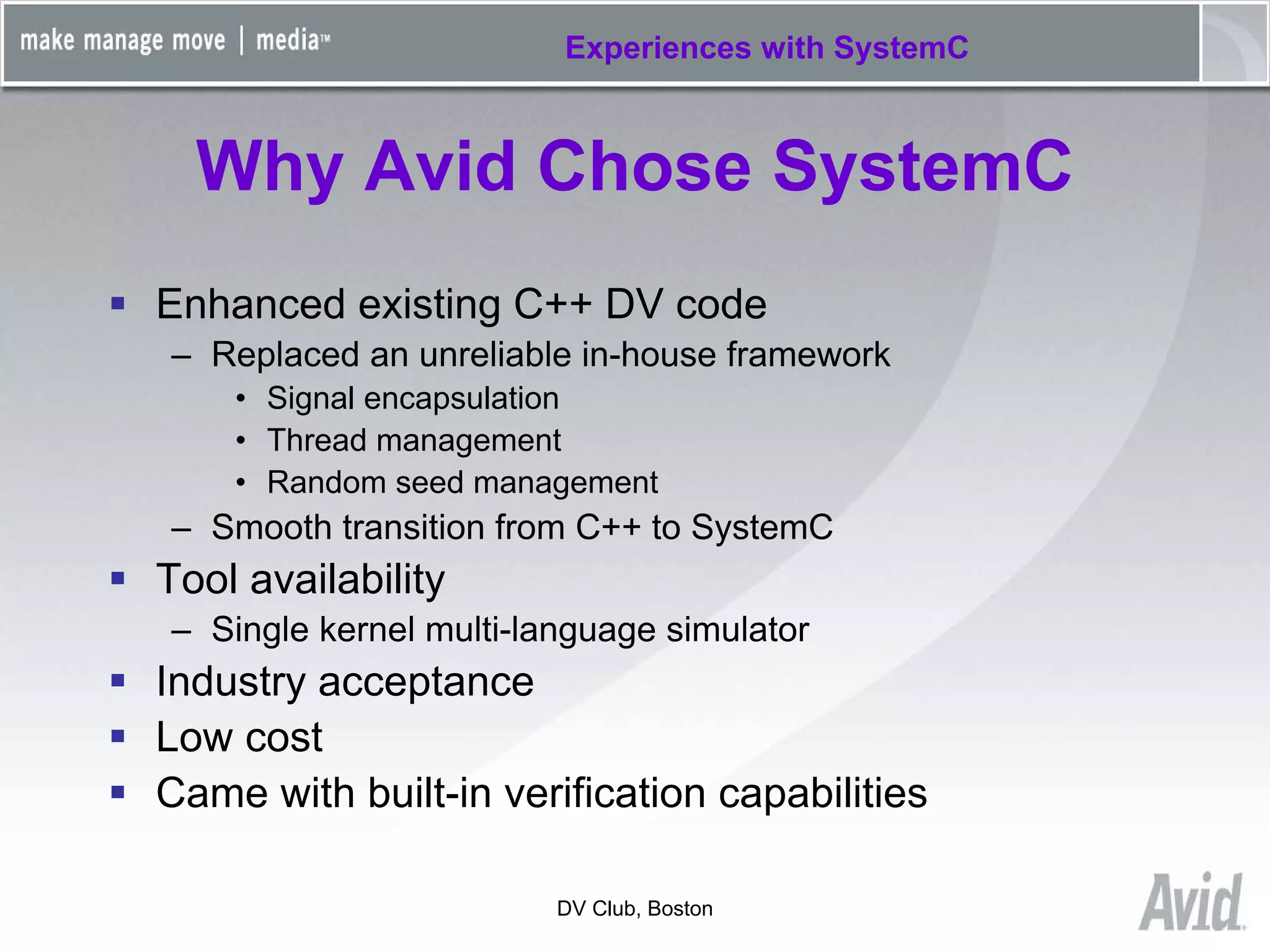
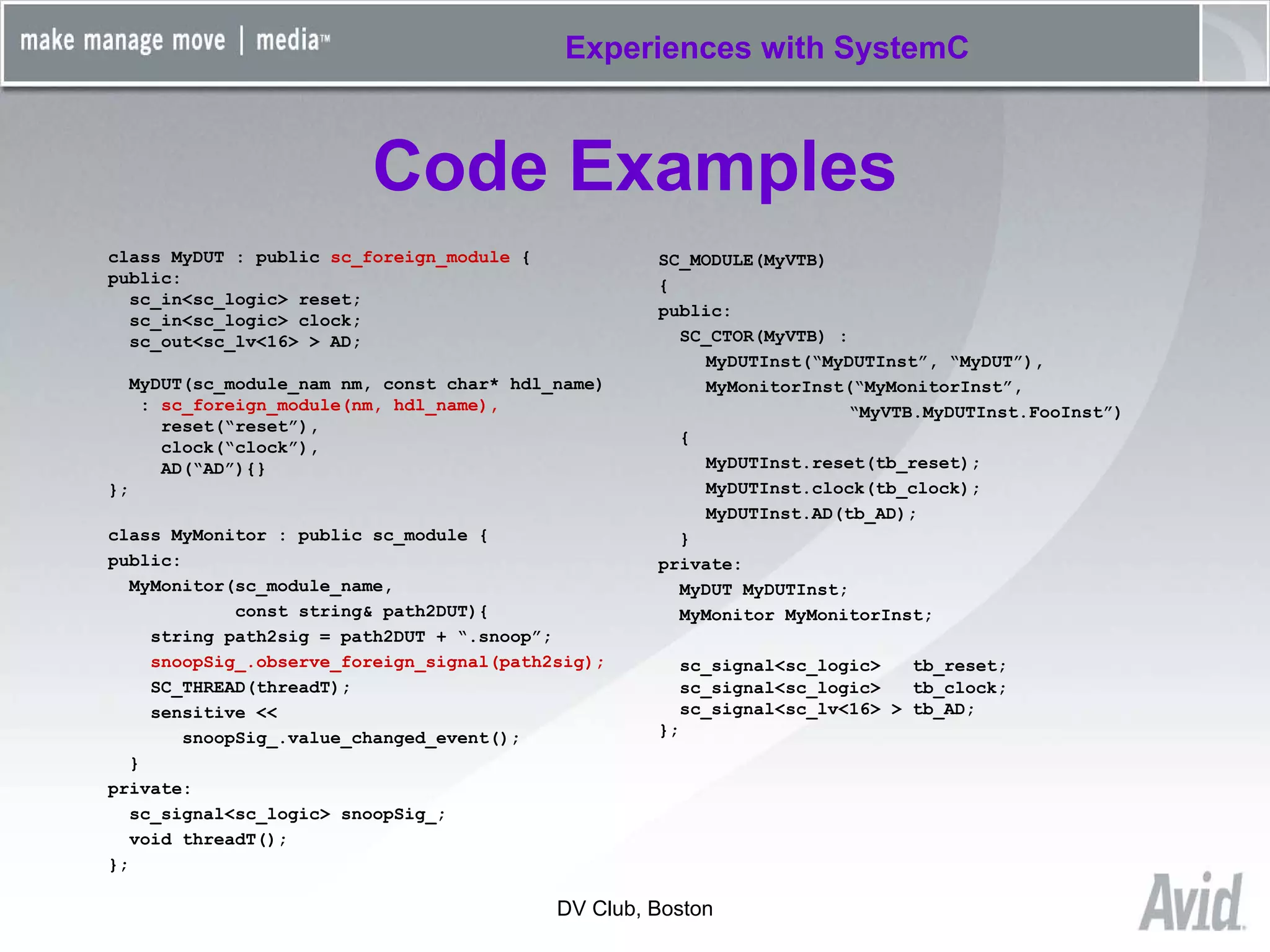
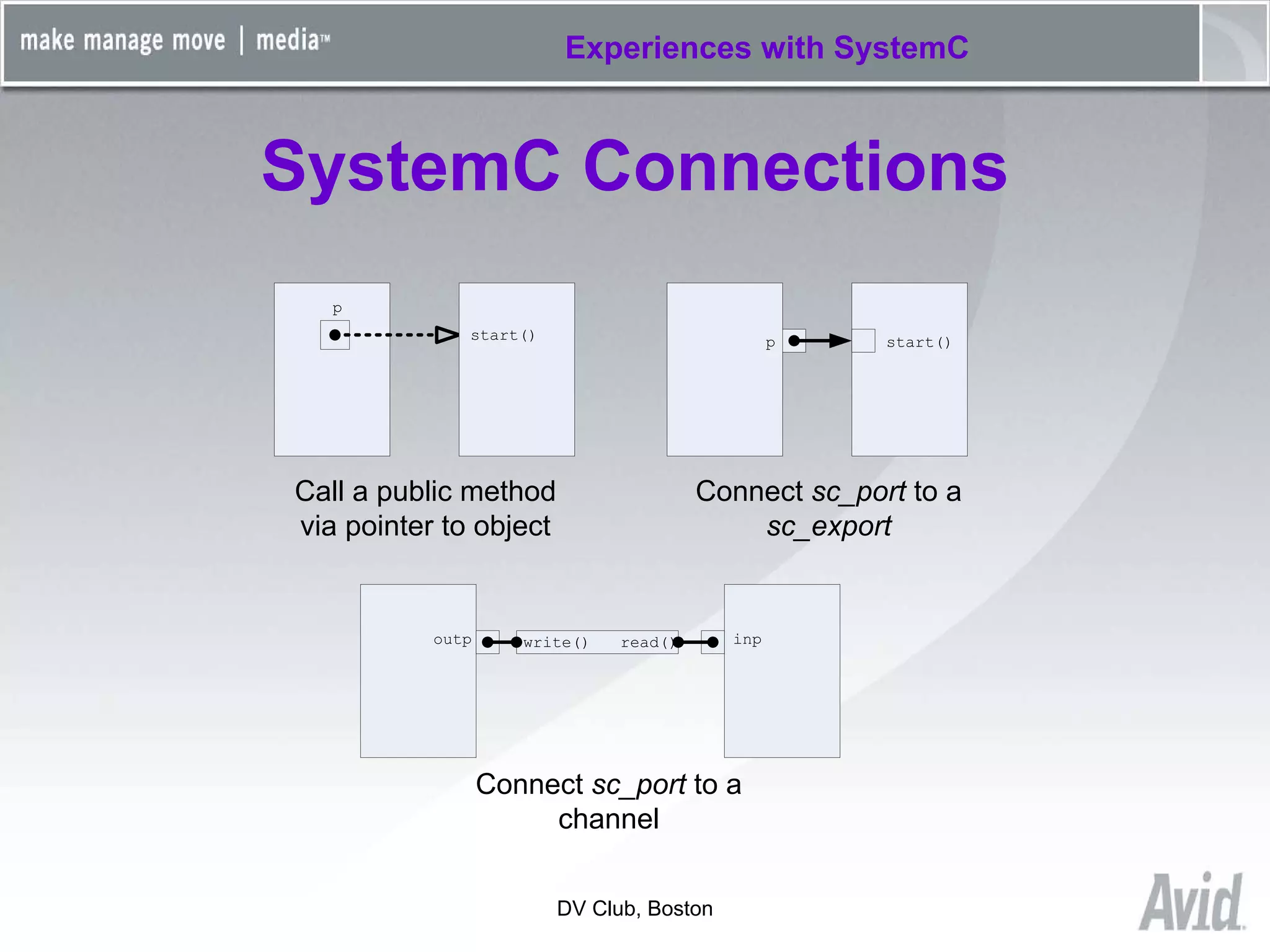
