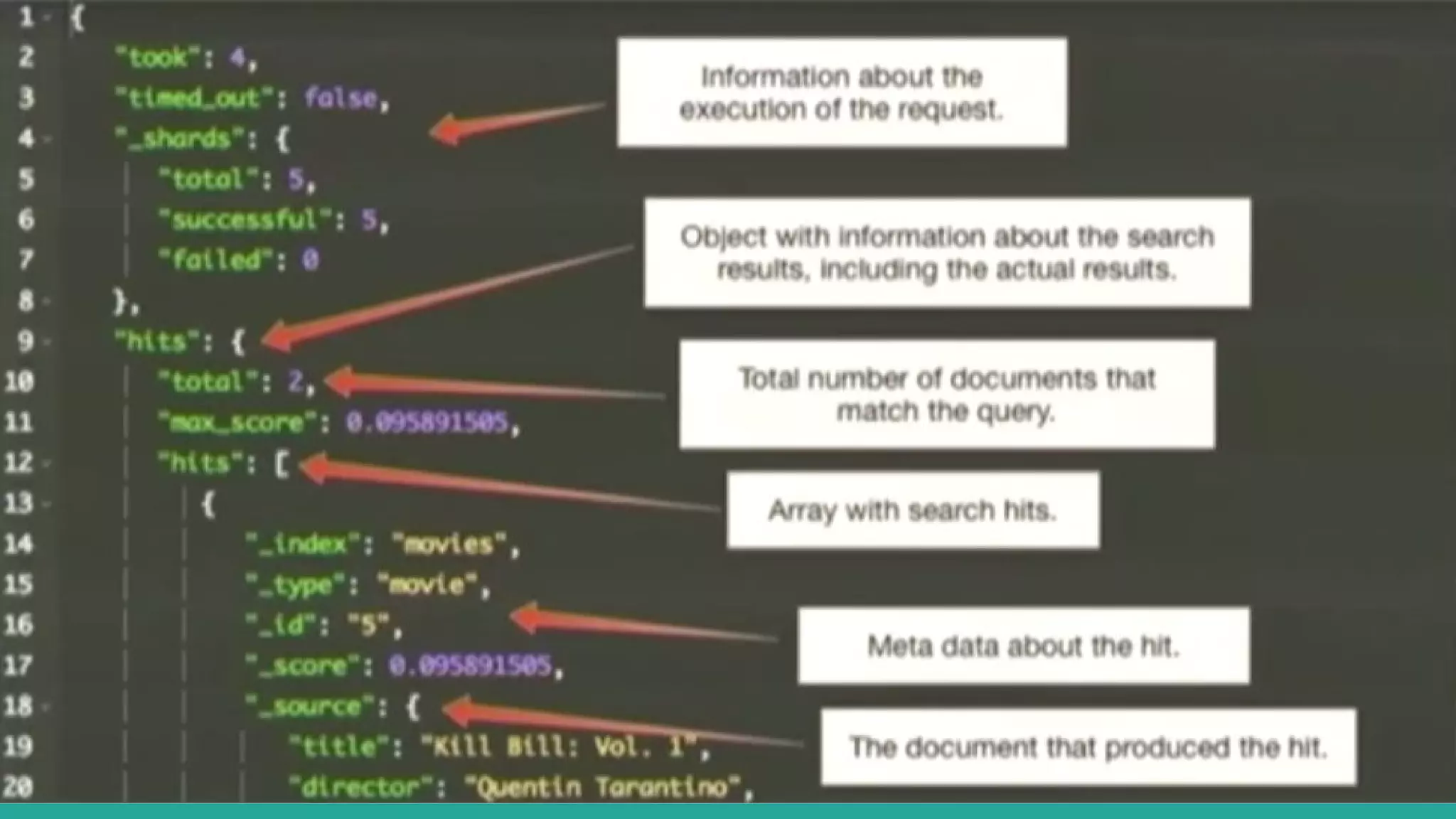
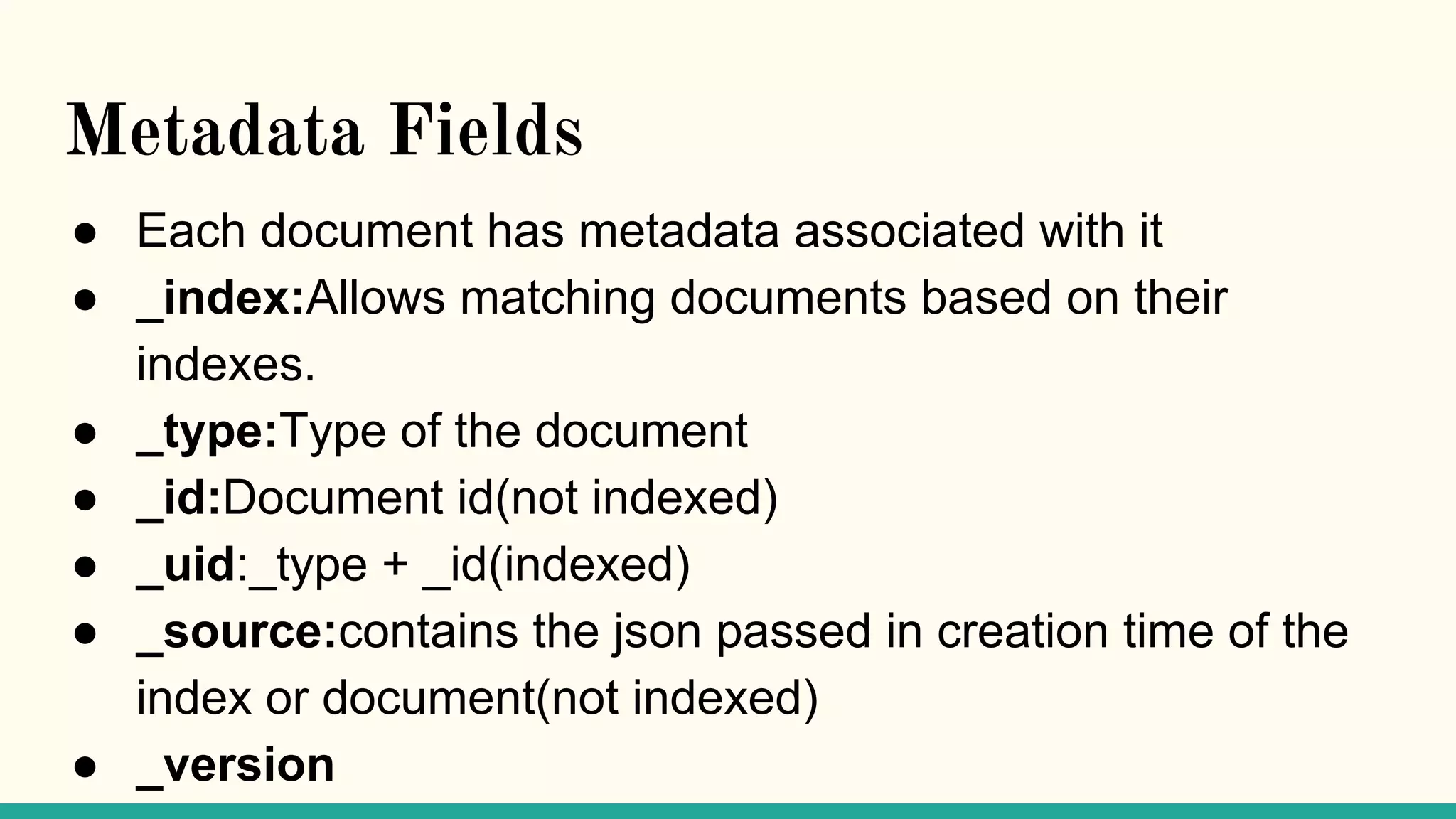
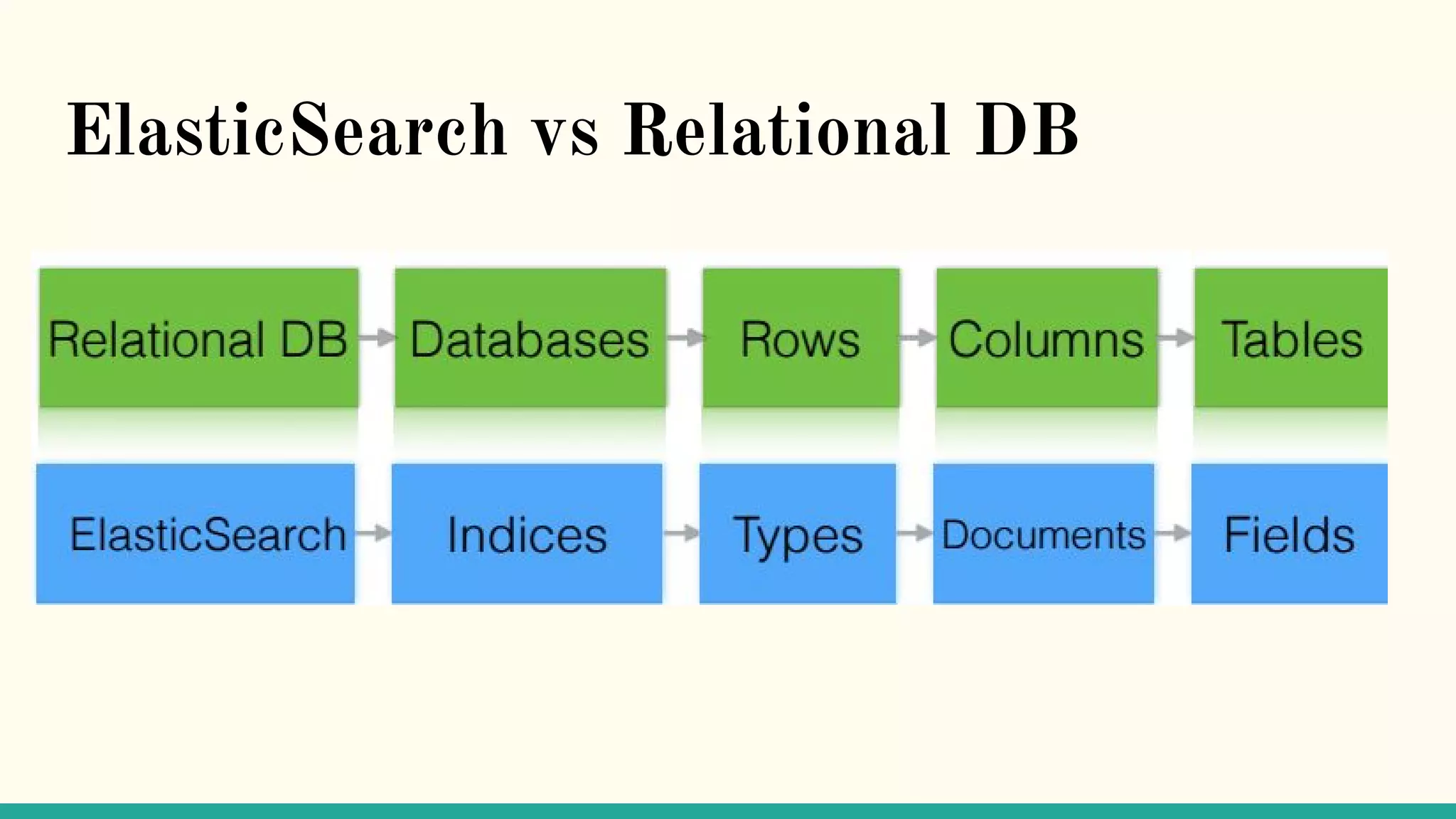
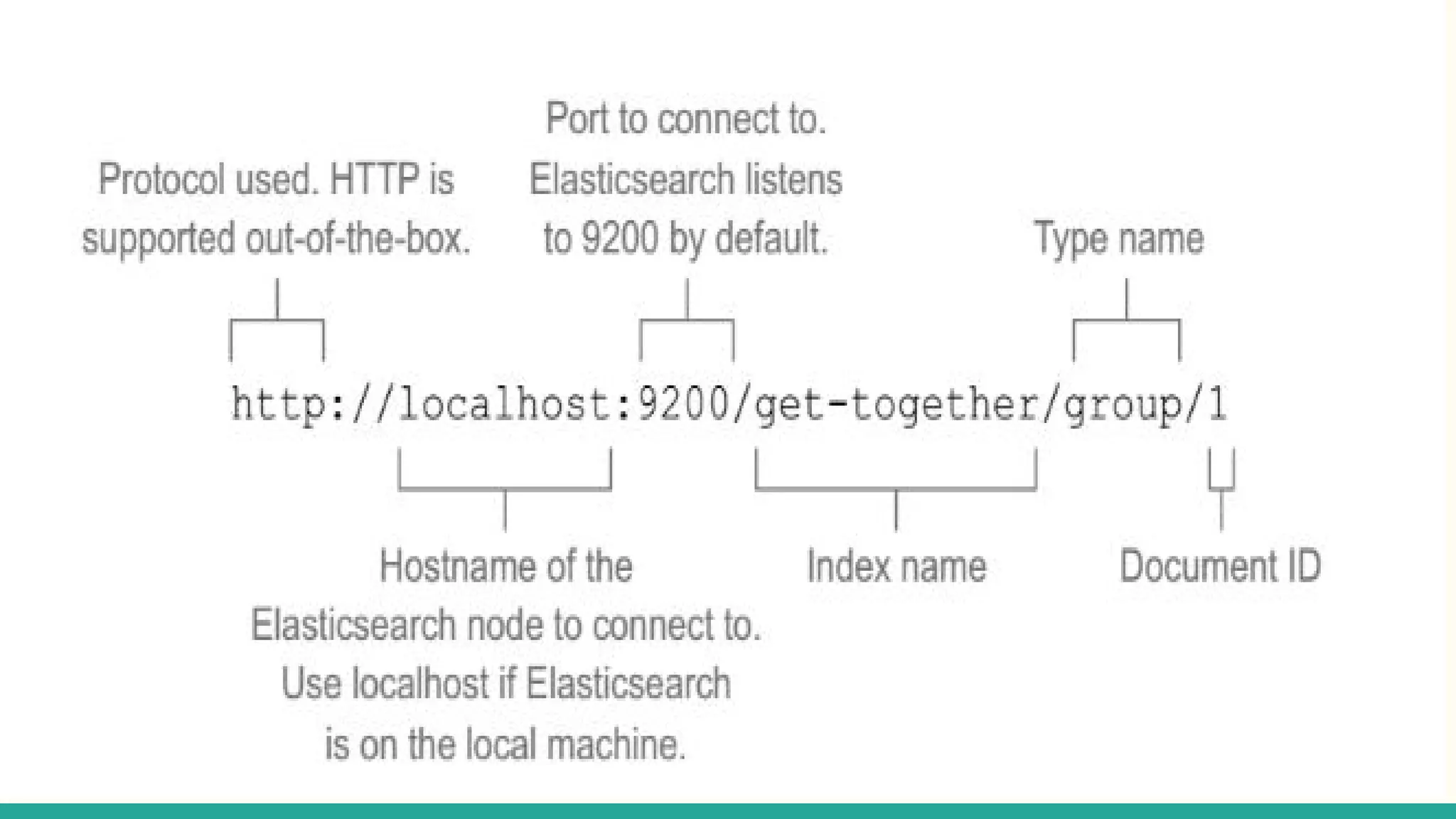
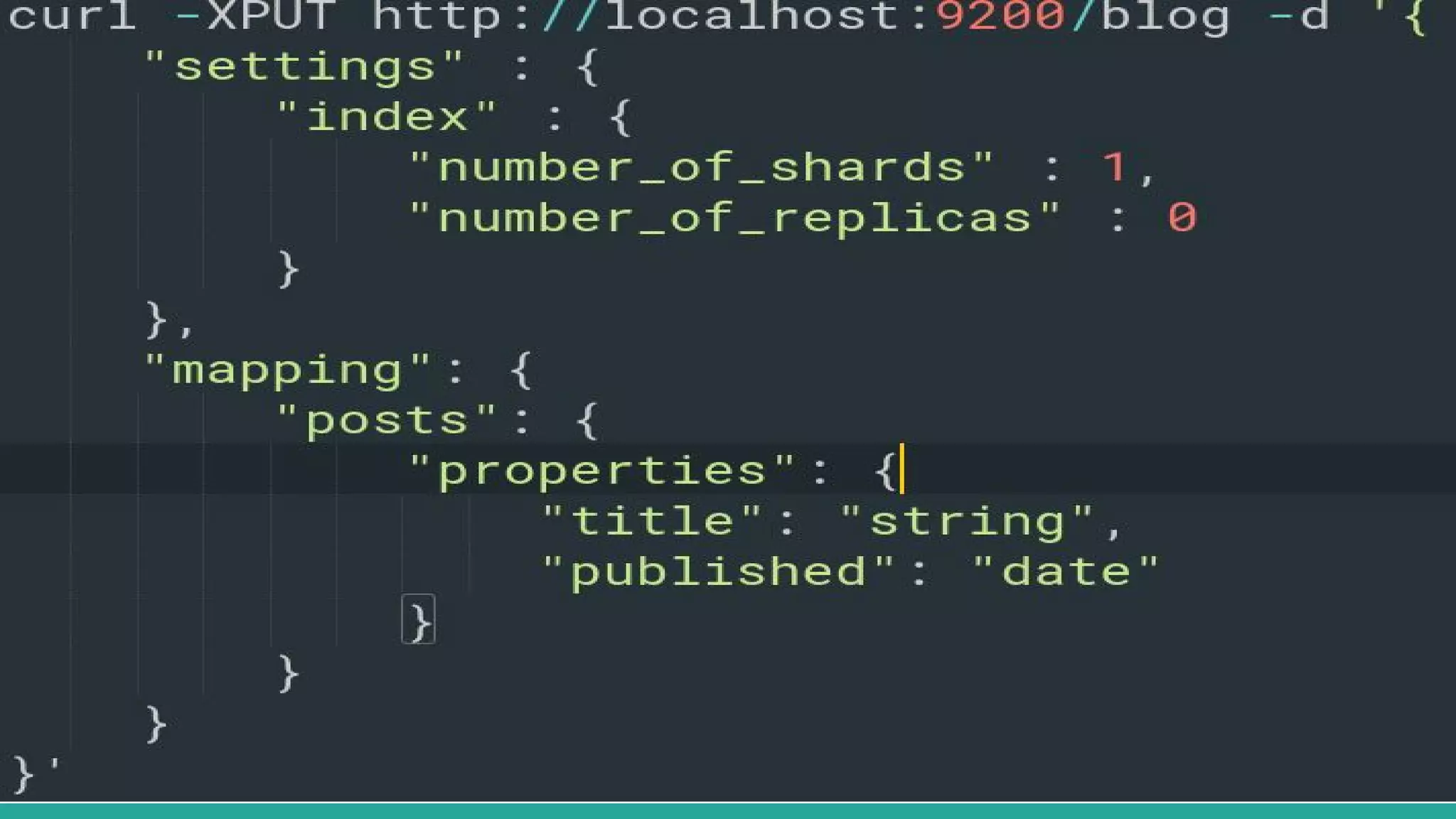
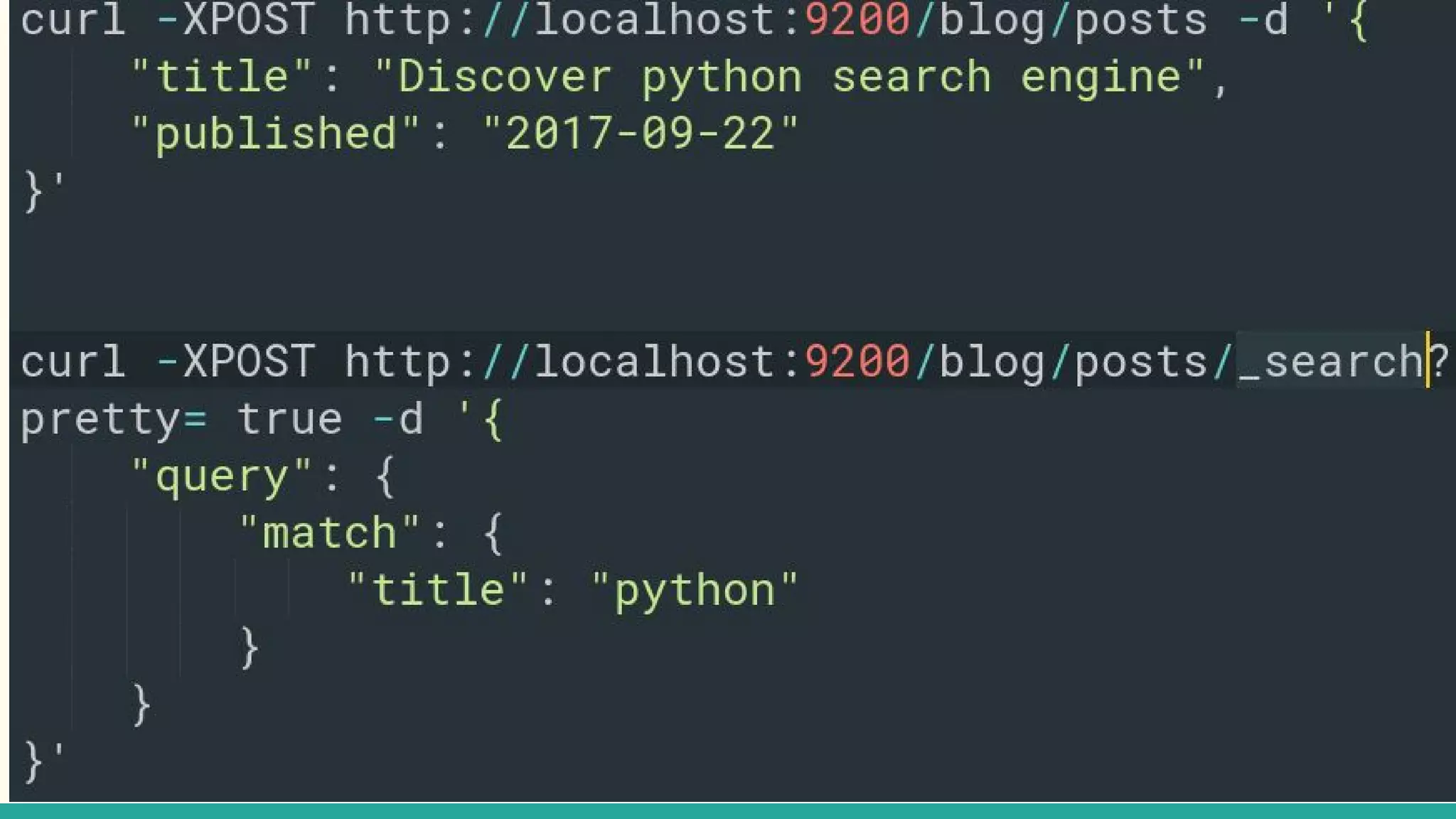
