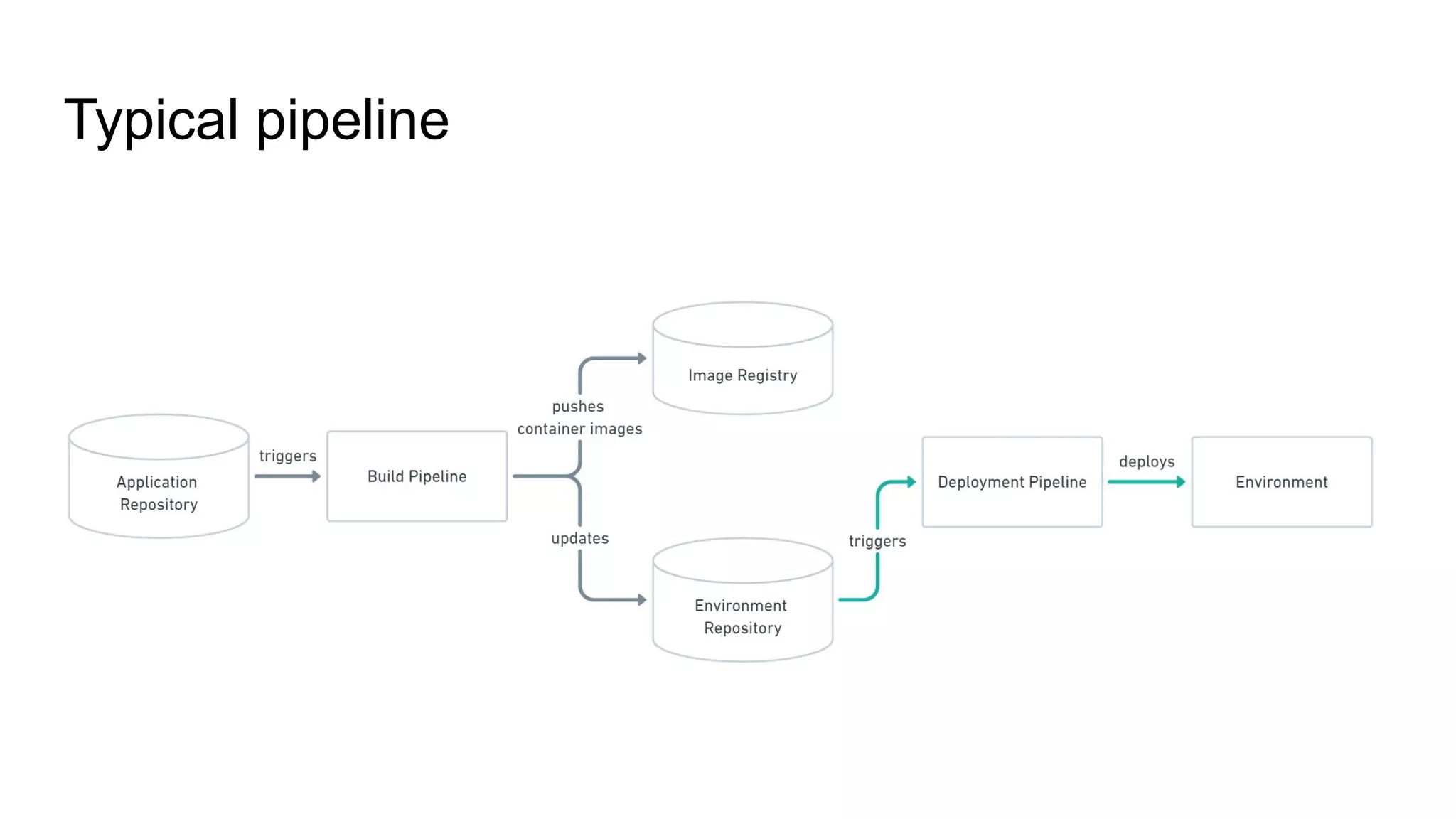
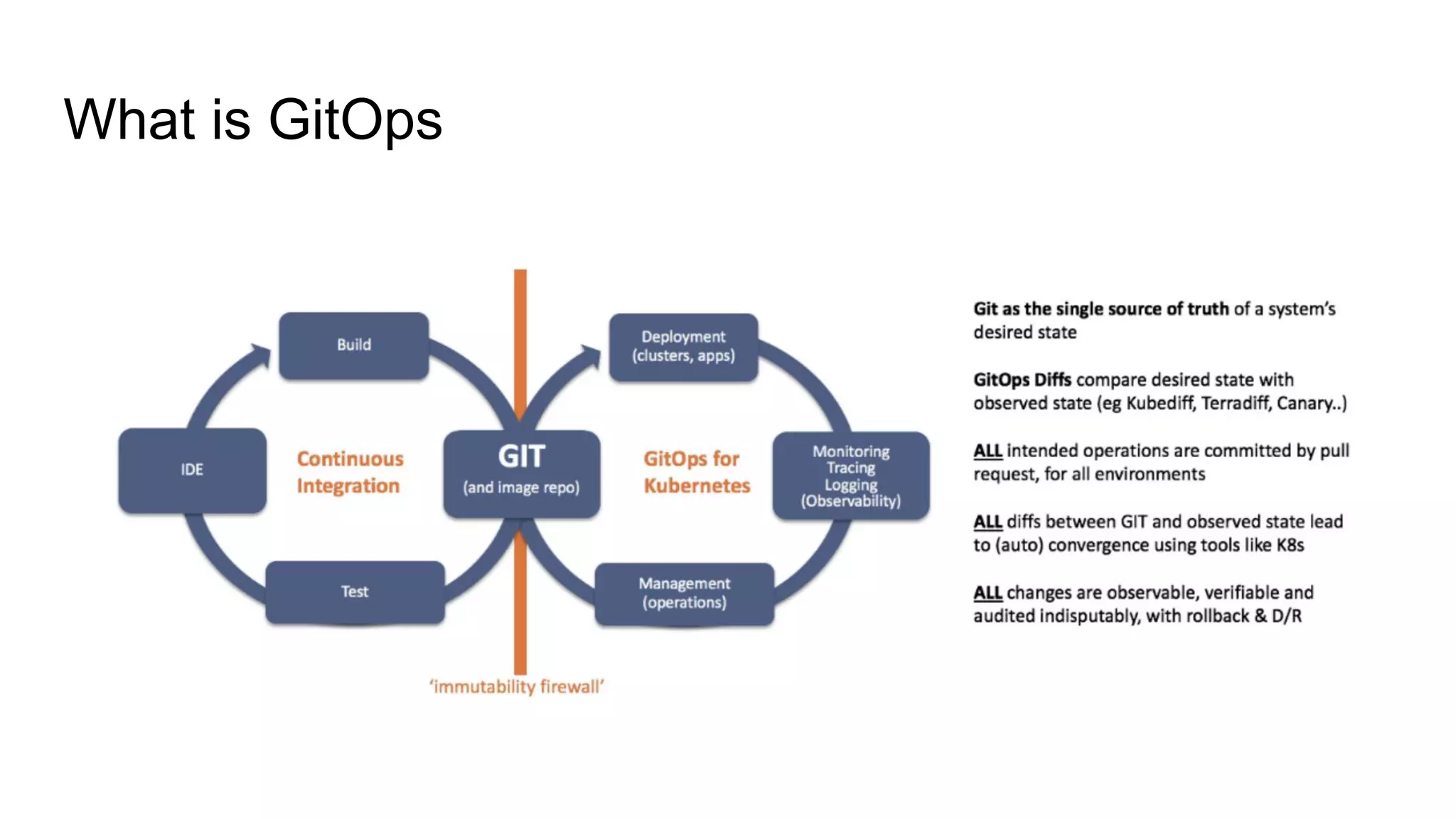
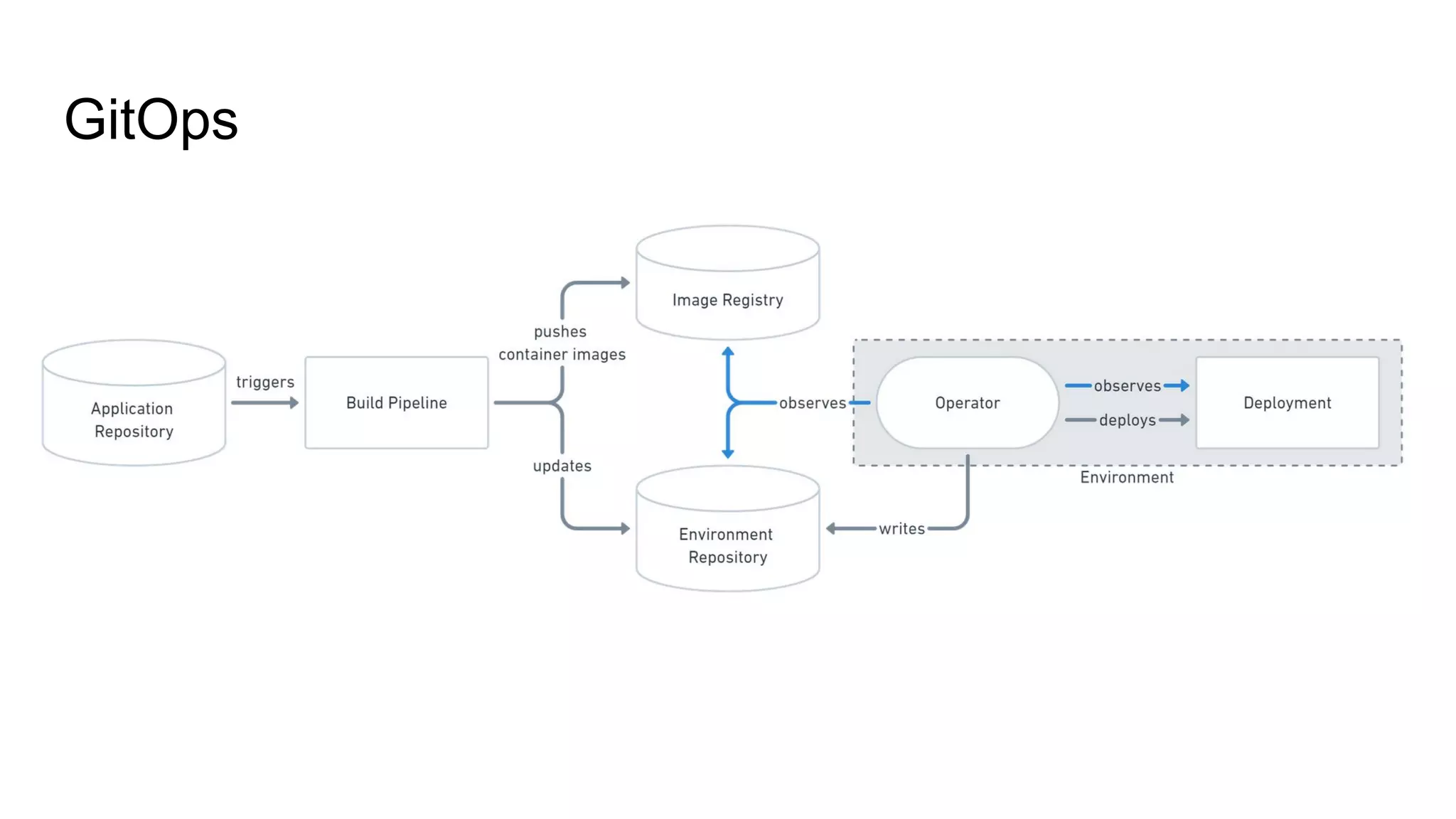
