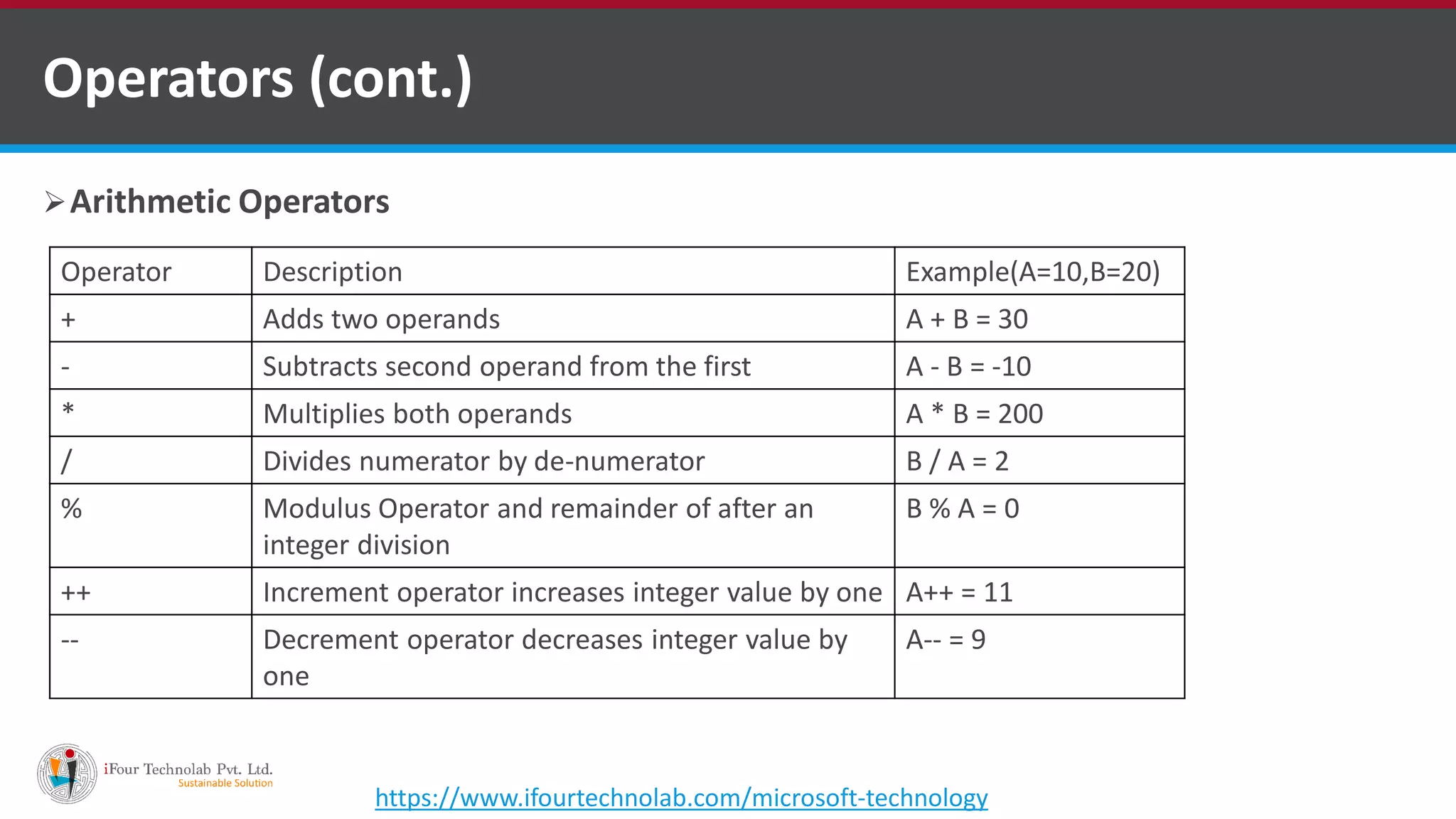
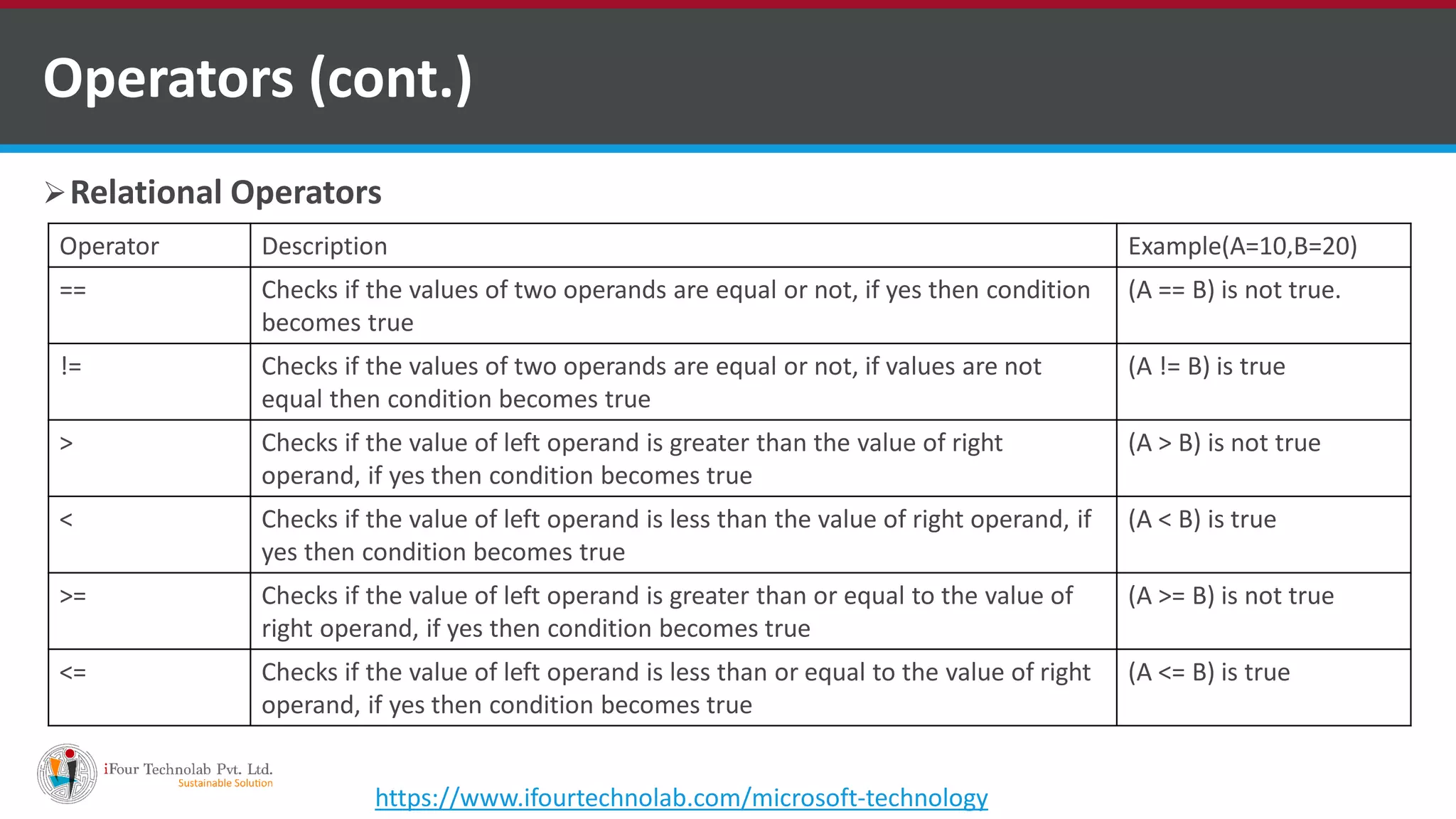