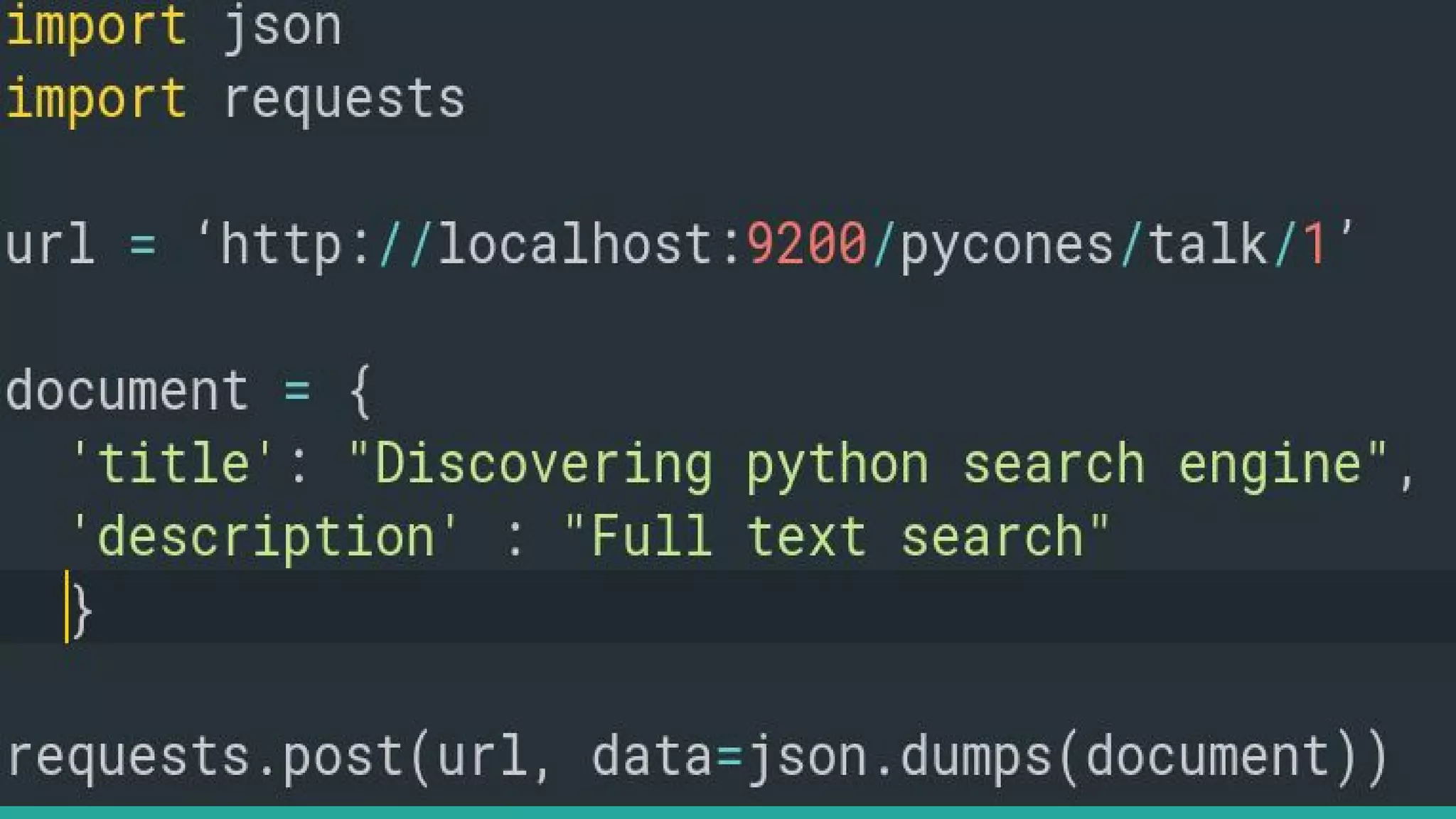
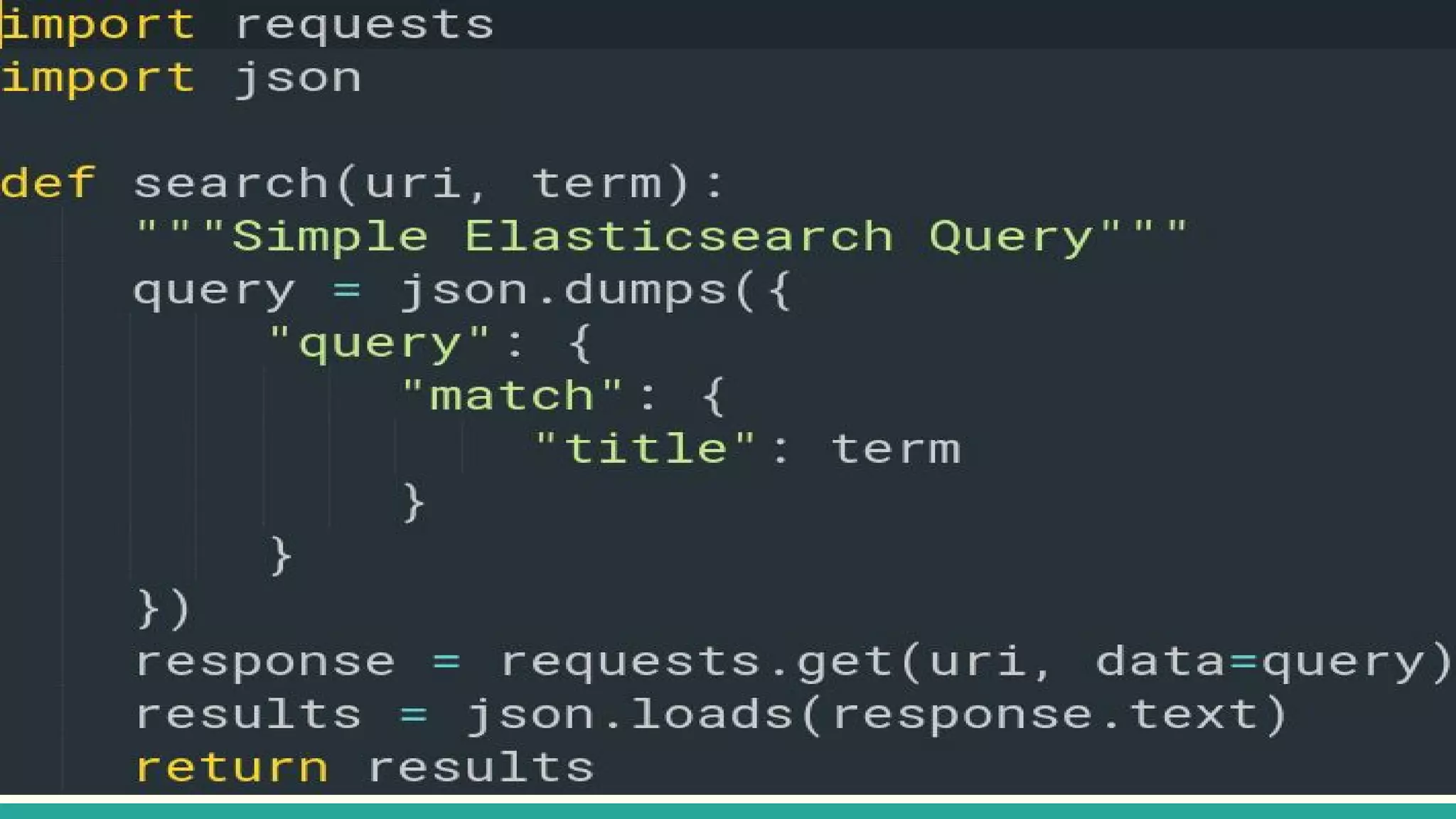
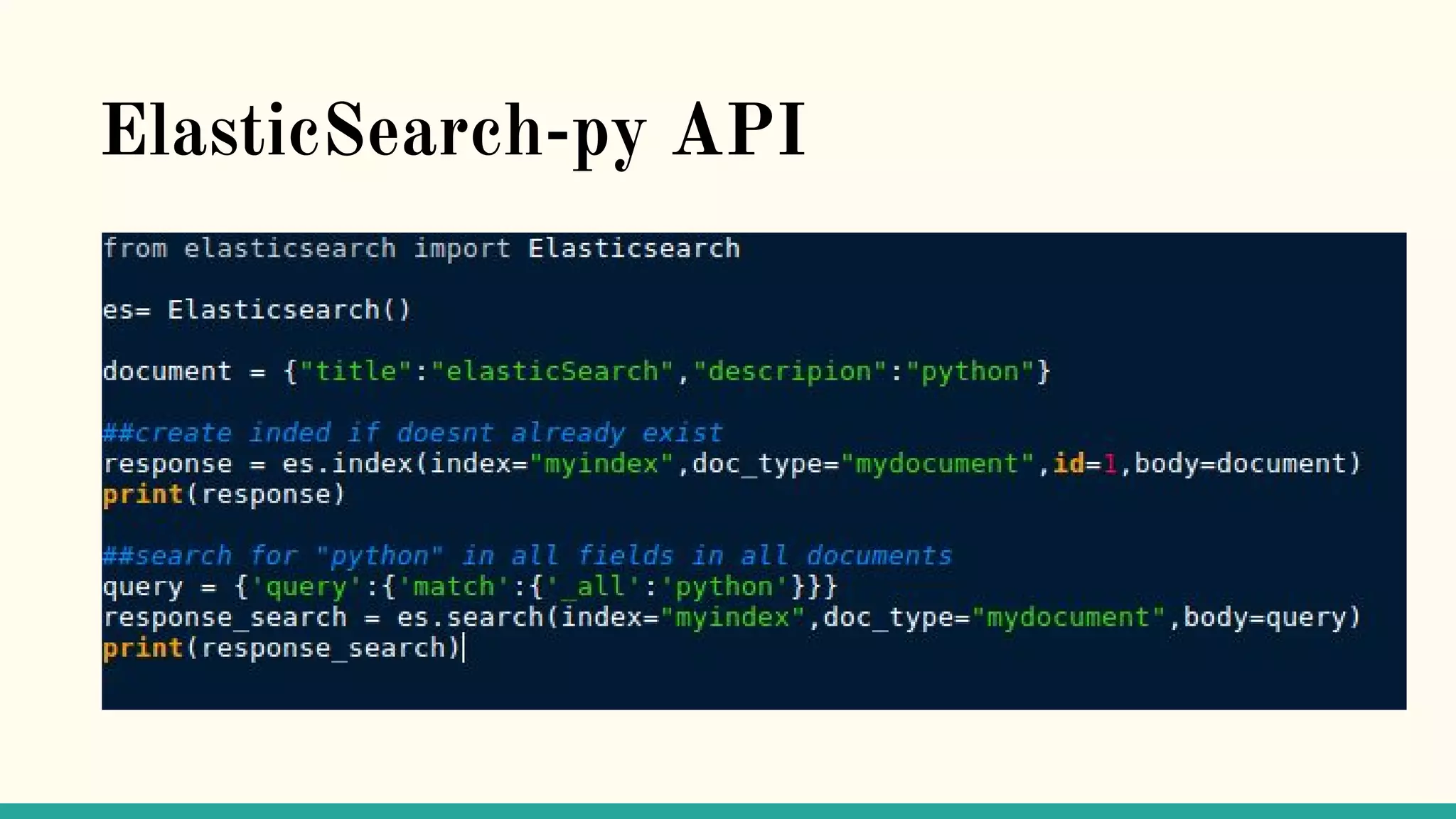
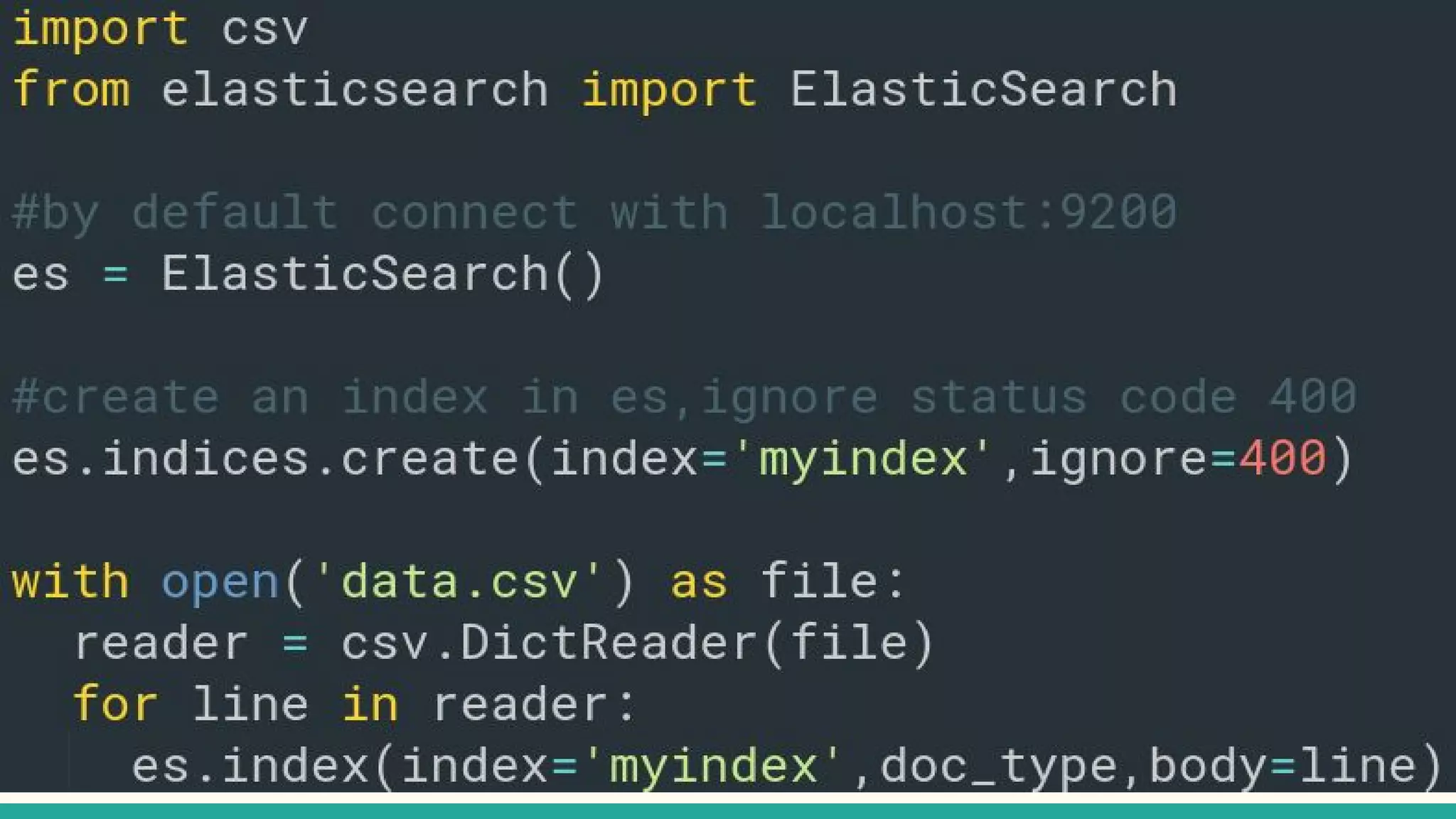
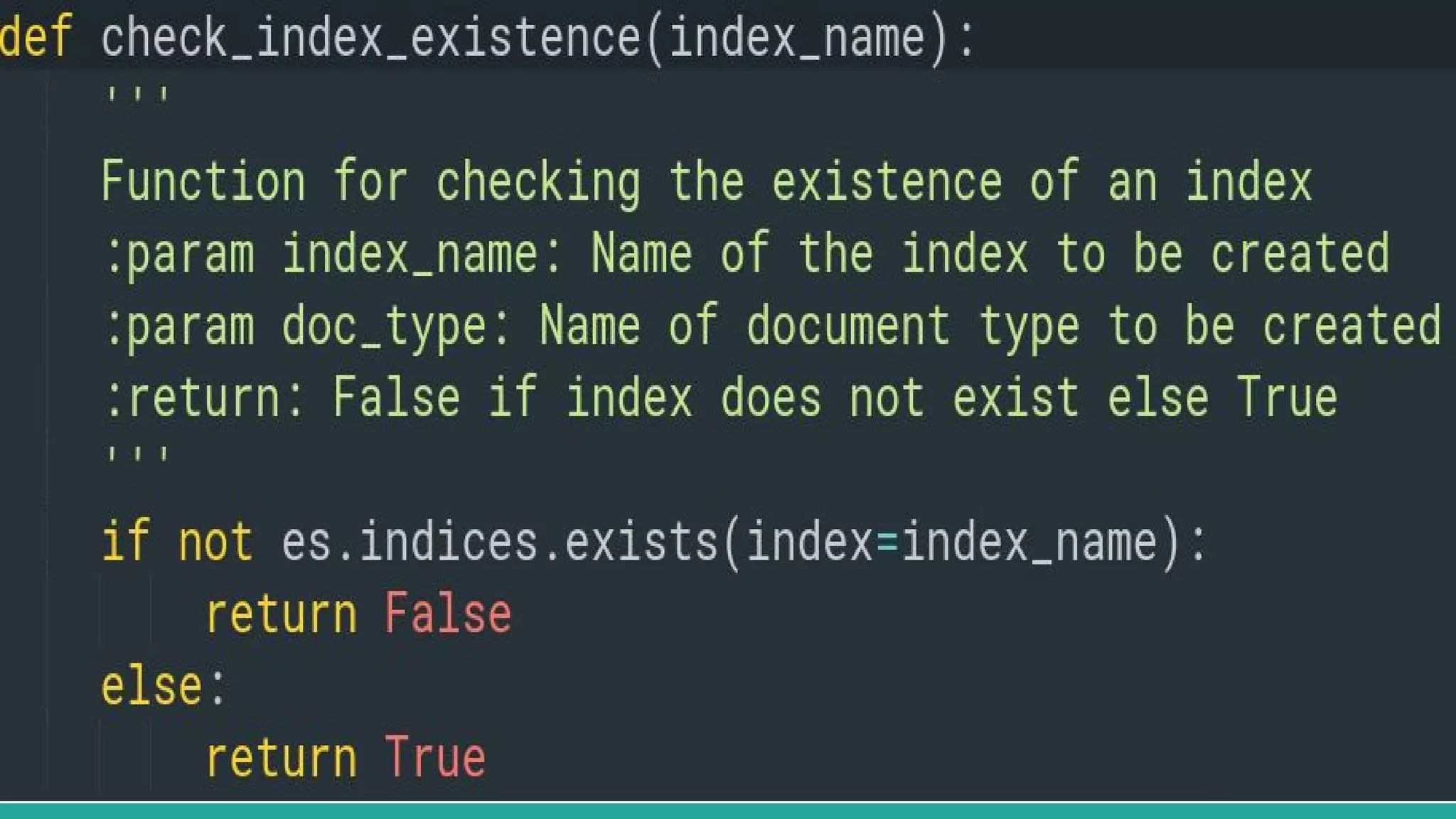
