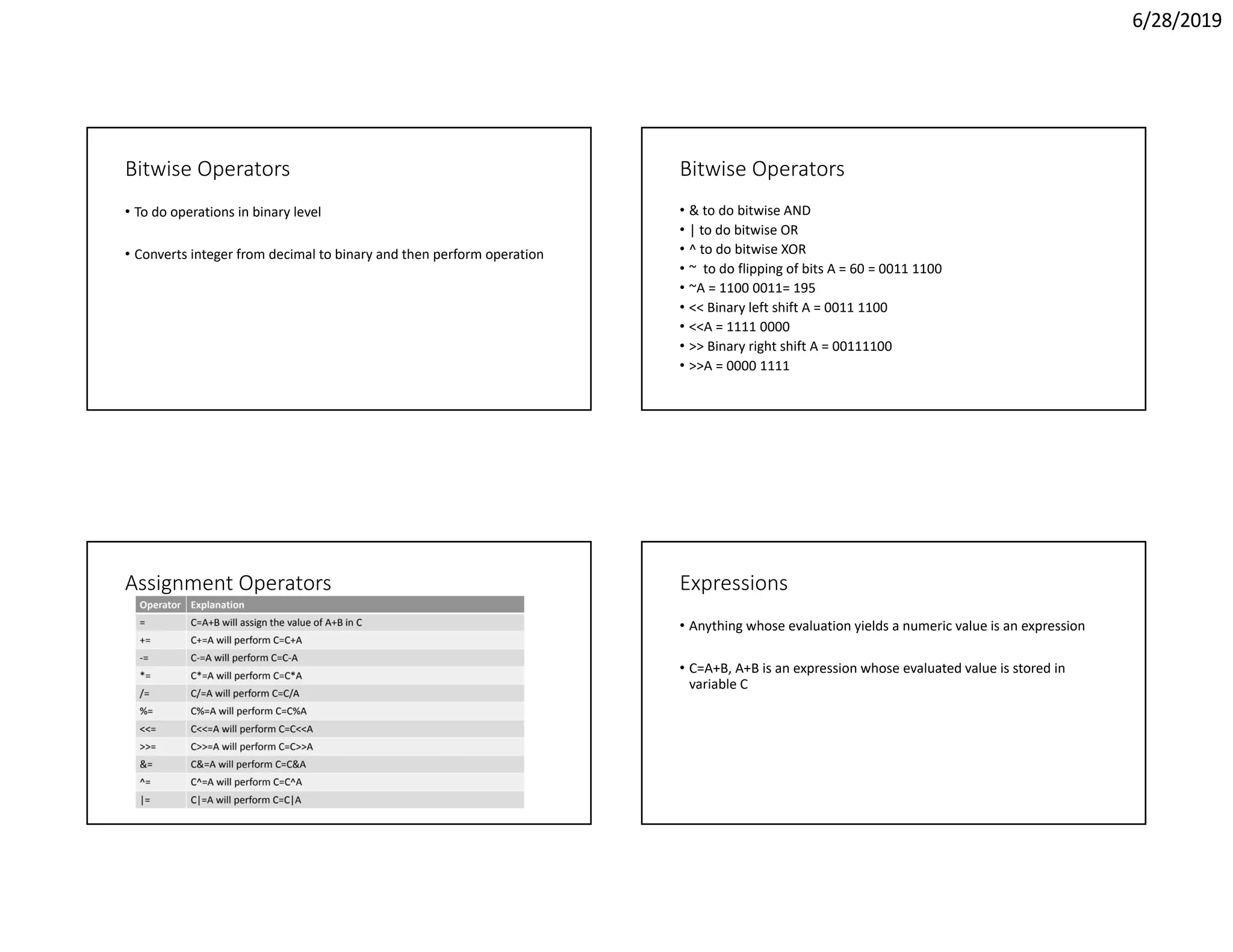
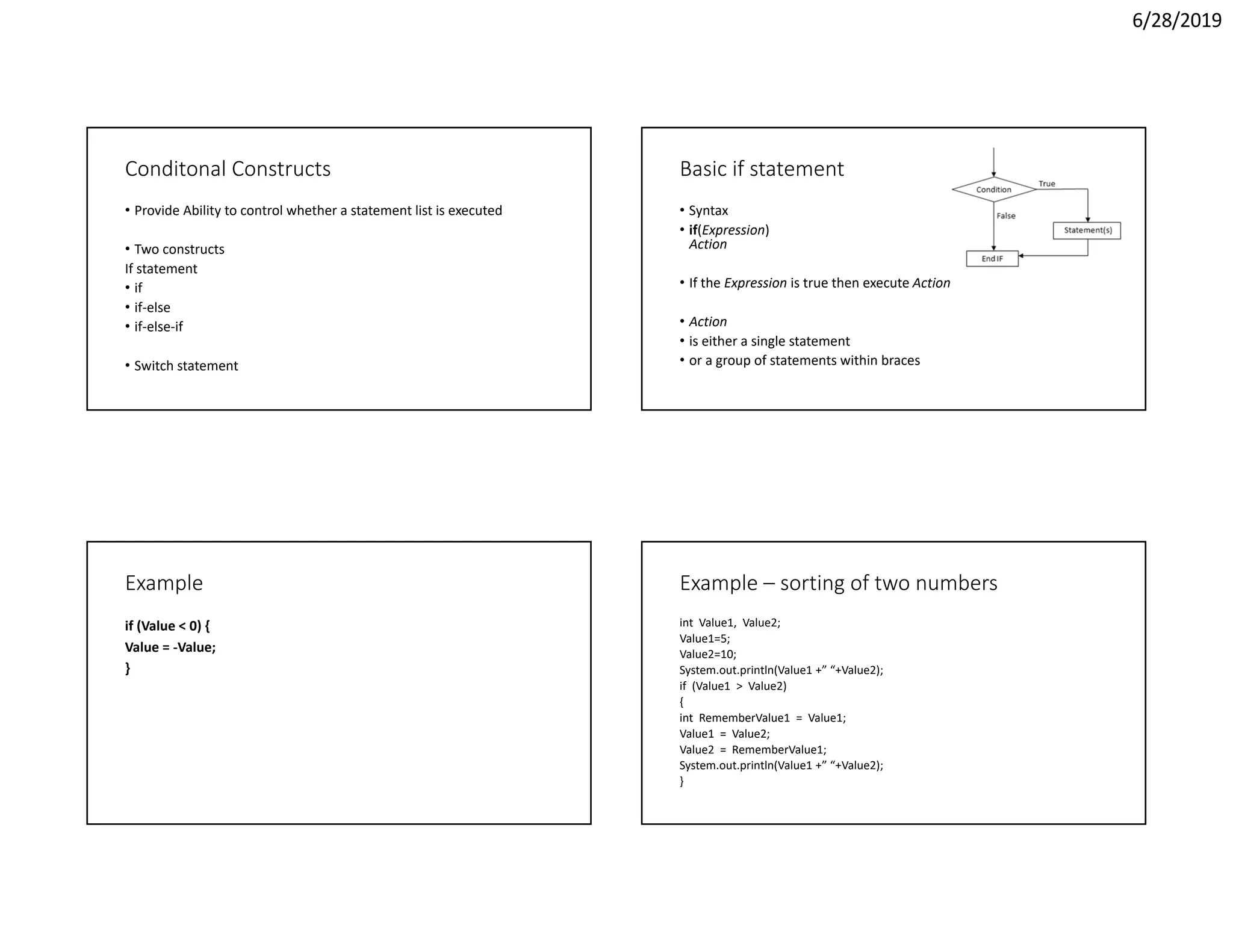
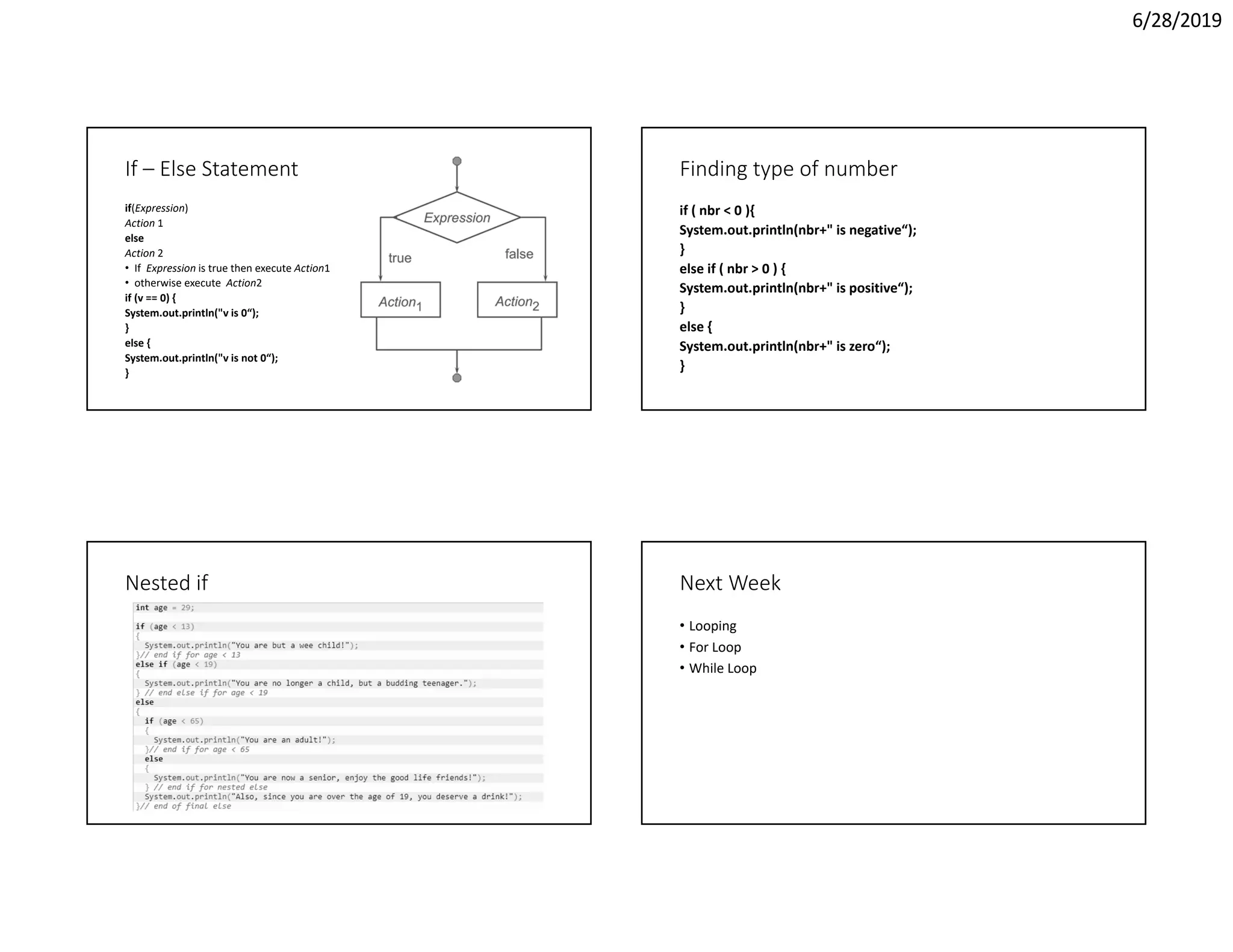
The document discusses object oriented programming concepts including operators, control statements, and conditional constructs. It covers various arithmetic, relational, logical, and bitwise operators in Java. It also explains the if-else conditional statement for controlling program flow based on conditions, including examples of using if-else statements to sort numbers and determine if a number is positive, negative, or zero.