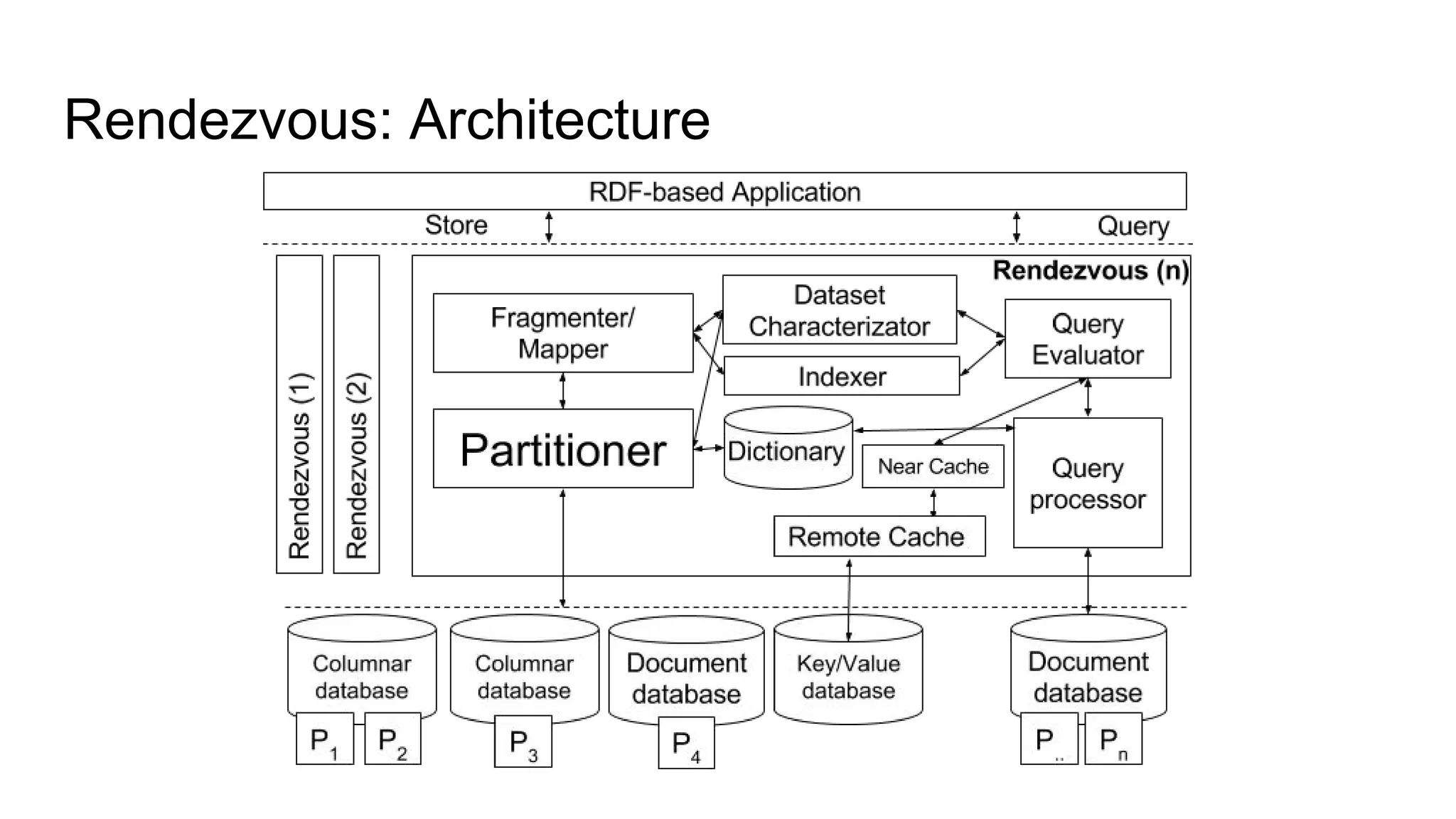
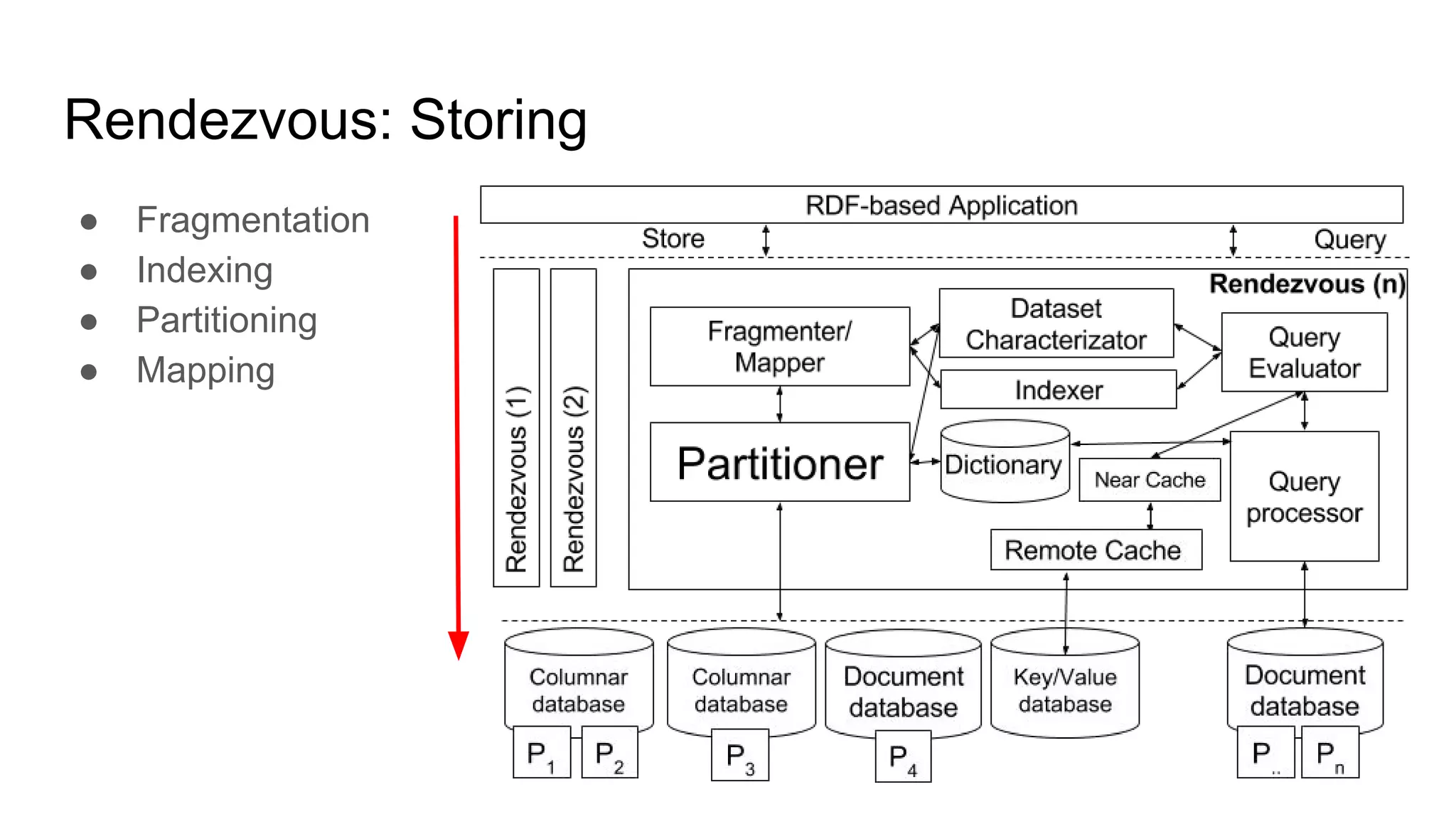
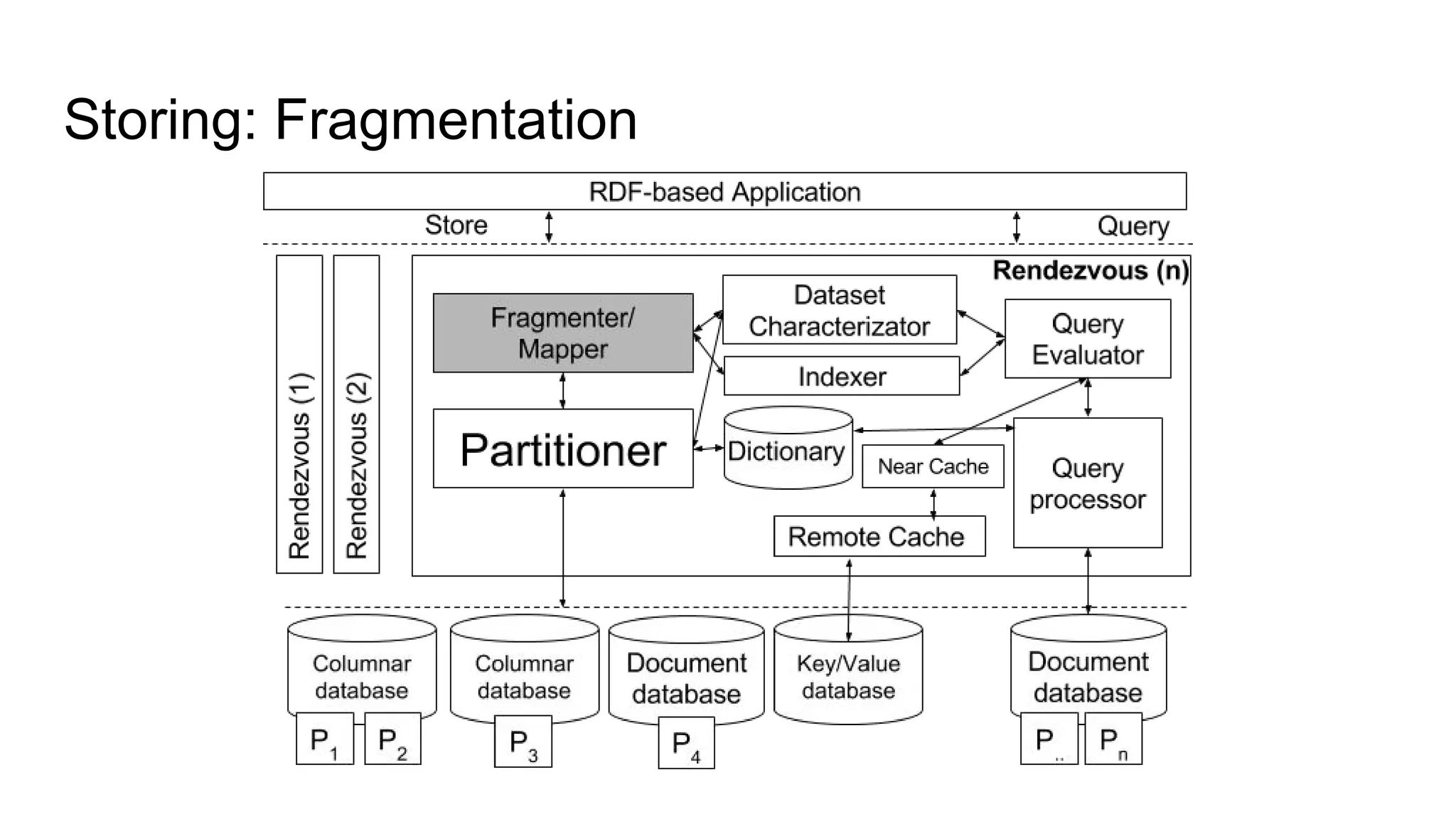
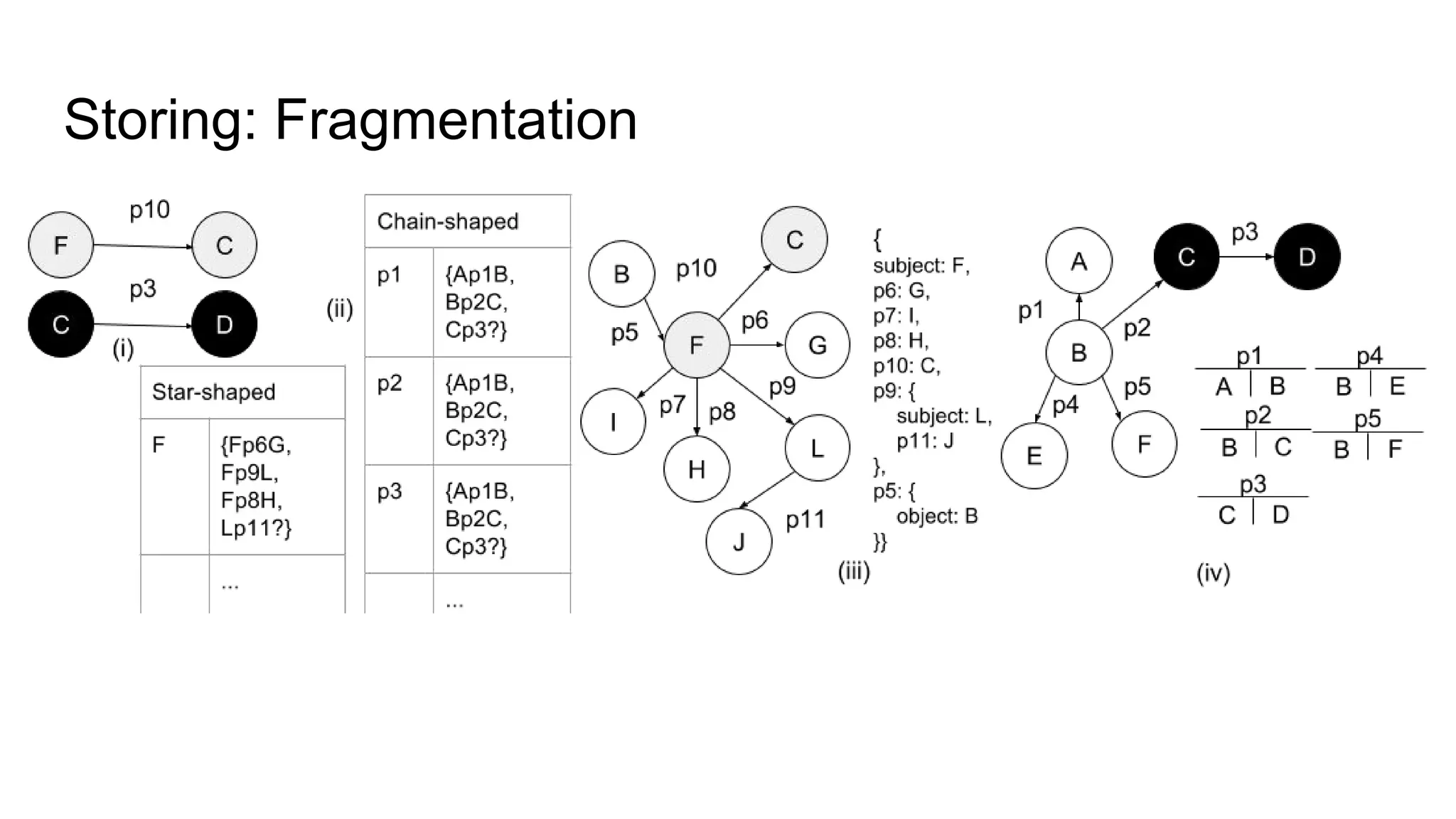
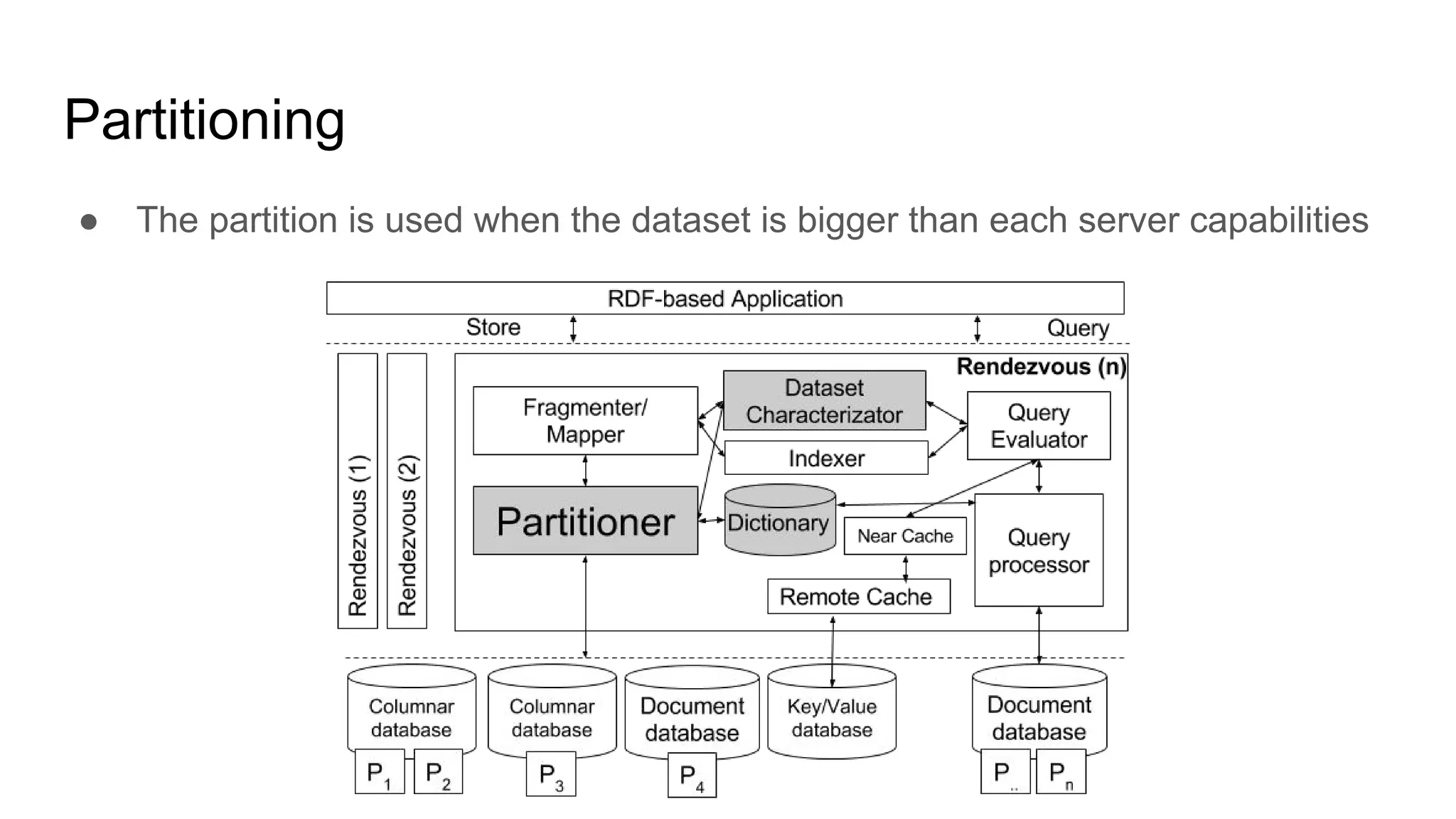