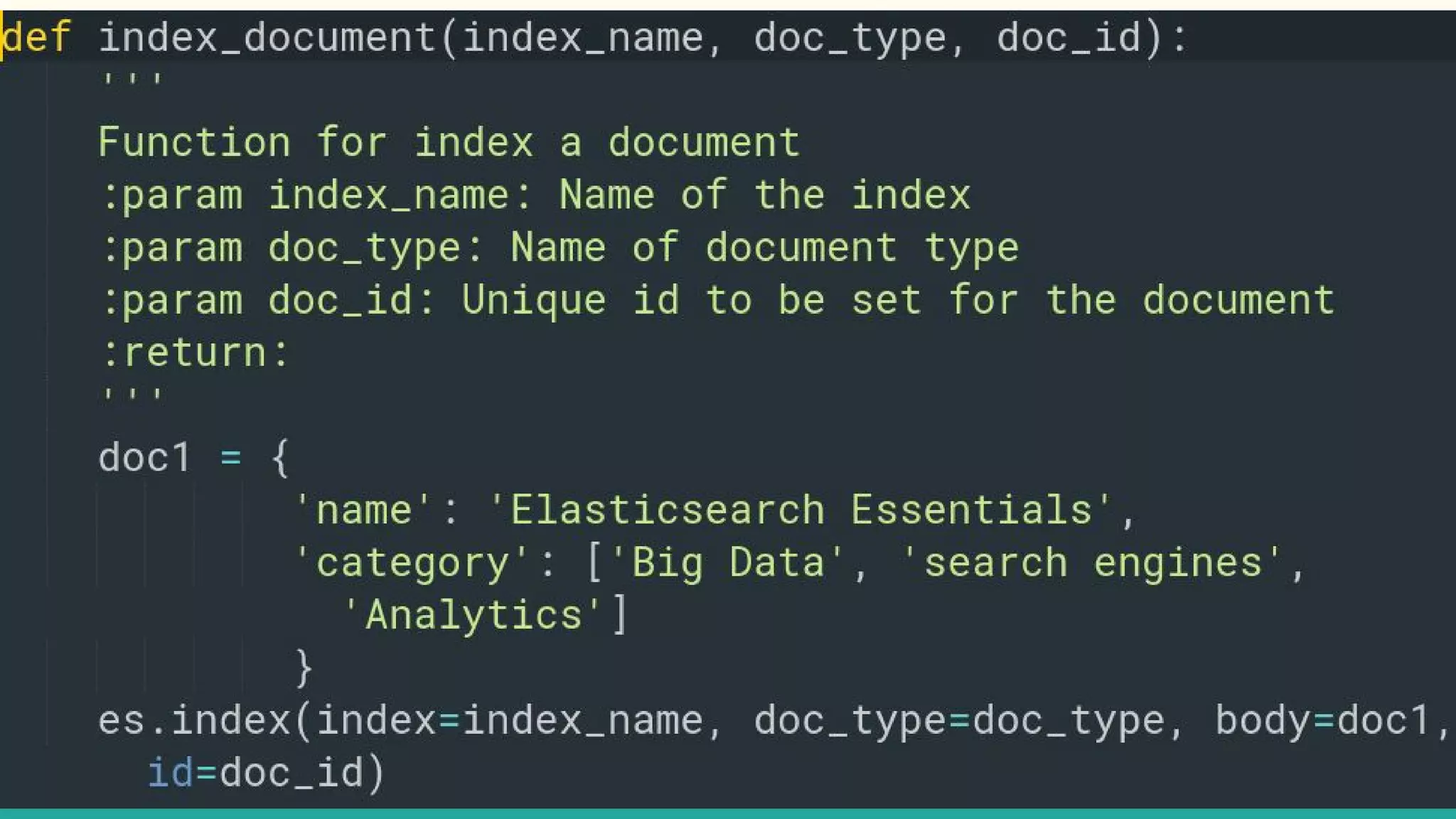
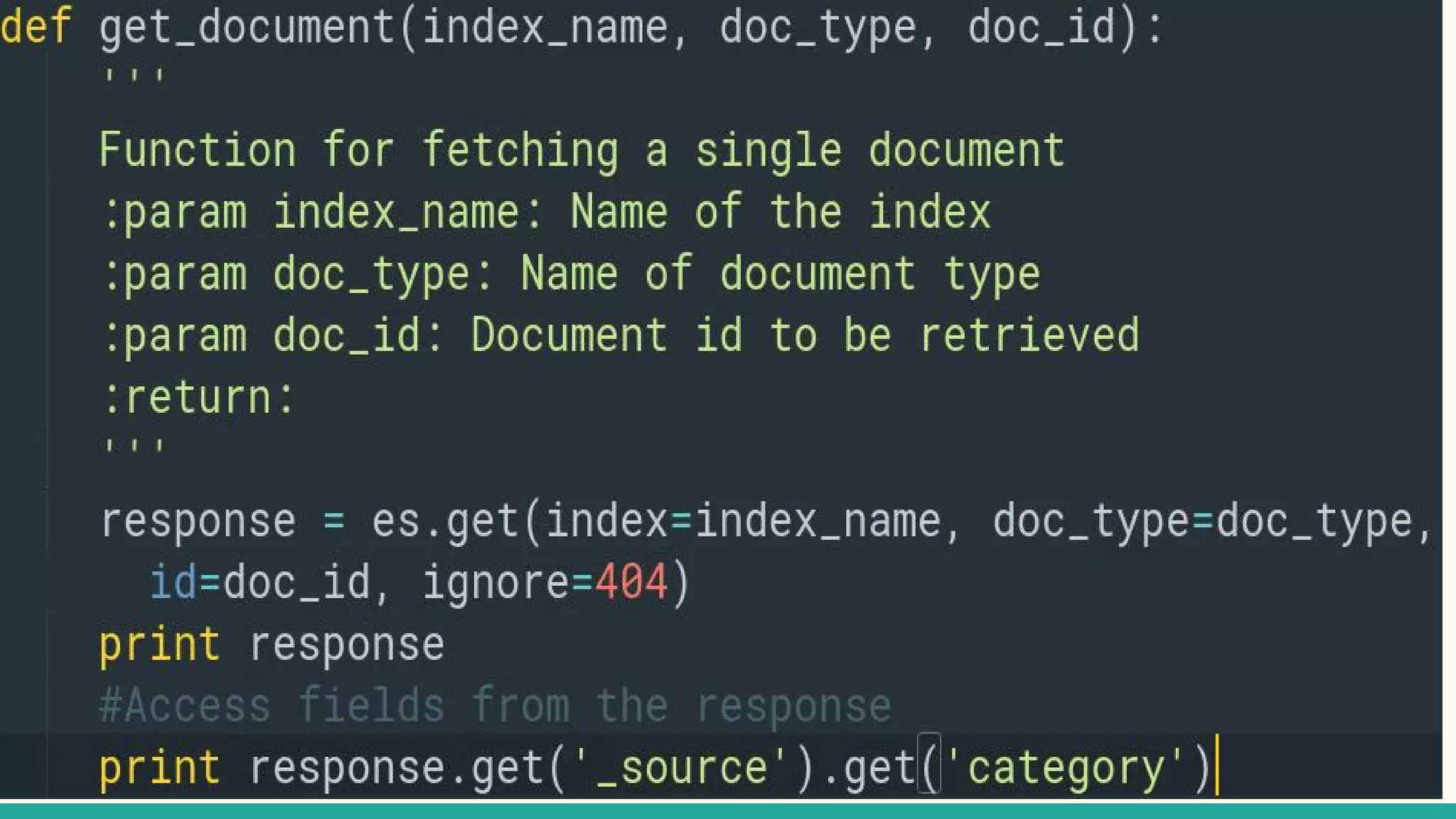
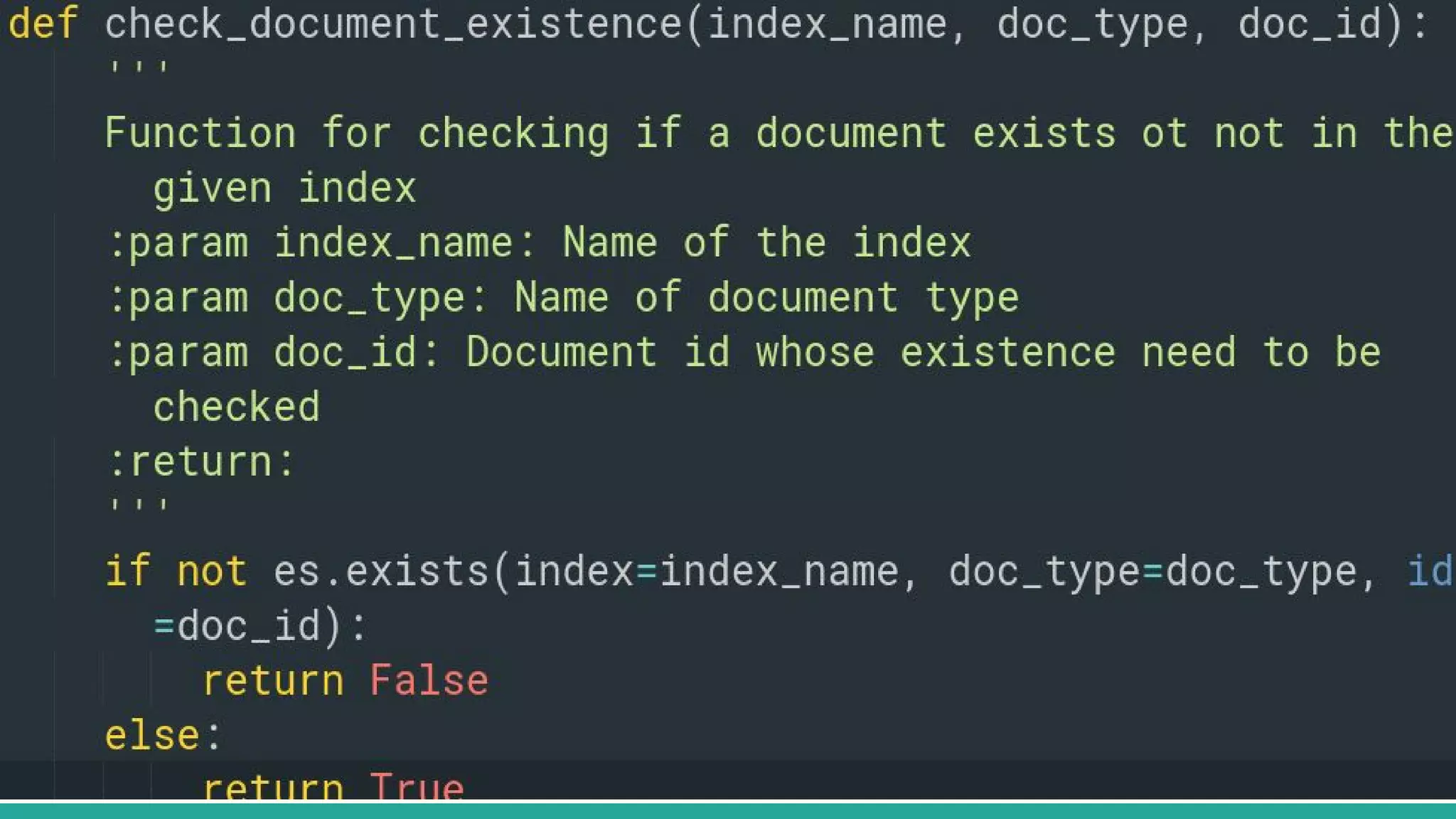
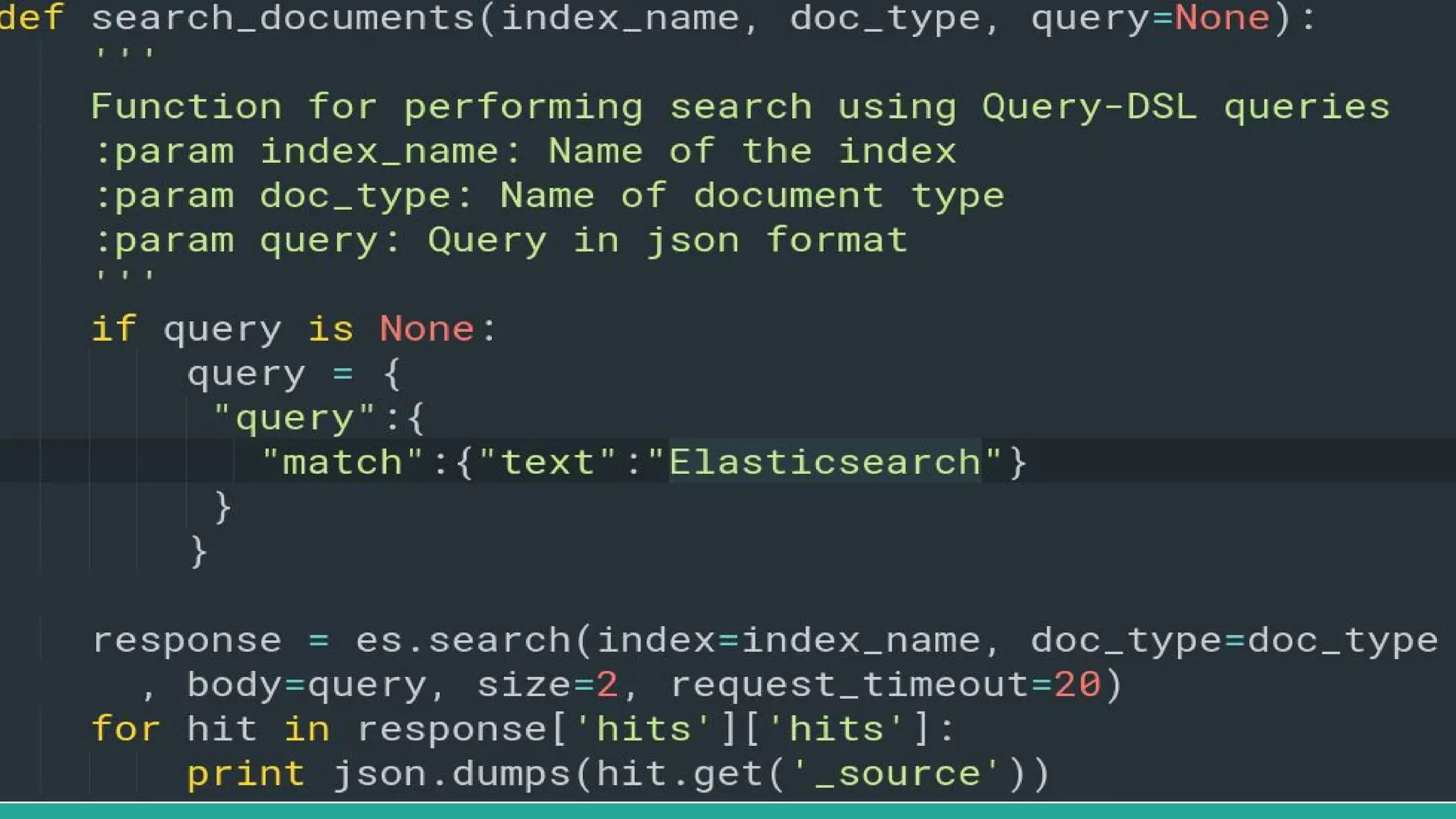
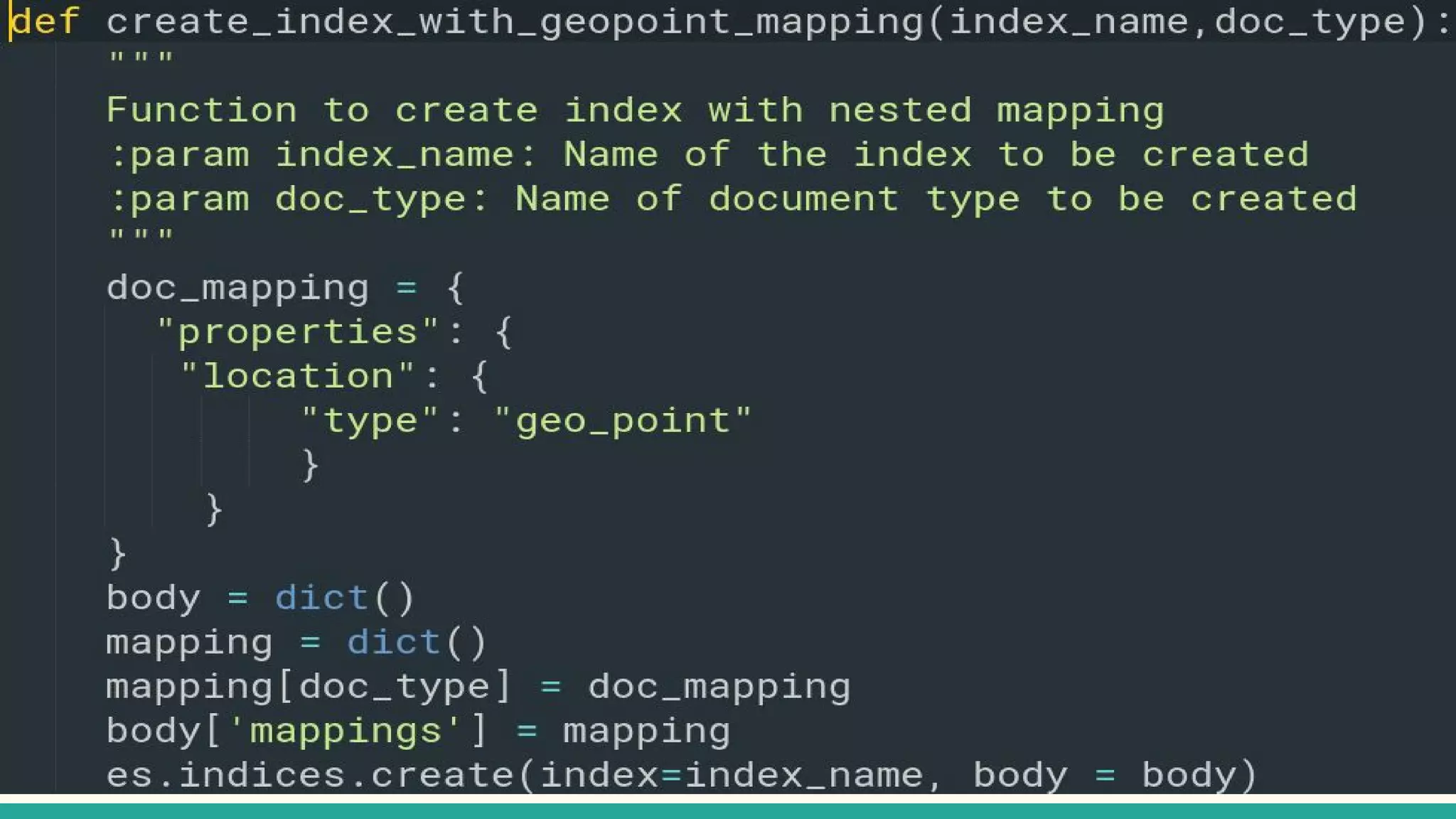
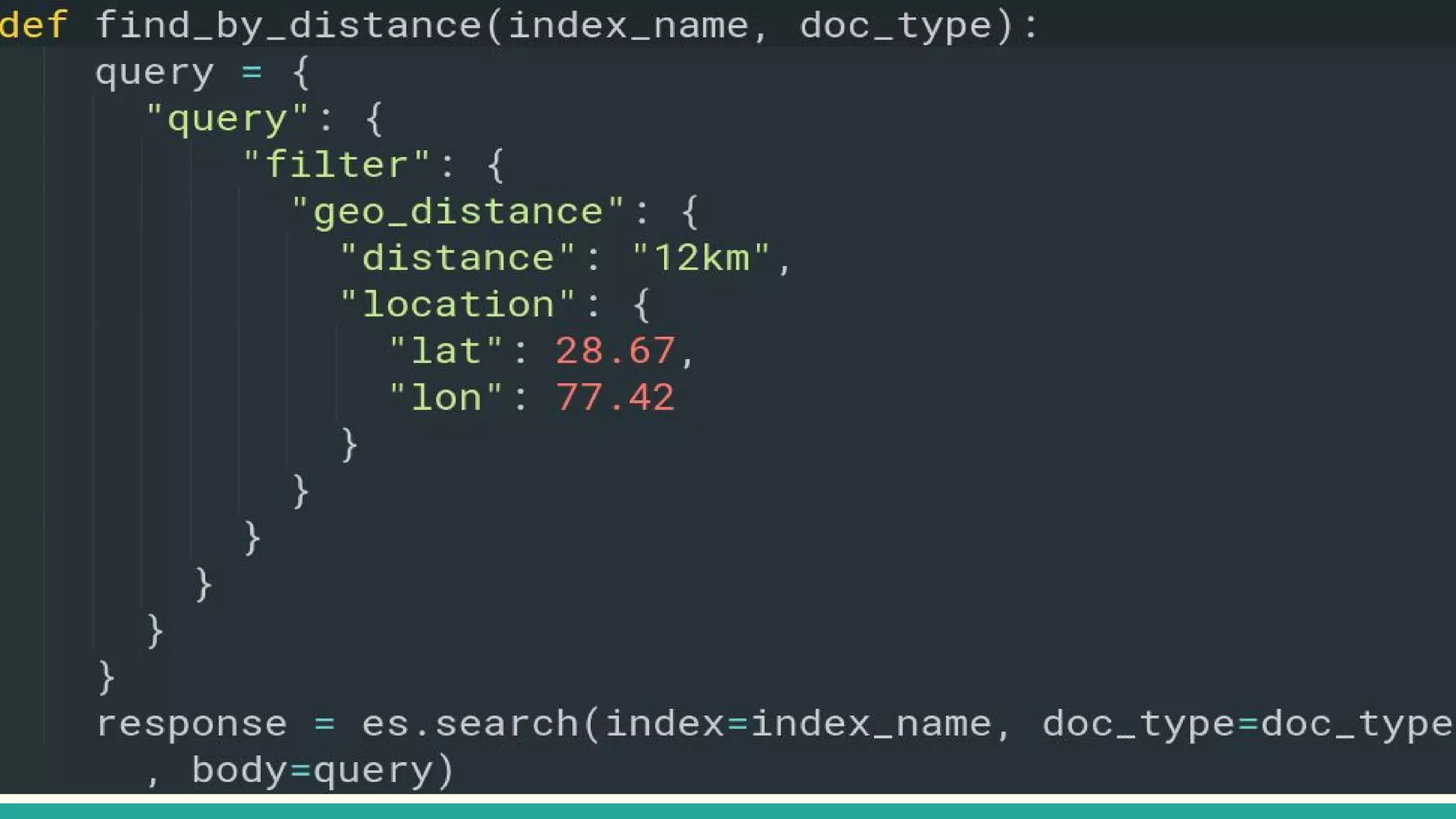