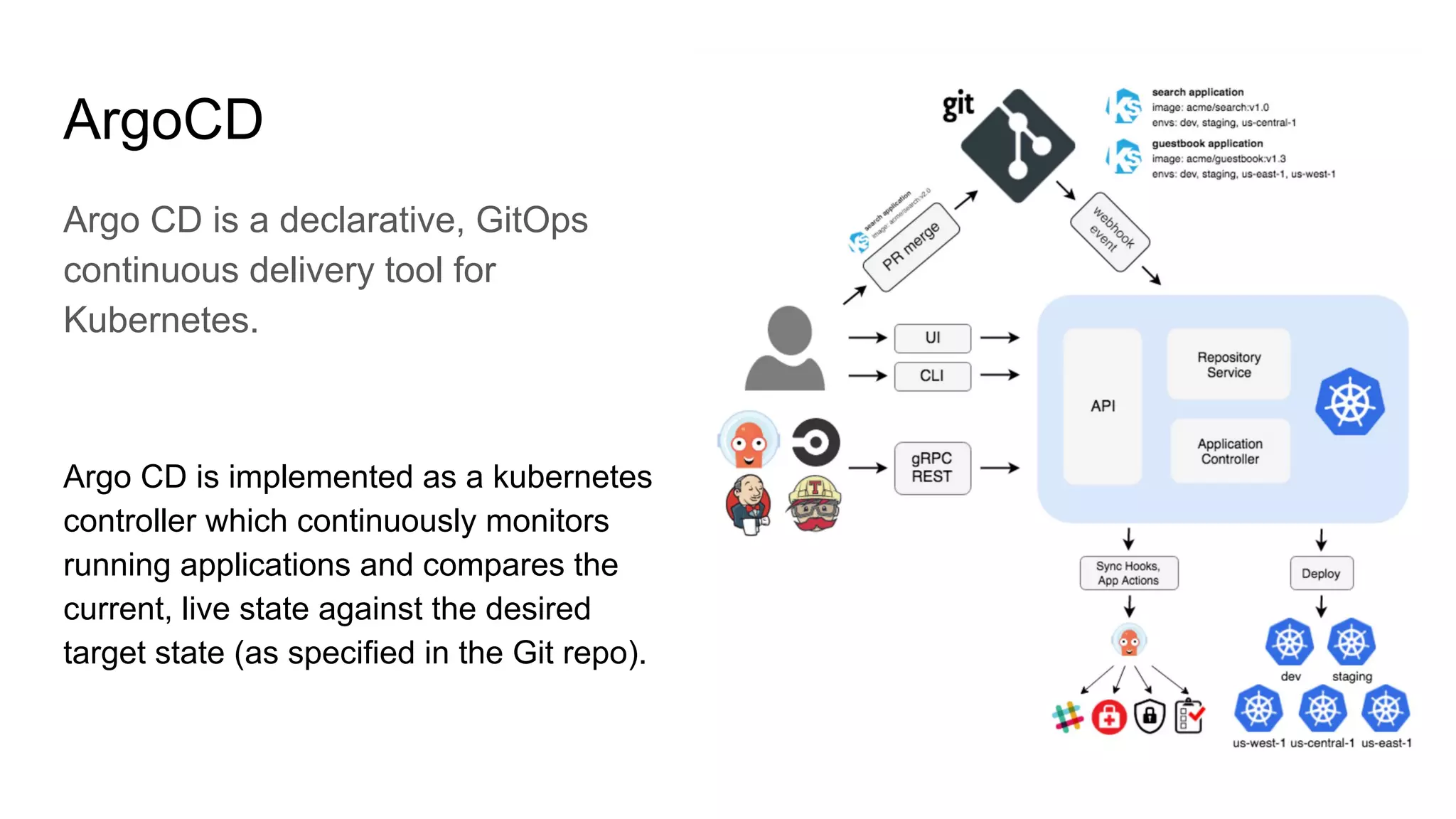
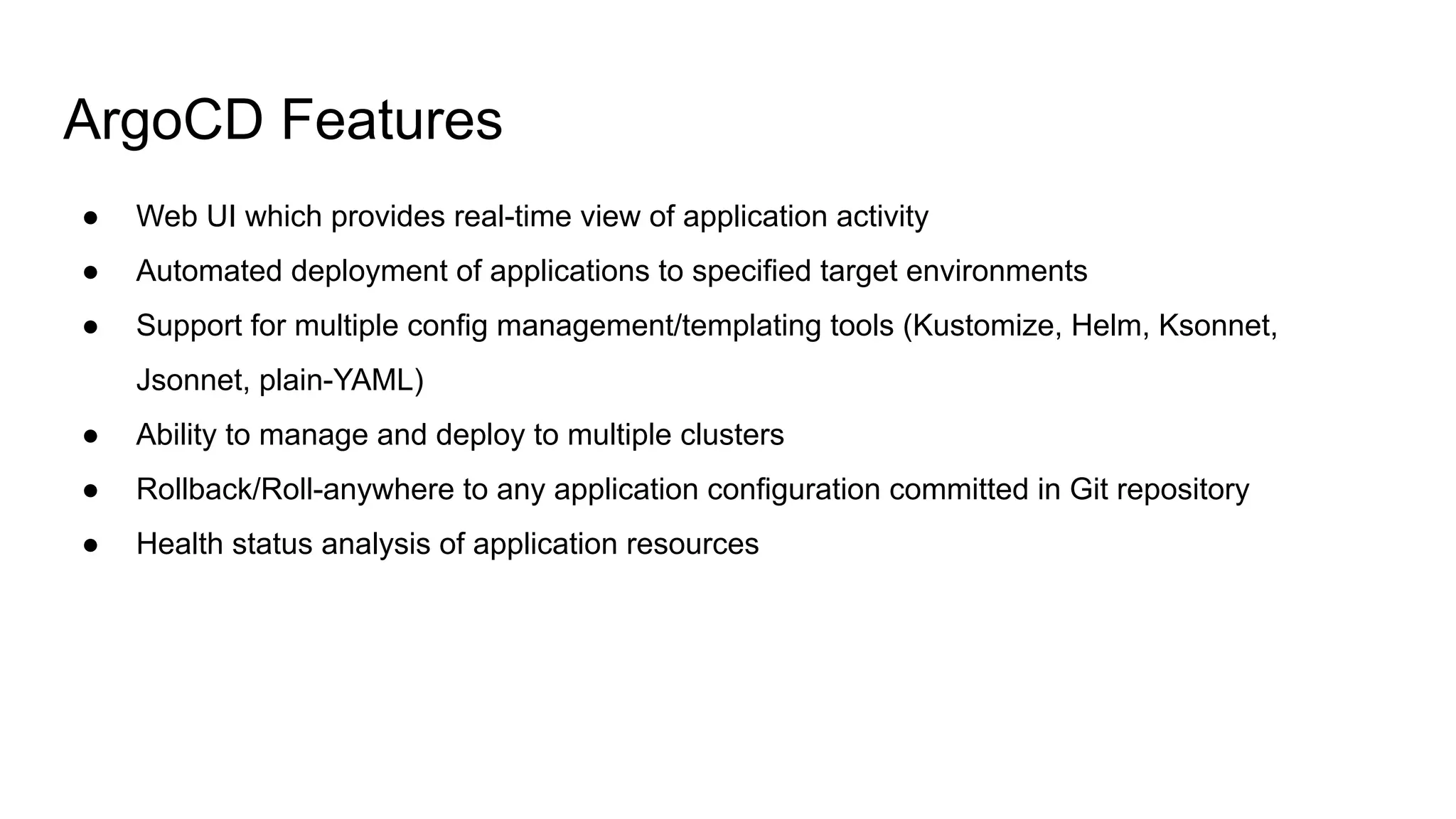
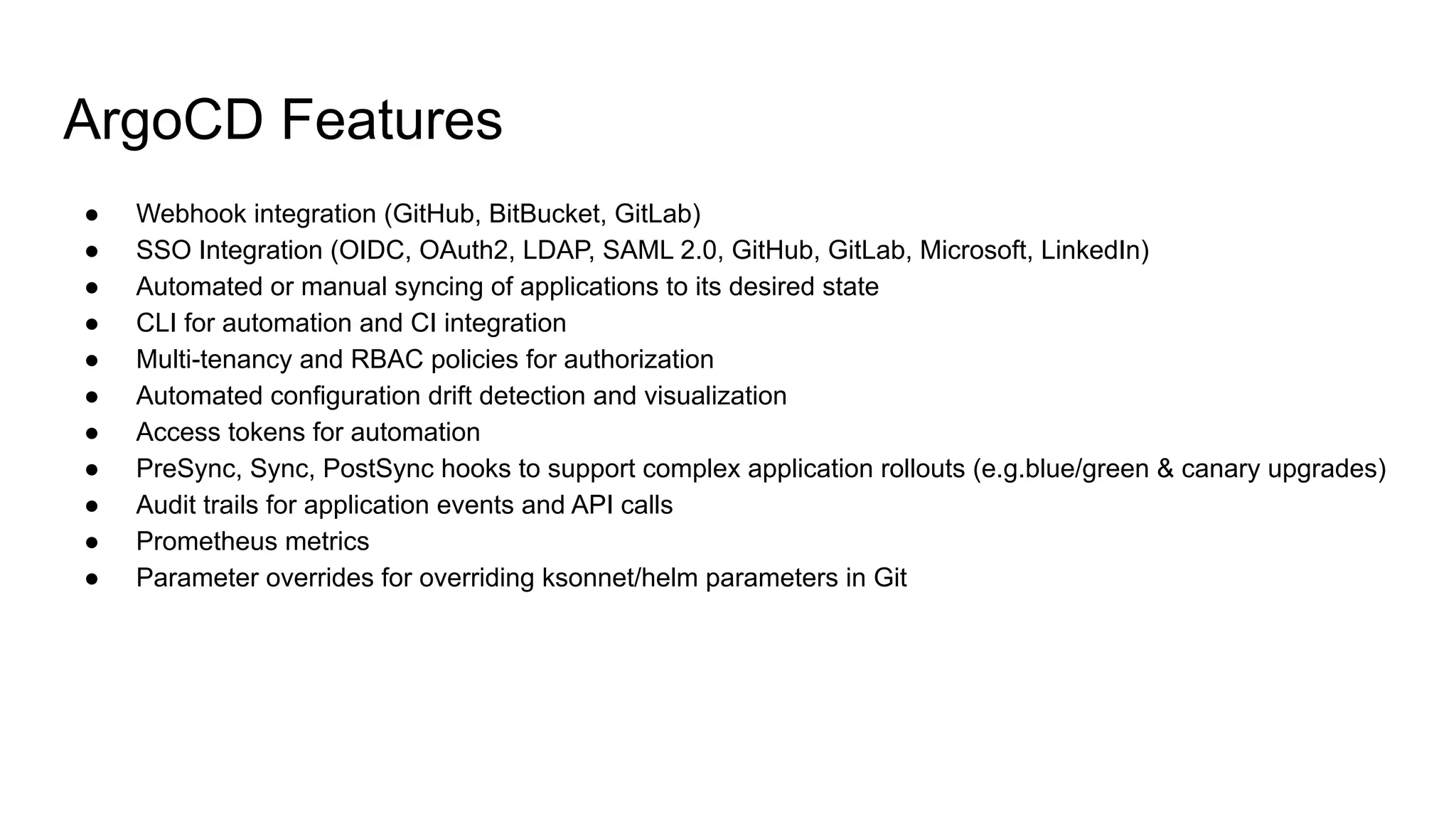
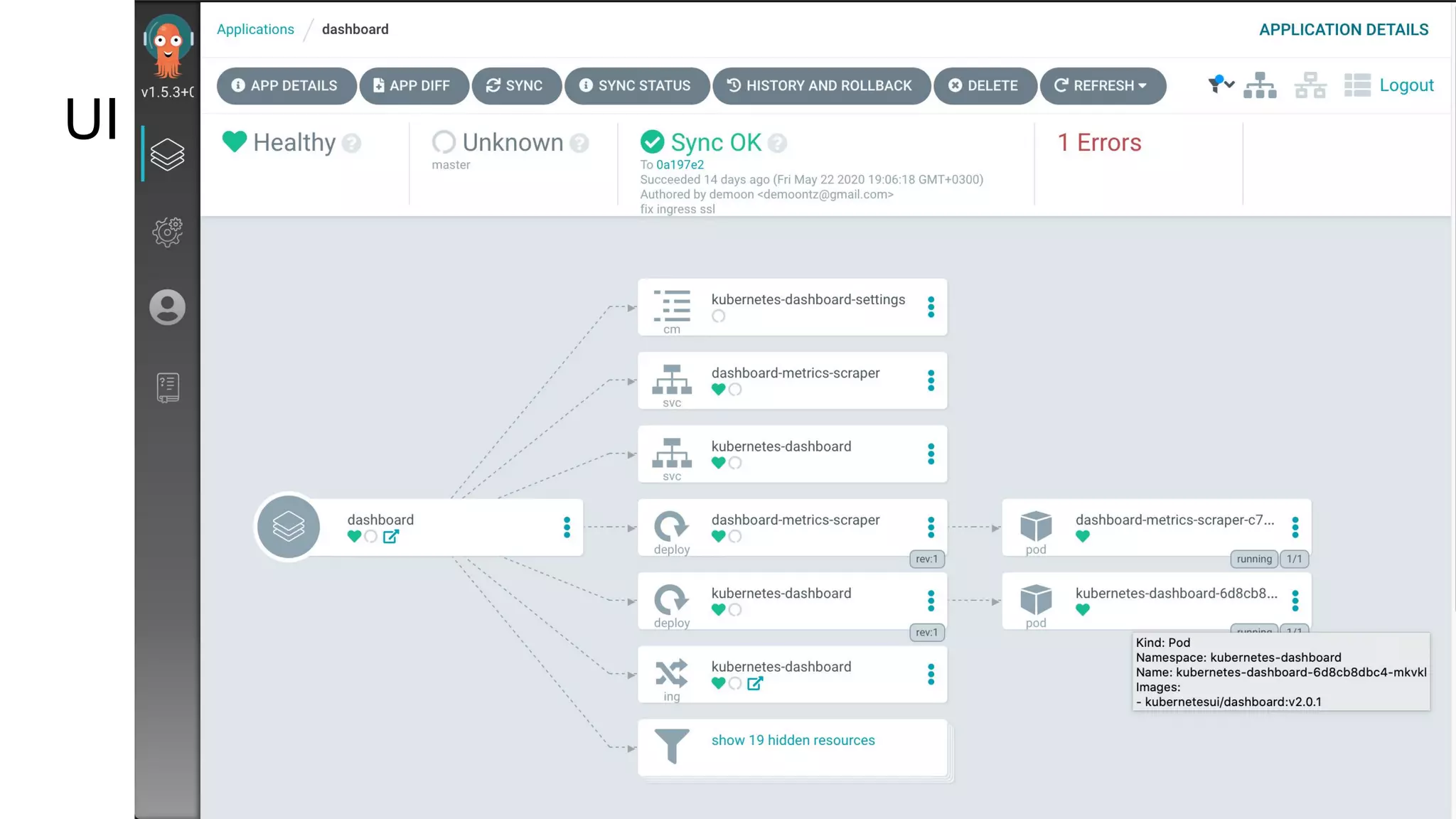