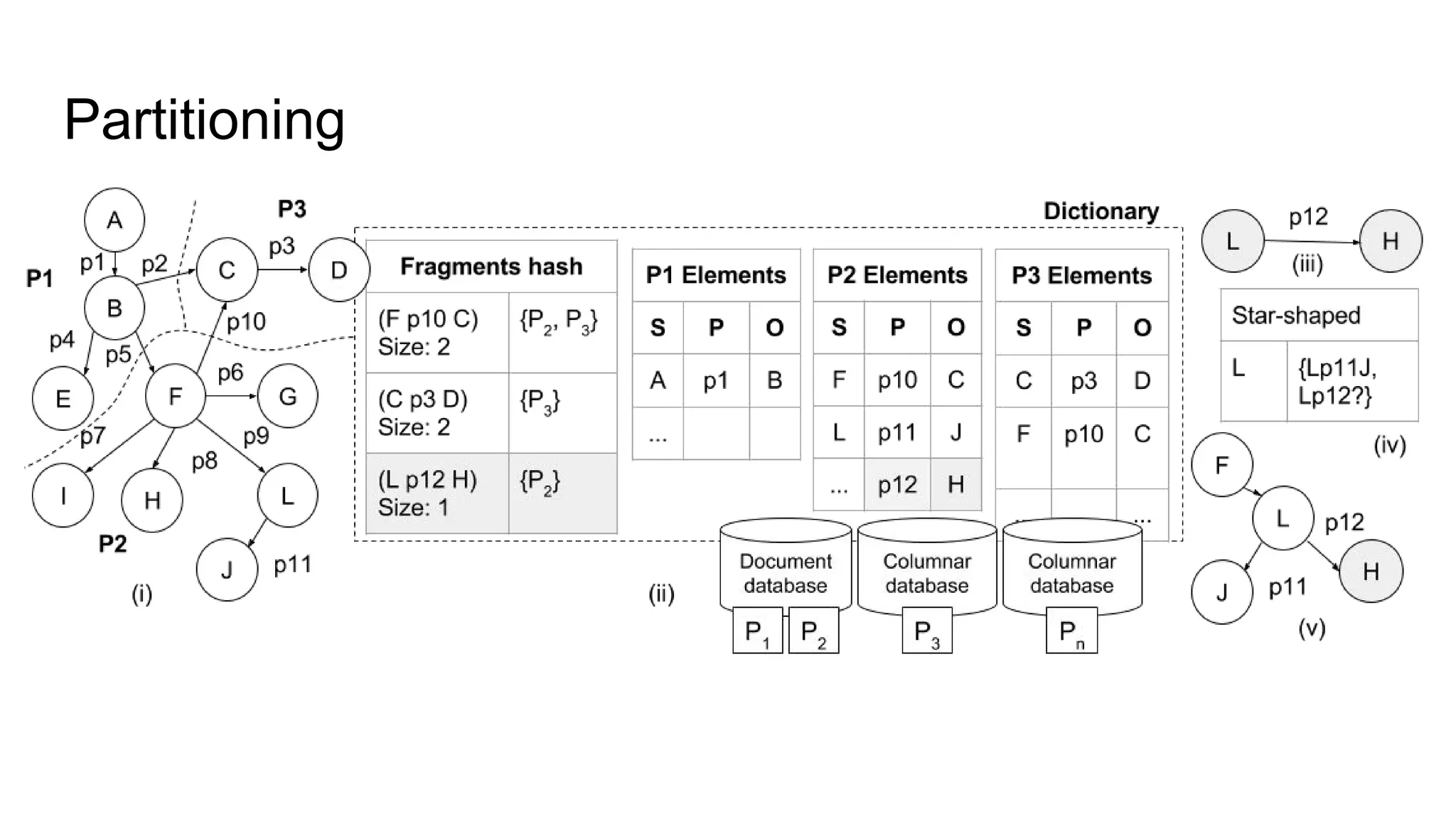
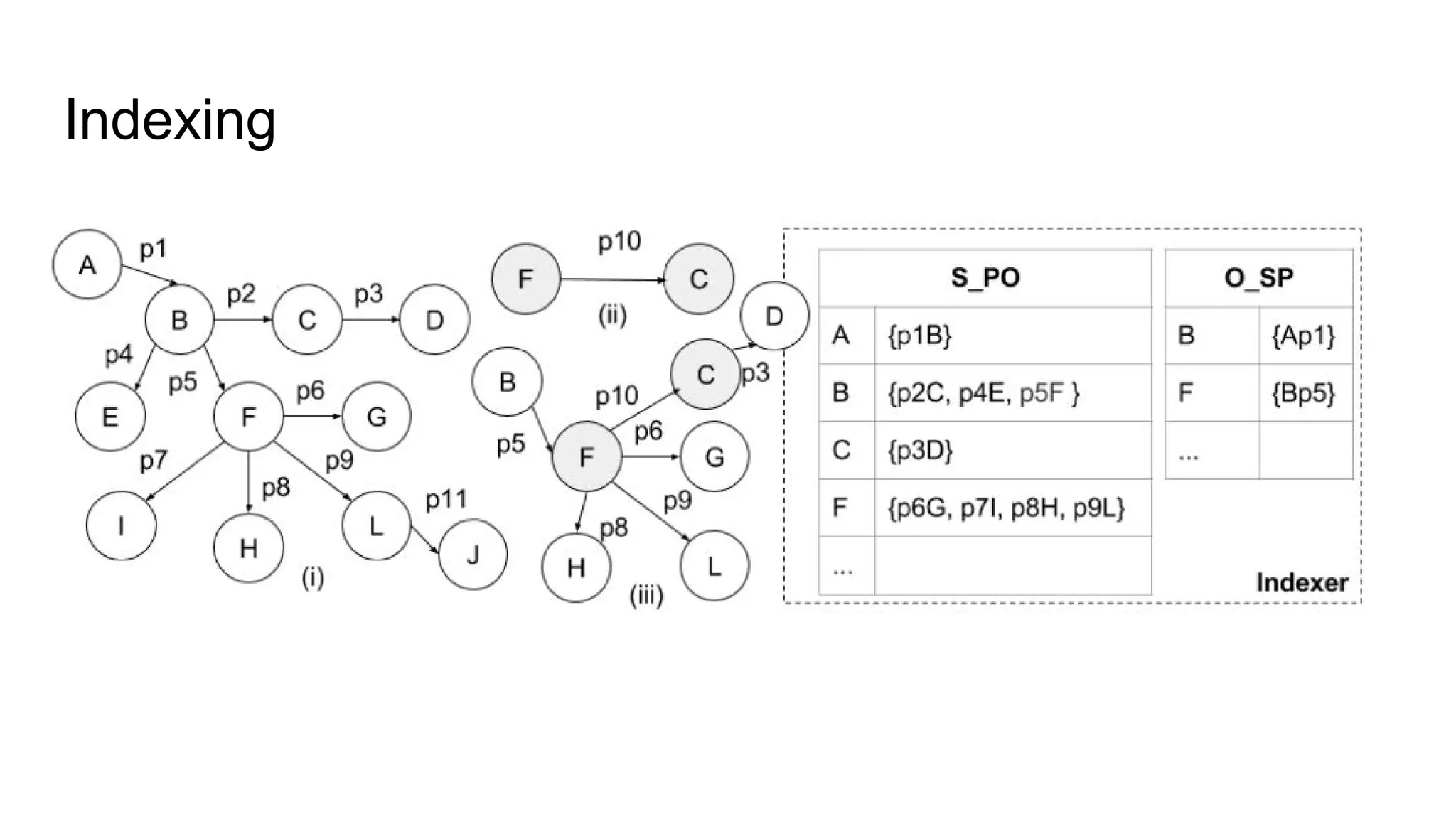
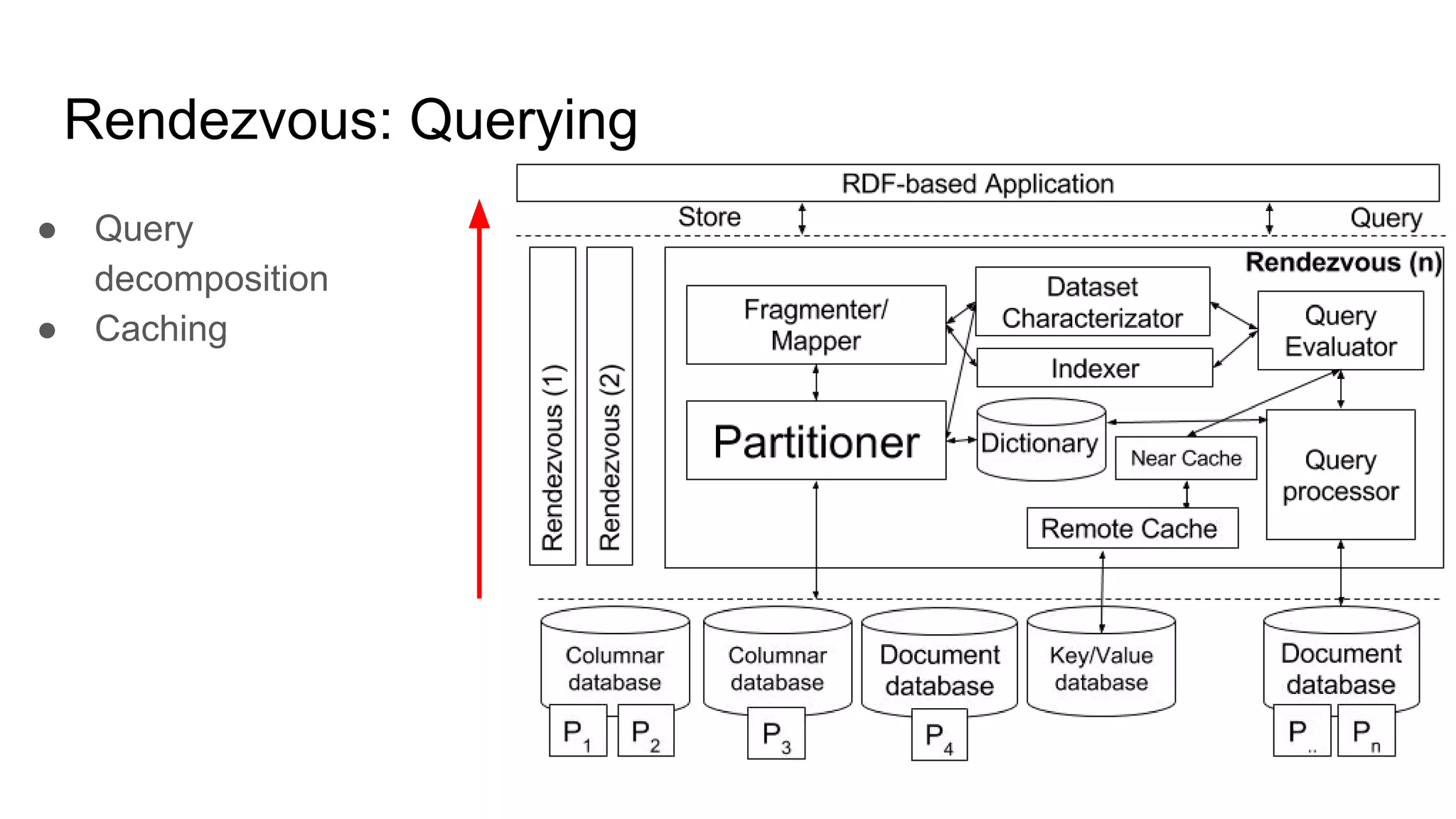
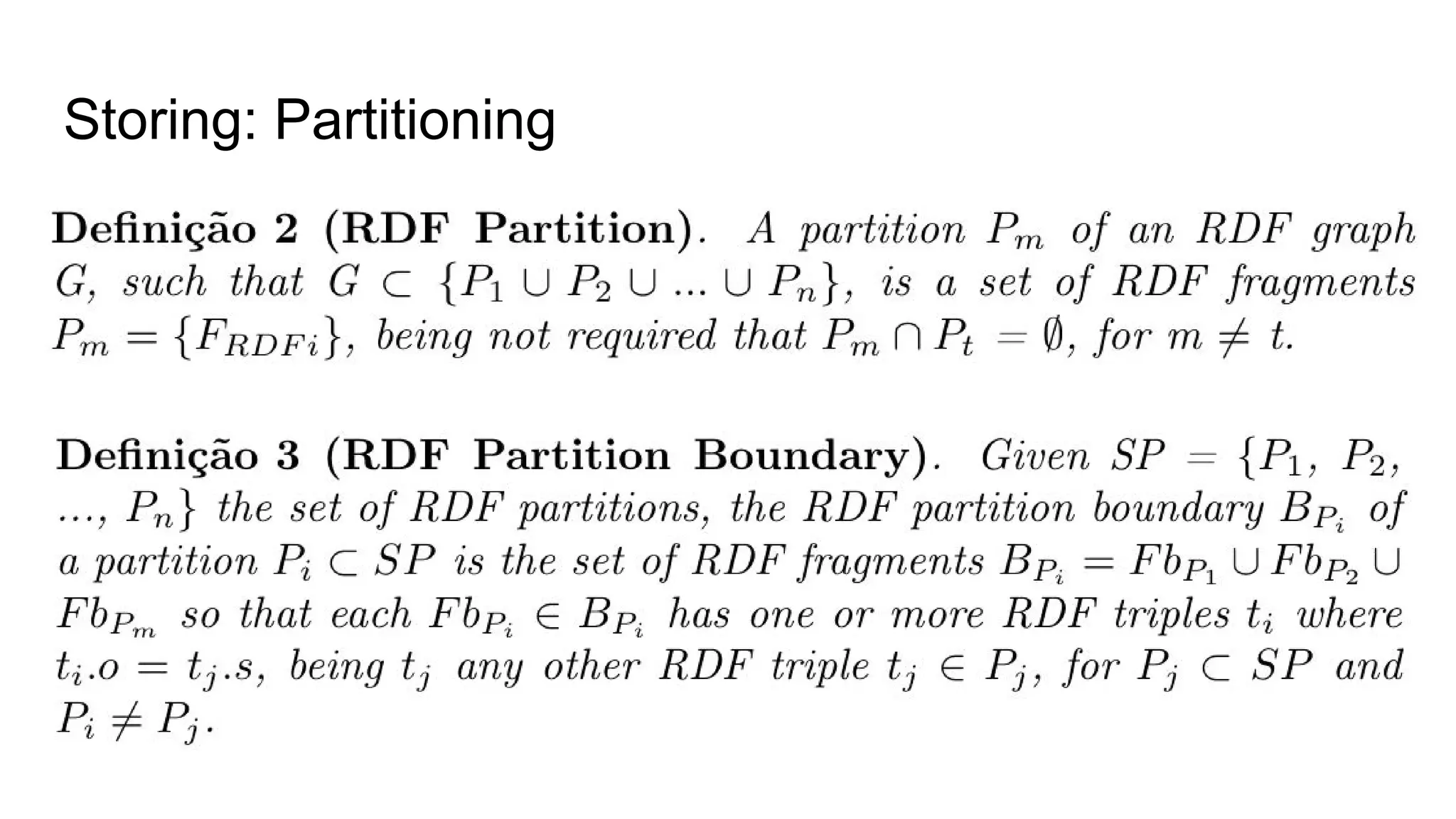