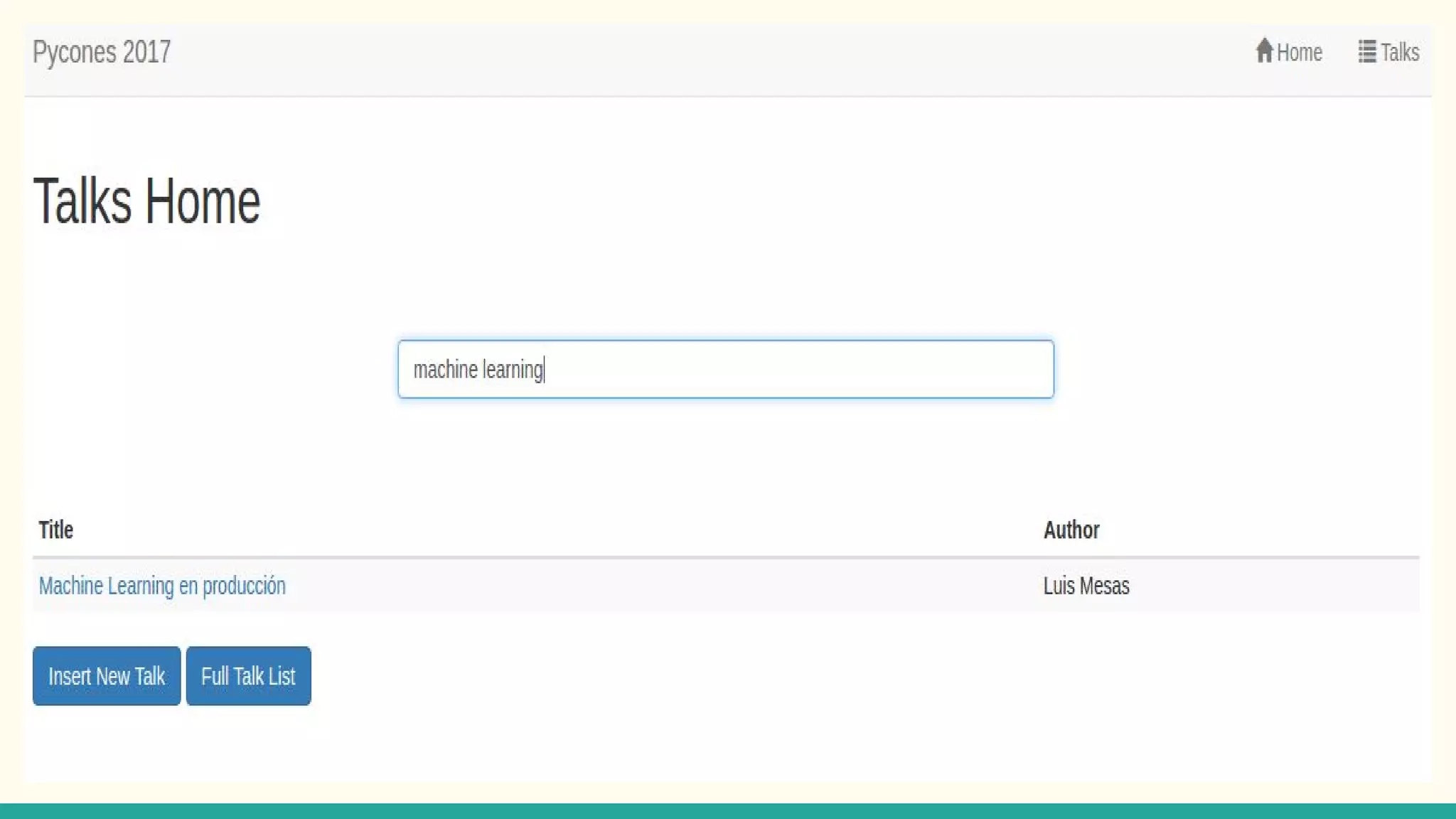
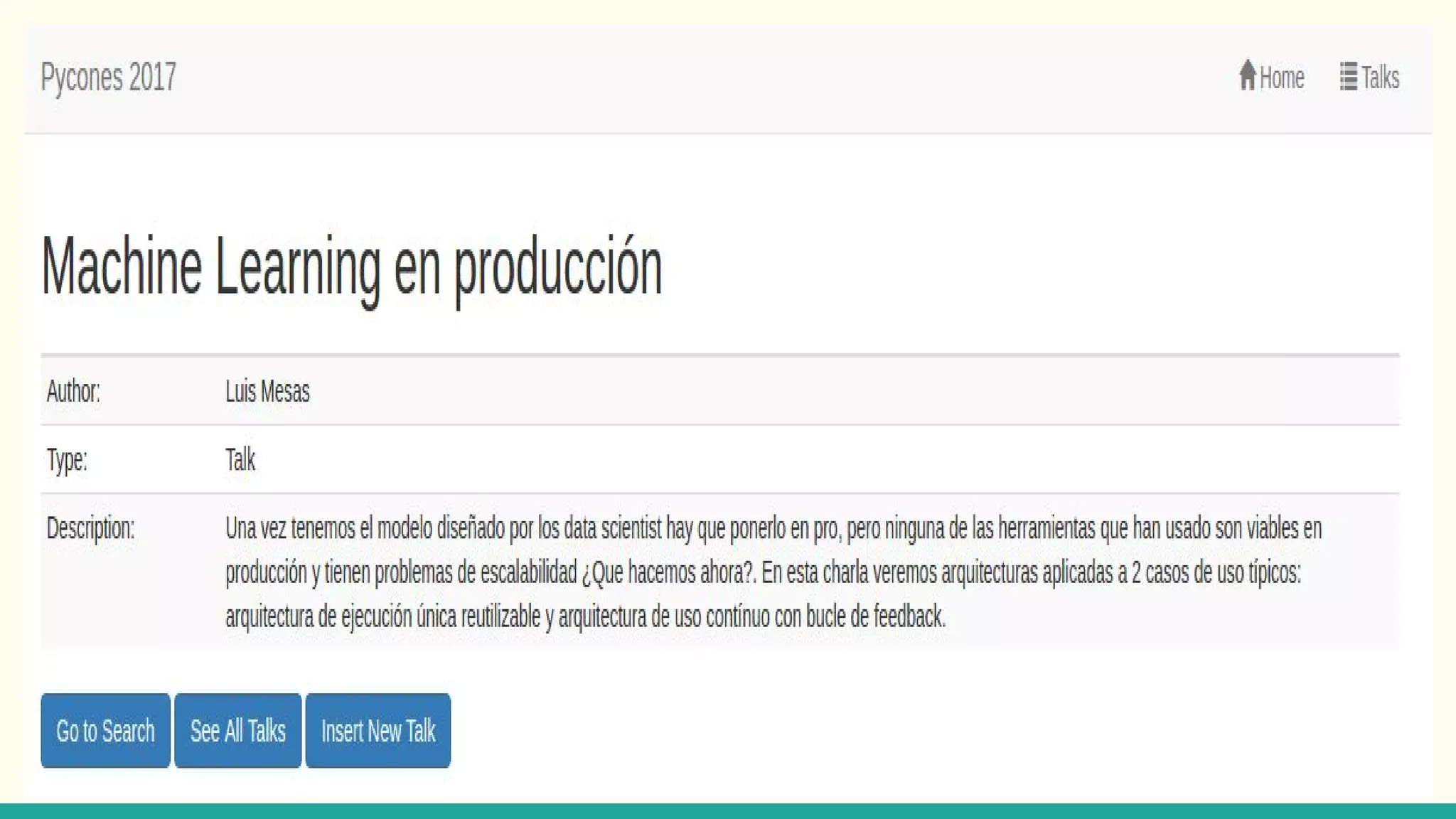
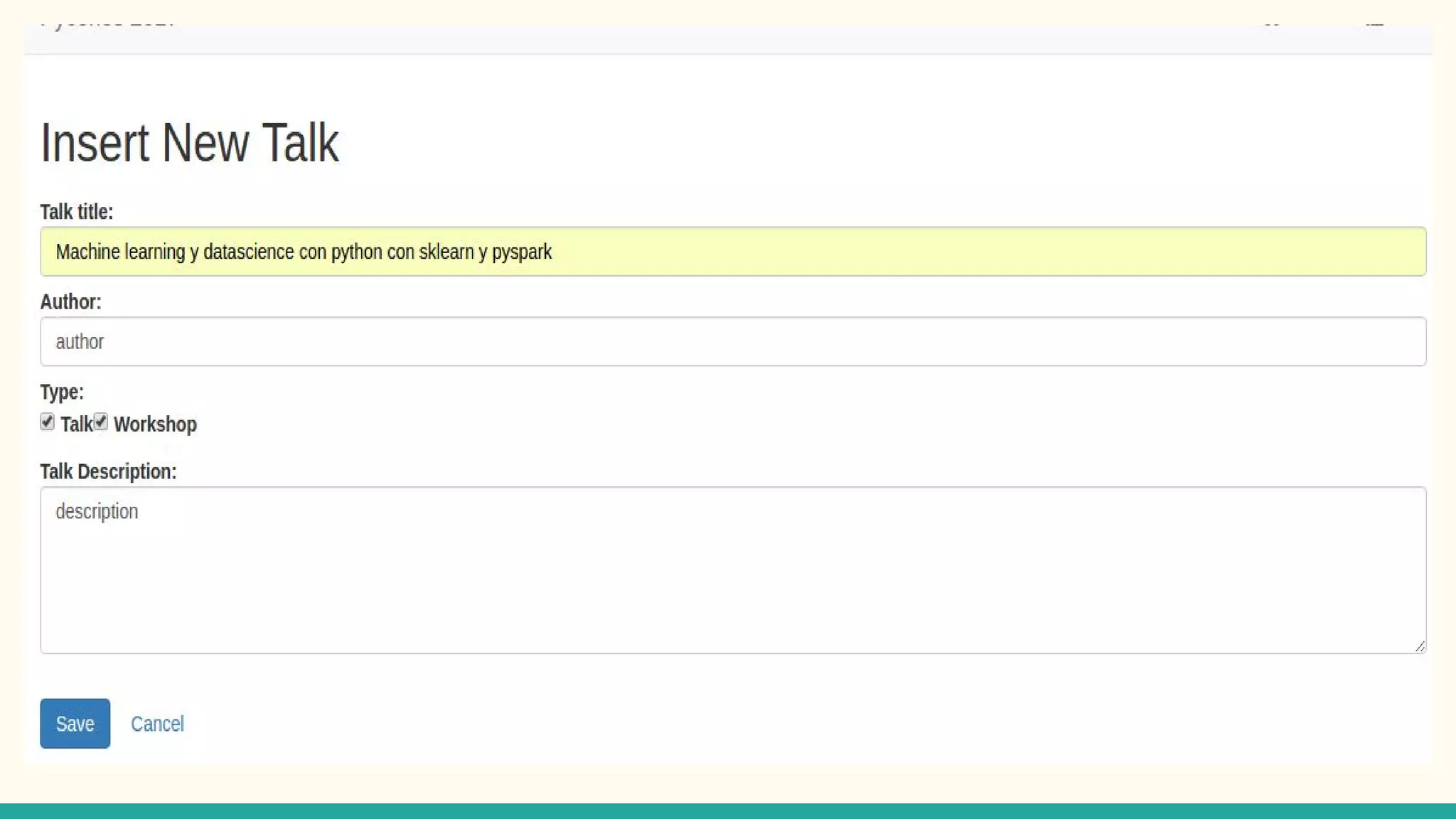
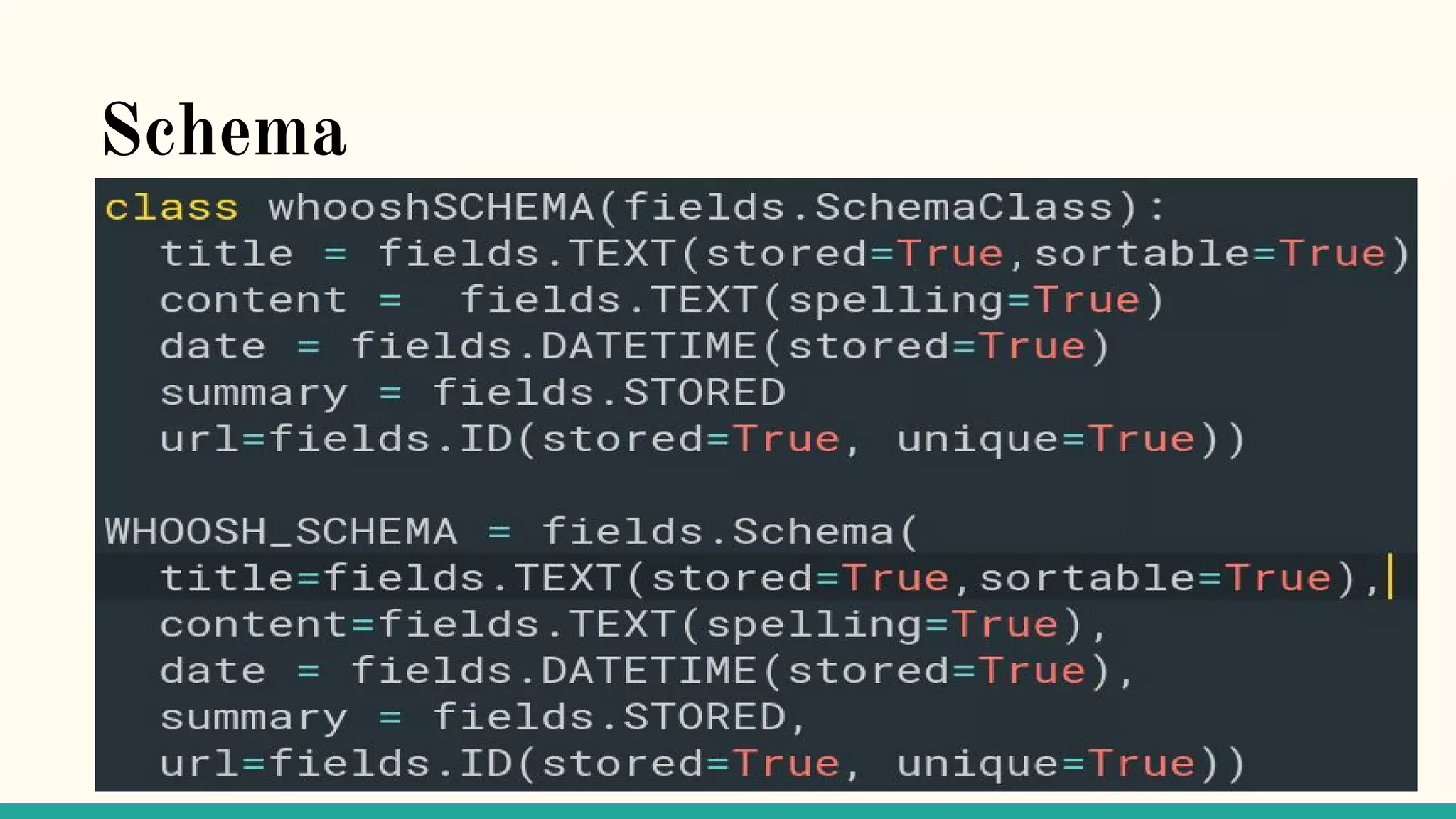
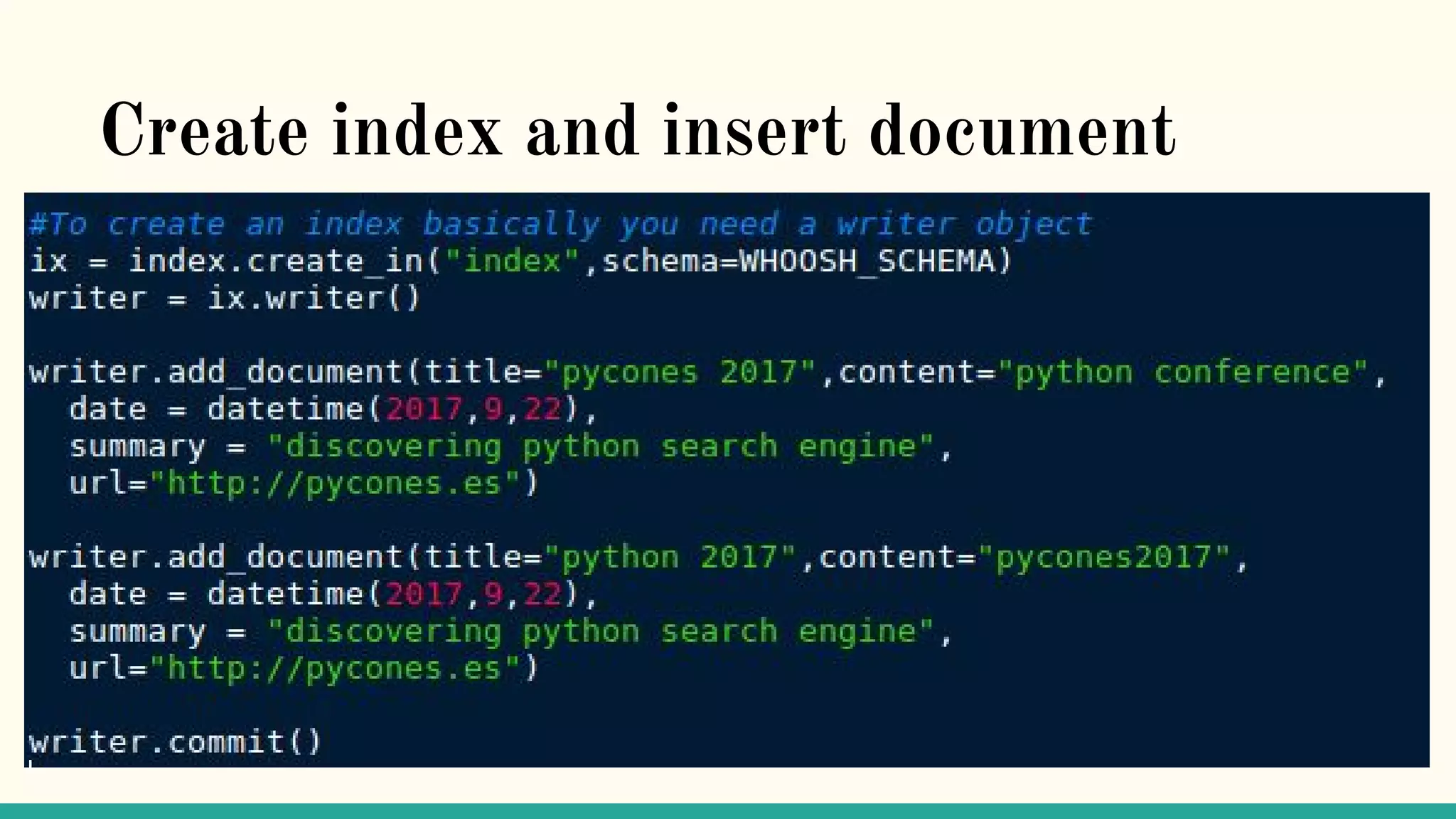