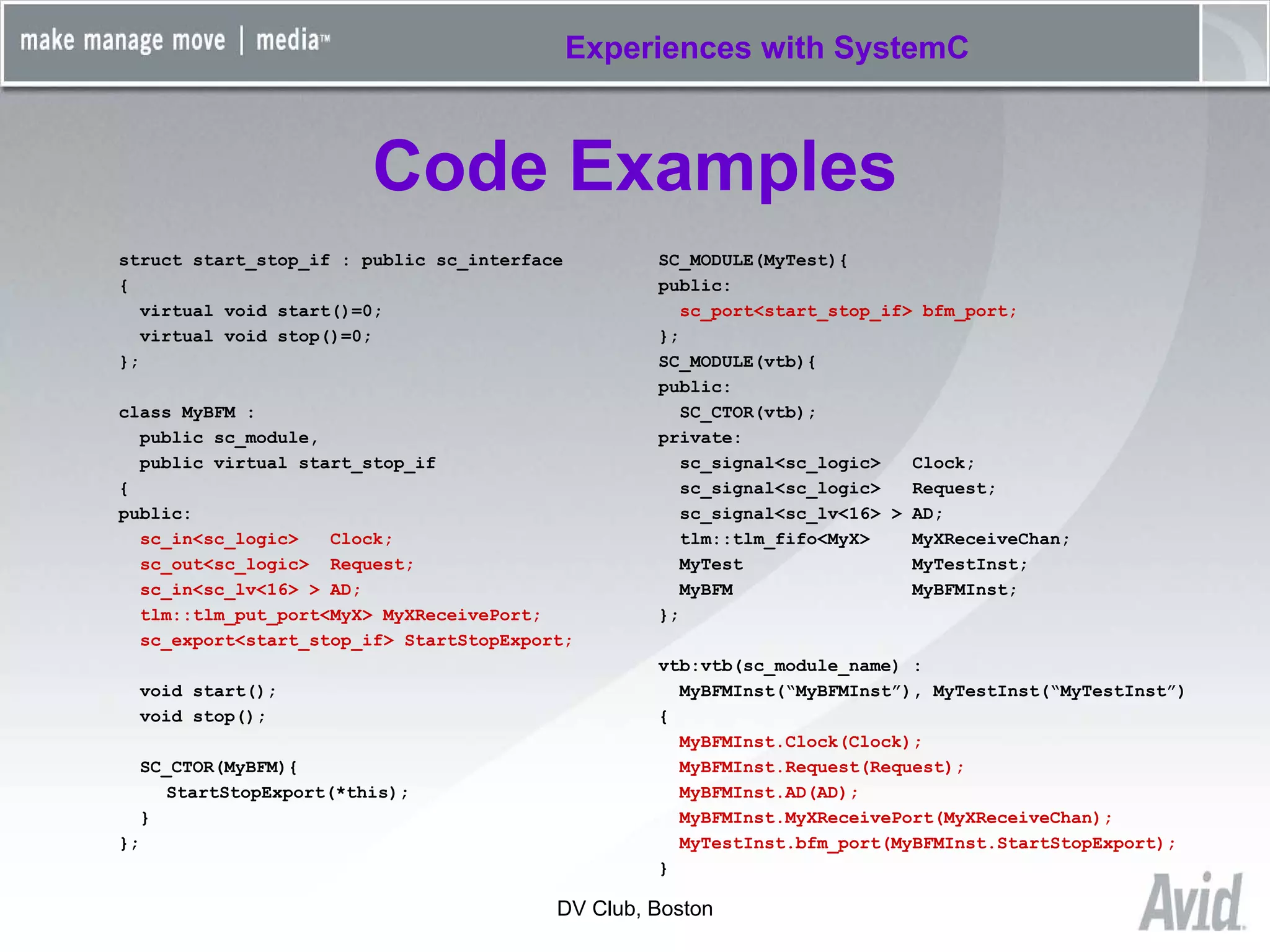
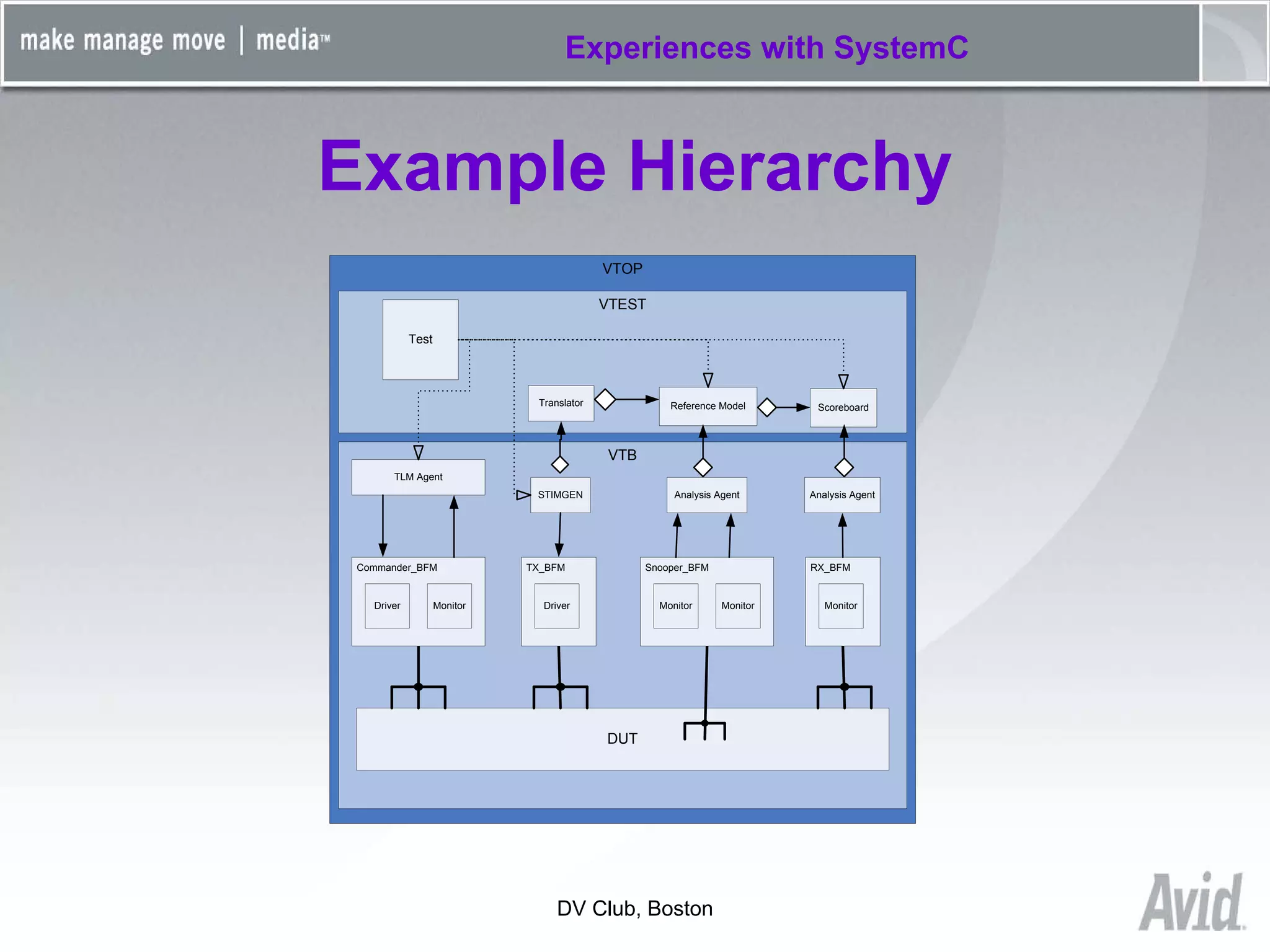
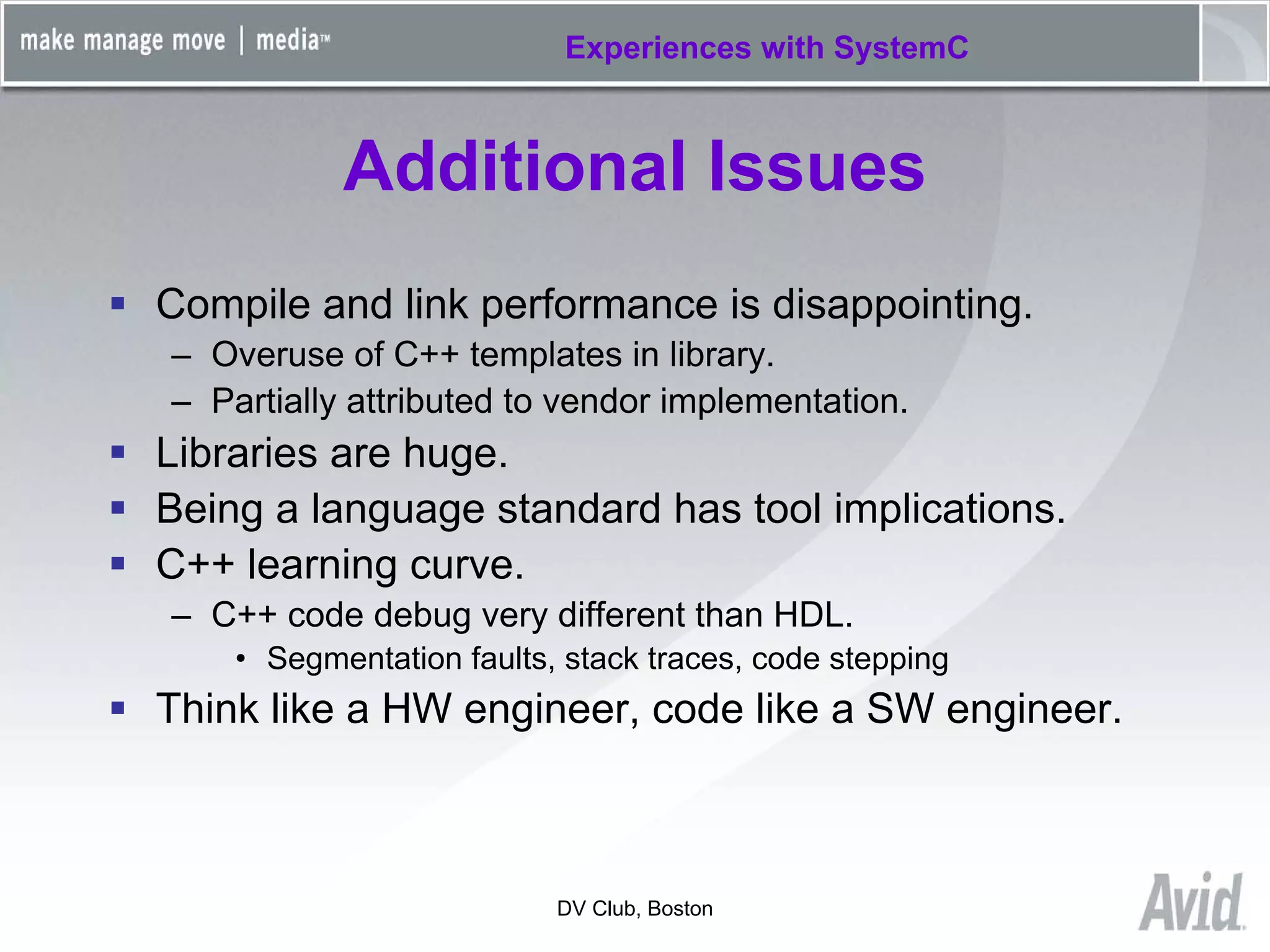