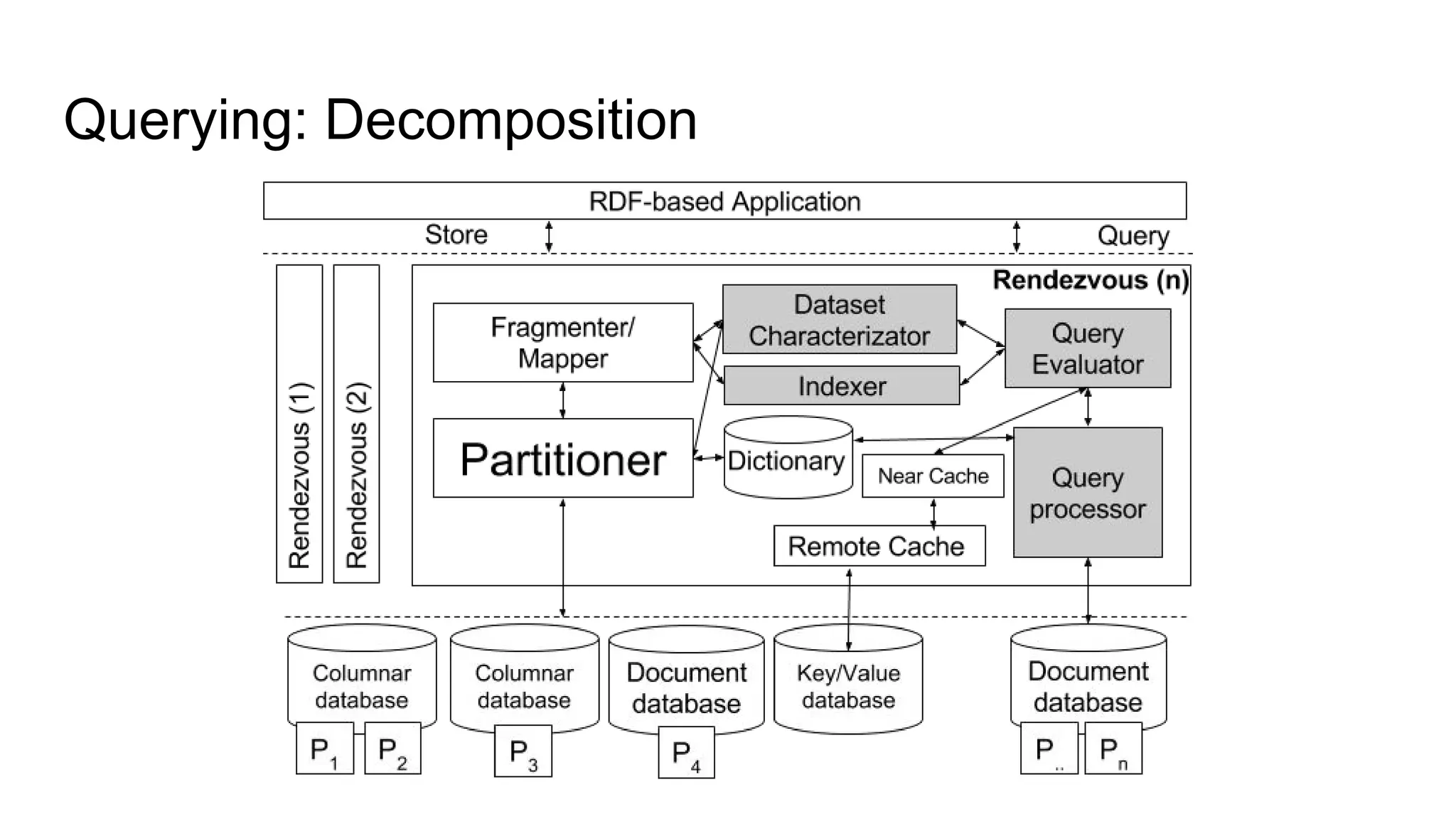
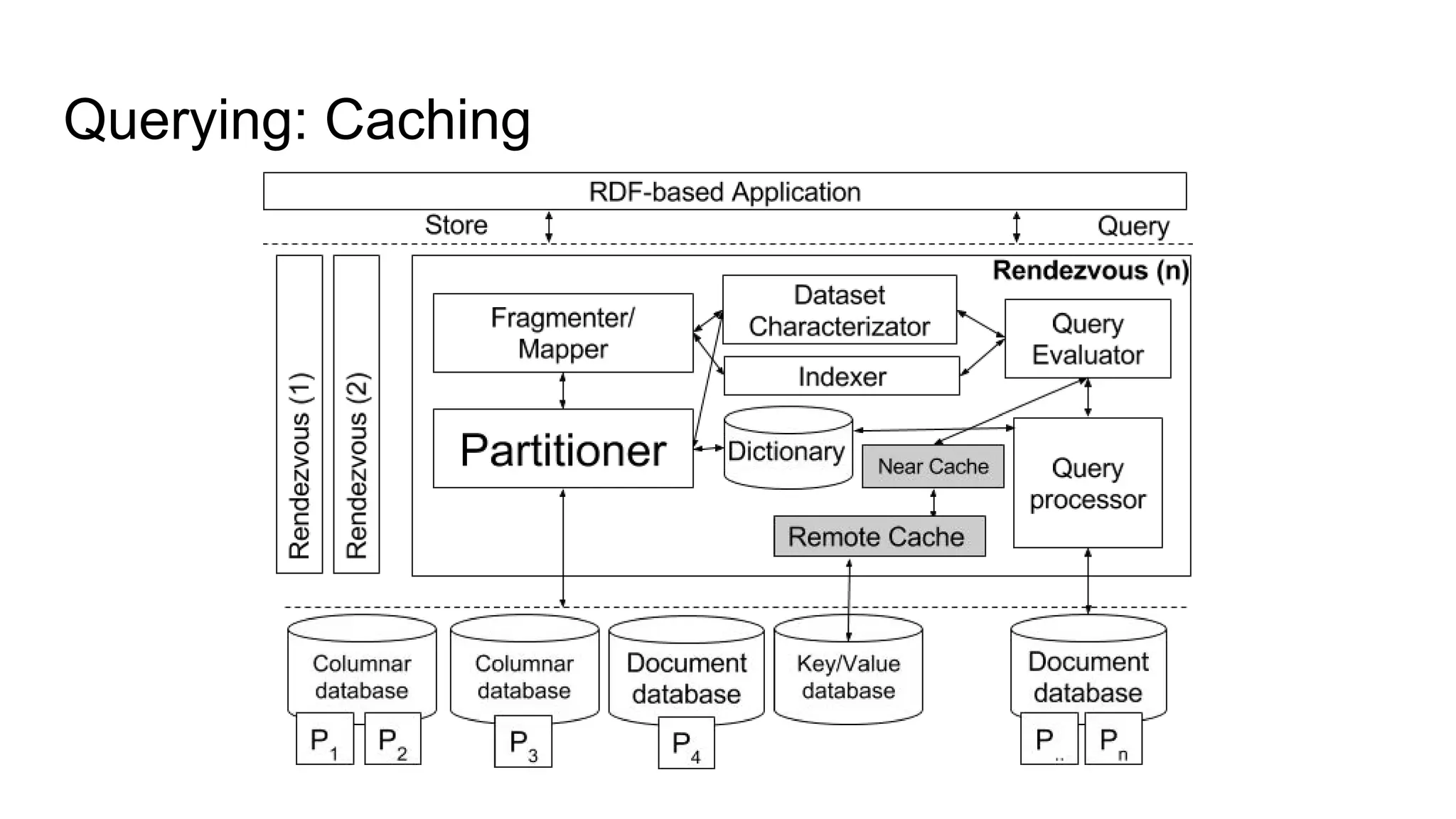
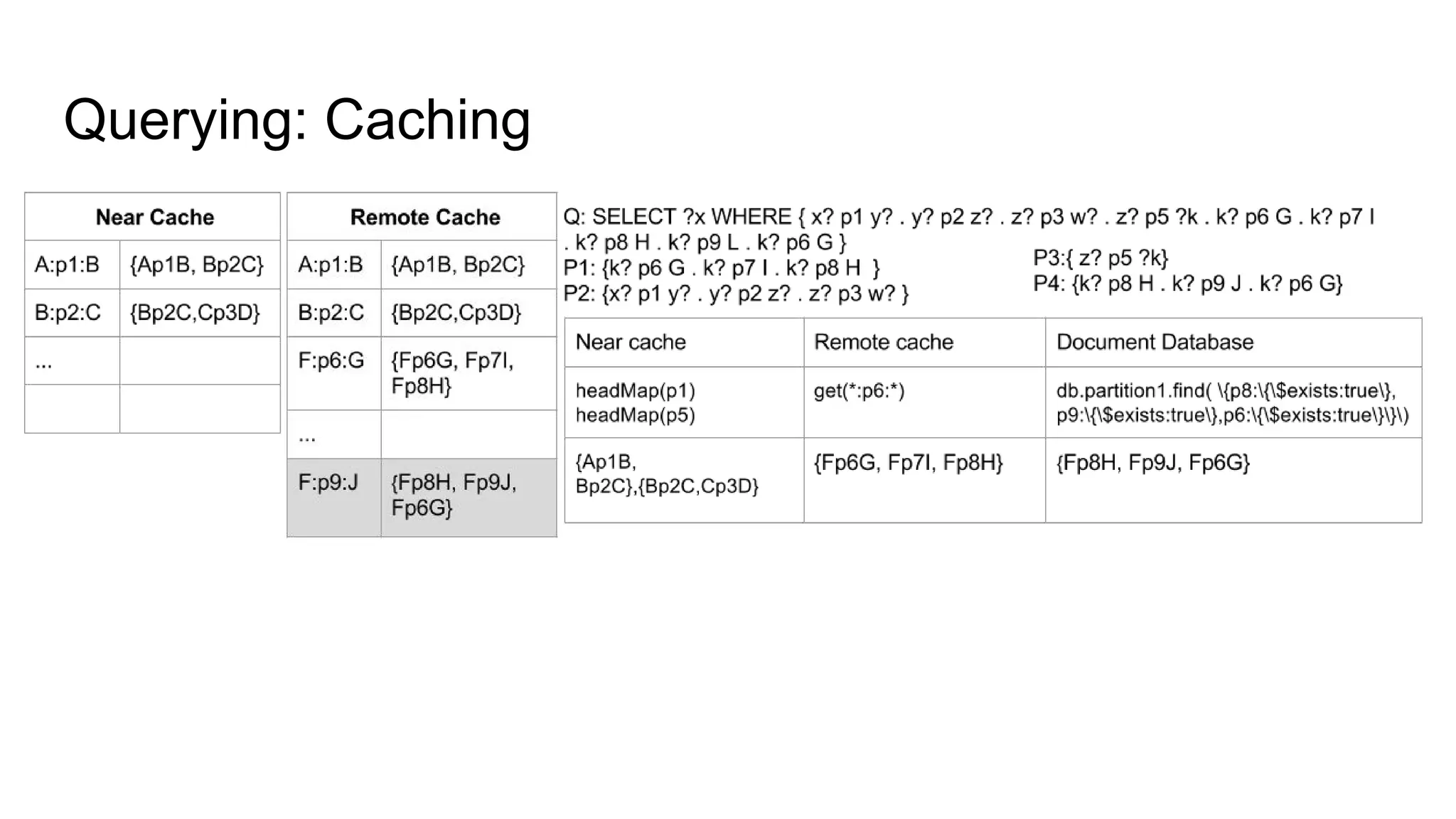
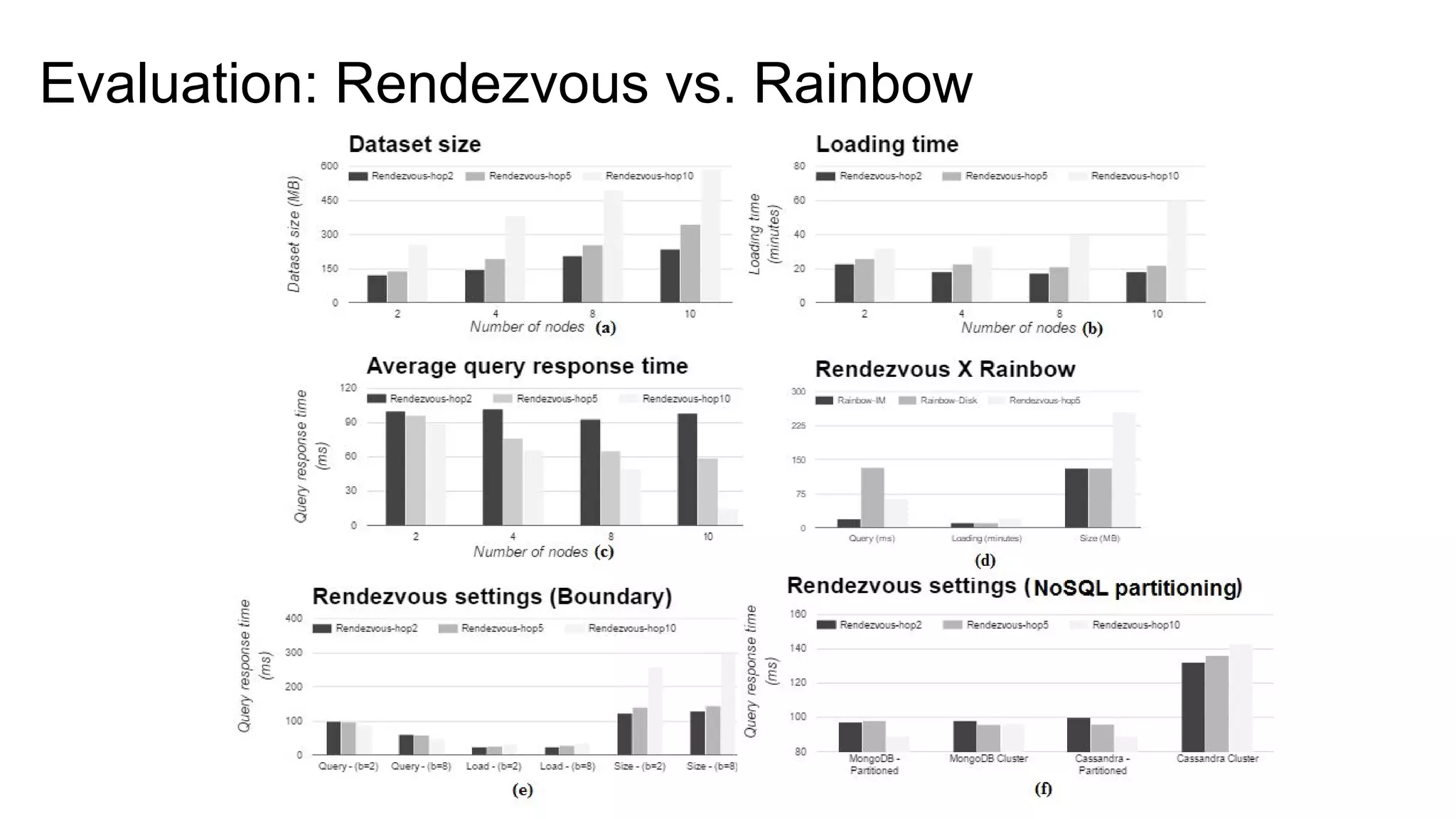
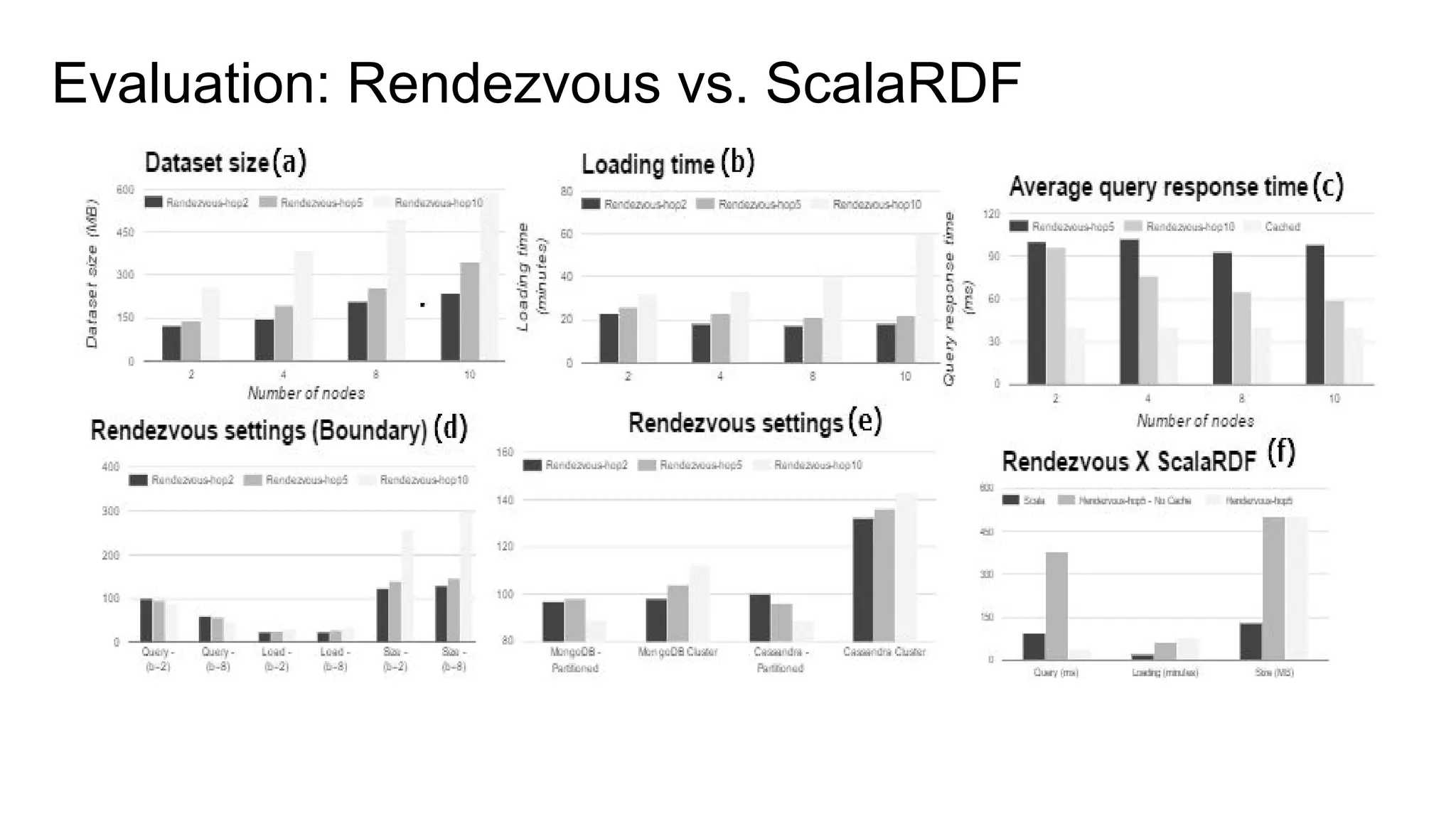