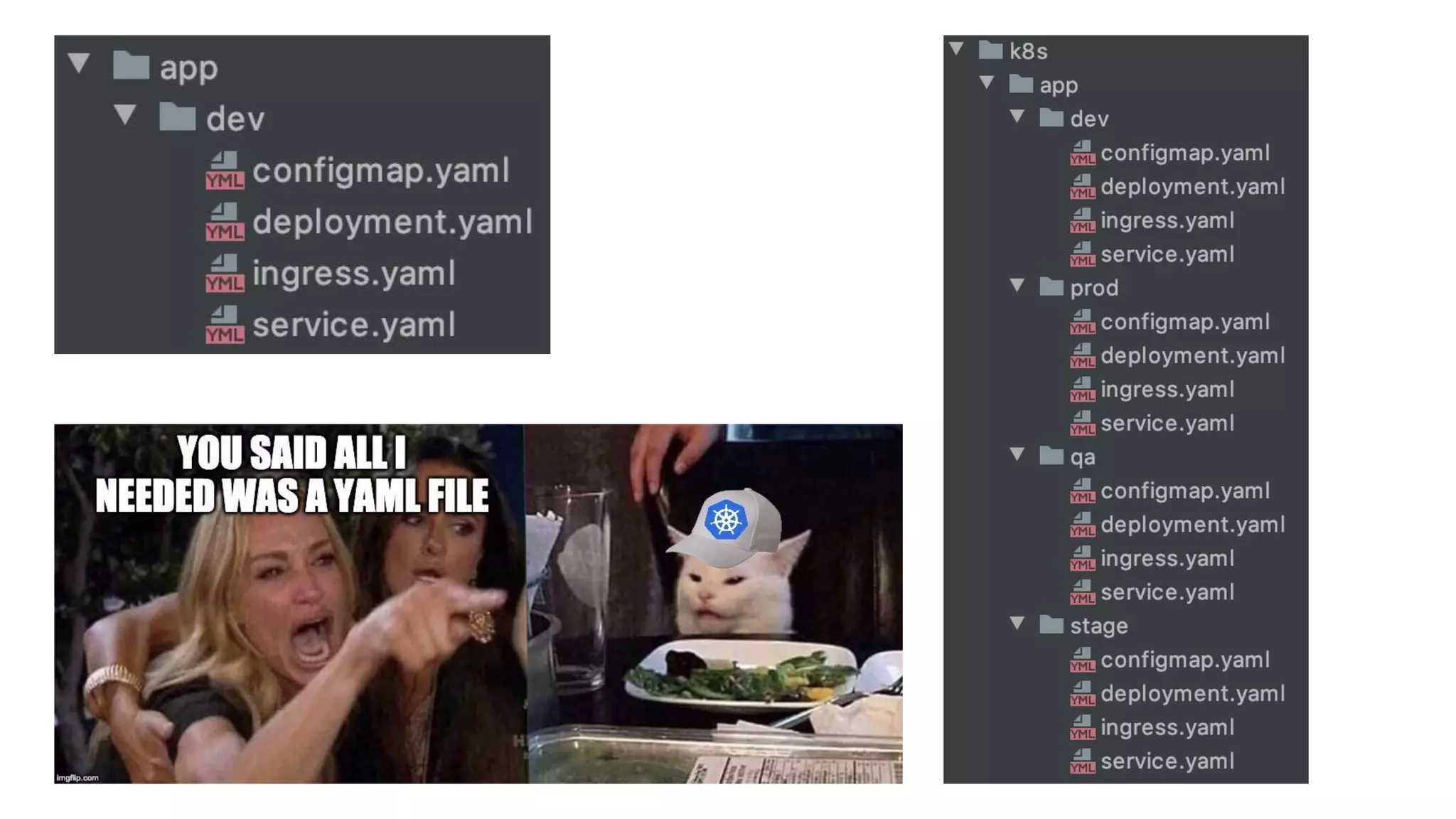
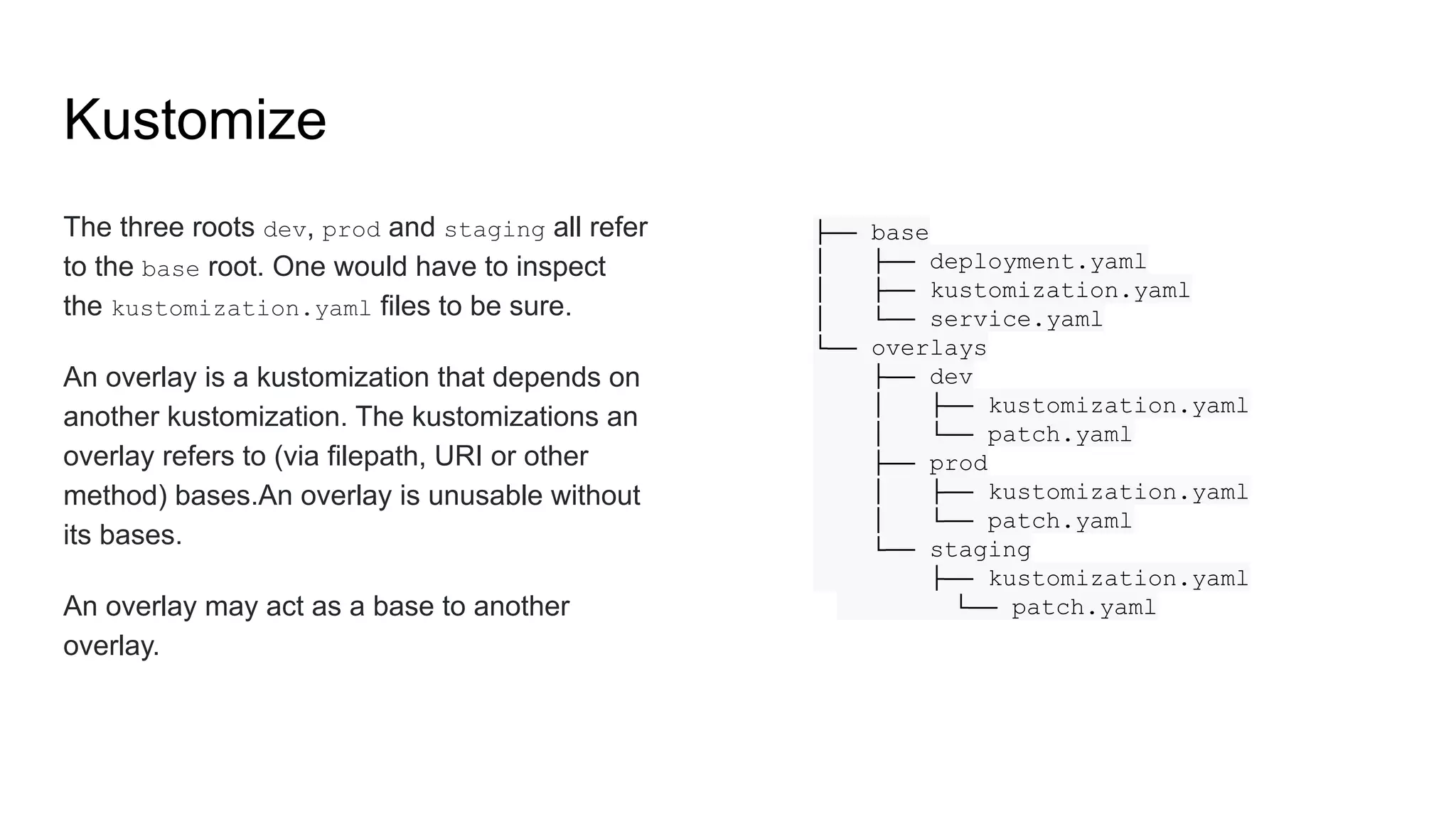
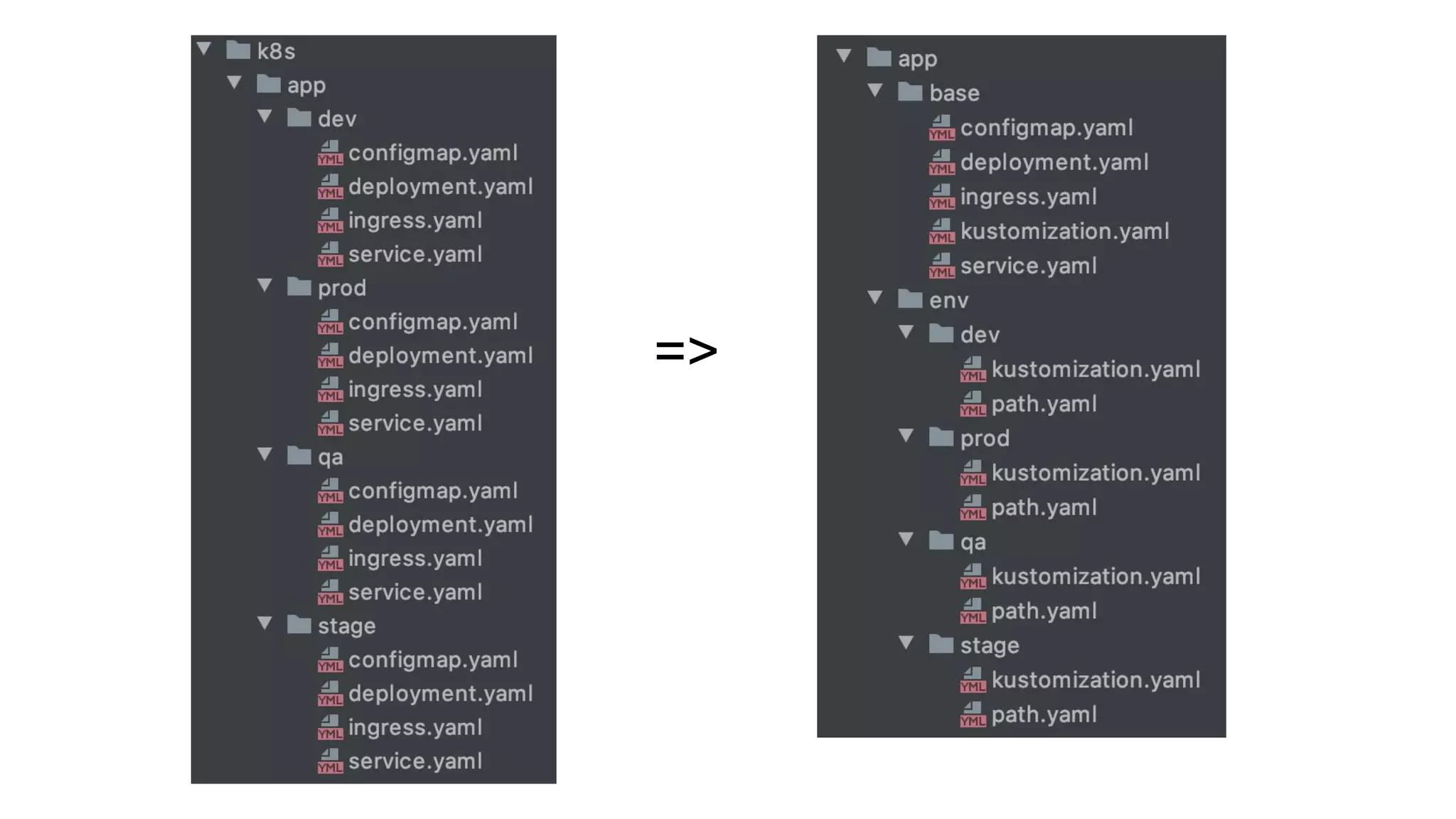