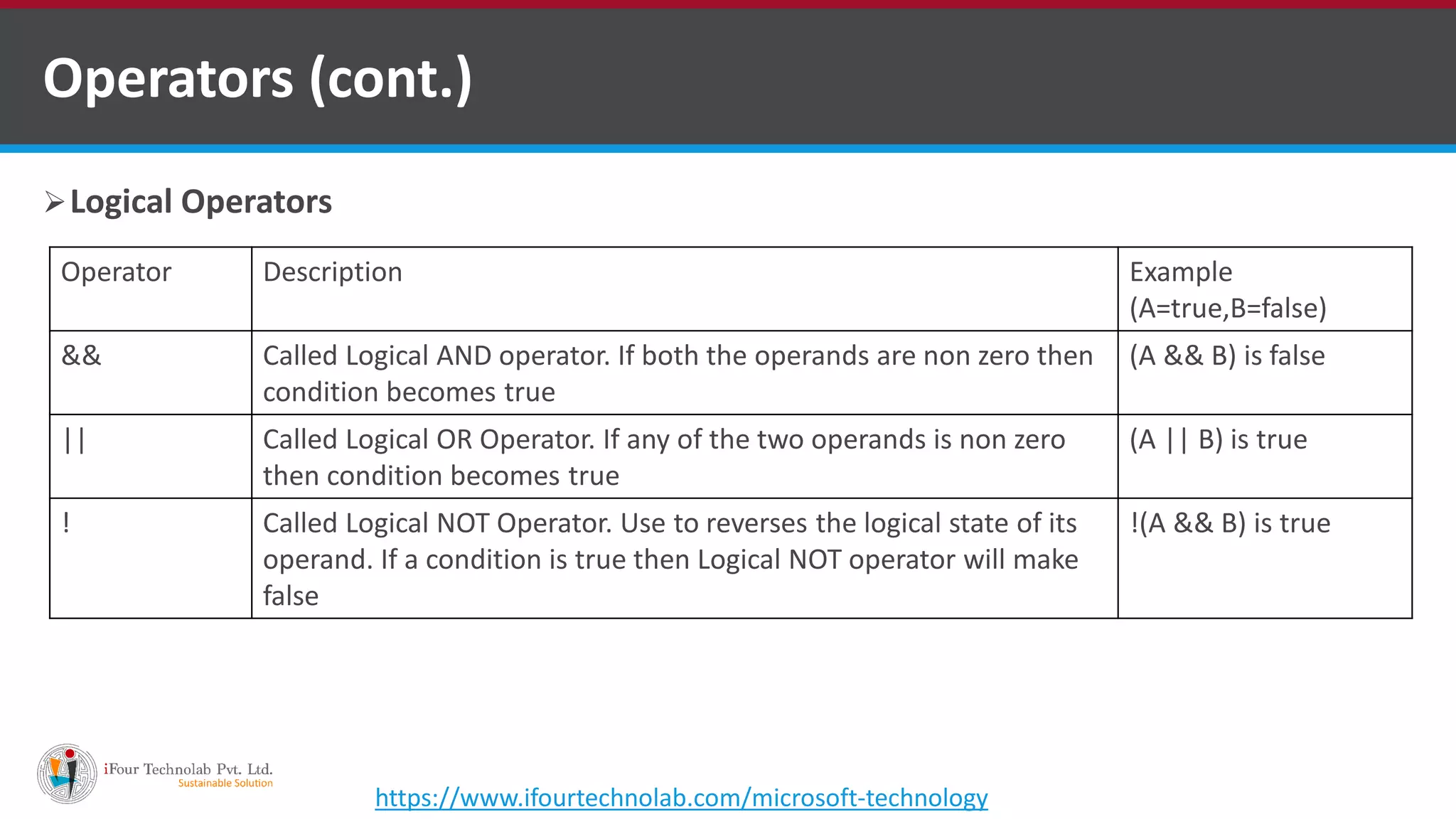
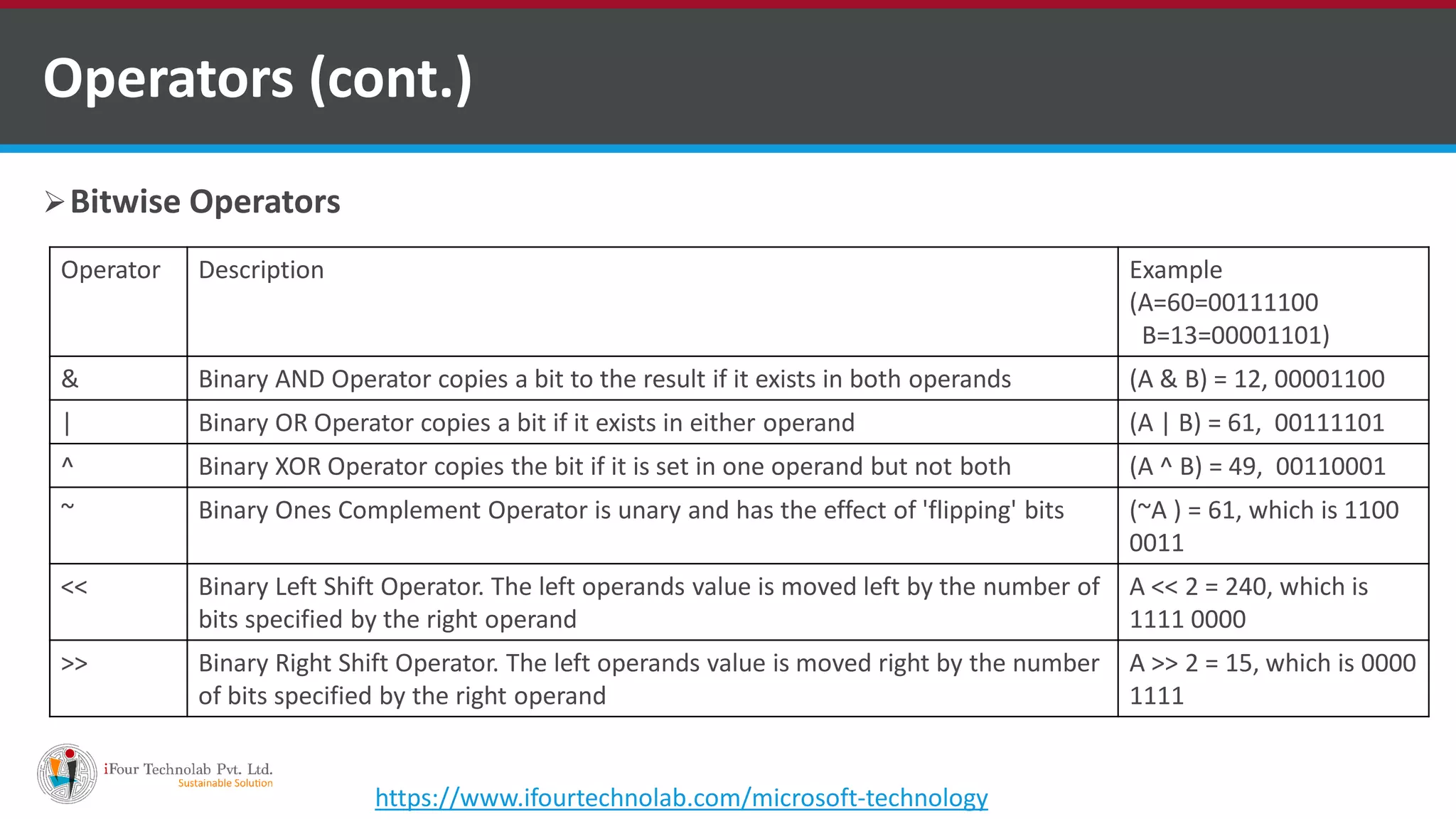
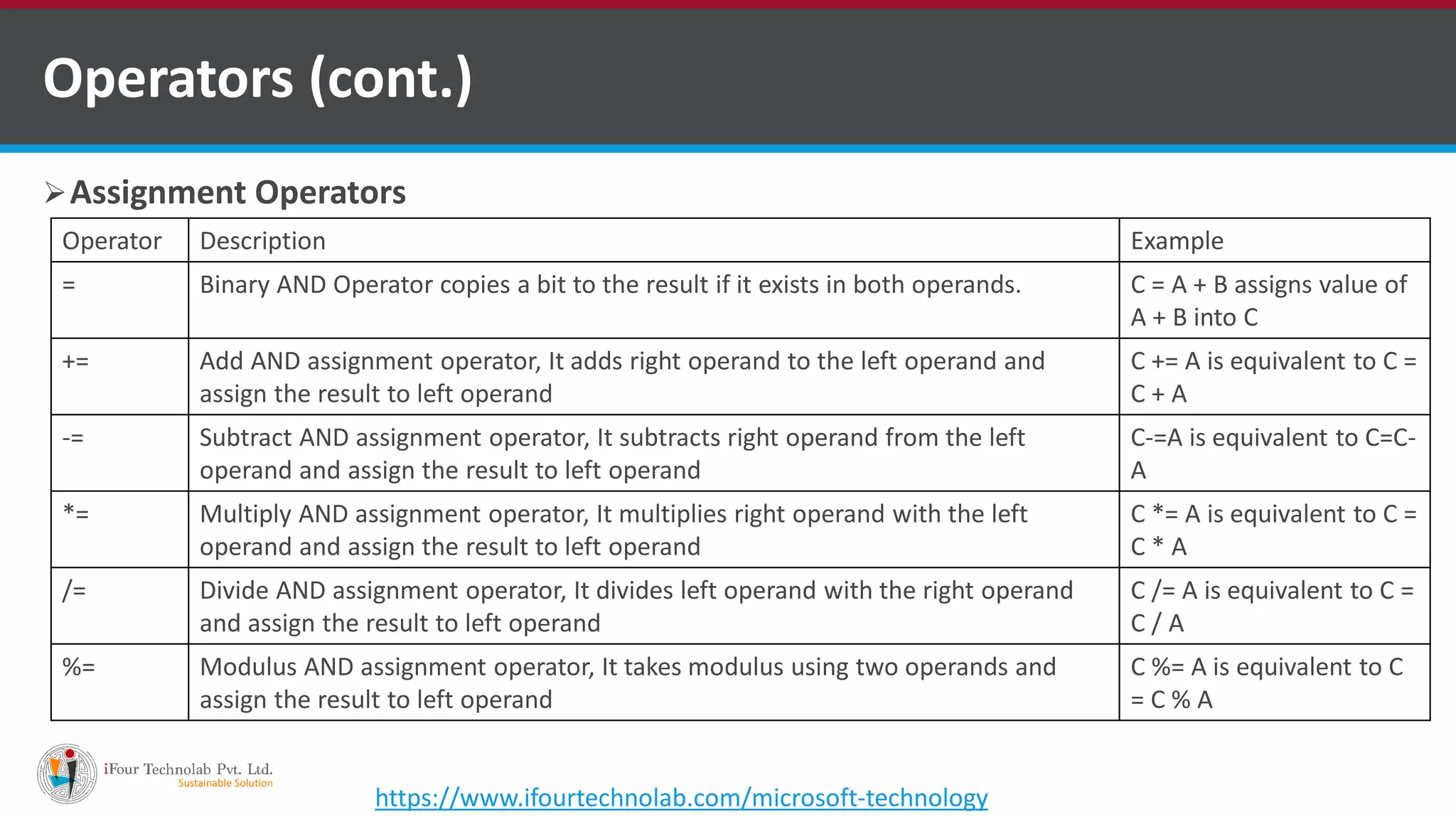