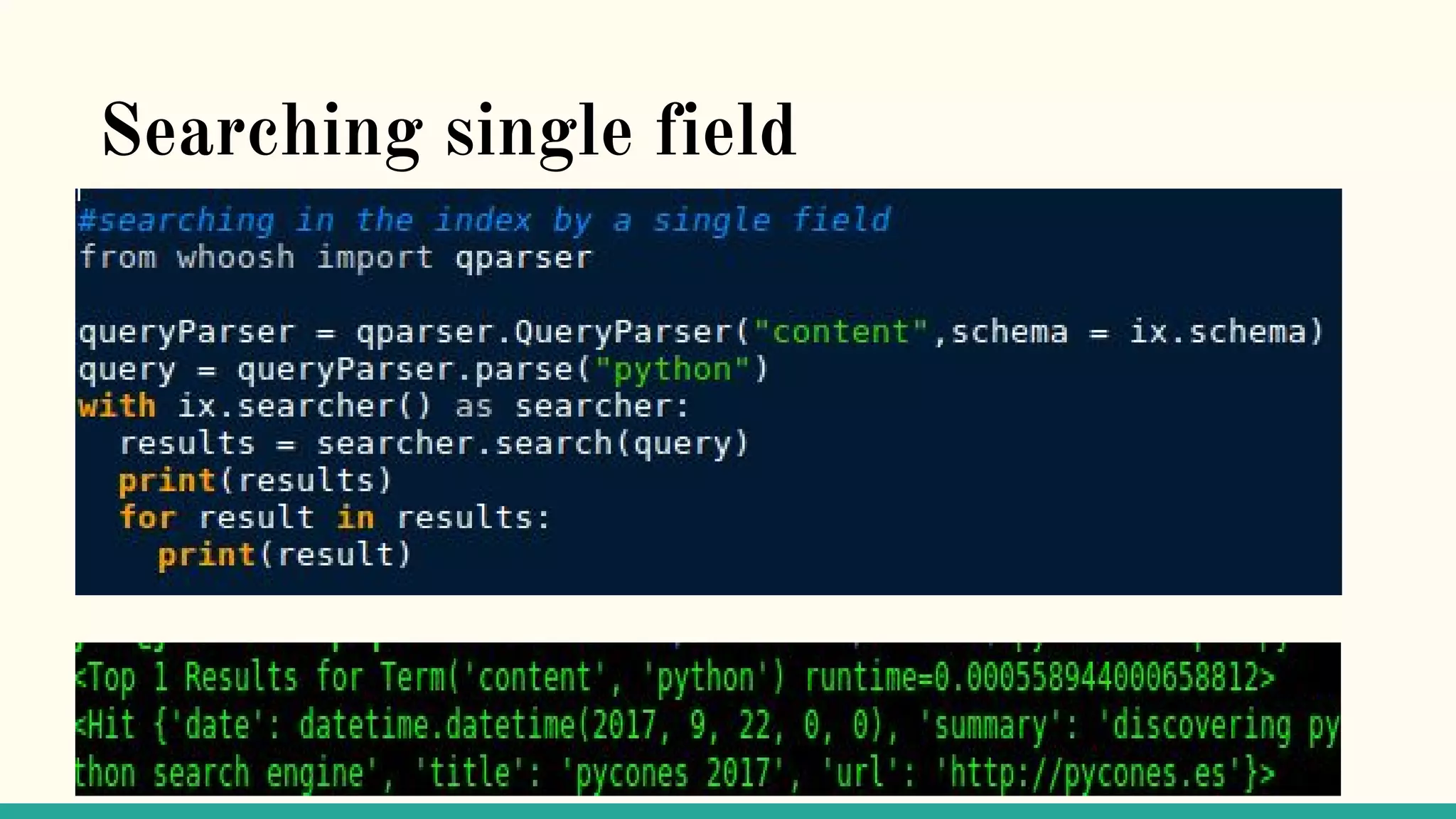
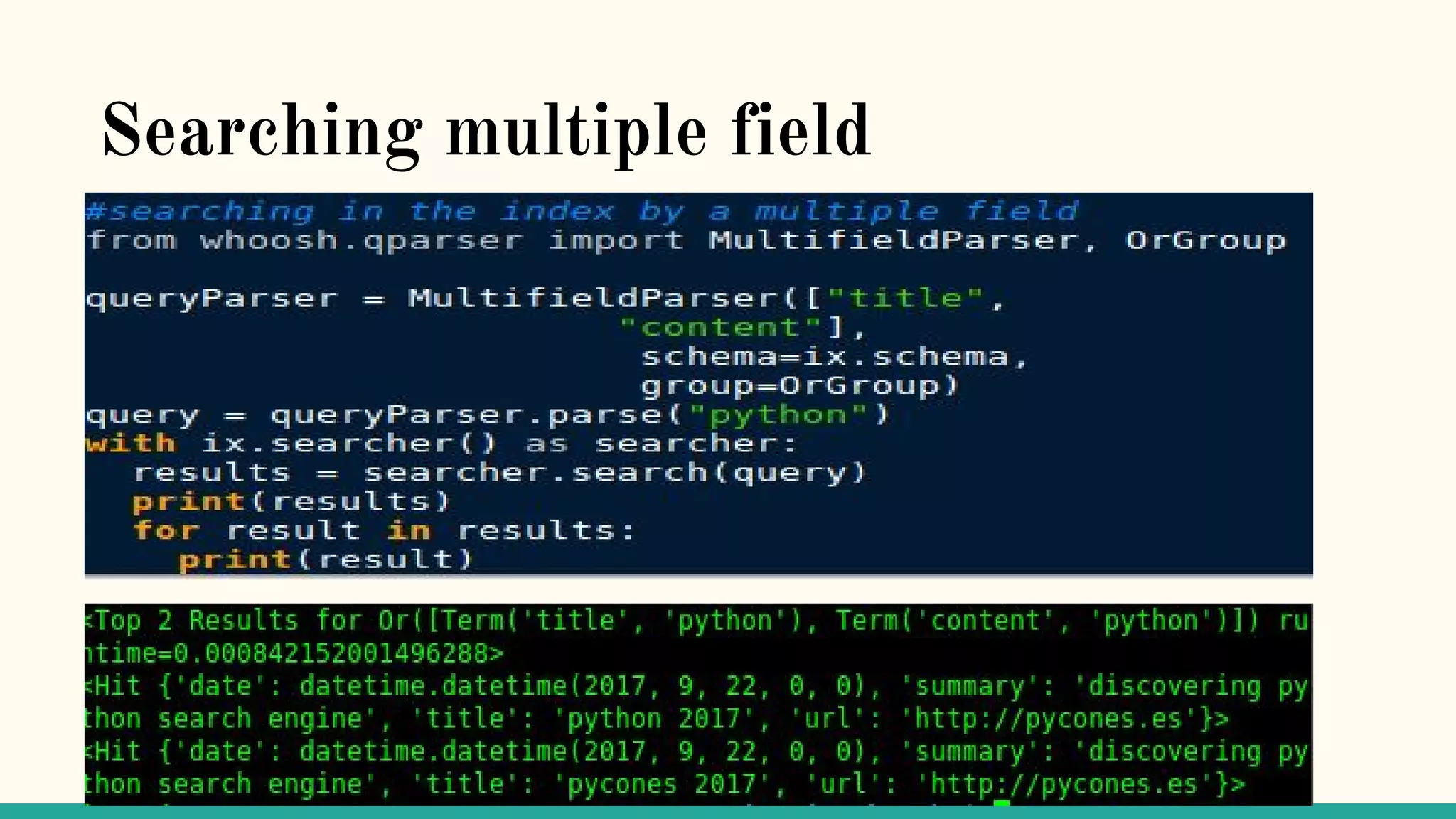
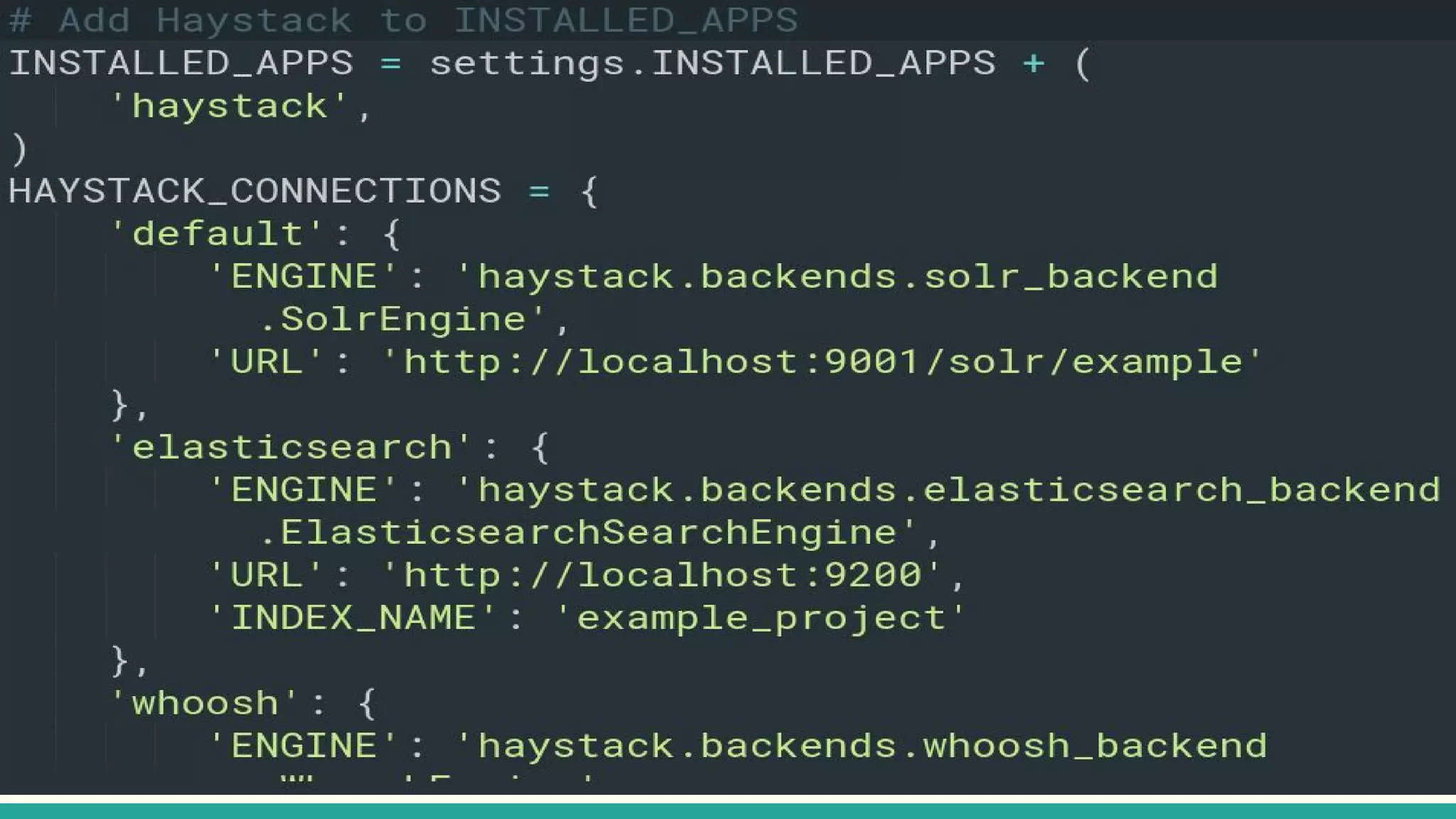
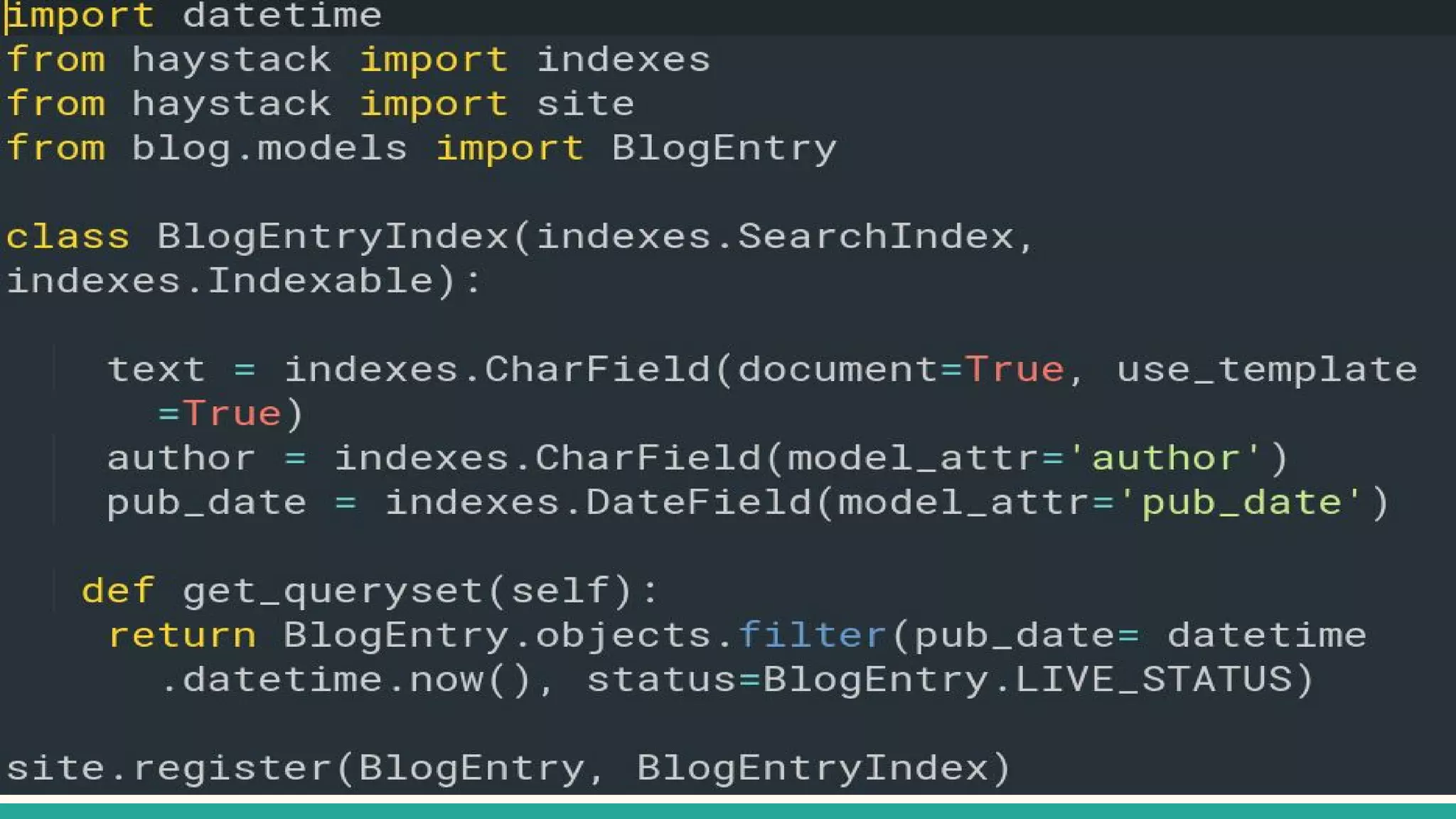
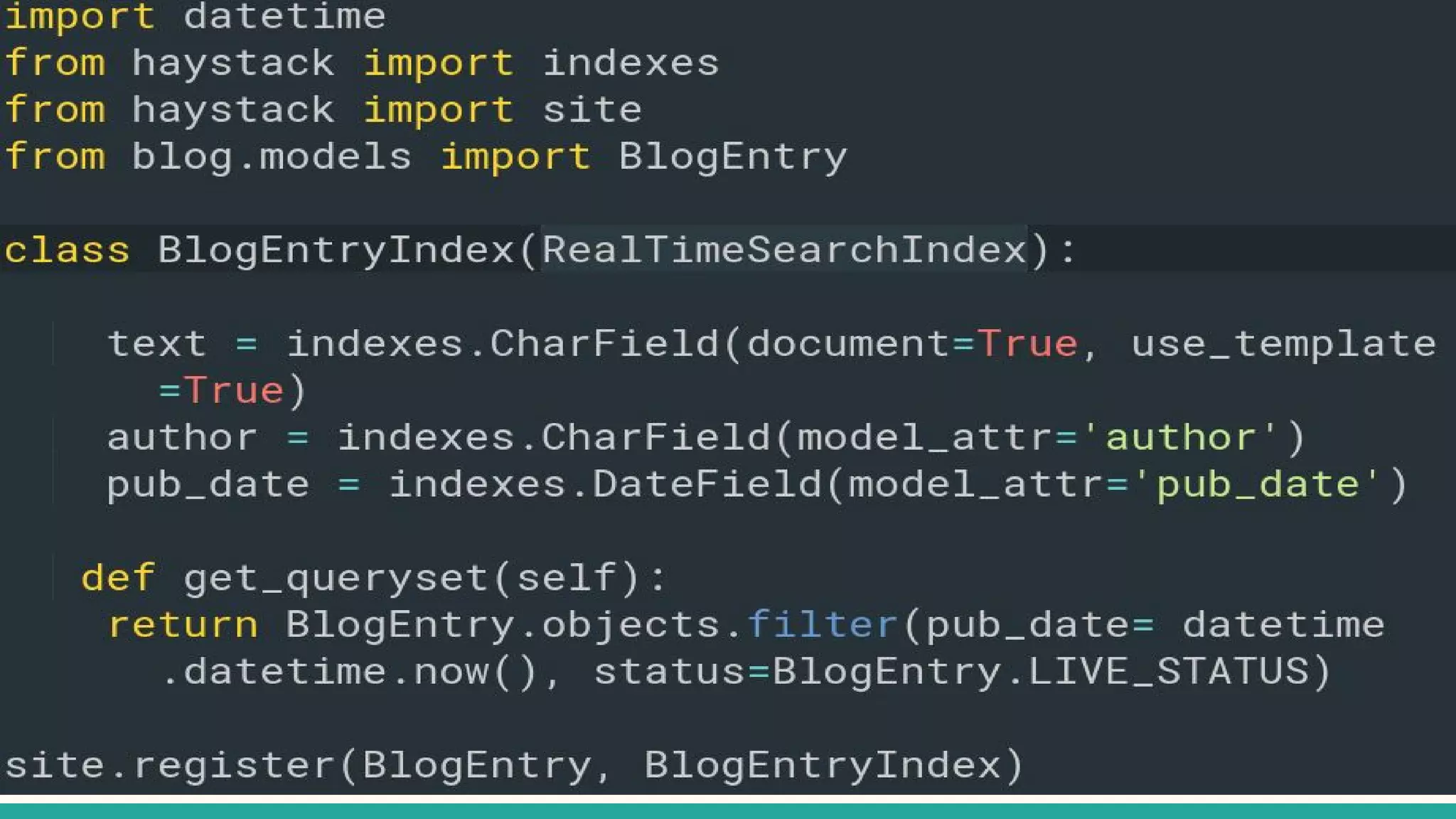
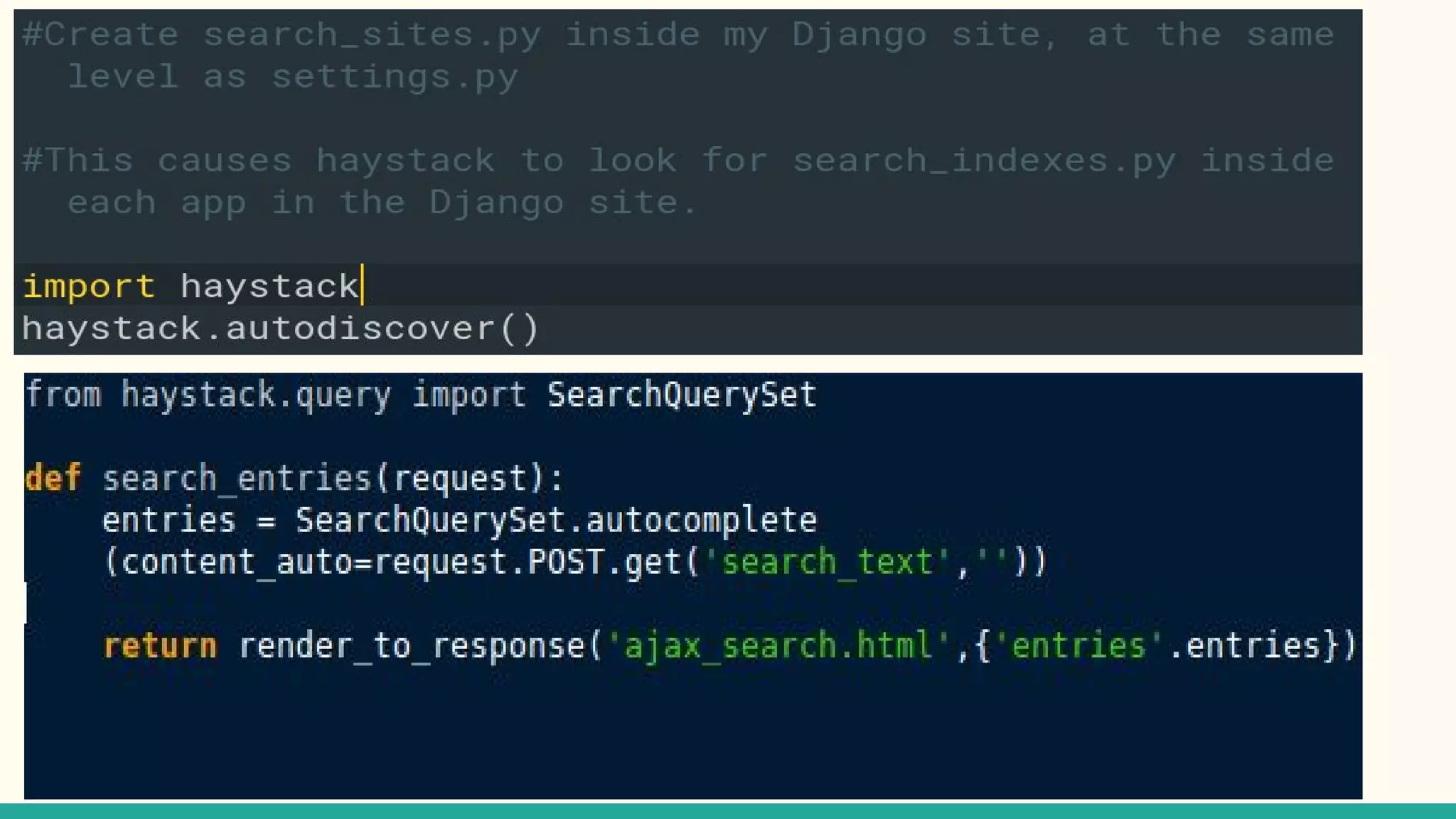