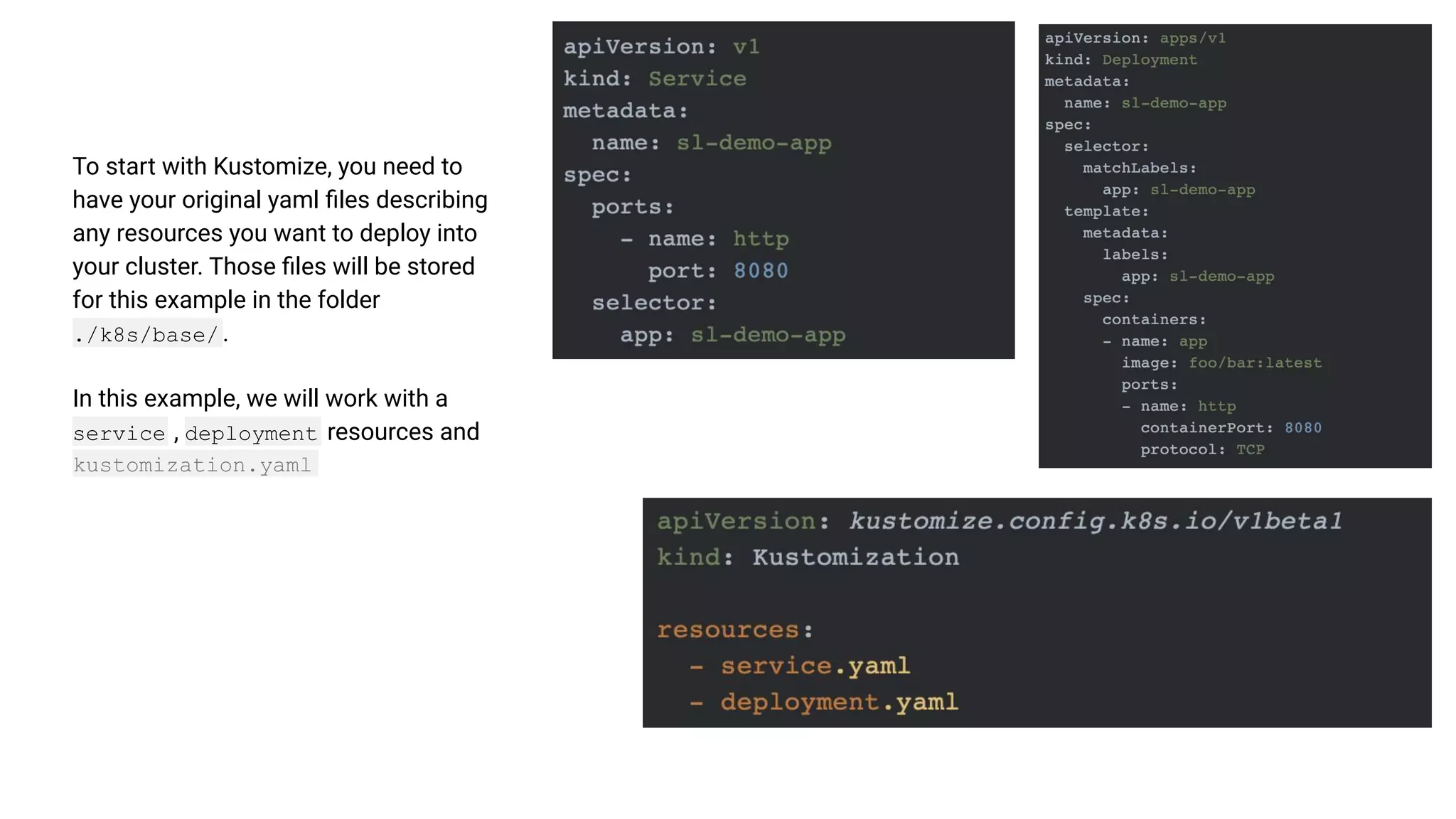
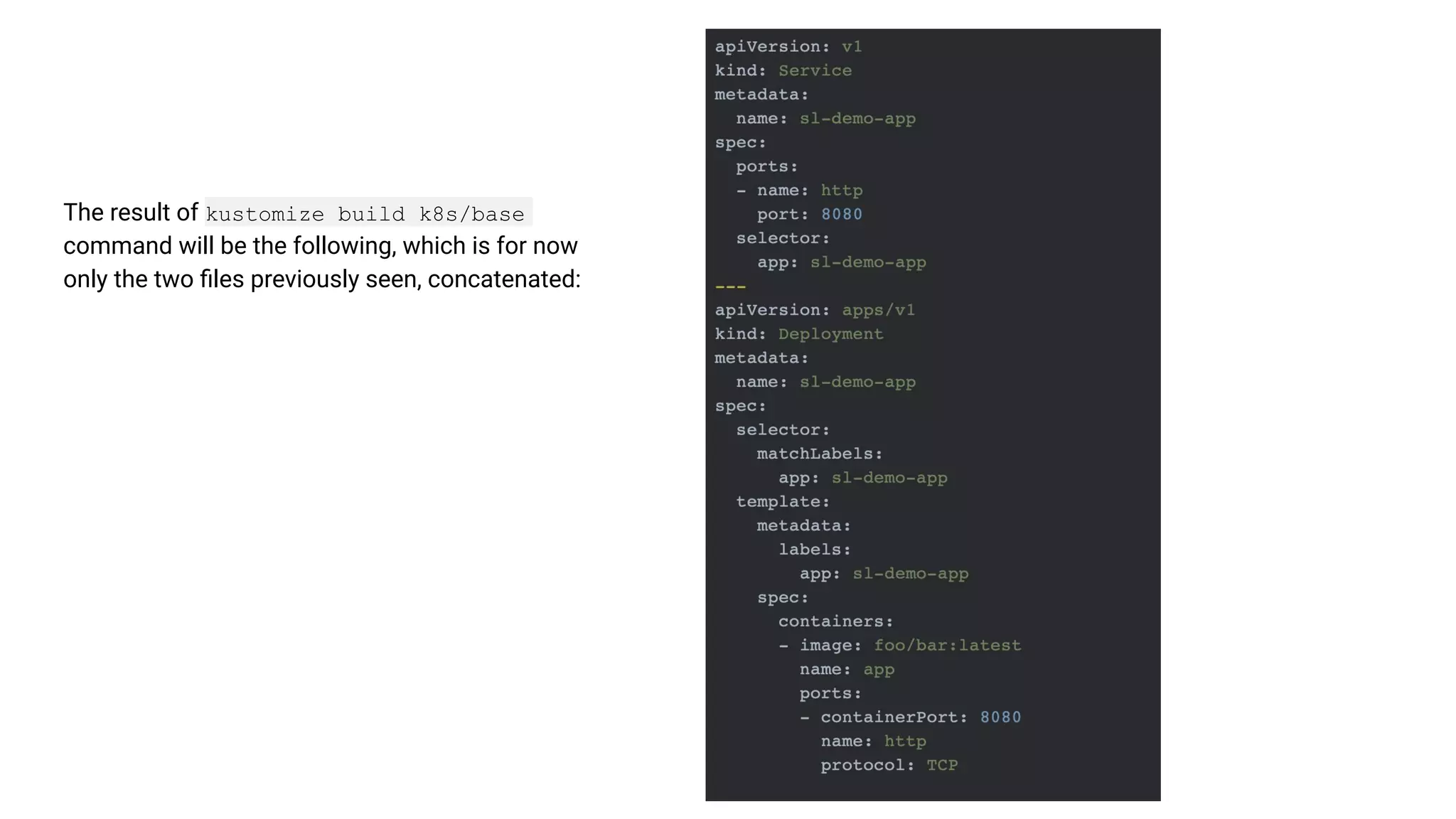
The document discusses GitOps and ArgoCD for managing Kubernetes applications. It defines GitOps as storing the desired state of systems in Git repositories and using continuous delivery tools to ensure the live systems match that state. ArgoCD is introduced as a GitOps tool that monitors applications and ensures the running state matches the target state defined in Git. Key features of ArgoCD include a web UI, automated deployments, support for different config formats, and rollback capabilities. The document provides an example of using Kustomize to customize Kubernetes resources through overlays.