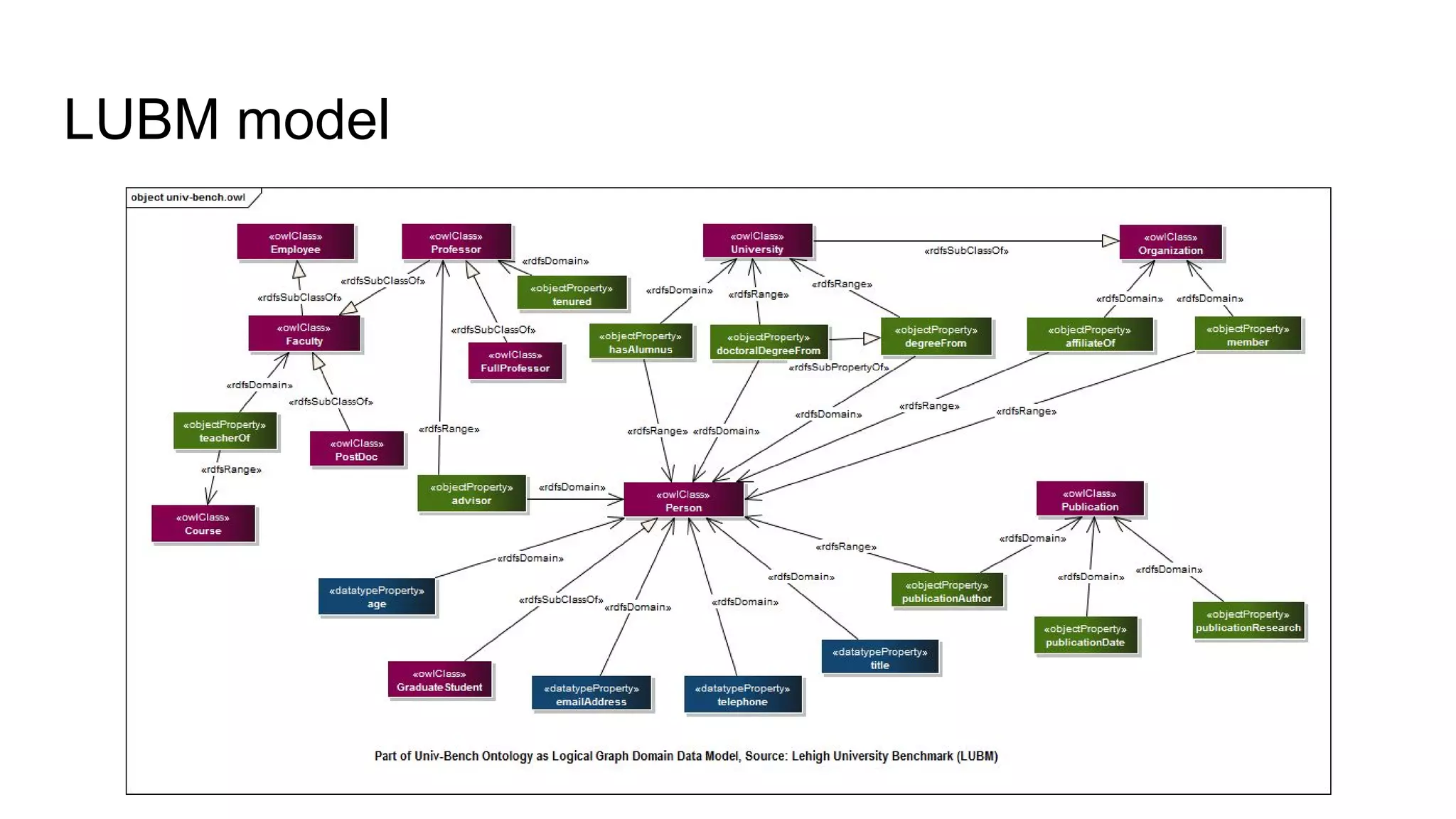
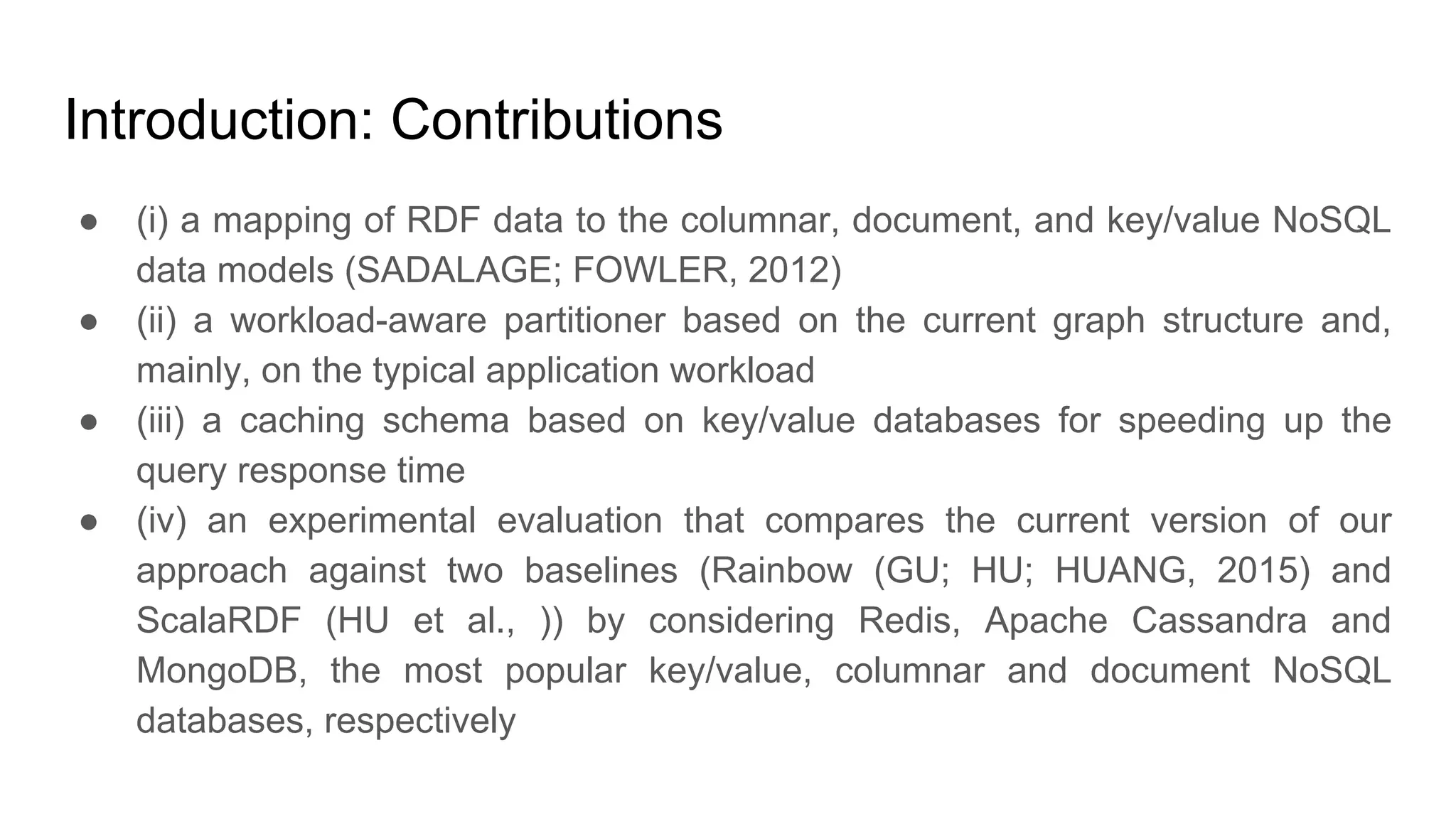
The document presents a proposed schedule for developing and evaluating Rendezvous, a middleware for storing massive RDF graphs in NoSQL databases. Key aspects of Rendezvous include a workload-aware partitioning approach, mapping RDF data to different NoSQL data models, and a caching structure to accelerate query response. The evaluation compares Rendezvous to existing approaches using LUBM, a standard RDF benchmark, and finds that Rendezvous outperforms alternatives with graph-aware partitioning and near caching. Future work is planned to improve Rendezvous with compression, updates, additional NoSQL support, and more complex workloads.