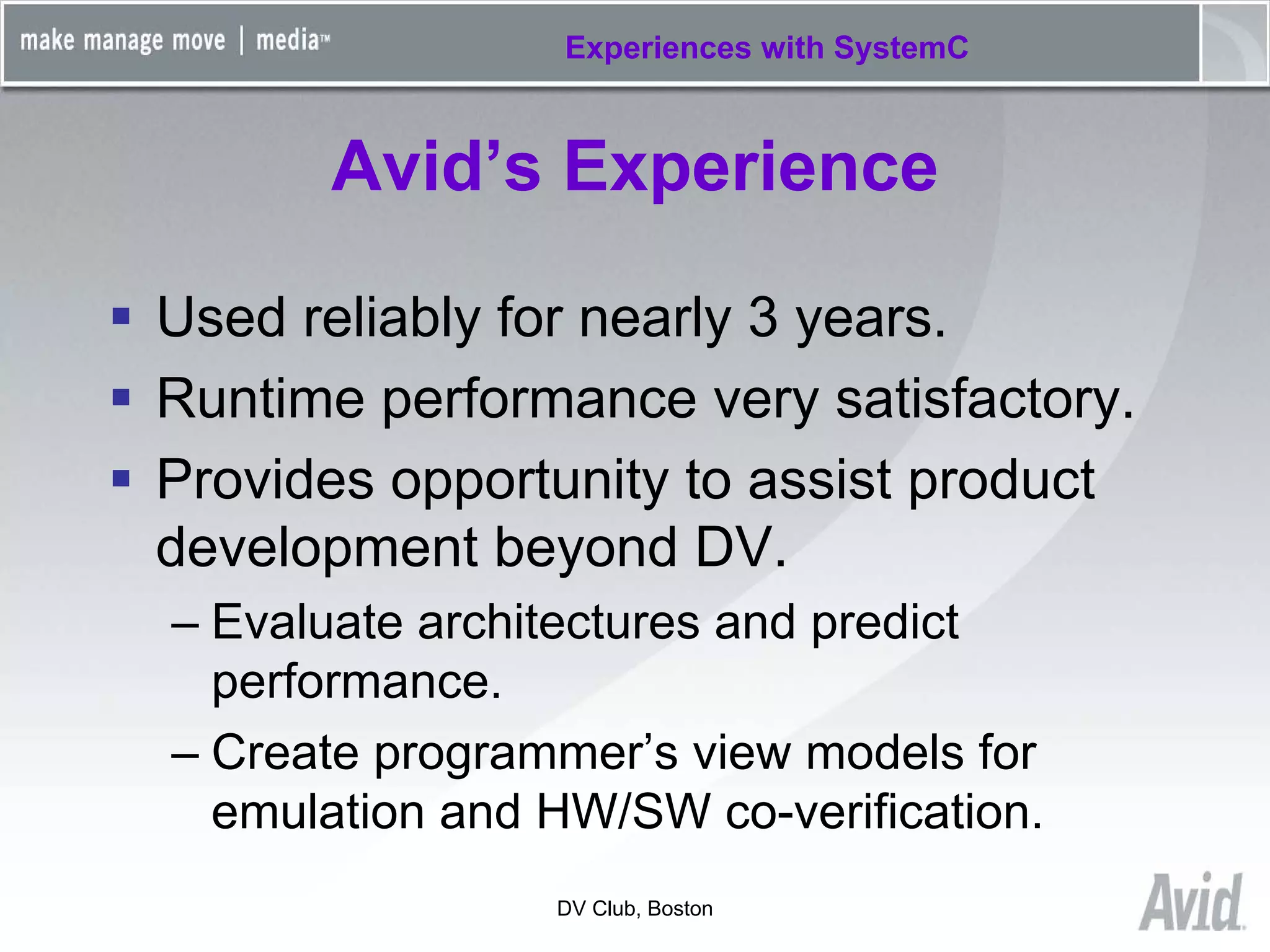
Greg Tierney of Avid presented on their experiences using SystemC for design verification. Some key points: 1) Avid chose SystemC to enhance their existing C++ verification code and take advantage of its built-in verification capabilities like randomization and multi-threading. 2) SystemC helped Avid solve problems like connecting entire HDL modules to their testbench and monitoring foreign signals. 3) While SystemC provided benefits, Avid also encountered issues with its compile/link performance and large library size. Overall, Avid found SystemC reliable for design verification over three years of use.