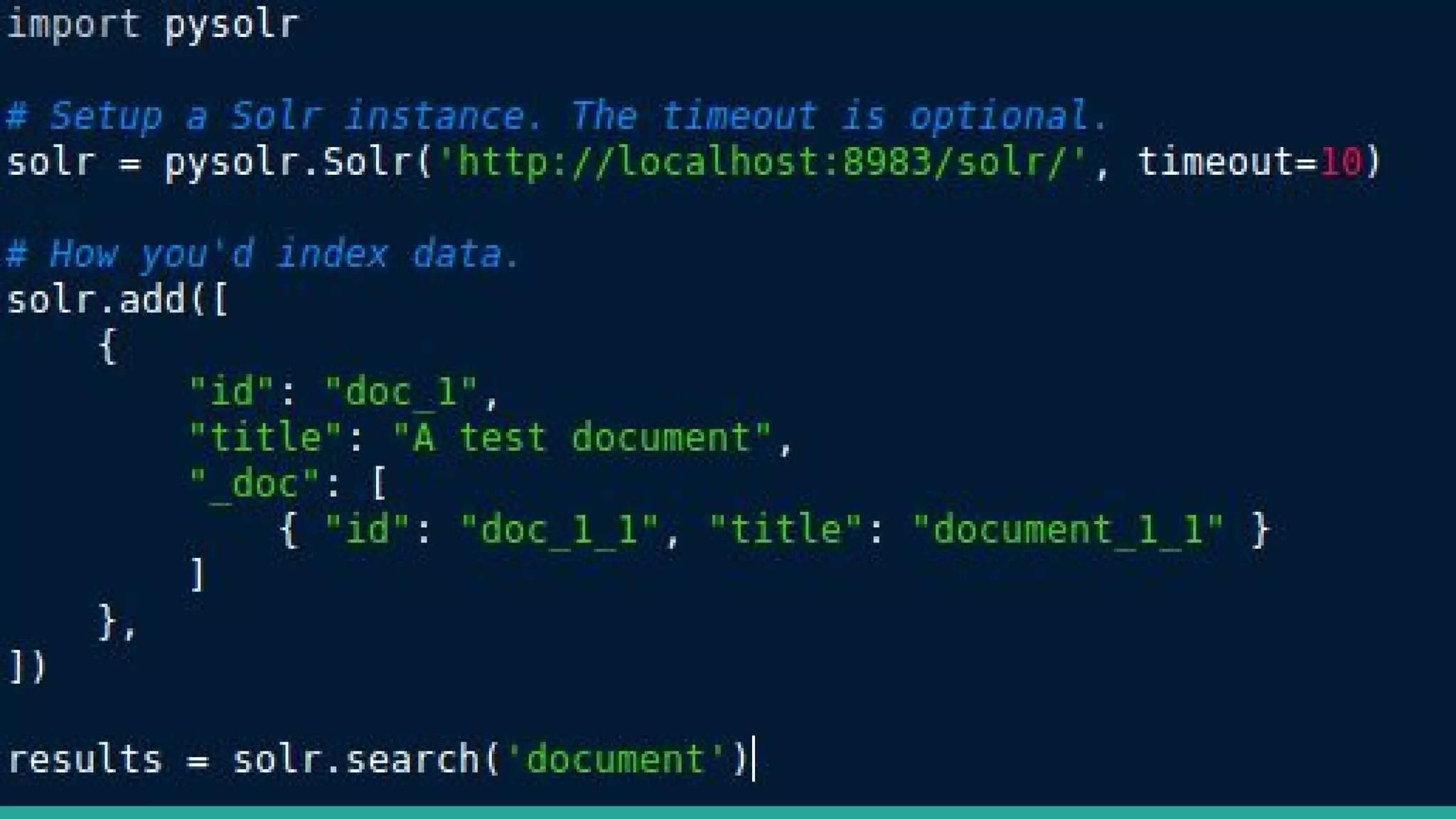
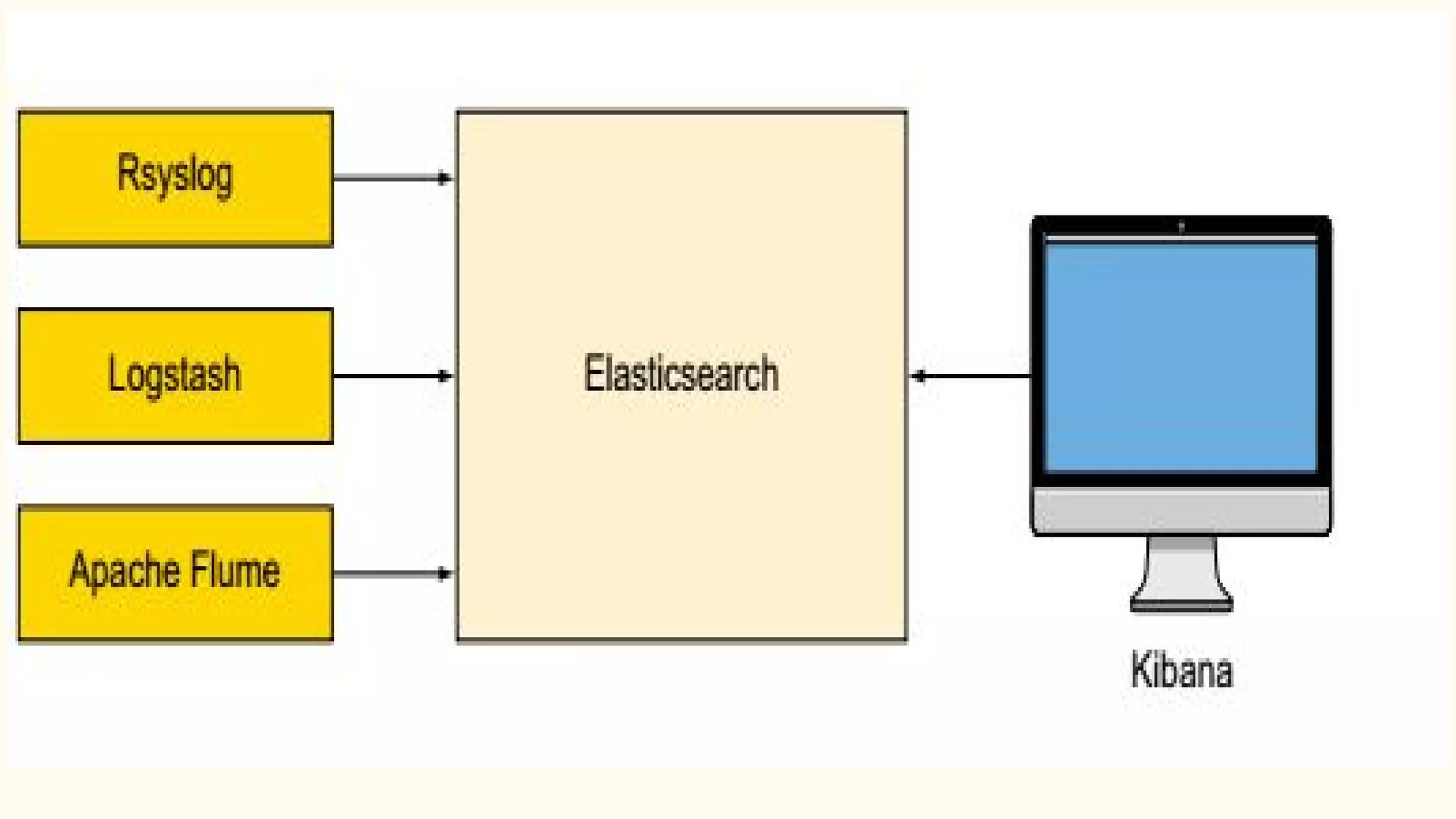
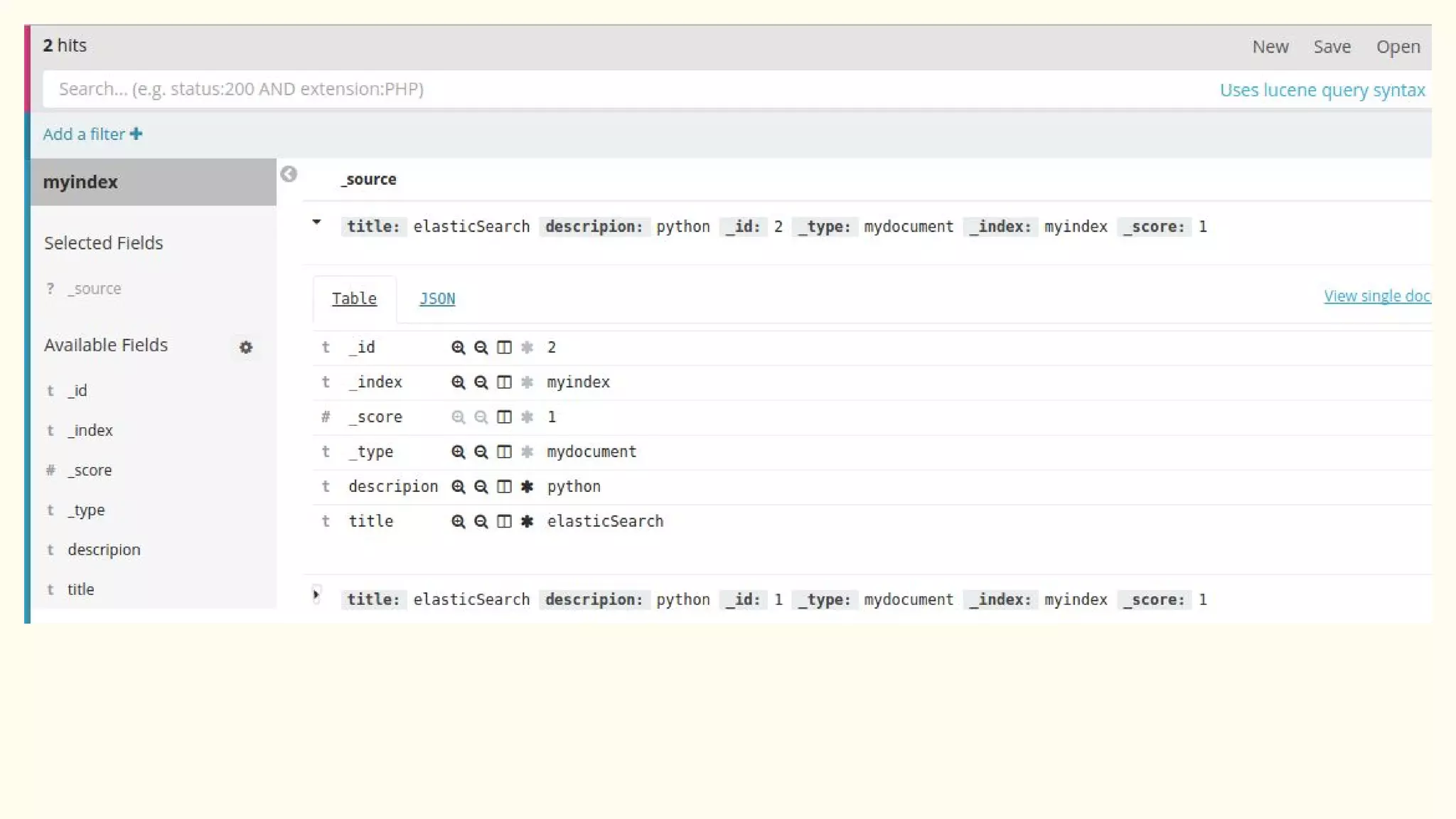
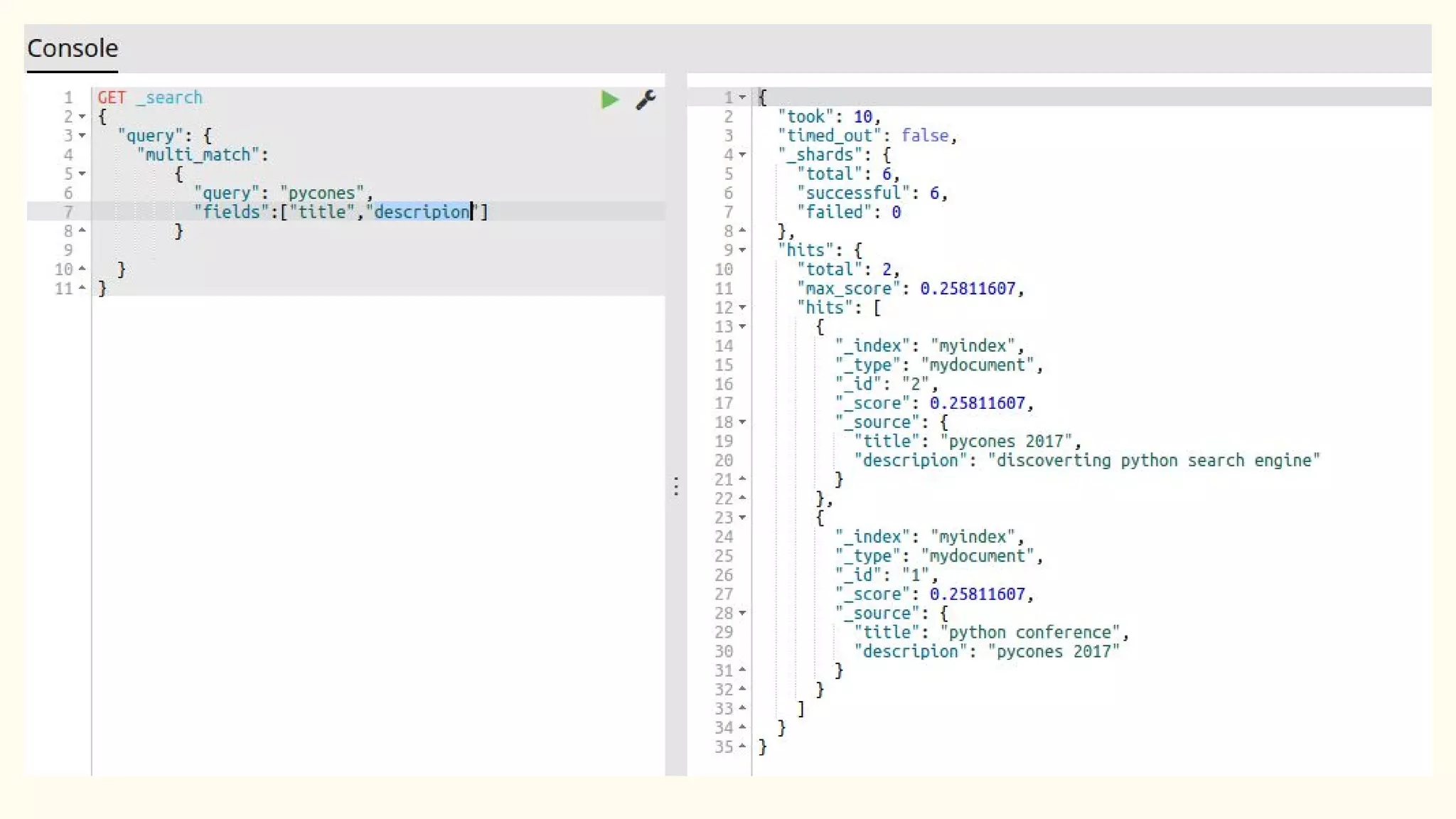
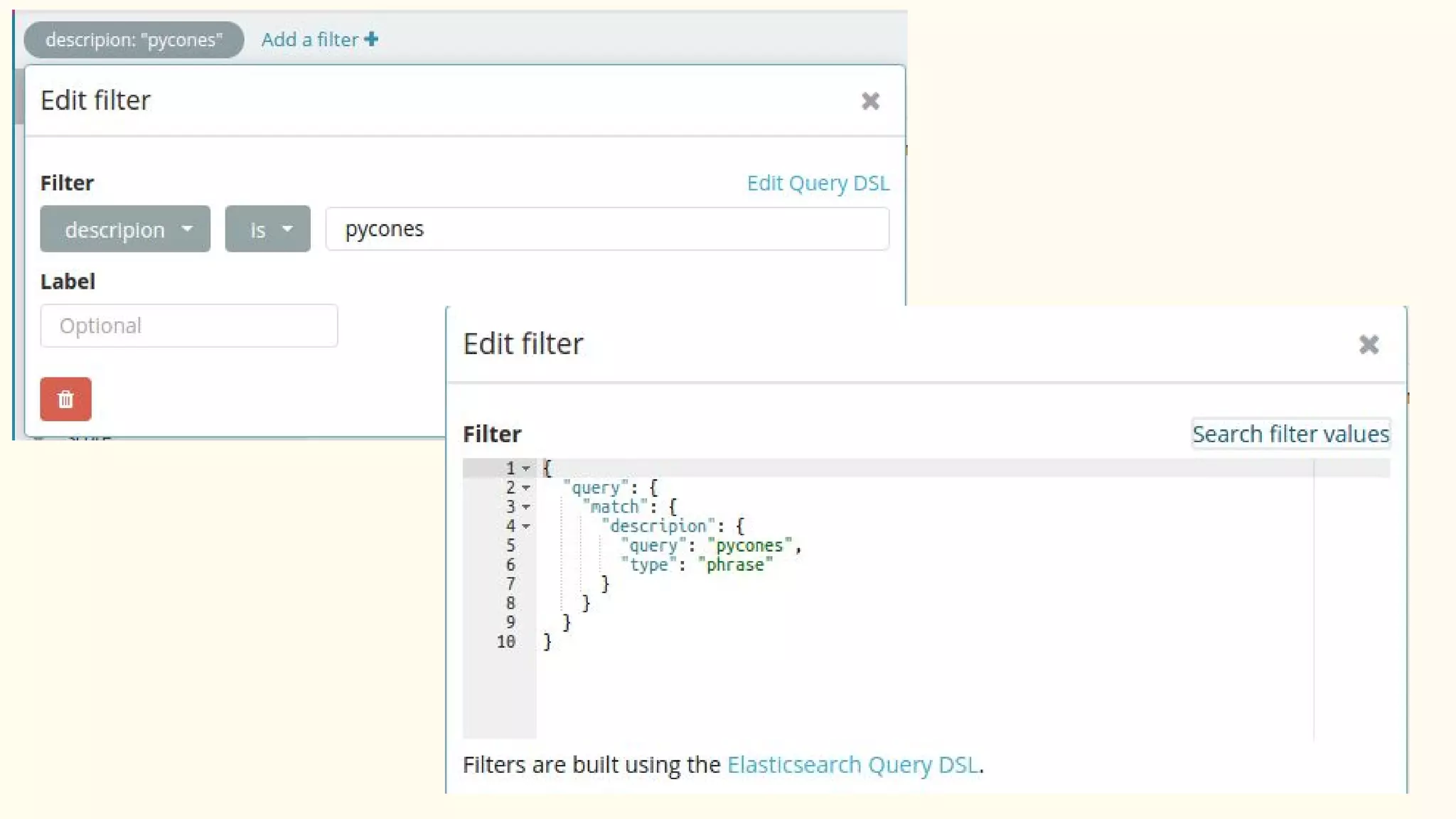
This document discusses various Python search engine options. It begins with an introduction to core search engine concepts like indexes, types, documents, and inverted indexes. It then provides an overview of ElasticSearch, including how to create indexes, add documents, and perform searches. Whoosh and Django Haystack are also summarized as alternative Python search libraries. Other solutions like Xapian, PostgreSQL, and Pysolr are briefly mentioned.