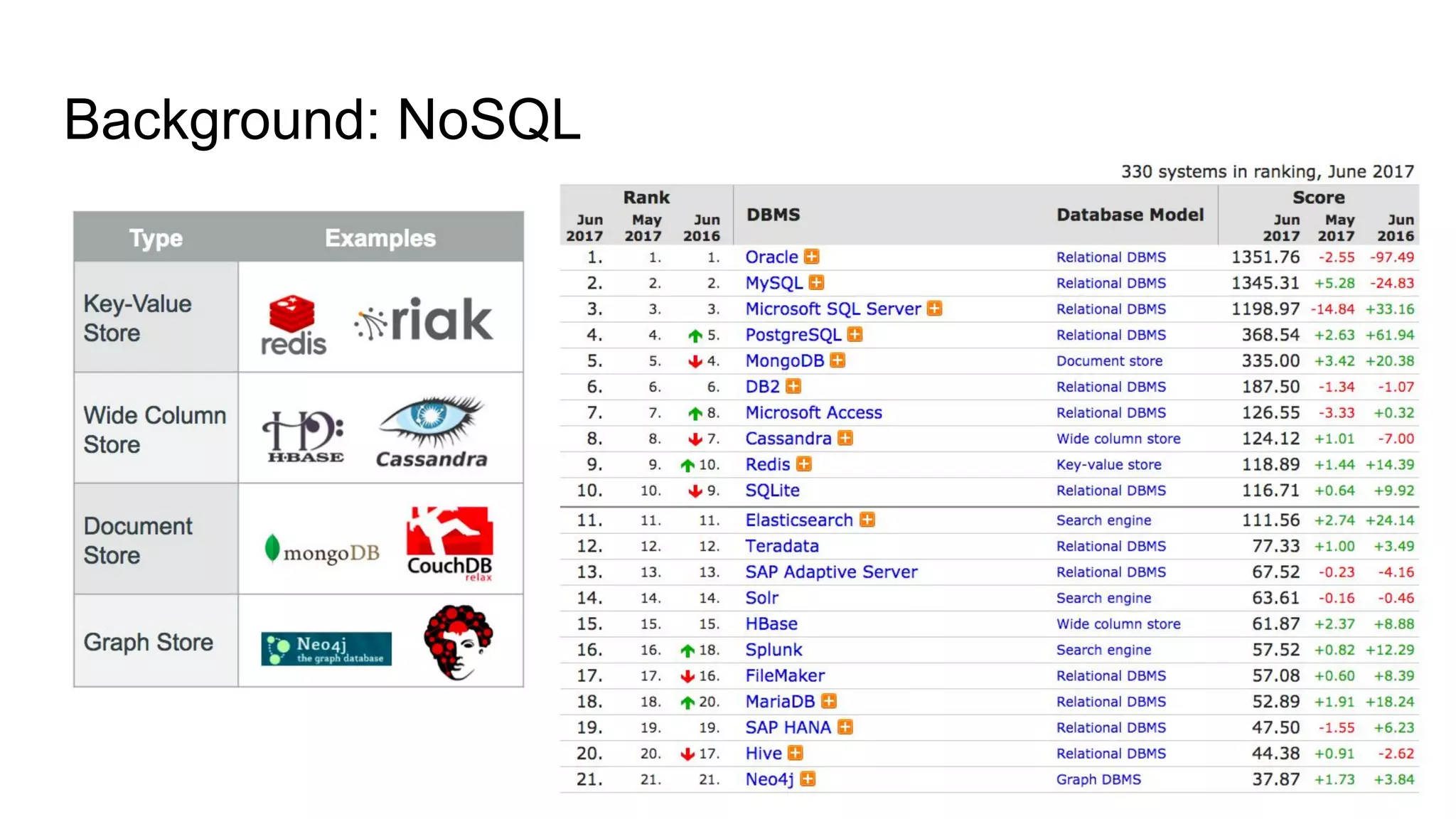


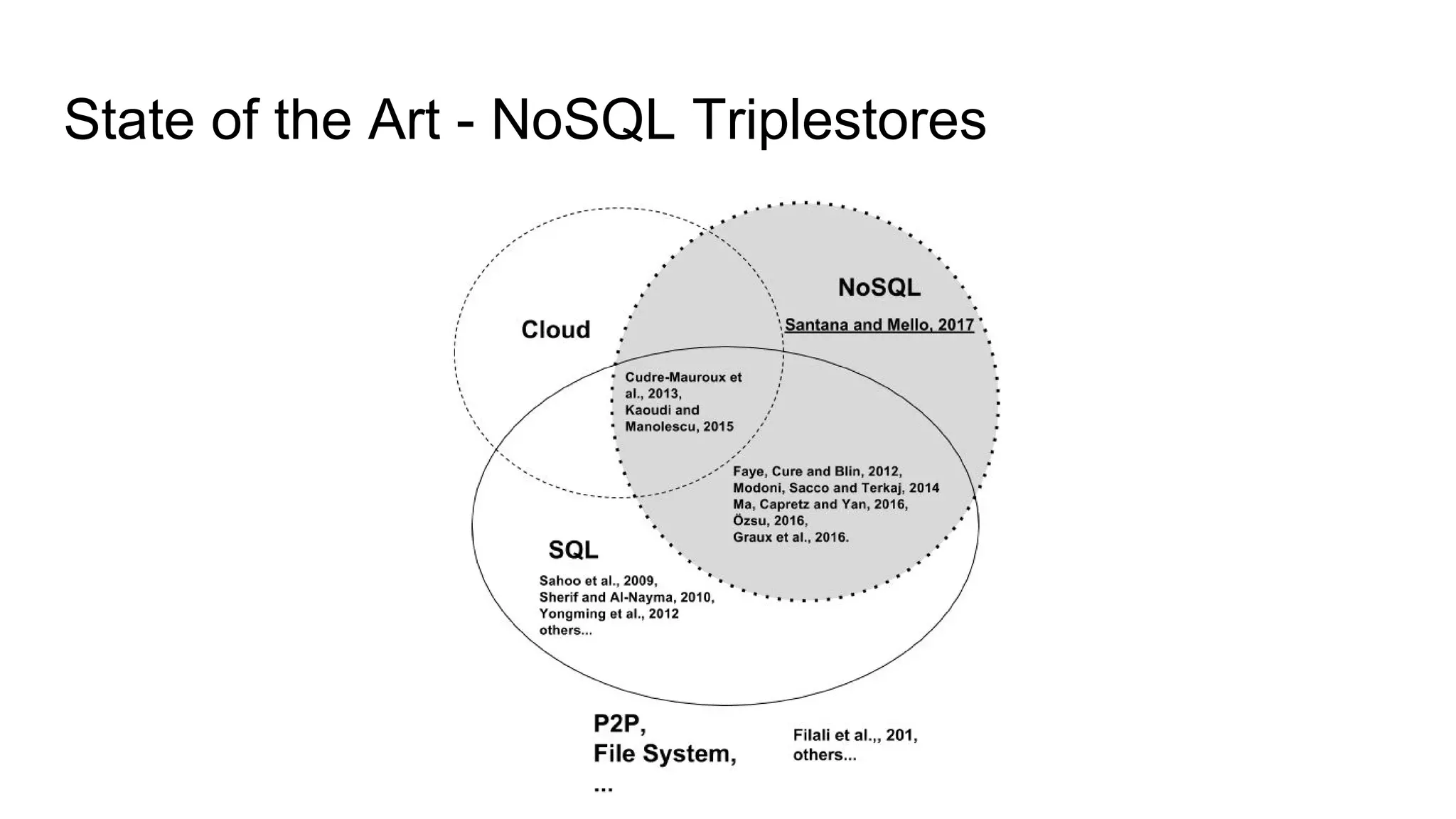

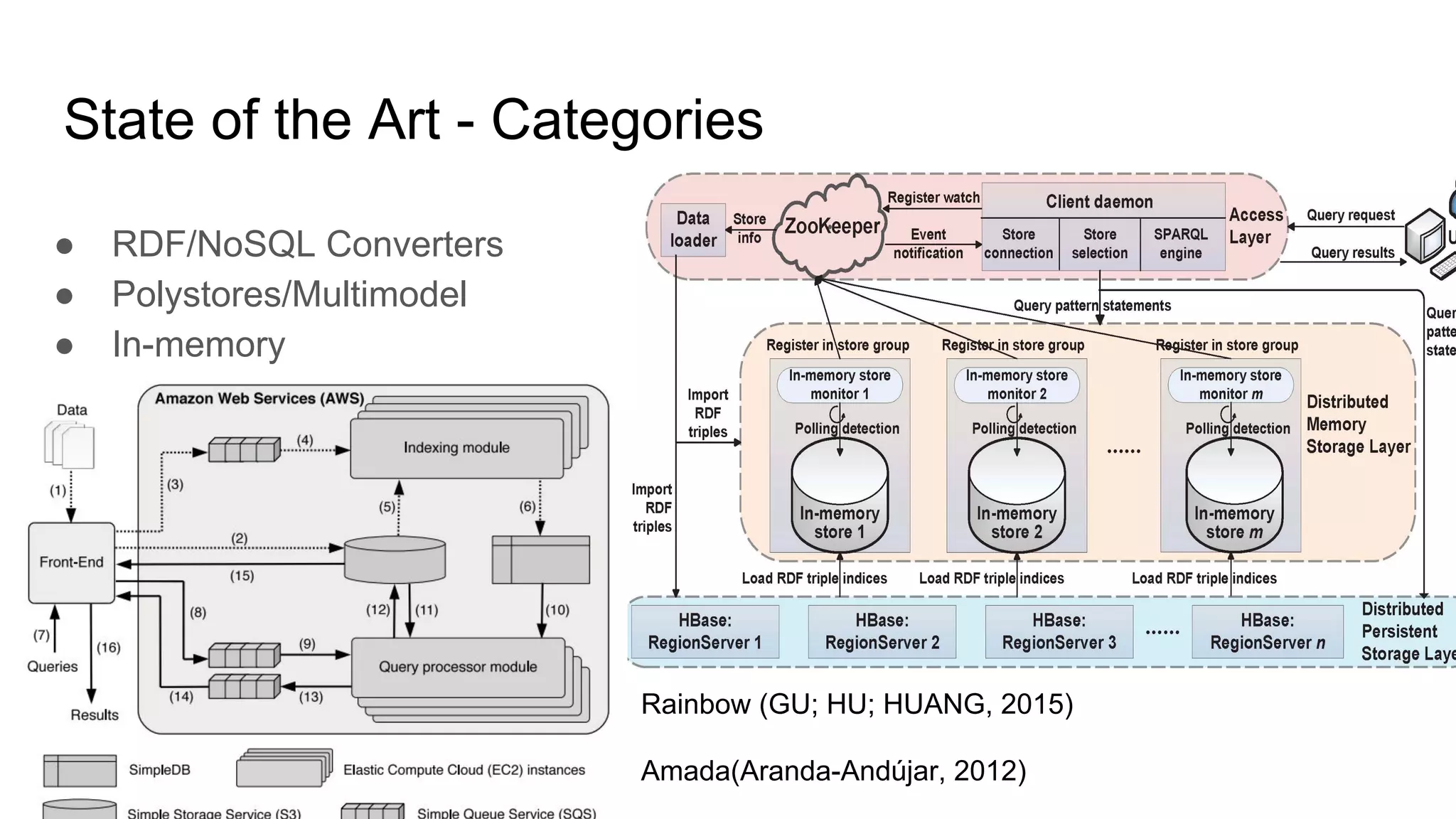
![State of the Art ● BUGIOTTI, F. et al. Invisible glue: scalable self-tuning multi-stores. In: Conference on Innovative Data Systems Research (CIDR). [S.l.: s.n.], 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualificacao2-170608161143/75/A-Workload-Aware-Middleware-for-Storing-Massive-RDF-Graphs-into-NoSQL-Databases-15-2048.jpg)