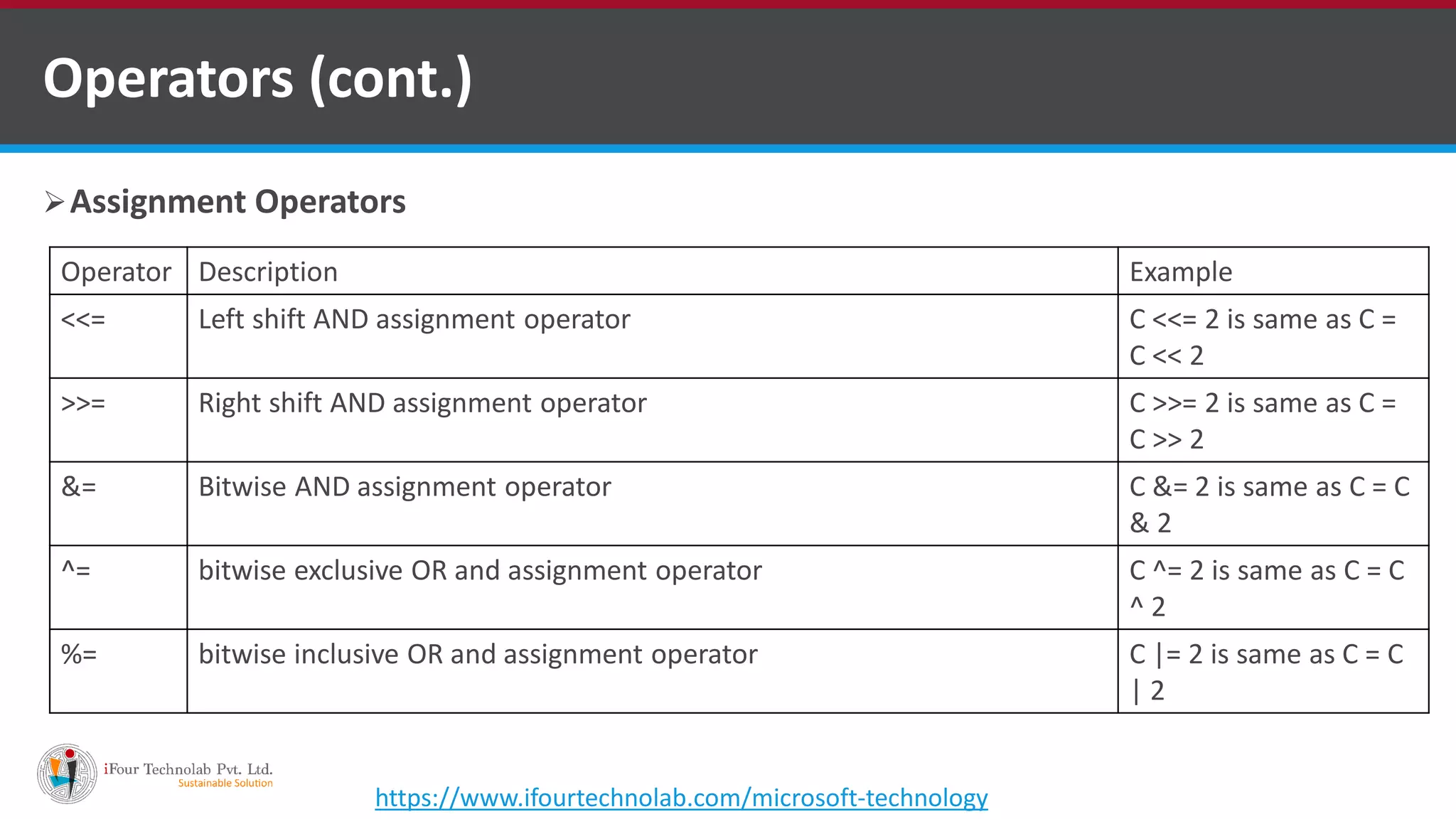
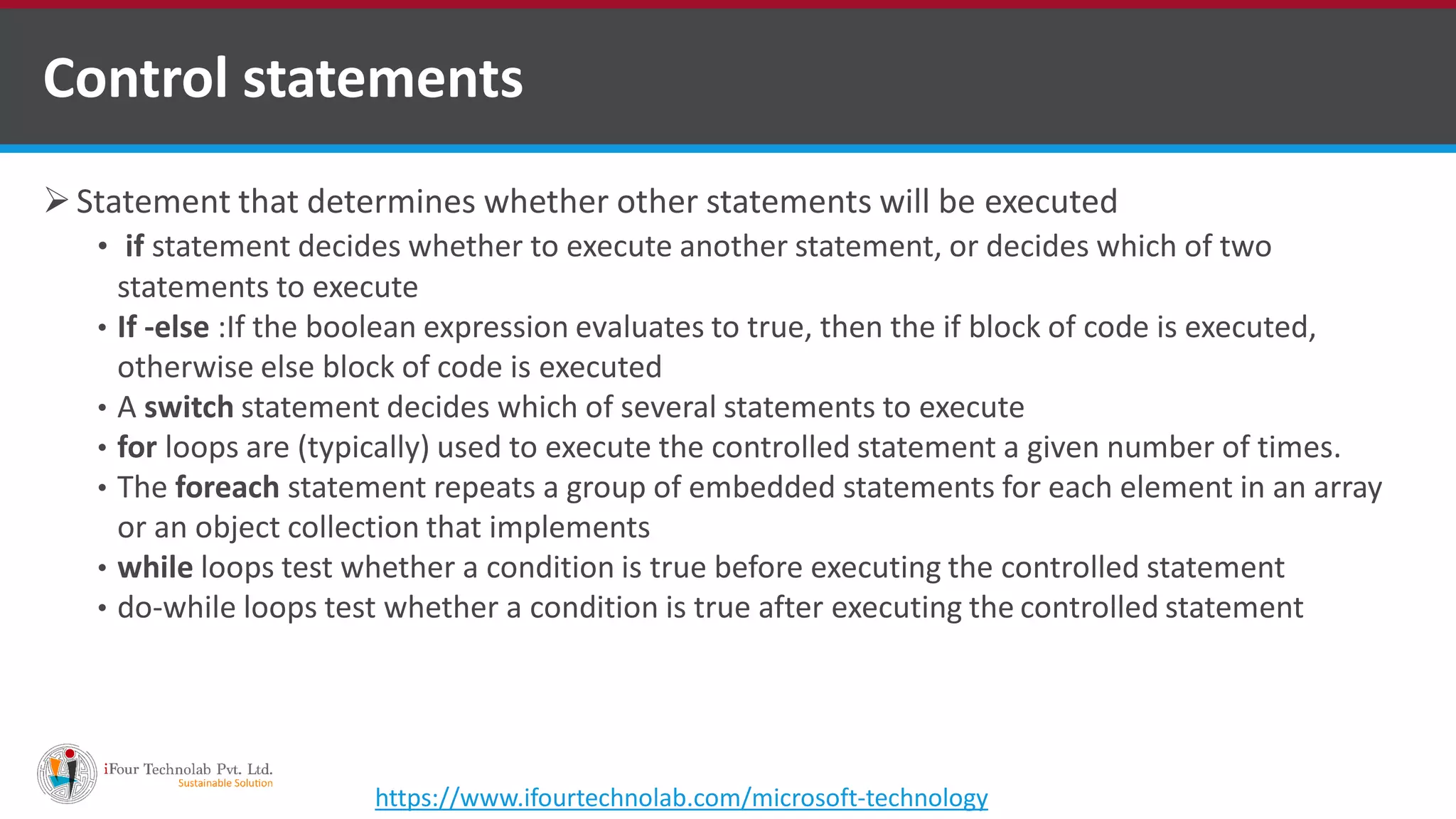
The document provides an overview of various types of operators in C#, including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, and miscellaneous operators. It explains how these operators function through examples and discusses control statements and access modifiers in C#. Additionally, it describes the accessibility levels of public, private, protected, internal, and protected internal members.